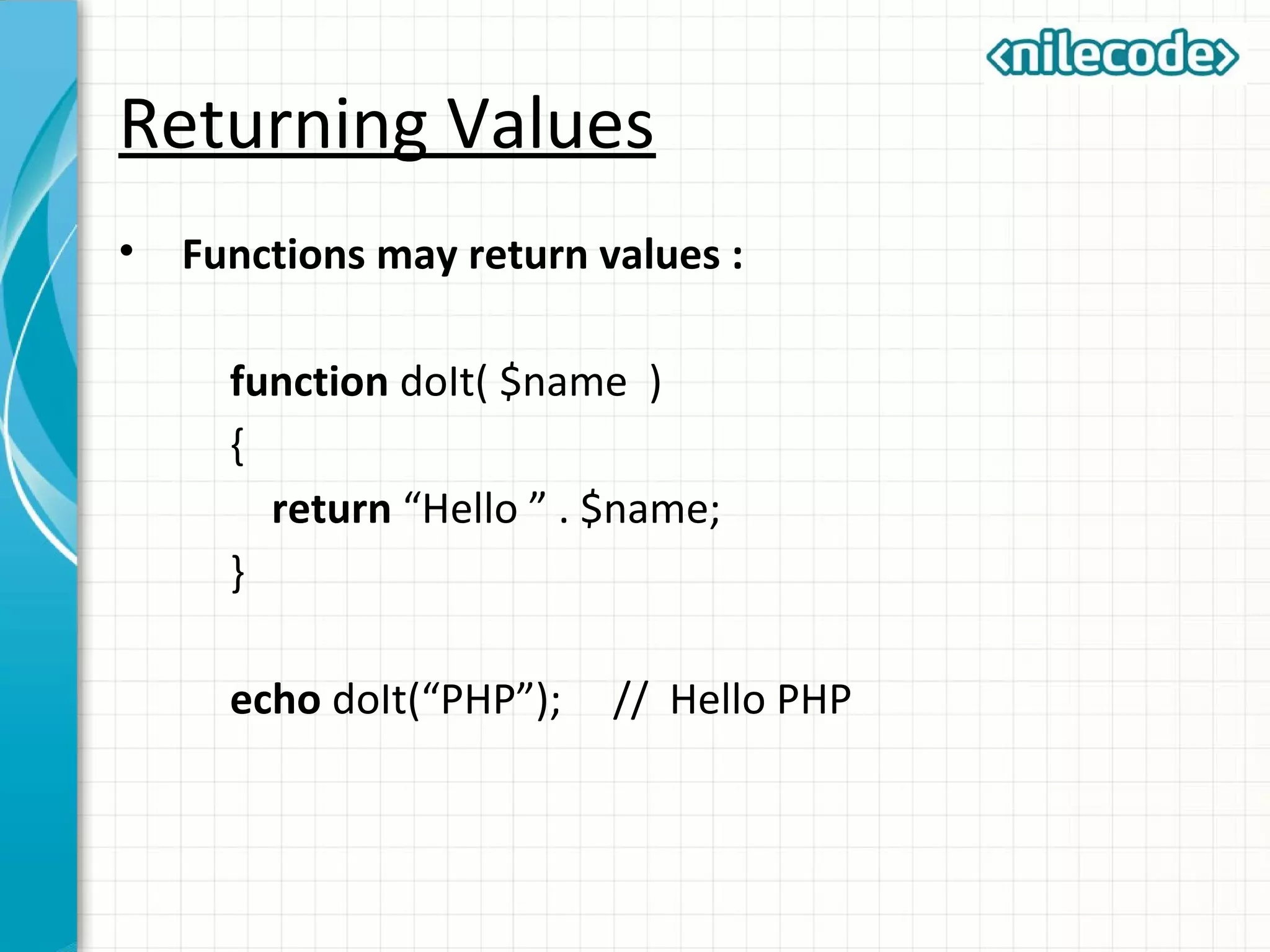
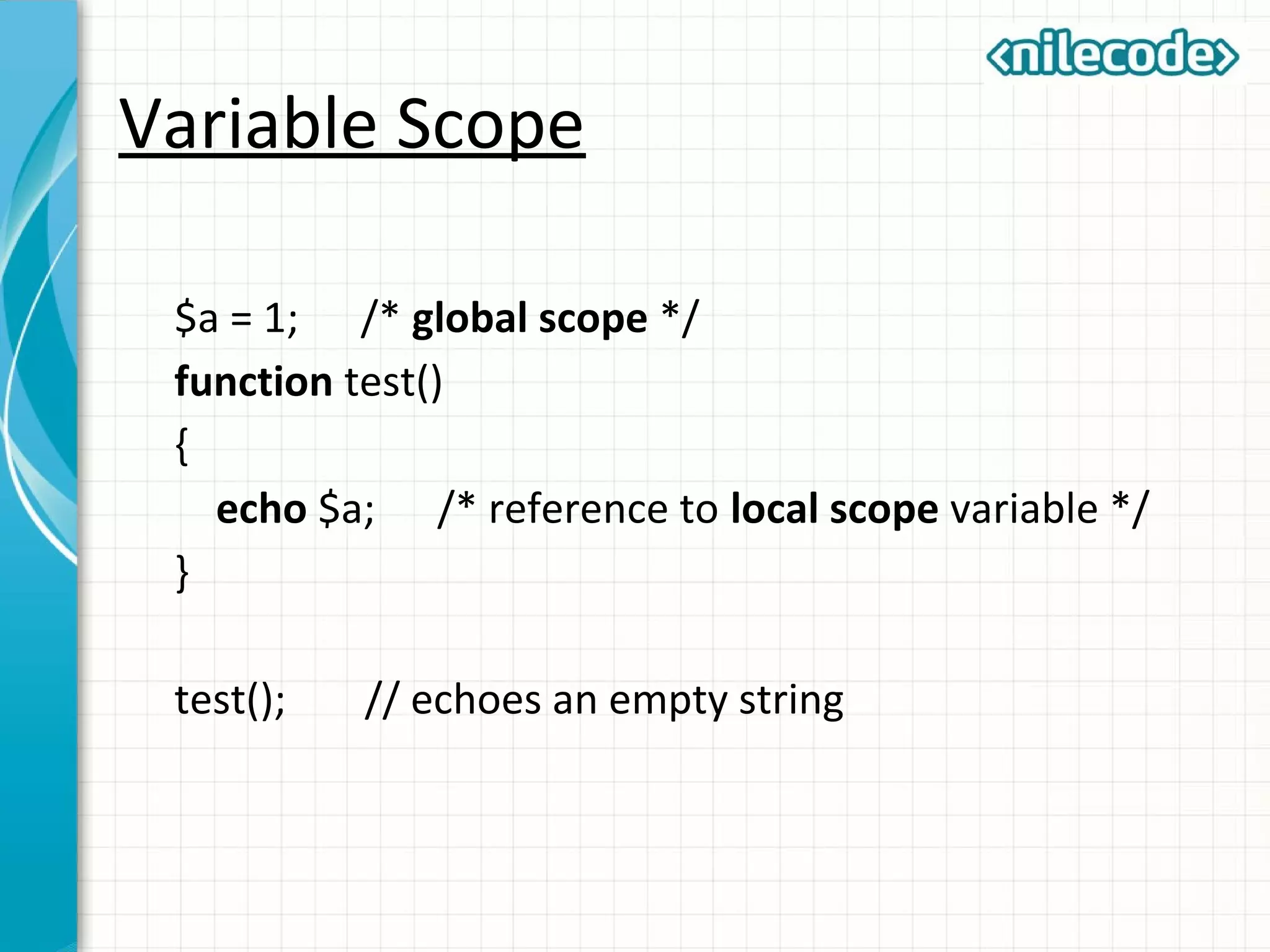
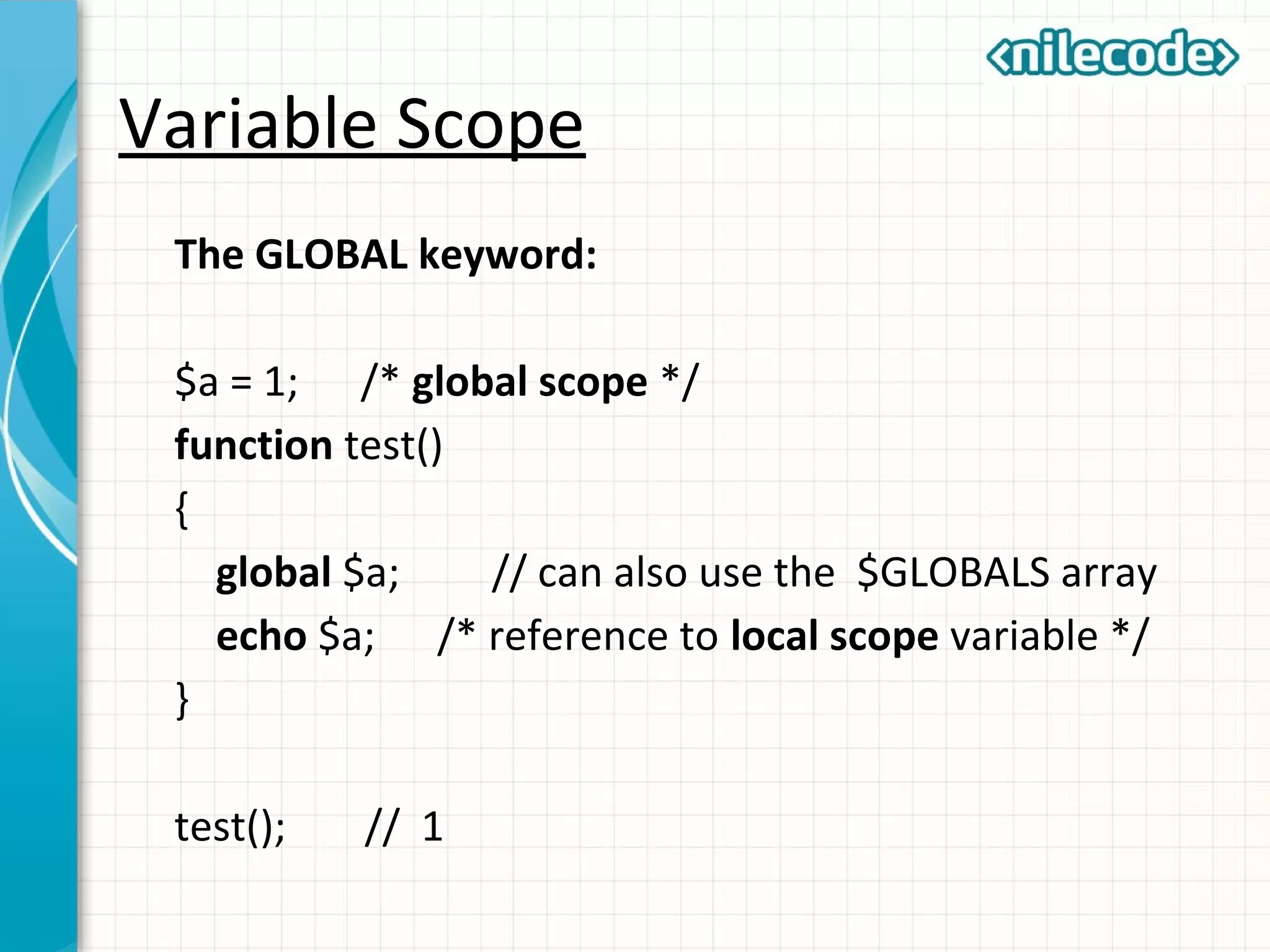
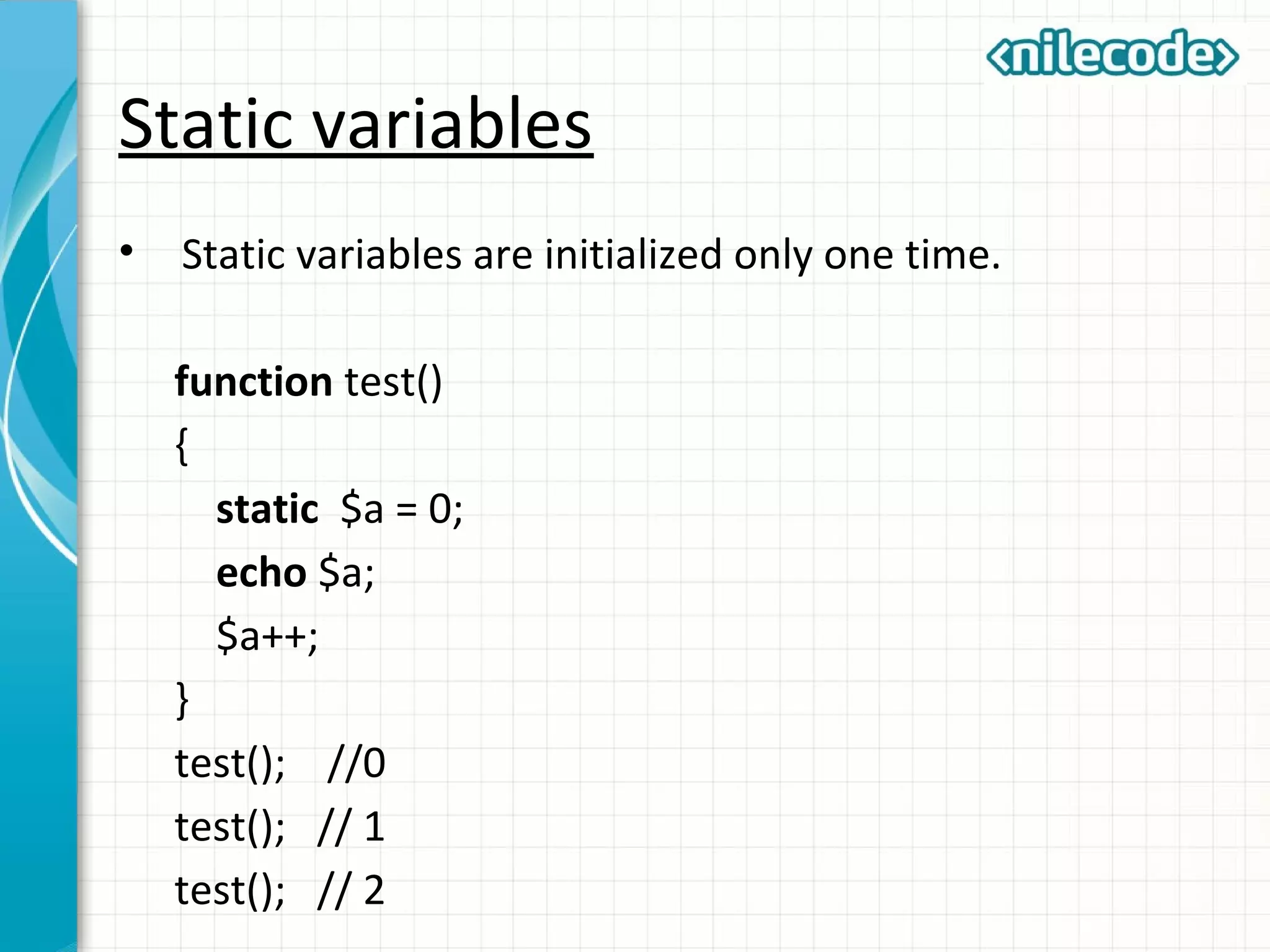
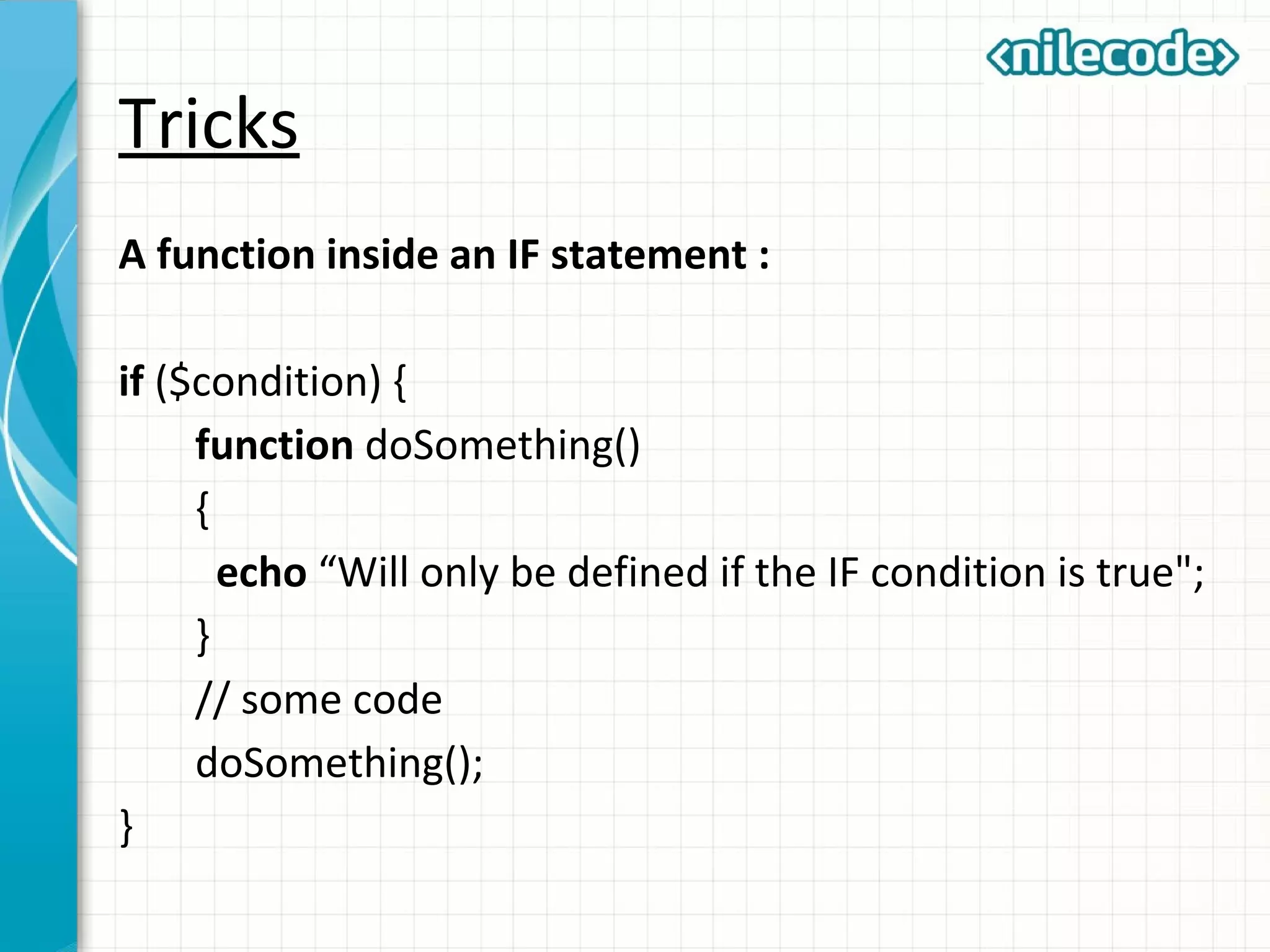
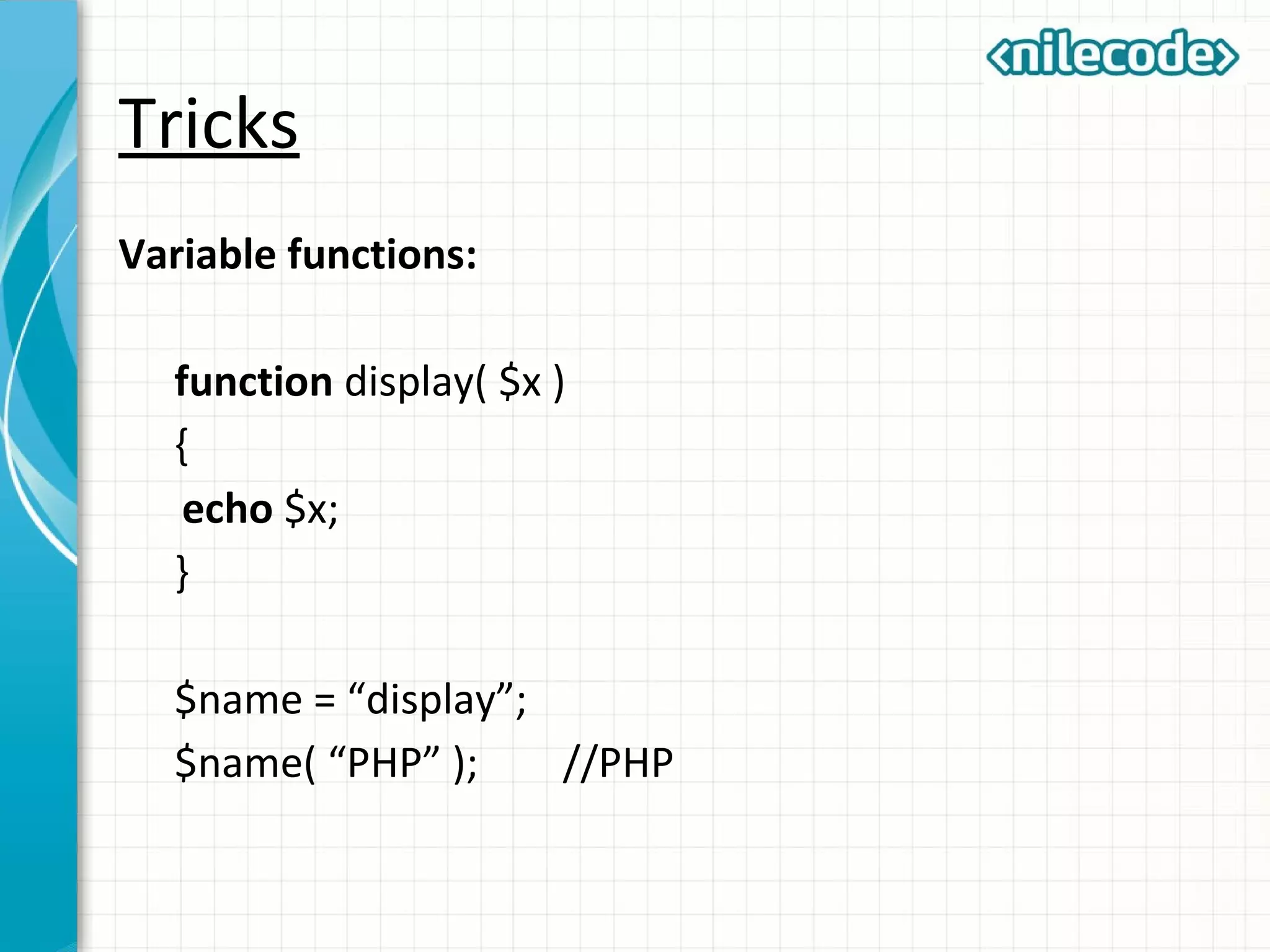
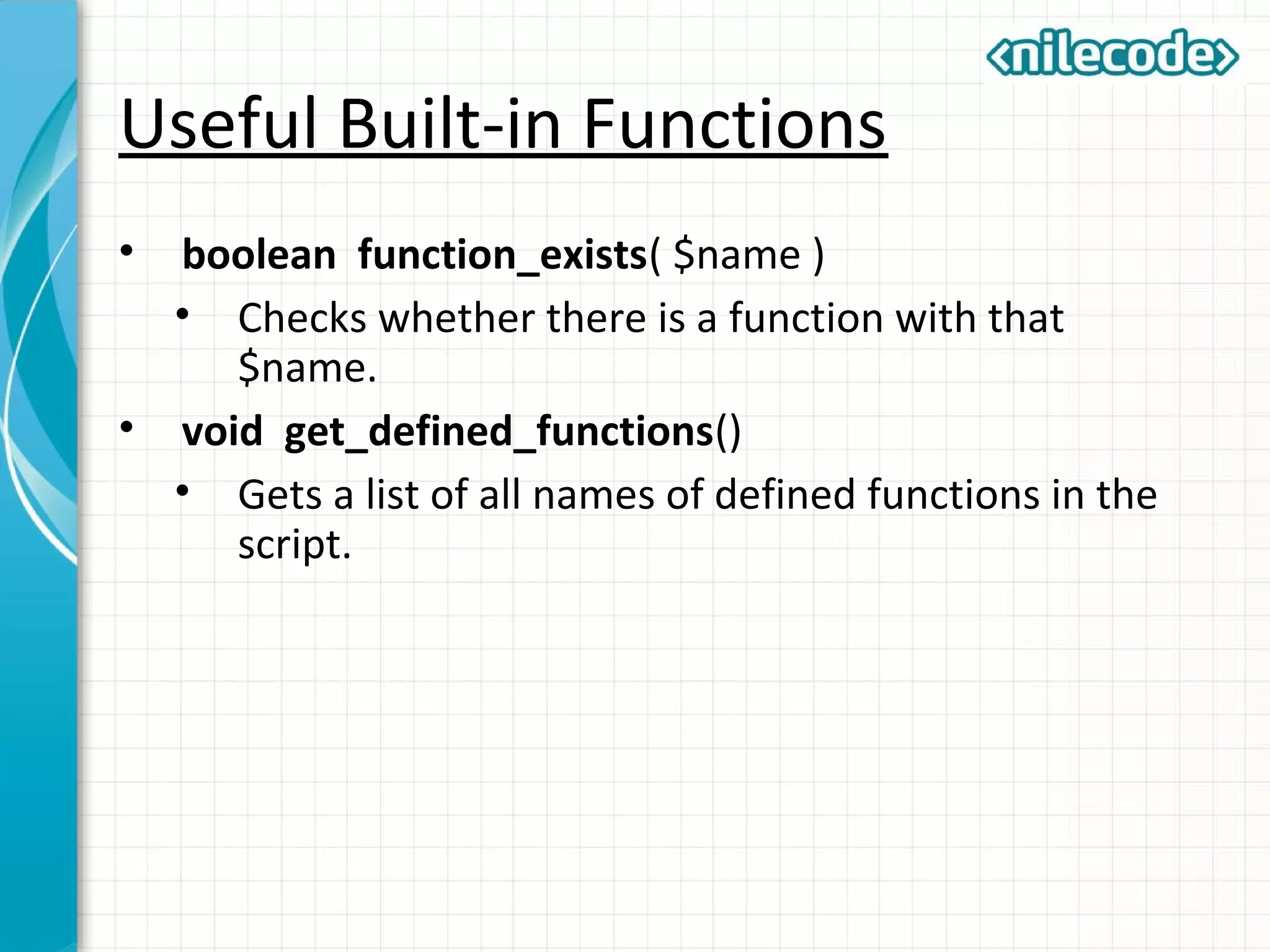
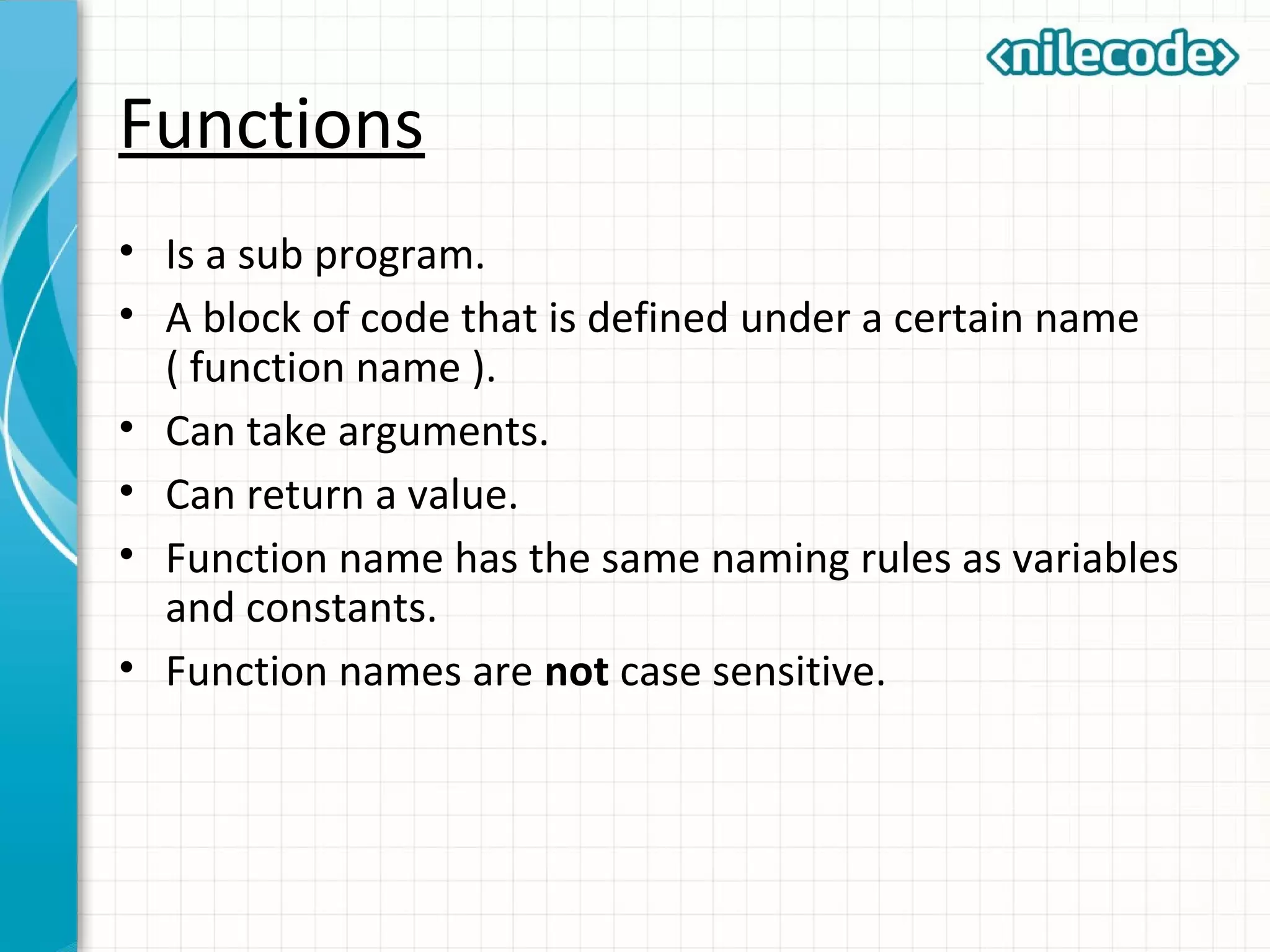
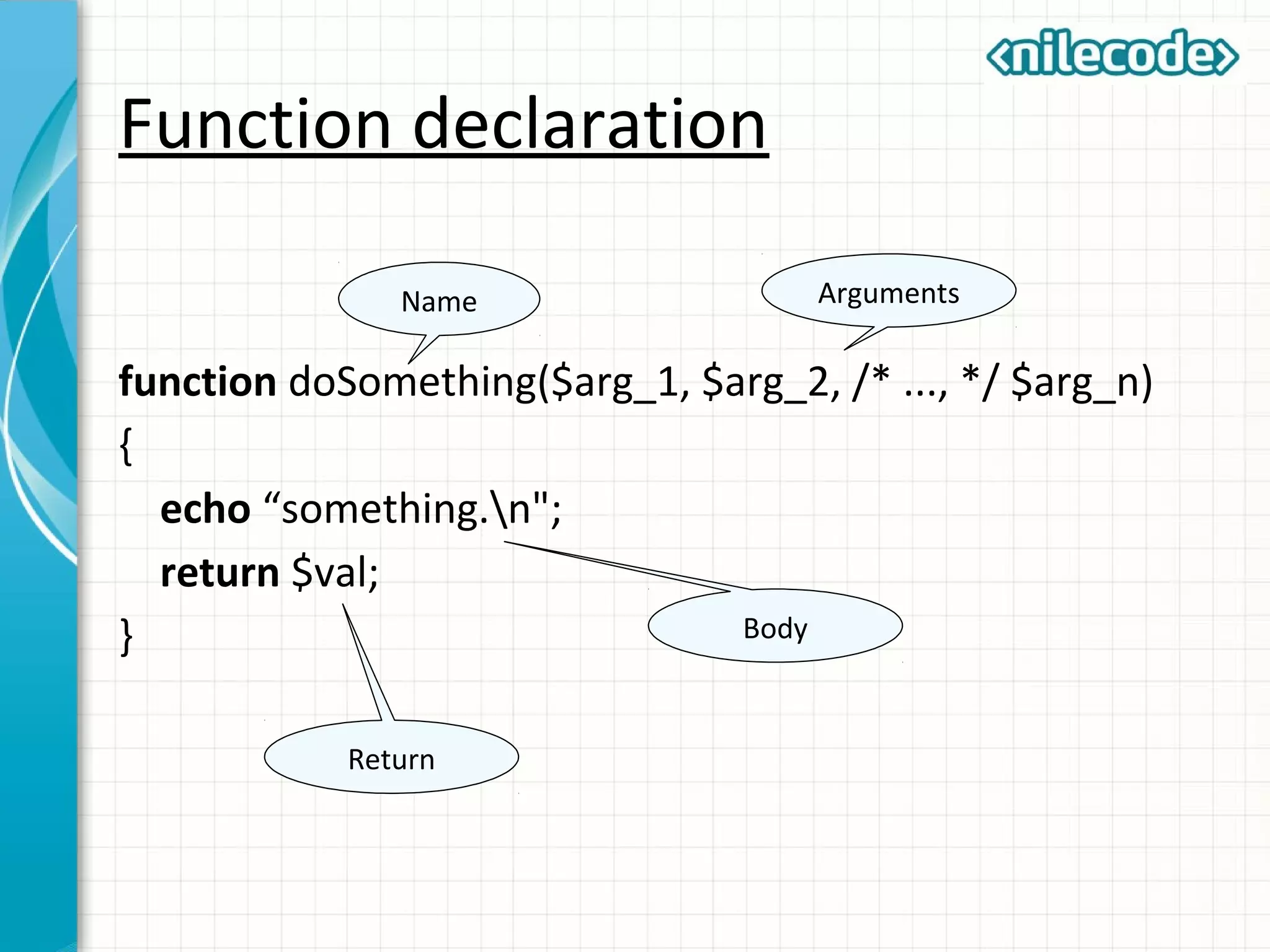
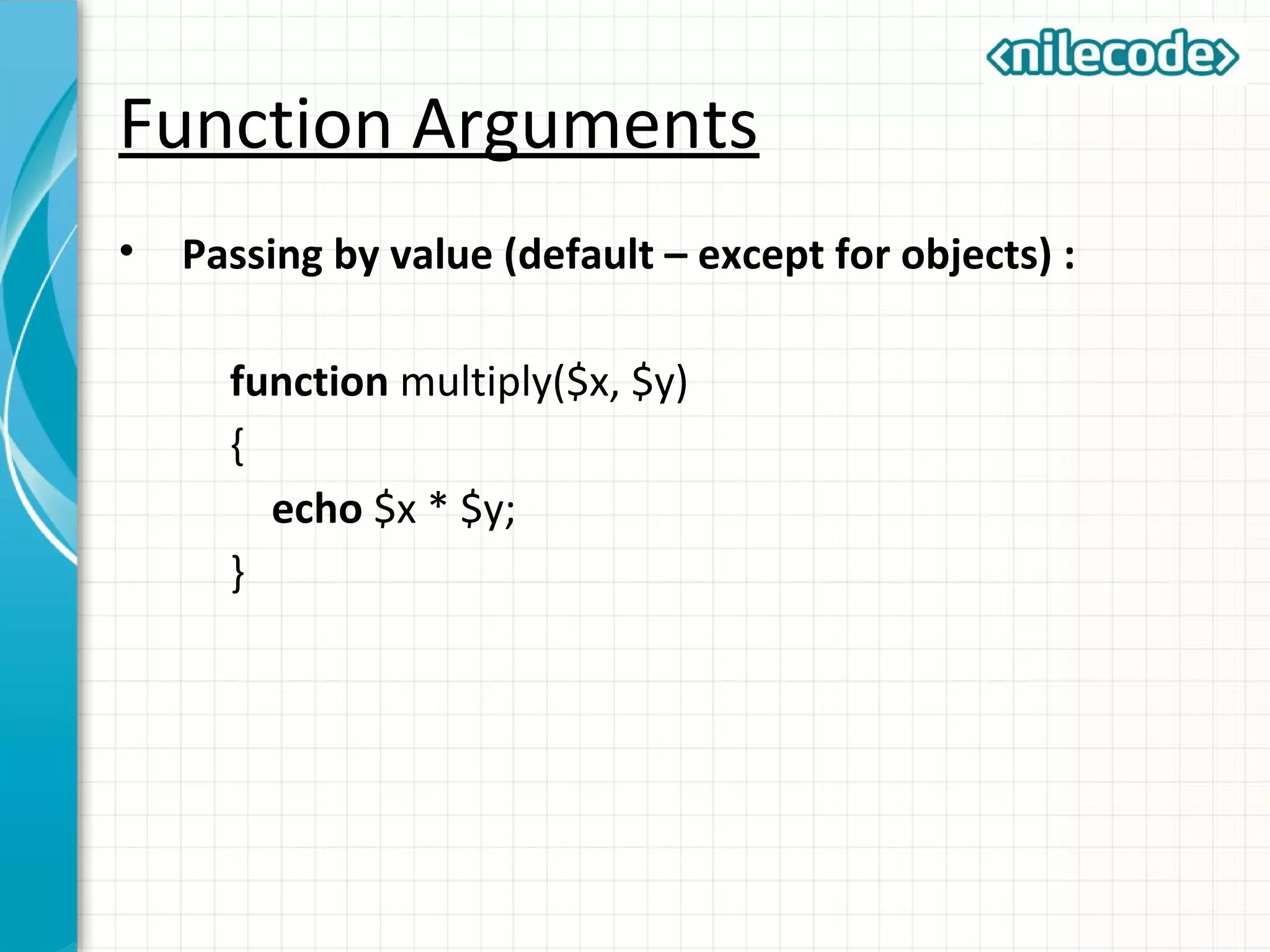
This document outlines PHP functions including function declaration, arguments, returning values, variable scope, static variables, recursion, and useful built-in functions. Functions are blocks of code that perform tasks and can take arguments. They are declared with the function keyword followed by the name and parameters. Functions can return values and arguments are passed by value by default but can also be passed by reference. Variable scope inside functions refers to the local scope unless specified as global. Static variables retain their value between function calls. Recursion occurs when a function calls itself. Useful built-in functions include function_exists() and get_defined_functions().

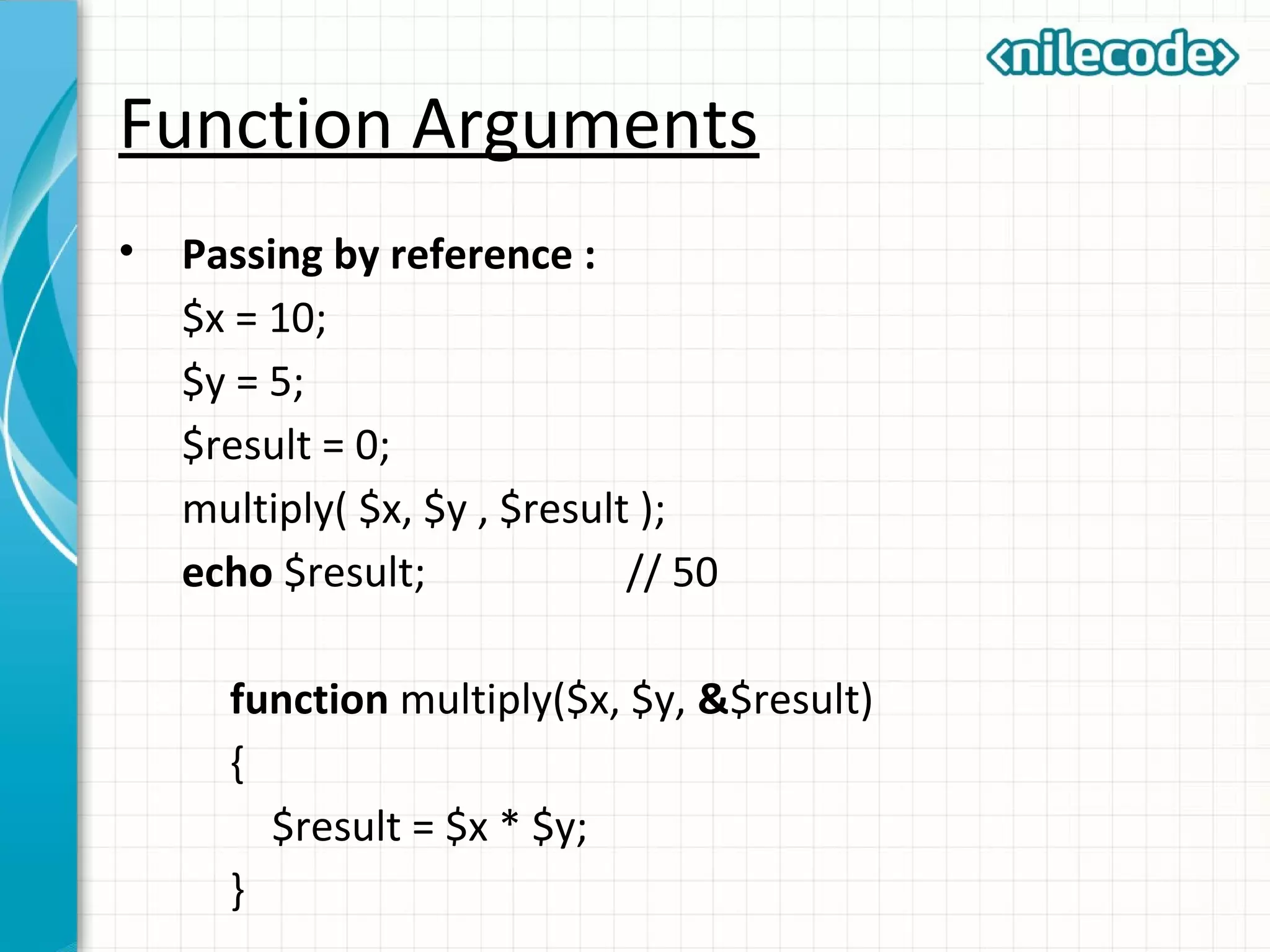
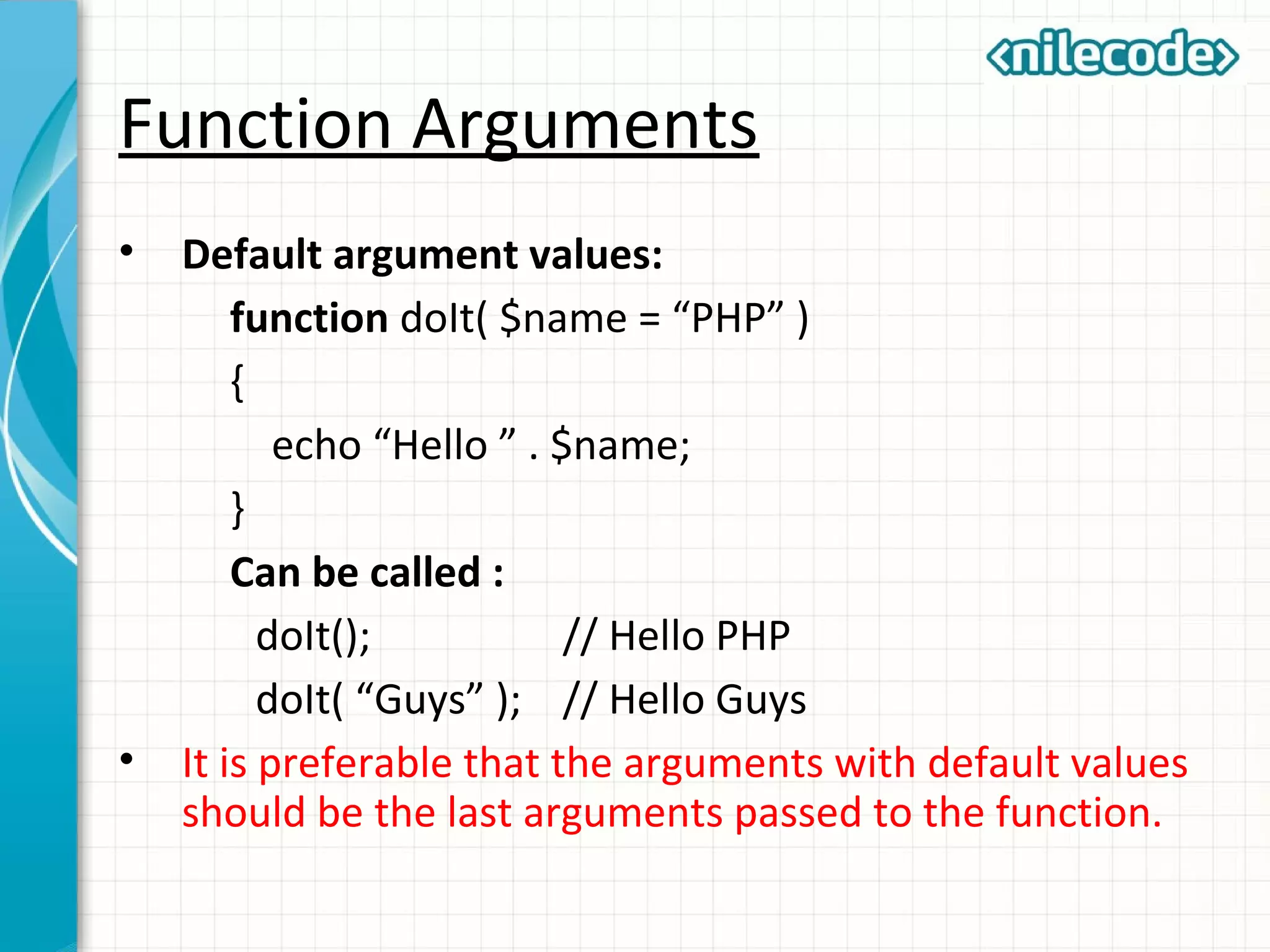
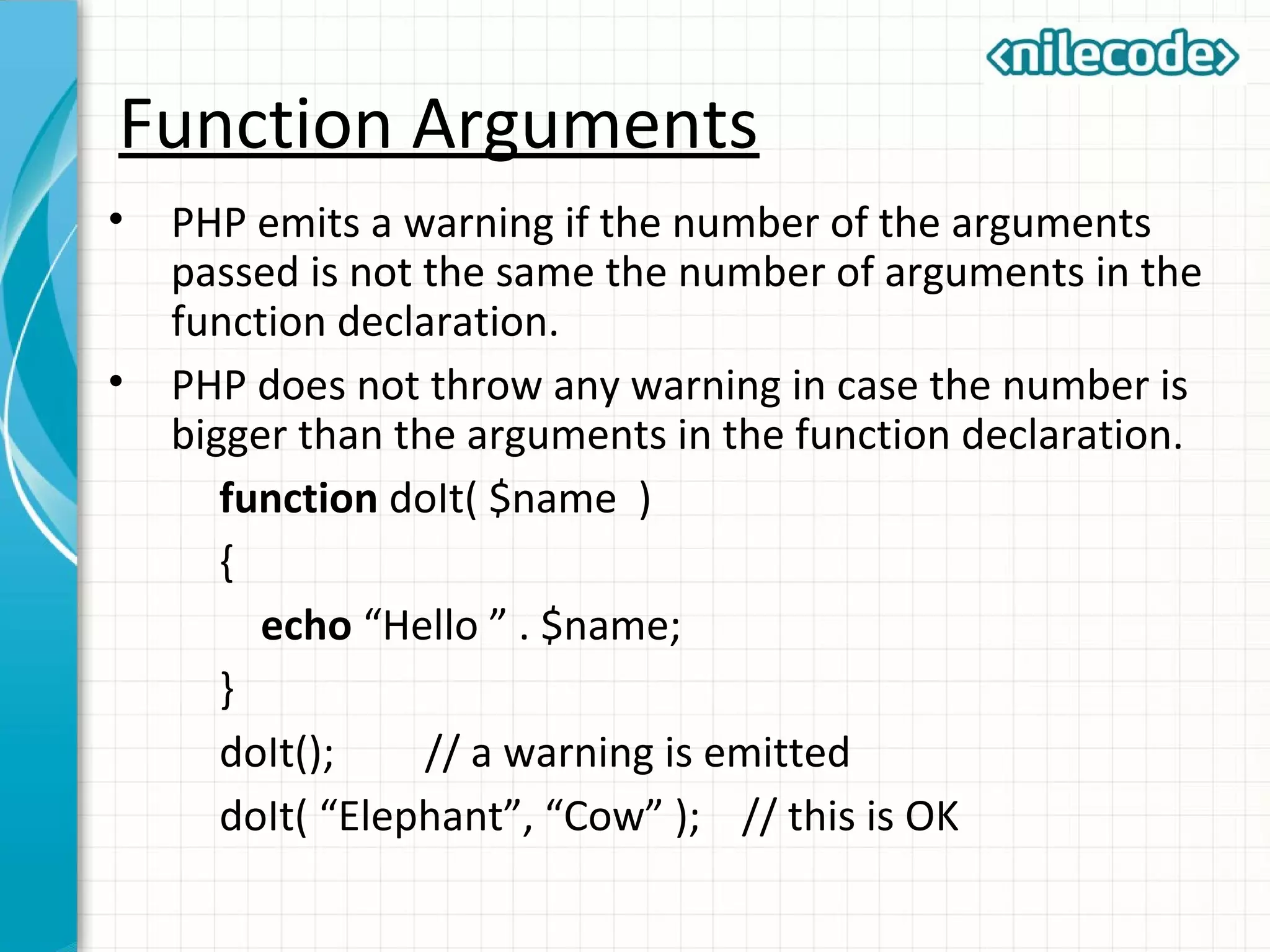
![Variable number of arguments • PHP allows you to create a function with unlimited number of arguments. function displayAll( ) { $numargs = func_num_args(); $arg_list = func_get_args(); for ($i = 0; $i < $numargs; $i++) { echo $arg_list[$i] . “ ”; } } displayAll( “This” , “is”, “a”, “good”, “thing.” );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class3-phpfunctions-150930071058-lva1-app6892/75/Class-3-PHP-Functions-10-2048.jpg)