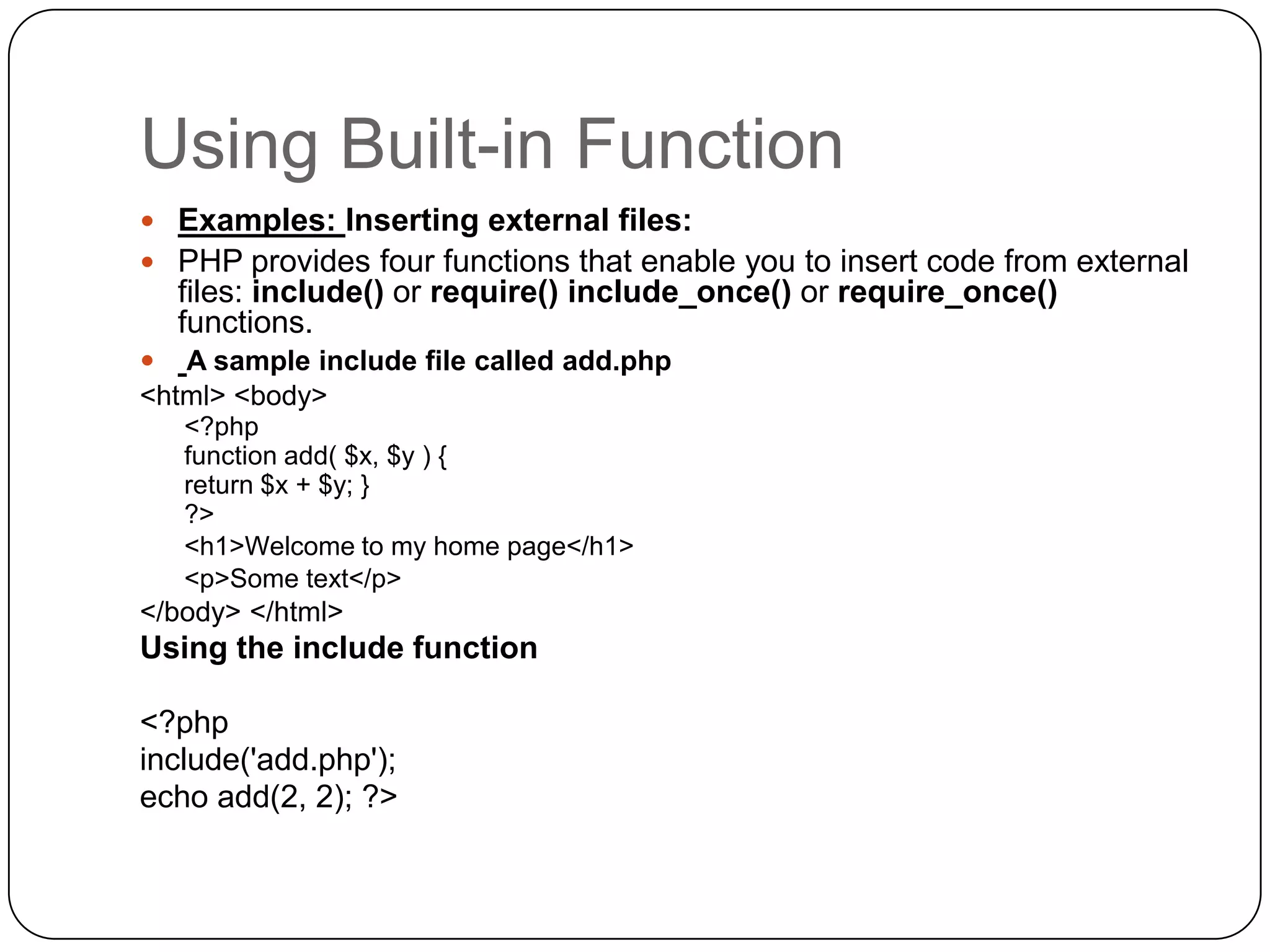
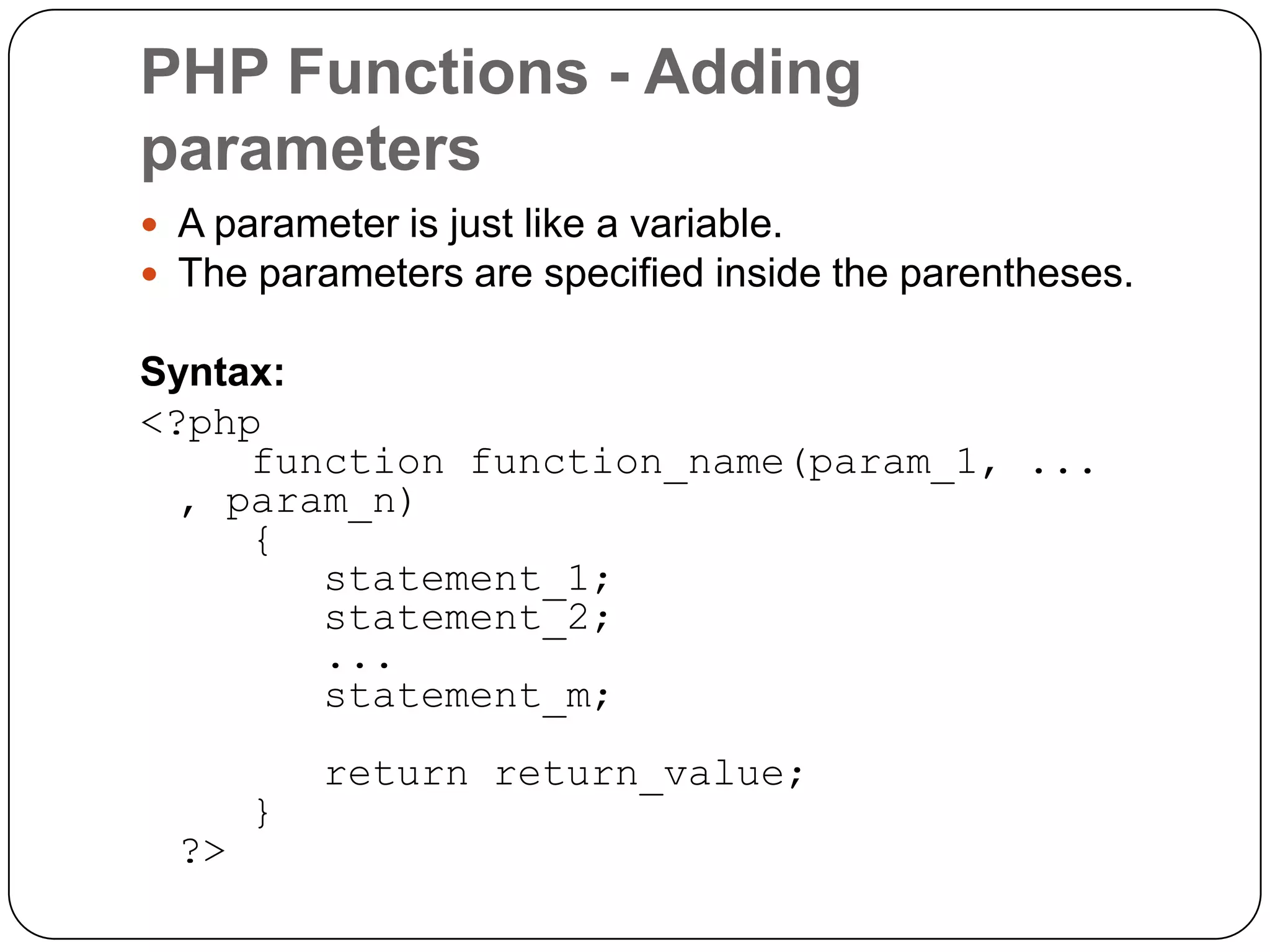
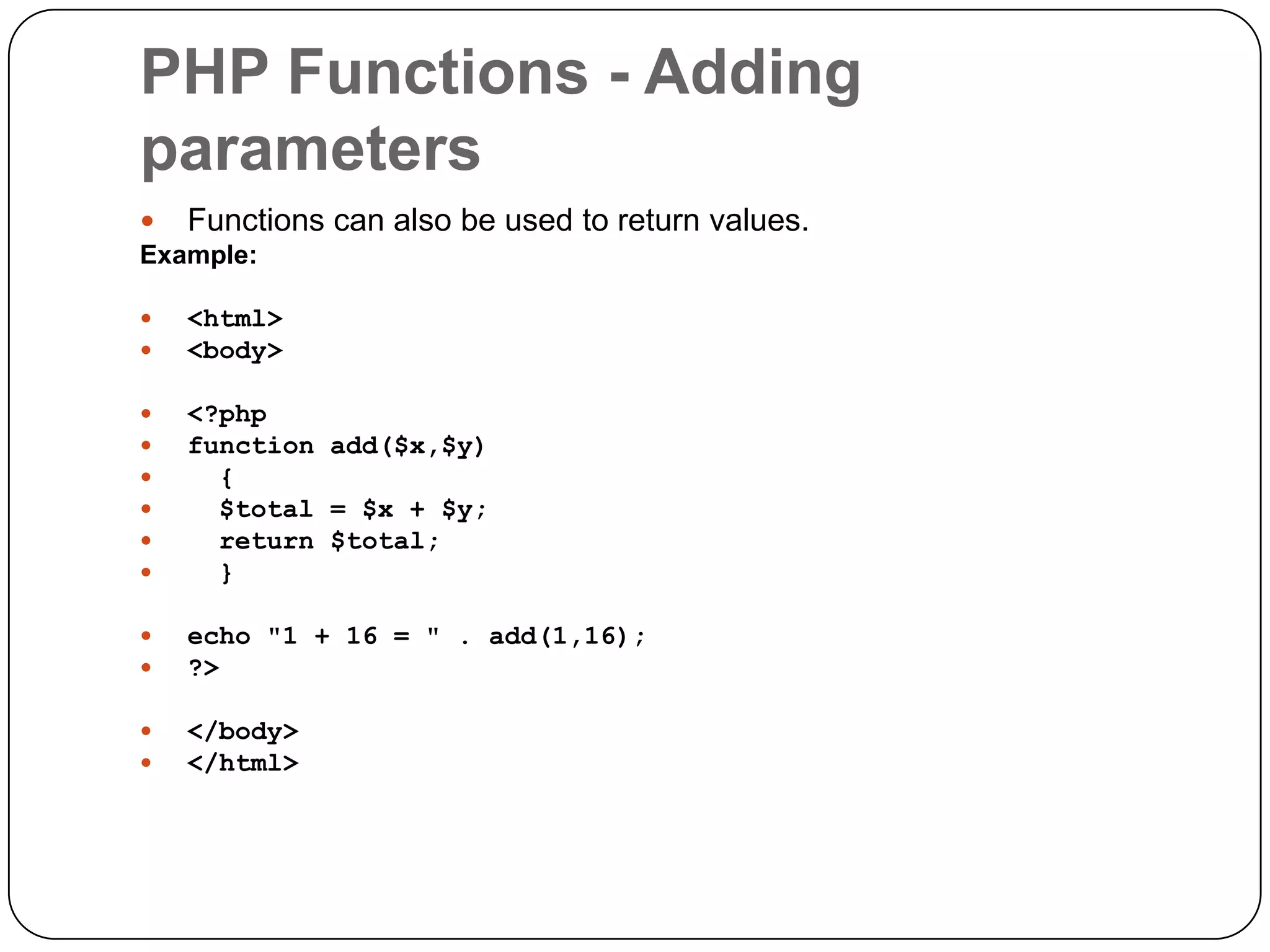
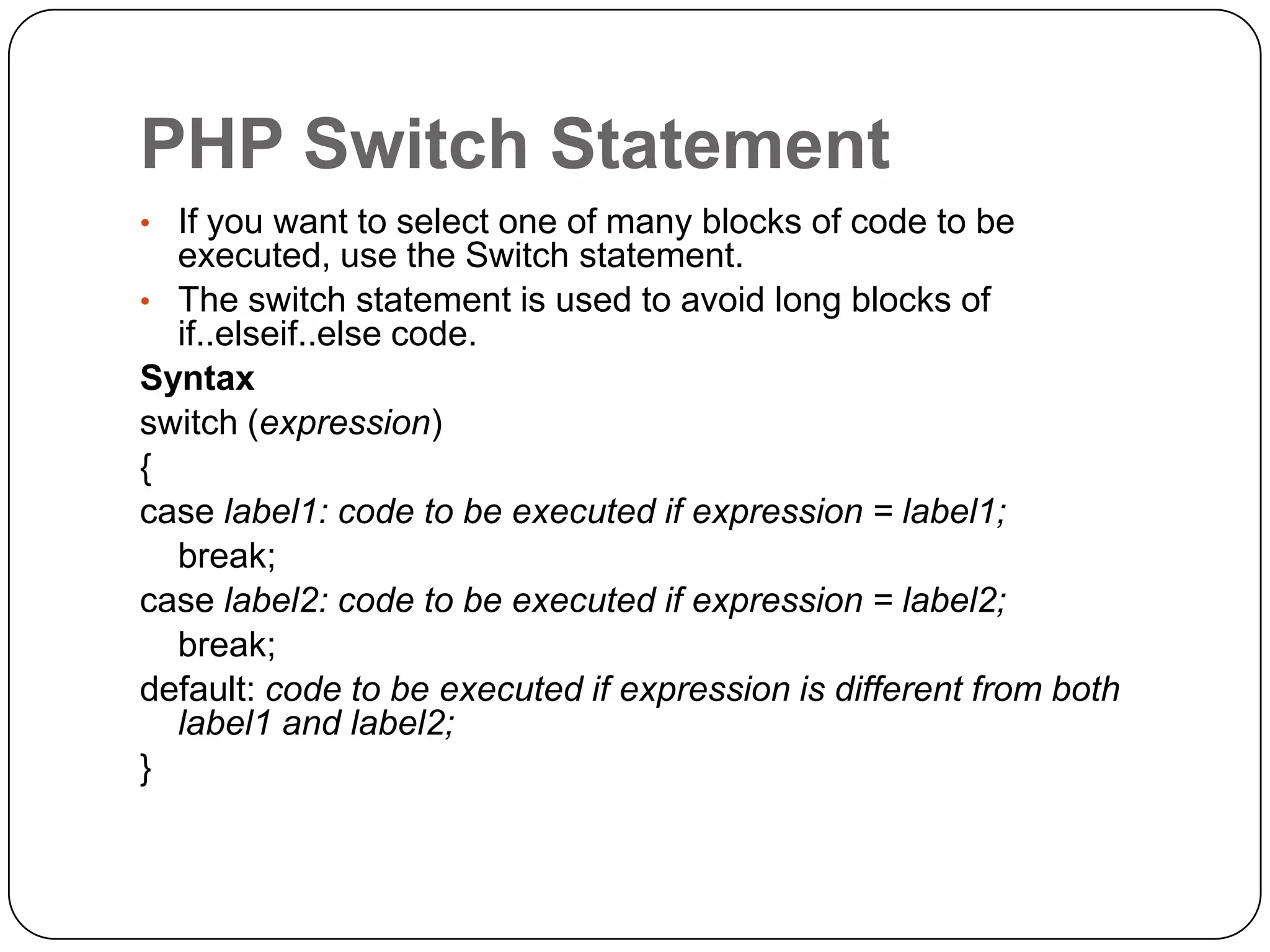
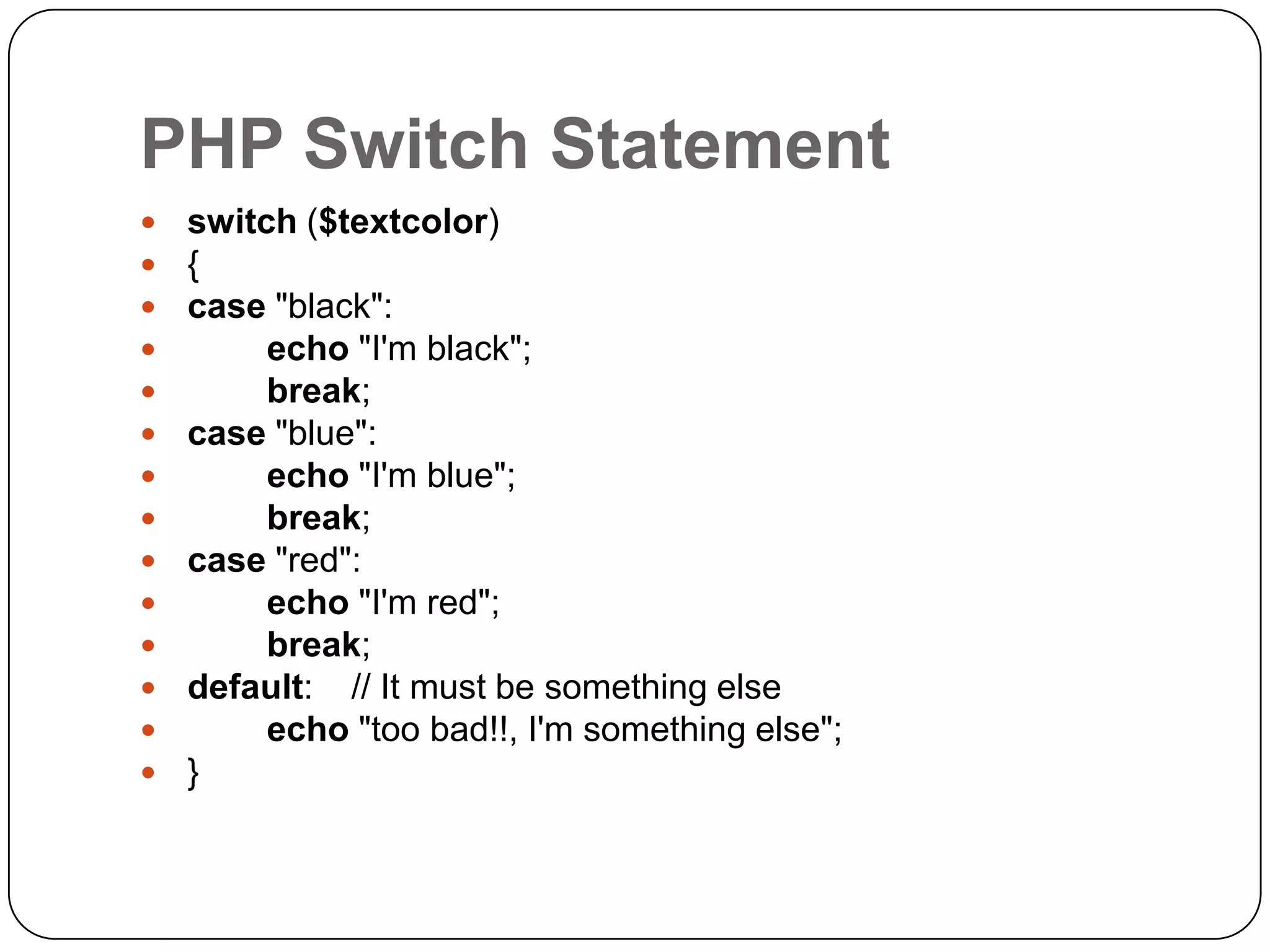
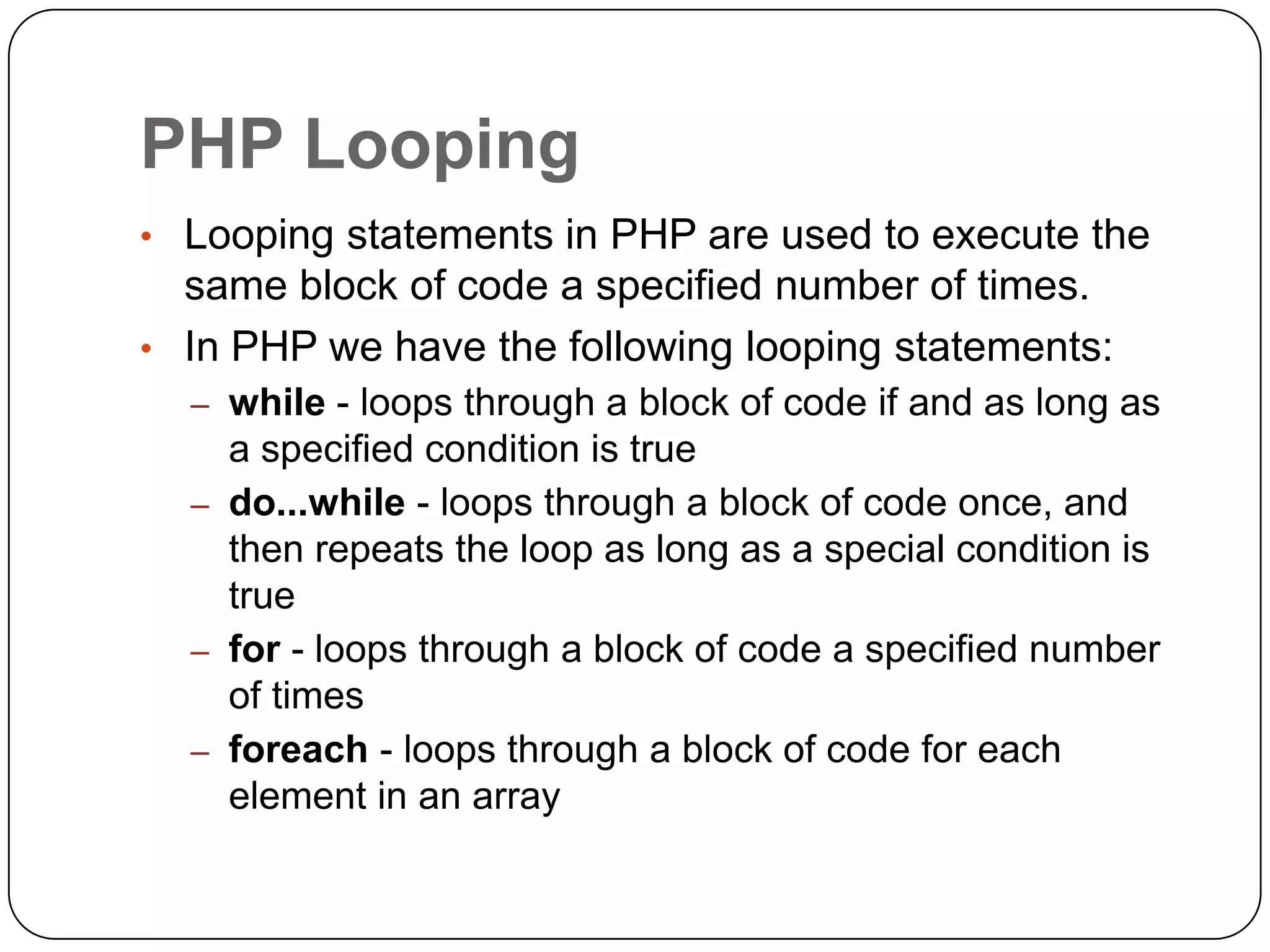
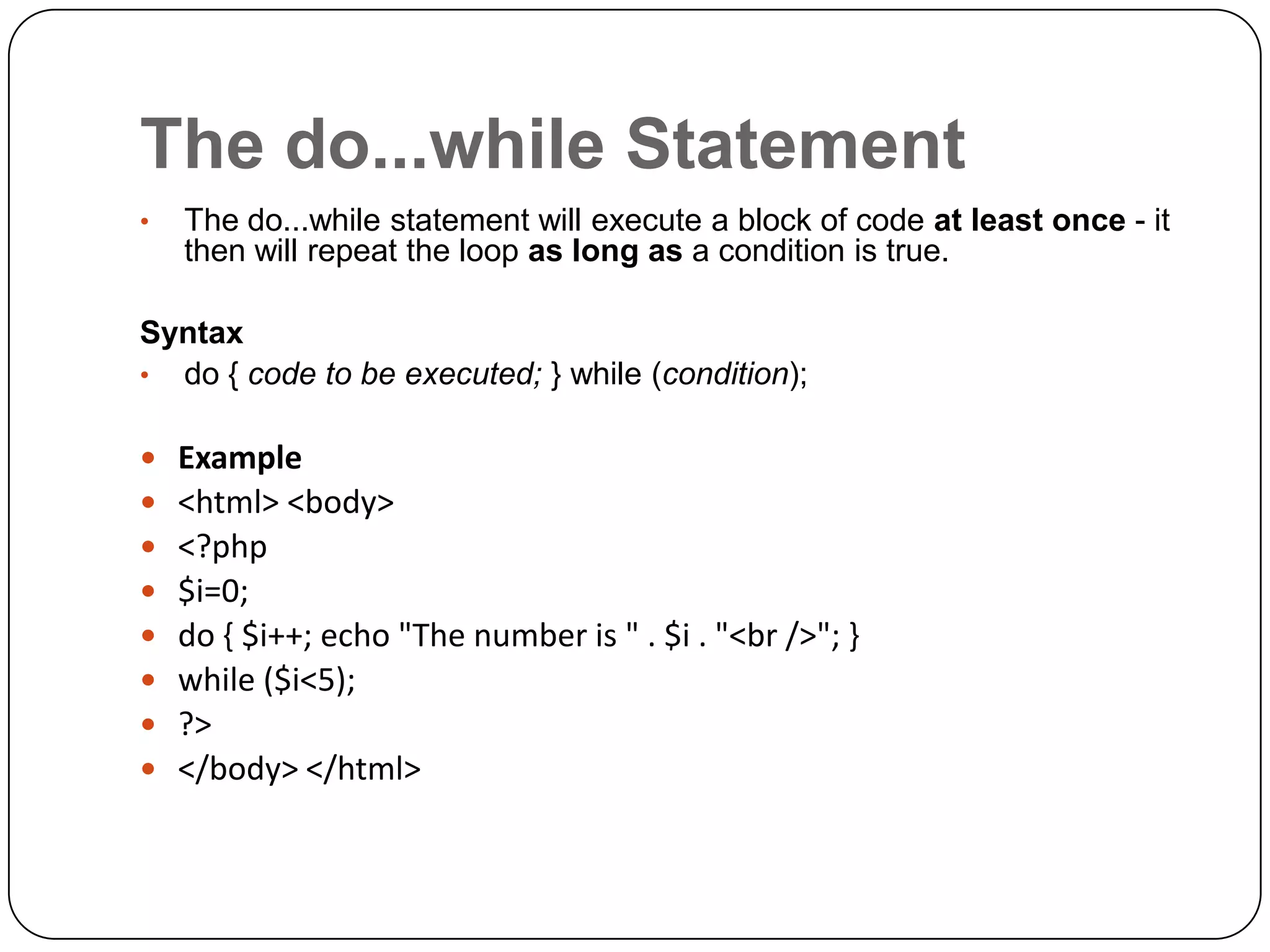
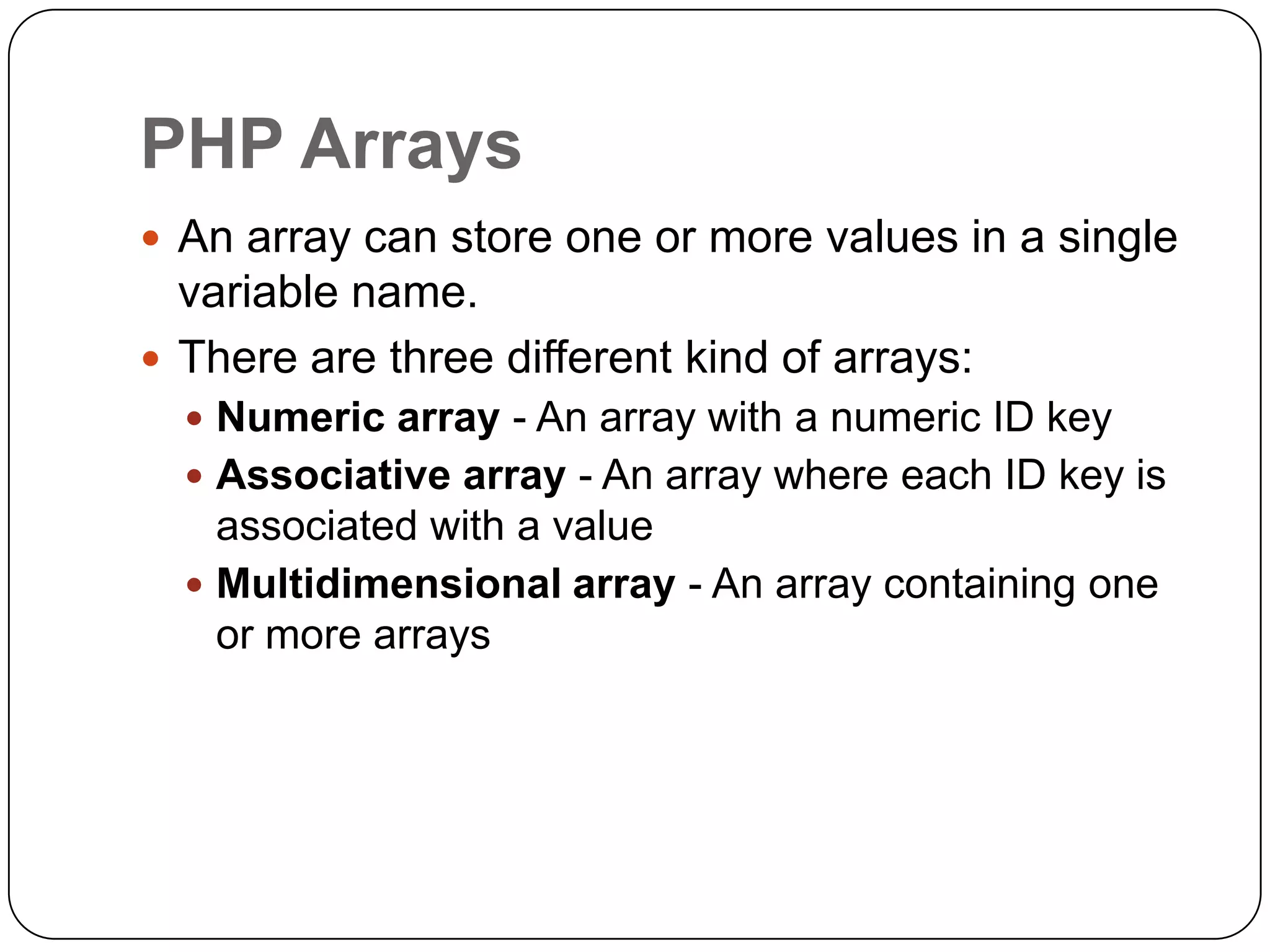
The document is an introduction to PHP, a server-side scripting language used for creating dynamic websites, developed in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf. It covers fundamental PHP concepts including its syntax, functions, control structures, and arrays, alongside the advantages of using PHP with Apache and MySQL for web development. Additionally, it explains how PHP scripts are processed on the server, and highlights variable usage, string handling, and looping techniques.








![Numeric Array • A numeric array stores each element with a numeric ID key. • There are different ways to create a numeric array: Example 1 • In this example the ID key is automatically assigned: • $names = array("Peter","Quagmire","Joe"); Example 2 • In this example we assign the ID key manually: $names[0] = "Peter"; $names[1] = "Quagmire"; $names[2] = "Joe";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-mysqlclassesinnavi-mumbaiphp-mysqlcourseprovider-in-navi-mumbaibestphp-mysqlclassesinnavi-mumbai-131028081515-phpapp02/75/Php-mysql-classes-in-navi-mumbai-php-mysql-course-provider-in-navi-mumbai-best-php-mysql-classes-in-navi-mumbai-26-2048.jpg)
![Associative Arrays • Each ID key is associated with a value. • When storing data about specific named values, a numerical array is not always the best way to do it. • There are two ways of creating Associative Array: Example 1 • $ages = array("Peter"=>32, "Quagmire"=>30, "Joe"=>34); Example 2 • $ages['Peter'] = "32"; $ages['Quagmire'] = "30"; $ages['Joe'] = "34";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-mysqlclassesinnavi-mumbaiphp-mysqlcourseprovider-in-navi-mumbaibestphp-mysqlclassesinnavi-mumbai-131028081515-phpapp02/75/Php-mysql-classes-in-navi-mumbai-php-mysql-course-provider-in-navi-mumbai-best-php-mysql-classes-in-navi-mumbai-27-2048.jpg)

![Multidimensional Arrays Example 2: The array above would look like this if written to the output: Array ( [Griffin] => Array ( [0] => Peter [1] => Lois [2] => Megan ) [Quagmire] => Array ( [0] => Glenn ) [Brown] => Array ( [0] => Cleveland [1] => Loretta [2] => Junior ) ) • displaying a single value from the array above: echo "Is " . $families['Griffin'][2] . " a part of the Griffin family?";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-mysqlclassesinnavi-mumbaiphp-mysqlcourseprovider-in-navi-mumbaibestphp-mysqlclassesinnavi-mumbai-131028081515-phpapp02/75/Php-mysql-classes-in-navi-mumbai-php-mysql-course-provider-in-navi-mumbai-best-php-mysql-classes-in-navi-mumbai-29-2048.jpg)