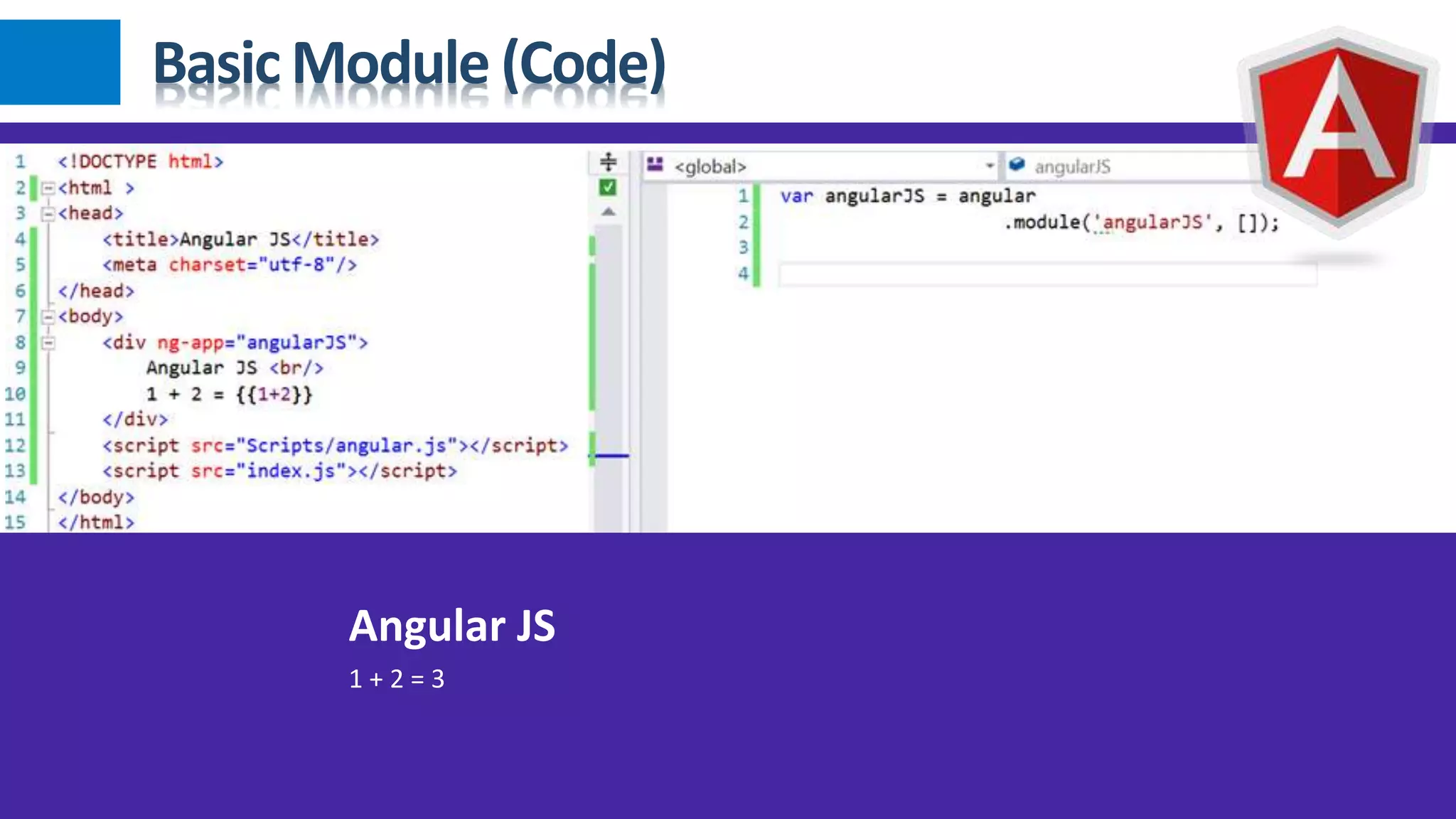
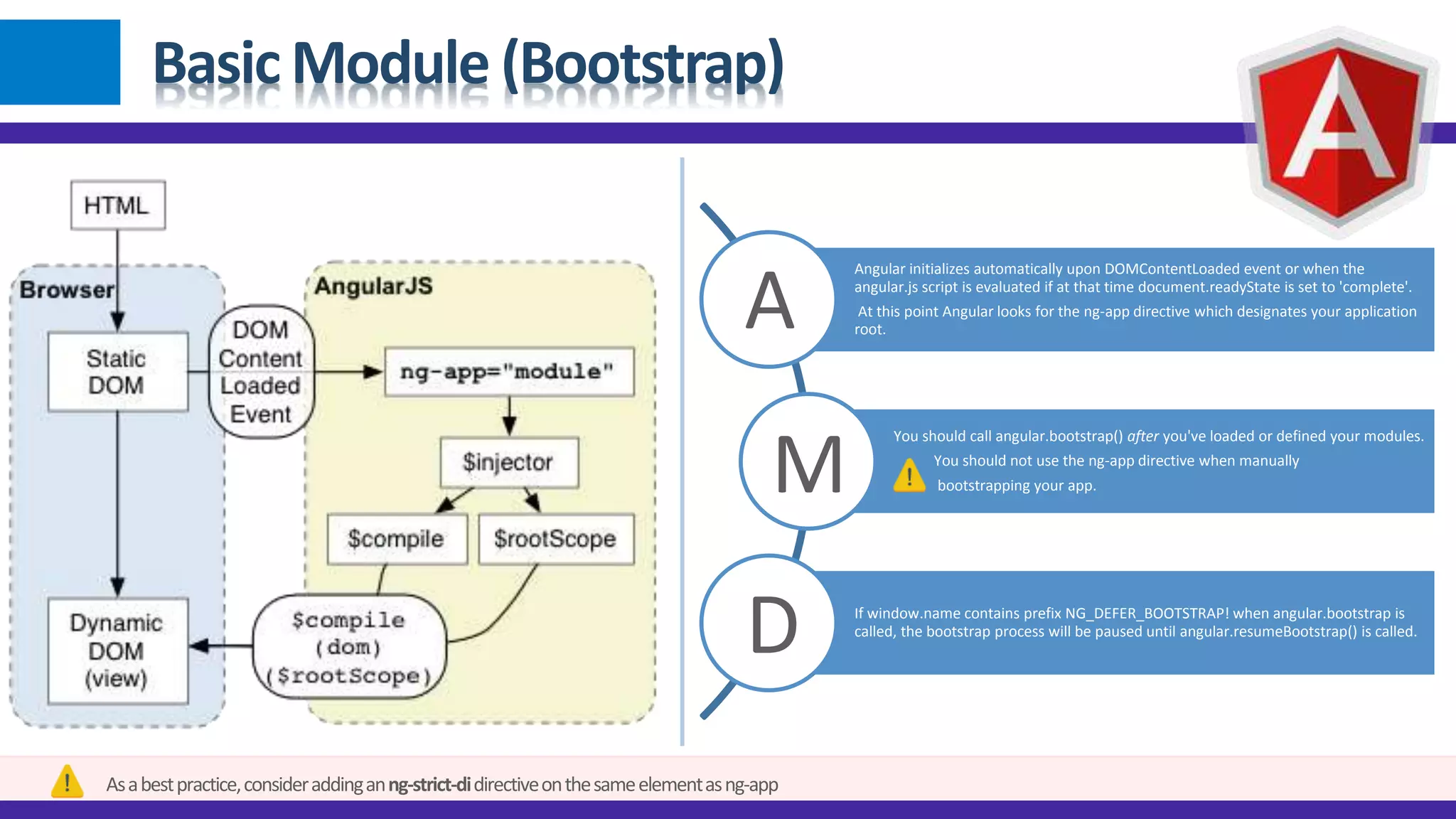
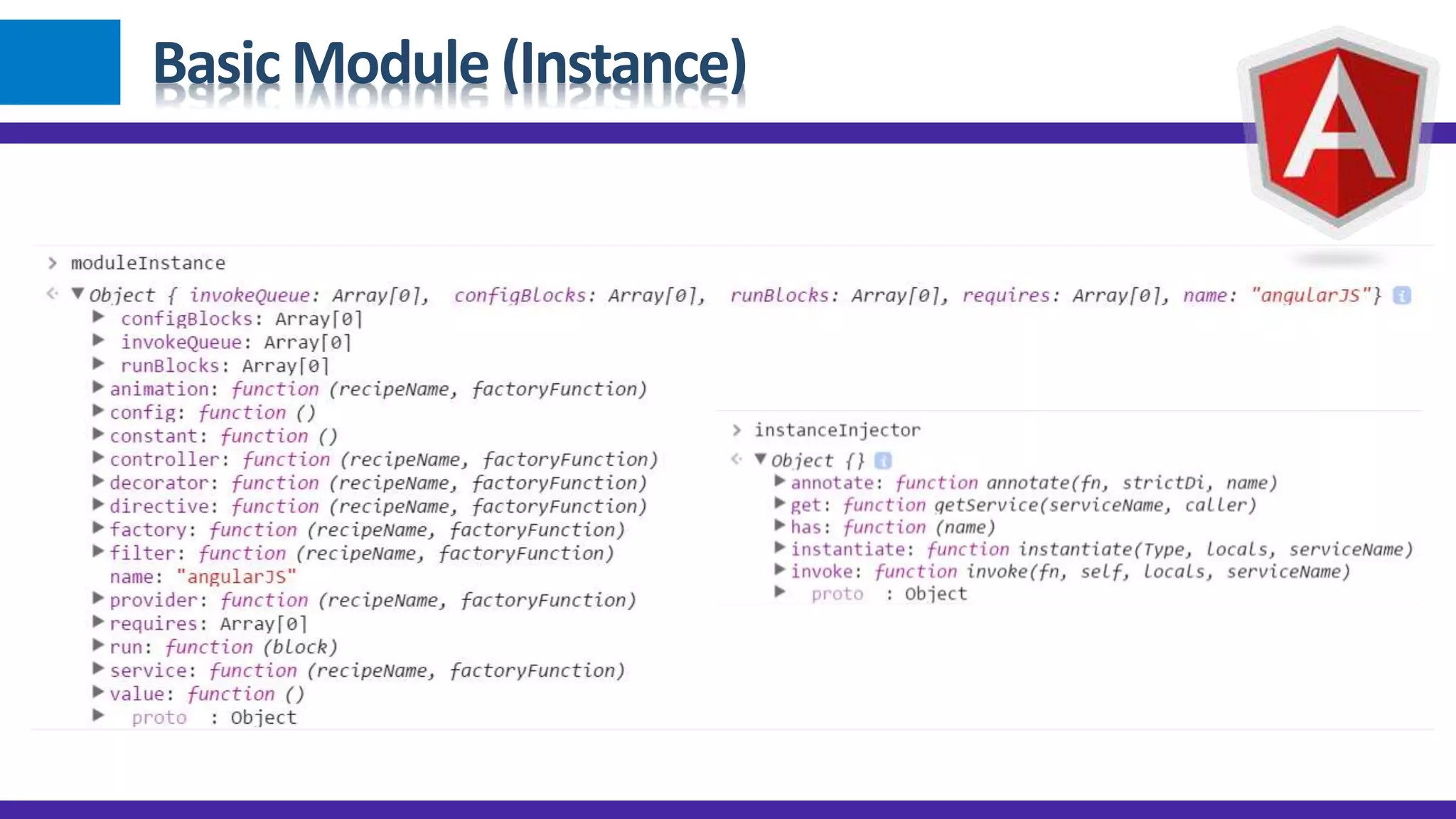
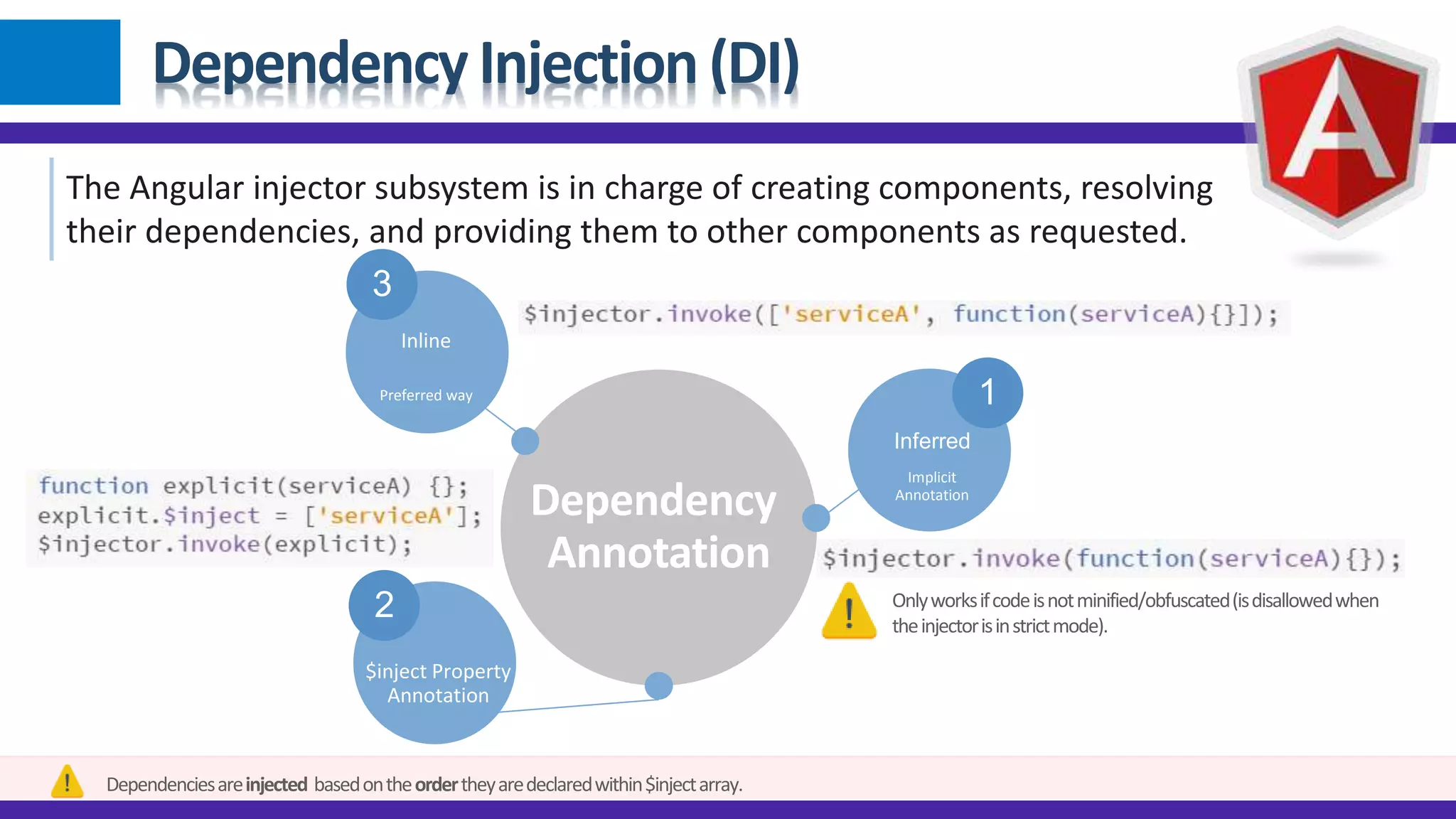
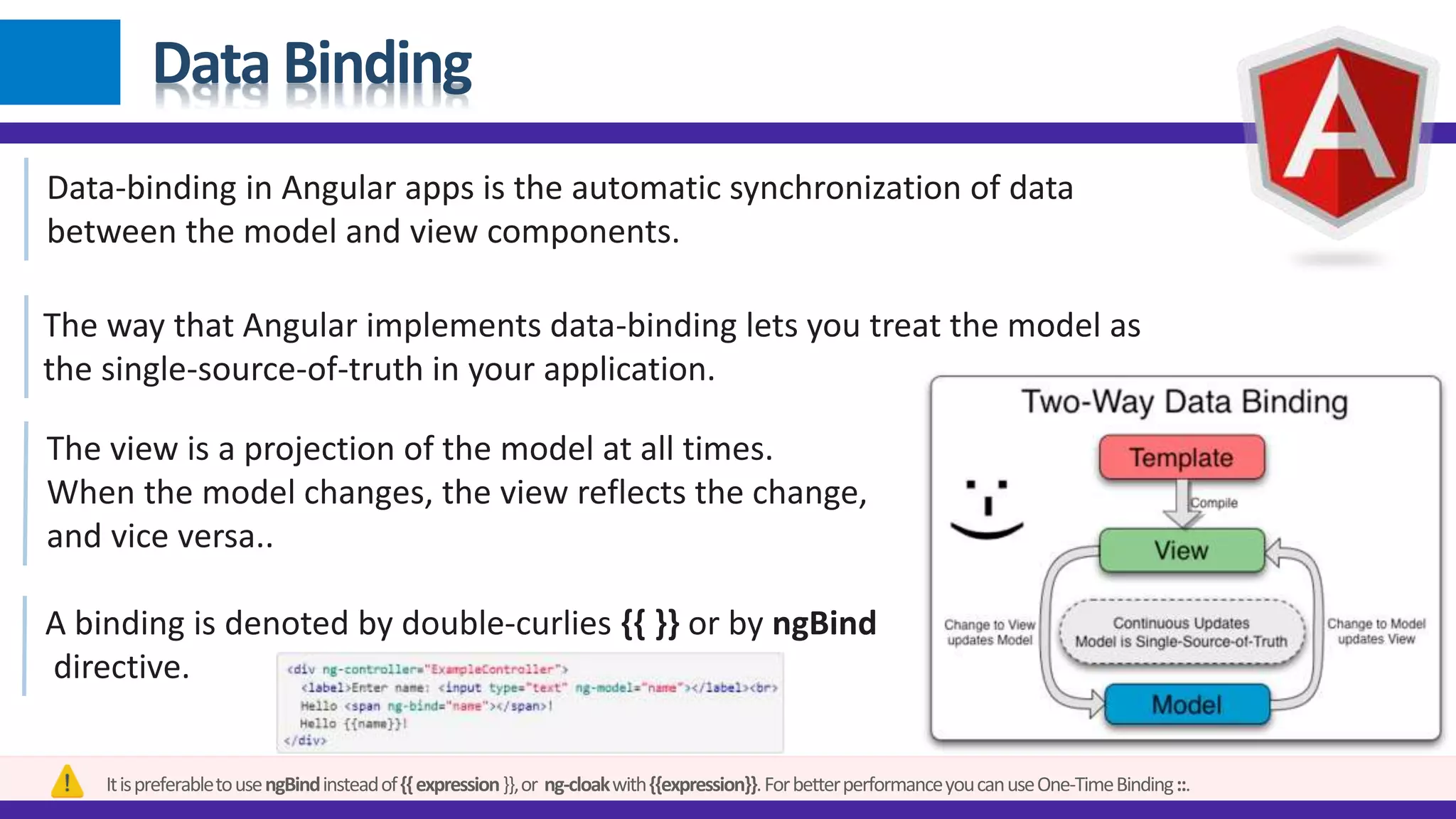
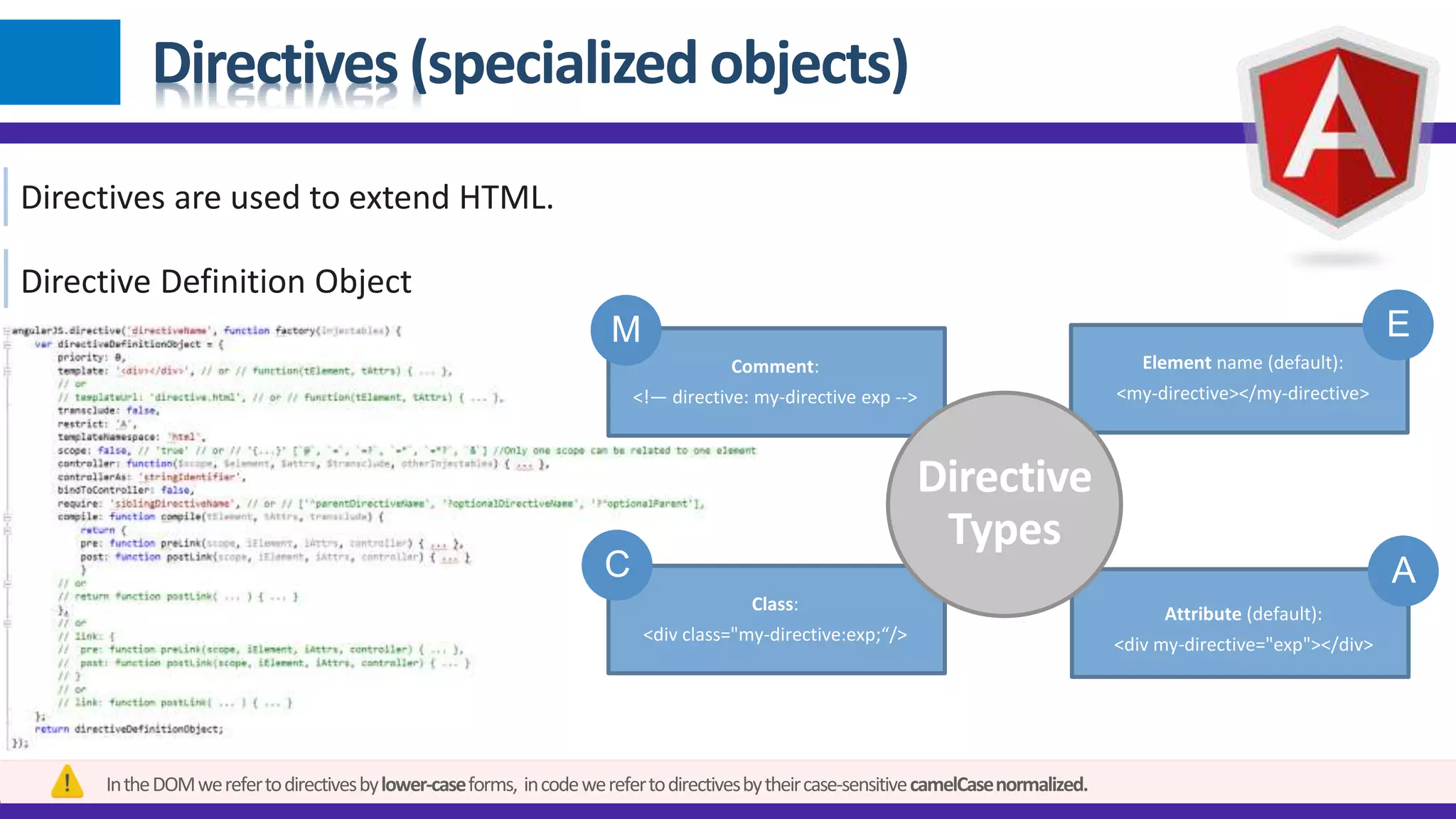
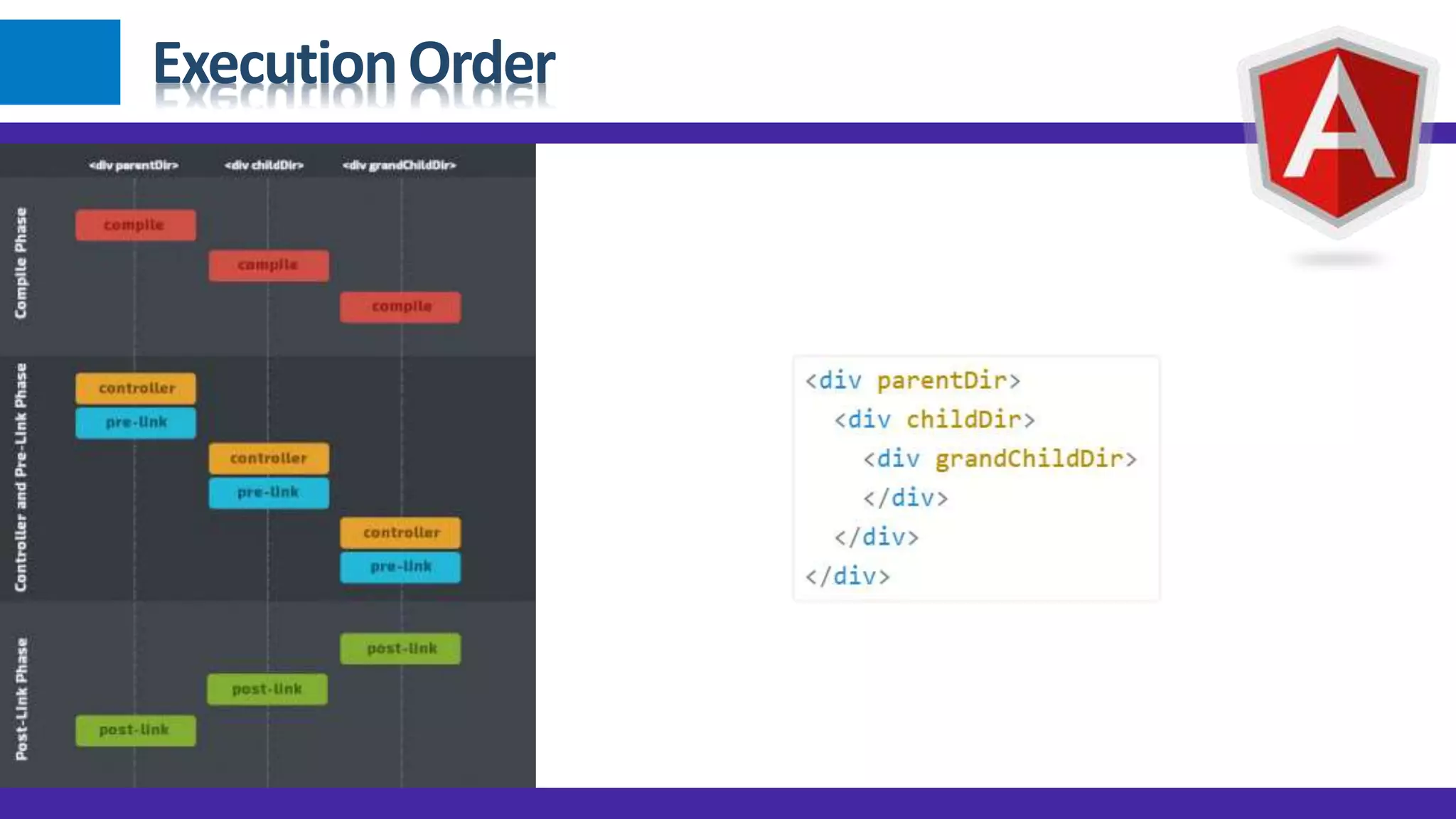
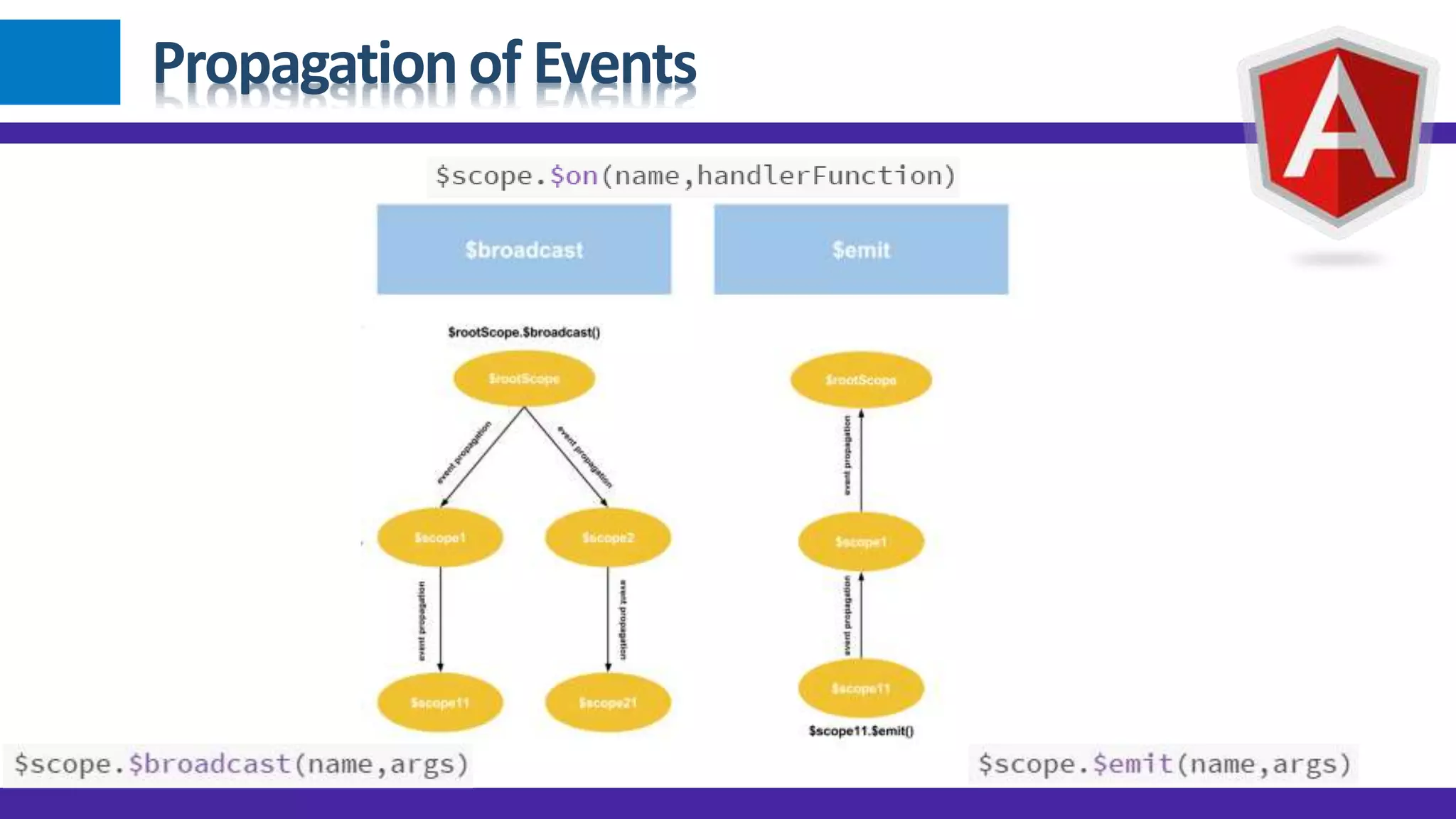
1) Angular JS modules allow you to organize an application into specific modules that contain controllers, services, filters and directives. A module is created using angular.module and can be retrieved later on. 2) Dependency injection in Angular allows components to receive dependencies from the injector. Dependencies can be annotated inline, through the $inject property or implicitly. 3) Data binding in Angular automatically synchronizes data between the model and view. The view reflects changes made to the model and vice versa using bindings like {{expression}} or ngBind.


![function module(name, requires, configFn)essions name==='hasOwnProperty' What is a Module? 01 02 04 You can think of a module as a container for the different parts of your app – controllers, services, filters, directives, etc. Creation Retrieval angular.module('myModule', []); angular.module('myModule'); Signature](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-arhitecture-160126045106/75/Angular-js-architecture-v1-4-8-3-2048.jpg)
![Basic Module (Steps) 01 Place the script at the bottom of the page. 02 Place ng-*app to the root of your application. *["ng-", "data-ng-", "ng:", "x-ng-"] 03 Create the ng-app module.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-arhitecture-160126045106/75/Angular-js-architecture-v1-4-8-4-2048.jpg)