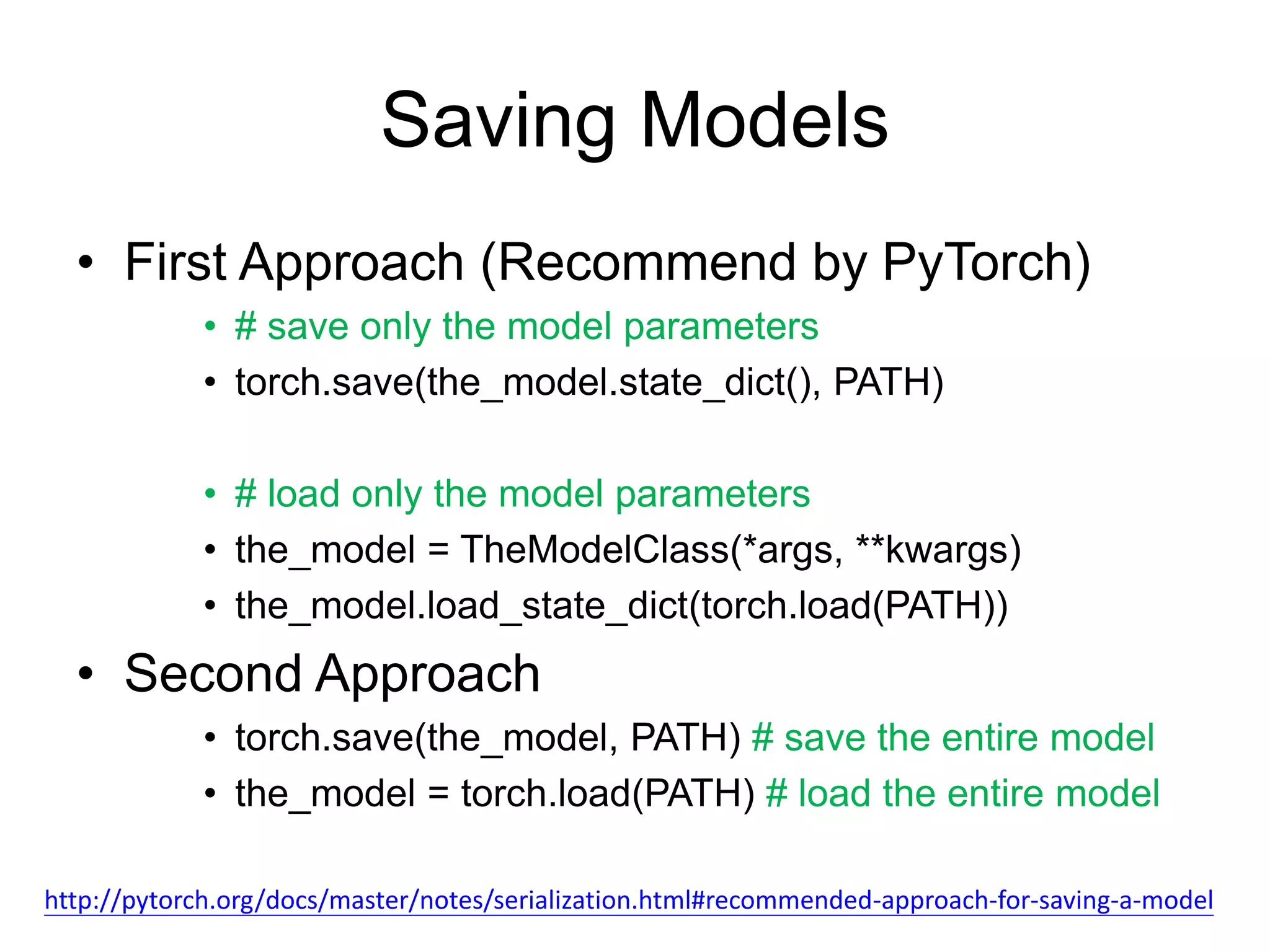
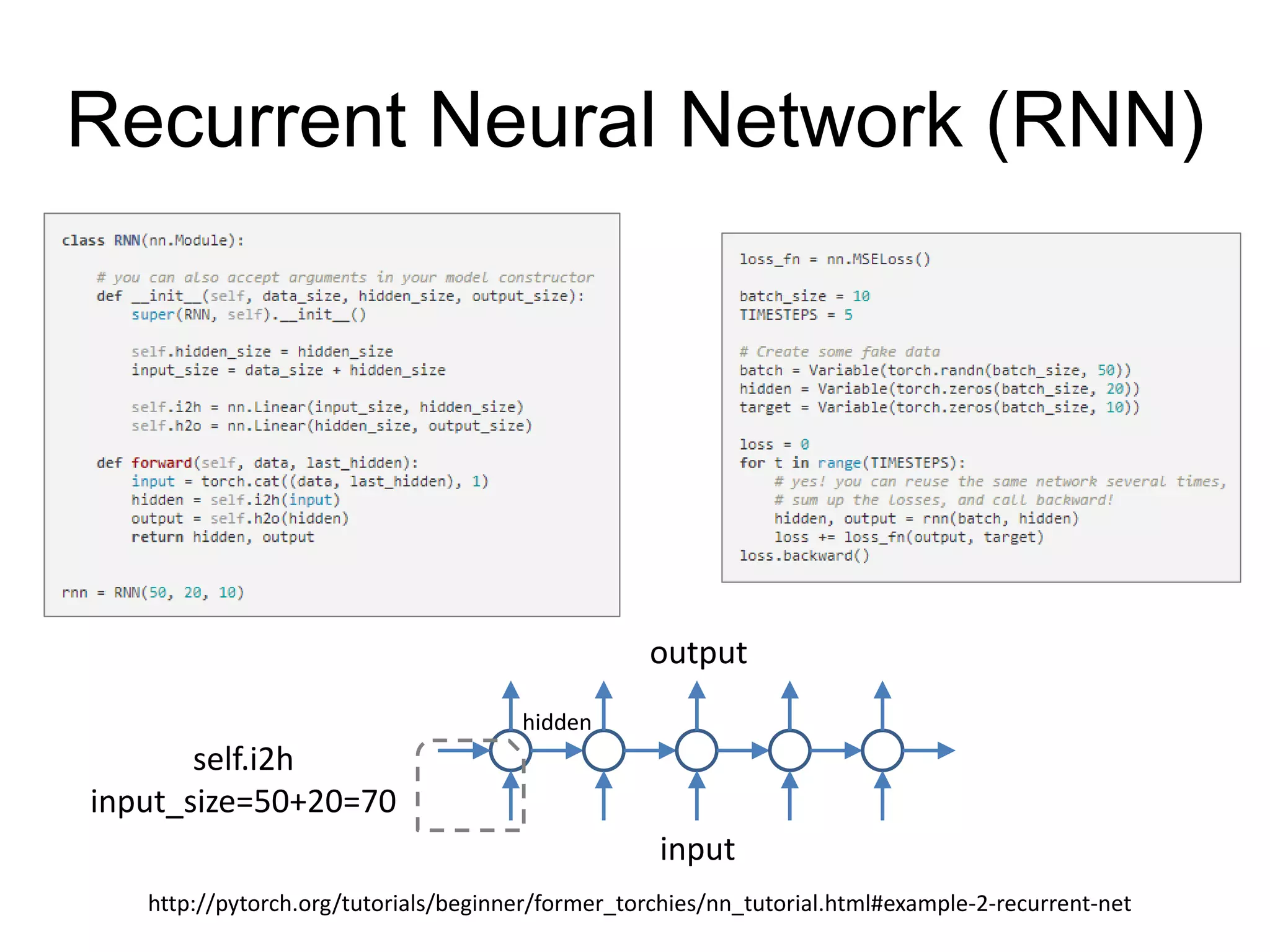
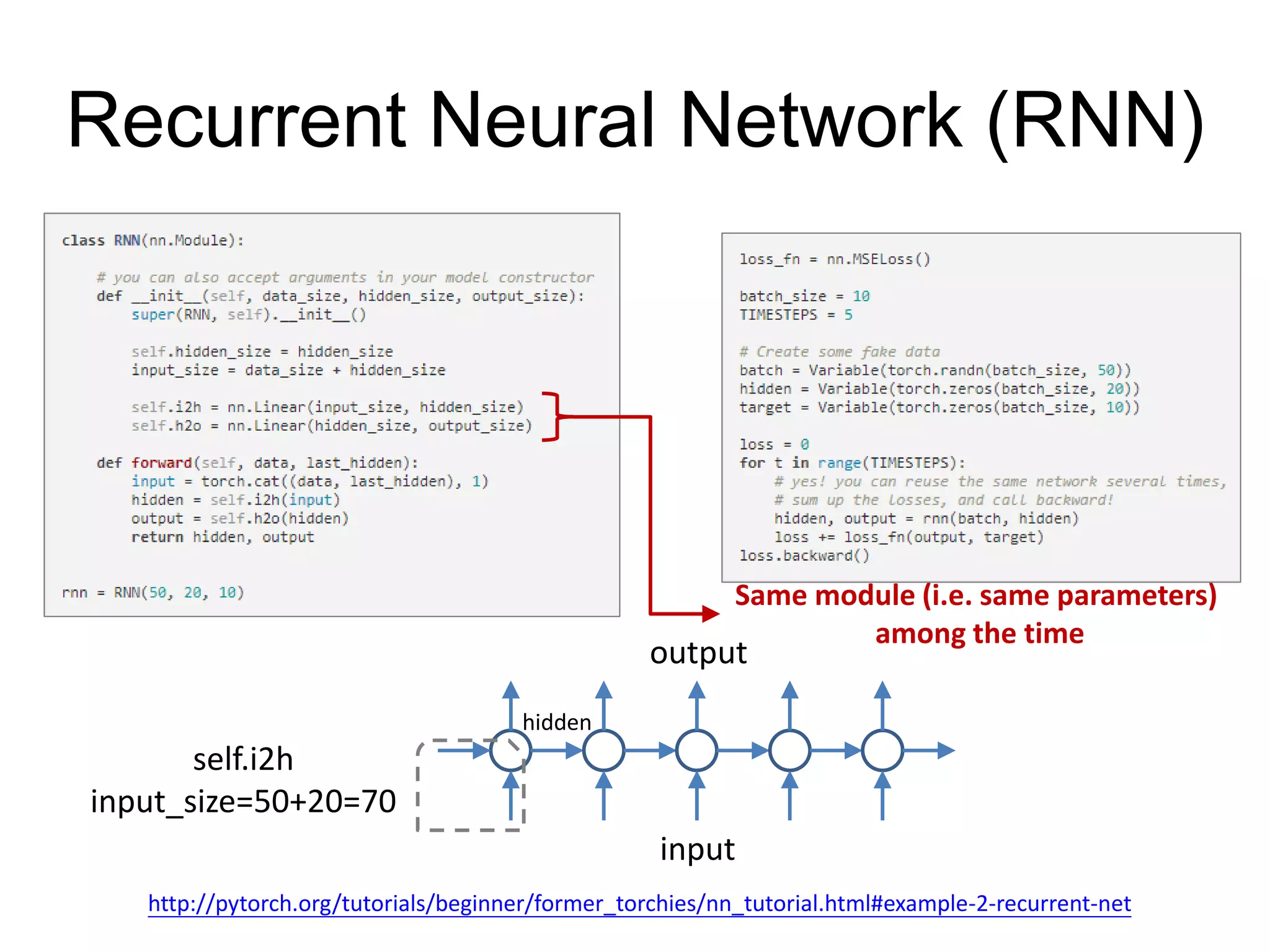
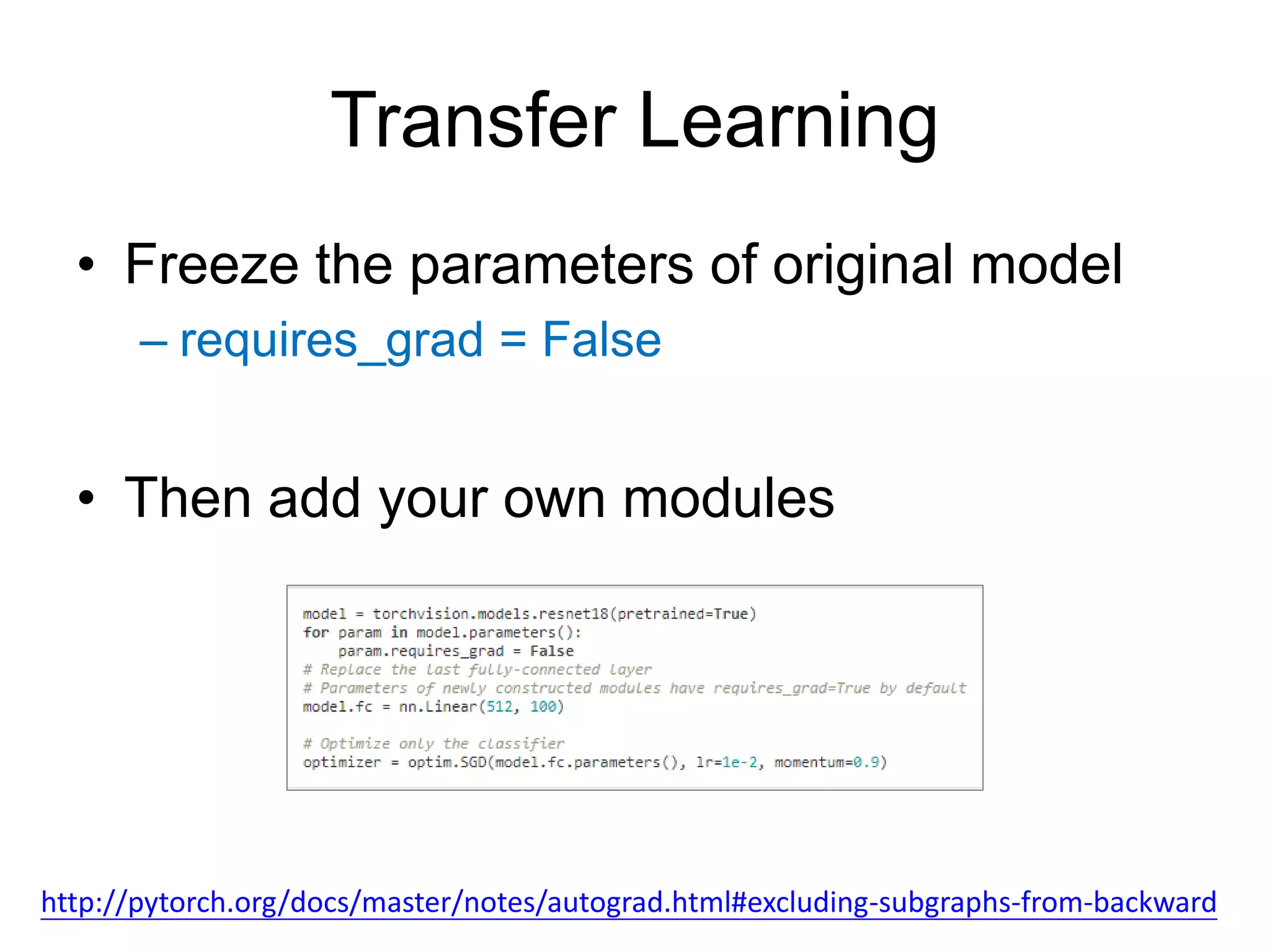
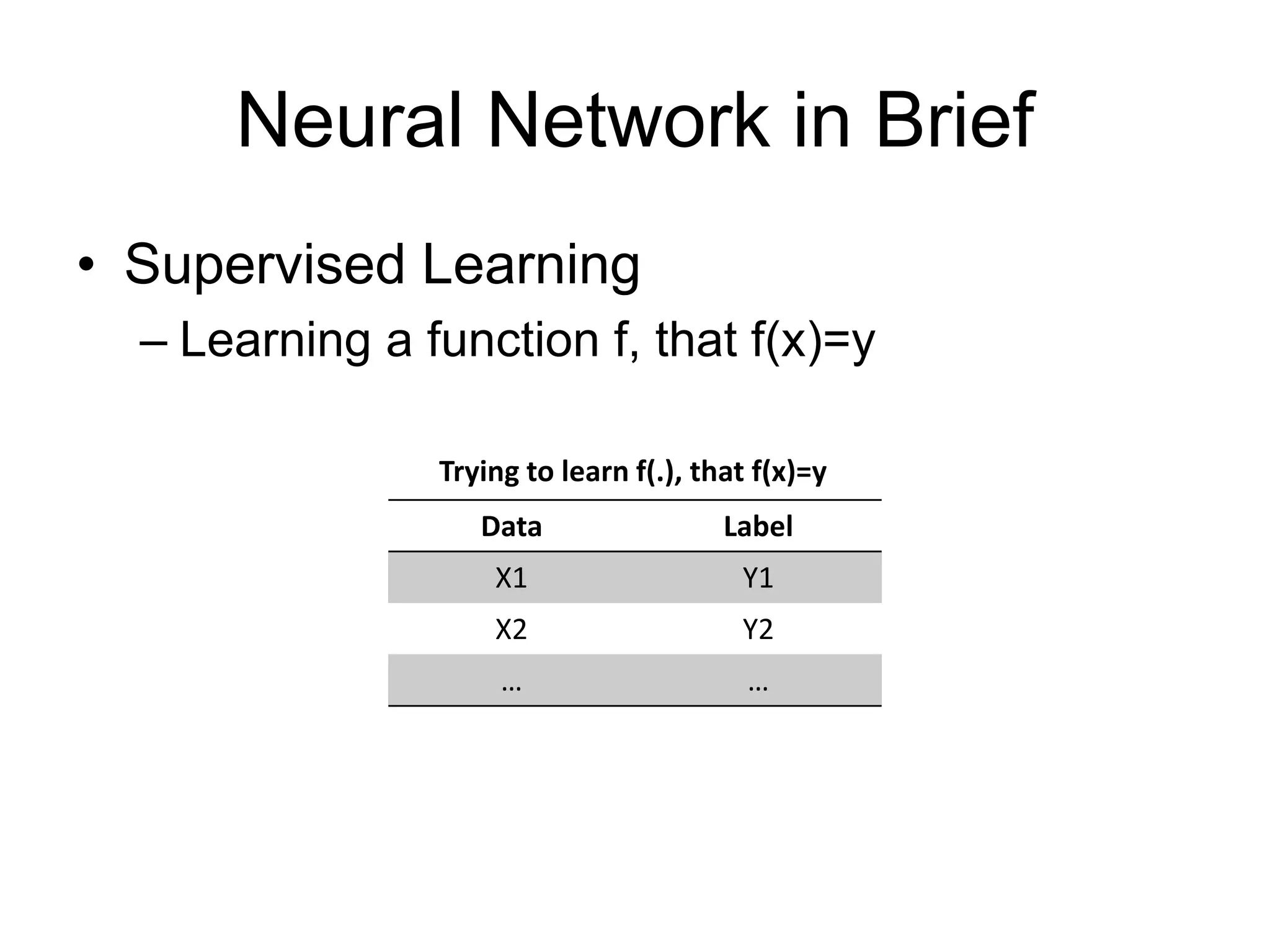
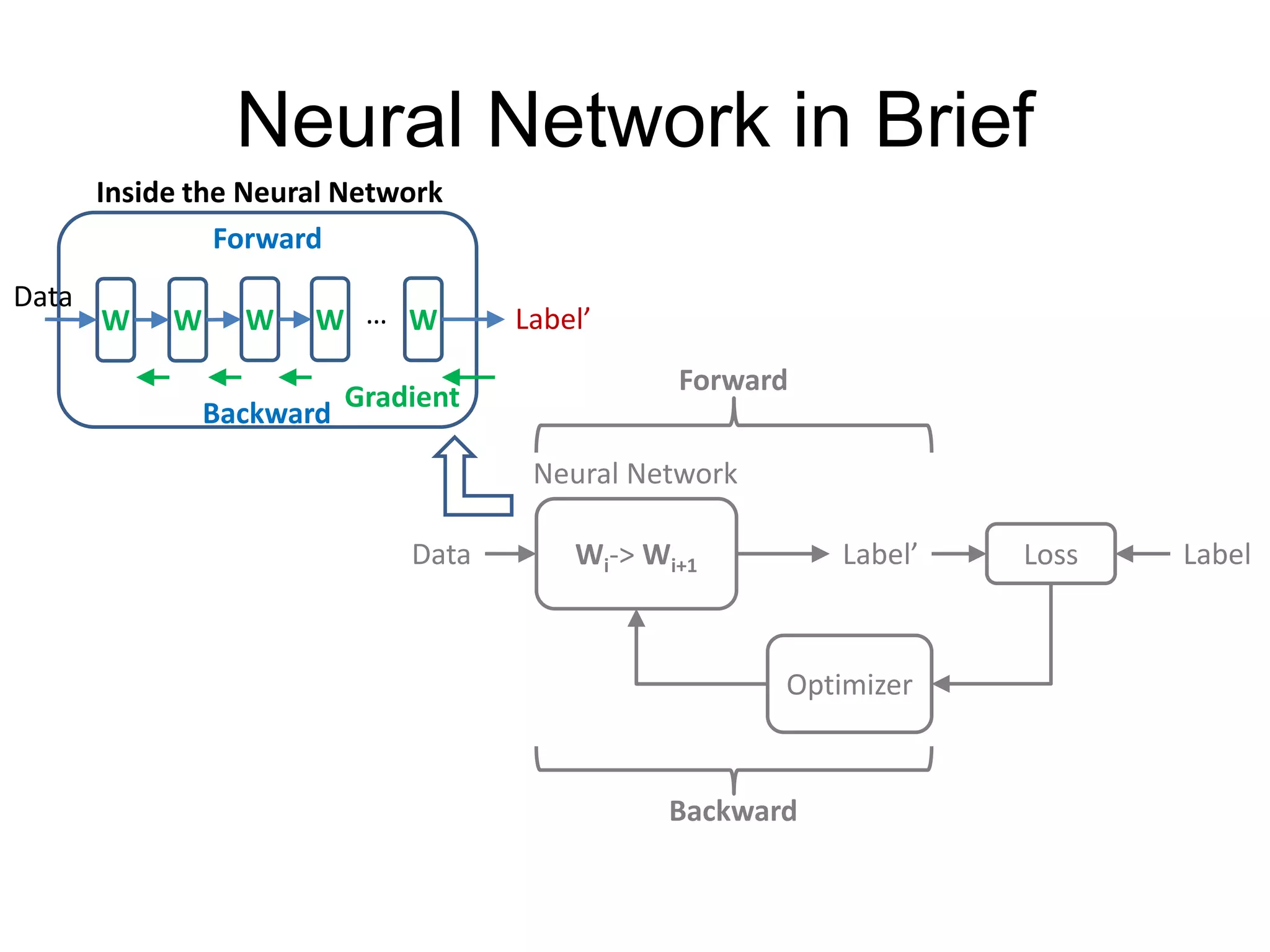
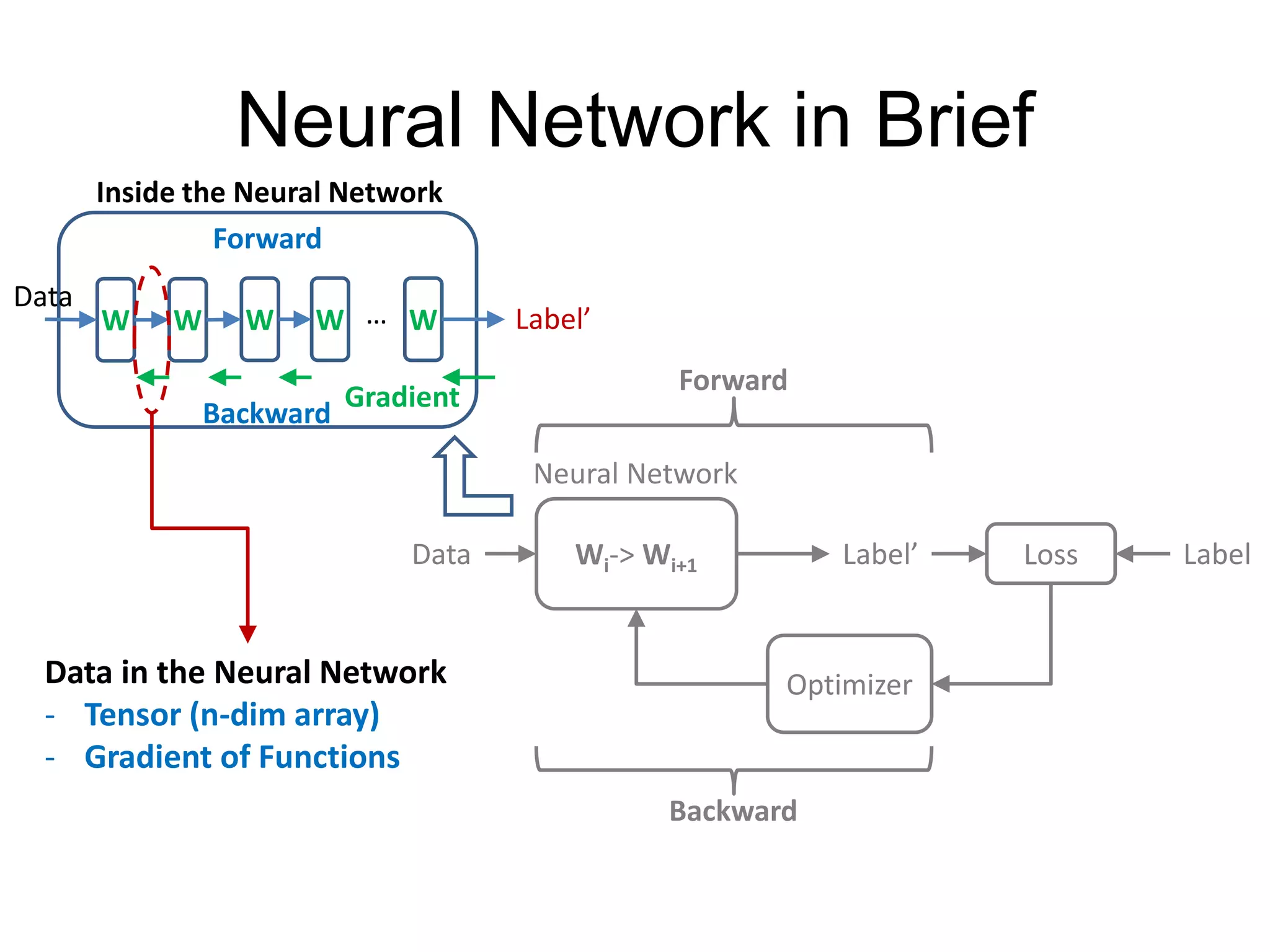
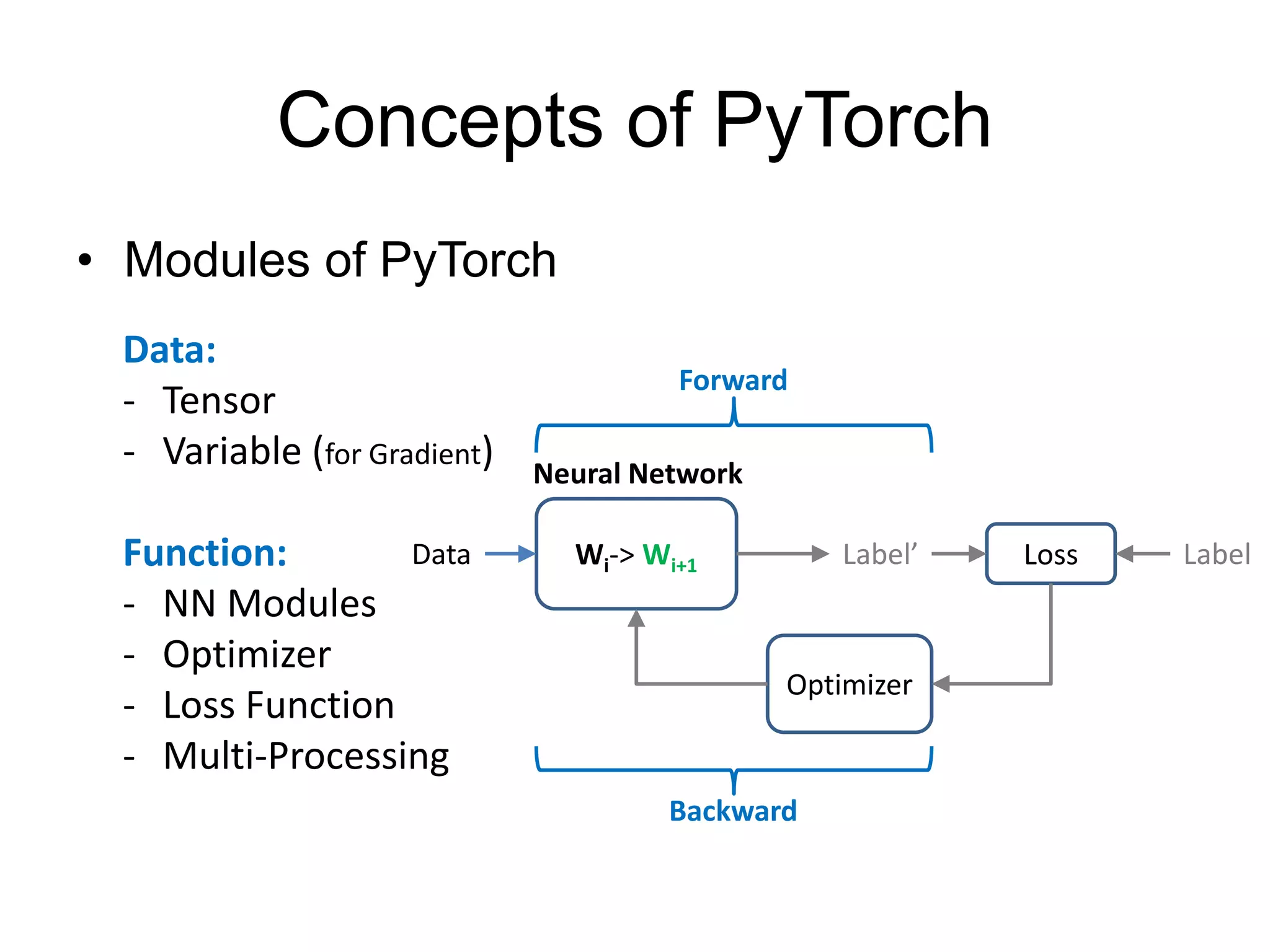
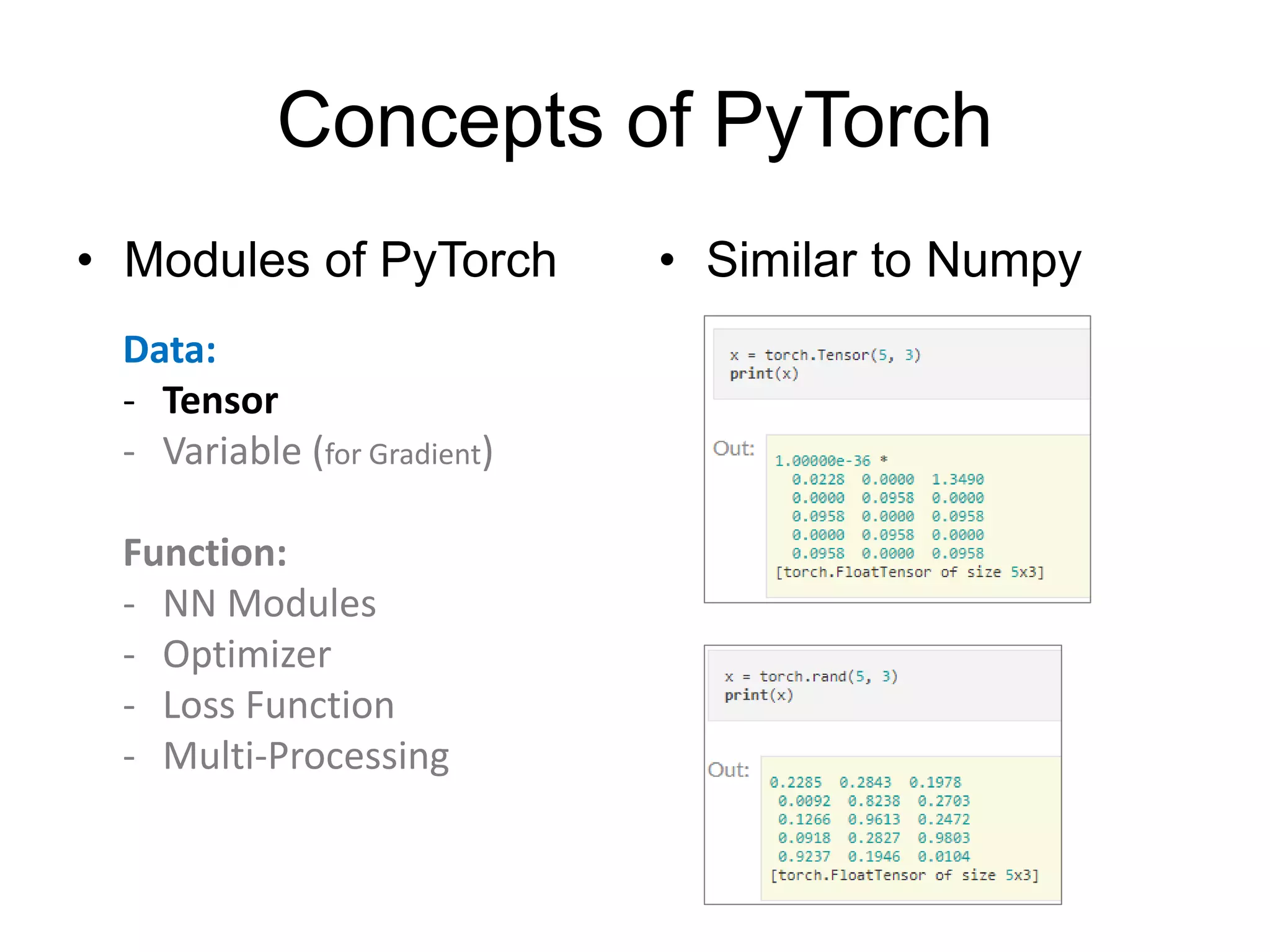
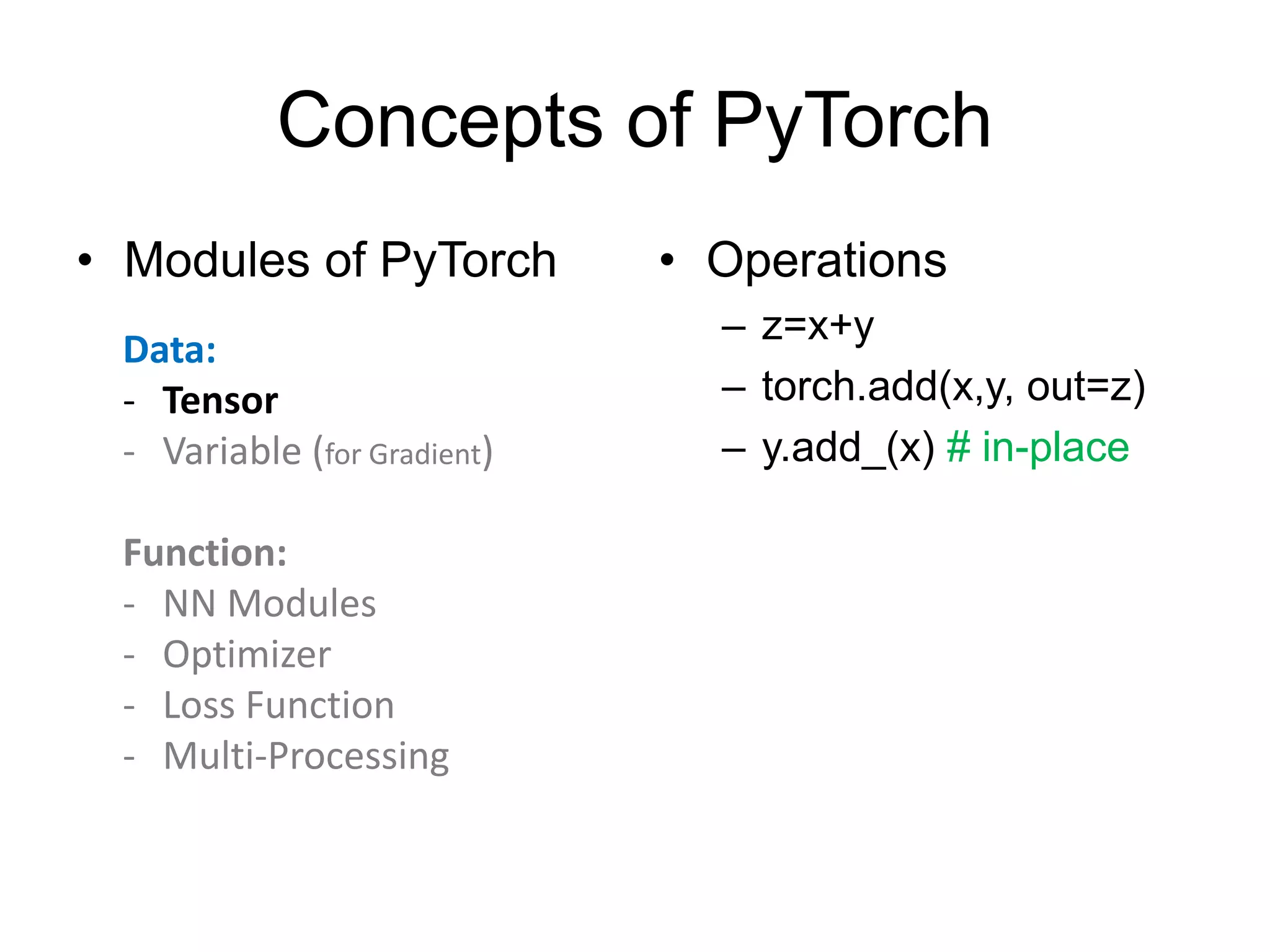
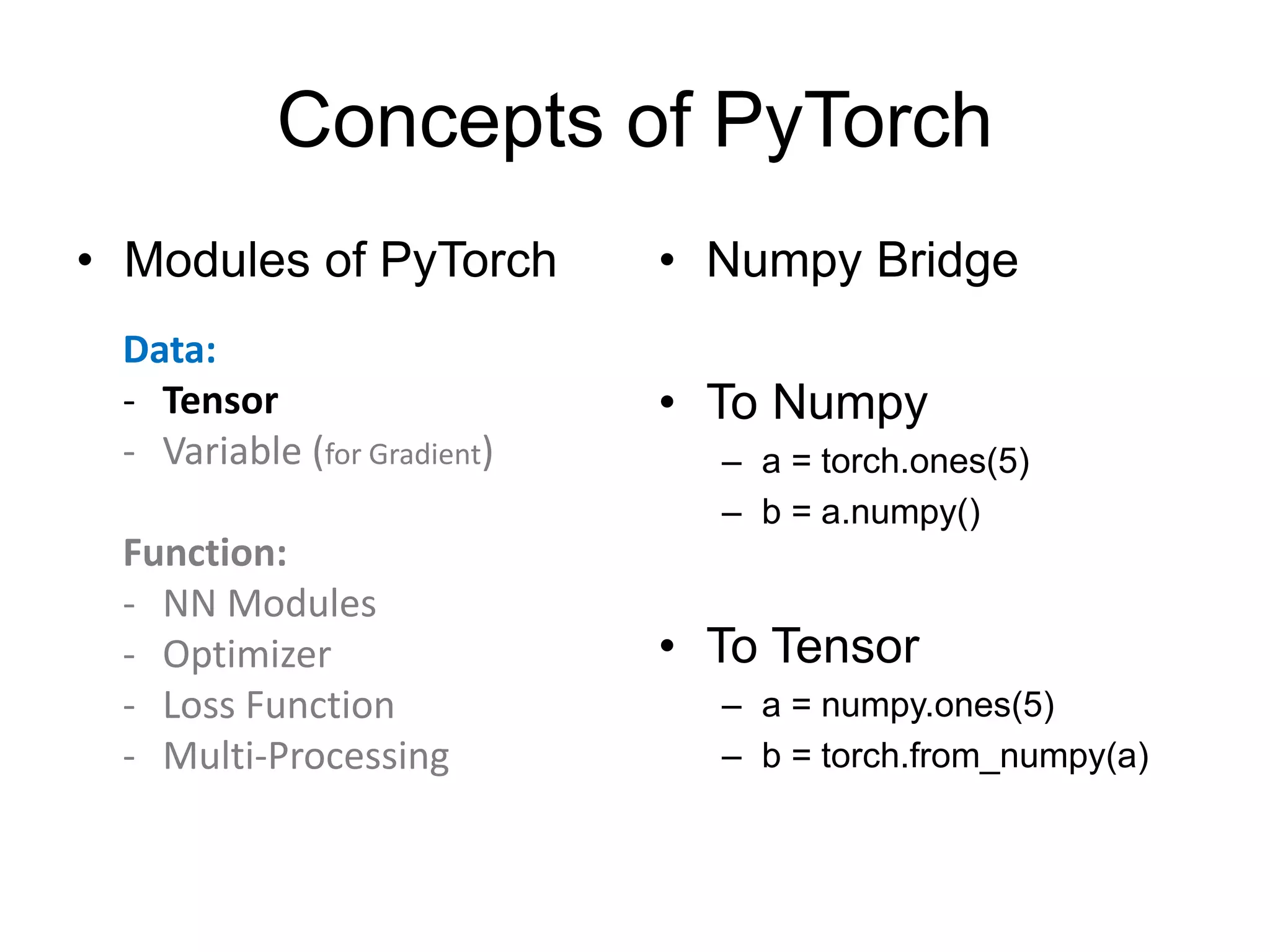
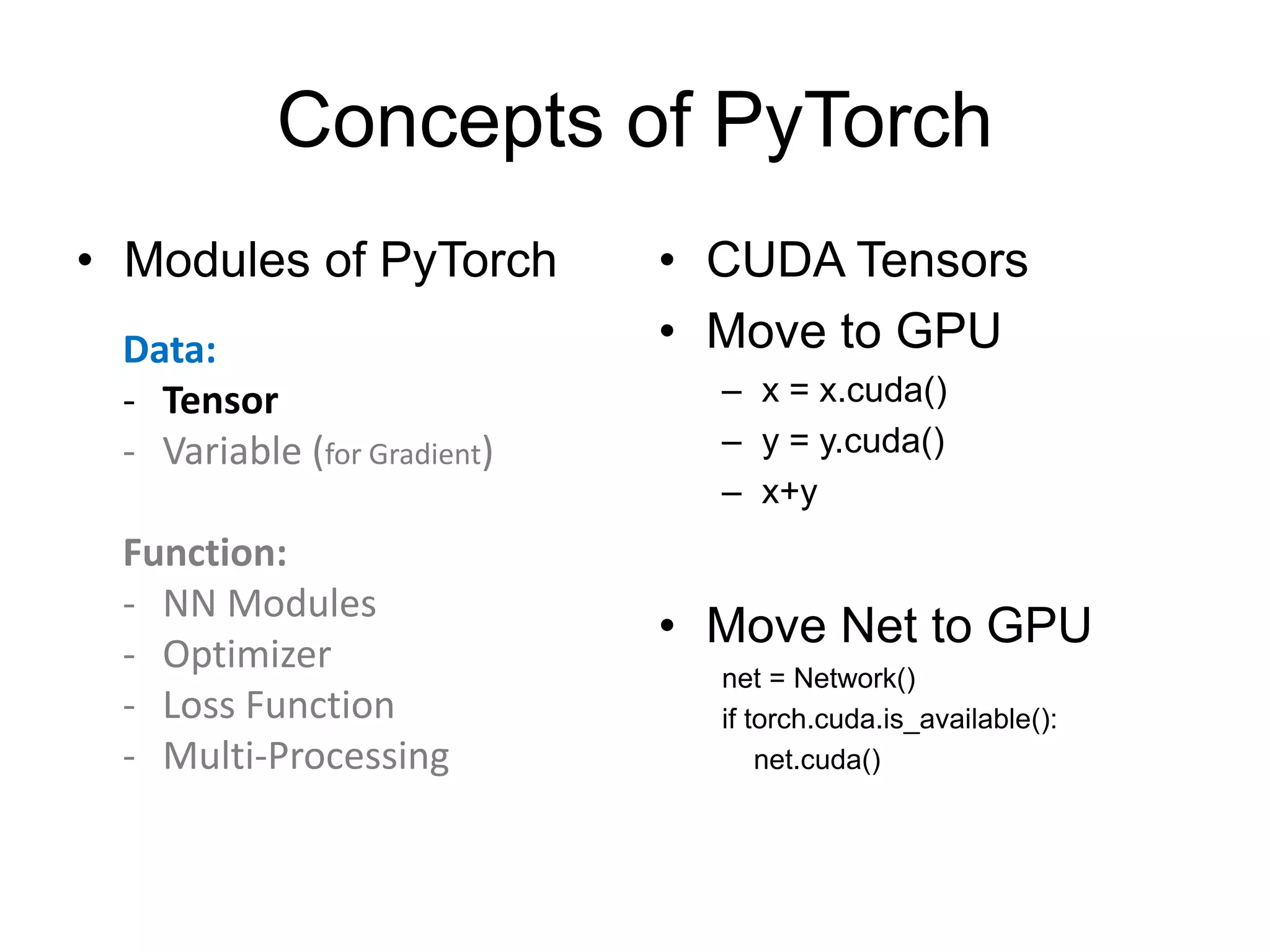
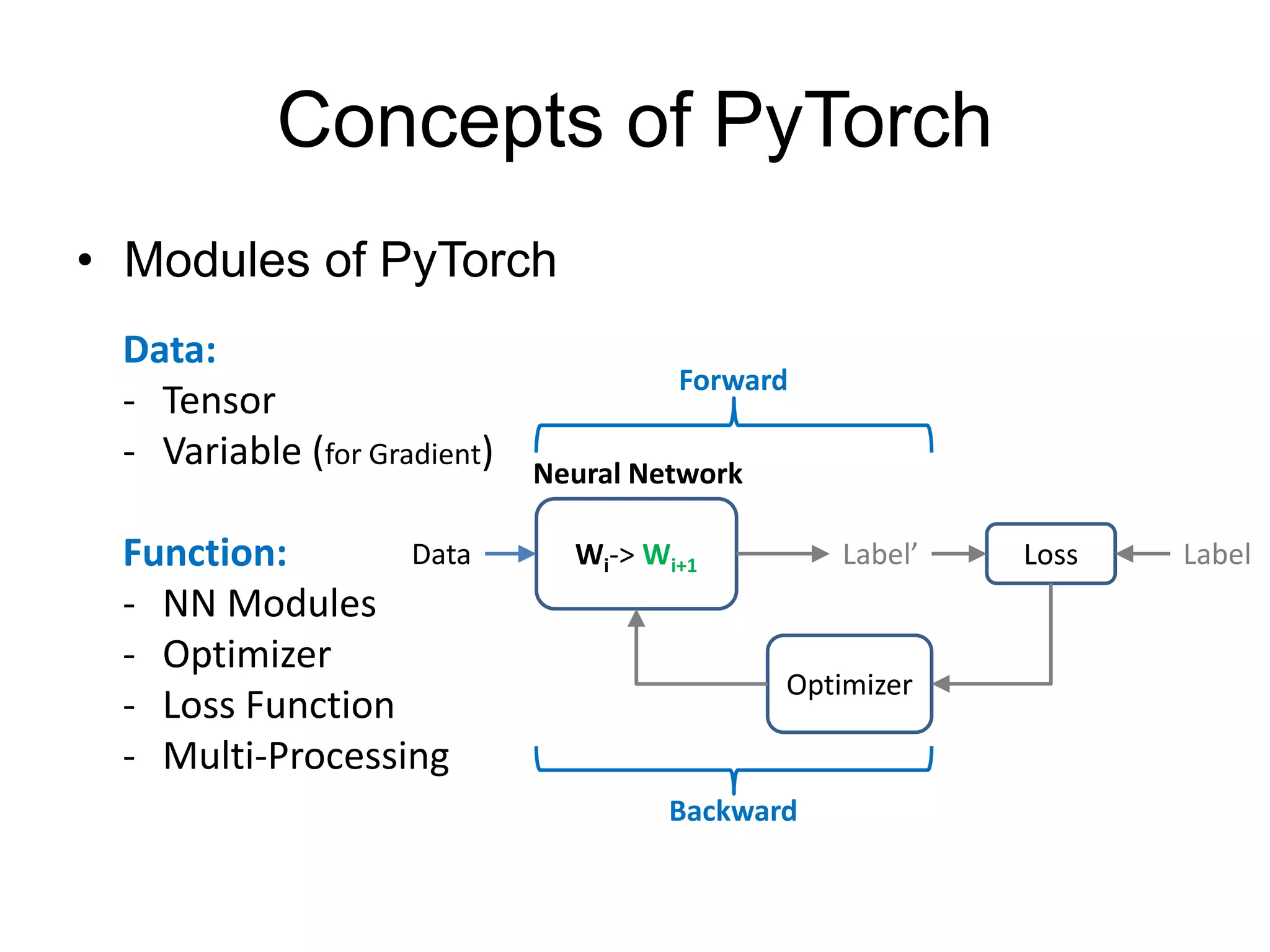
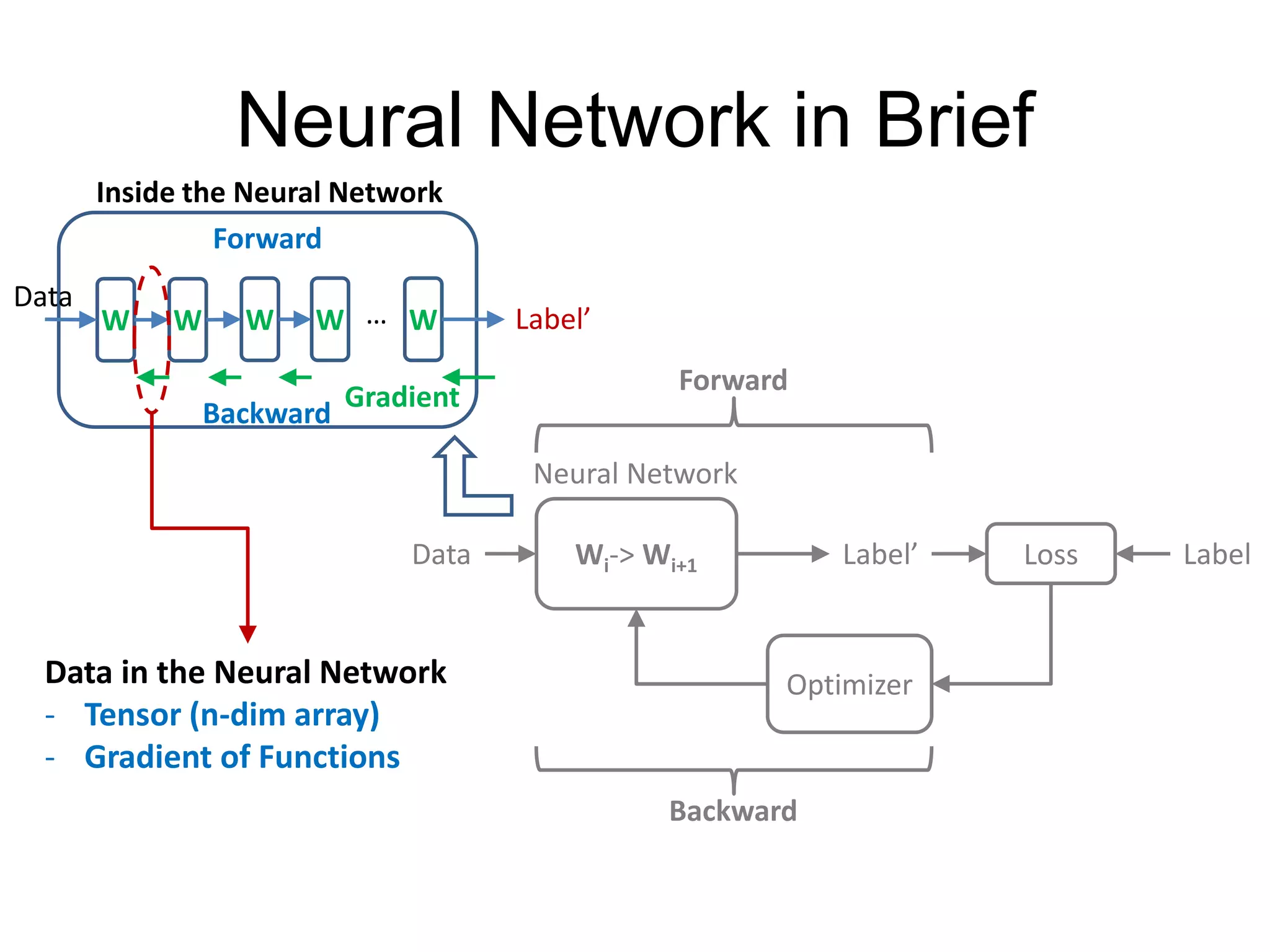
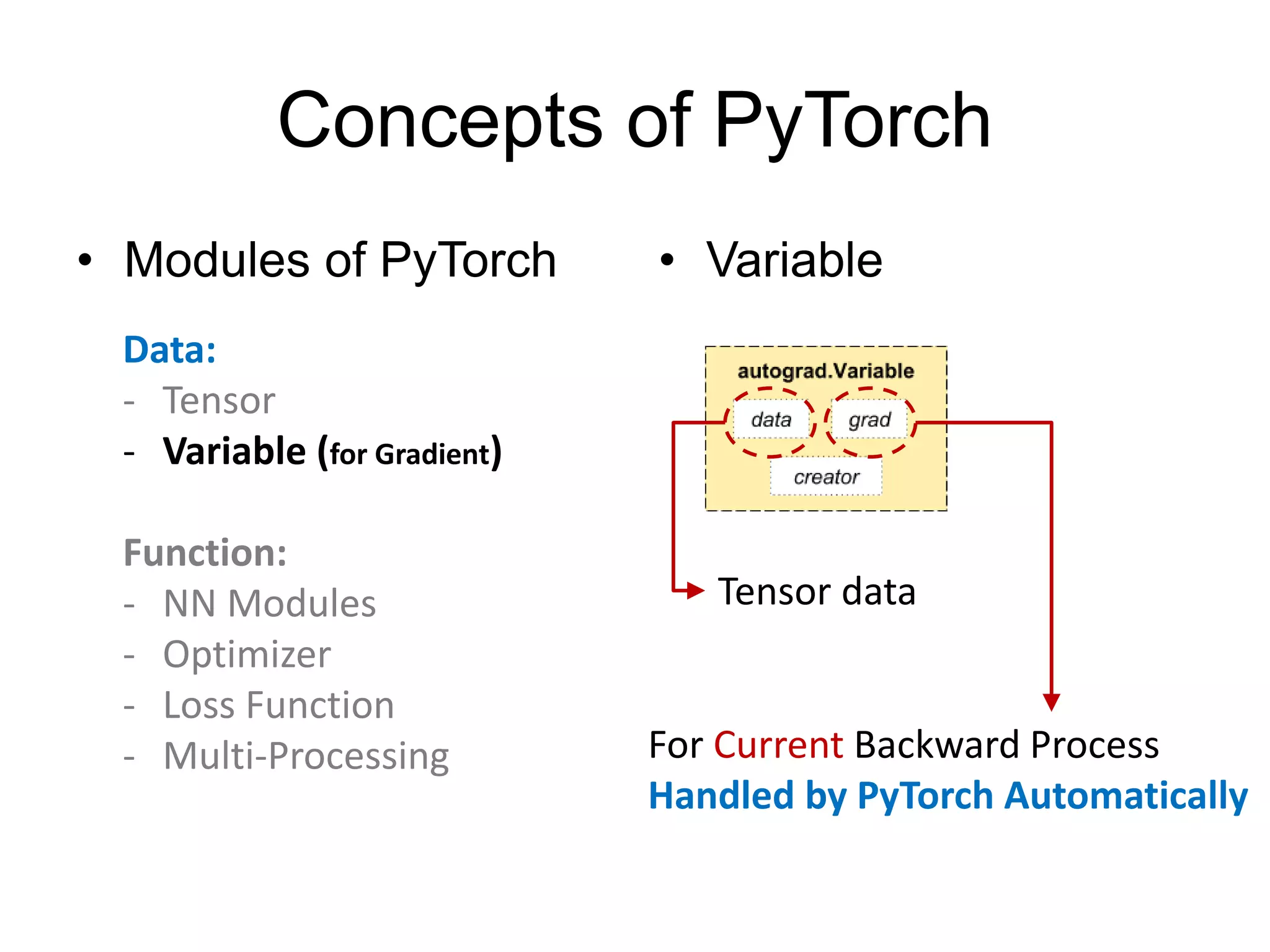
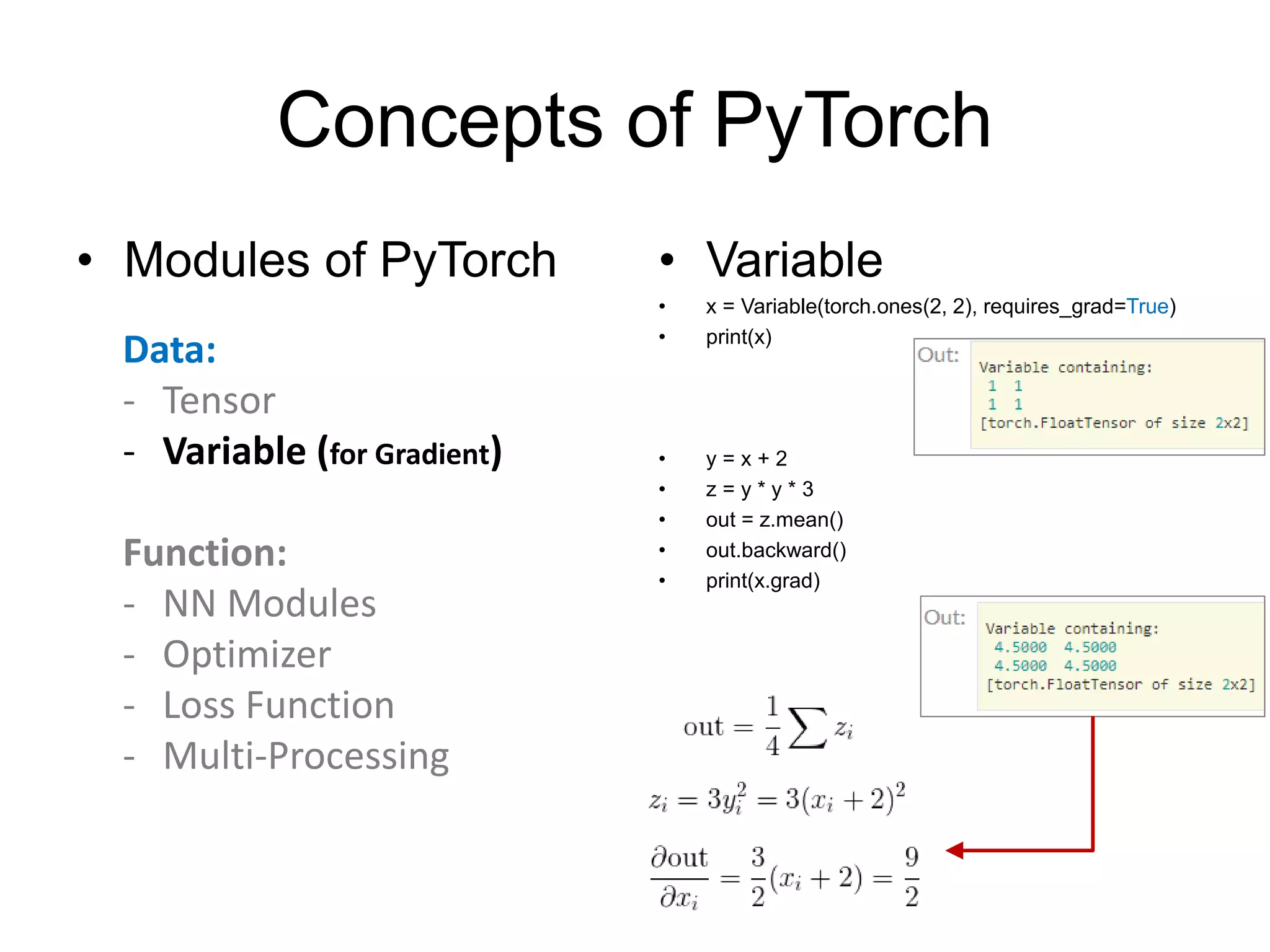
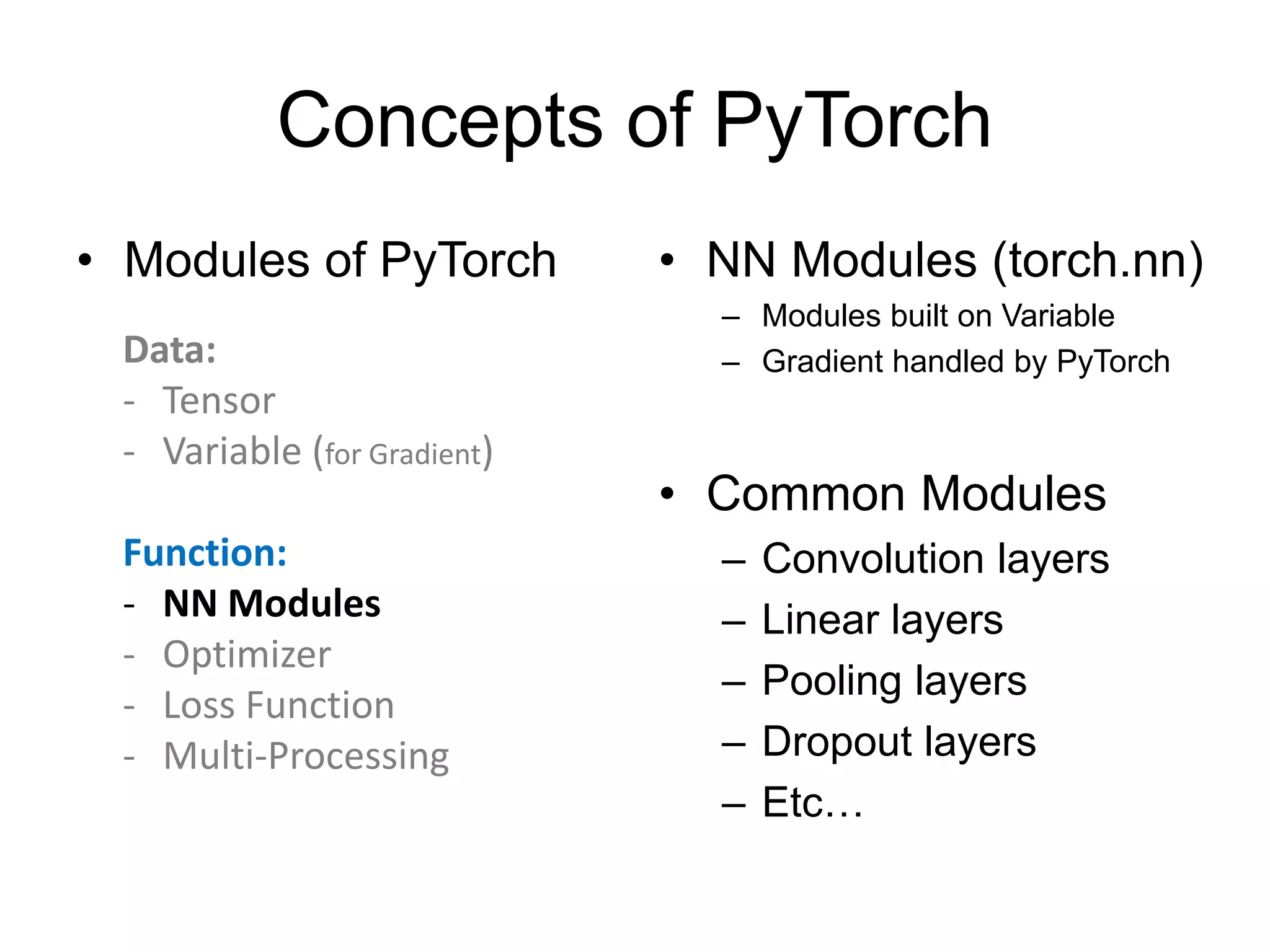
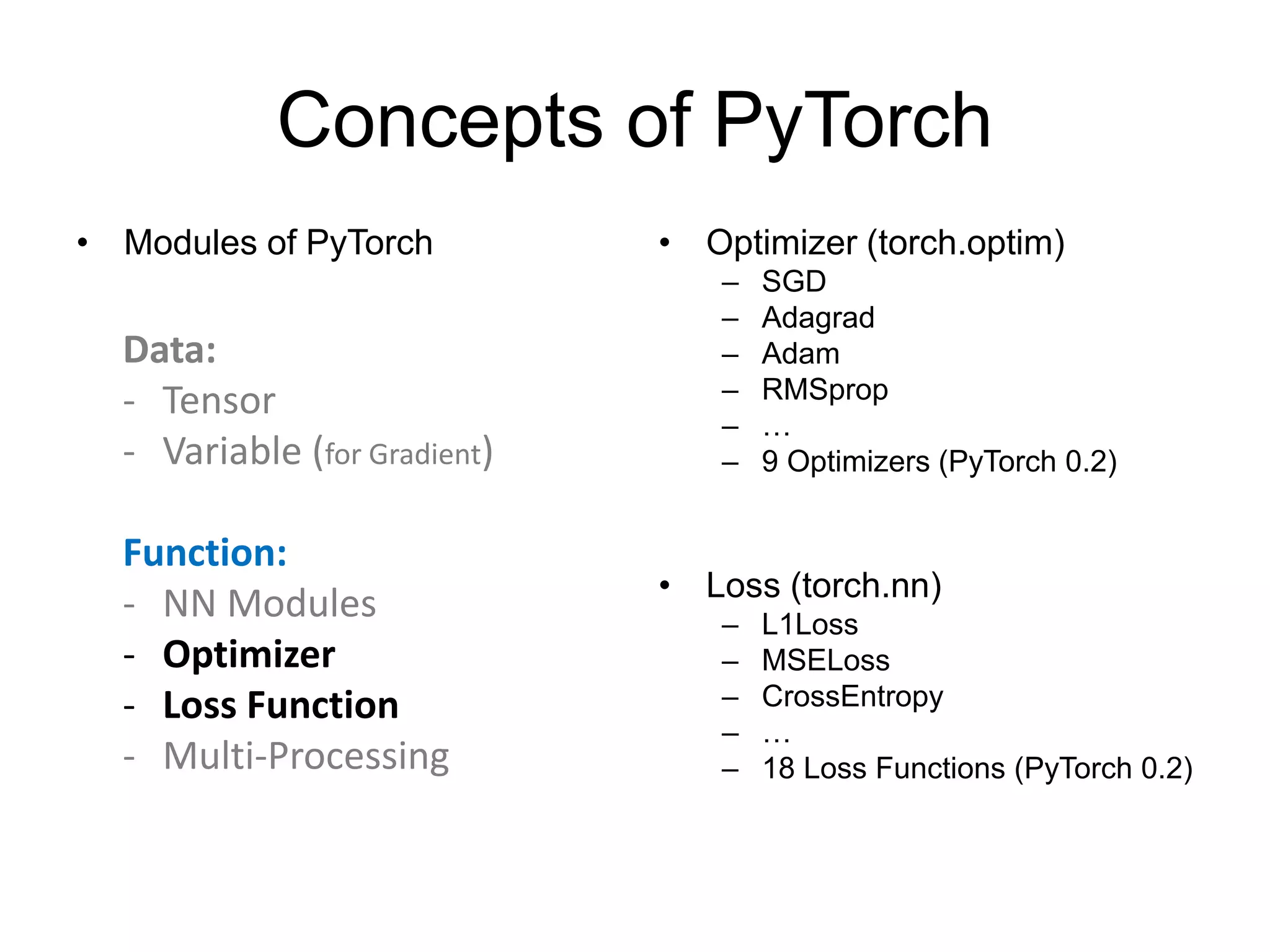
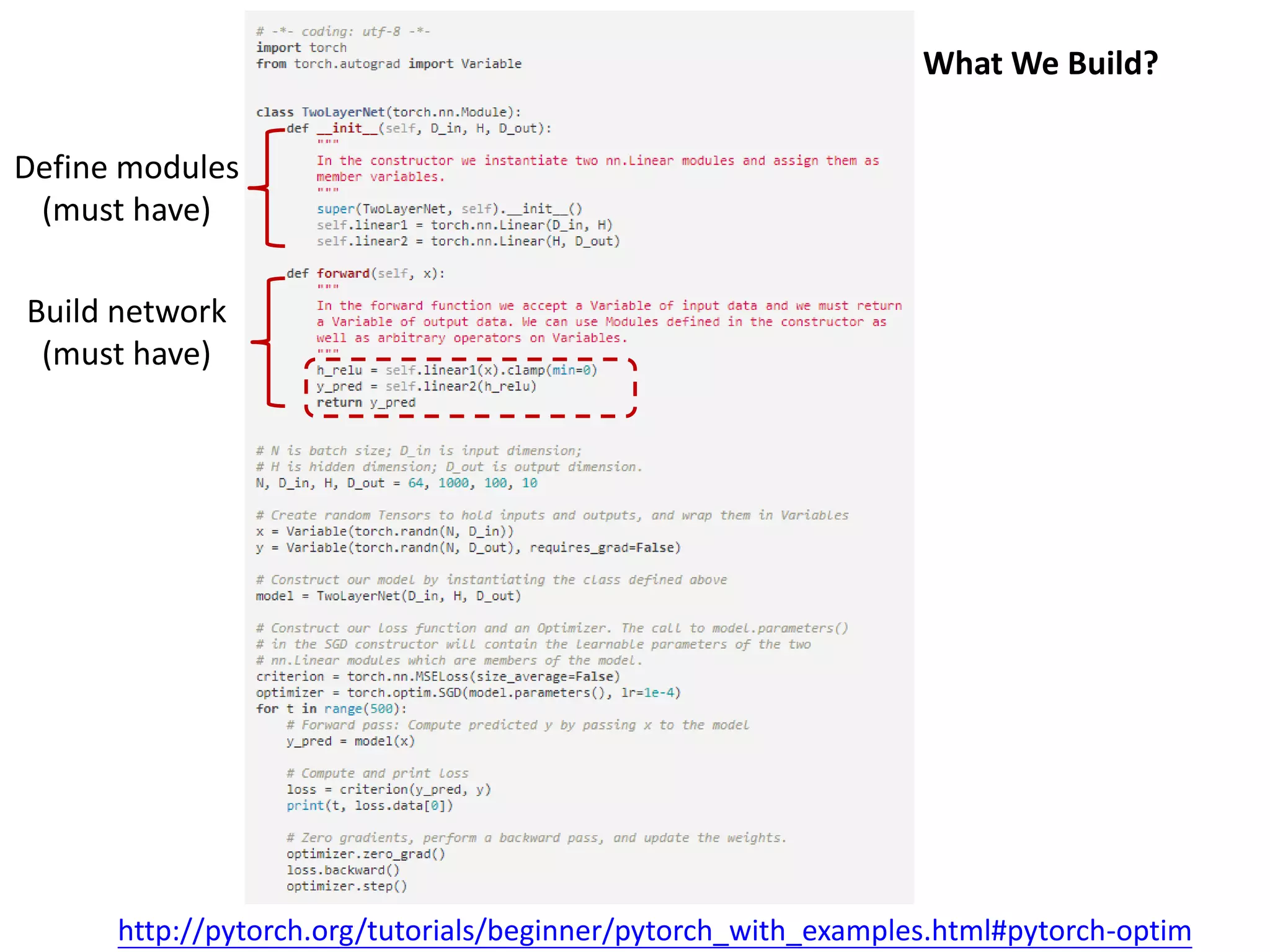
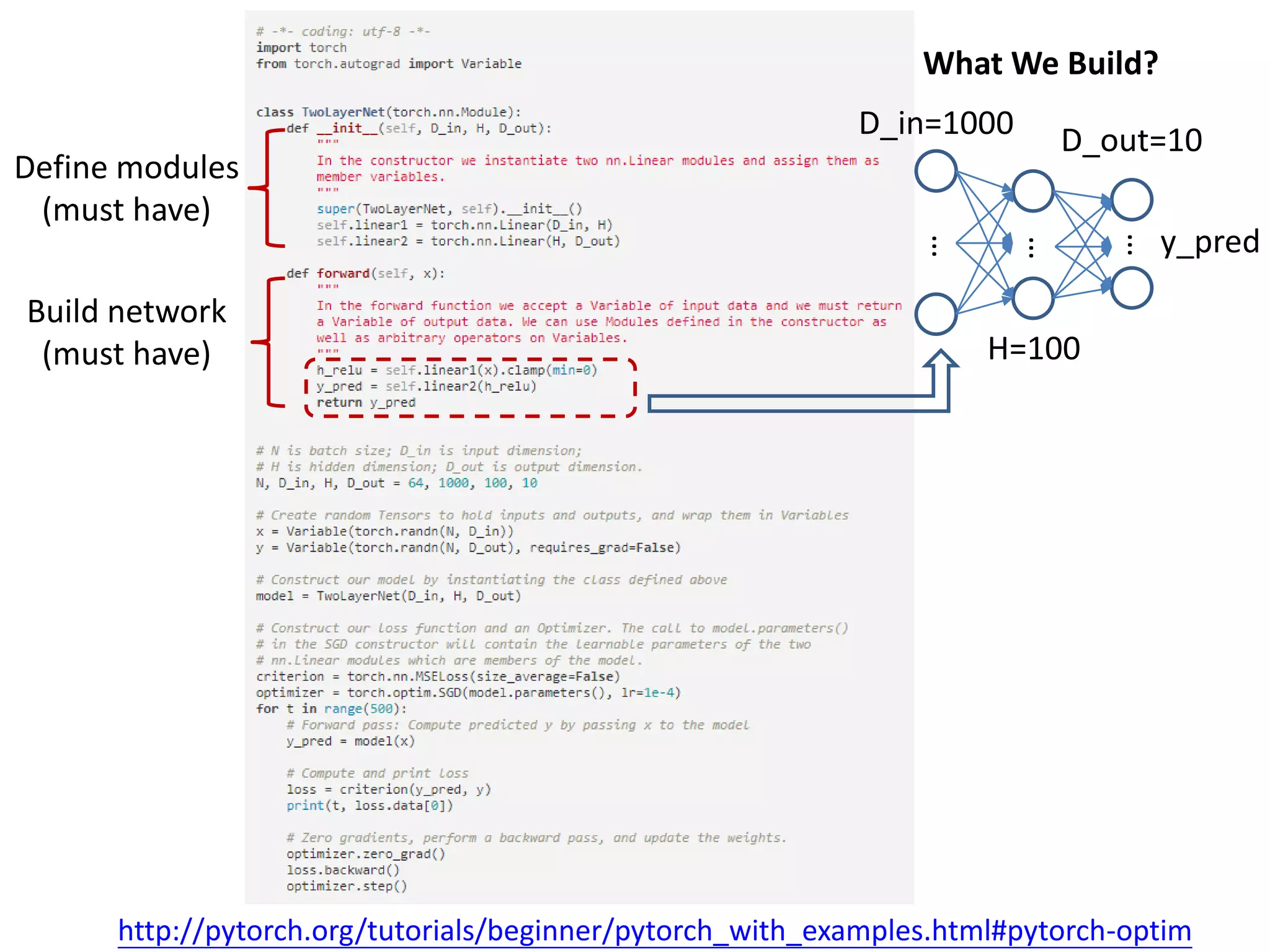
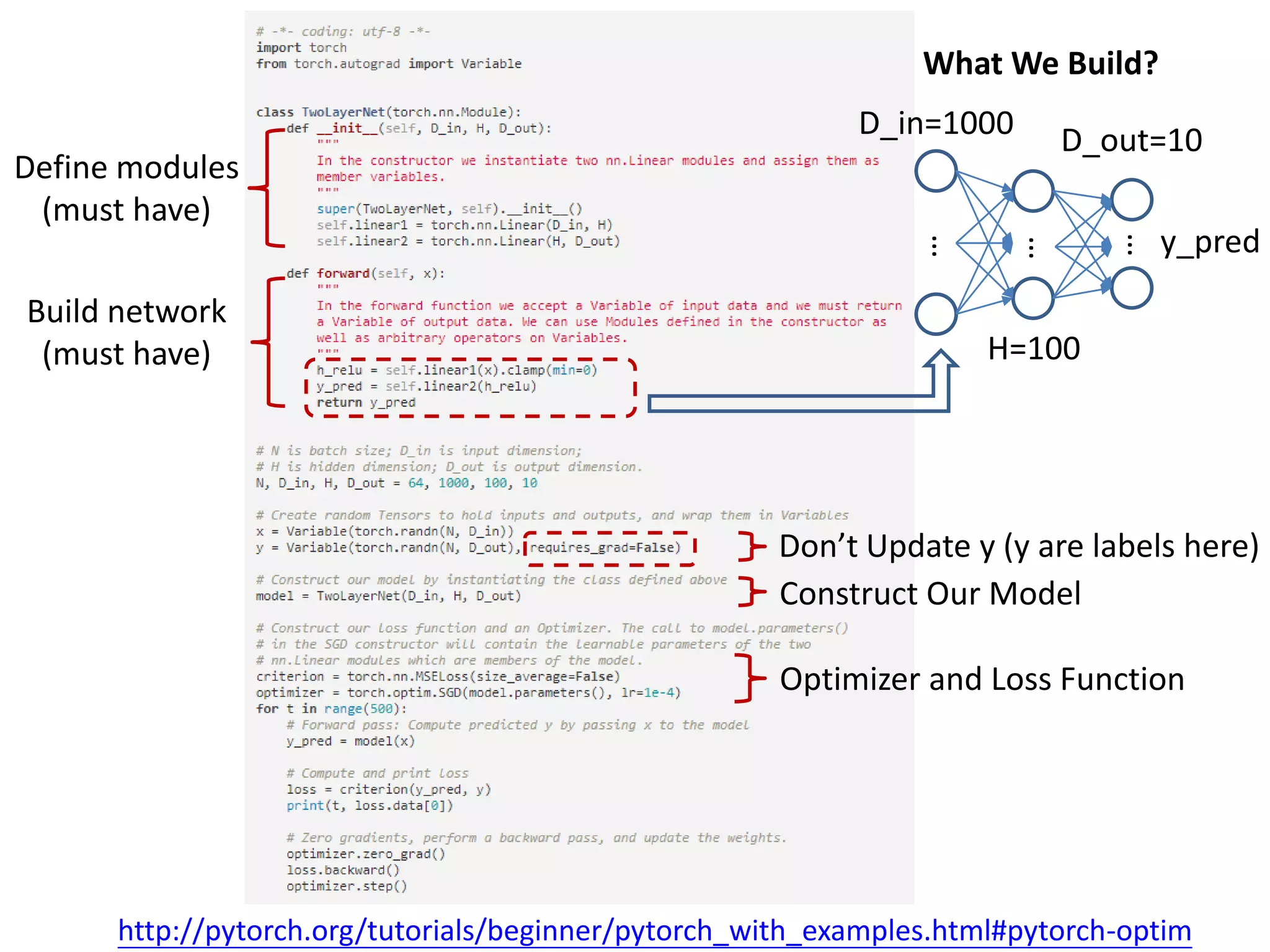
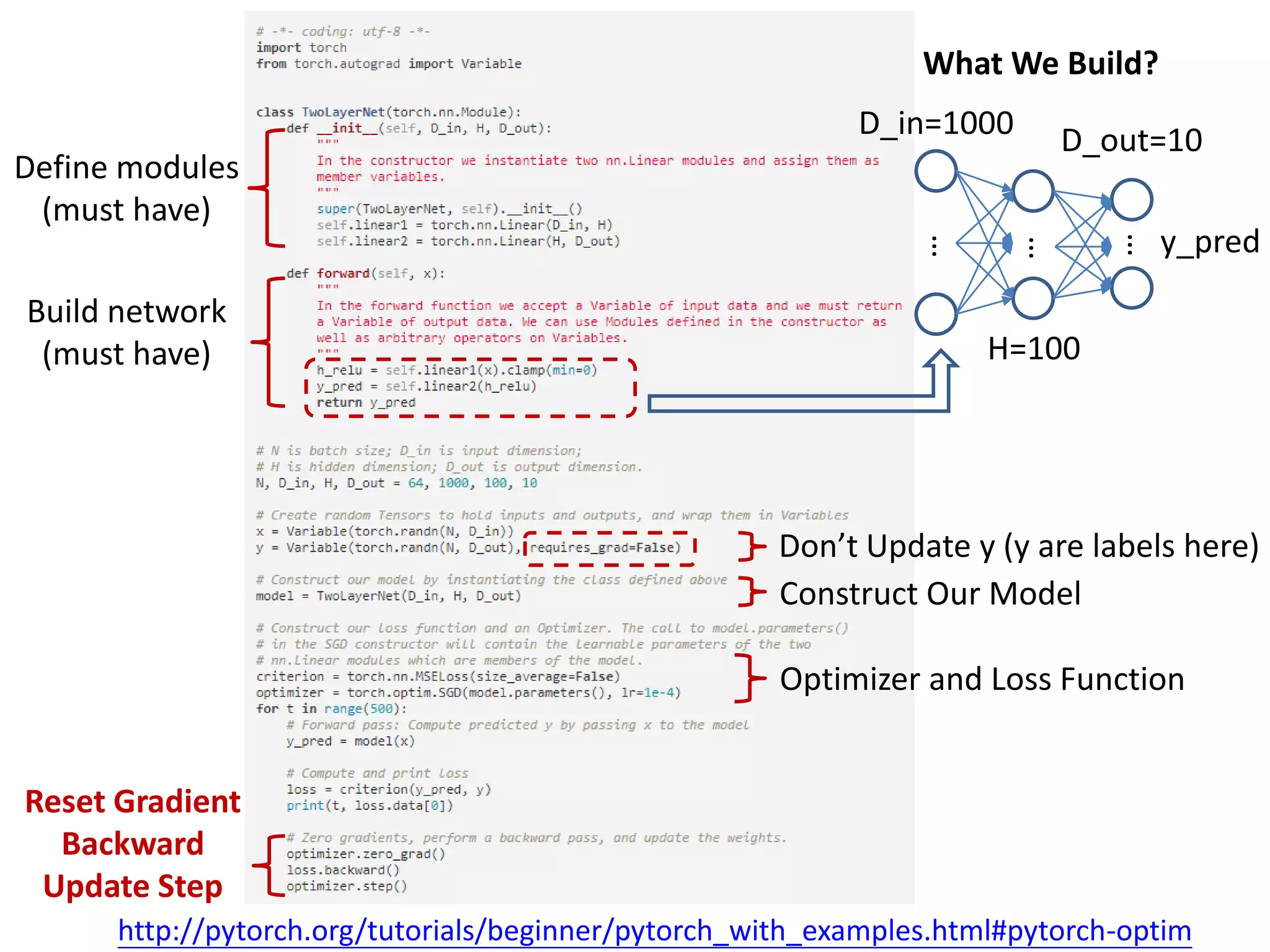
This document provides an overview and tutorial for PyTorch, a popular deep learning framework developed by Facebook. It discusses what PyTorch is, how to install it, its core packages and concepts like tensors, variables, neural network modules, and optimization. The tutorial also outlines how to define neural network modules in PyTorch, build a network, and describes common layer types like convolution and linear layers. It explains key PyTorch concepts such as defining modules, building networks, and how tensors and variables are used to represent data and enable automatic differentiation for training models.
![PyTorch Tutorial (Updated) -NTU Machine Learning Course- Lyman Lin 林裕訓 Nov. 03, 2017 lymanblue[at]gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-1-2048.jpg)


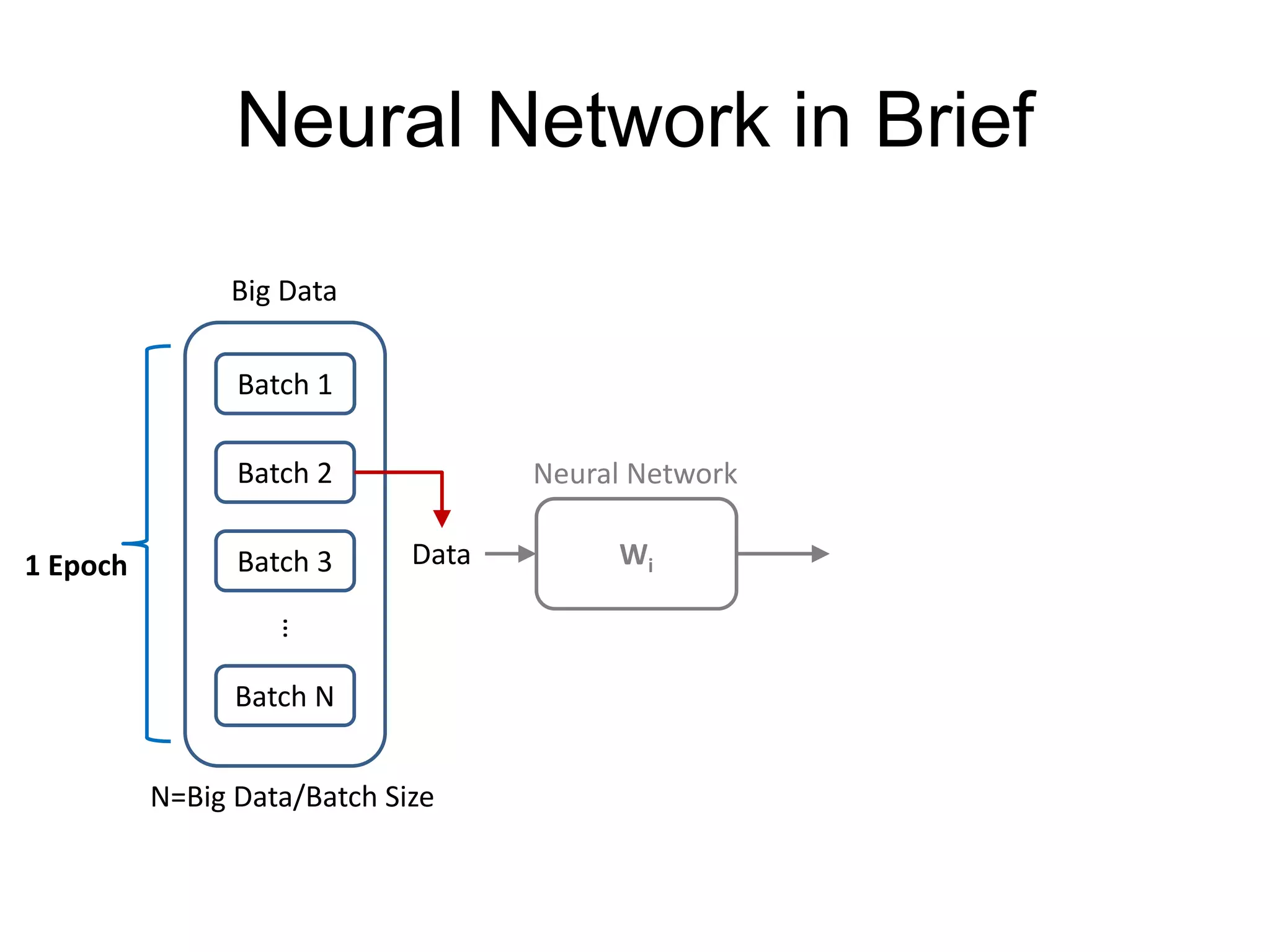
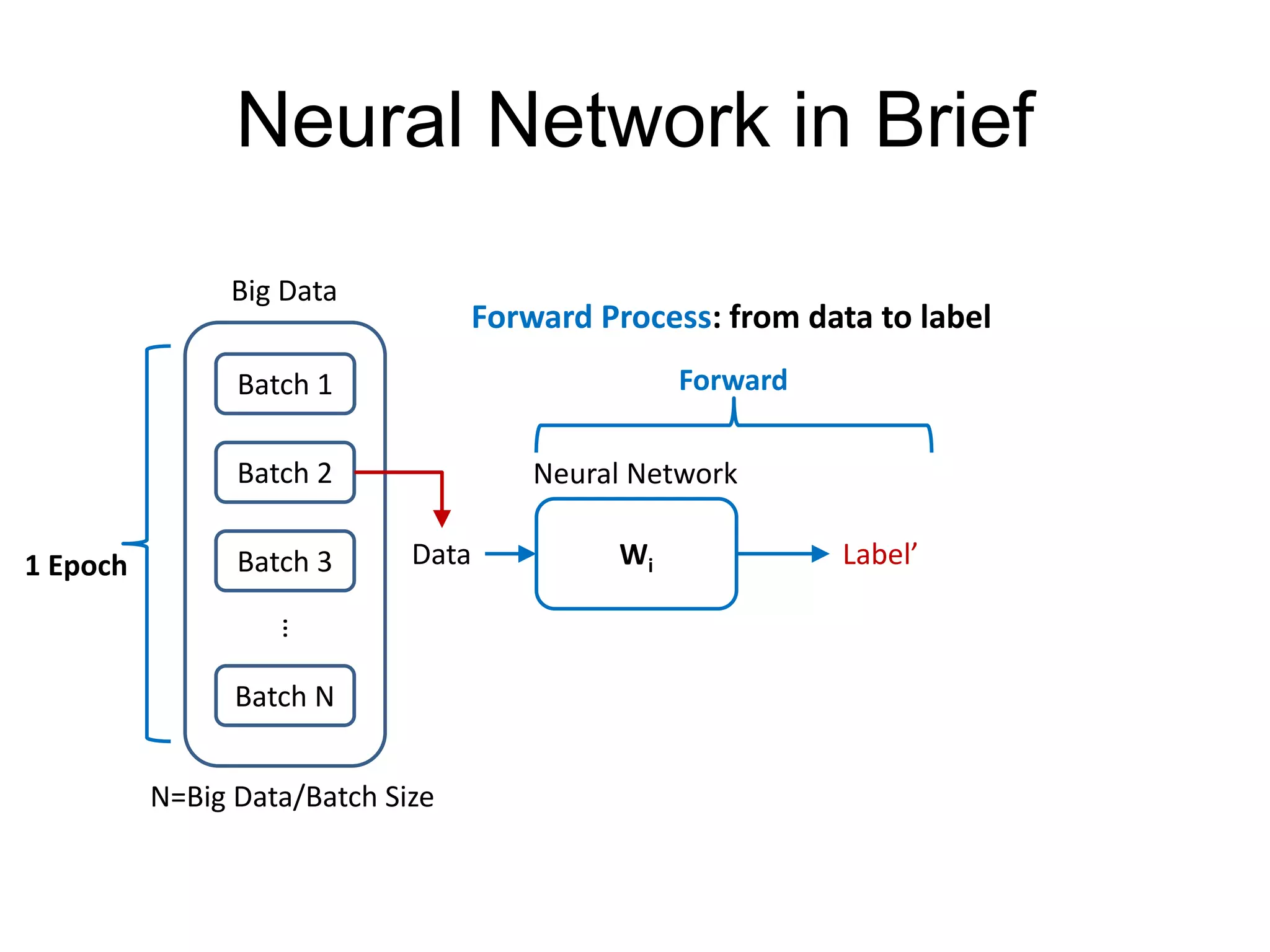
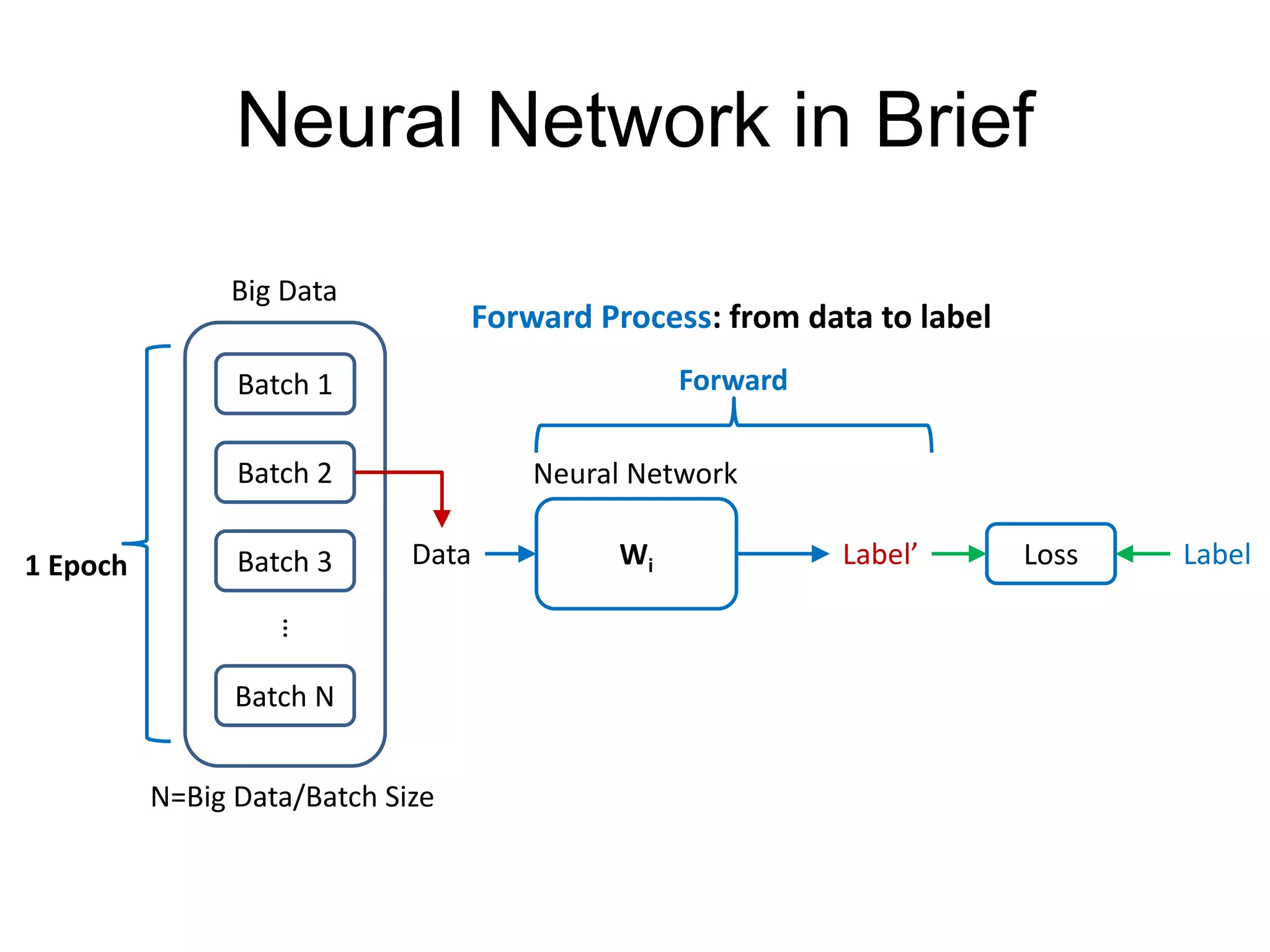
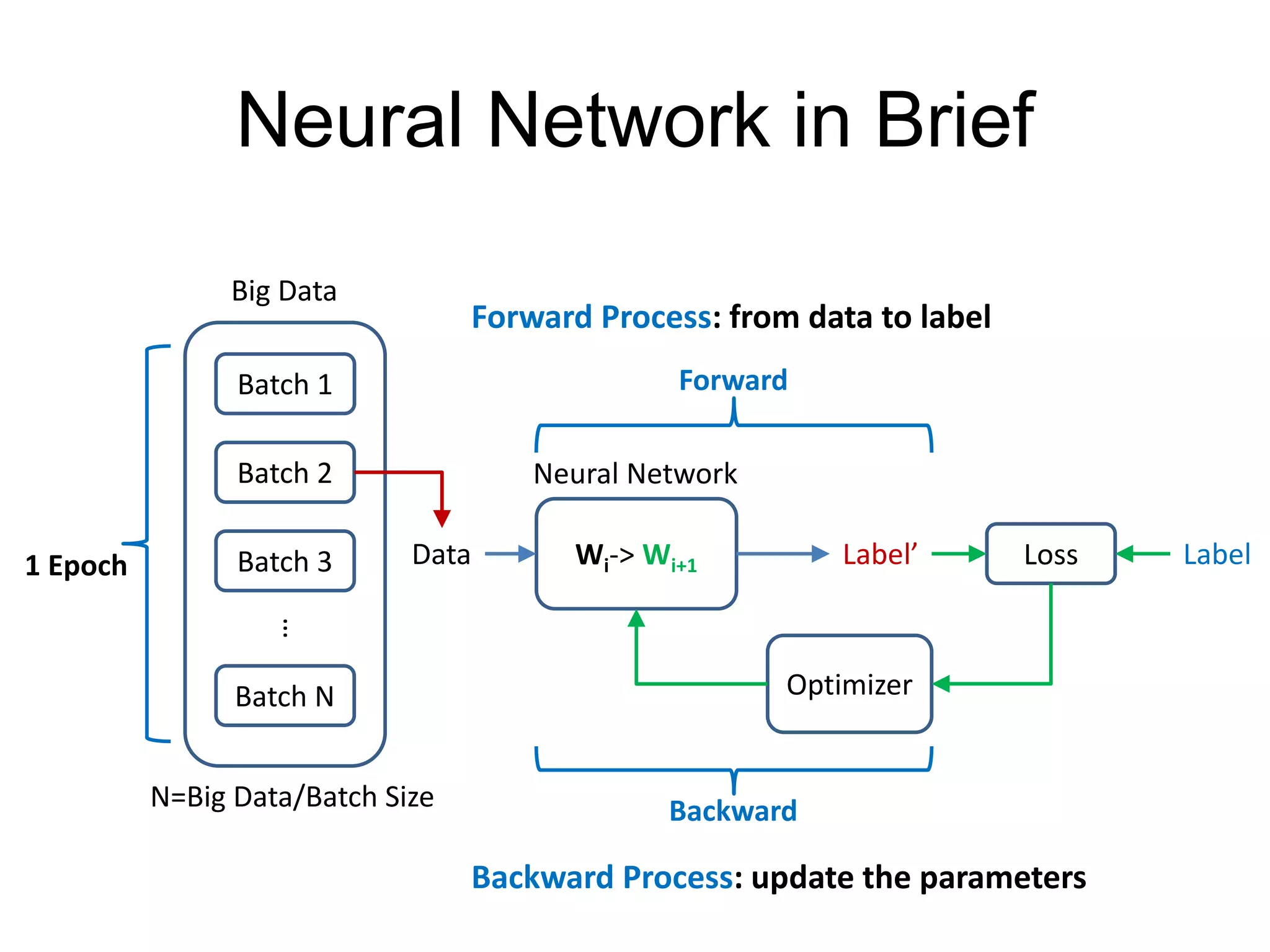
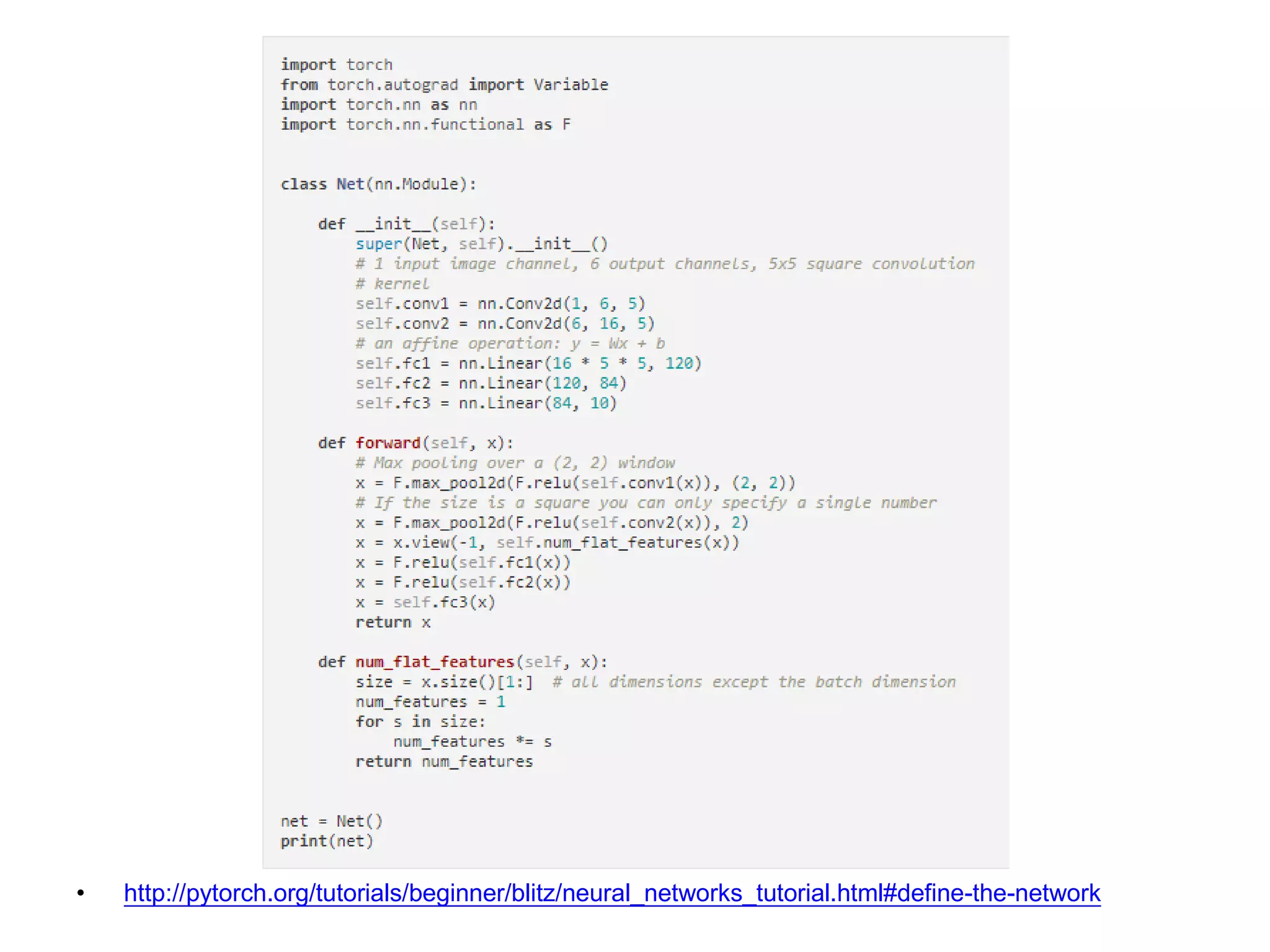

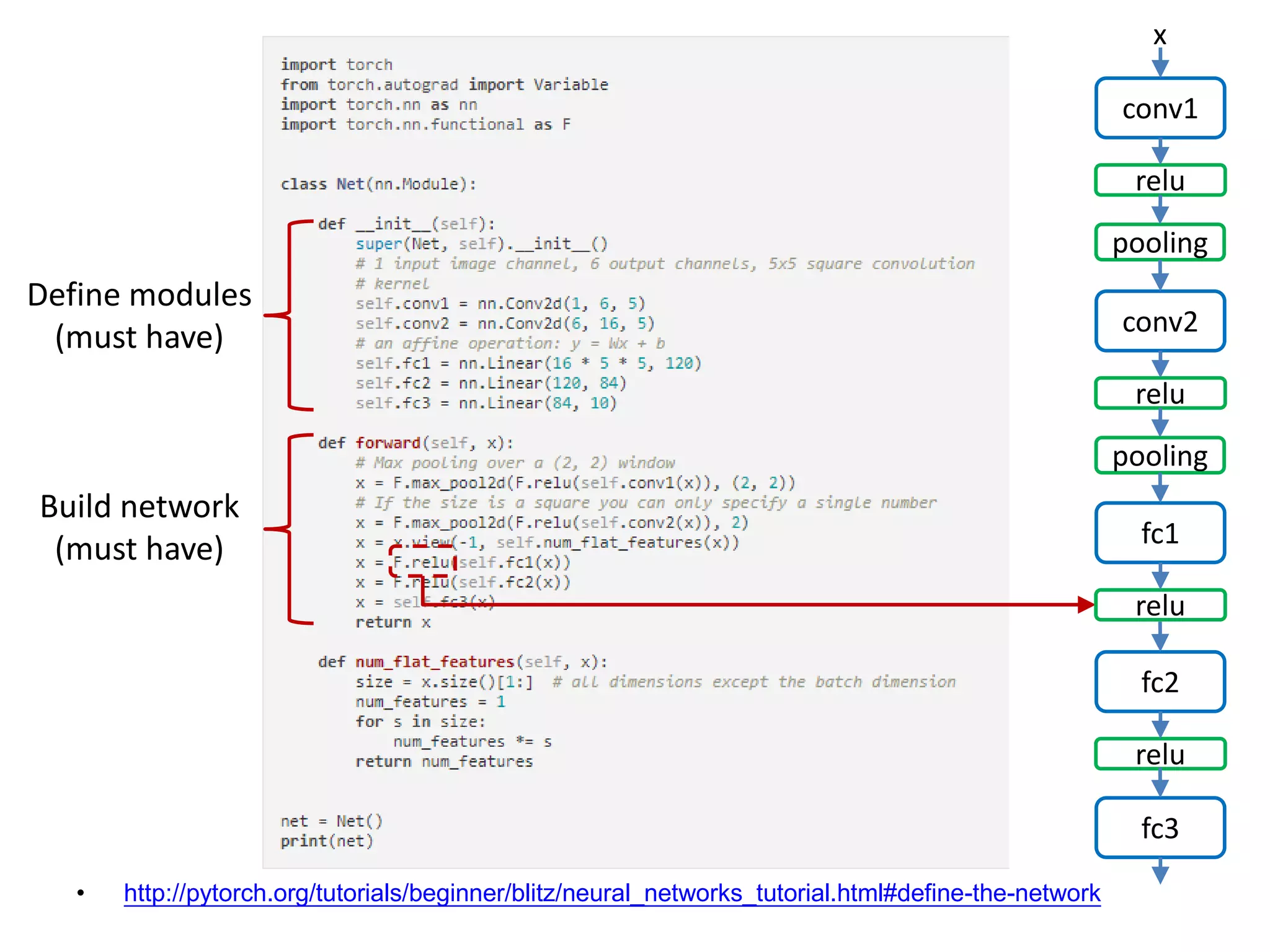
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network conv1 x relu pooling conv2 relu pooling fc1 relu fc2 relu fc3 Define modules (must have) Build network (must have) [Channel, H, W]: 1x32x32->6x28x28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-24-2048.jpg)
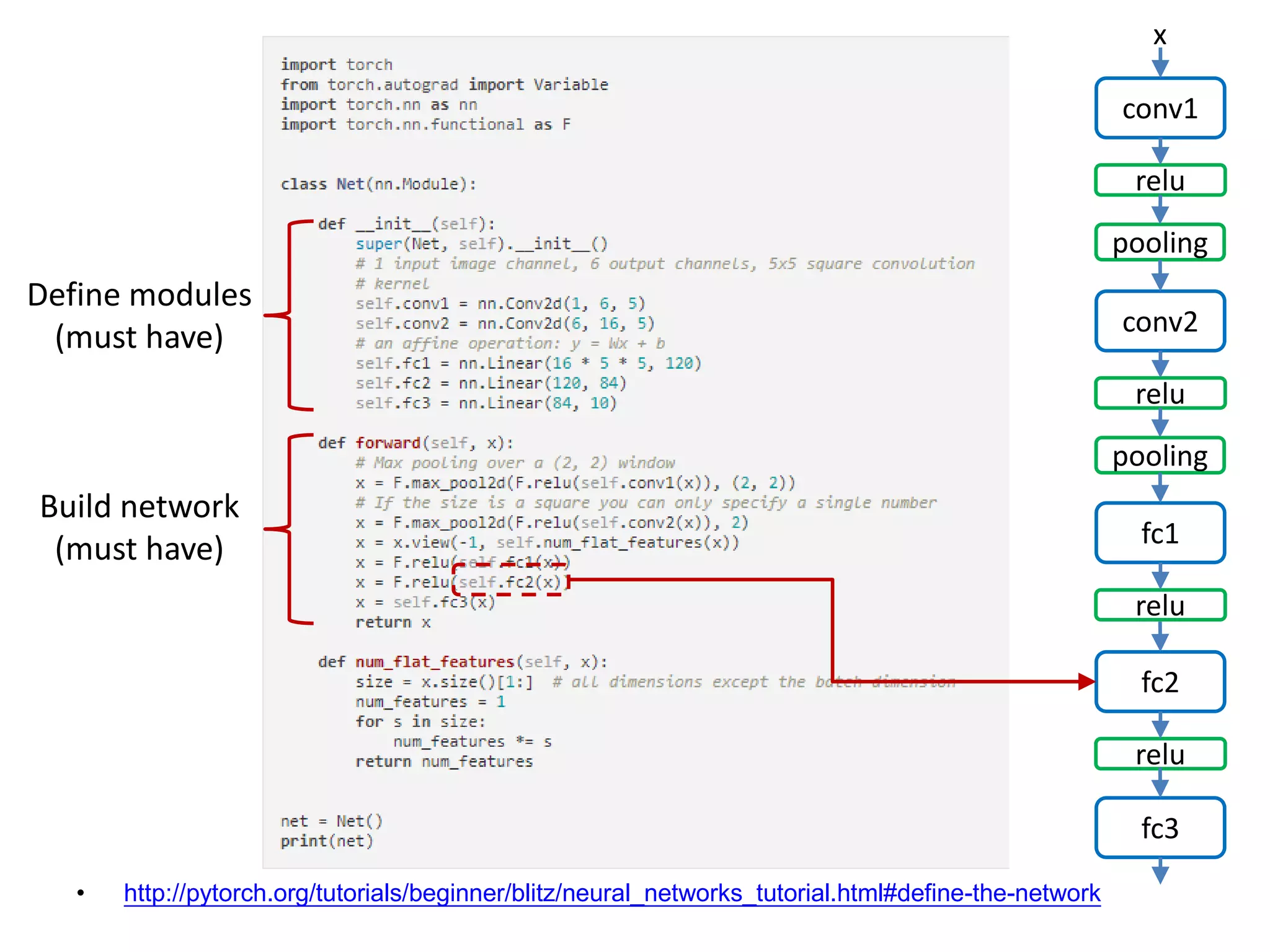
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network conv1 x relu pooling conv2 relu pooling fc1 relu fc2 relu fc3 Define modules (must have) Build network (must have) [Channel, H, W]: 6x28x28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-25-2048.jpg)
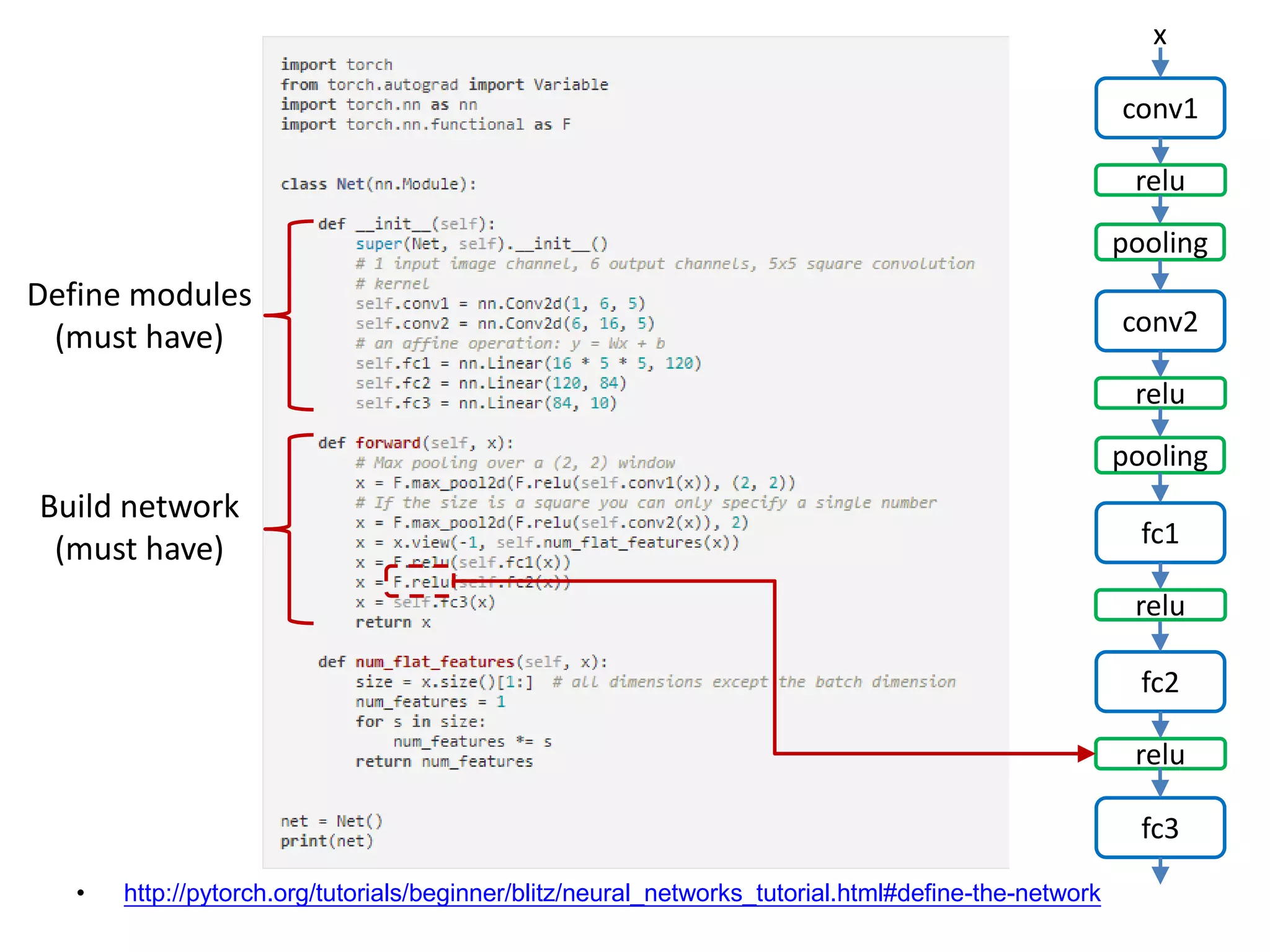
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network conv1 x relu pooling conv2 relu pooling fc1 relu fc2 relu fc3 Define modules (must have) Build network (must have) [Channel, H, W]: 6x28x28 -> 6x14x14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-26-2048.jpg)
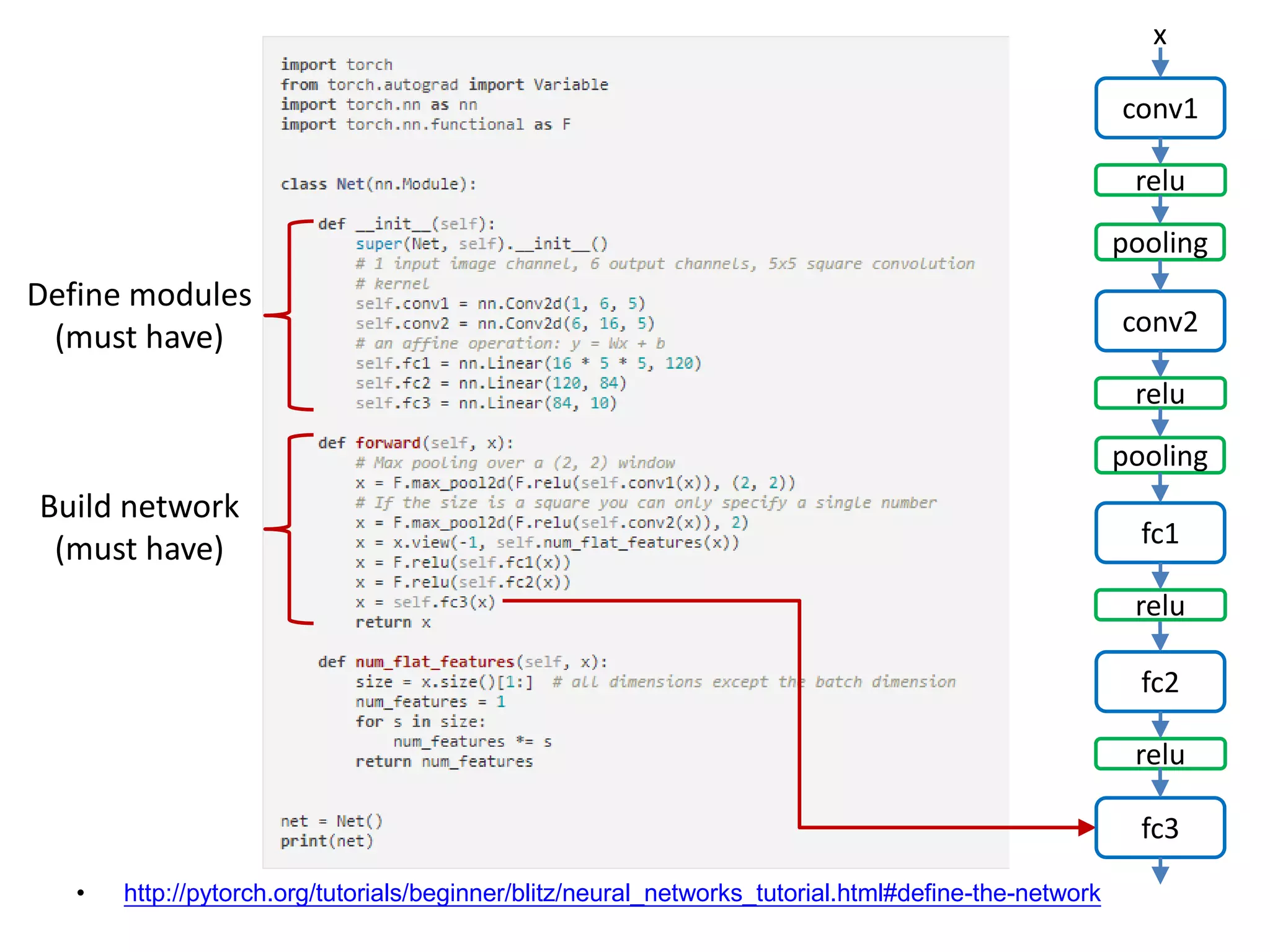
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network conv1 x relu pooling conv2 relu pooling fc1 relu fc2 relu fc3 Define modules (must have) Build network (must have) [Channel, H, W]: 6x14x14 -> 16x10x10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-27-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network conv1 x relu pooling conv2 relu pooling fc1 relu fc2 relu fc3 Define modules (must have) Build network (must have) [Channel, H, W]: 16x10x10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-28-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network conv1 x relu pooling conv2 relu pooling fc1 relu fc2 relu fc3 Define modules (must have) Build network (must have) [Channel, H, W]: 16x10x10 -> 16x5x5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-29-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network conv1 x relu pooling conv2 relu pooling fc1 relu fc2 relu fc3 Flatten the Tensor Define modules (must have) Build network (must have) 16x5x5 Tensor: [Batch N, Channel, H, W]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-30-2048.jpg)

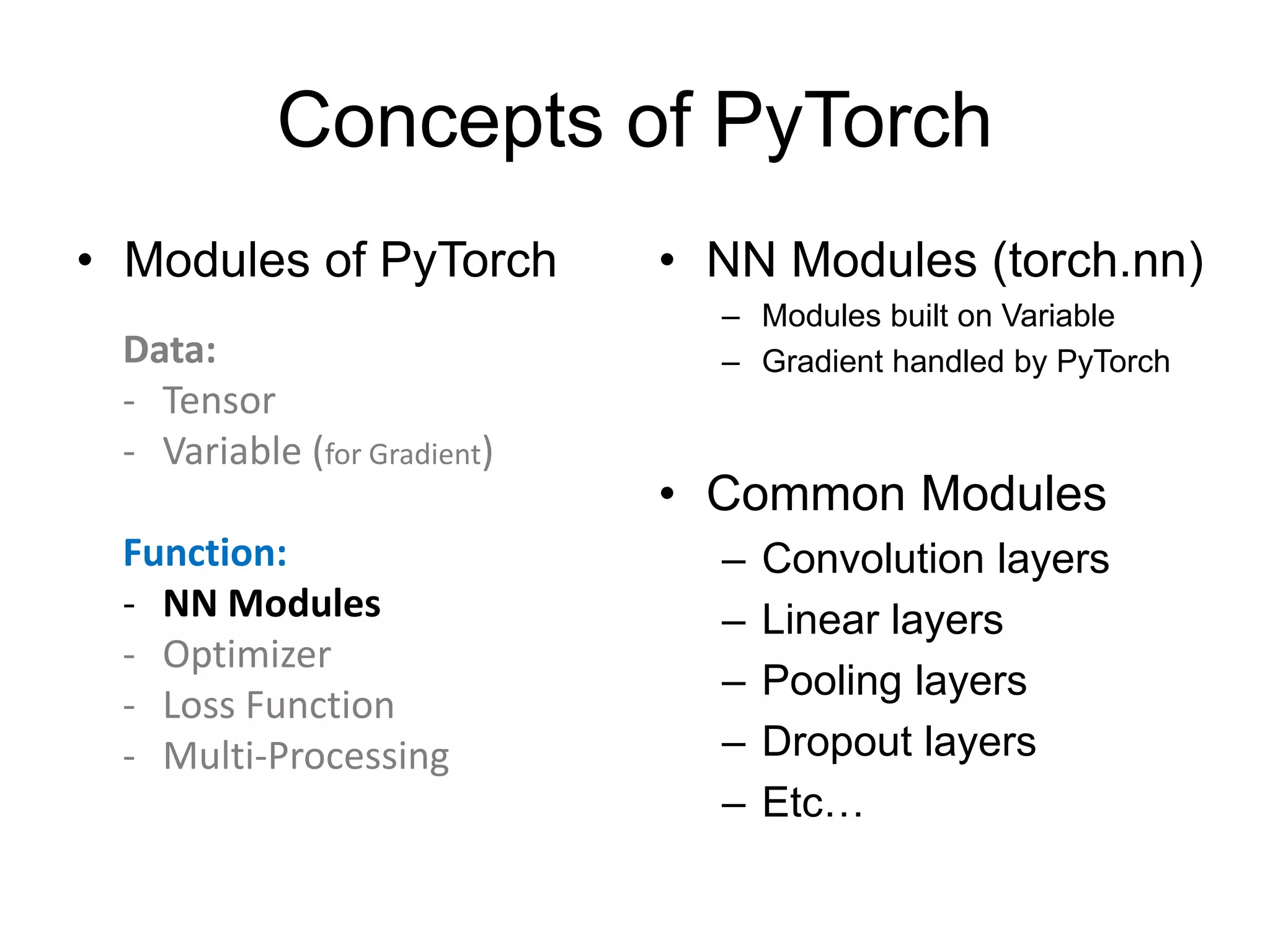
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D – Example: – torch.nn.conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, padding=1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-37-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d Win Cin *: convolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-38-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin * 1st kernel *: convolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-39-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin Hout Wout 1 * 1st kernel = *: convolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-40-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin Hout Wout 1 * 1st kernel = *: convolution k=3d=1 s=1, moving step size p=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-41-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin Hout Wout 1 * 1st kernel = *: convolution k=3d=1 p=1 p=1 s=1, moving step size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-42-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin Hout Wout 1 * 1st kernel = *: convolution k=3d=1 p=1 k=3 p=1 s=1, moving step size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-43-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin Hout Wout 1 * 1st kernel = *: convolution k=3d=1 p=1 k=3 s=1 p=1 s=1, moving step size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-44-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin Hout Wout 1 * 1st kernel Cout-th kernel k k Cin Hout Wout 1 * = = *: convolution … …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-45-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin Hout Wout 1 * 1st kernel Cout-th kernel k k Cin Hout Wout 1 * = = Hout Wout Cout *: convolution … …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-46-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules • Convolution Layer – N-th Batch (N), Channel (C) – torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D – torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D – torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D Hin Input for Conv2d k k Win Cin Cin * 1st kernel Cout-th kernel k k Cin * *: convolution … # of parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-47-2048.jpg)
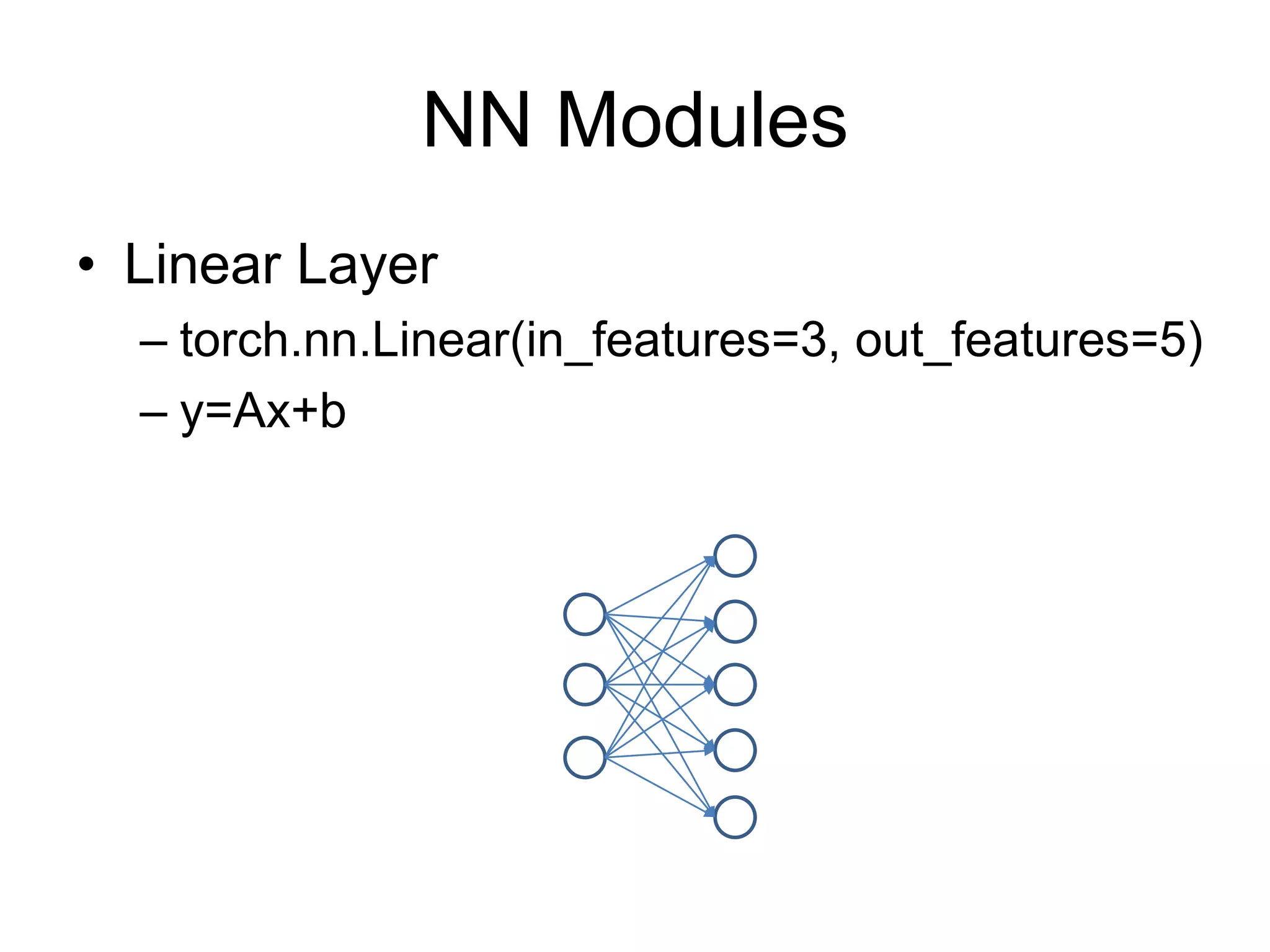
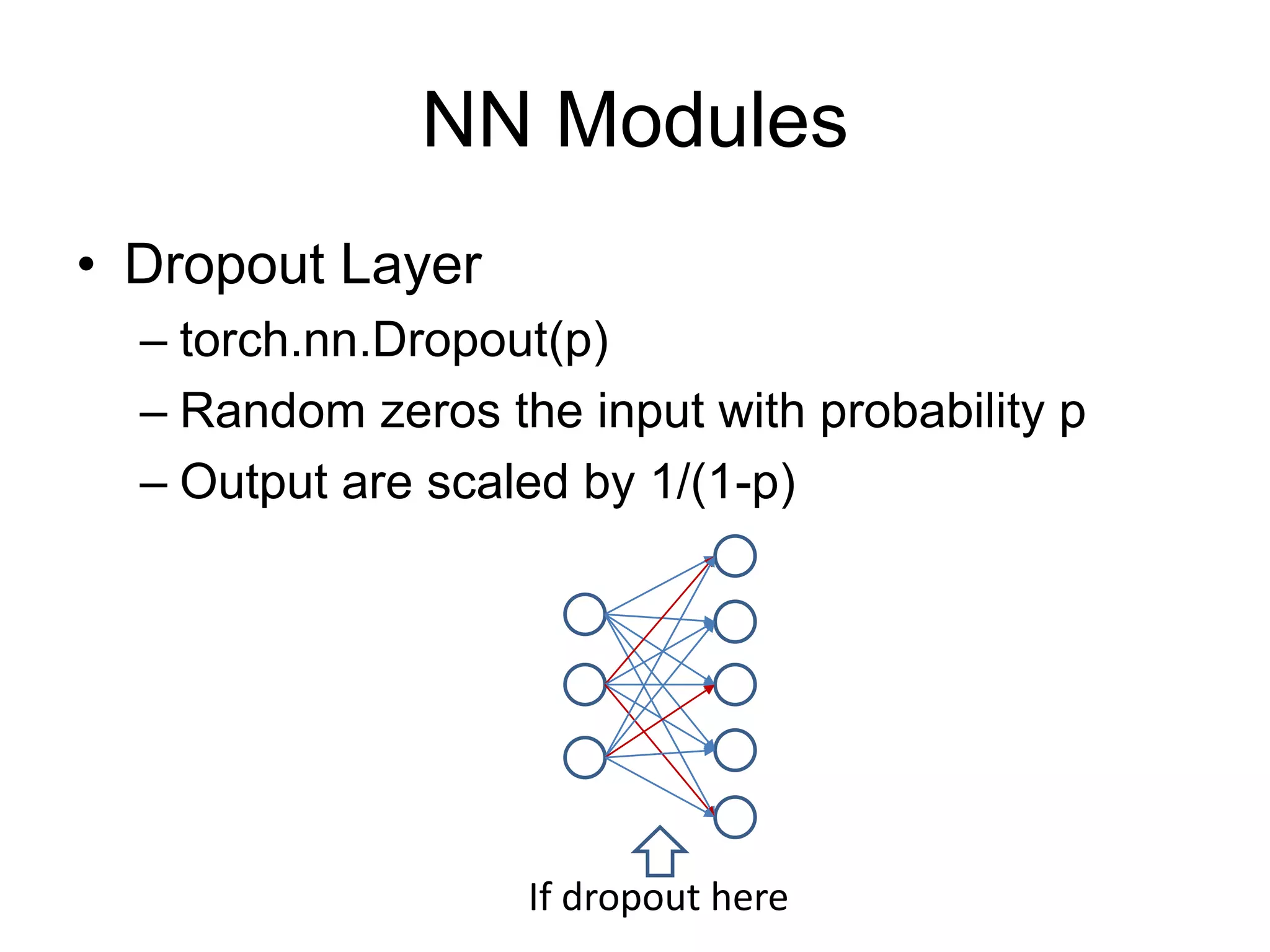
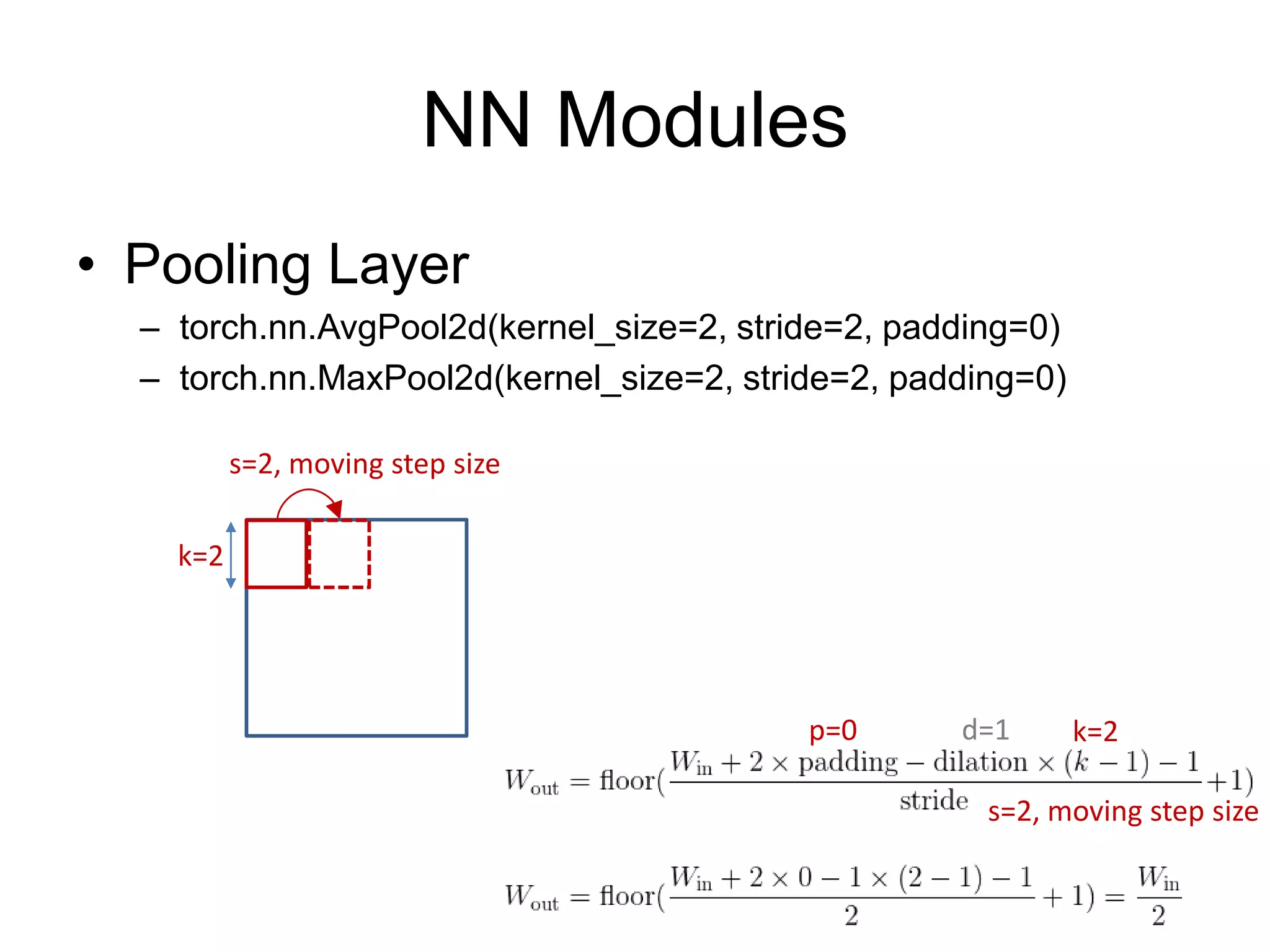
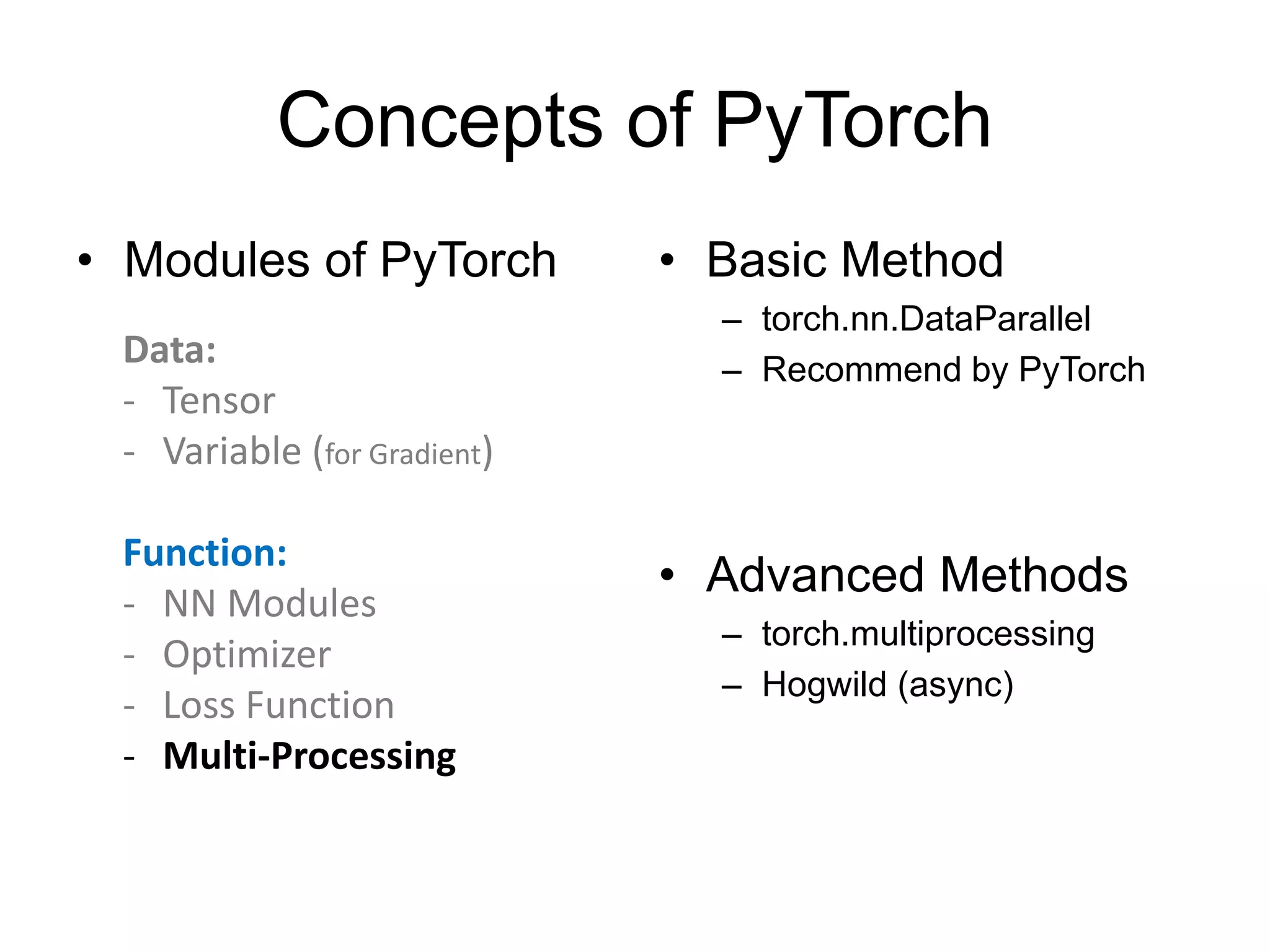
![Multi-GPU Processing • torch.nn.DataParallel – gpu_id = '6,7' – os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = gpu_id – net = torch.nn.DataParallel(model, device_ids=[0, 1]) – output = net(input_var) • Important Notes: – Device_ids must start from 0 – (batch_size/GPU_size) must be integer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171103060015/75/Update-PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-58-2048.jpg)