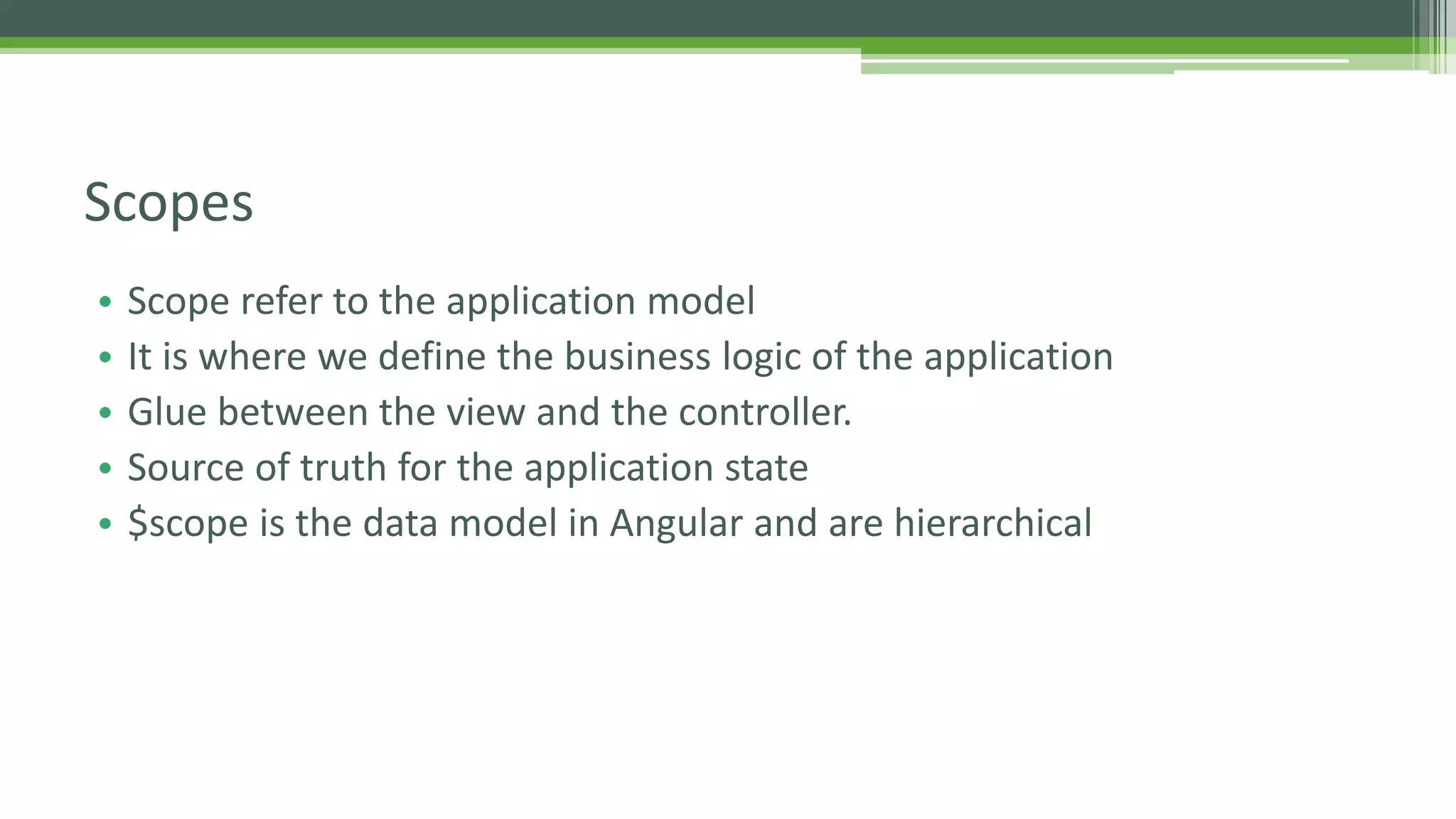
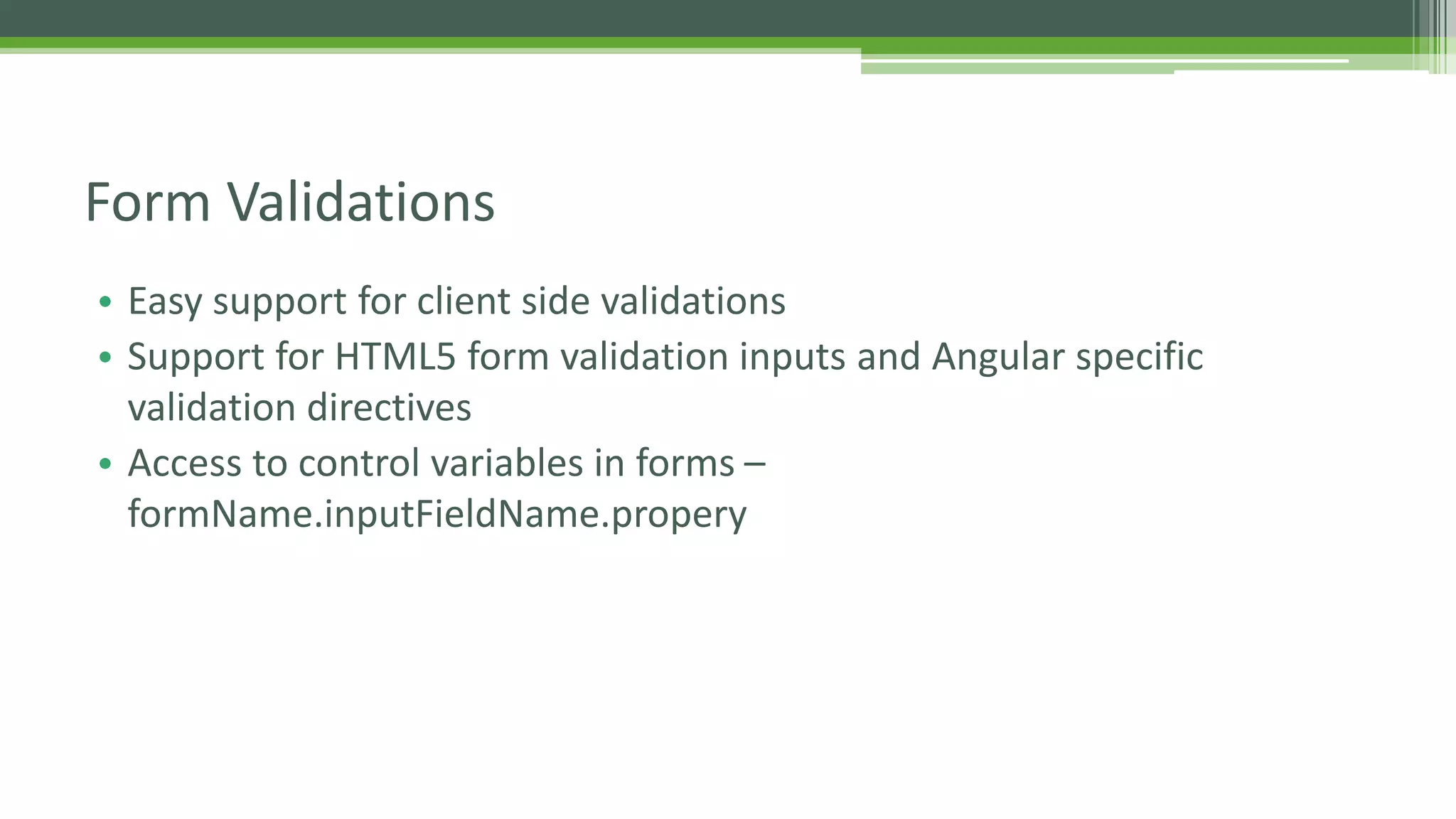
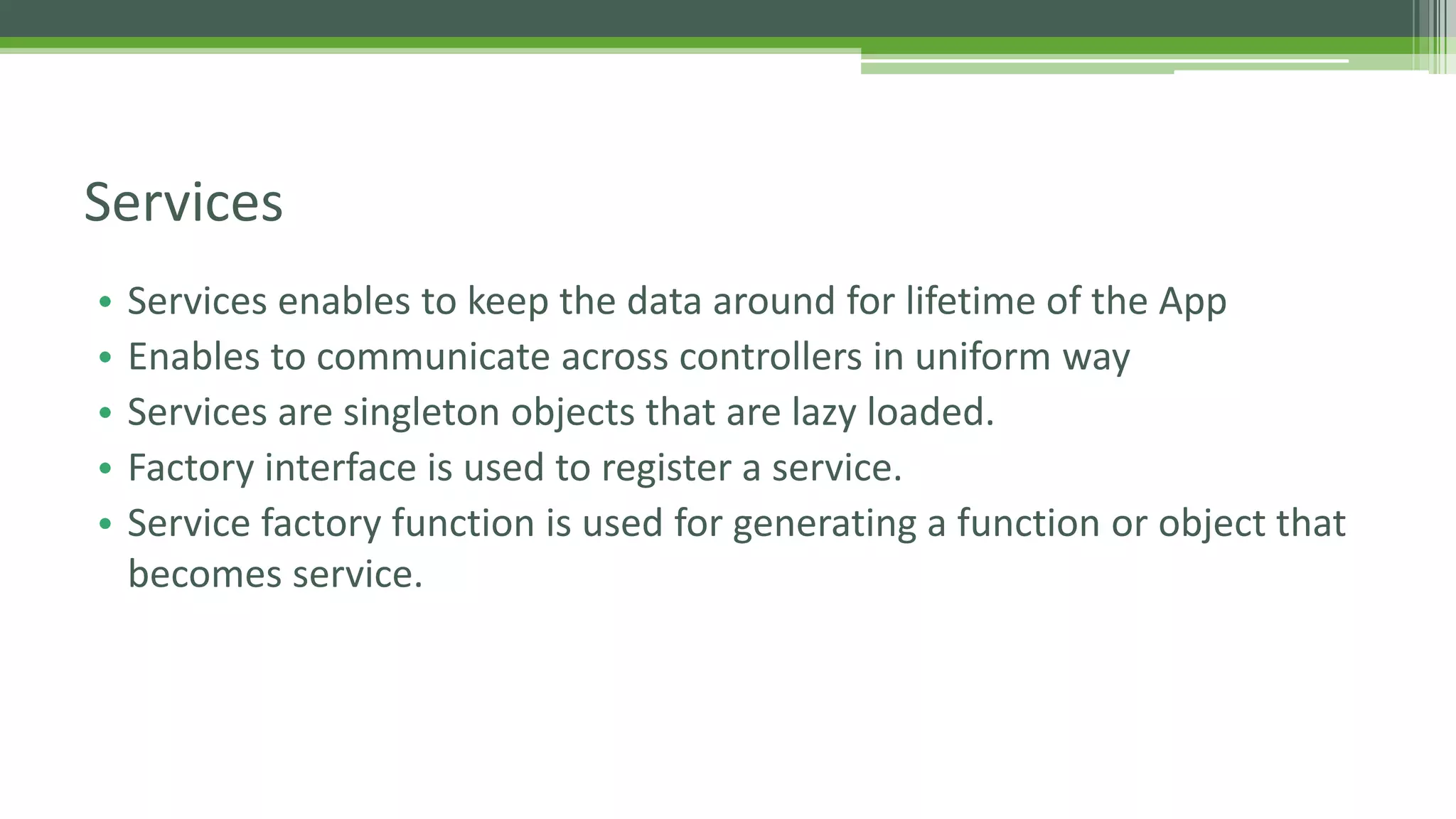
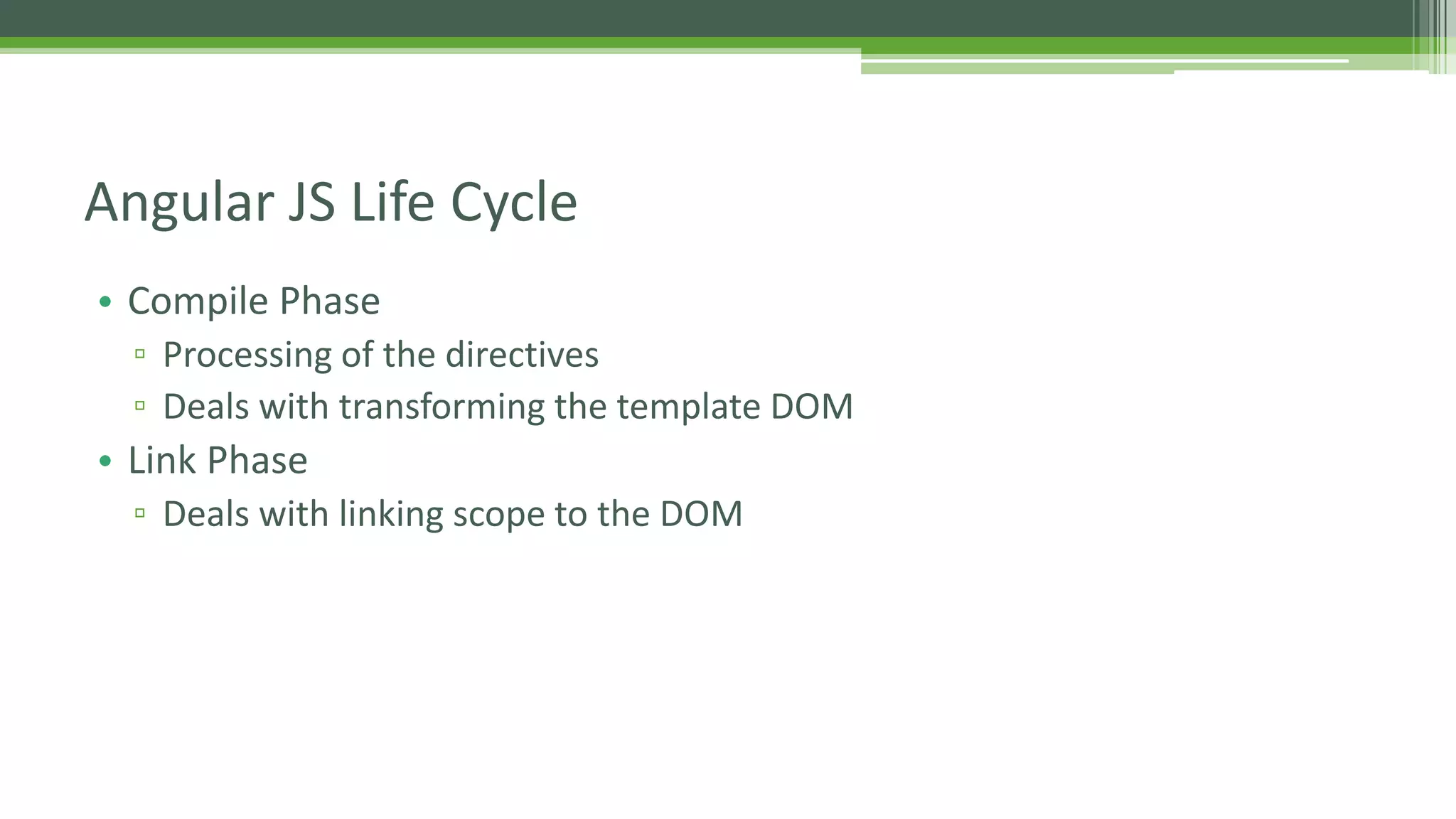
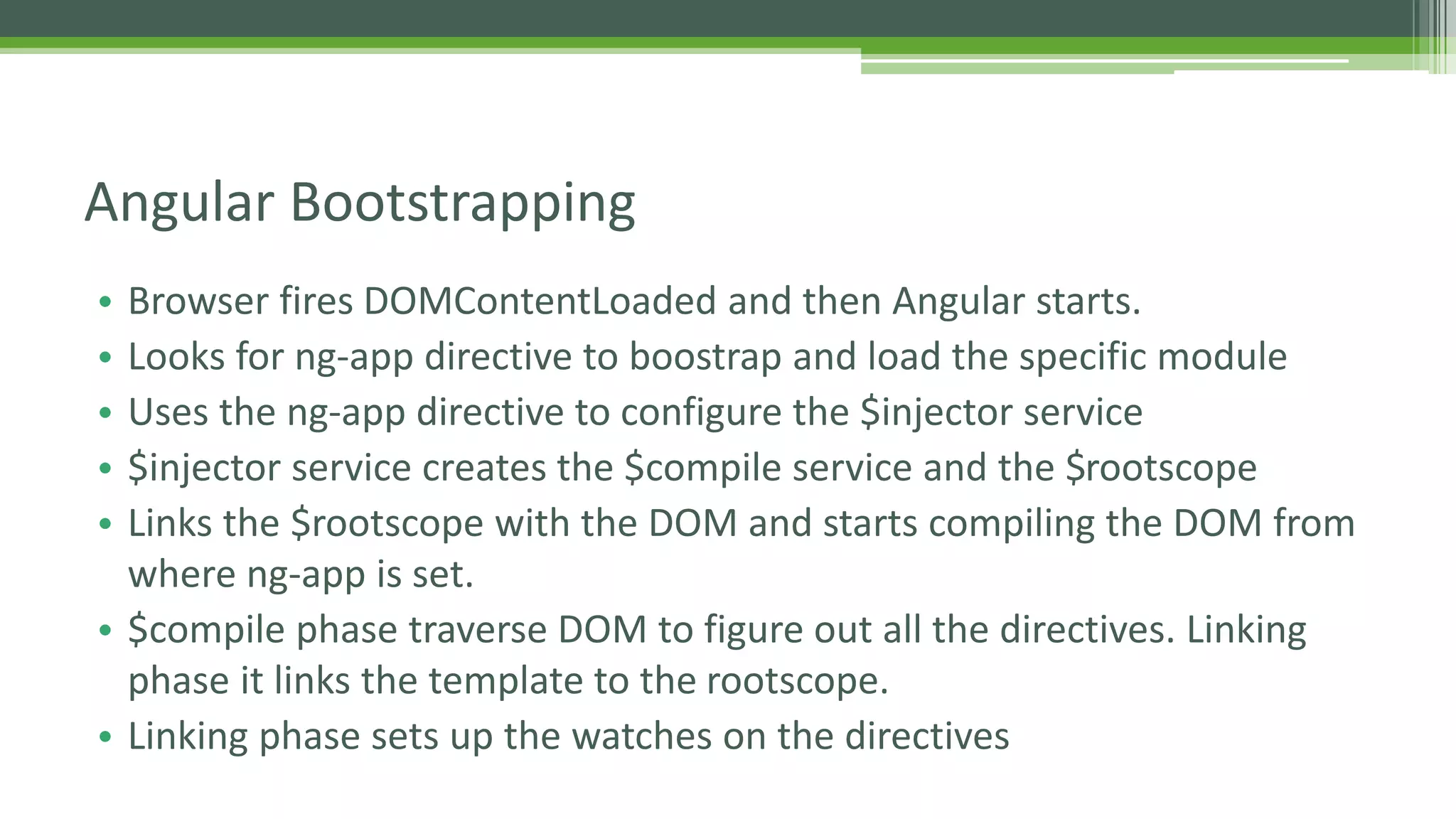
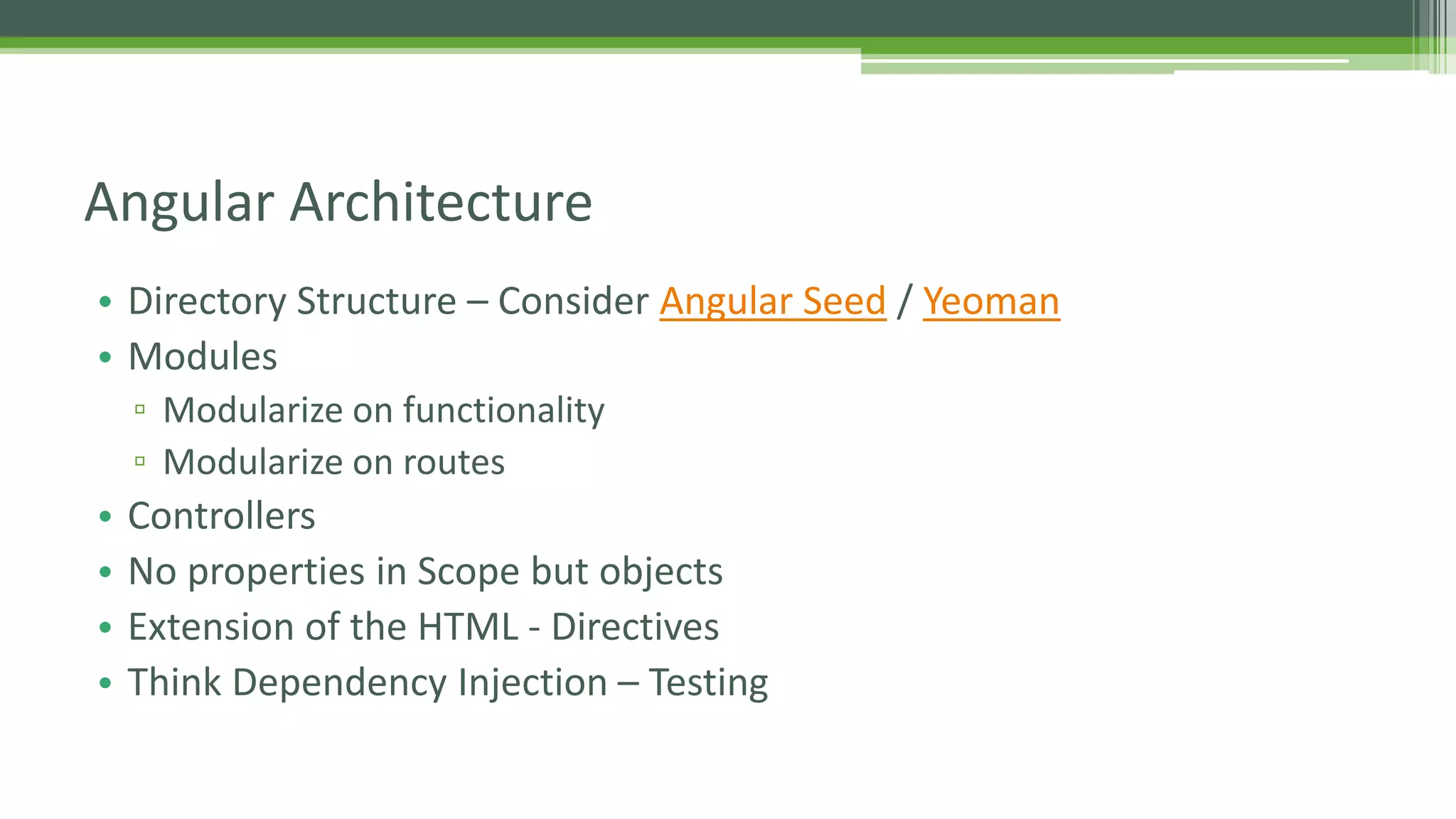
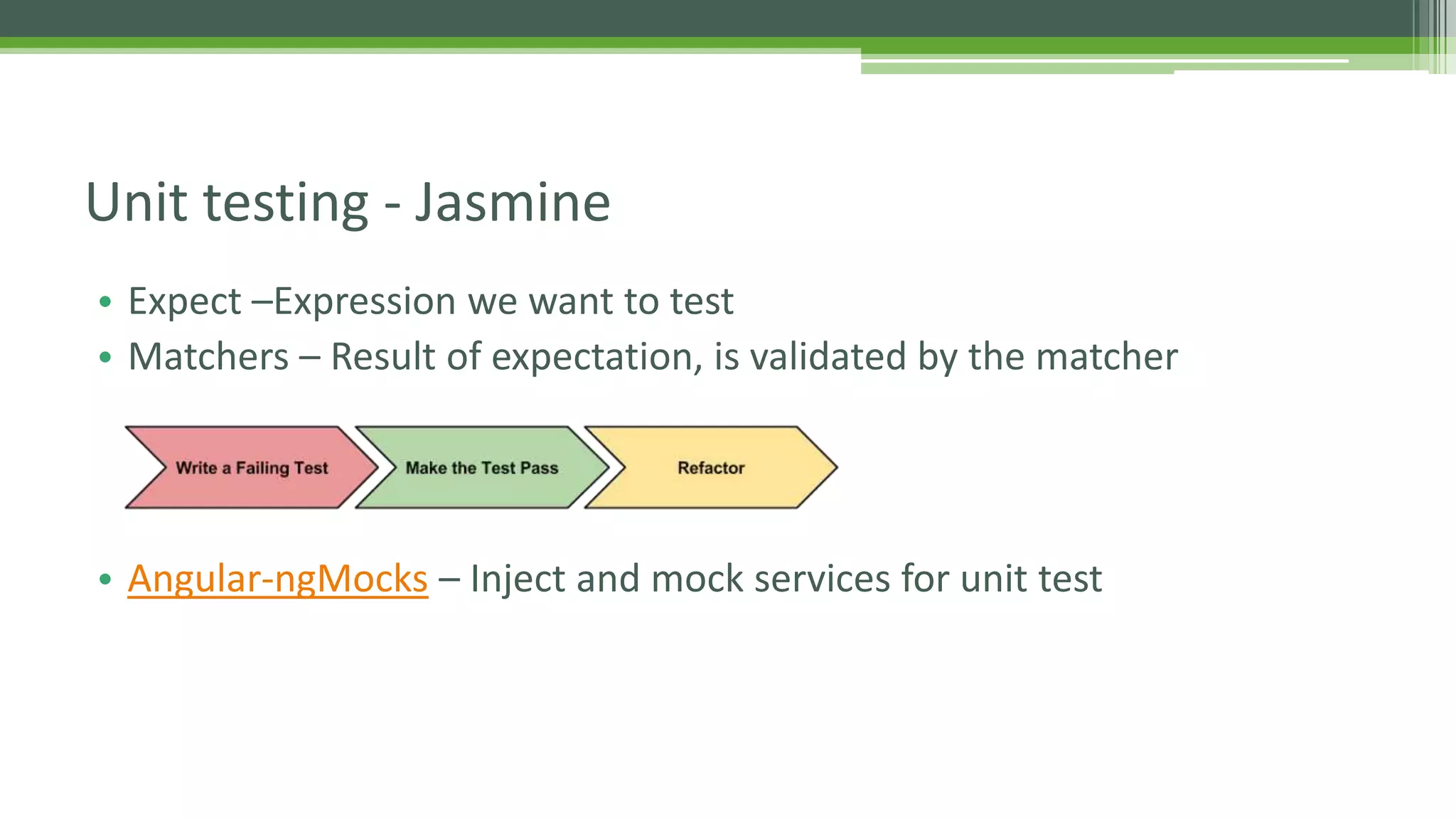
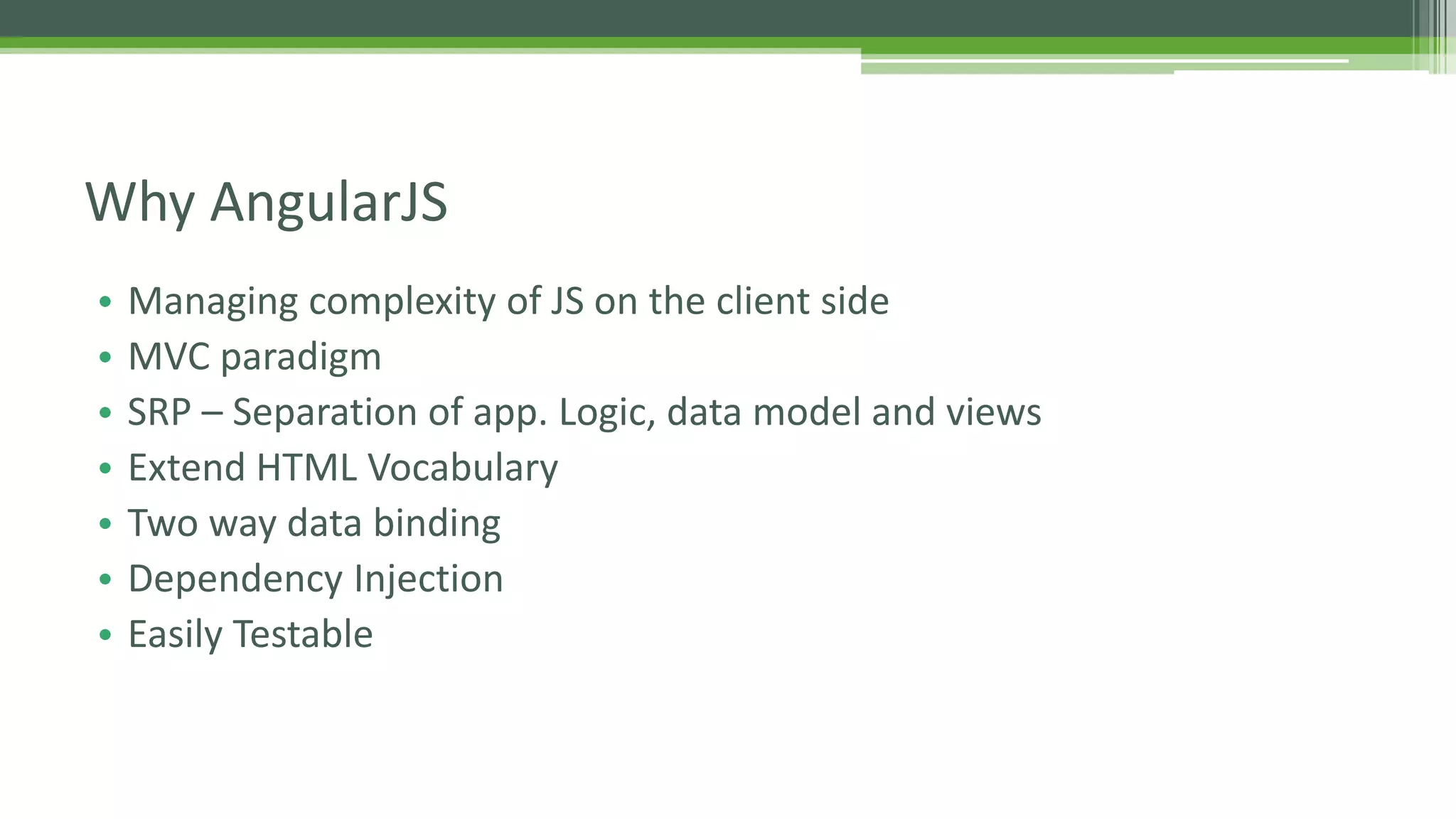
This document provides an overview of AngularJS fundamentals including controllers, services, directives, dependency injection, routing, forms, and testing. It discusses key AngularJS concepts like scopes, expressions, filters, and the digest loop. Sample code is presented to demonstrate modules, controllers, and directives. Various options for server communication, caching, debugging, localization, and animation are also covered. Guidelines for optimizing AngularJS applications are provided at the end.





![• Module is entry point for the AngularJs App • Keeping global namespace clean • Allow to load different parts of the app in any order • Example - angular.module('myApp', []); Modules](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-1-160513090435/75/Angular-js-1-0-fundamentals-9-2048.jpg)