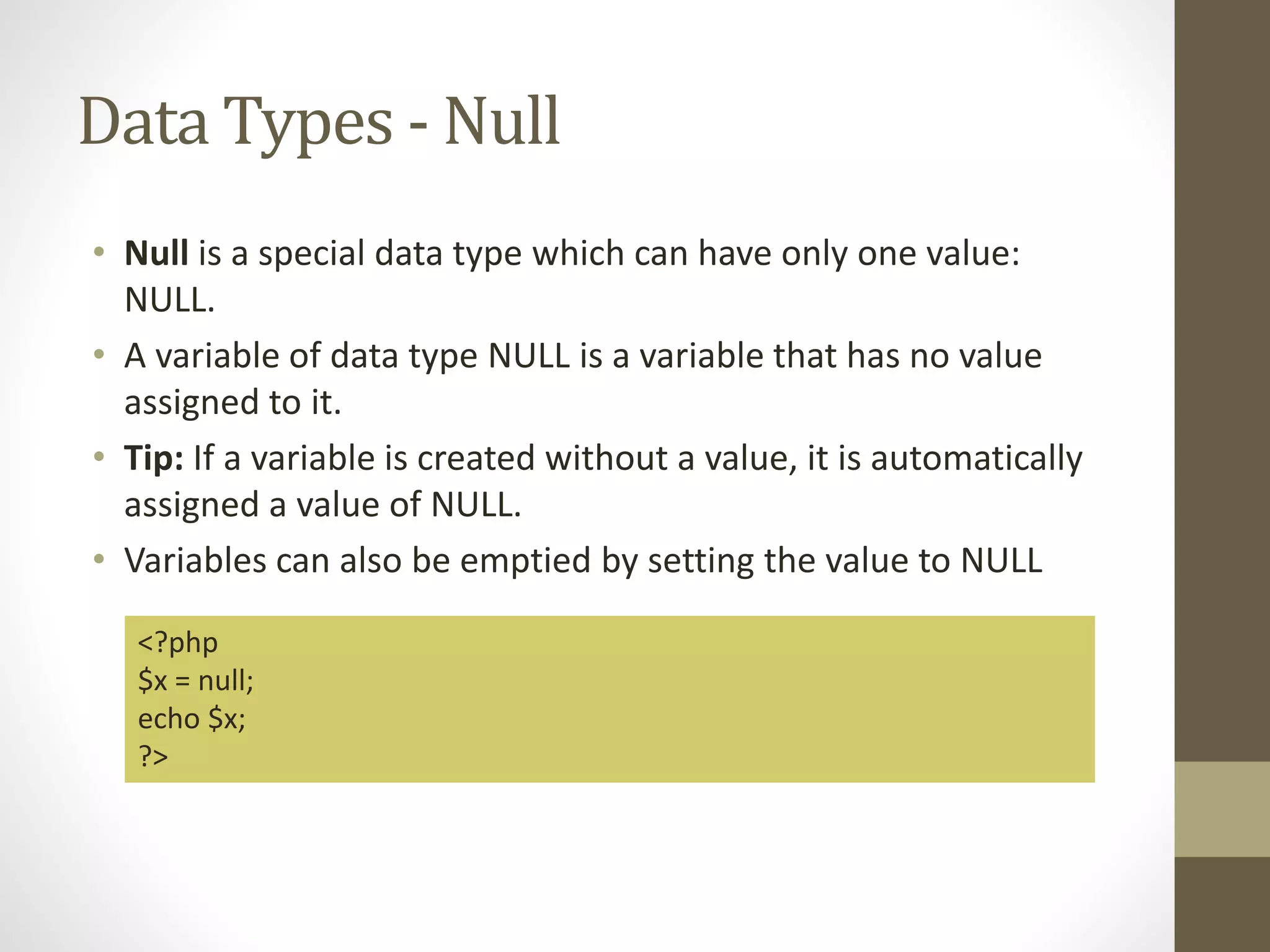
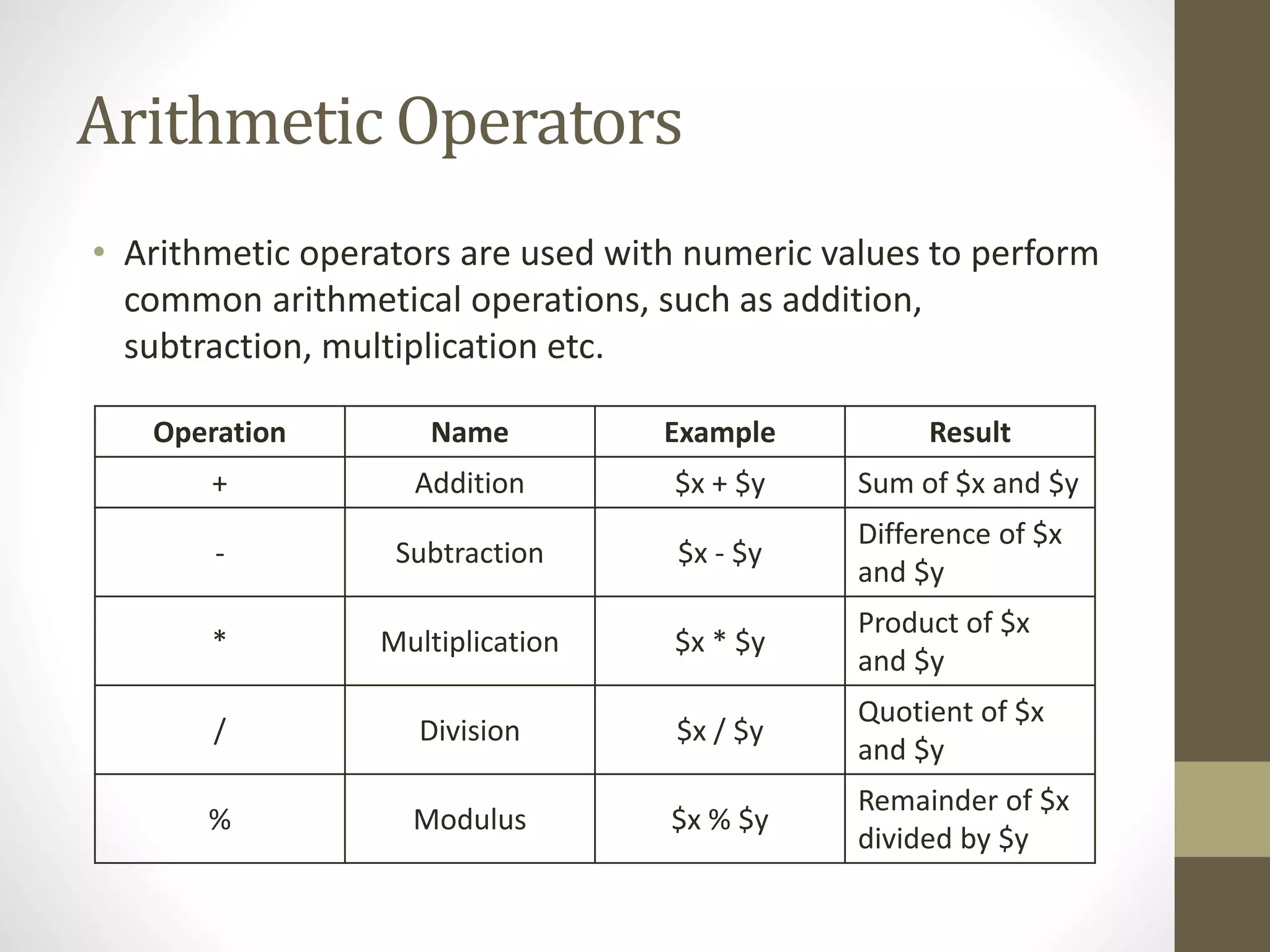
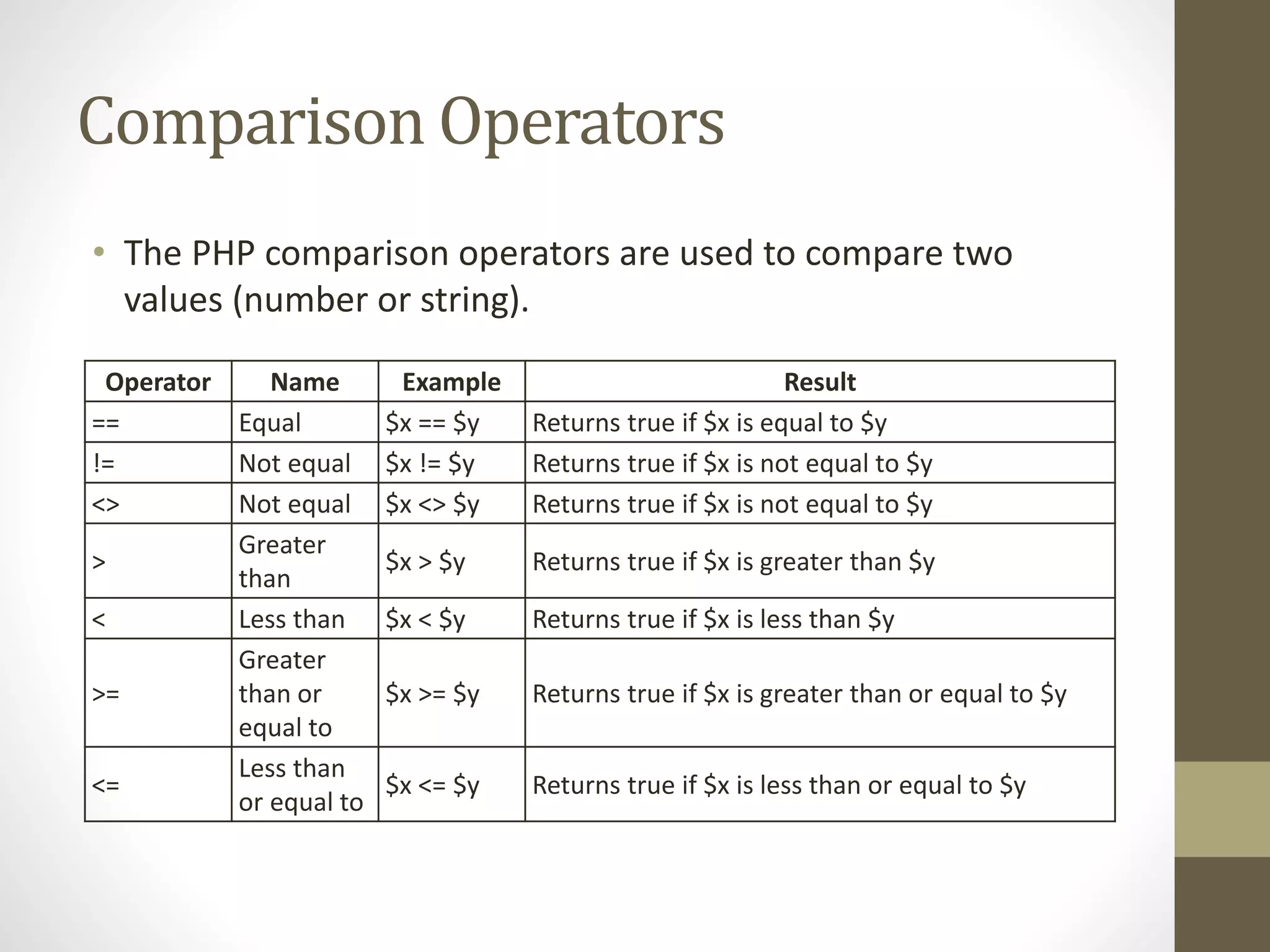
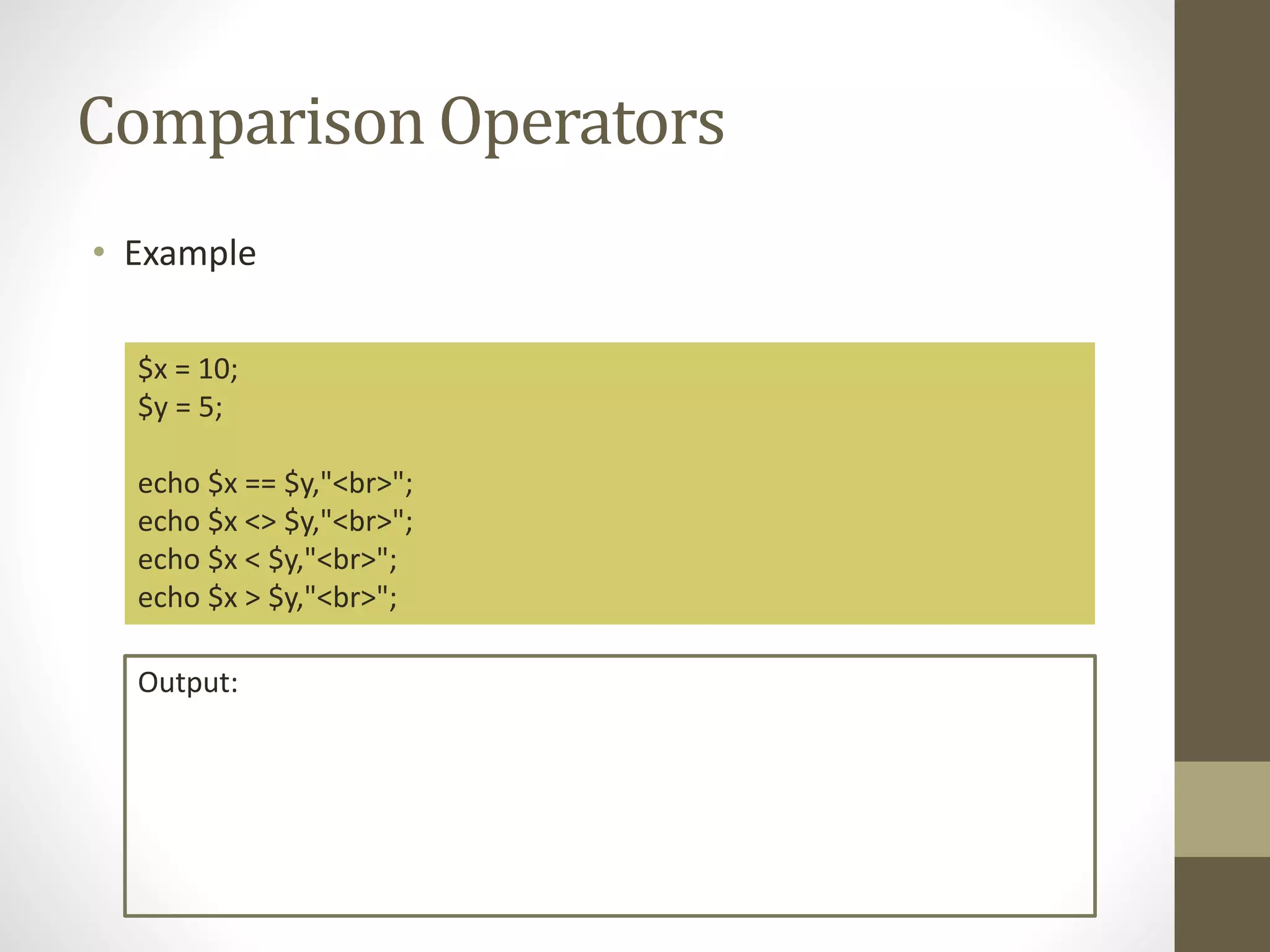
Here are the solutions to the equations given in the quiz: a) $x + $x + $y = 10 + 10 + 5 = 25 b) $x - $y + $x = 10 - 5 + 10 = 15 c) $x + $y * $x = 10 + 5 * 10 = 10 + 50 = 60 d) $x / $y + $x = 10 / 5 + 10 = 2 + 10 = 12 e) $x > $y = 10 > 5 = True f) $y != $x = 5 != 10 = True g) ++$x = 11 h) $y-- = 4



























![Data Types - Array • An array stores multiple values in one single variable. • In the following example $cars is an array. <?php $cars = array("Volvo","BMW","Toyota","Honda"); echo $cars[0],"<br>"; echo $cars[1],"<br>"; echo $cars[2],"<br>"; echo $cars[3],"<br>"; ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cn5109chapter1-210219041911/75/Web-Application-Development-using-PHP-Chapter-1-35-2048.jpg)