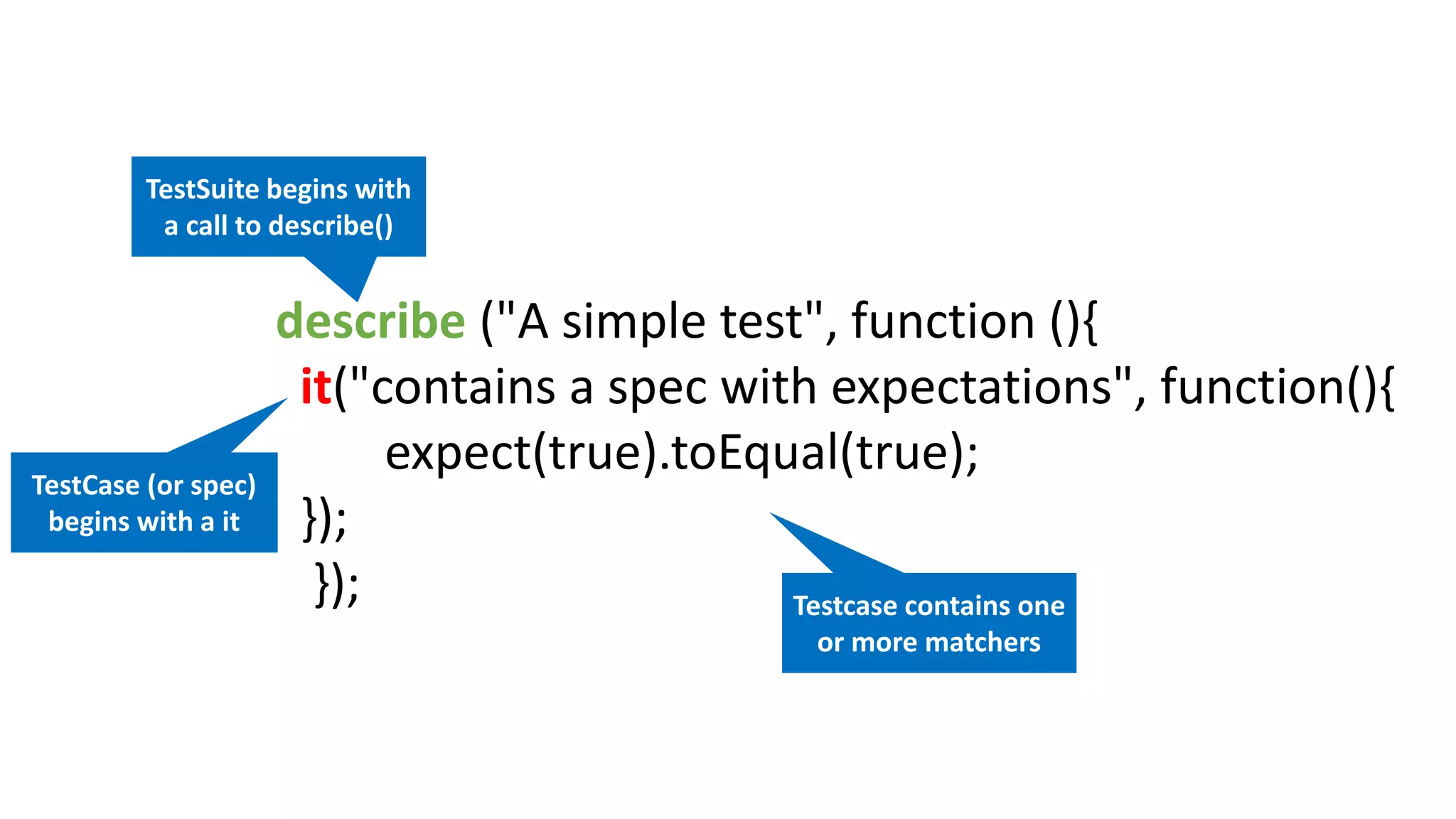
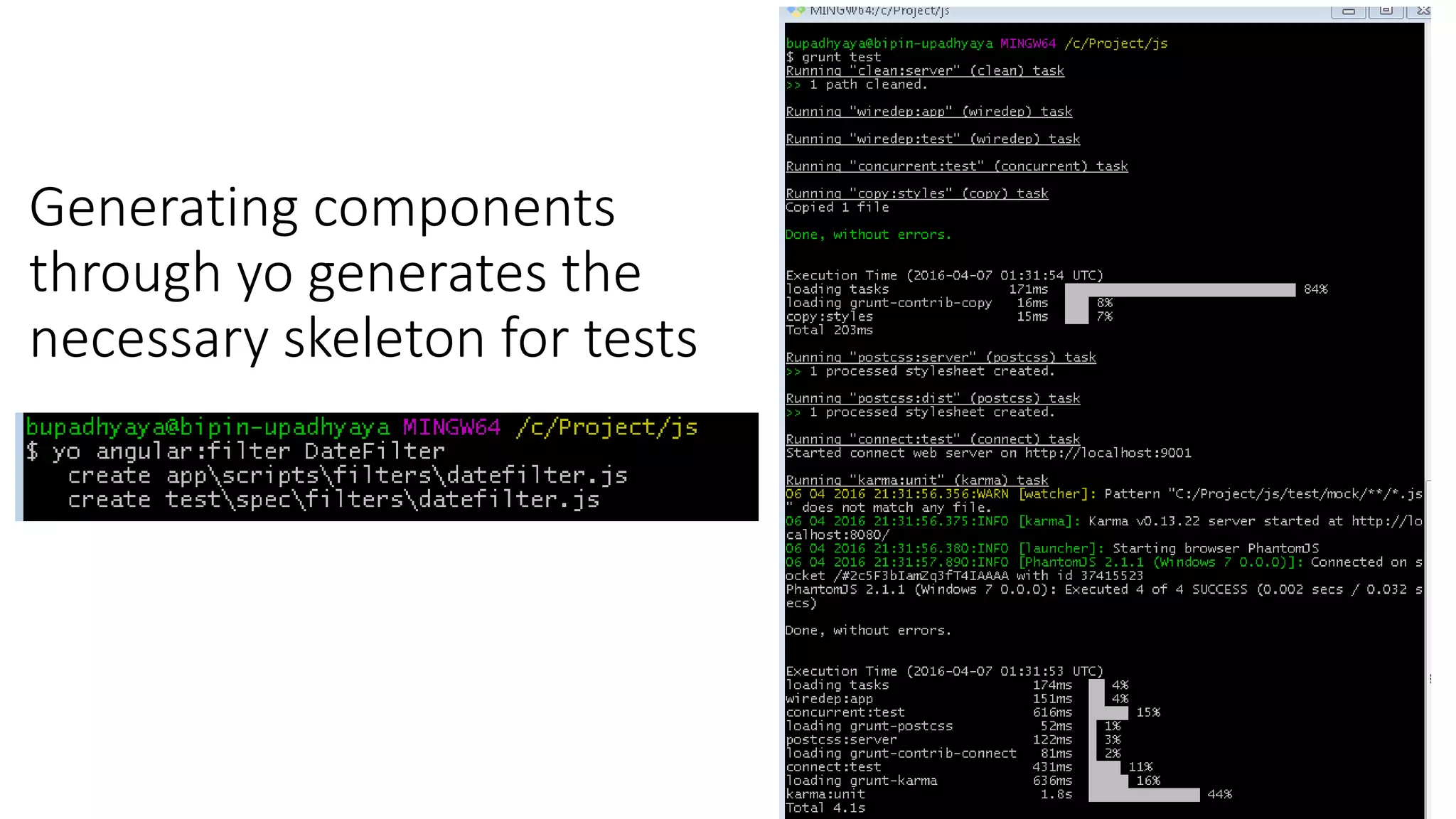
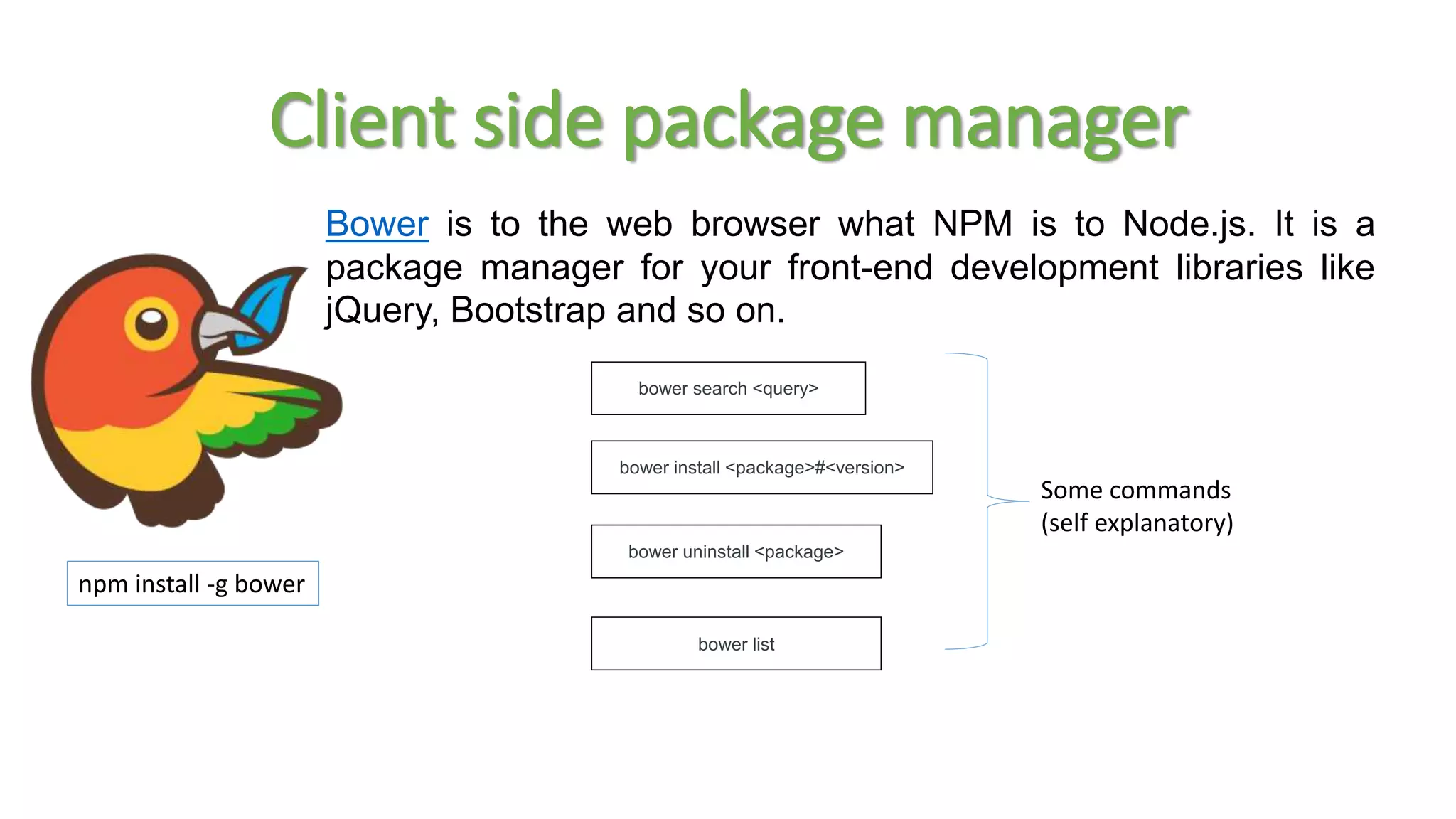
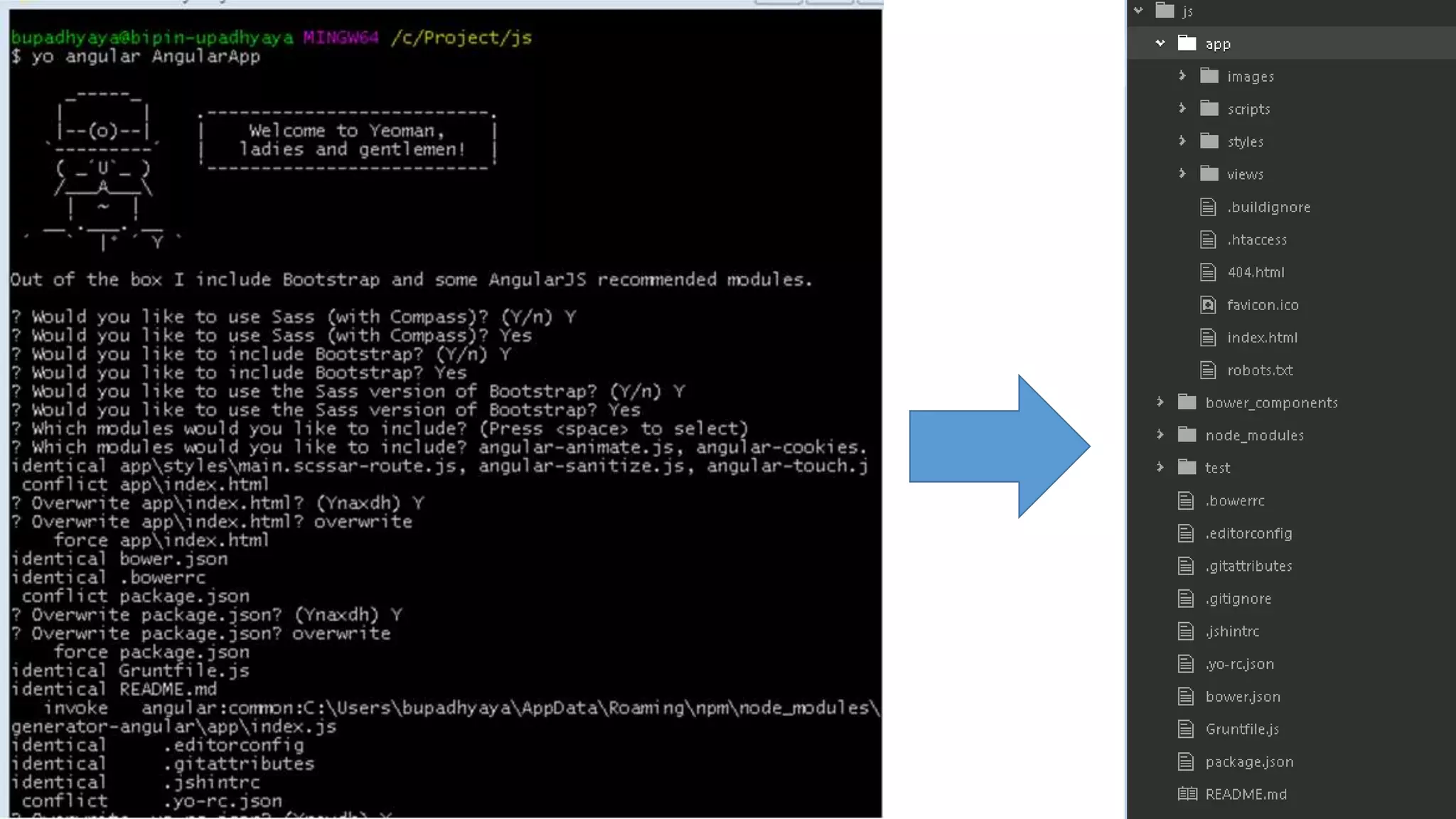
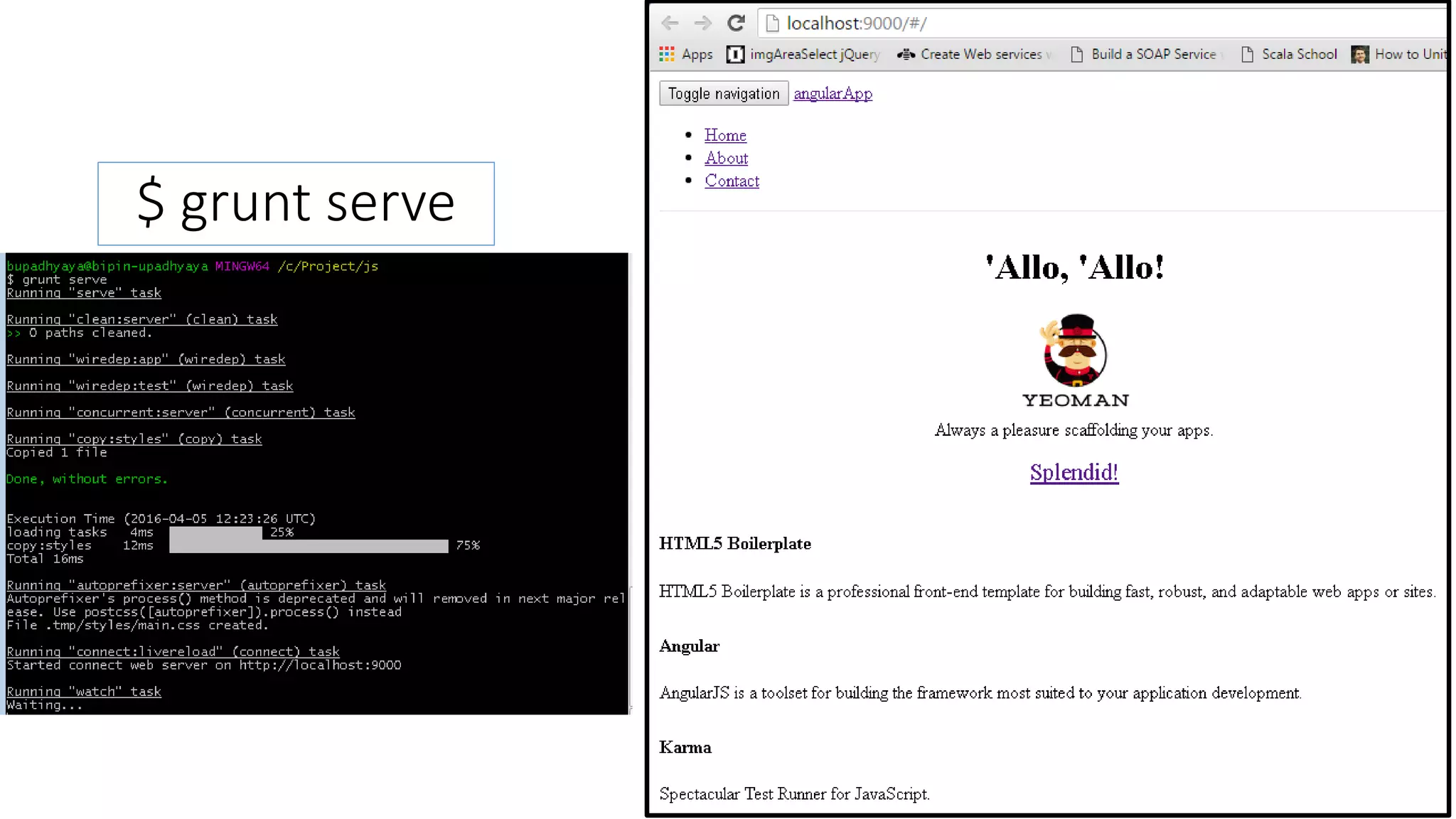
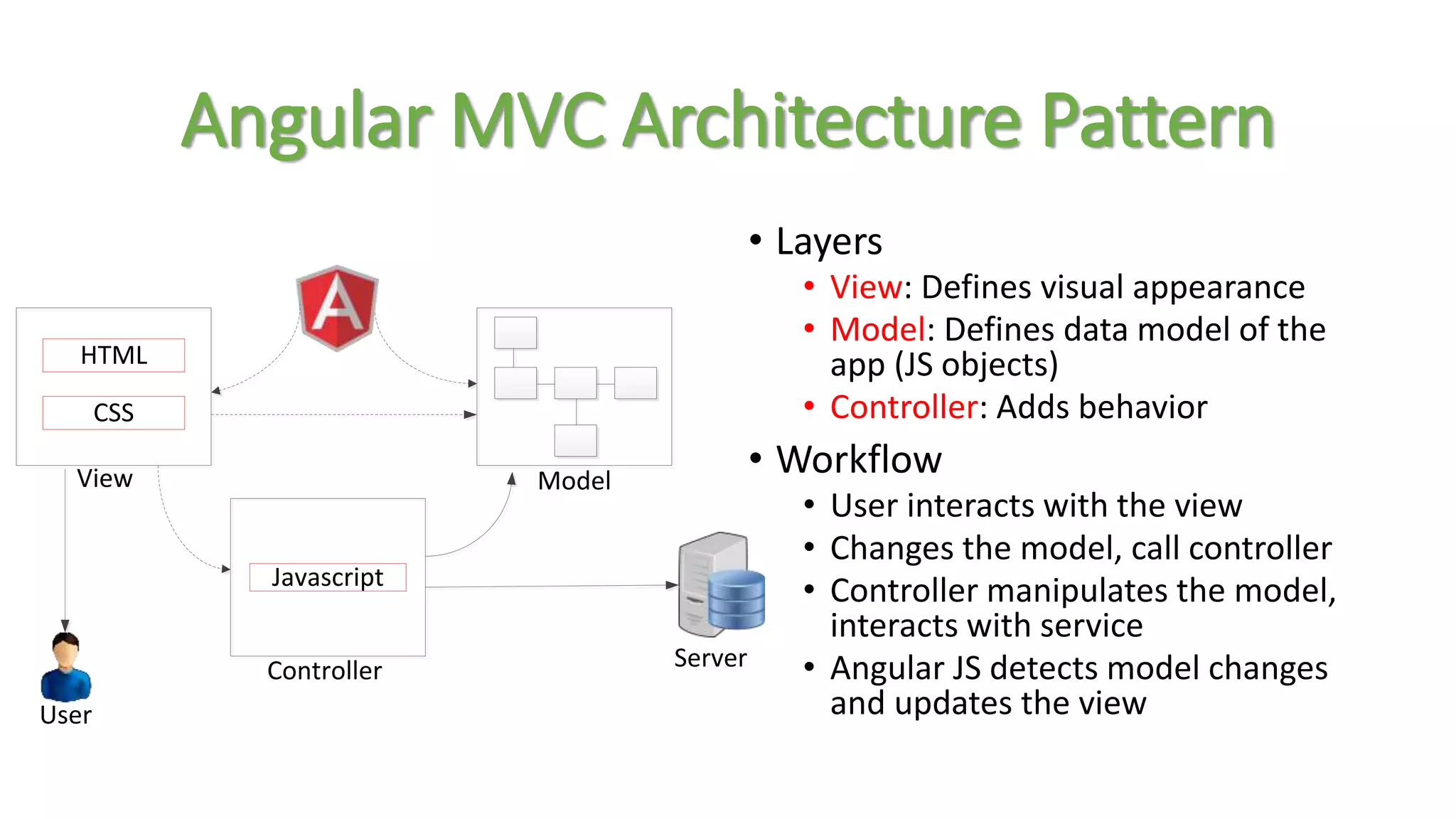
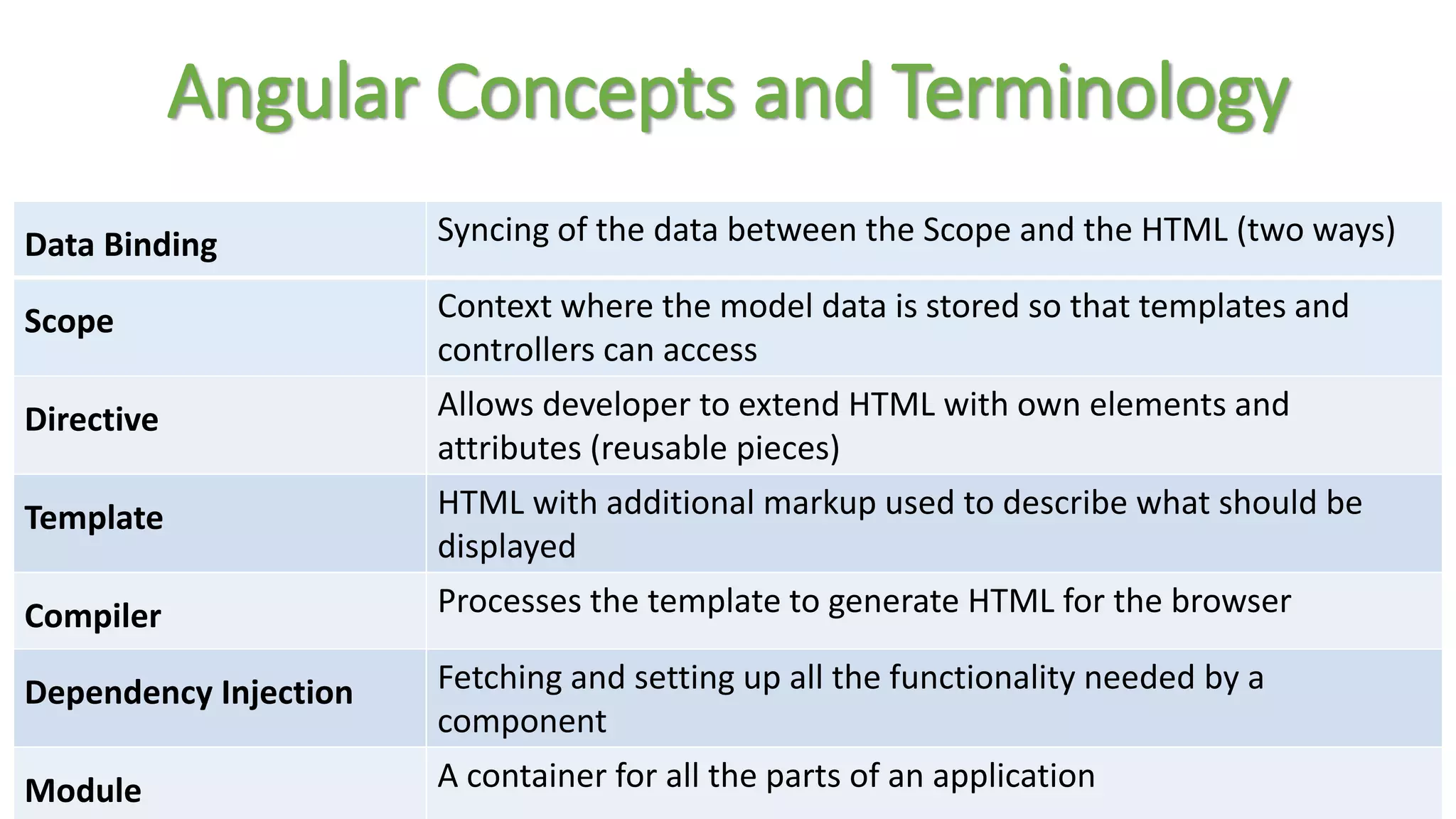
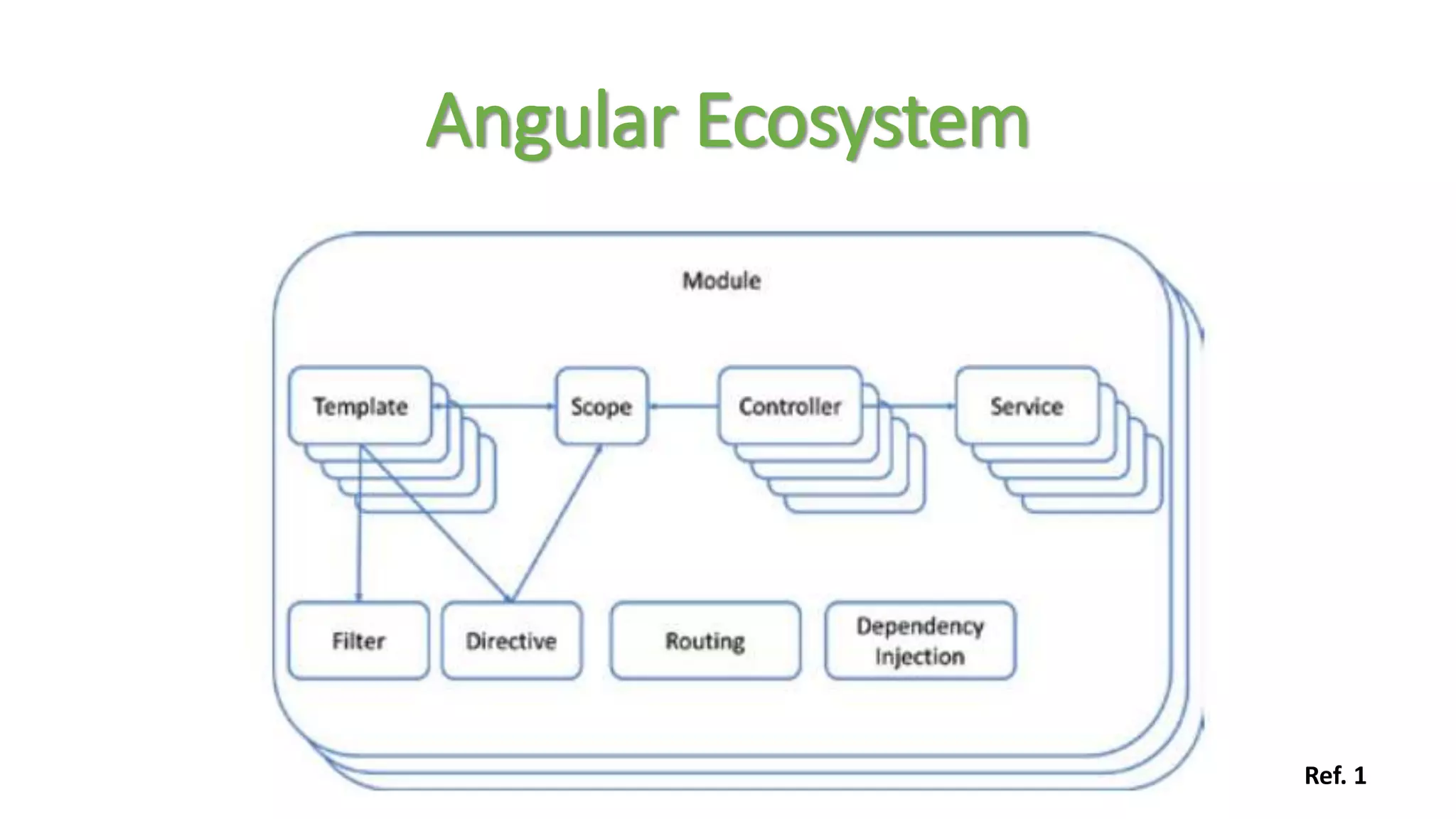
Node package manager (NPM) initializes projects and manages front-end packages. Bower manages client-side packages like jQuery. Grunt and Gulp automate workflows. Yo generates application scaffolding. Angular uses MVC architecture with views, models, and controllers. Data binding syncs models and views. Directives extend HTML. Modules contain components and support dependency injection. Routes define application states. Filters format data. Controllers manipulate scope data. Values, services, and factories support dependency injection of reusable code. Testing uses Karma, Jasmine, and generated test skeletons.





![var demoApp = angular.module(‘AngularApp', []); What's the Array for? var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', ['helperModule']); Module that demoApp depends on Creating a Module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-13-2048.jpg)
![Module Phases Config • happens early while the application is still being built. Only provider services and constant services are ready for dependency injection at this stage. RUN • happens once the module has loaded all of its services and dependencies. var module = angular.module(‘AngularApp', []); module.config([function() { alert('I run first'); }]); module.run([function() { alert('I run second'); }]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-14-2048.jpg)
![Module Components and Dependency Injection • AngularJS lets you inject services (either from its own module or from other modules) with the following pattern: var module = angular.module(‘AngularApp', []); module.service('serviceA', function() { ... }); module.service('serviceB', function(serviceA) { ... });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-15-2048.jpg)

![<html data-ng-app=""> ... <div class="container" data-ng-init="names=['Dave','Napur','Heedy','Shriva']"> <h3>Looping with the ng-repeat Directive</h3> <ul> <li data-ng-repeat="name in names">{{ name }}</li> </ul> </div> ... </html> Iterate through names Iterating with the ng-repeat Directive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-17-2048.jpg)
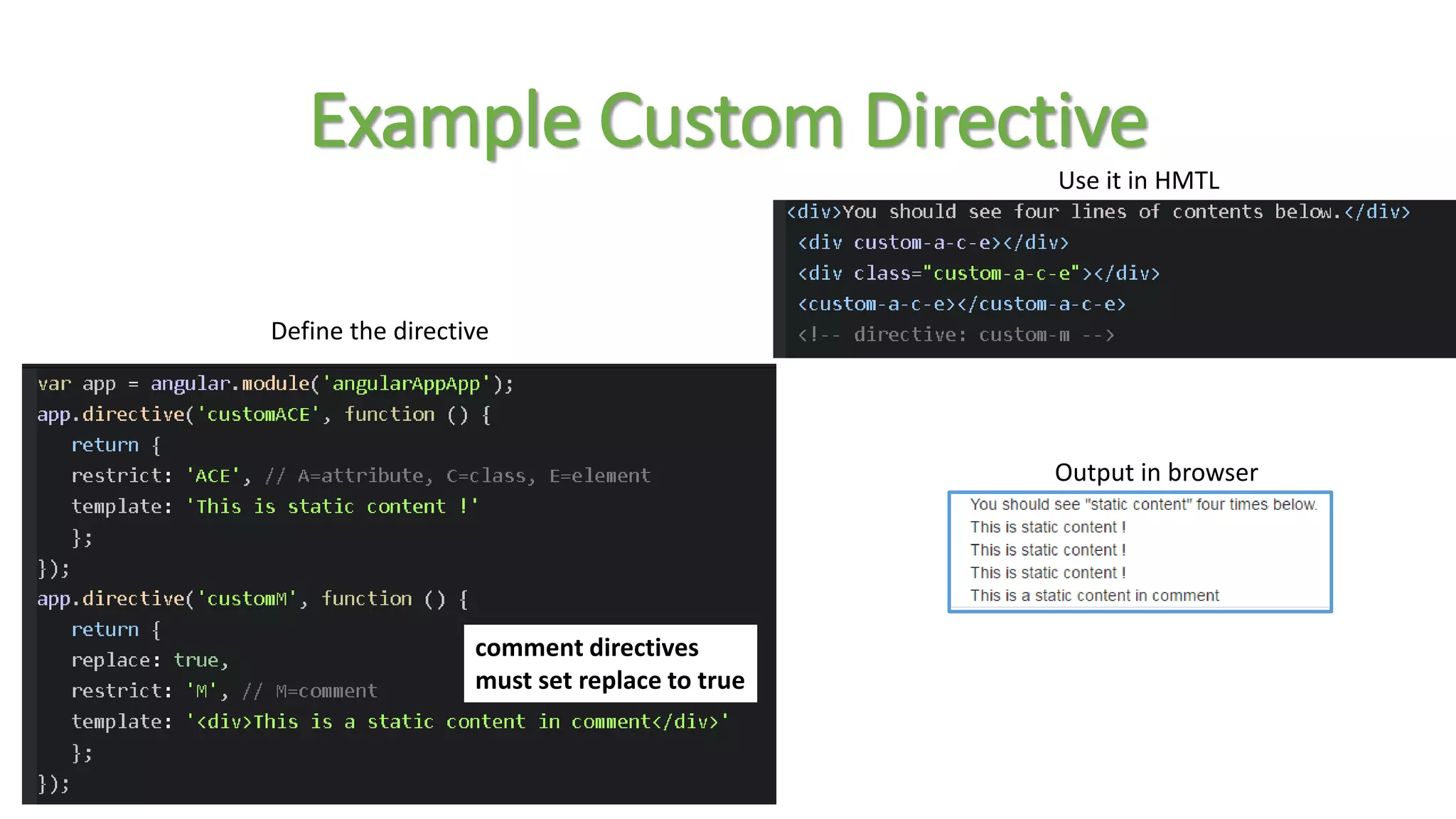
![Naming Custom Directive • When defining a directive in JavaScript, the name is in camel case format: • When we activate that directive we use a lower case form: module.directive('myDirective', [function() { ... }]); <my-directive></my-directive> <div my-directive></div>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-18-2048.jpg)
![Defining Routes var demoApp = angular.module(‘AngularApp', ['ngRoute']); demoApp.config(function ($routeProvider) { $routeProvider .when('/', { controller: 'SimpleController', templateUrl:'View1.html' }) .when('/view2', { controller: 'SimpleController', templateUrl:'View2.html' }) .otherwise({ redirectTo: '/' }); }); Define Module Routes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-20-2048.jpg)
![var demoApp = angular.module(‘AngularApp', []); demoApp.controller('SimpleController', function ($scope) { $scope.customers = [ { name: 'Dave Jones', city: 'Phoenix' }, { name: 'Jamie Riley', city: 'Atlanta' }, { name: 'Heedy Wahlin', city: 'Chandler' }, { name: 'Thomas Winter', city: 'Seattle' } ]; }); Define a Module Define a Controller Creating a Controller in a Module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-22-2048.jpg)
![<div class="container" ng-controller="SimpleController"> <h3>Adding a Simple Controller</h3> <ul> <li data-ng-repeat="cust in customers"> {{ cust.name }} - {{ cust.city }} </li> </ul> </div> <script> function SimpleController($scope) { $scope.customers = [ { name: 'Dave Jones', city: 'Phoenix' }, { name: 'Jamie Riley', city: 'Atlanta' }, { name: 'Heedy Wahlin', city: 'Chandler' }, { name: 'Thomas Winter', city: 'Seattle' } ]; } </script> Define the controller to use Basic controller $scope injected dynamically Access $scope Creating a View and Controller](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-23-2048.jpg)
![Value • The value recipe stores a value within an injectable service. • A value can store any service type: a string, a number, a function, and object, etc. • This value of this service can now be injected into any controller, filter, or service. //define a module var myModule = angular.module(‘AngularApp', []); //define a value myModule.value('clientId', 'a12345654321x'); //define a controller that injects the value myModule.controller('myController', ['$scope', 'clientId', function ($scope, clientId) { $scope.clientId = clientId; }]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-24-2048.jpg)
![Service • The service recipe will generate a singleton of an instantiated object. //define a service myModule.service('person', [function() { this.first = 'John'; this.last = 'Jones'; this.name = function() { return this.first + ' ' + this.last; }; }]); //inject the person service myModule.controller('myController', ['$scope', 'person', function($scope, person) { $scope.name = person.name(); }]); $http $q $timeout …..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tnspresentation-160407214736/75/Front-end-development-with-Angular-JS-25-2048.jpg)