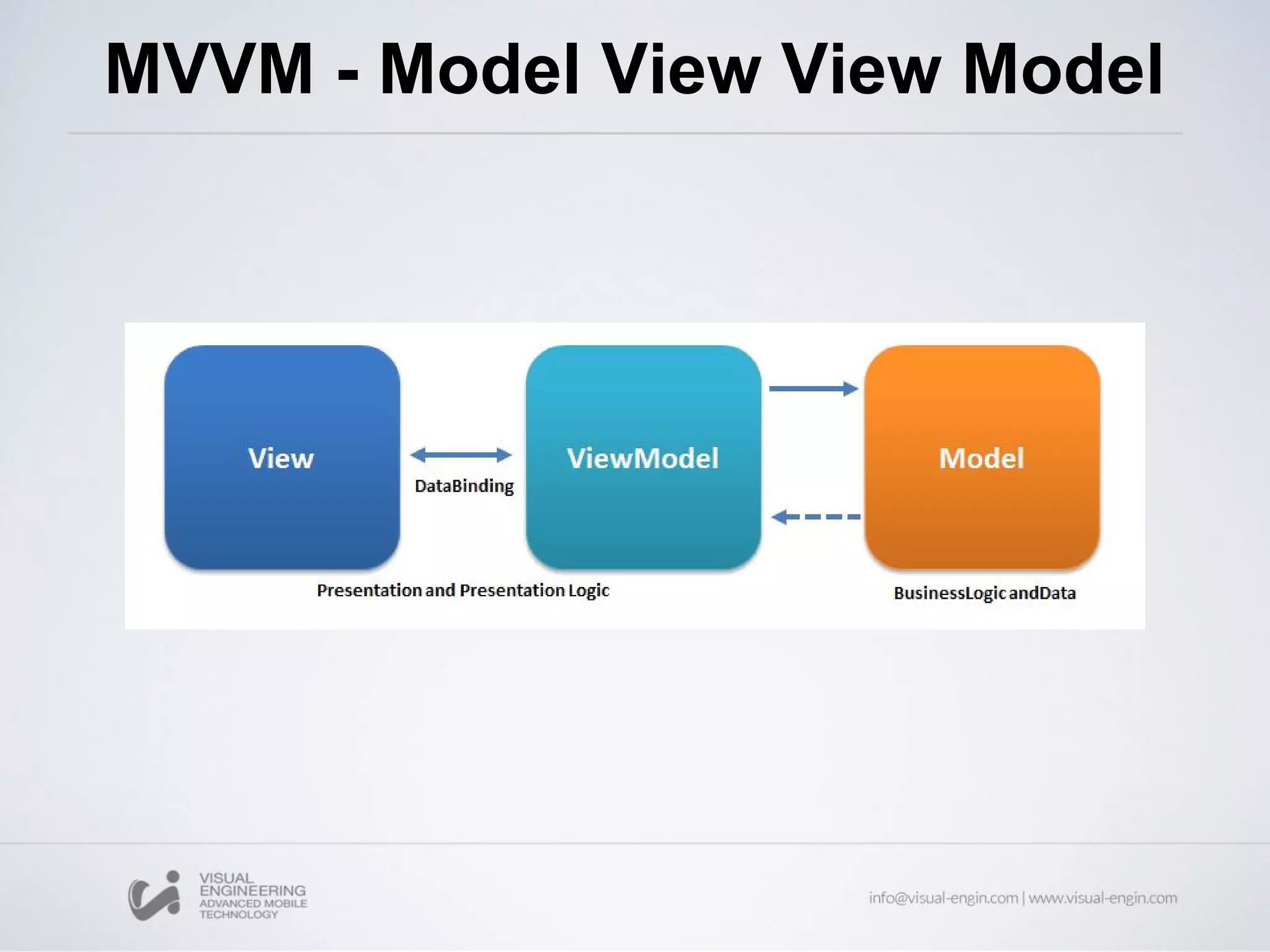
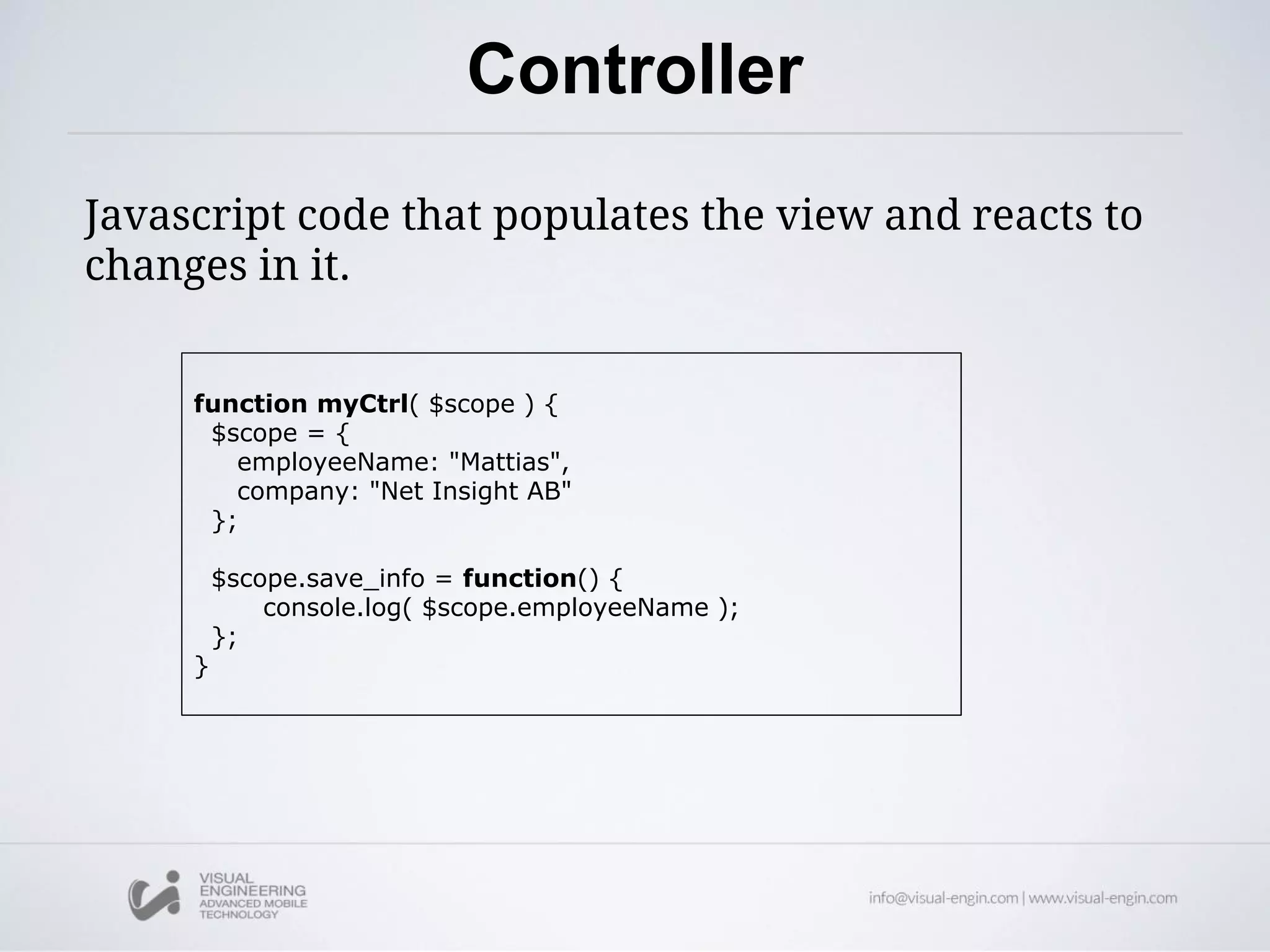
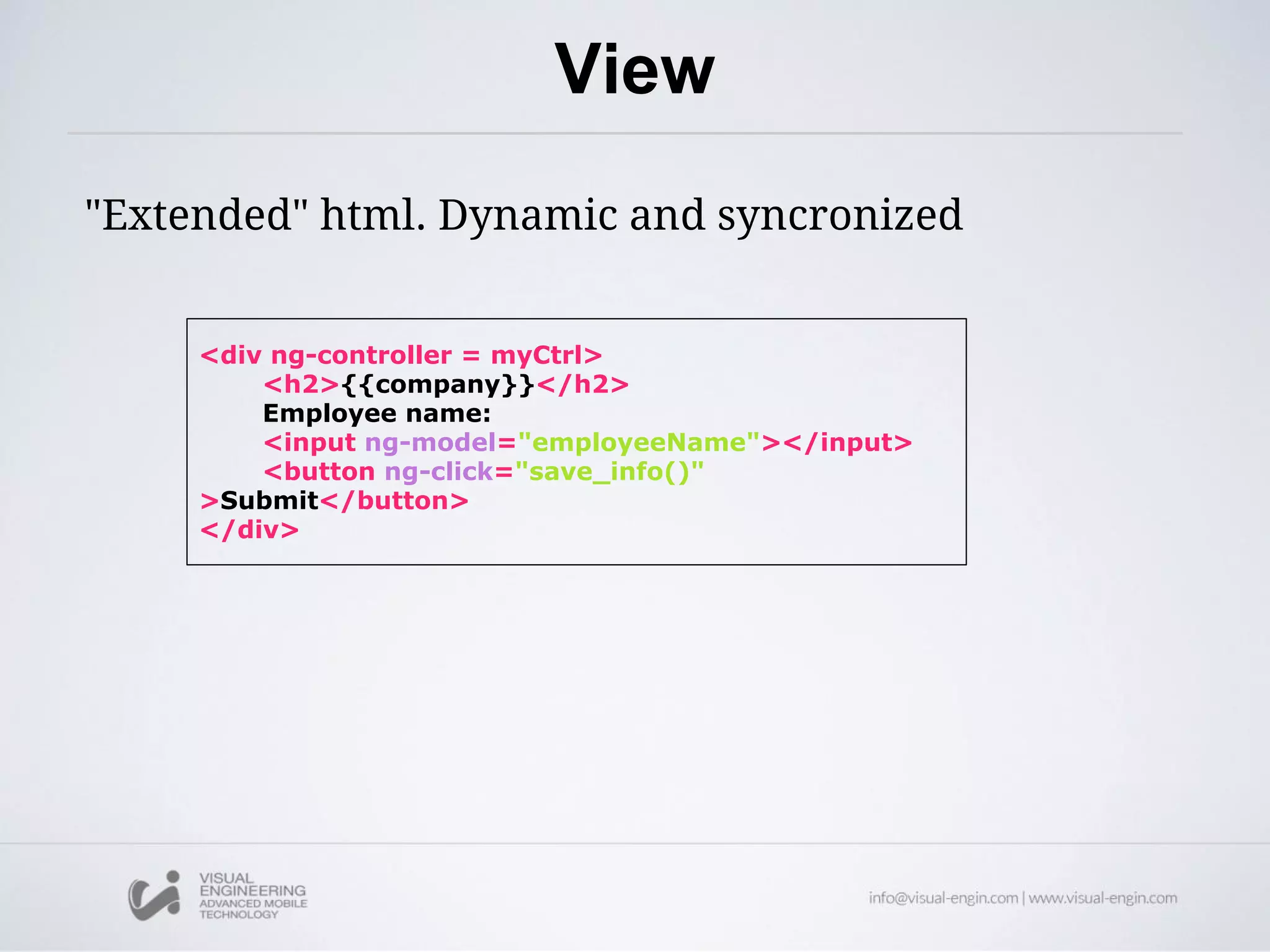
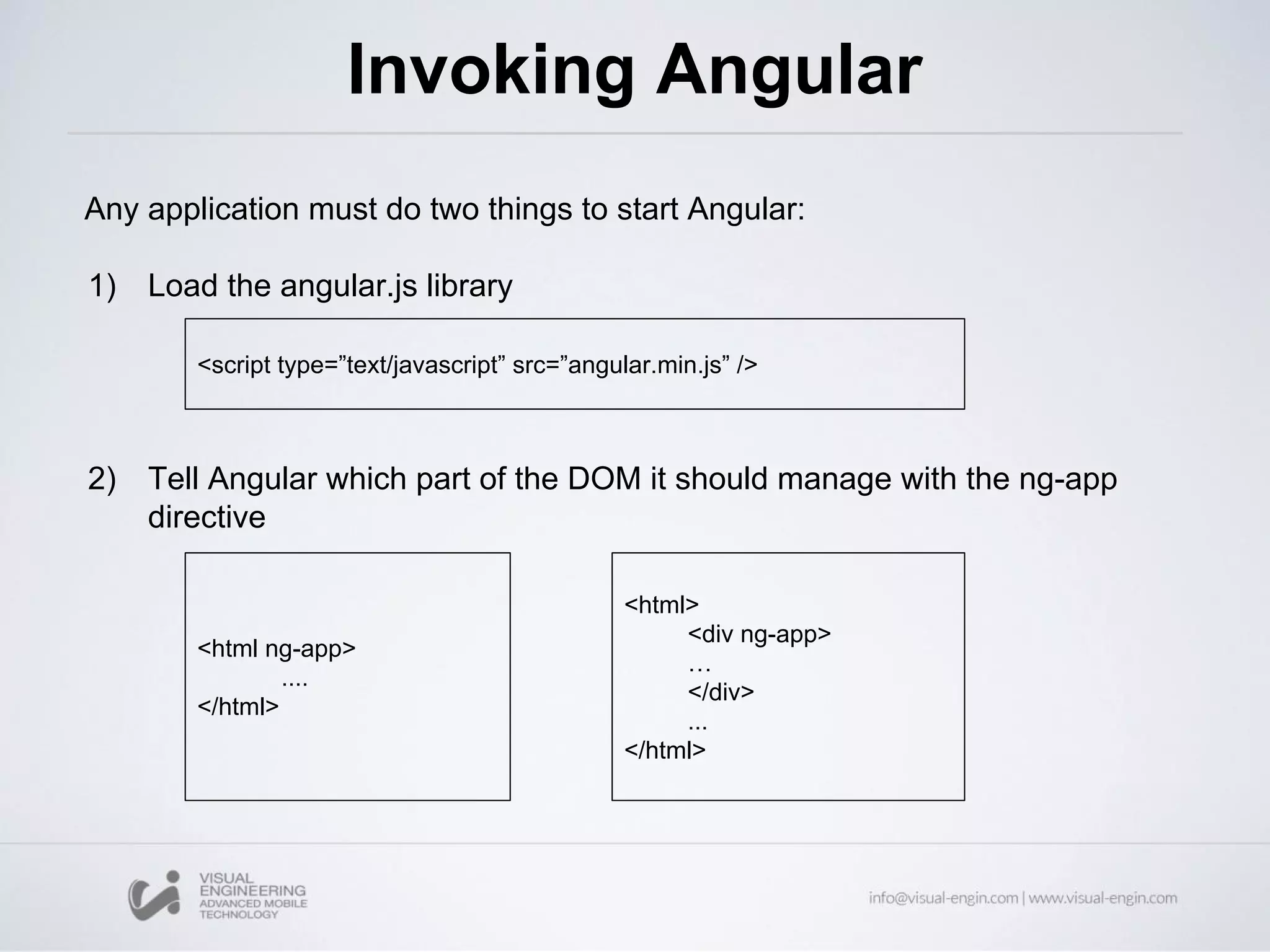
The document provides an overview of AngularJS, an open-source web application framework designed for client-side MVC and MVVM architectures, and discusses its history, features, and core concepts. Key components covered include data binding, directives, filters, modules, controllers, and services, along with examples of how to implement them in applications. Overall, it highlights AngularJS's capability to enhance HTML for dynamic web applications and improve user experience through various functionalities.






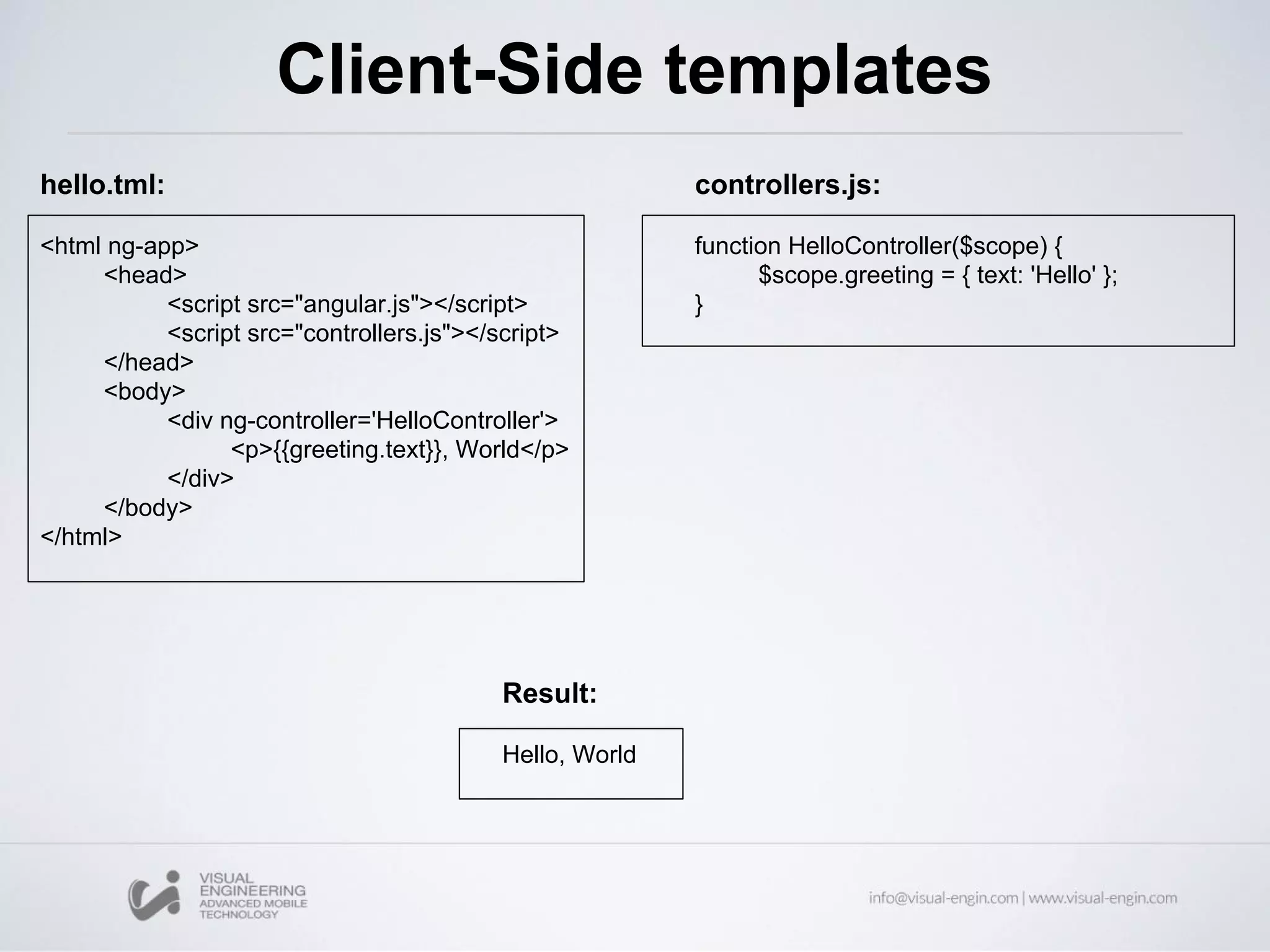
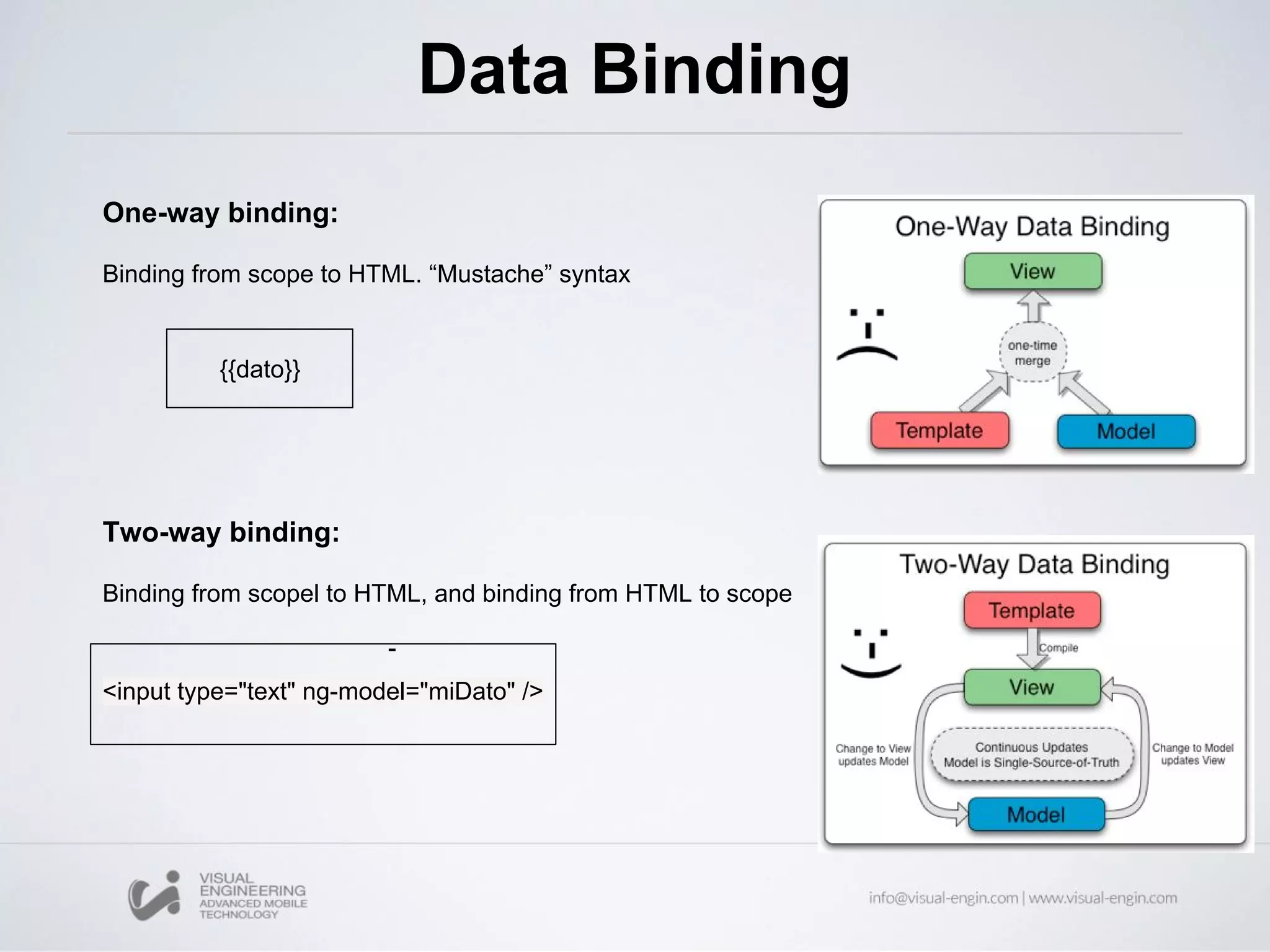
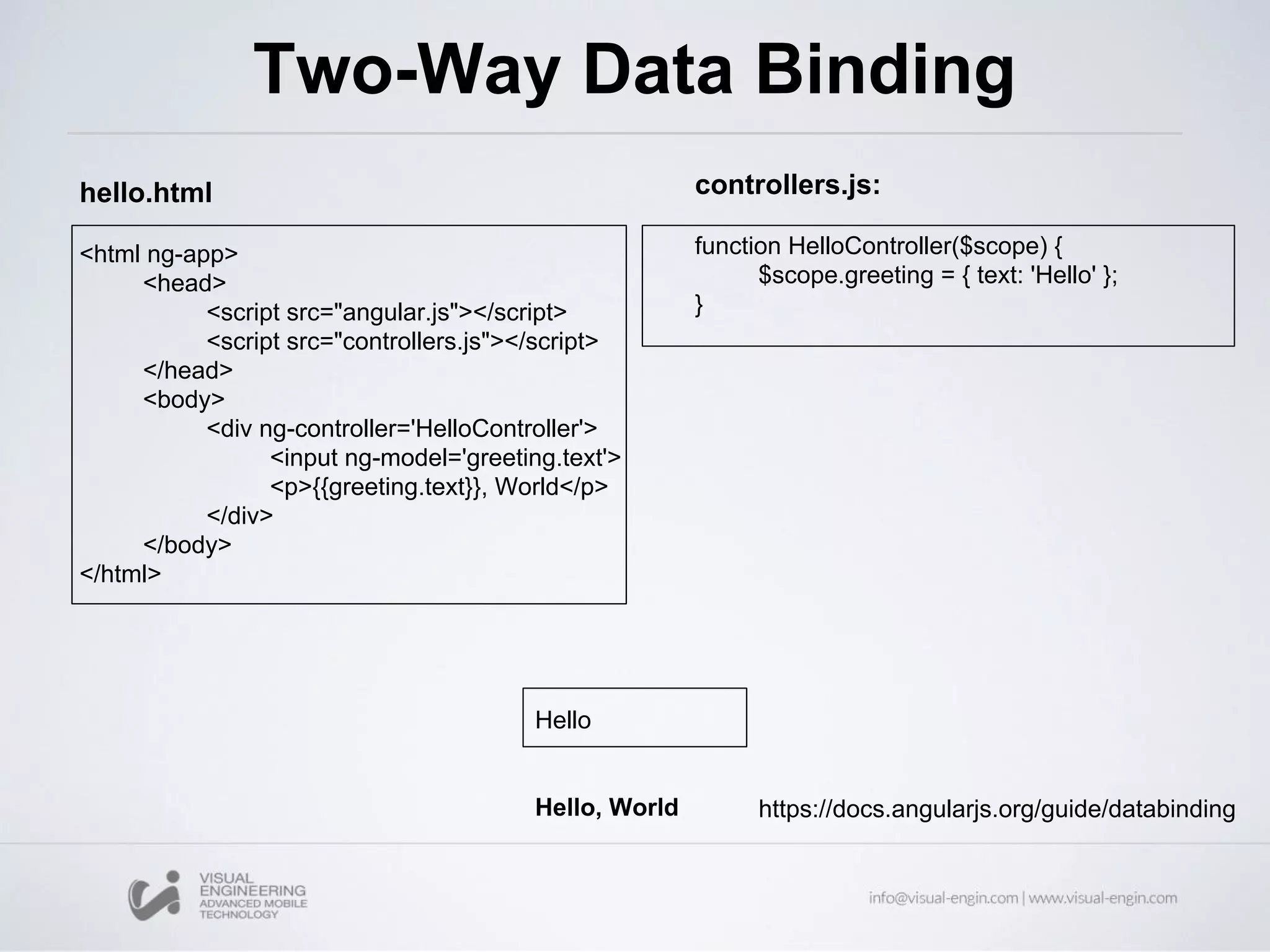


![ng-model With the ng-model directive you can bind the value of an input field to a variable created in AngularJS <div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl"> Name: <input ng-model="name"> </div> <script> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) { $scope.name = "John Doe"; }); </script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-partei-160510084859/75/Workshop-12-AngularJS-Parte-I-17-2048.jpg)
![ng-repeat <h3>FIFA Golden Ball:</h3> <div ng-app ng-controller="MyCtrl"> <ul> <li ng-repeat="player in players">{{name}}: {{num}}</li> </ul> </div> function MyCtrl($scope) { $scope.players = [ { name: “Roger” num: 6 }, { name: “Messi” num: 5 }, { name: “Cristiano Ronaldo” num: 3 } ]; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-partei-160510084859/75/Workshop-12-AngularJS-Parte-I-18-2048.jpg)

![Filters ● Angular filters format data for display to the user. {{ expression [| filter_name[:parameter_value]...] }} {{ totalCost | currency }} ● Filters can be chained and can take optional arguments. {{ totalCost | currency | filter2 | filter3 }} {{ totalCost | currency:”USD$” }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-partei-160510084859/75/Workshop-12-AngularJS-Parte-I-20-2048.jpg)

![Filters <div ng-init="friends = [{name:'John', phone:'555-1276'}, {name:'Mary', phone:'800-BIG-MARY'}, {name:'Mike', phone:'555-4321'}]"></div> <label>Search: <input ng-model="searchText"></label> <table id="searchTextResults"> <tr><th>Name</th><th>Phone</th></tr> <tr ng-repeat="friend in friends | filter:searchText | orderBy:'name'"> <td>{{friend.name}}</td> <td>{{friend.phone}}</td> </tr> </table>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-partei-160510084859/75/Workshop-12-AngularJS-Parte-I-22-2048.jpg)

![Modules var app = angular.module(‘moduleName’, [] ); Dependencies Creating: Including the module: <html ng-app=”moduleName”> .... </html> <html> <div ng-app=”moduleName”> … </div> ... </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-partei-160510084859/75/Workshop-12-AngularJS-Parte-I-25-2048.jpg)
![Modules var app = angular.module(‘moduleName’, [] ) .config(function () { ... }).run(function () { ... }); app.controller(function(){ … }); app.service(function(){ … }); app.directive(function(){ … });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-partei-160510084859/75/Workshop-12-AngularJS-Parte-I-26-2048.jpg)
![Controllers Controllers are where we define our app’s behavior by defining functions and values. app.controller('ViewCtrl', ['$scope', '$location', 'recipe', function($scope, $location, recipe) { $scope.recipe = recipe; $scope.edit = function() { $location.path('/edit/' + recipe.id); }; }]); <html> <div ng-controller=·ViewCtrl”> … </div> ... </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-partei-160510084859/75/Workshop-12-AngularJS-Parte-I-27-2048.jpg)