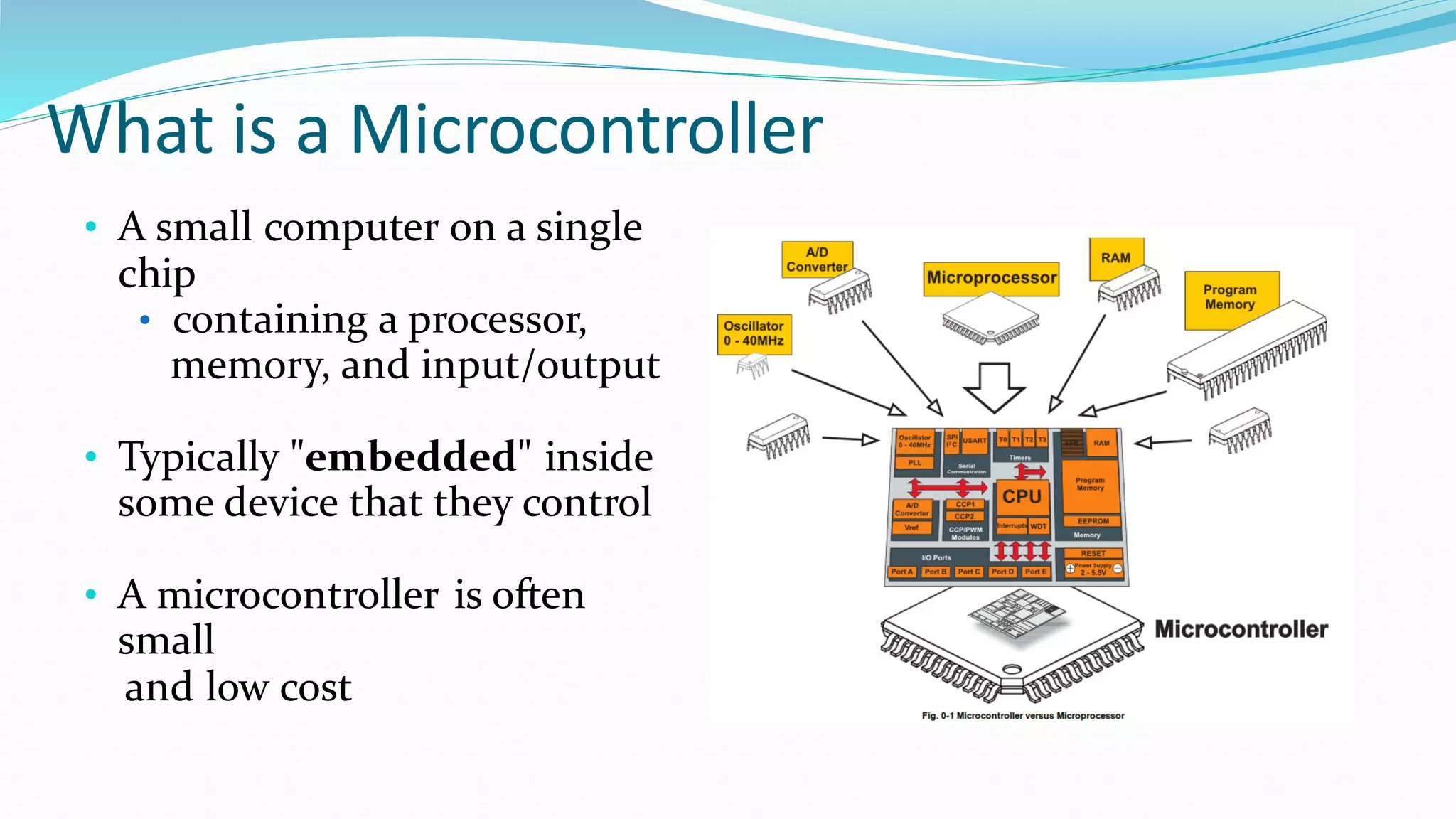
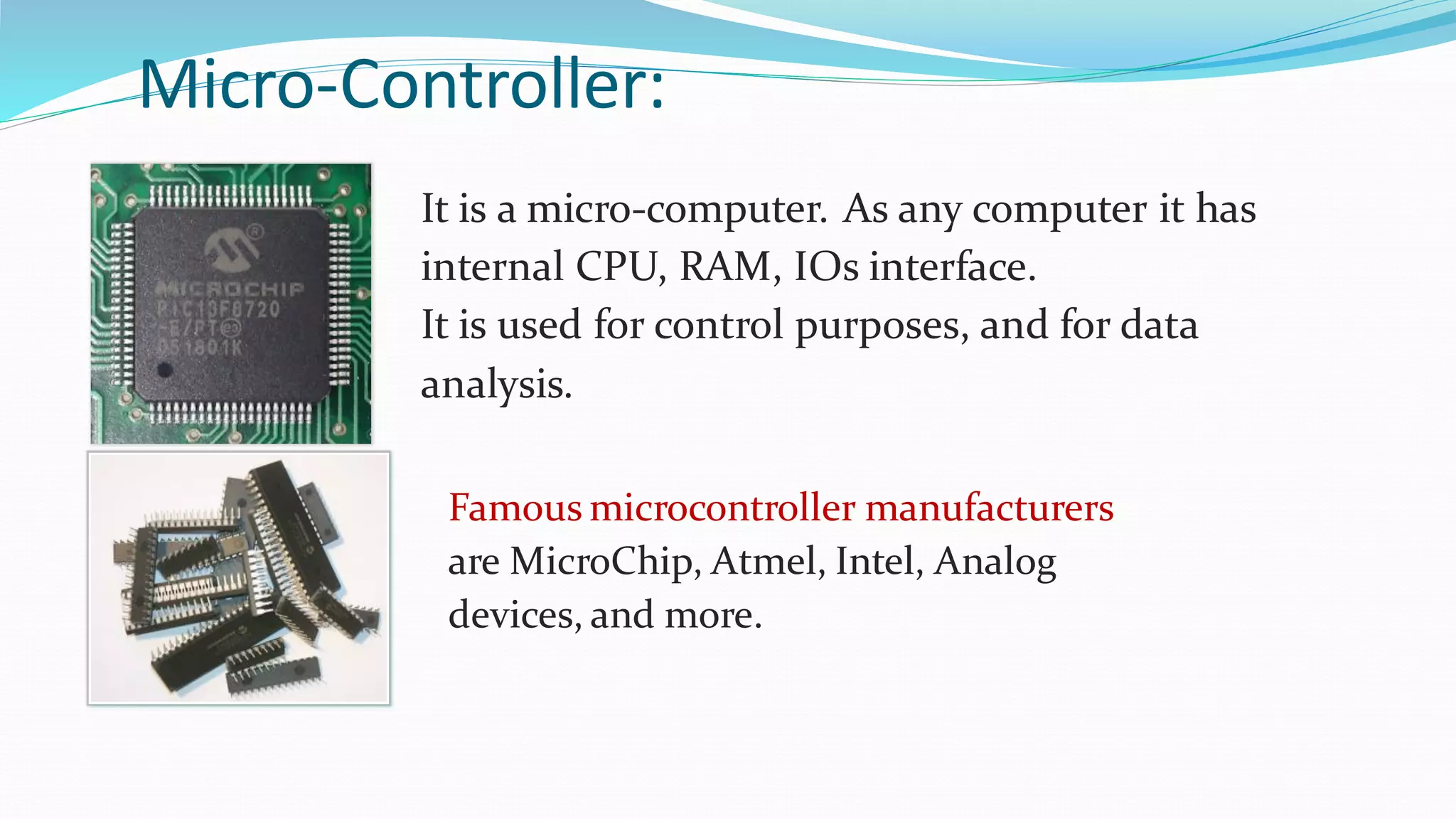
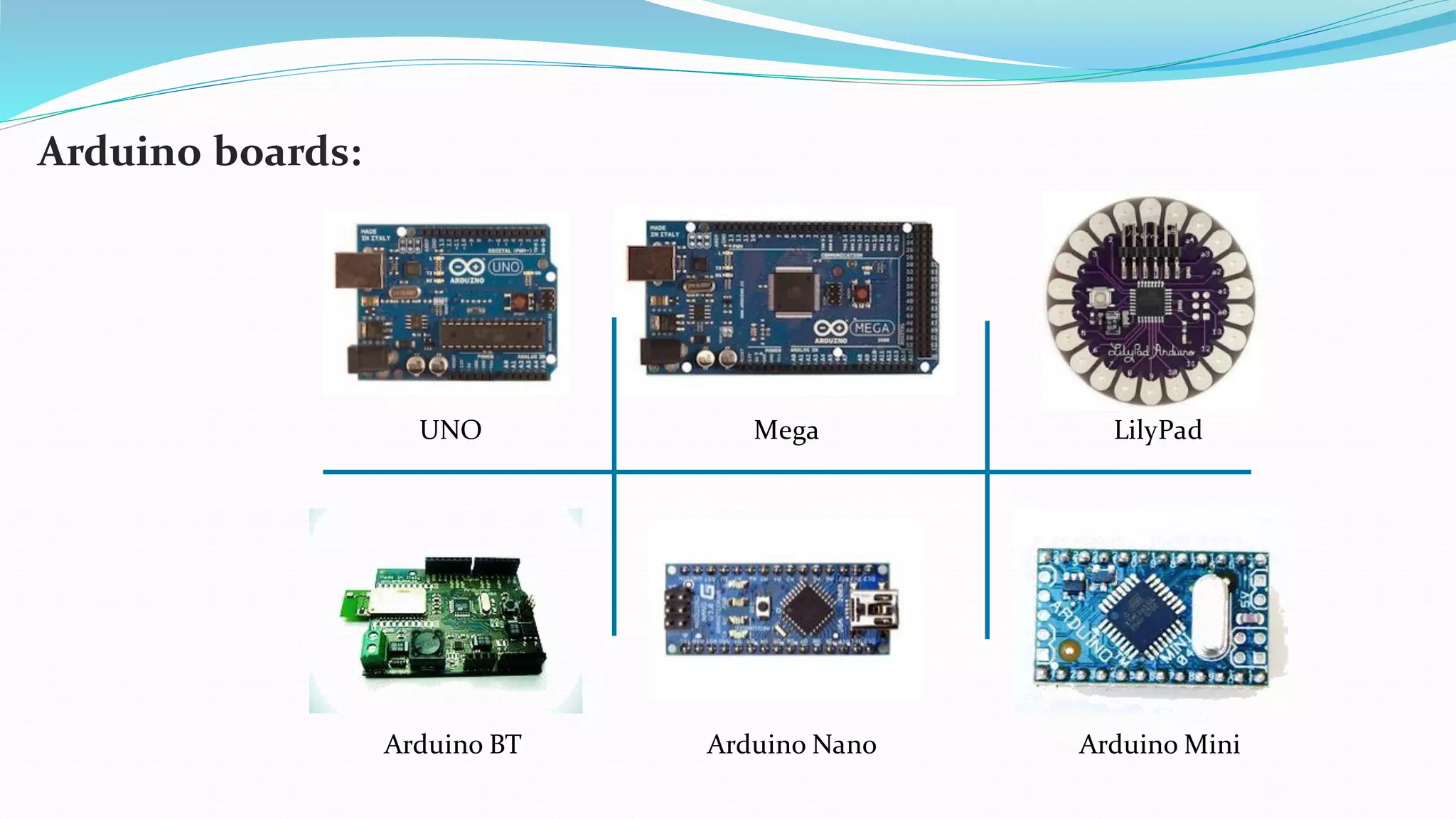
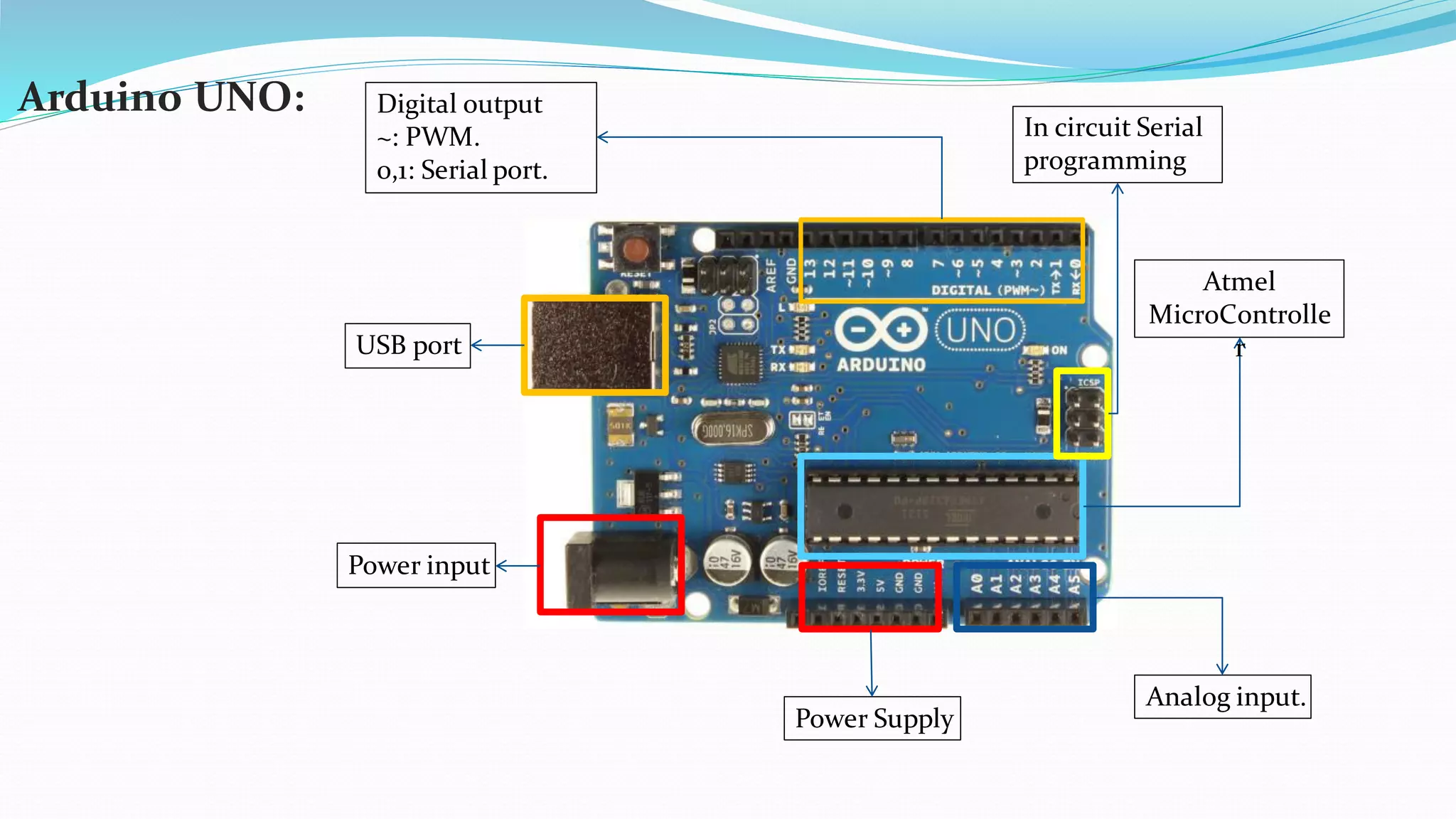
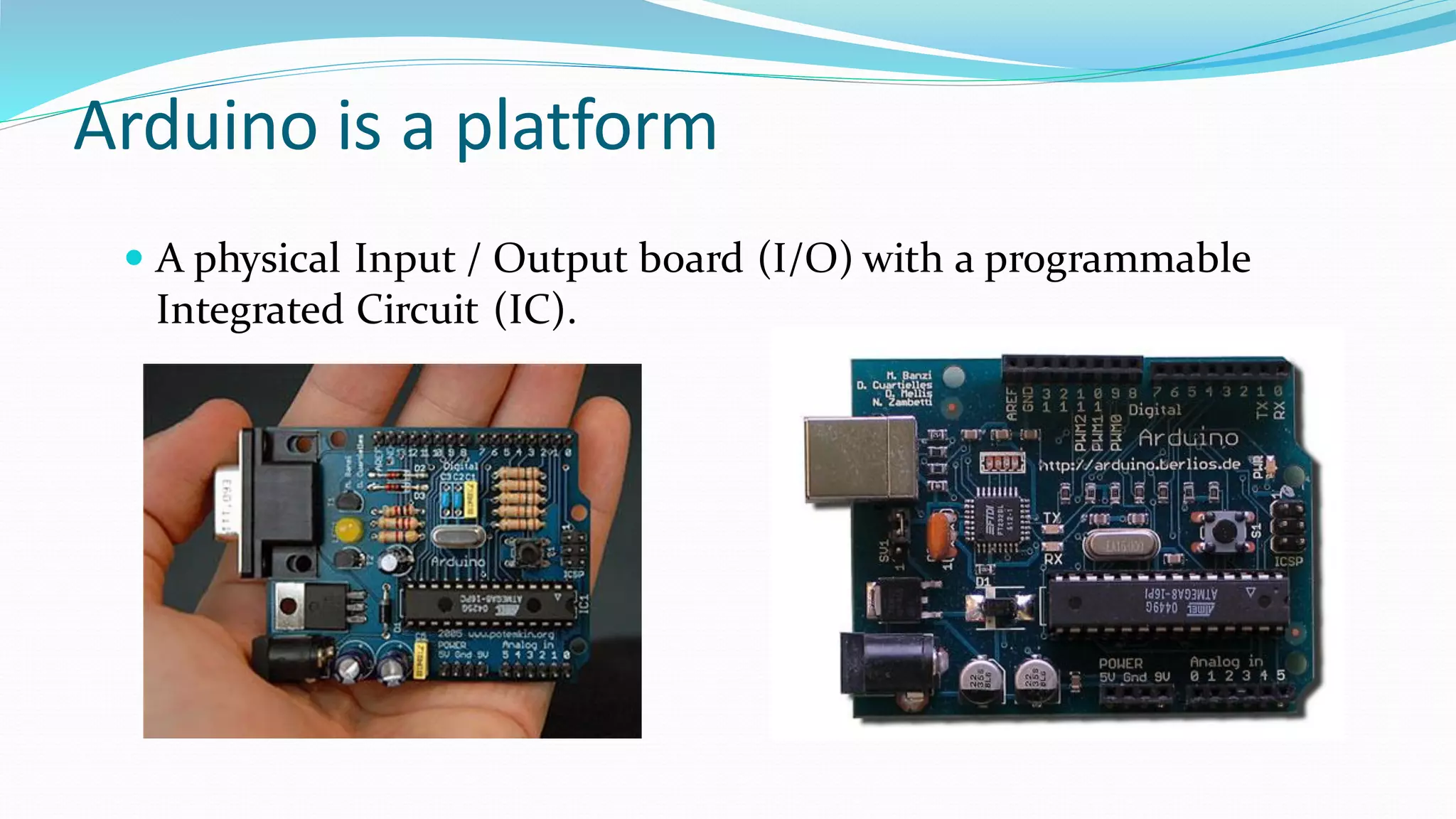
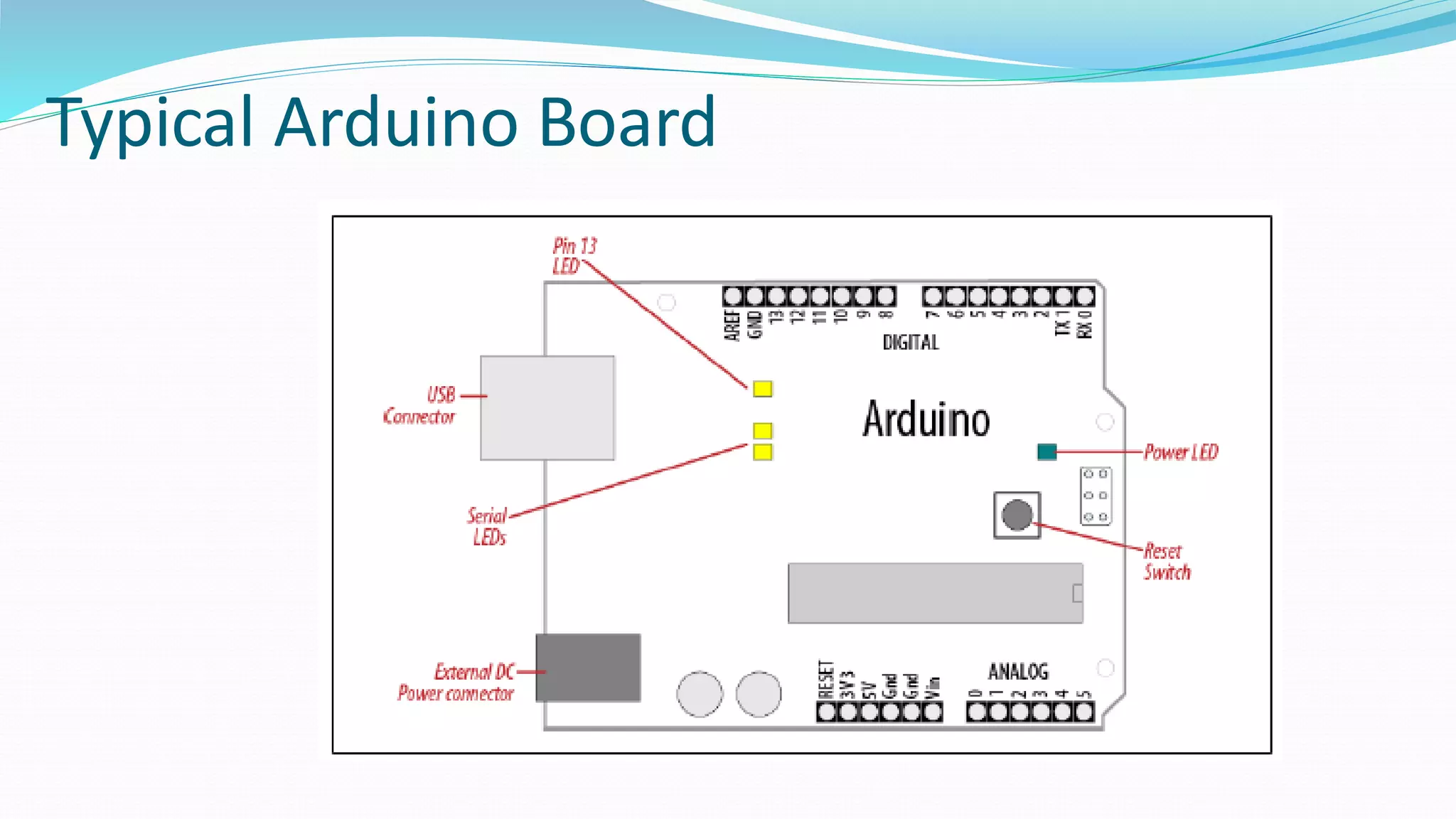
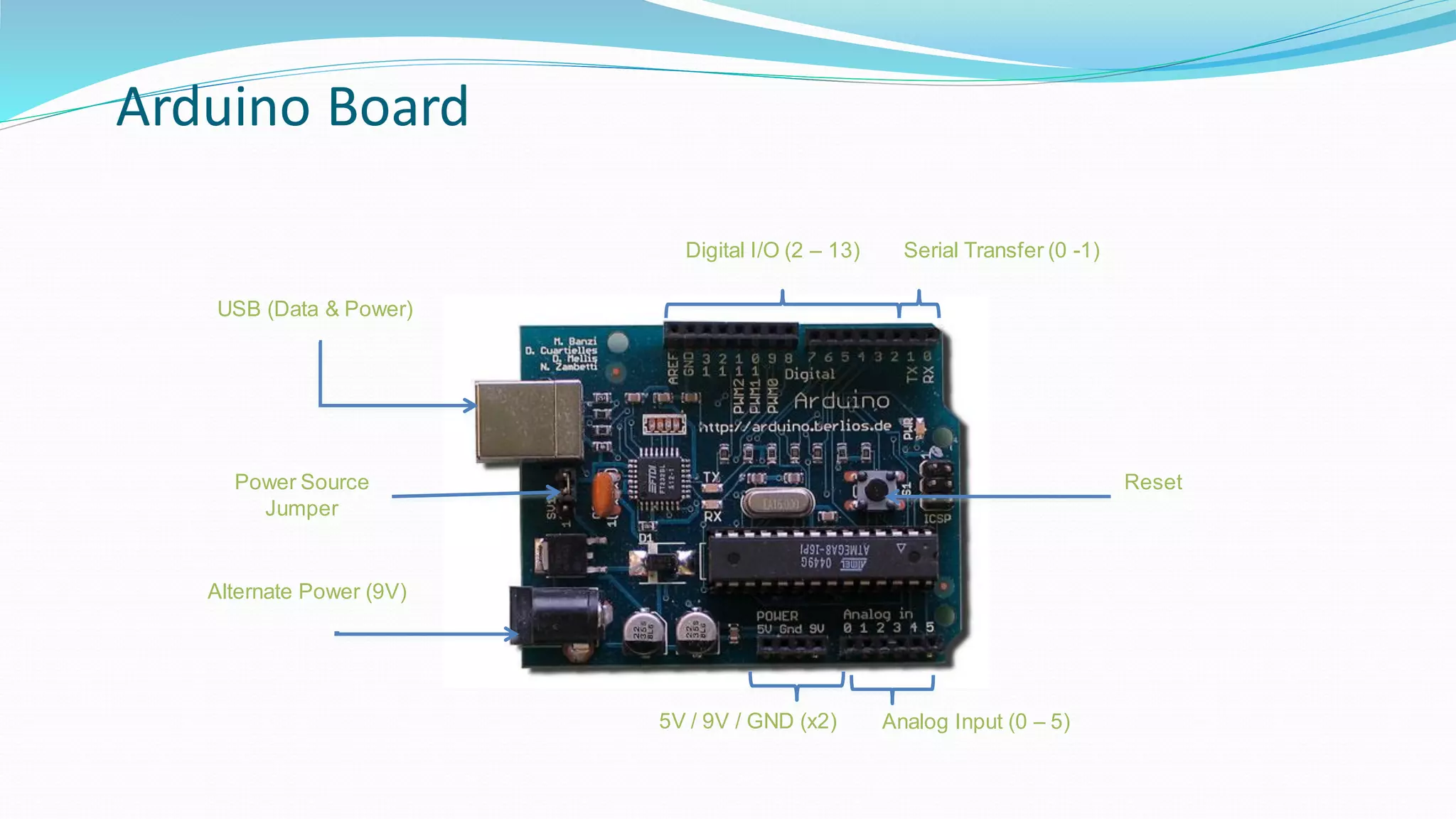
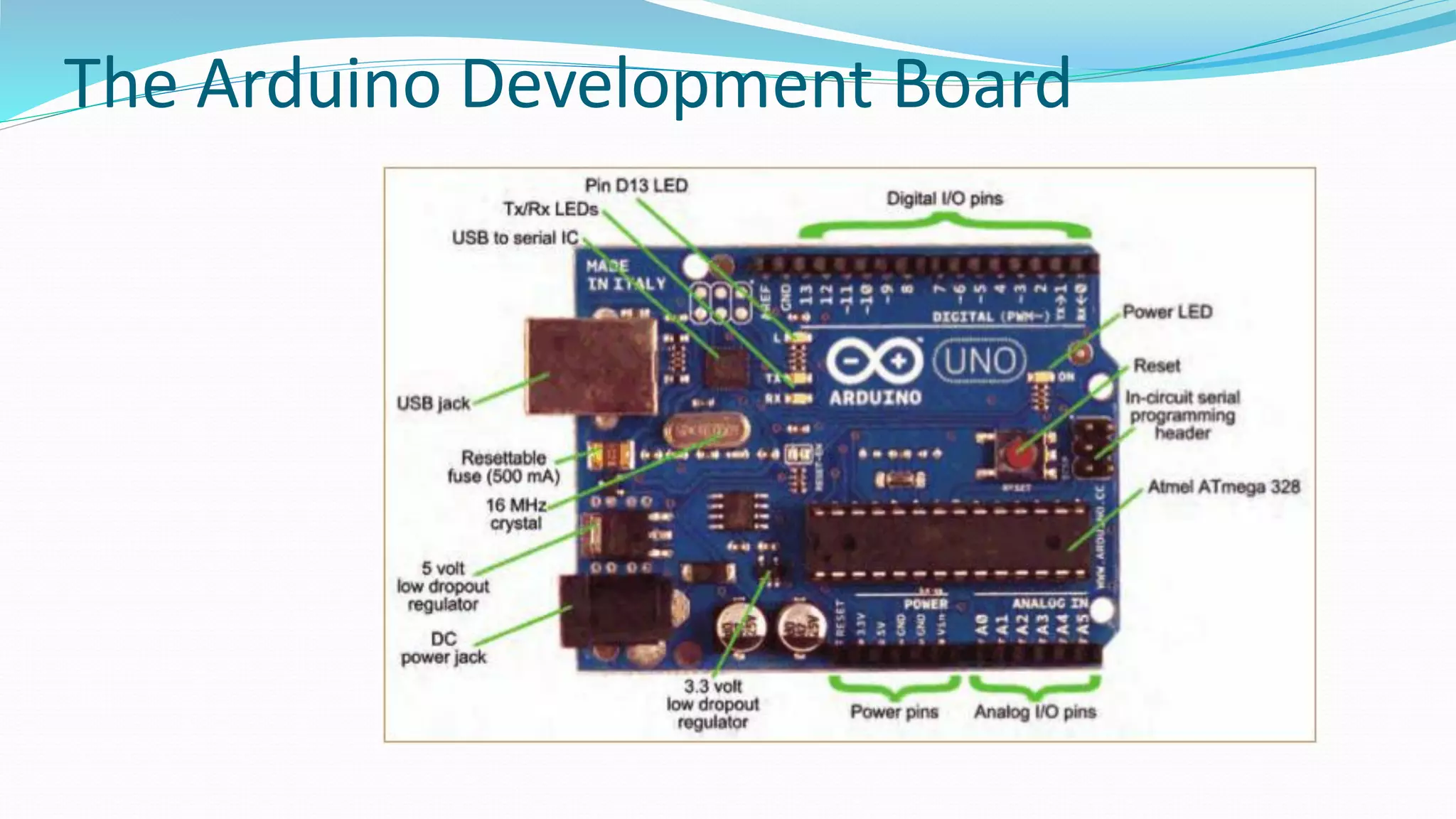
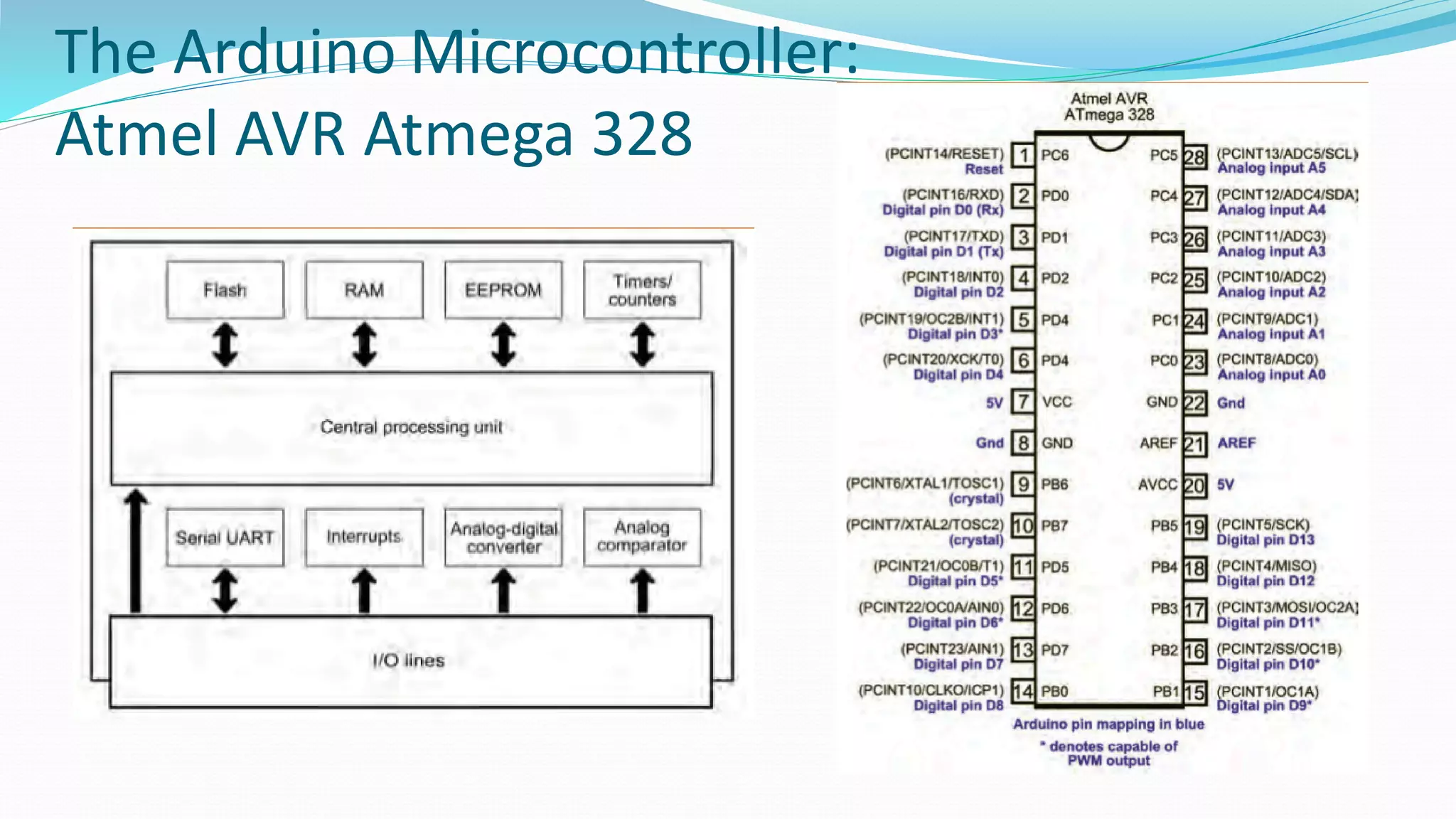
This document provides an overview of microcontrollers and the Arduino platform. It defines a microcontroller as a small computer on a chip containing a processor, memory, and input/output. It then discusses Arduino specifically, defining it as an open-source electronics prototyping platform consisting of affordable hardware boards and software. The document outlines what Arduino is used for, including physical computing projects, interactive installations, and rapid prototyping. It also provides basic steps for getting started with Arduino development.