This document discusses PHP forms and form validation. It explains that forms allow users to enter and submit data via HTML forms. The form data is sent to a PHP file for processing via the POST or GET HTTP methods. It provides examples of basic PHP forms using POST and GET, and how to display submitted form data. The document also discusses the differences between GET and POST, and emphasizes the importance of validating form data on the server-side to protect against hackers and spam. It provides examples of validating URLs, emails, names, and other common form fields.

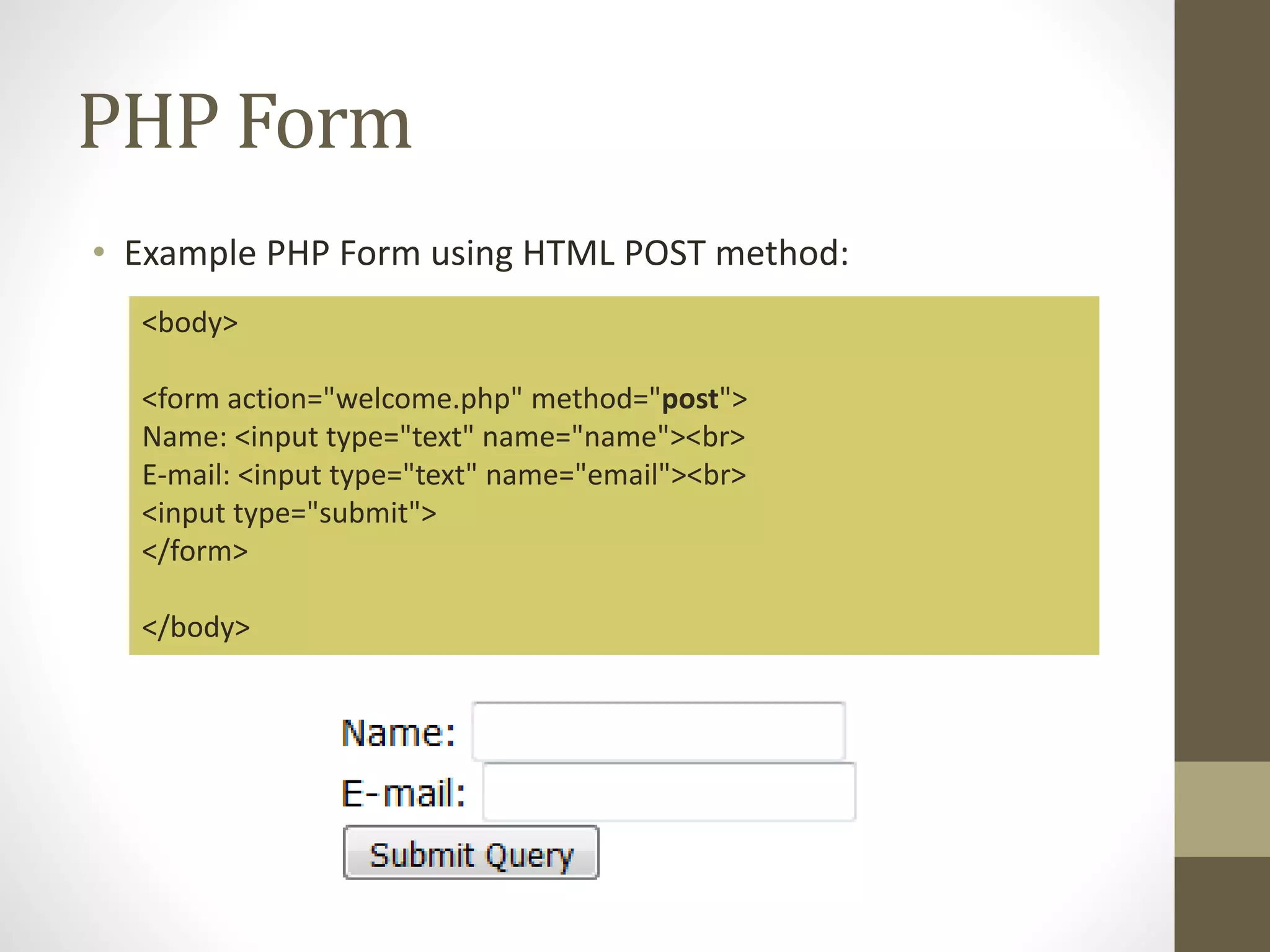
![PHP Form • To display the submitted data you could simply echo all the variables. • The "welcome.php" looks like this: <body> Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?><br> Your email address is: <?php echo $_POST["email"]; ?> </body>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cn5109chapter5-210219041913/75/Web-Application-Development-using-PHP-Chapter-5-4-2048.jpg)

![PHP Form • The "welcome_get.php" looks like this: <body> Welcome <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?><br> Your email address is: <?php echo $_GET["email"]; ?> </body>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cn5109chapter5-210219041913/75/Web-Application-Development-using-PHP-Chapter-5-6-2048.jpg)


![Example • Below code shows validation of URL: • Below code shows validation of Email address $website = input($_POST["site"]); if (!preg_match("/b(?:(?:https?|ftp)://|www.)[-a-z0- 9+&@#/%?=~_|!:,.;]*[-a-z0-9+&@#/%=~_|]/i",$website)) { $websiteErr = "Invalid URL"; } $email = input($_POST["email"]); if (!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL)) { $emailErr = "Invalid format and please re-enter valid email"; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cn5109chapter5-210219041913/75/Web-Application-Development-using-PHP-Chapter-5-11-2048.jpg)
![Example • The code below shows a simple way to check if the name field only contains letters and whitespace. • If the value of the name field is not valid, then store an error message: $name = test_input($_POST["name"]); if (!preg_match("/^[a-zA-Z ]*$/",$name)) { $nameErr = "Only letters and white space allowed"; } preg_match – this function is used to perform a pattern match on a string. It returns true if a match is found and false if a match is not found.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cn5109chapter5-210219041913/75/Web-Application-Development-using-PHP-Chapter-5-12-2048.jpg)
![Example • In the code below, if the e-mail address is not well-formed, then store an error message: $email = test_input($_POST["email"]); if (!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL)) { $emailErr = "Invalid email format"; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cn5109chapter5-210219041913/75/Web-Application-Development-using-PHP-Chapter-5-13-2048.jpg)