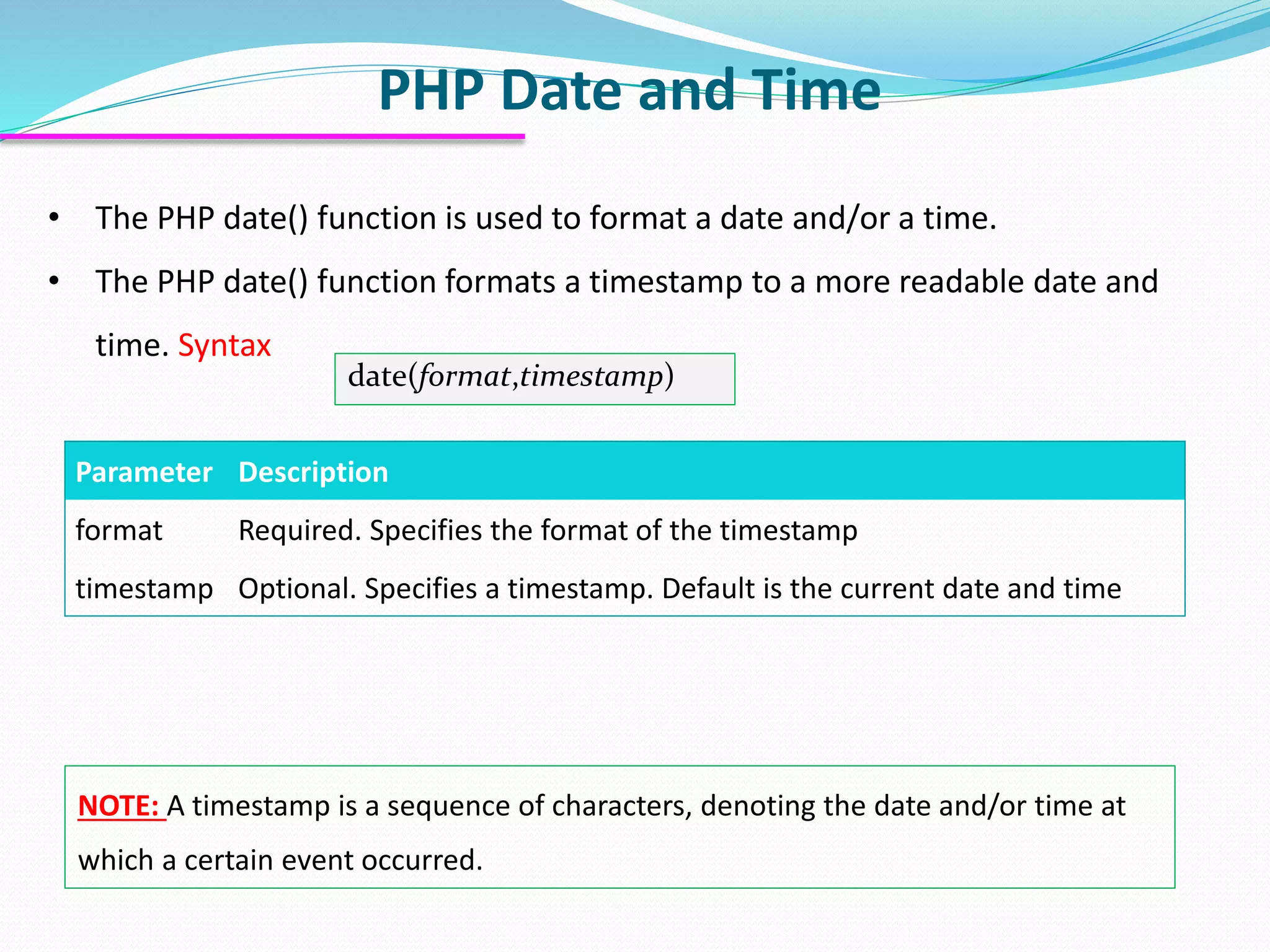
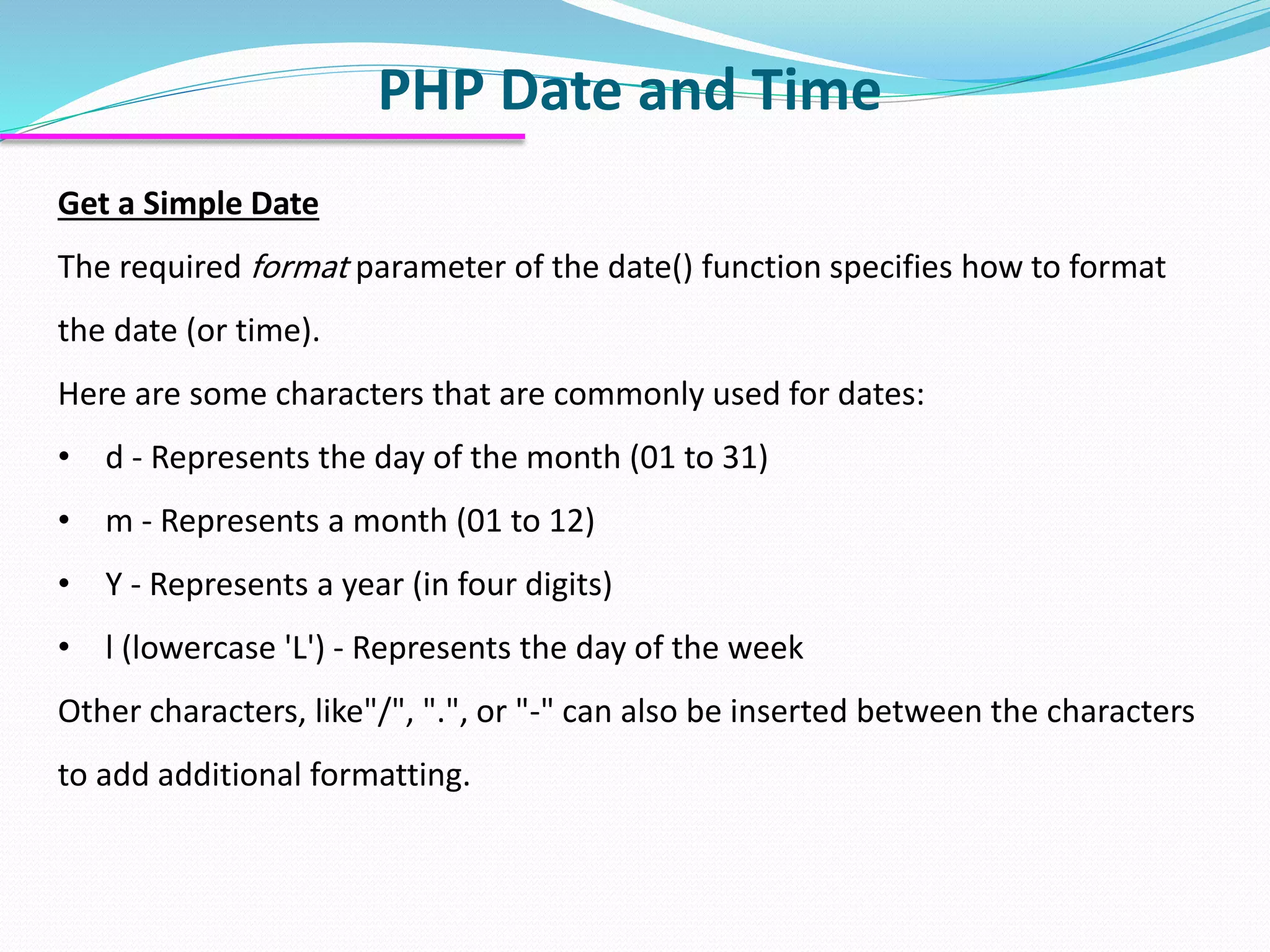
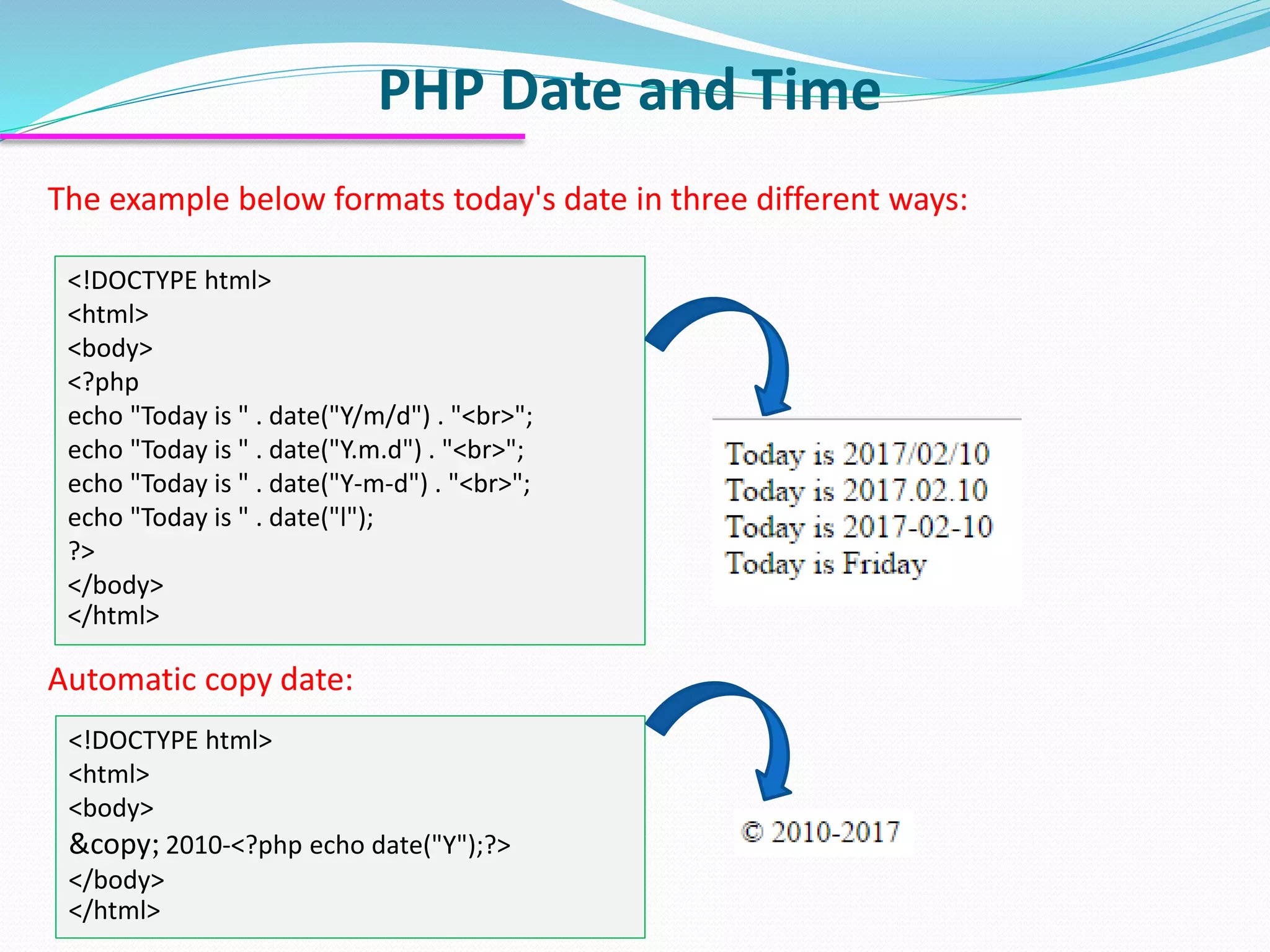
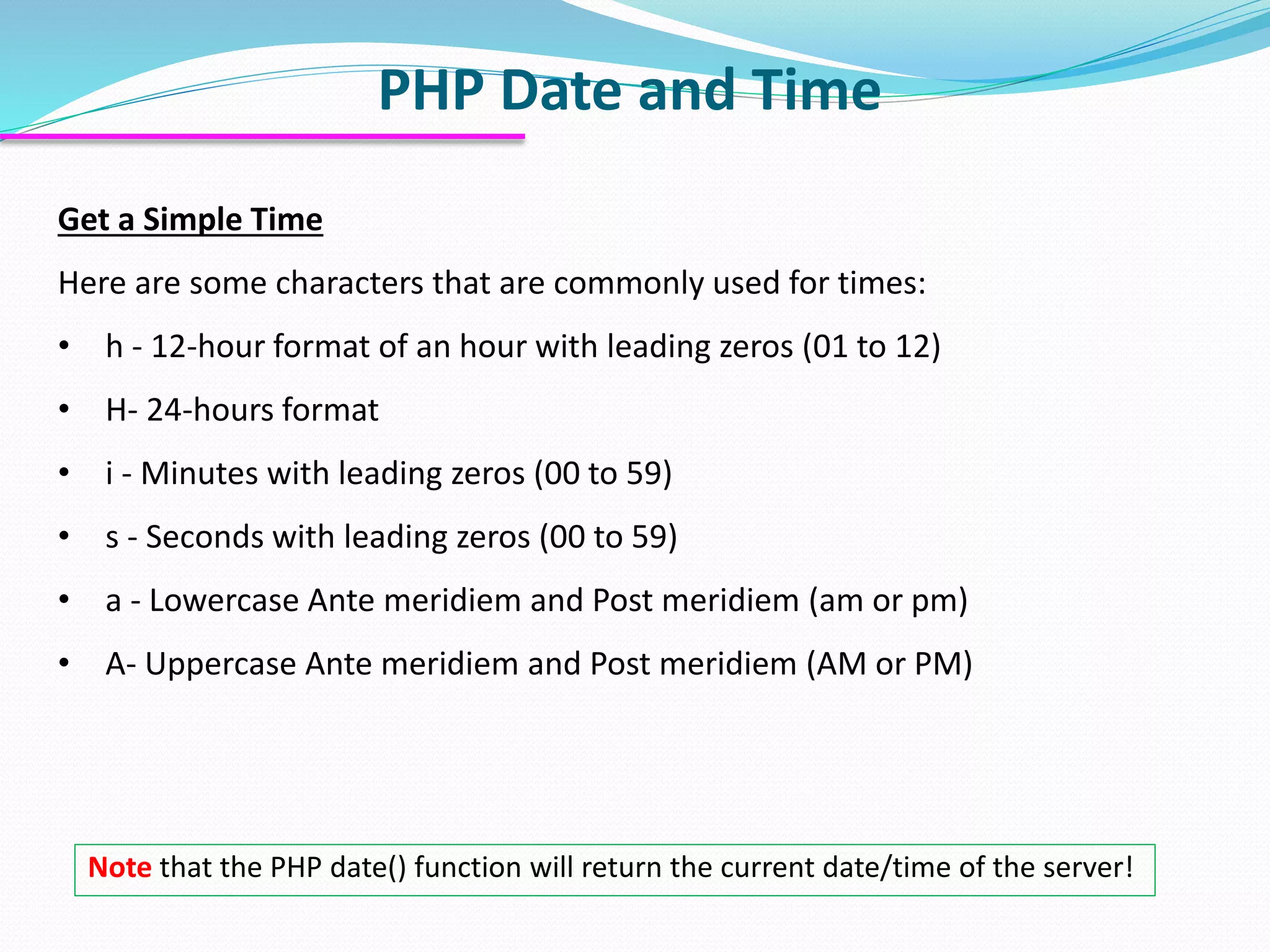
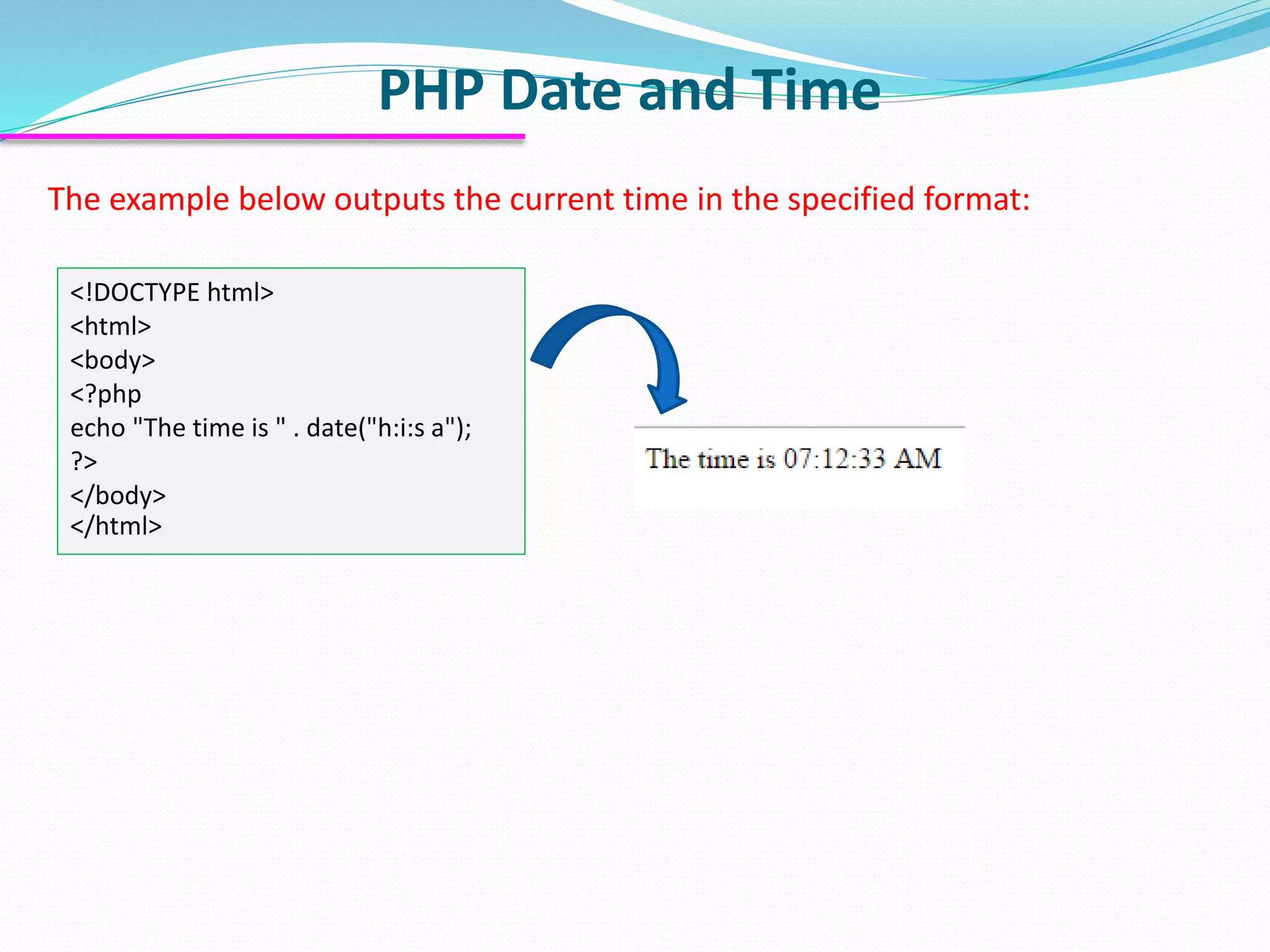
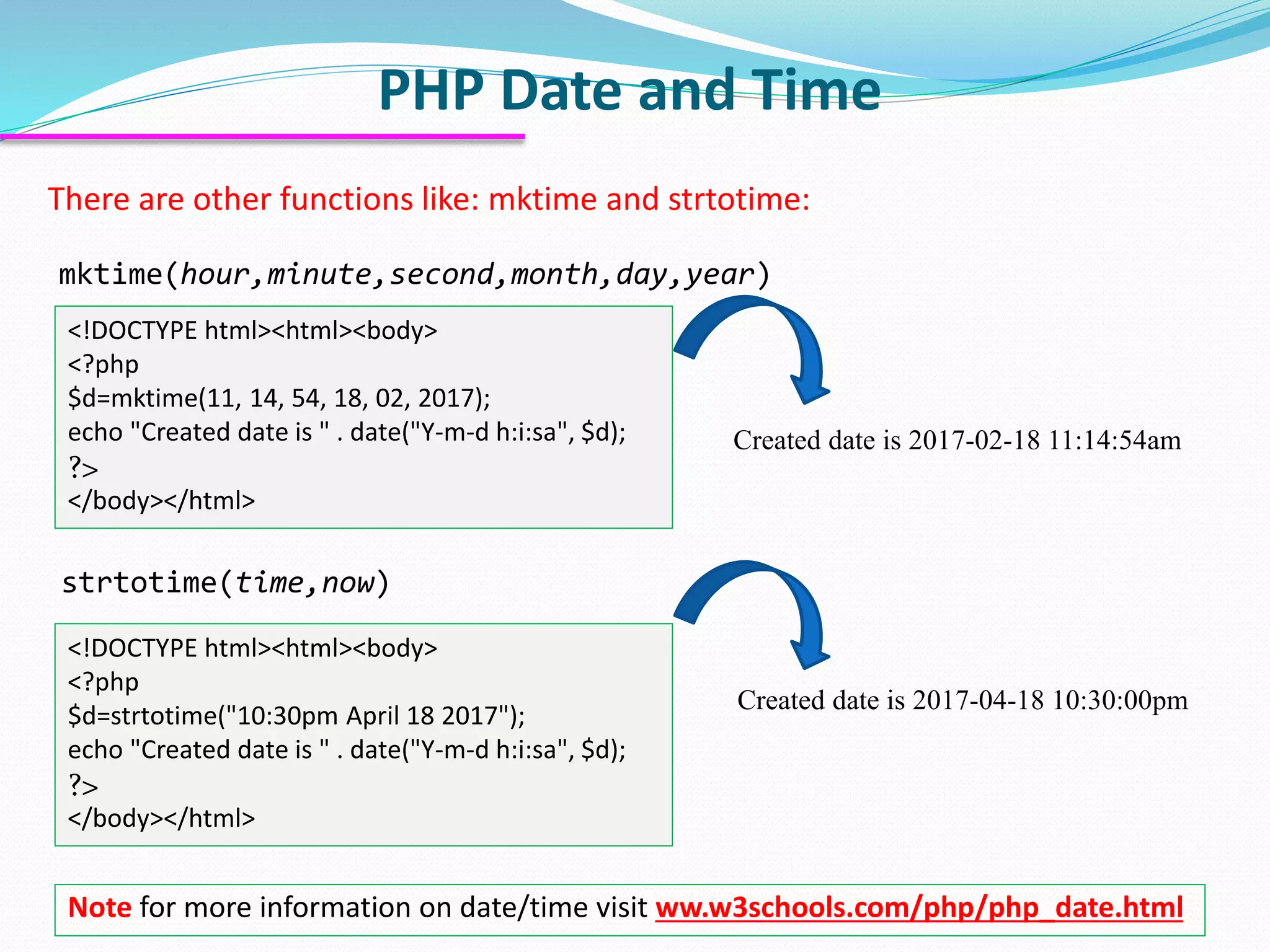
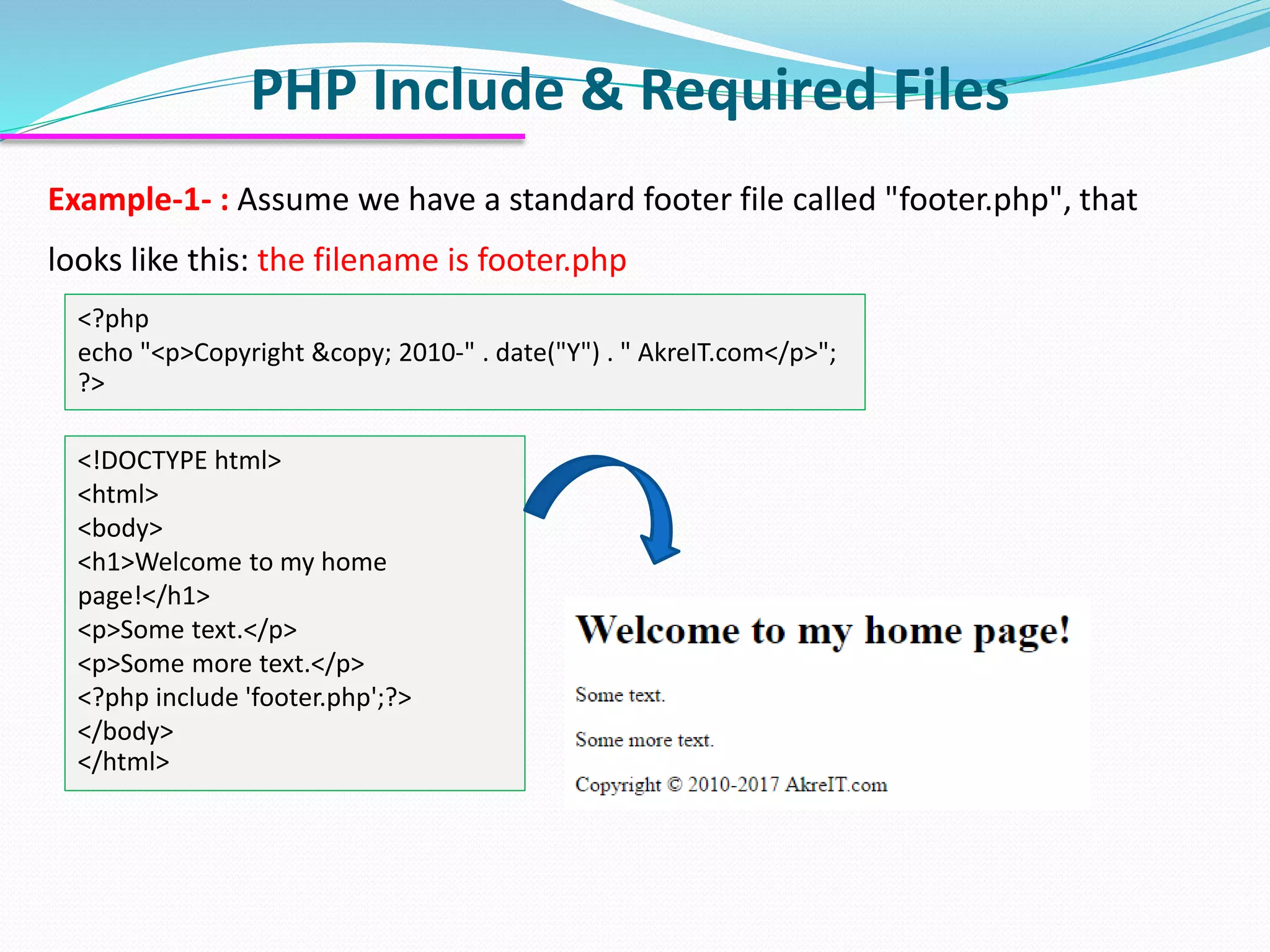
The document discusses PHP forms and form handling. It explains that the $_GET and $_POST superglobals are used to collect form data submitted via GET or POST methods. It provides an example HTML form that submits to a PHP file and displays the submitted data. The differences between GET and POST are outlined, including when each method should be used. Validation of required fields is demonstrated with PHP code. Other PHP topics like dates, times, and including files are briefly covered.

![PHP Forms PHP Form Handling: The PHP superglobals $_GET and $_POST are used to collect form-data. • The example below displays a simple HTML form with two input fields and a submit button: • When the user fills out the form and clicks the submit button, the form data is sent for processing to a PHP file named "welcome.php". The form data is sent with the HTTP POST method. <!DOCTYPE HTML><html><body> <form action="welcome.php" method="post"> Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br> E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br> <input type="submit“ name=‘submit’ value=‘submit’> </form> </body></html> <?php echo “Welocme”.$_POST["name"]; echo “<br>Your email address is: “ .$_POST["email"]; ?> HTML PHP file](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningphplecture2-180817175844/75/Web-Development-Course-PHP-lecture-2-2-2048.jpg)

![PHP Forms Example: <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <body> <h2>PHP Form Sumbit Example</h2> <form method="post" action="<?php $_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’];?>"> Name: <input type="text" name="name"> <br><br> E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br> Address: <input type="text" name="address"><br> Comment: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea> <br> Gender: <input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female <input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male <br> <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit"> </form> </body> </html> HTML After submitting form it will return to the same page, also you can use the page name itself or leave it empty if you want to send information to the same page.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningphplecture2-180817175844/75/Web-Development-Course-PHP-lecture-2-6-2048.jpg)
![PHP Forms Example: continued <?php $name = $email = $gender = $comment = $address = ""; if (isset($_POST['submit'])) { $name = $_POST["name"]; $email = $_POST["email"]; $address = $_POST["address"]; $comment = $_POST["comment"]; $gender = $_POST["gender"]; echo "<h2>Your Input:</h2>"; echo $name; echo "<br>"; echo $email; echo "<br>"; echo $address; echo "<br>"; echo $comment; echo "<br>"; echo $gender; } ?> PHP Initiate variables When the submit button in the form is clicked The method is POST so use $_POST to get text box values Output the form values to the browser..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningphplecture2-180817175844/75/Web-Development-Course-PHP-lecture-2-7-2048.jpg)
![PHP Forms What is the $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] variable? • The $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] is a super global variable that returns the filename of the currently executing script. • So, the $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] sends the submitted form data to the page itself, instead of jumping to a different page. This way, the user will get error messages on the same page as the form. What is the htmlspecialchars() function? The htmlspecialchars() function converts special characters to HTML entities. This means that it will replace HTML characters like < and > with < and >. This prevents attackers from exploiting the code by injecting HTML or Javascript code (Cross-site Scripting attacks) in forms. <form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars ($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningphplecture2-180817175844/75/Web-Development-Course-PHP-lecture-2-8-2048.jpg)
![PHP Forms (validation) Example: required fields: <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <style> .error {color: #FF0000;} </style> </head> <body> <h2>PHP Form Validation Example</h2> <p><span class="error">* required field.</span></p> <form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>"> Name: <input type="text" name="name"><span class="error">*<?php echo $nameErr;?></span> <br><br> E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><span class="error">*<?php echo $emailErr;?></span> <br><br> Address: <input type="text" name="address"><span class="error">*<?php echo $addressErr;?></span> <br><br> Comment: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea> <br><br> Gender: <input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female <input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male <span class="error">* <?php echo $genderErr;?></span> <br><br> <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit"> </form> </body> </html> HTML FORM Note for more information about validation(name, email, websites) visit www.w3schools.com/php/php_form_url_email.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningphplecture2-180817175844/75/Web-Development-Course-PHP-lecture-2-9-2048.jpg)
![PHP Forms(validation) Example: required fields: Validation with PHP <?php $nameErr = $emailErr = $genderErr = $addressErr = ""; $name = $email = $gender = $comment = $address = ""; if (isset($_POST['submit'])) { if (empty($_POST["name"])) { $nameErr = "Name is required"; } else { $name = $_POST["name"]; } if (empty($_POST["email"])) { $emailErr = "Email is required"; } else { $email = $_POST["email"]; } if (empty($_POST["address"])) { $addressErr = "address is required"; } else { $address = $_POST["address"]; } if (empty($_POST["comment"])) { $comment = ""; } else { $comment =$_POST["comment"]; } if (empty($_POST["gender"])) { $genderErr = "Gender is required"; } else { $gender = $_POST["gender"]; } echo "<h2>Your Input:</h2>"; echo $name; echo "<br>"; echo $email; echo "<br>"; echo $address; echo "<br>"; echo $comment; echo "<br>"; echo $gender; } ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningphplecture2-180817175844/75/Web-Development-Course-PHP-lecture-2-10-2048.jpg)