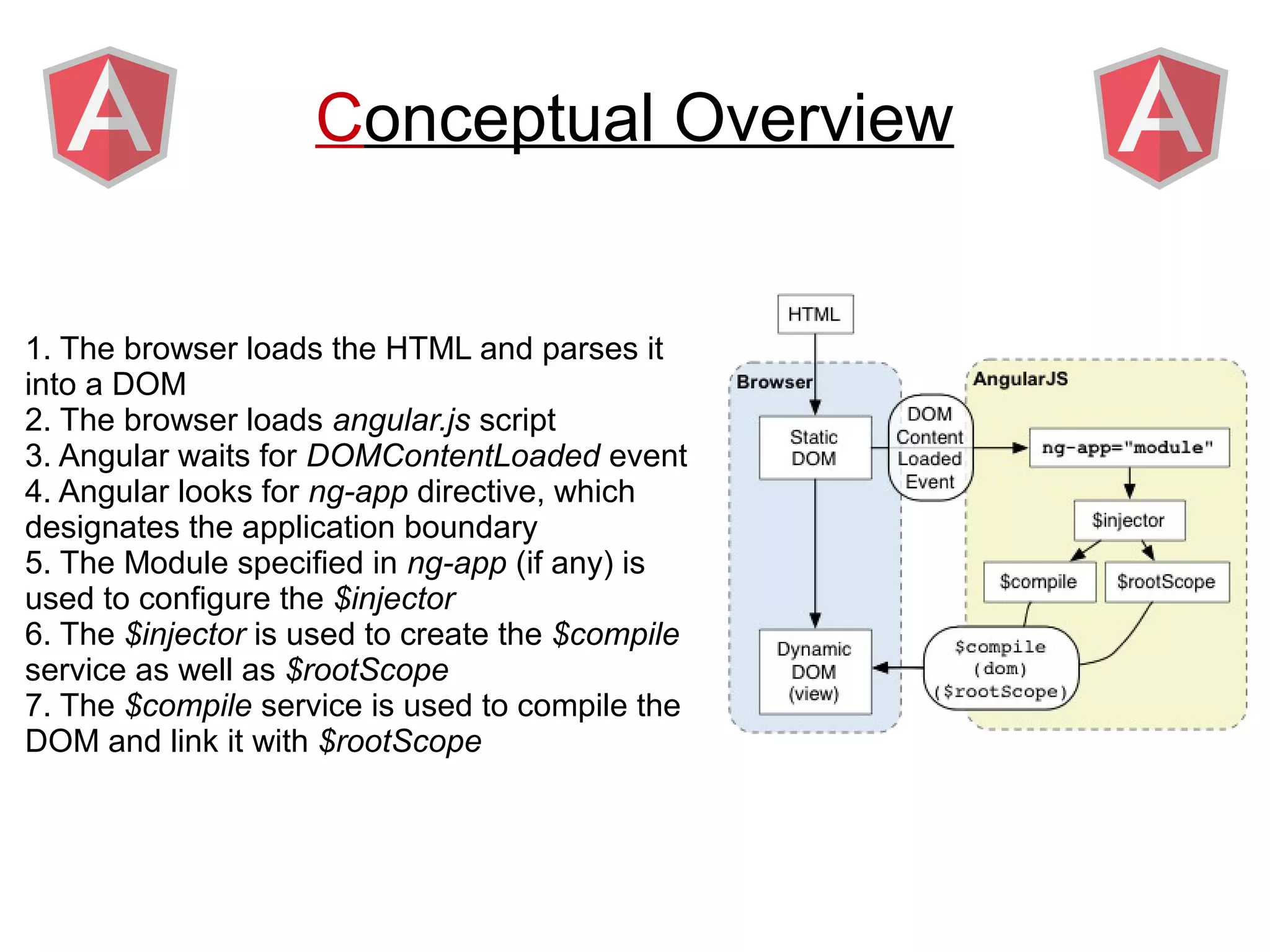
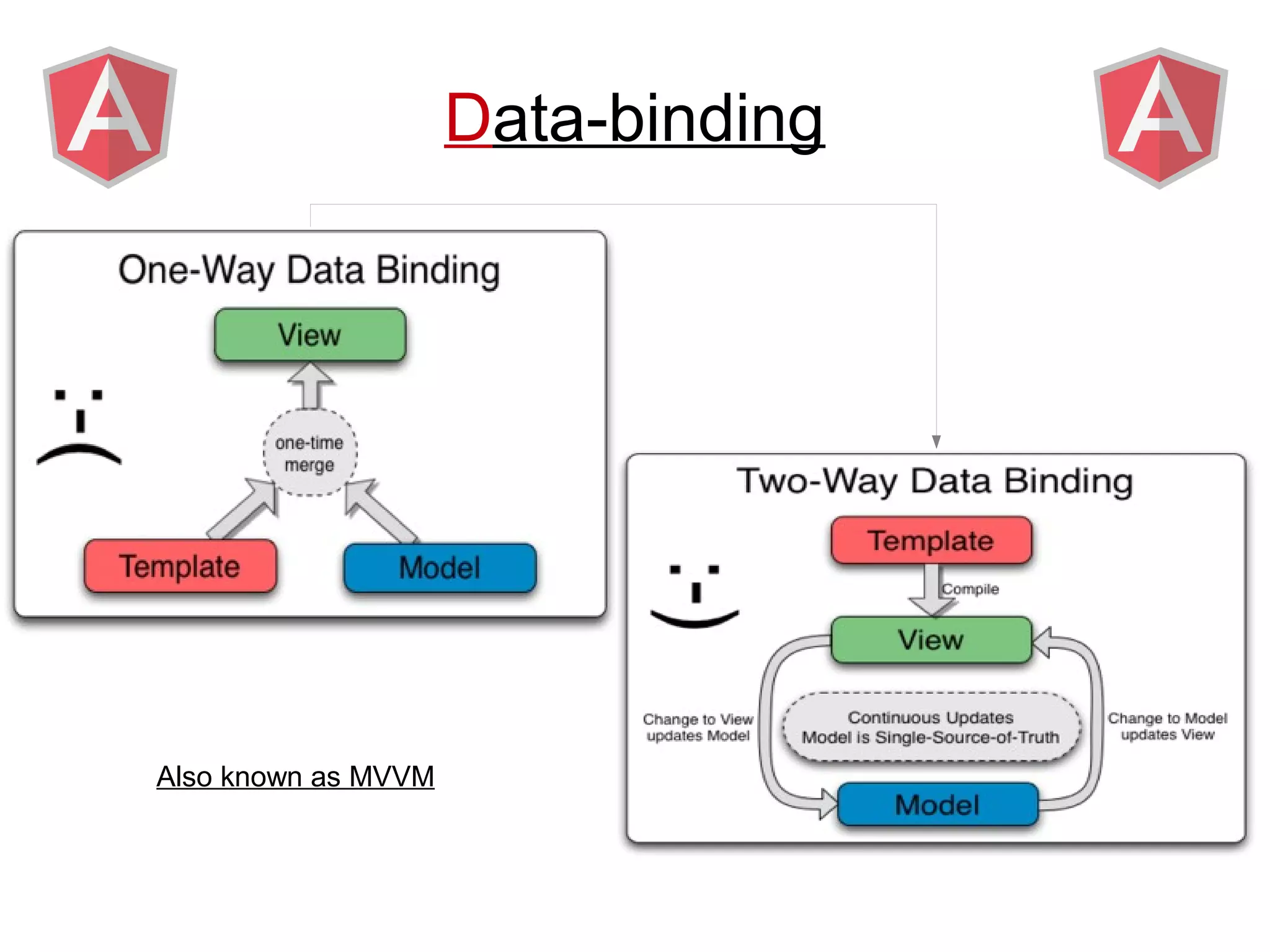
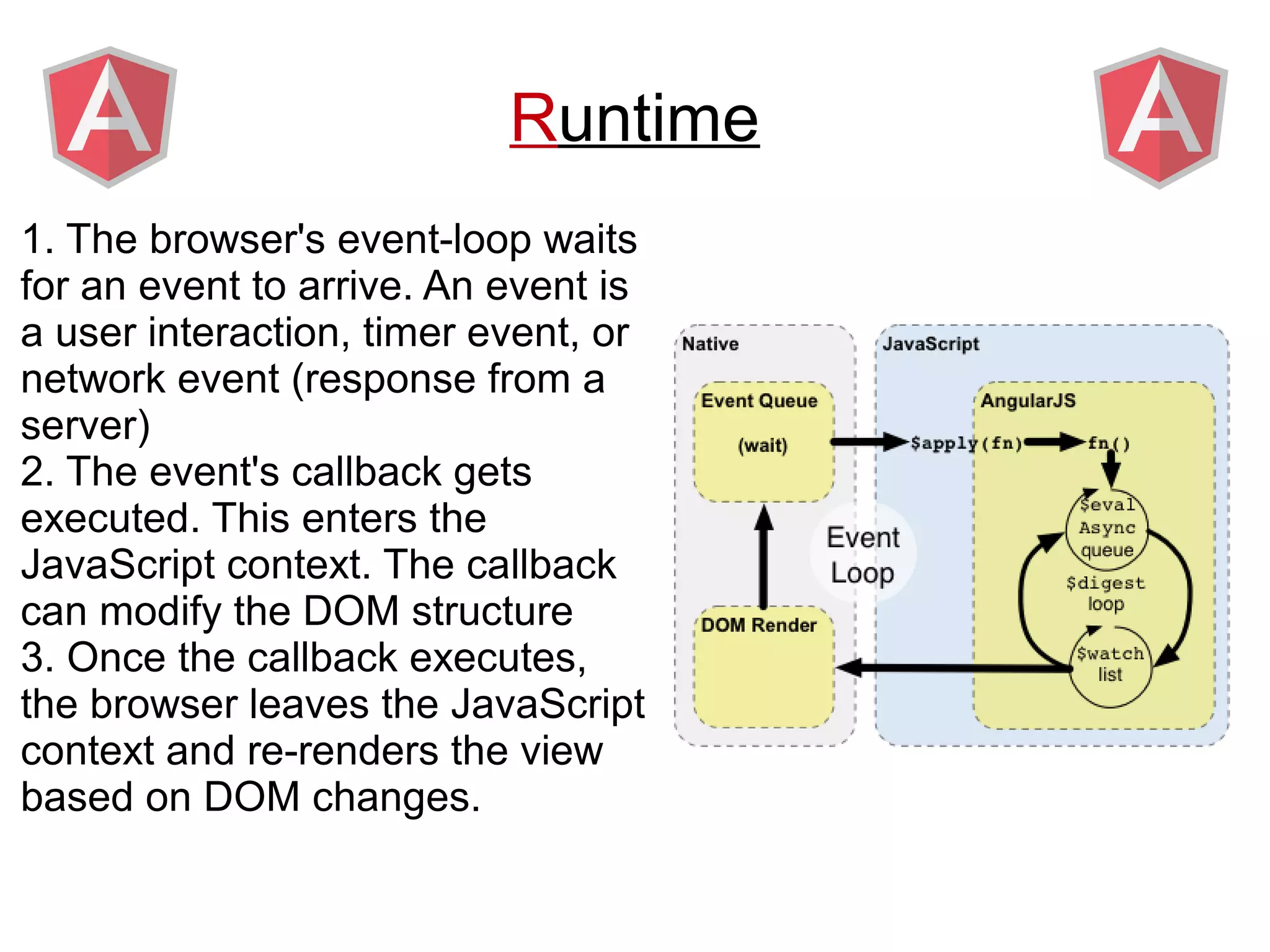
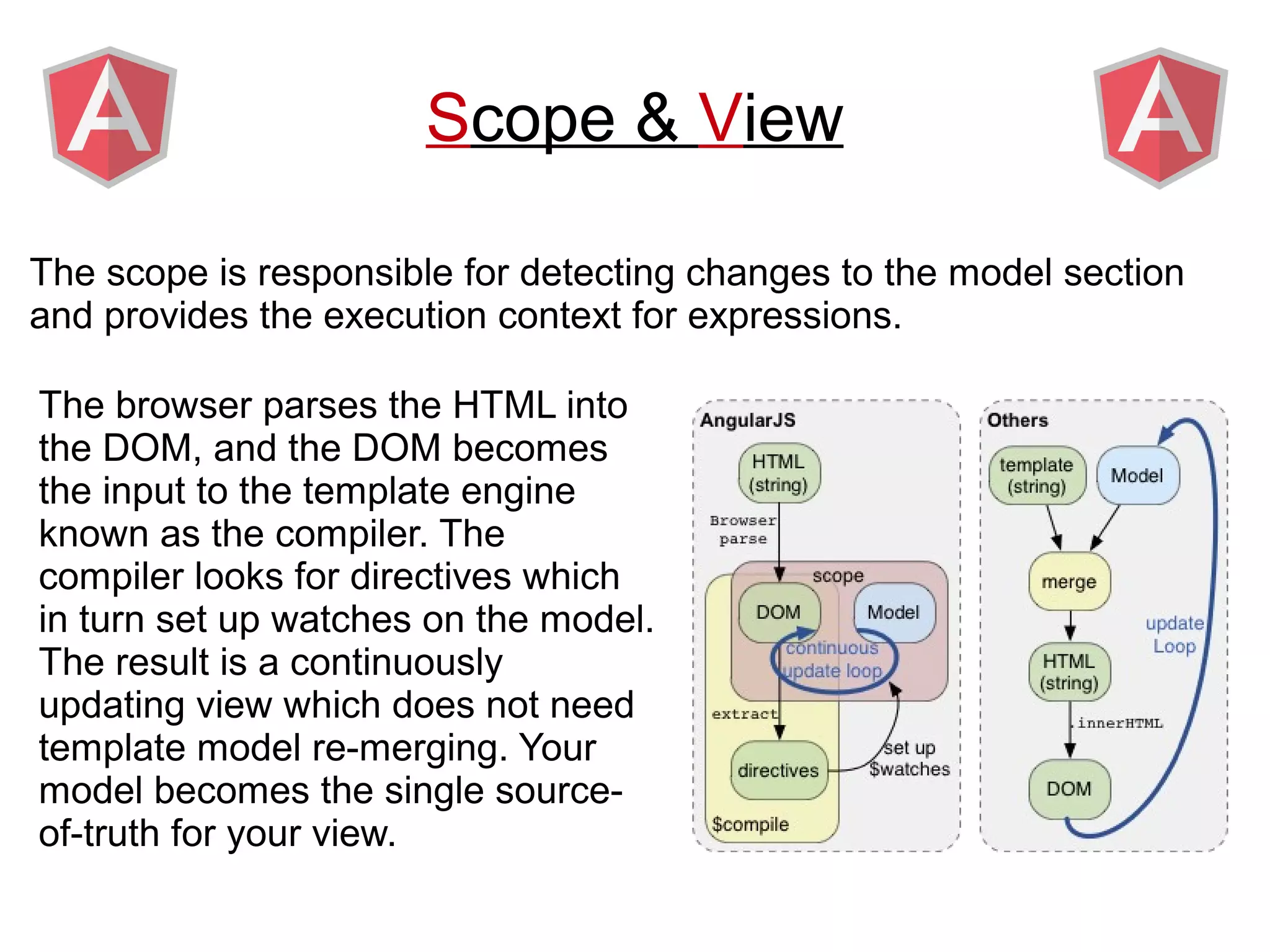
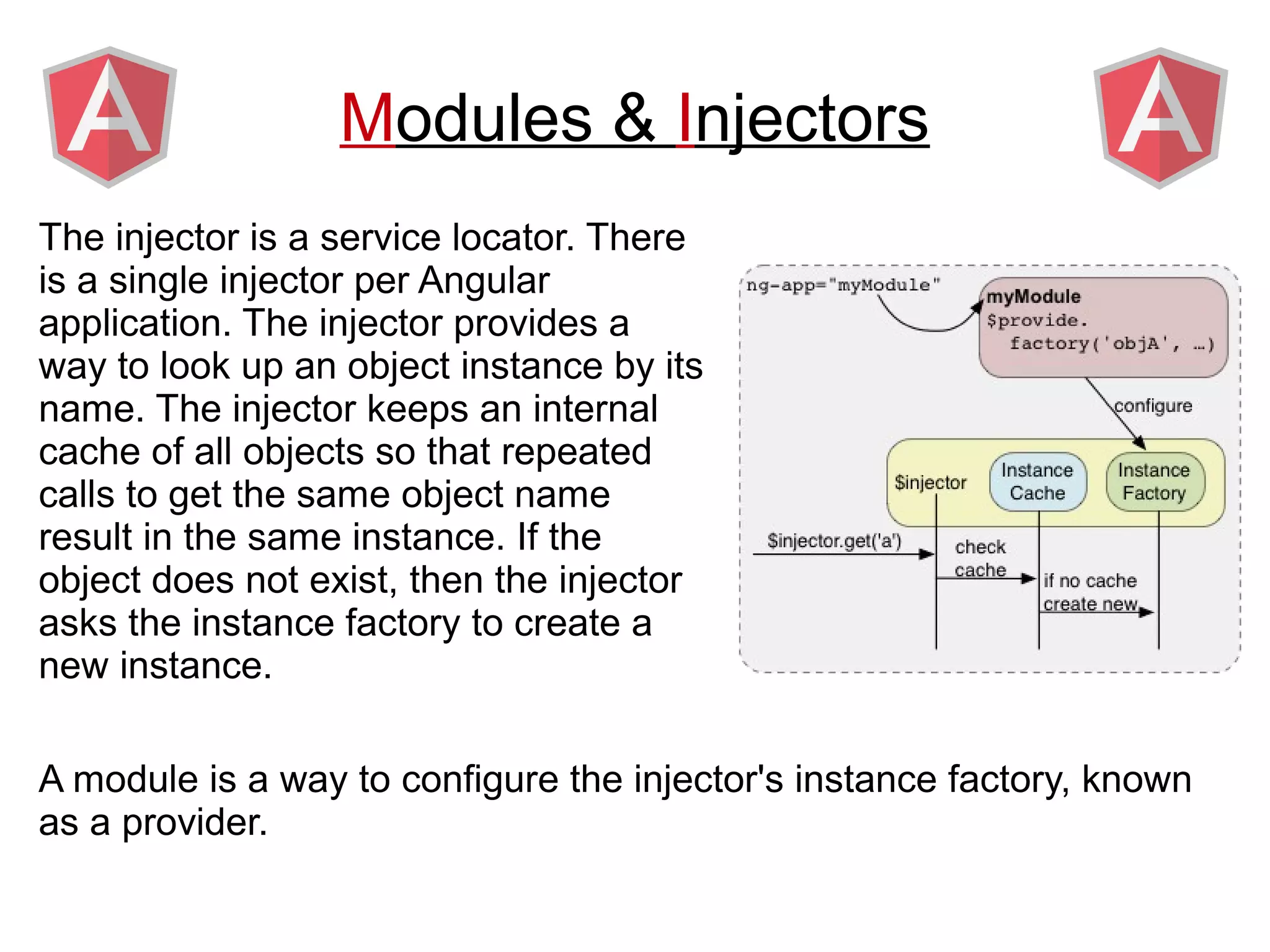
Angular provides a framework for building client-side web applications. It enhances HTML with directives, data binding, and dependency injection to allow web applications to be developed with MVC architecture. The key concepts of Angular include directives, modules, scopes, and data binding which allow building dynamic views that update automatically based on changes to the underlying model/data.