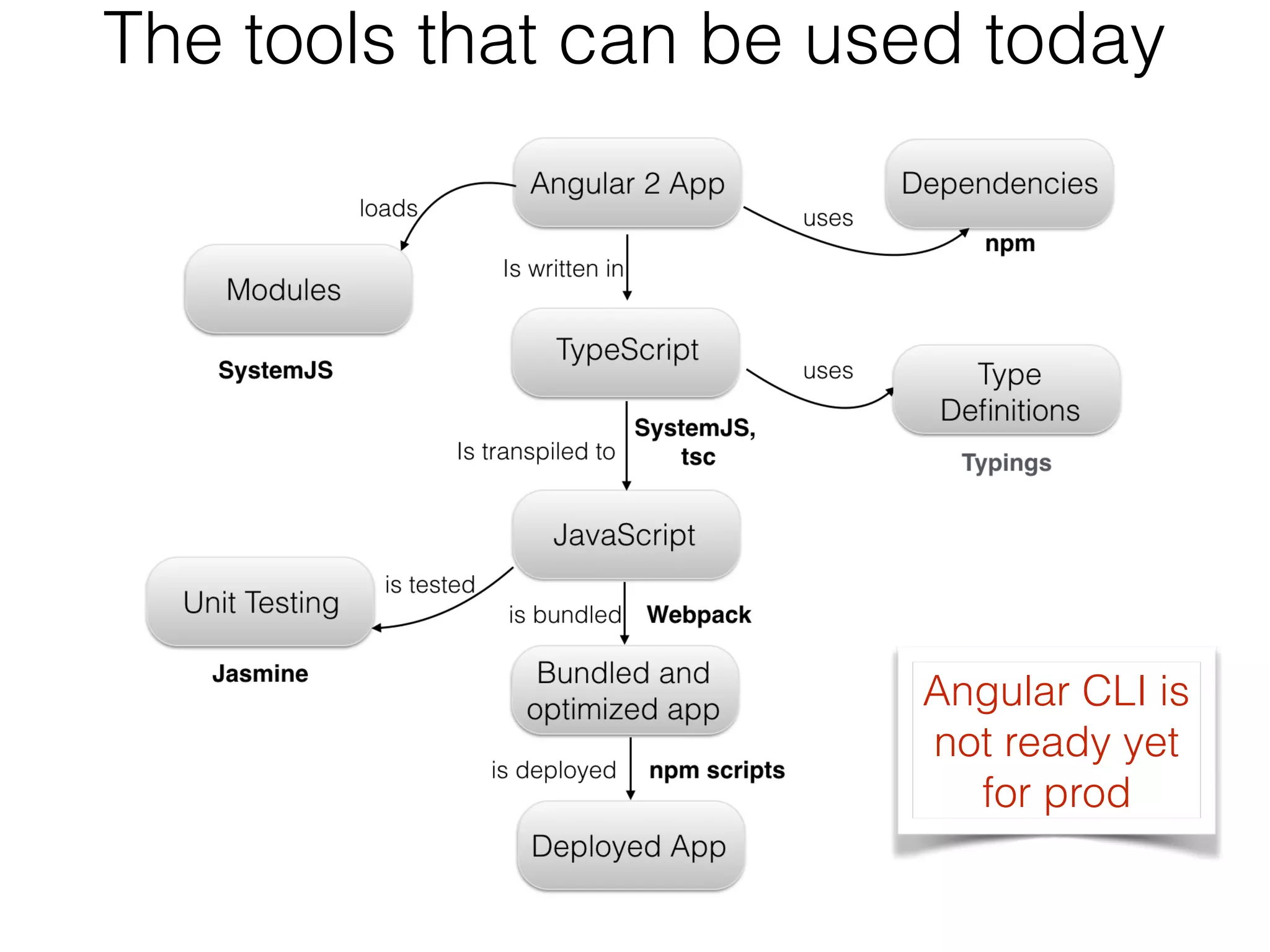
This document provides an overview of Angular 2 development for Java developers. It discusses key aspects of Angular 2 including components, templates, data binding, dependency injection, and routing. It also covers TypeScript and how it adds types, classes and interfaces to JavaScript. The document uses examples to demonstrate classes, interfaces, generics, and inheritance in TypeScript.







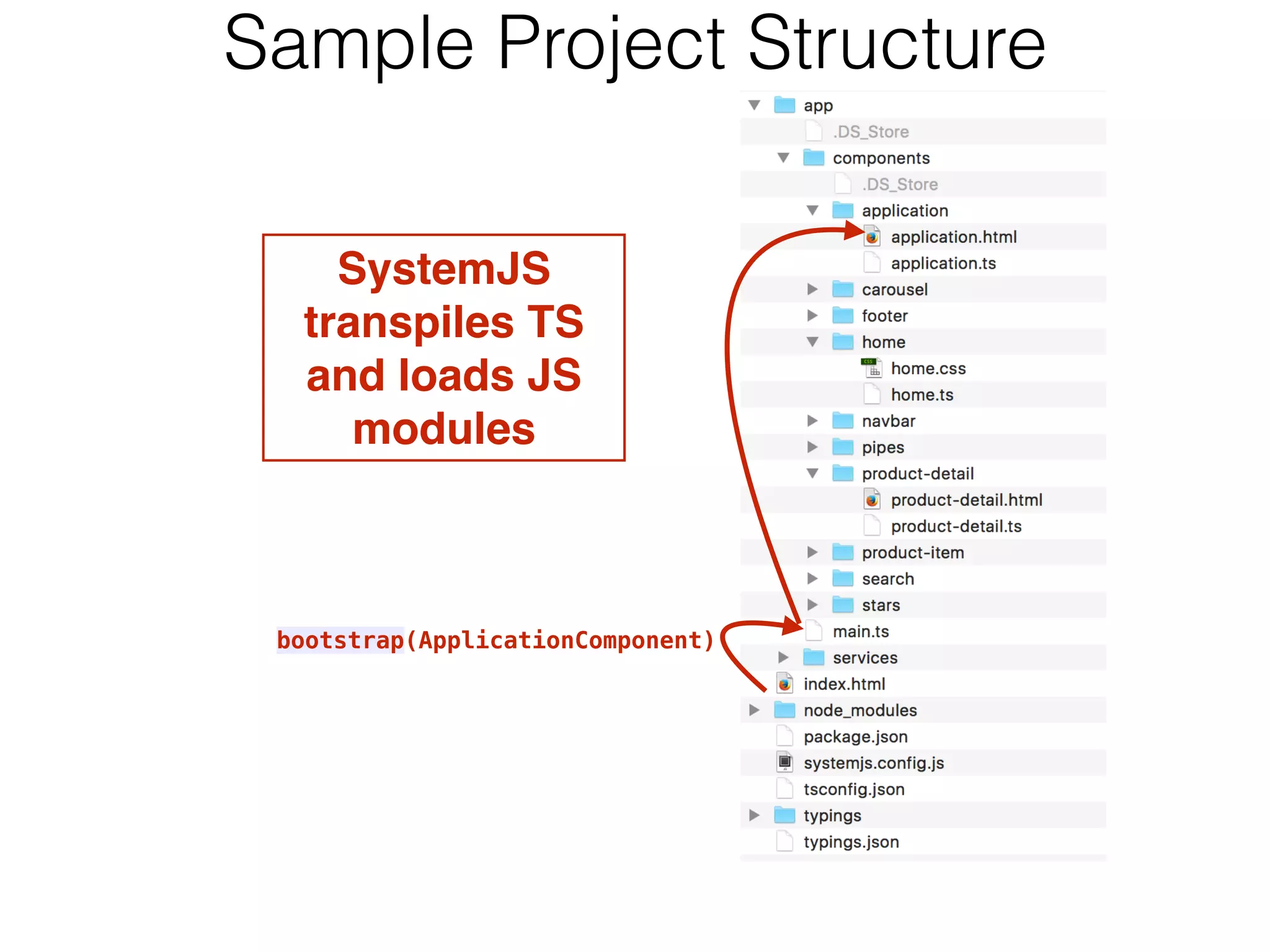
![// import …
@Component({
selector: 'auction-application',
templateUrl: 'app/components/application/application.html',
directives: [
NavbarComponent,
FooterComponent,
SearchComponent,
HomeComponent
]
})
@Routes([
{path: '/', component: HomeComponent},
{path: '/products/:prodTitle', component: ProductDetailComponent}
])
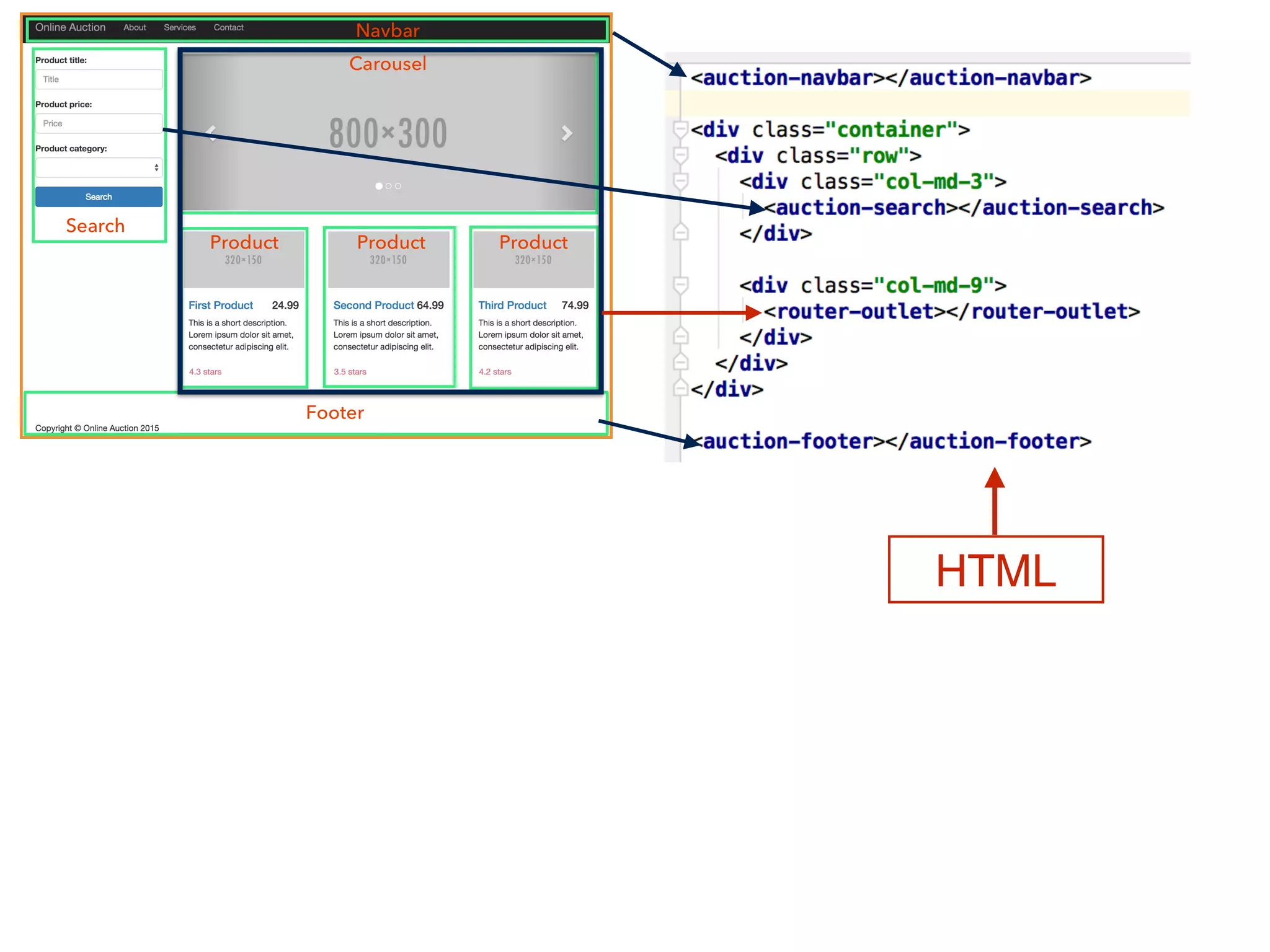
export default class ApplicationComponent {} HTML Router Configuration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-17-2048.jpg)
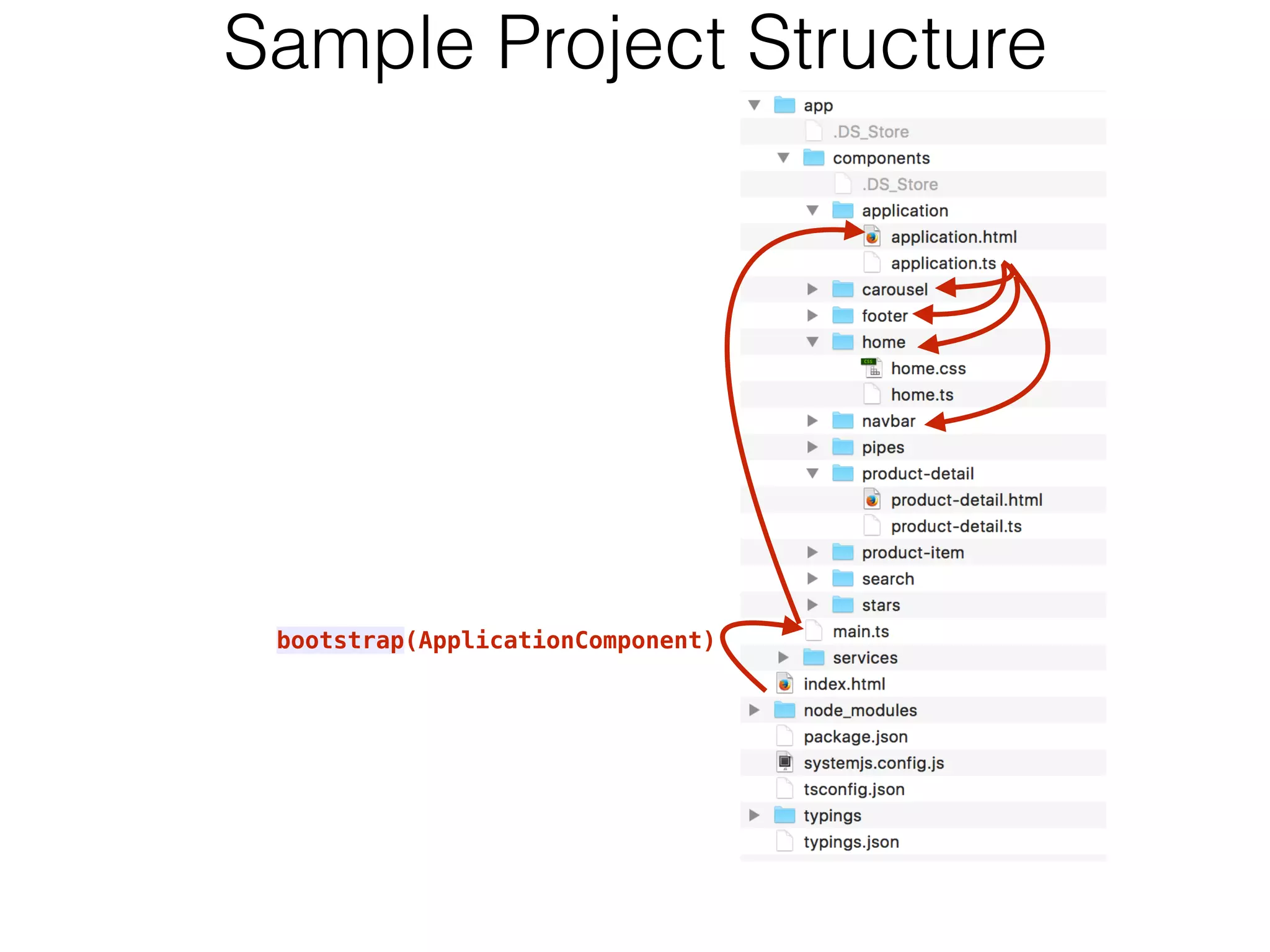
![Component Router: main elements • @Routes - map URLs to components to render inside the <router-outlet>
• RouterLink ([routerLink]) - a link to a named route
• RouterOutlet (<router-outlet>) - where the router should render the component • RouteSegment - a map of key-value pairs to pass parameters to the route template: `<a [routerLink]="['/Home']">Home</a>
<a [routerLink]="['/ProductDetail', {id:1234}]">Product Details</a>` @Routes([
{path: '/', component: HomeComponent},
{path: '/product/:id', component: ProductDetailComponentParam}
] constructor(params: RouteSegment){
this.productID = params.getParam('id');
} template: `… <router-outlet></router-outlet>
`](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-18-2048.jpg)
![import …
@Component({
selector: 'auction-home-page',
directives: [
CarouselComponent,
ProductItemComponent
],
styleUrls: ['app/components/home/home.css'],
template: `
<div class="row carousel-holder">
<div>
<auction-carousel></auction-carousel>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<div *ngFor=“let product of products">
<auction-product-item [product]="product">
</auction-product-item>
</div>
</div>
`
})
export default class HomeComponent {
products: Product[] = [];
constructor(private productService: ProductService) {
this.products = productService.getProducts();
}
} HomeComponent DI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-19-2048.jpg)
![Unidirectional Binding From code to template: <h1>Hello {{ name }}!</h1> <span [hidden]=“isZipcodeValid”>Zip code is not valid</span> From template to code: <button (click)="placeBid()">Place Bid</button> <input placeholder= "Product name" (input)="onInputEvent()"> Properties Events](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-20-2048.jpg)
![Two-way Binding Synchronizing Model and View: <input [(ngModel)] = "myComponentProperty"> The value property of the <input> and myComponentProperty will be always in sync](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-21-2048.jpg)
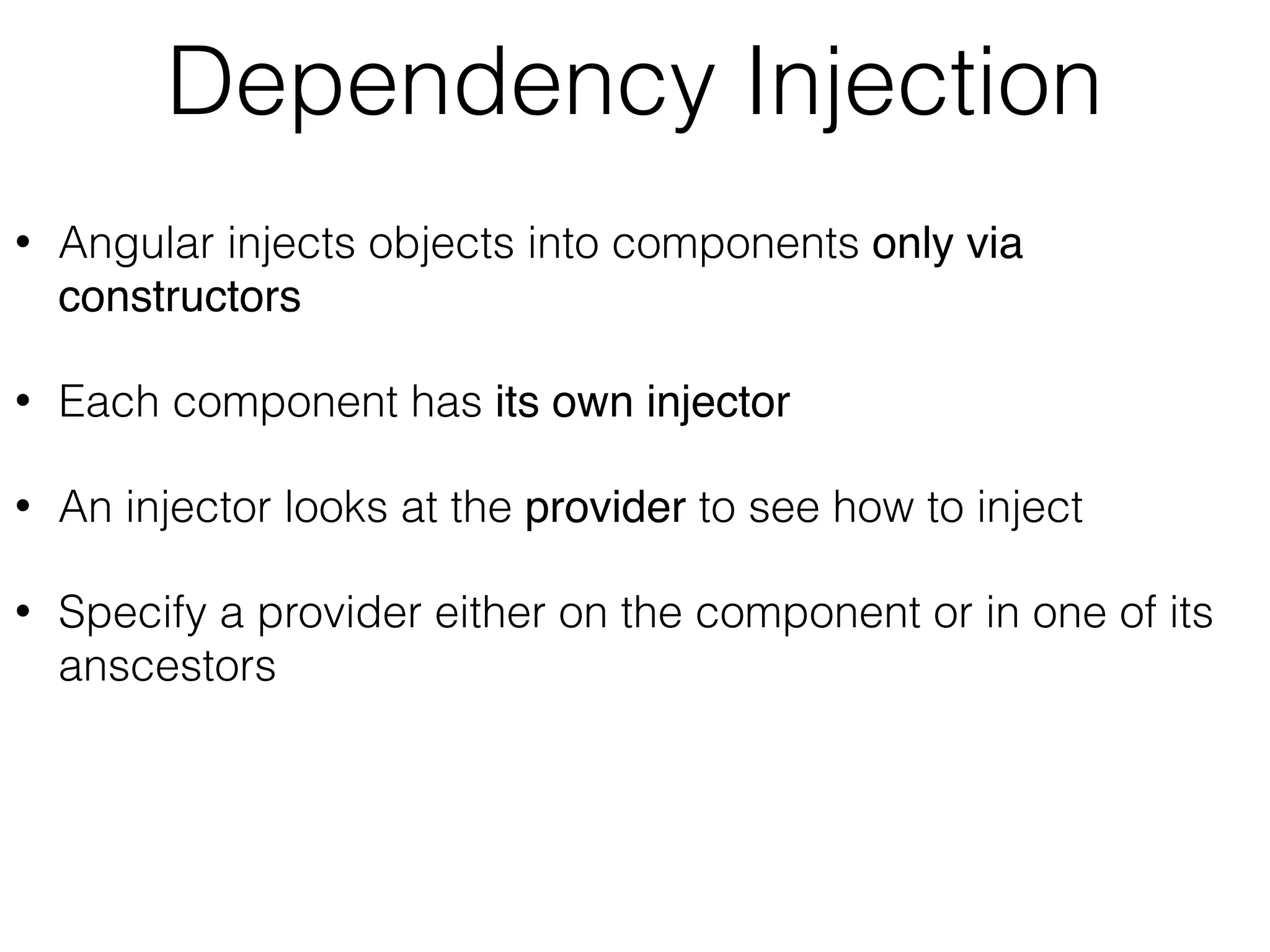
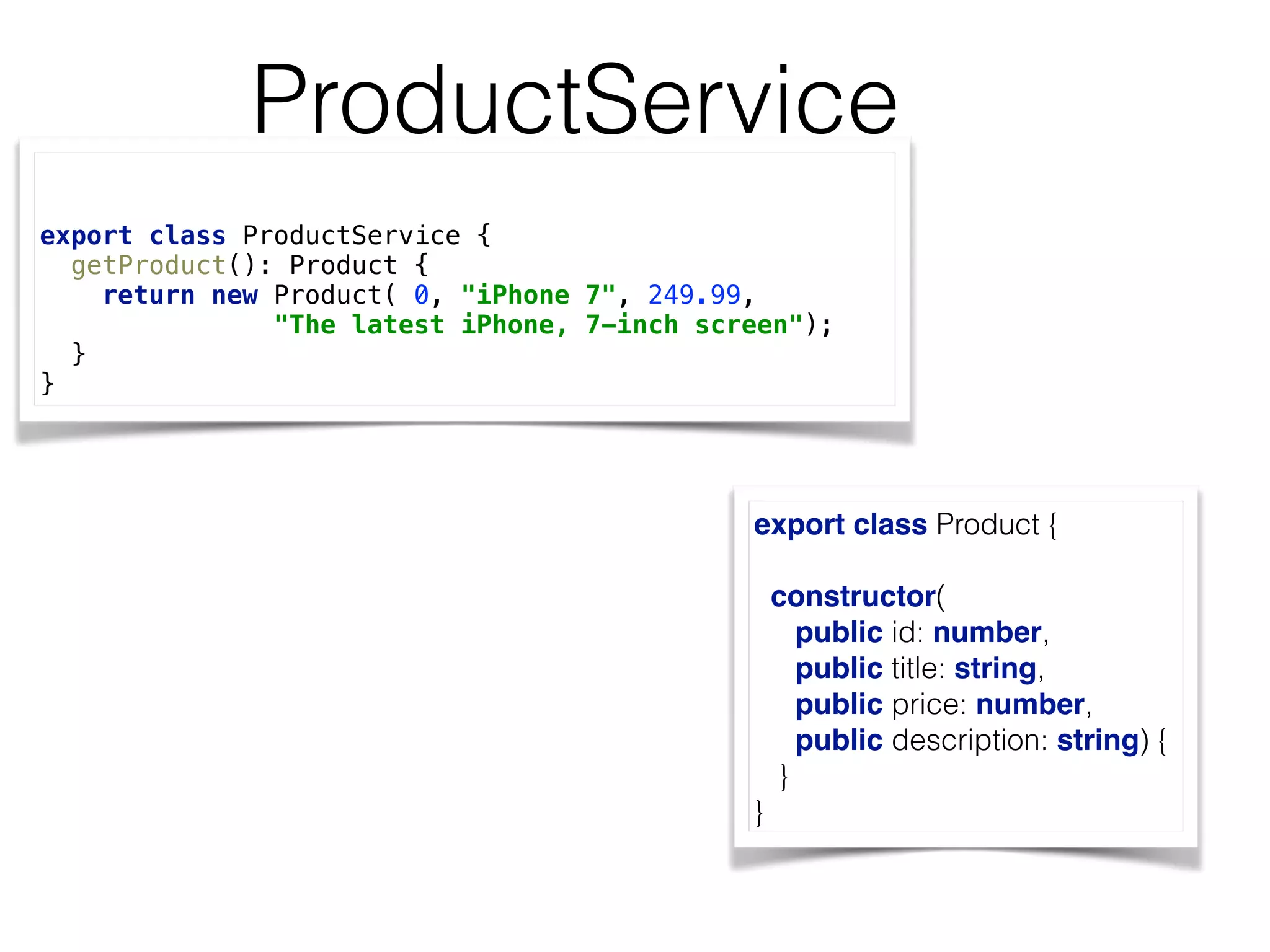
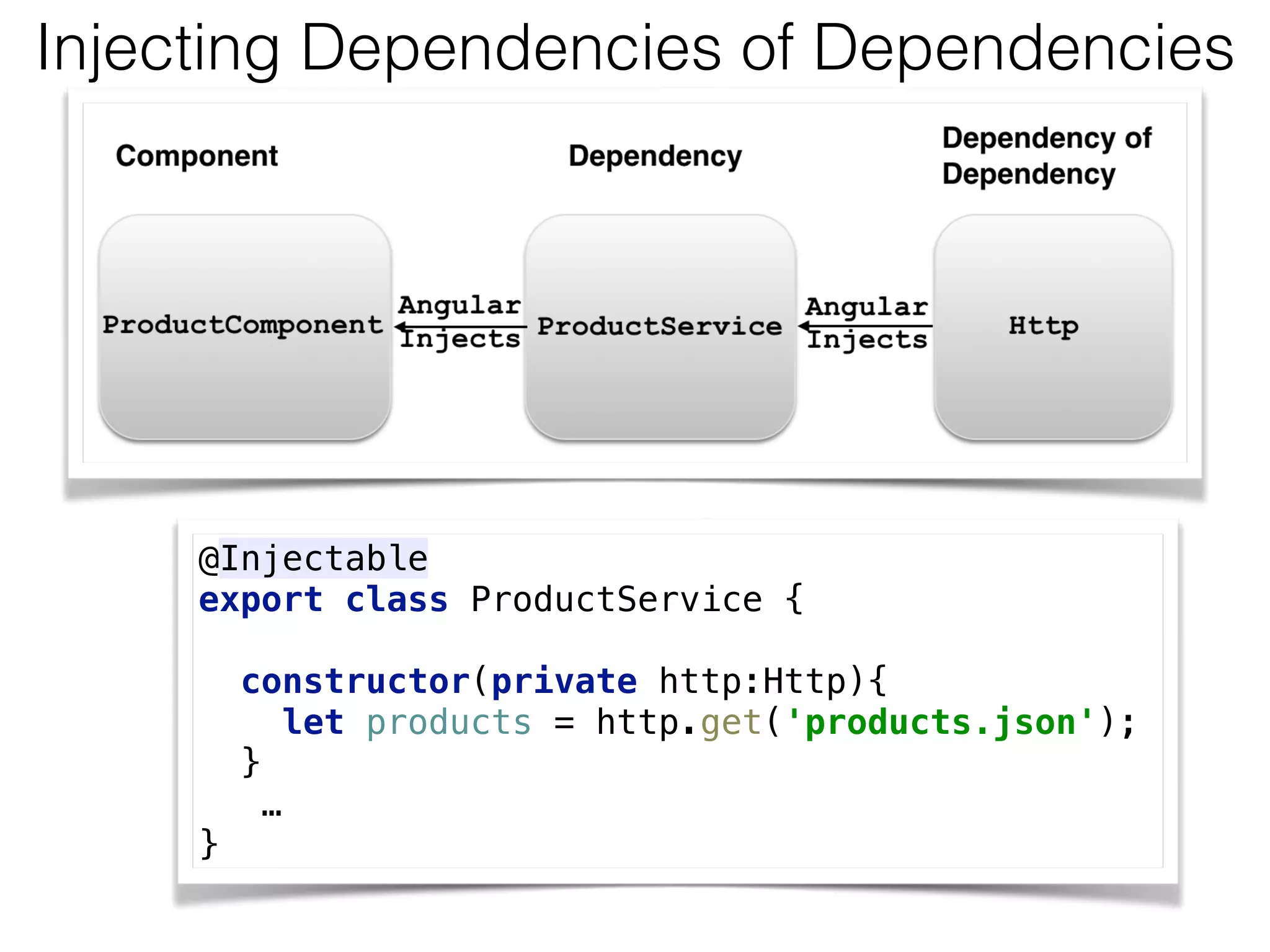
![Injecting ProductService import {Component, bind} from ‘@angular/core';
import {ProductService, Product} from "../services/product-service";
@Component({
selector: 'di-product-page',
template: `<div>
<h1>Product Details</h1>
<h2>Title: {{product.title}}</h2>
<h2>Description: {{product.description}}</h2>
</div>`,
providers:[ProductService]
})
export default class ProductComponent {
product: Product;
constructor( productService: ProductService) {
this.product = productService.getProduct();
}
}
A provider can be a class, factory, or a value An injection point](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-24-2048.jpg)
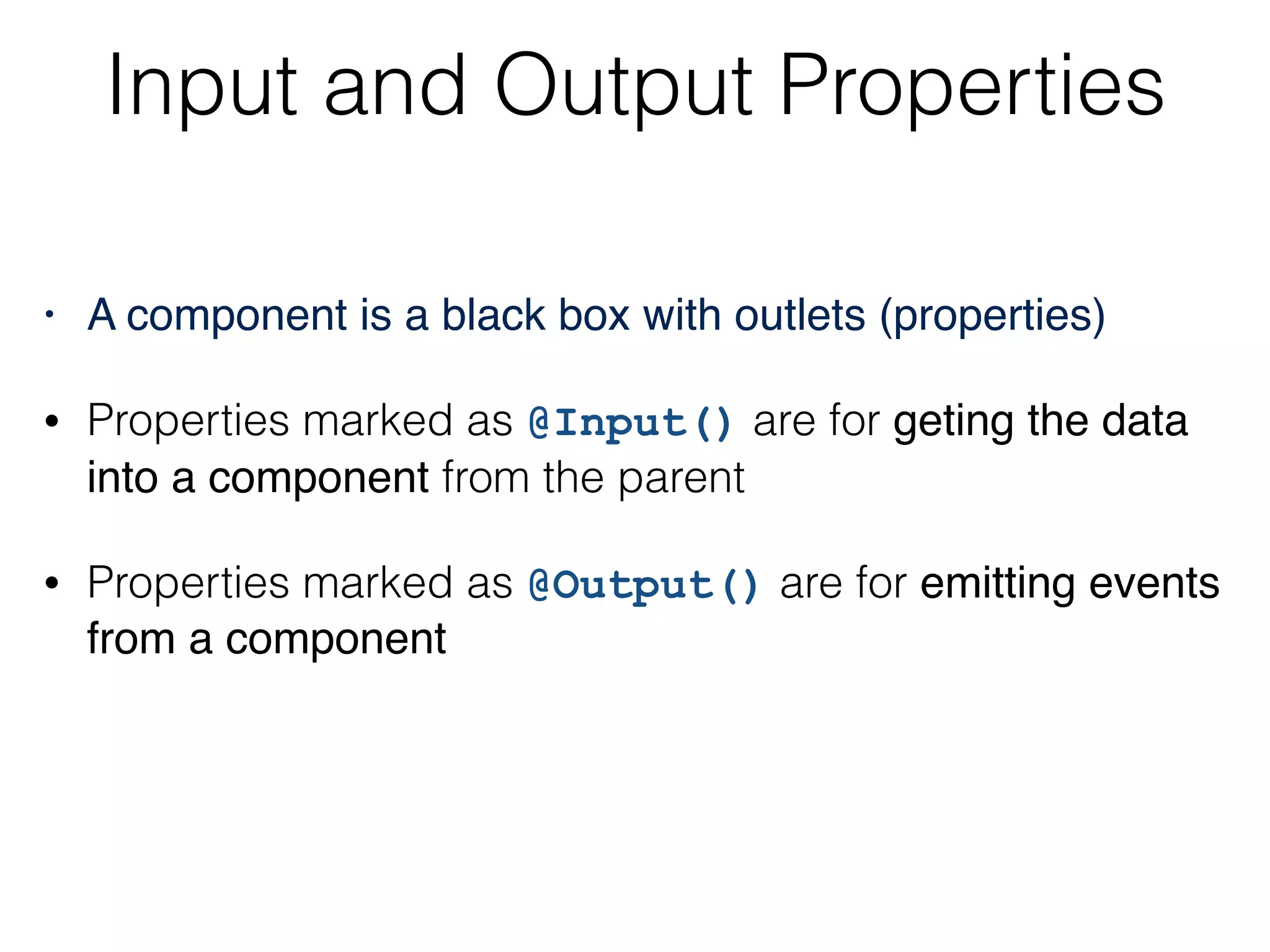
![Binding to child’s inputs @Component({
selector: 'app',
template: `
<input type="text" placeholder="Enter stock (e.g. AAPL)"
(change)="onInputEvent($event)">
<br/>
<order-processor [stockSymbol]=“stock"></order-processor>
`,
directives: [OrderComponent]
})
class AppComponent {
stock:string;
onInputEvent({target}):void{
this.stock=target.value;
}
} Binding to the child’s prop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-27-2048.jpg)
![Using Destructuring @Component({
selector: 'app',
template: `
<input type="text" placeholder="Enter stock (e.g. AAPL)"
(change)="onInputEvent($event)">
<br/>
<order-processor [stockSymbol]=“stock"></order-processor>
`,
directives: [OrderComponent]
})
class AppComponent {
stock:string;
onInputEvent({target}):void{
this.stock=target.value;
}
} Destructuring](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-28-2048.jpg)
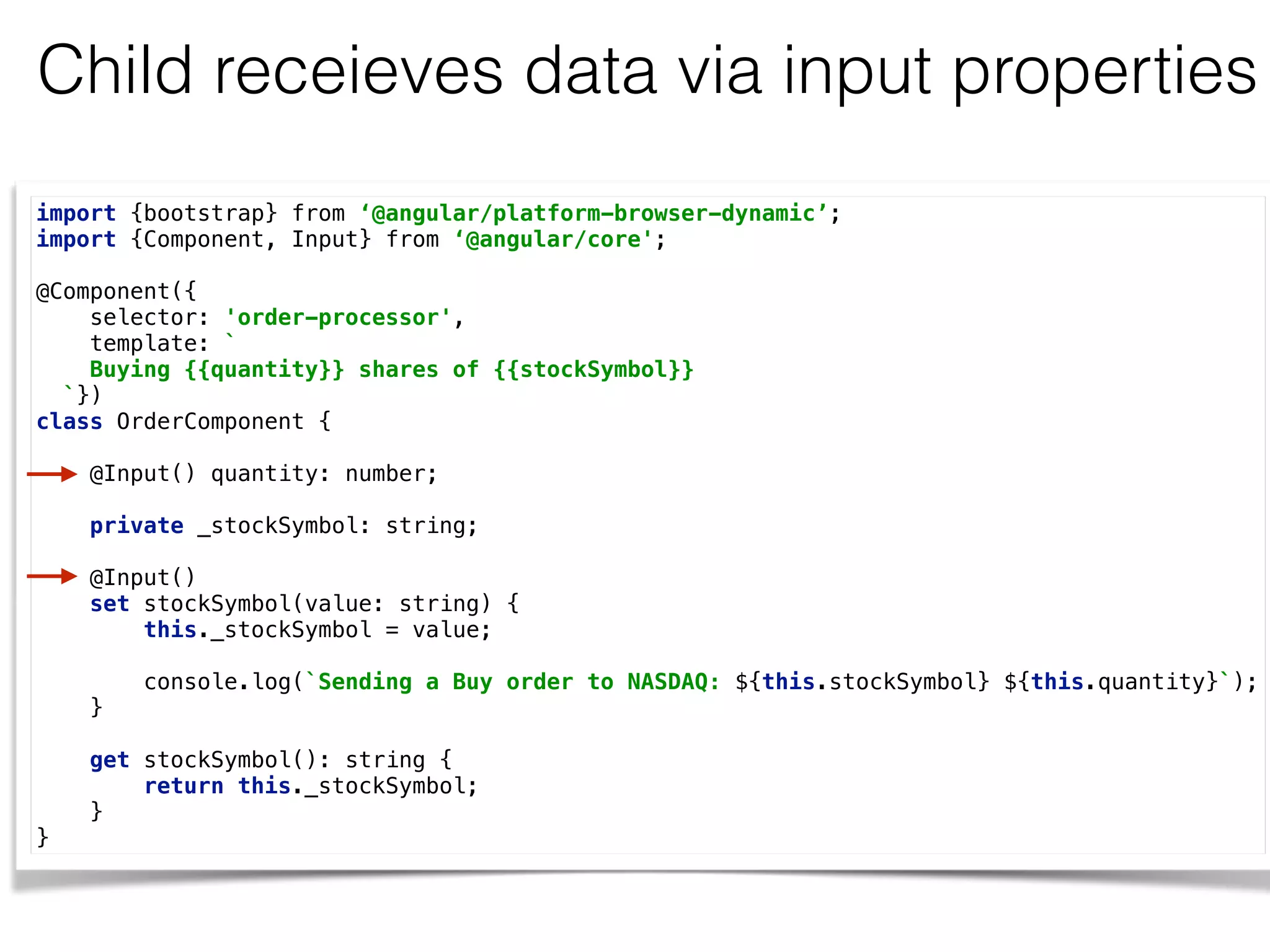
![Child sends events via an output property @Component({
selector: 'price-quoter',
template: `<strong>Inside PriceQuoterComponent:
{{stockSymbol}} {{price | currency:'USD':true:'1.2-2'}}</strong>`,
styles:[`:host {background: pink;}`]
})
class PriceQuoterComponent {
@Output() lastPrice: EventEmitter <IPriceQuote> = new EventEmitter();
stockSymbol: string = "IBM";
price:number;
constructor() {
setInterval(() => {
let priceQuote: IPriceQuote = {
stockSymbol: this.stockSymbol,
lastPrice: 100*Math.random()
};
this.price = priceQuote.lastPrice;
this.lastPrice.emit(priceQuote);
}, 1000);
}
} A child emits events
via output properties](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-30-2048.jpg)
![Parent listens to an event @Component({
selector: 'app',
template: `
<price-quoter (lastPrice)=“priceQuoteHandler($event)"></price-quoter><br>
AppComponent received: {{stockSymbol}} {{price | currency:’USD’:true:'1.2-2'}} `,
directives: [PriceQuoterComponent]
})
class AppComponent {
stockSymbol: string;
price:number;
priceQuoteHandler(event:IPriceQuote) {
this.stockSymbol = event.stockSymbol;
this.price = event.lastPrice;
}
} interface IPriceQuote {
stockSymbol: string;
lastPrice: number;
} pipe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-31-2048.jpg)
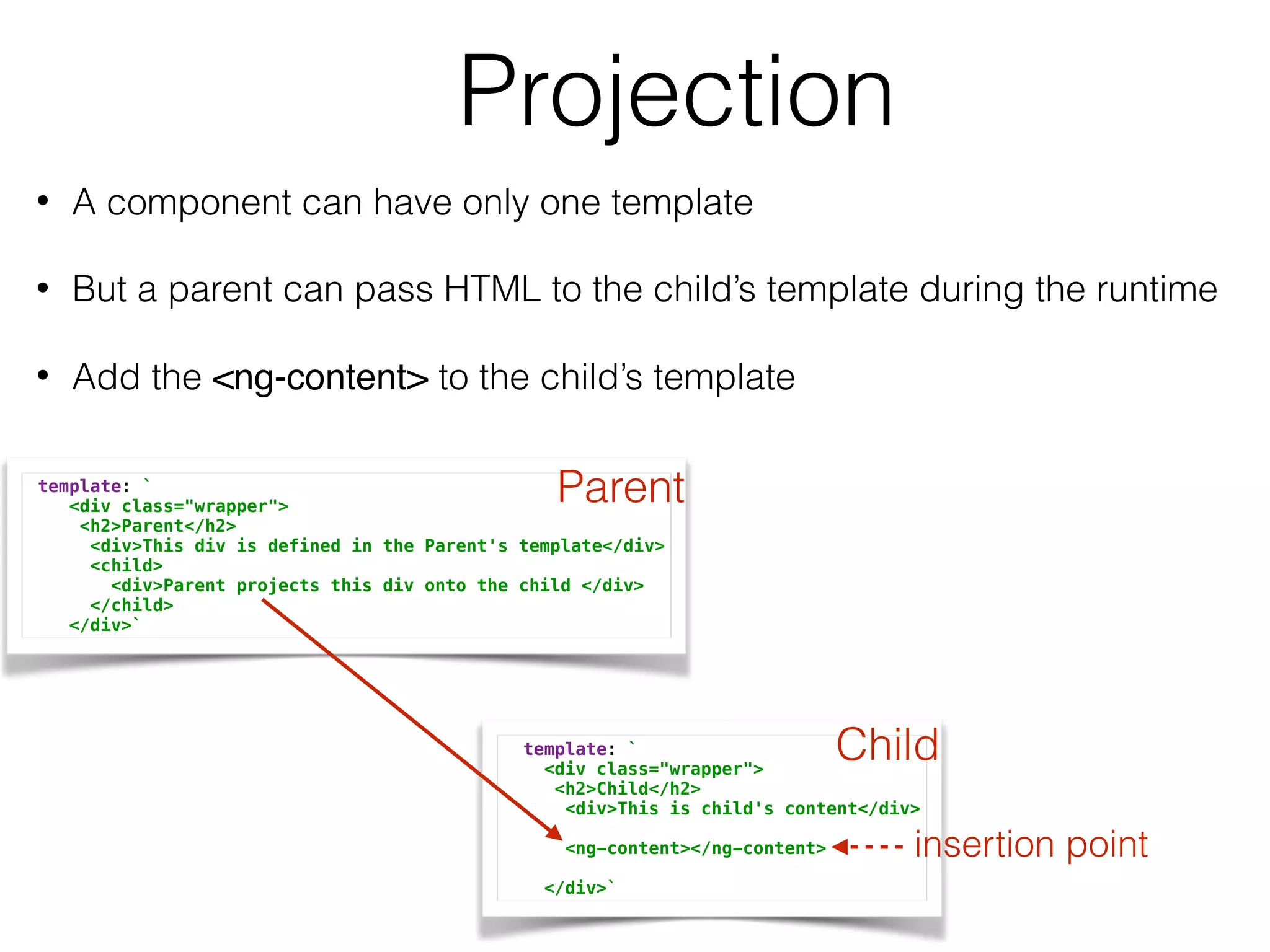
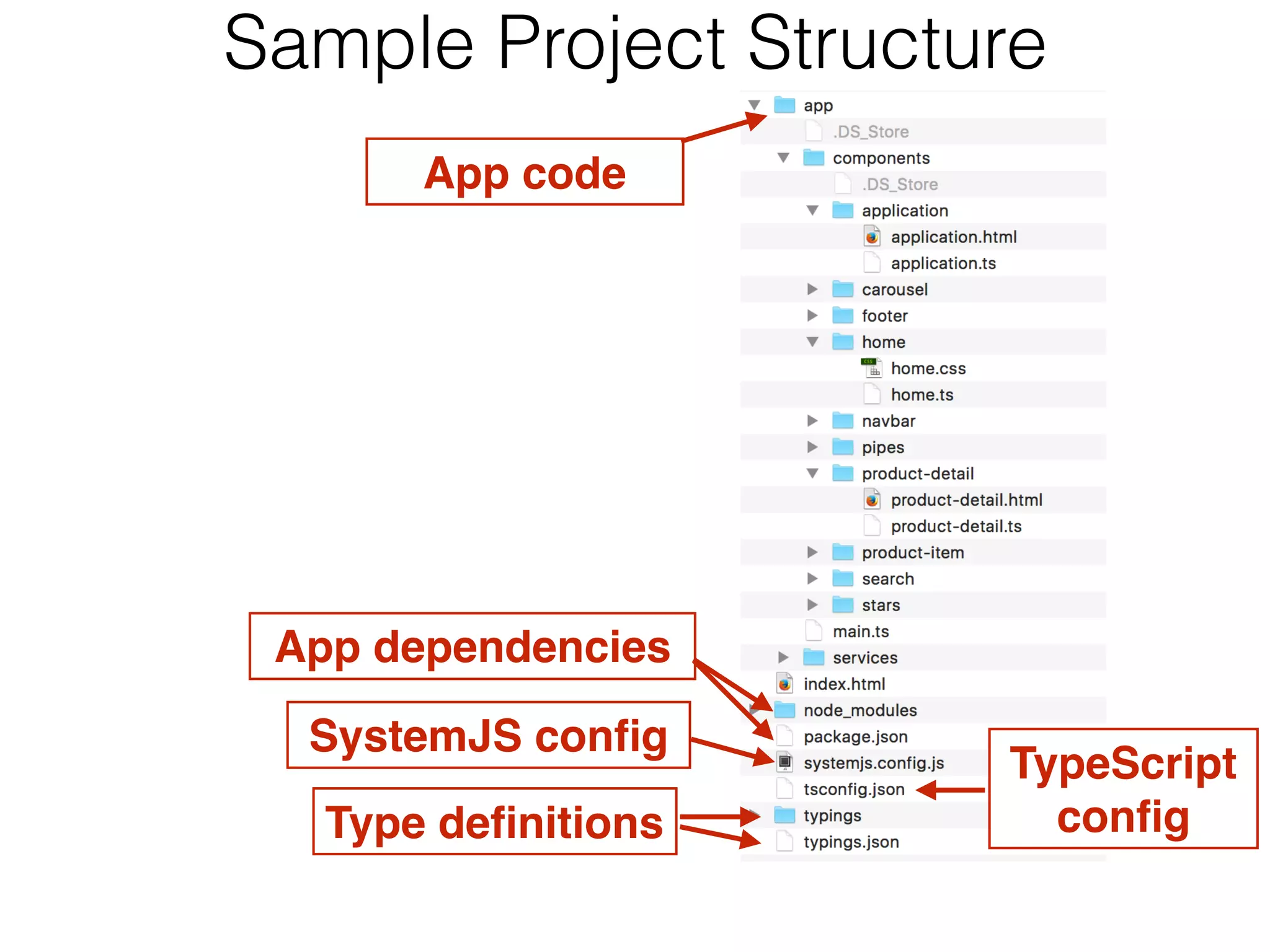



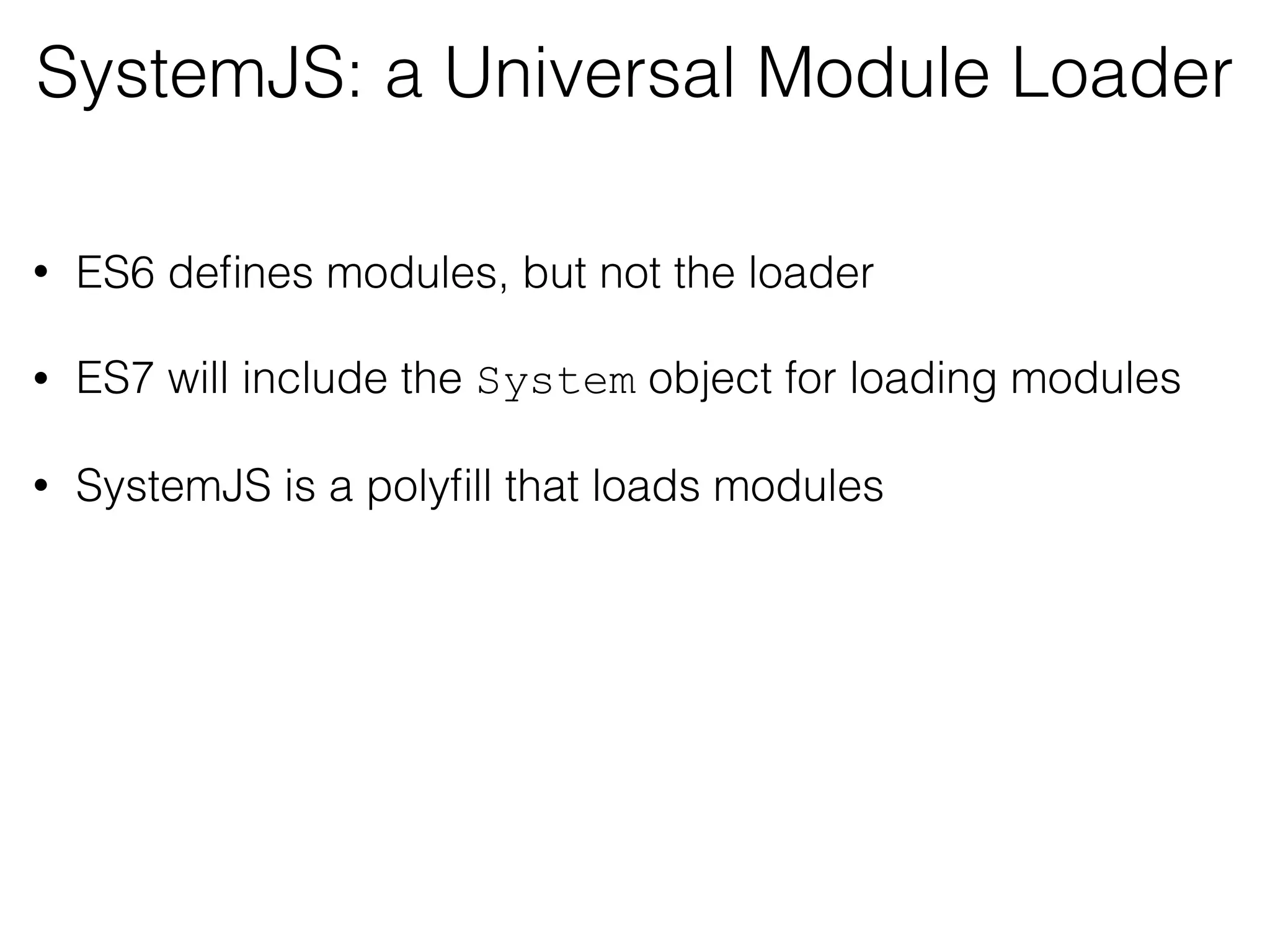

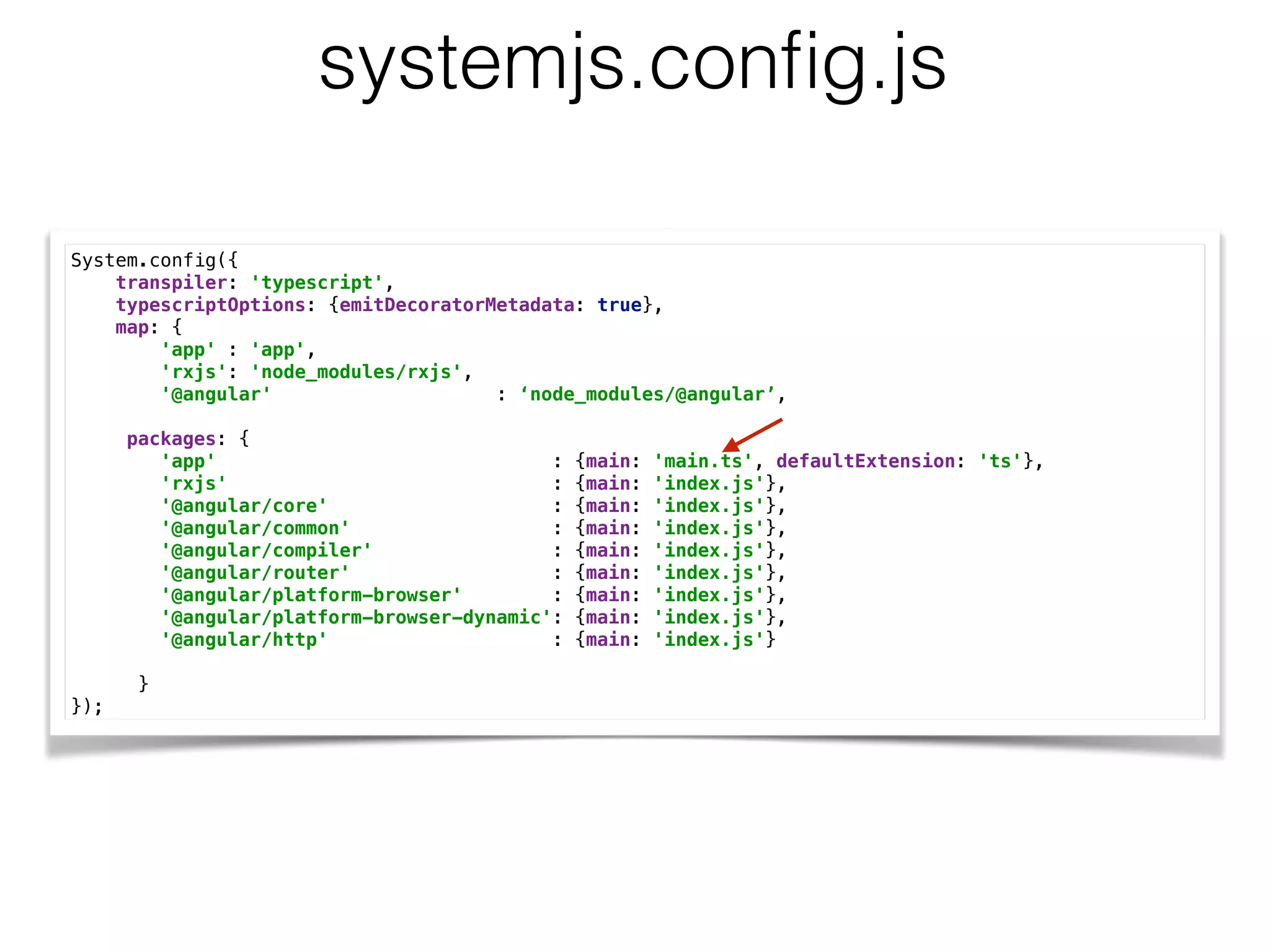

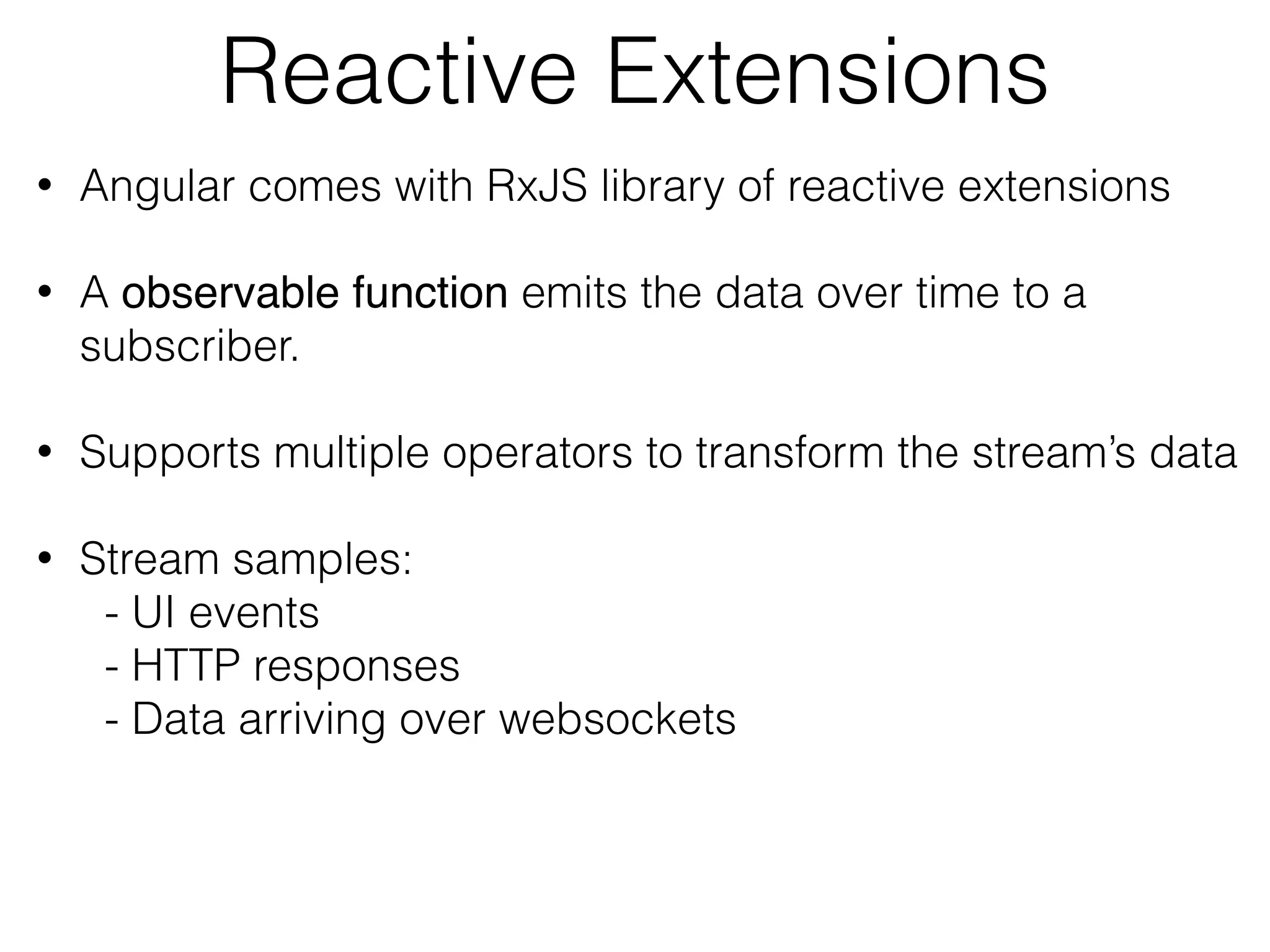


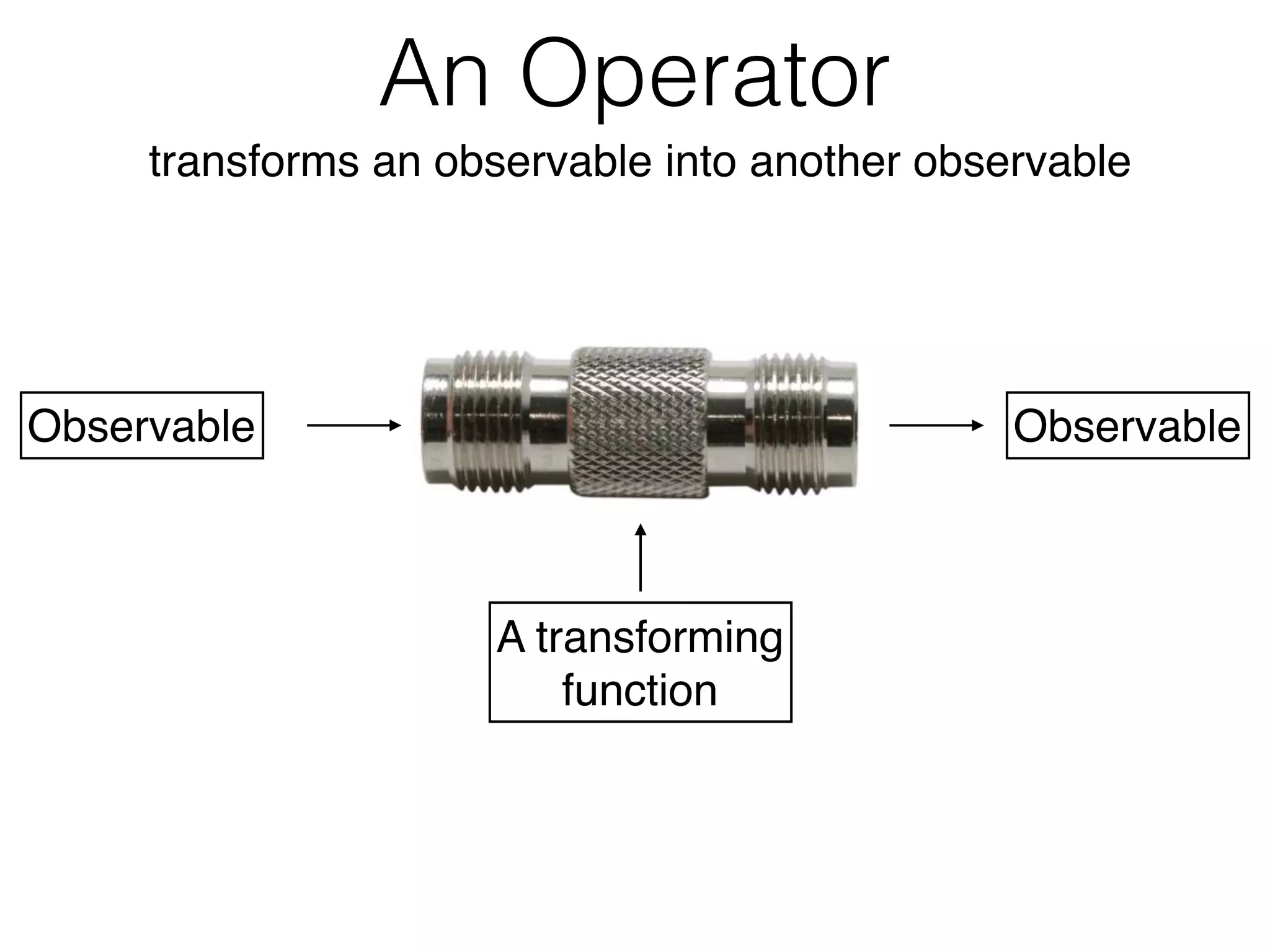
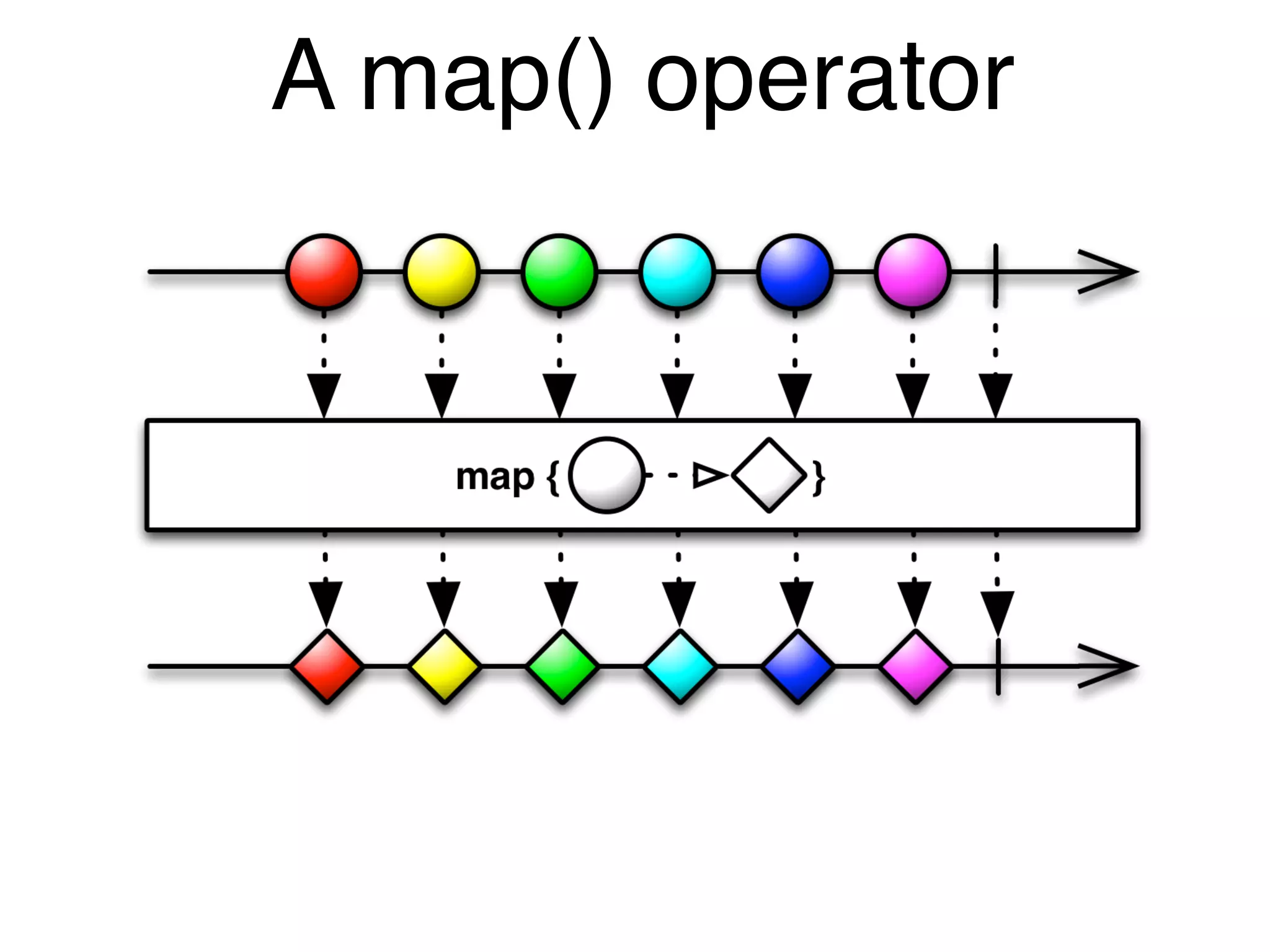
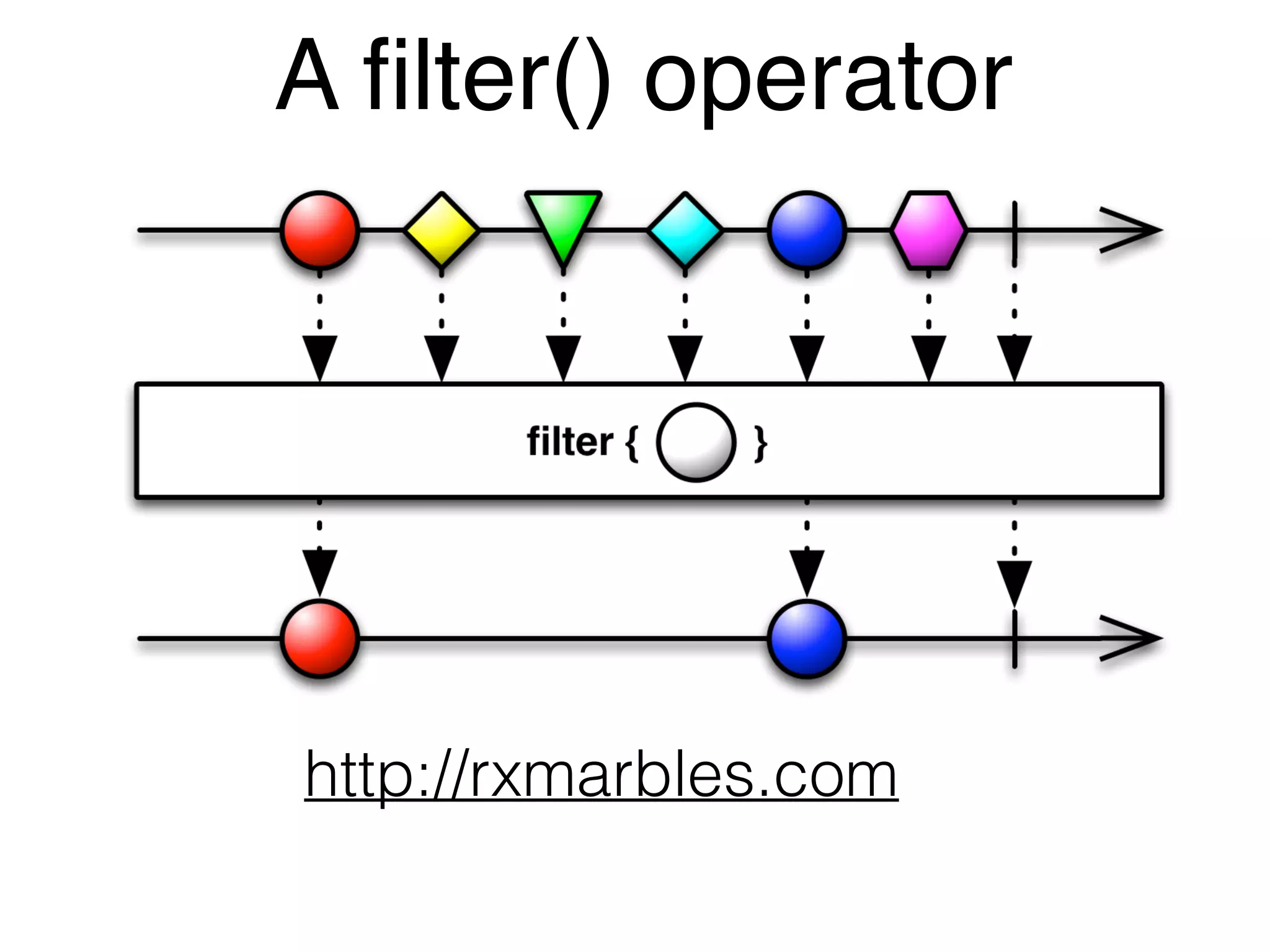
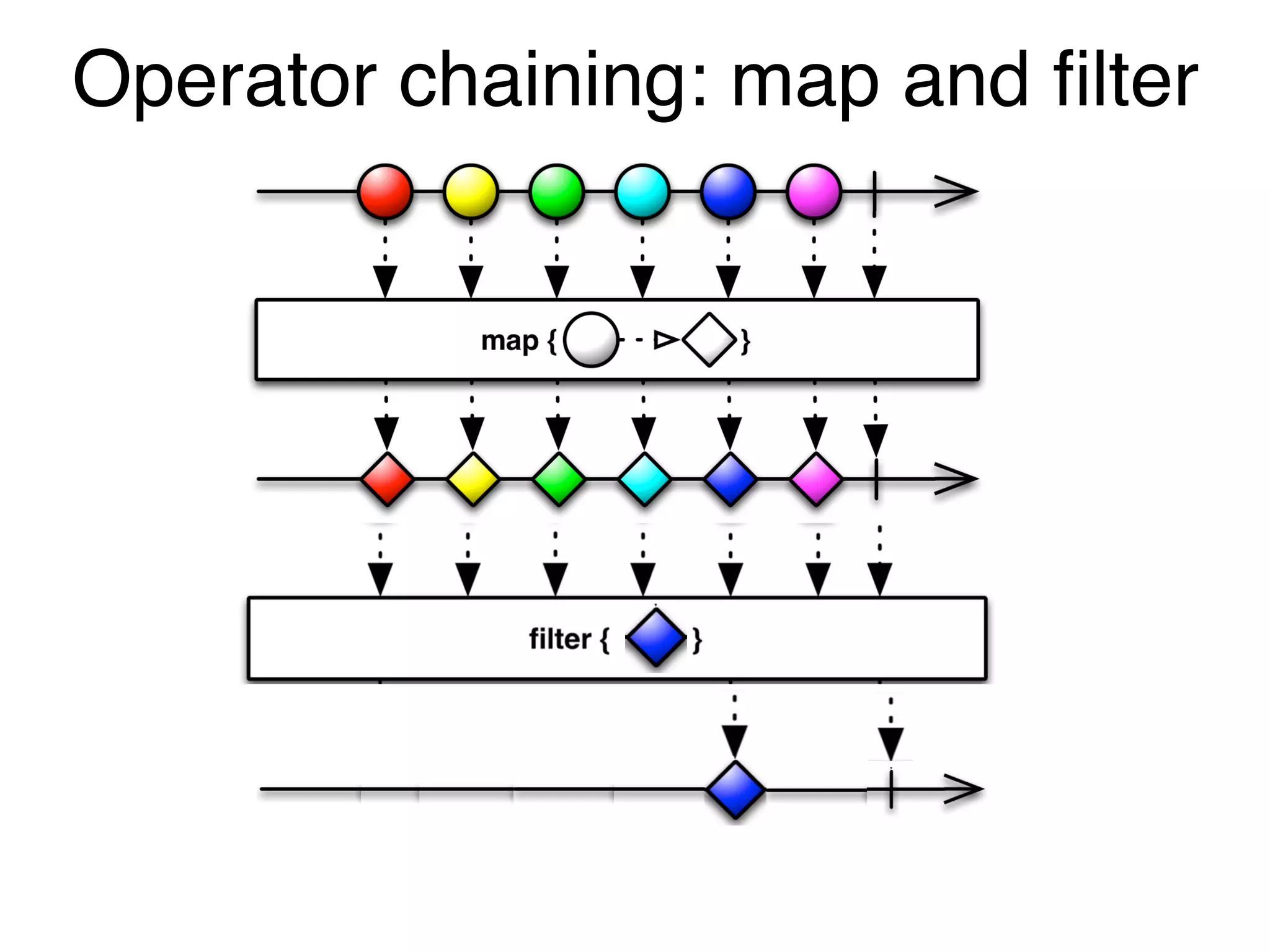
![Observables in the UI@Component({
selector: "app",
template: `
<h2>Observable events demo</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="Enter stock" [ngFormControl]="searchInput">
`
})
class AppComponent {
searchInput: Control;
constructor(){
this.searchInput = new Control('');
this.searchInput.valueChanges
.debounceTime(500)
.subscribe(stock => this.getStockQuoteFromServer(stock));
}
getStockQuoteFromServer(stock) {
console.log(`The price of ${stock} is ${100*Math.random().toFixed(4)}`);
}
} Observable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-53-2048.jpg)
![Http and Observables
class AppComponent {
products: Array<string> = [];
constructor(private http: Http) {
this.http.get(‘http://localhost:8080/products')
.map(res => res.json())
.subscribe(
data => {
this.products=data;
},
err =>
console.log("Can't get products. Error code: %s, URL: %s ",
err.status, err.url),
() => console.log('Product(s) are retrieved')
);
}
} DI O b s e r v e r](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-54-2048.jpg)




![const path = require('path');
const CommonsChunkPlugin = require('webpack/lib/optimize/CommonsChunkPlugin');
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin');
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin');
const DedupePlugin = require('webpack/lib/optimize/DedupePlugin');
const DefinePlugin = require('webpack/lib/DefinePlugin');
const OccurenceOrderPlugin = require('webpack/lib/optimize/OccurenceOrderPlugin');
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('webpack/lib/optimize/UglifyJsPlugin');
const ENV = process.env.NODE_ENV = 'production';
const metadata = {
env: ENV
};
module.exports = {
debug: false,
devtool: 'source-map',
entry: {
'main' : './src/main.ts',
'vendor': './src/vendor.ts'
},
metadata: metadata,
module: {
loaders: [
{test: /.css$/, loader: 'to-string!css', exclude: /node_modules/},
{test: /.css$/, loader: 'style!css', exclude: /src/},
{test: /.html$/, loader: 'raw'},
{test: /.ts$/, loader: 'ts', query: {compilerOptions: {noEmit: false}}}
]
},
output: {
path : './dist',
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
new CommonsChunkPlugin({name: 'vendor', filename: 'vendor.bundle.js', minChunks: Infinity}),
new CompressionPlugin({regExp: /.css$|.html$|.js$|.map$/}),
new CopyWebpackPlugin([{from: './src/index.html', to: 'index.html'}]),
new DedupePlugin(),
new DefinePlugin({'webpack': {'ENV': JSON.stringify(metadata.env)}}),
new OccurenceOrderPlugin(true),
new UglifyJsPlugin({
compress: {screw_ie8 : true},
mangle: {screw_ie8 : true}
})
],
resolve: {extensions: ['', '.ts', '.js']}
}; webpack.prod.config](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2jeeconf-160531112340/75/Angular2-Development-for-Java-developers-63-2048.jpg)


