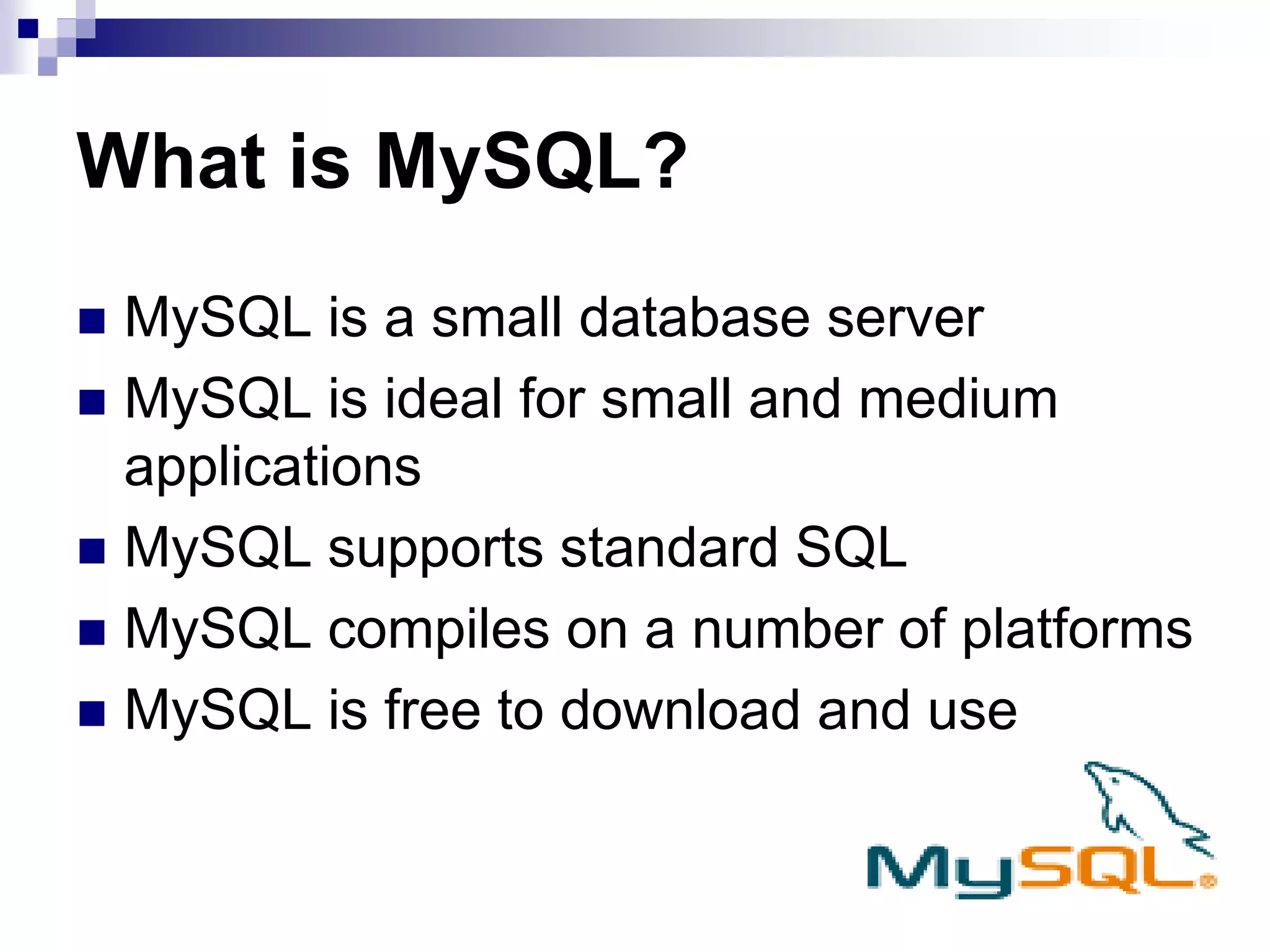
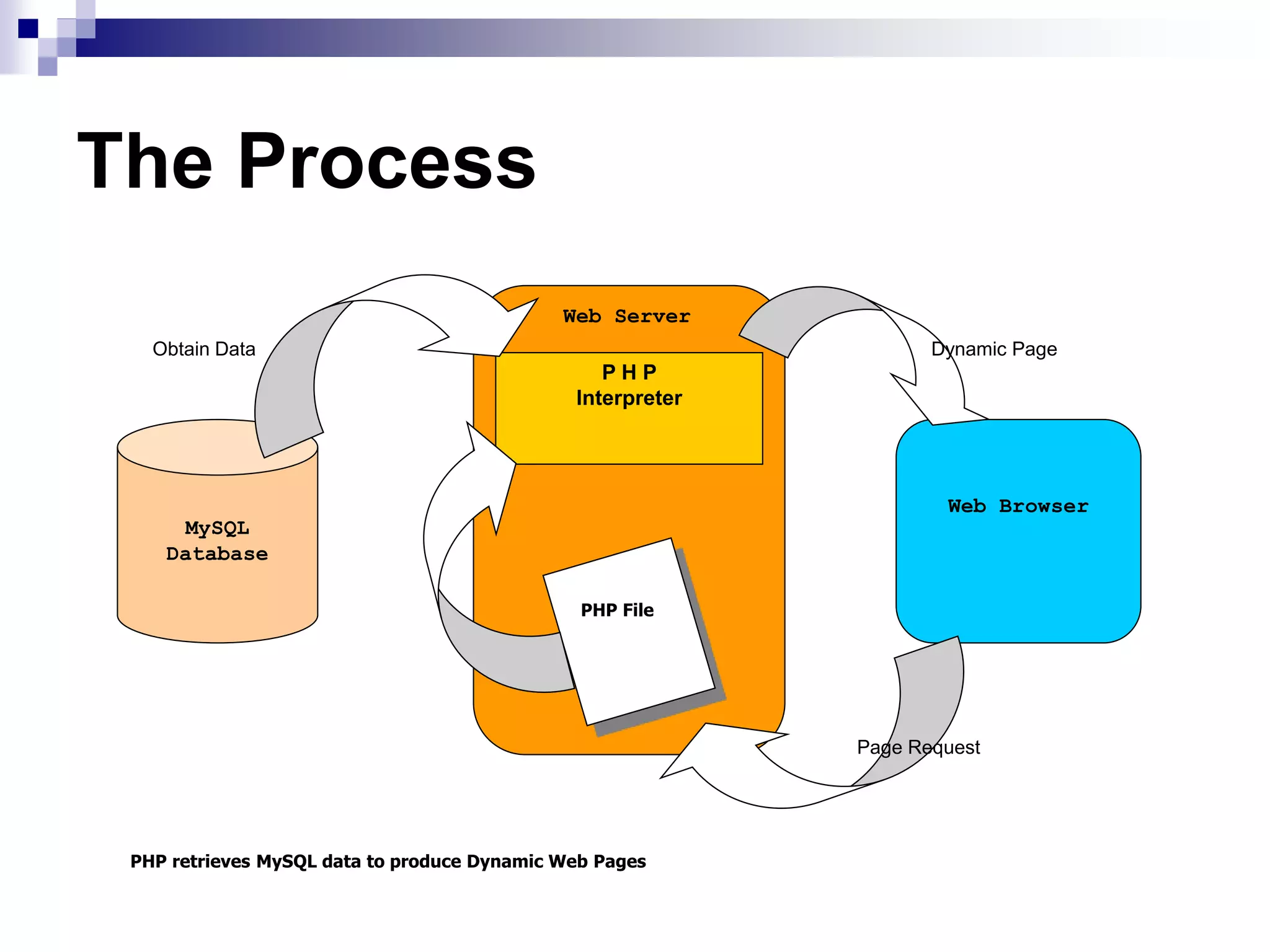
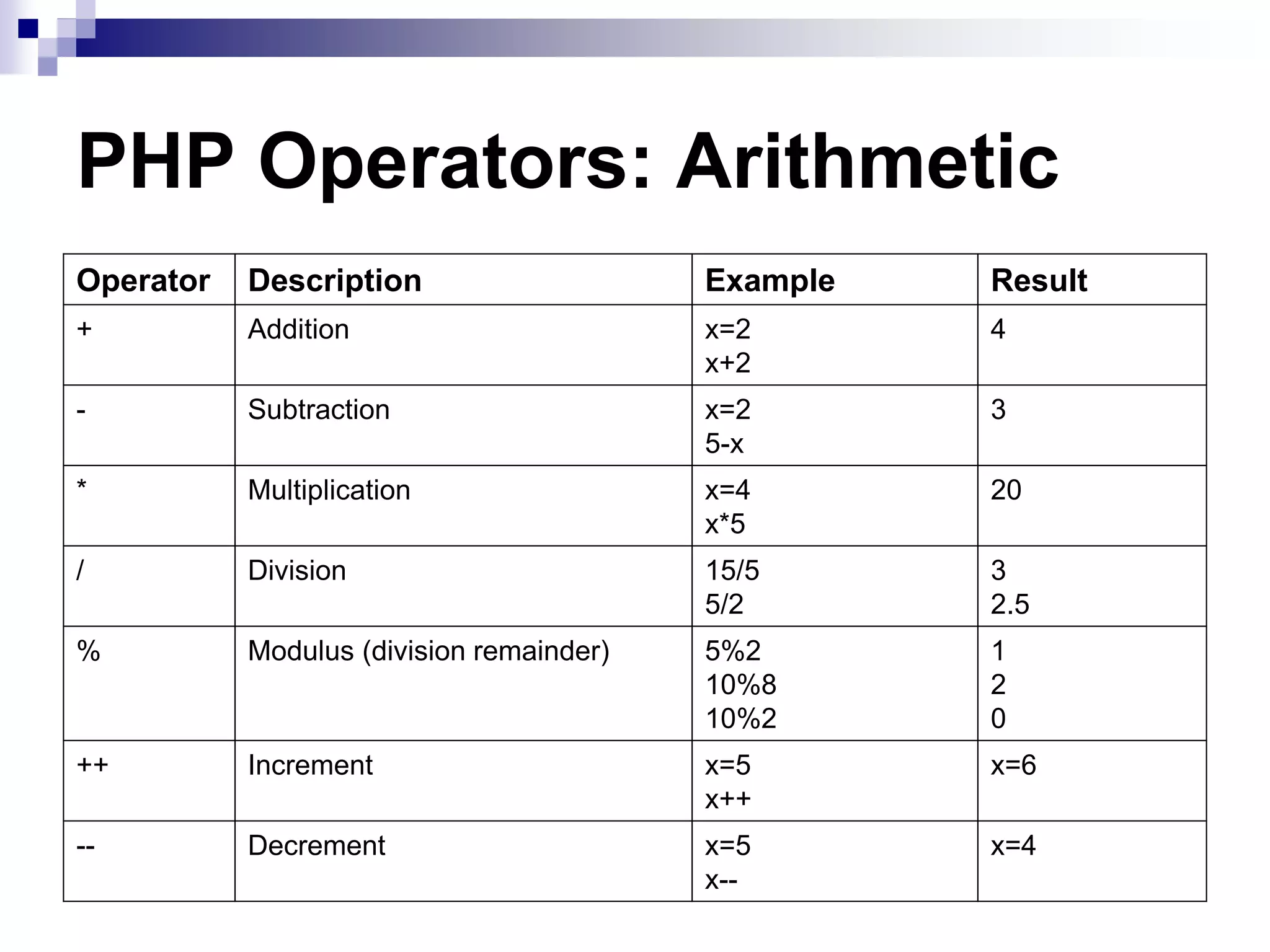
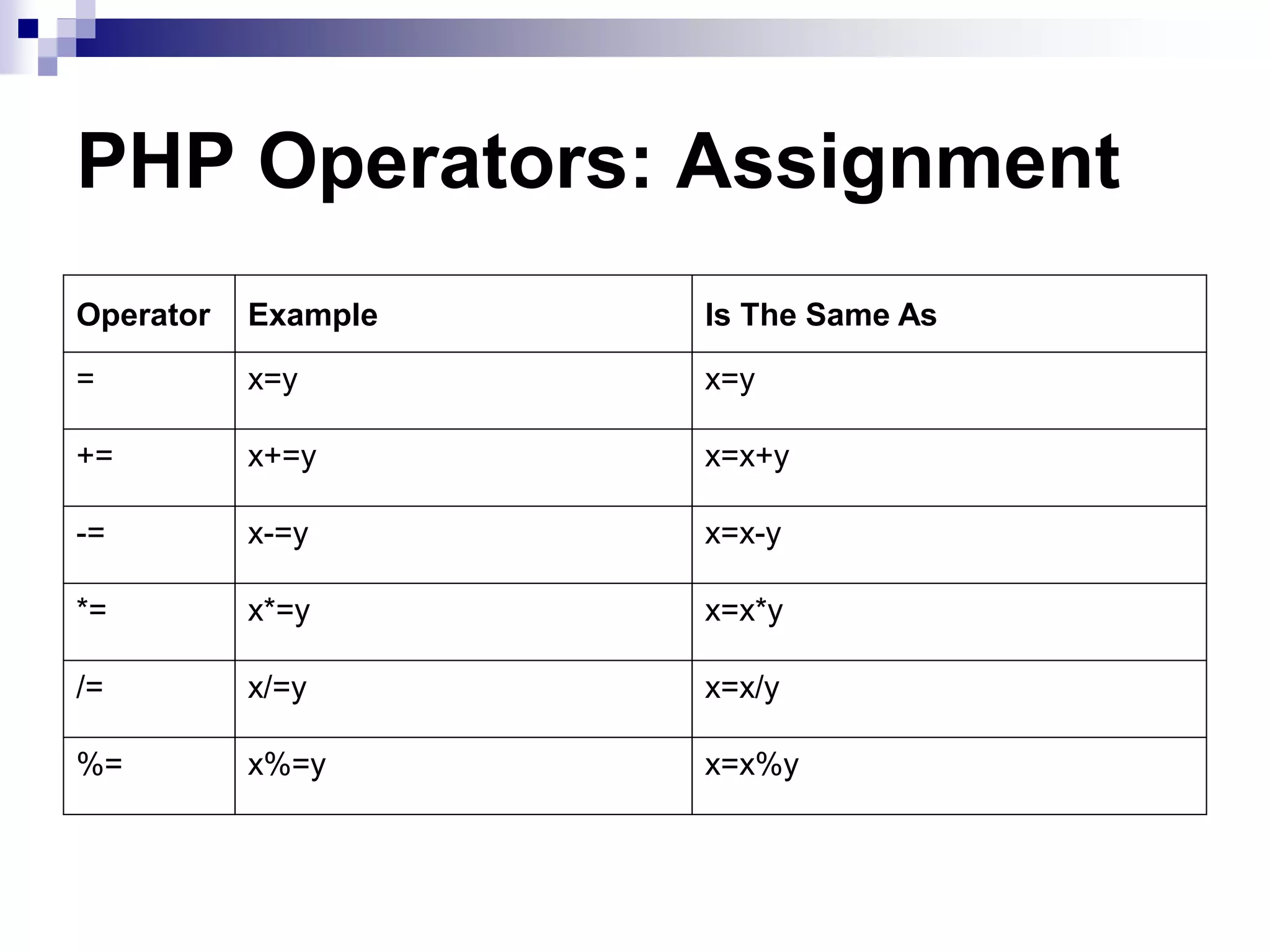
The document provides an overview of PHP and MySQL, detailing their functions, file structures, and syntax for creating dynamic web pages. It covers PHP's compatibility with various platforms and web servers, basic syntax, variable management, arithmetic and comparison operators, control structures, and cookie handling. Additionally, it outlines how to connect PHP with MySQL to perform database operations such as querying, inserting, updating, and deleting records.



























![The welcome.php File <html> <body> Welcome <?php echo $_POST[‘name’]; ?> <br>You are <?php echo $_POST[‘age’]; ?> years old! </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpandmysql-230221222124-18570480/75/PHP-and-MySQL-ppt-35-2048.jpg)


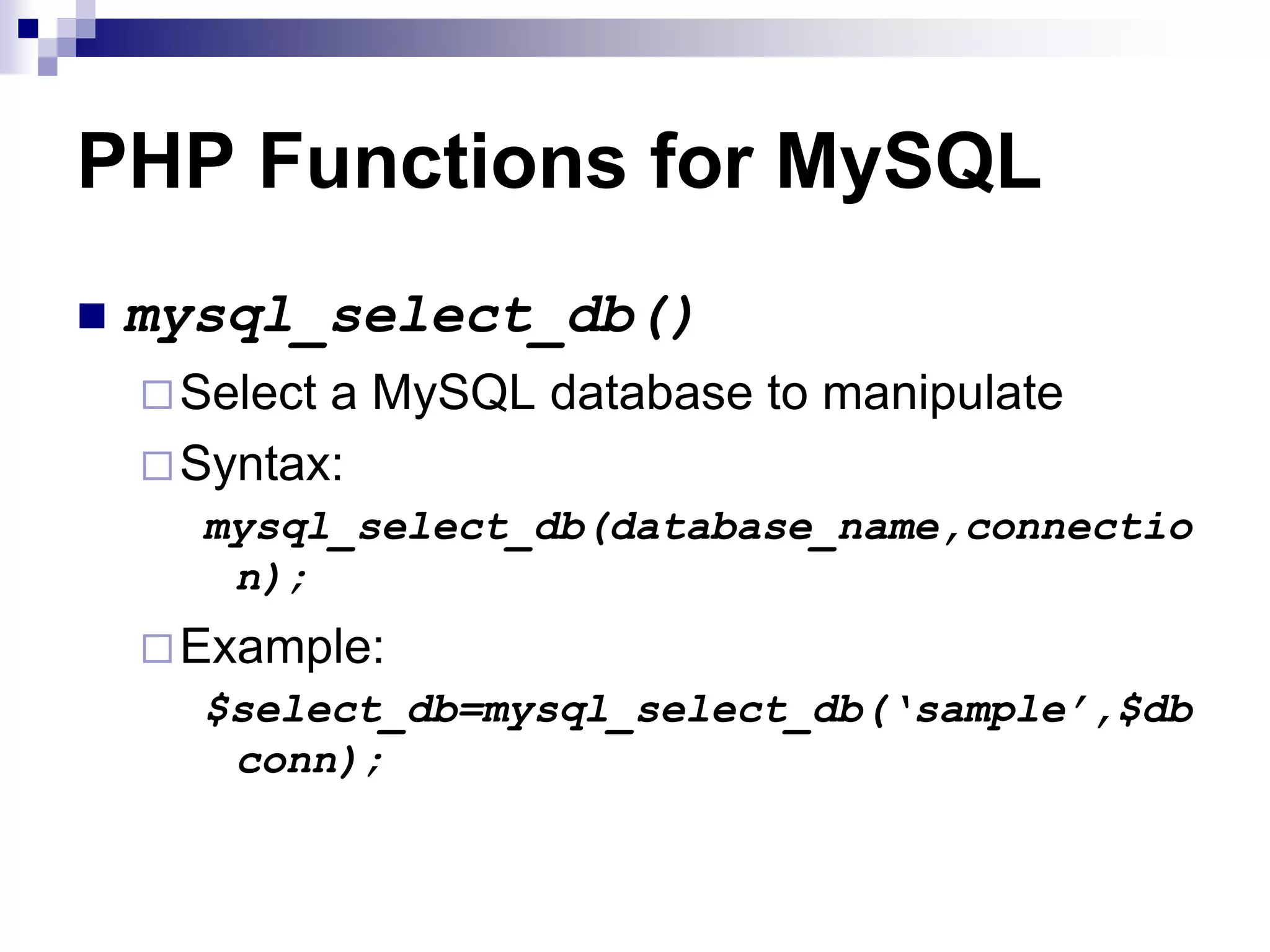
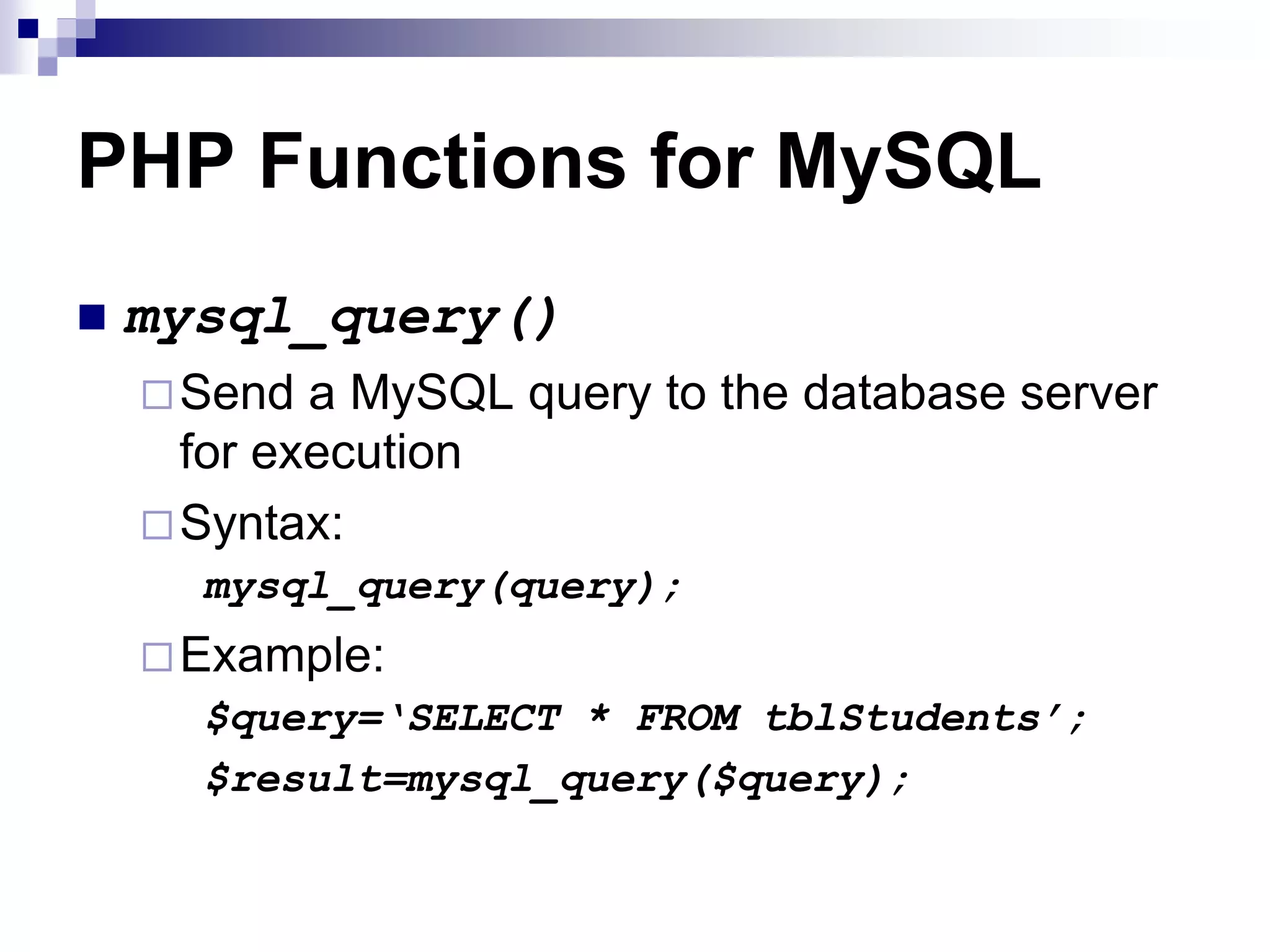
![PHP Functions for MySQL mysql_fetch_array() Fetch a result row as an associative array, a numeric array, or both Syntax: mysql_fetch_array(query); Example: $result = mysql_query("SELECT id, name FROM mytable"); while ($row = mysql_fetch_array($result)) { printf("ID: “ . $row[‘id’] Name: “ . $row[‘name’]); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpandmysql-230221222124-18570480/75/PHP-and-MySQL-ppt-41-2048.jpg)






![Example: Retrieving a Cookie <html> <body> <?php if (isset($_COOKIE["uname"])){ echo "Welcome " . $_COOKIE["uname"] . "!<br>"; }Else{ echo "You are not logged in!<br>"; } ?> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpandmysql-230221222124-18570480/75/PHP-and-MySQL-ppt-48-2048.jpg)
