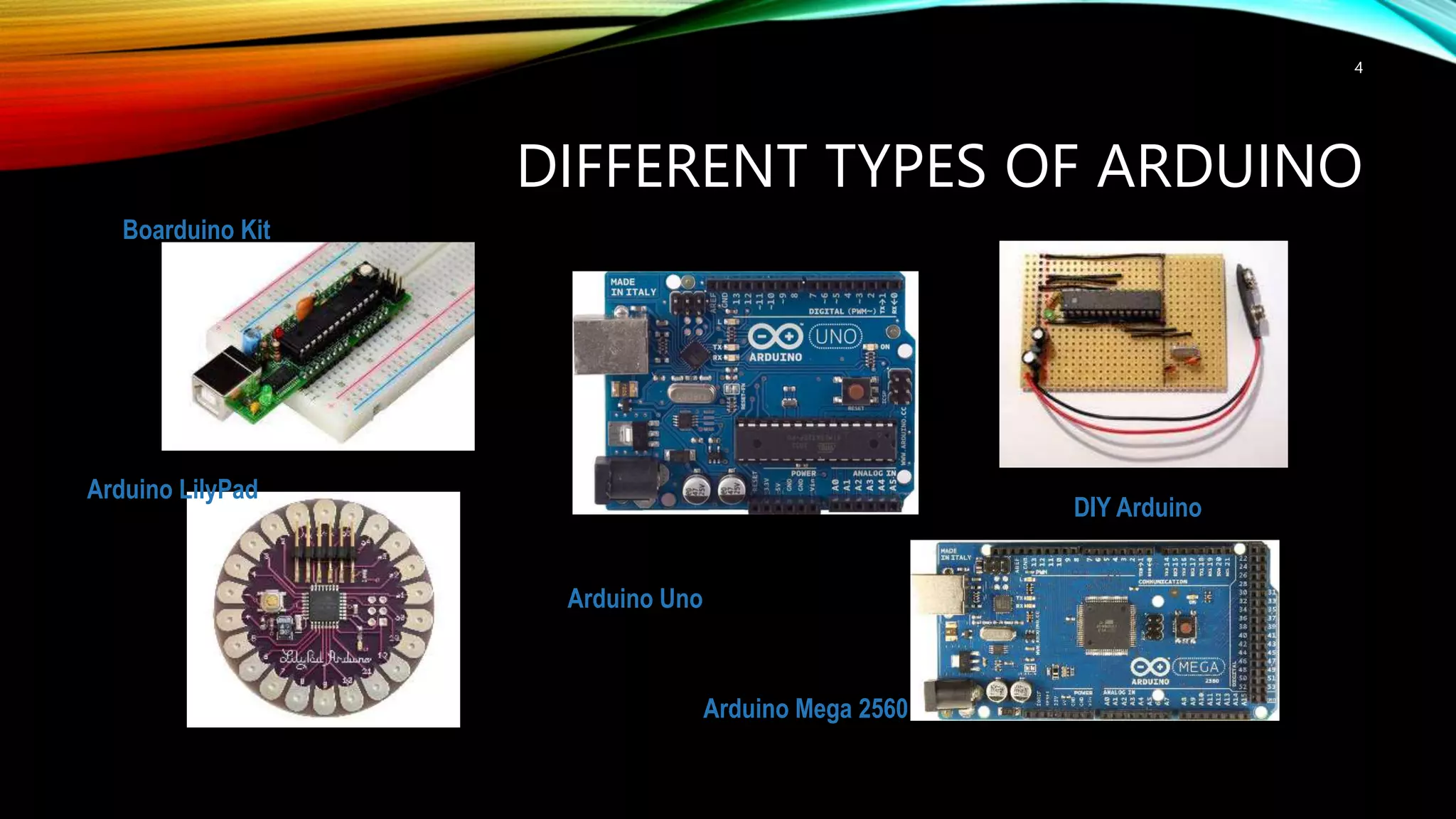
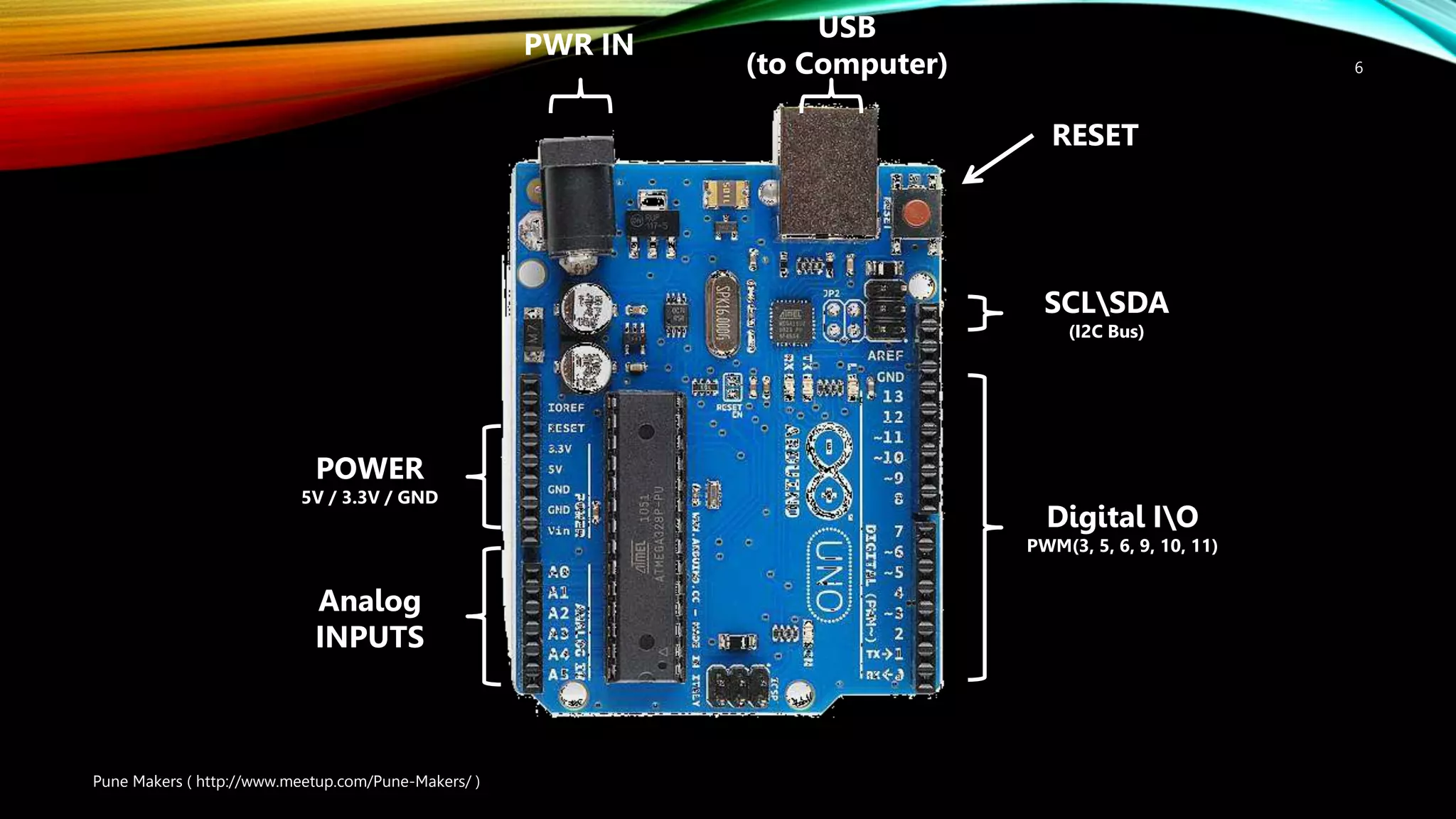
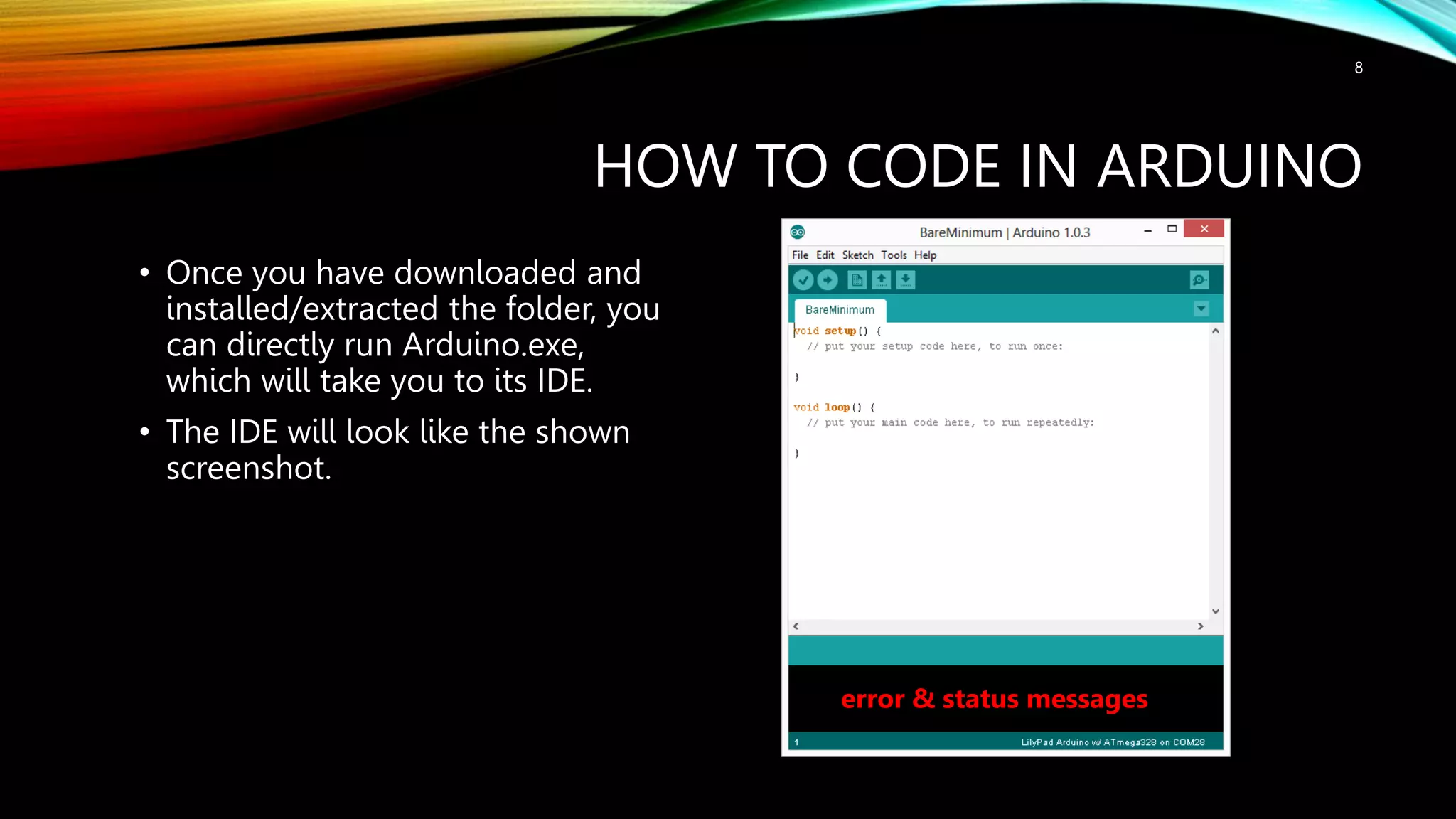
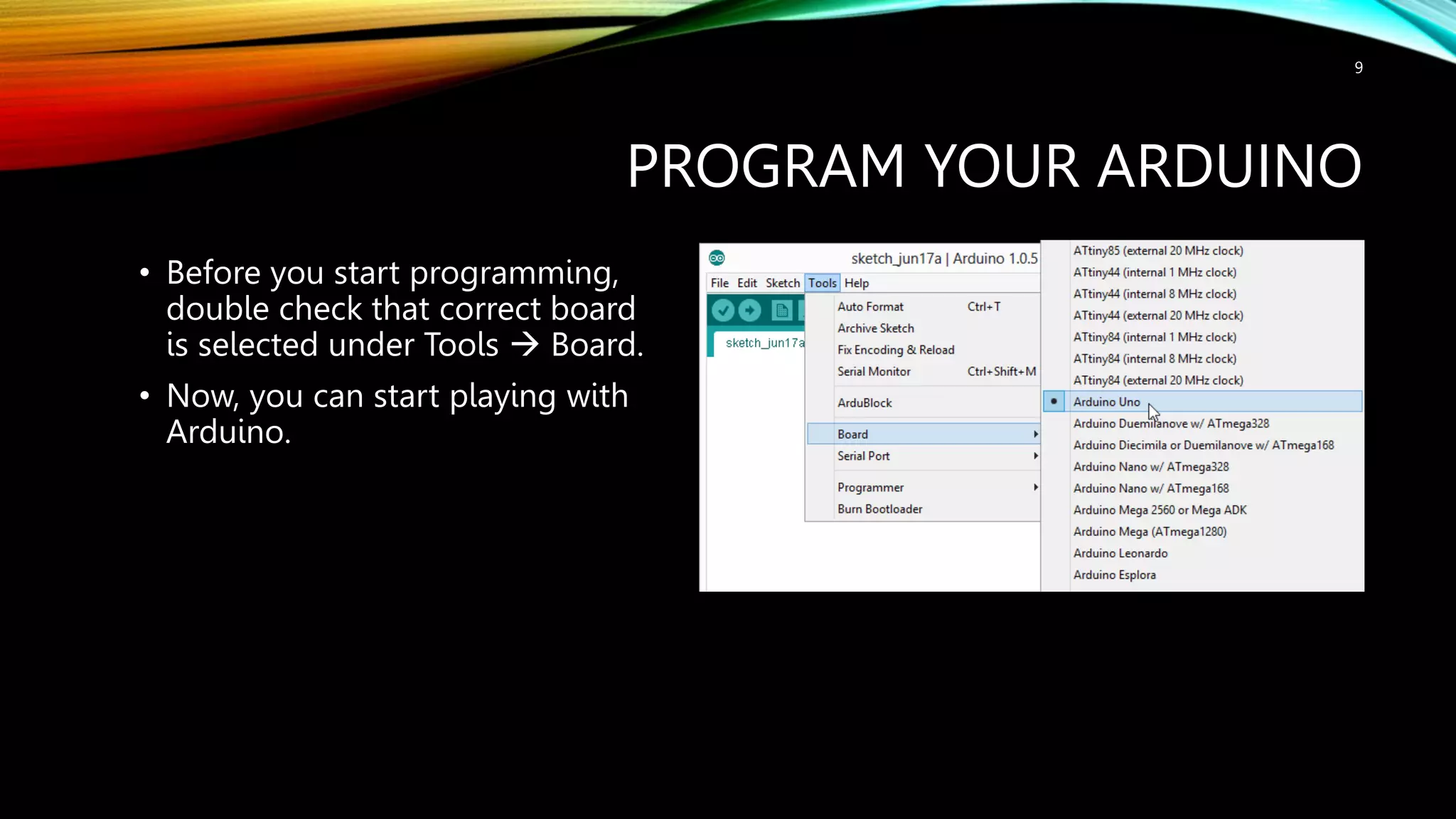
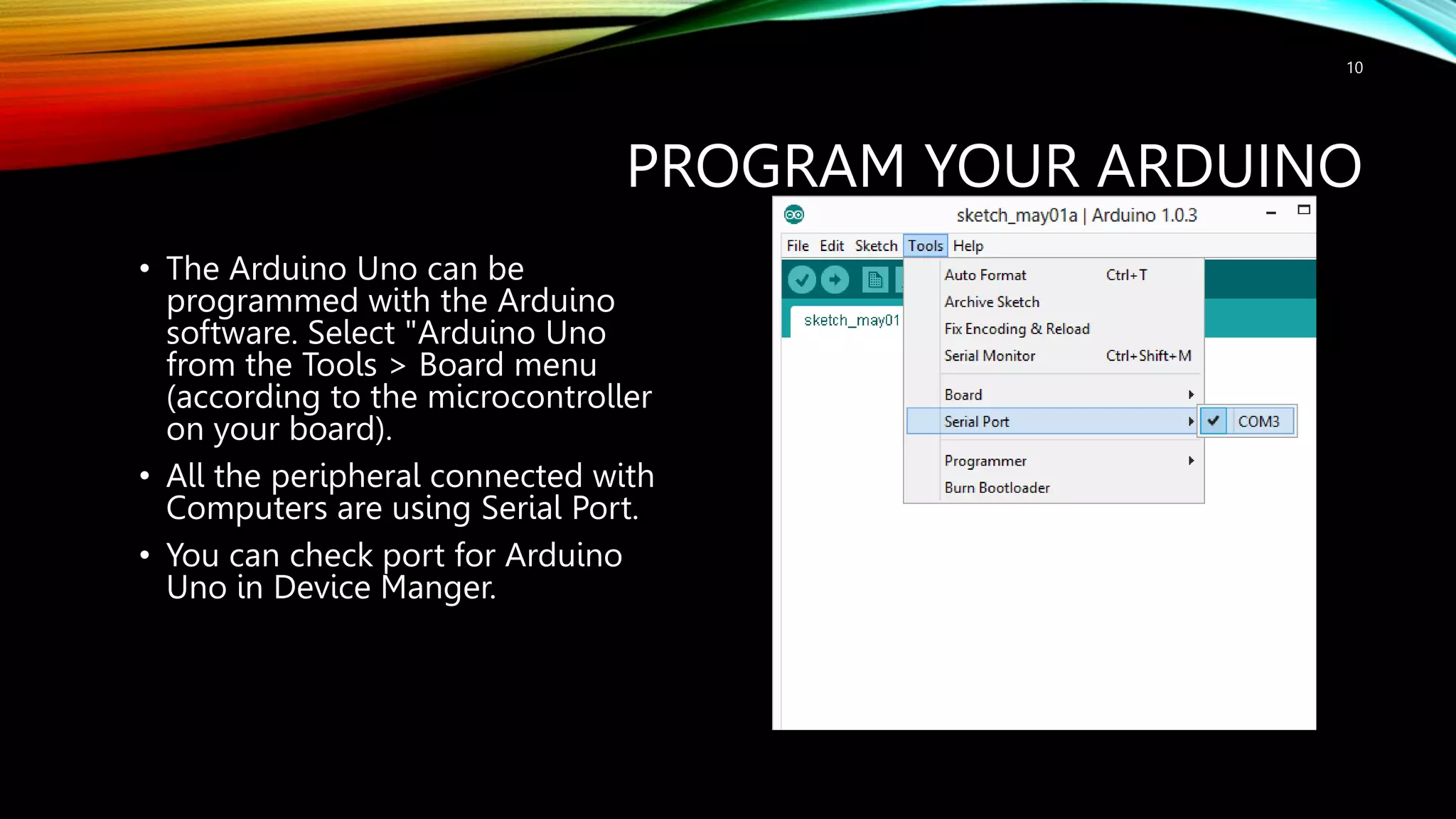
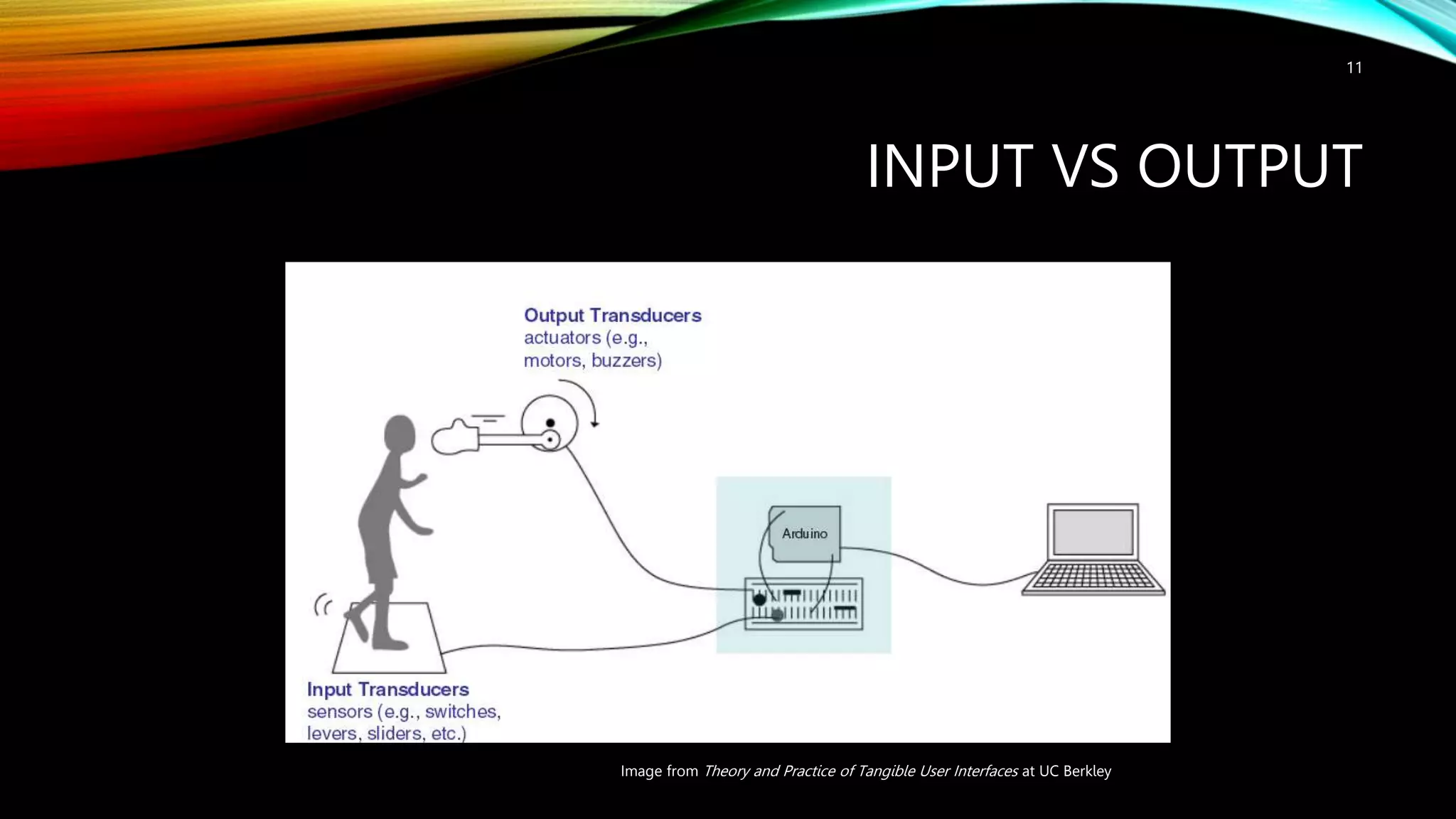
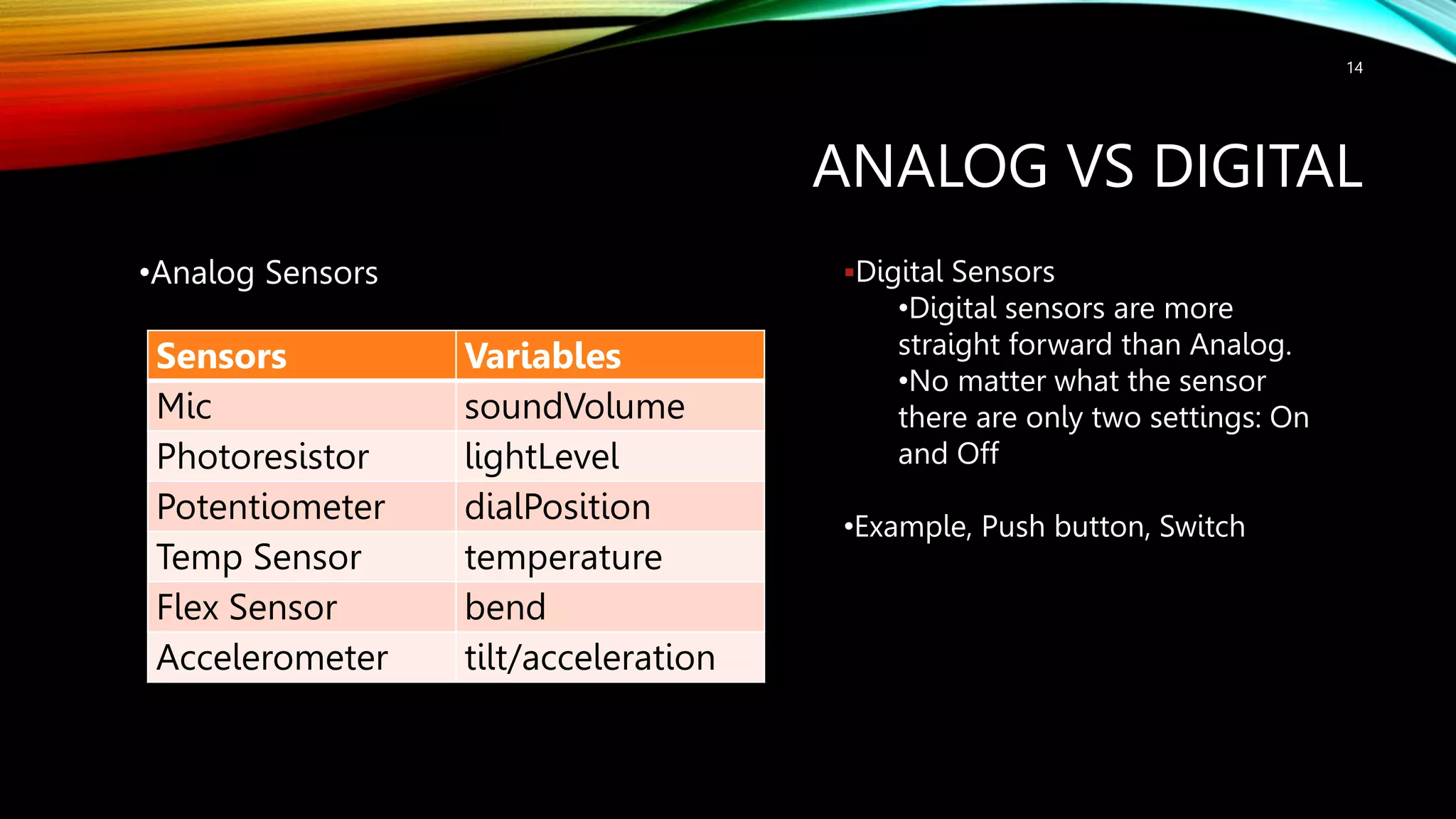
This document provides an introduction to Arduino, including: - What Arduino is and its uses for artists, students, and hobbyists. - That Arduino is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 chip, which has 32KB of flash memory, 2KB of SRAM, and 1KB of EEPROM. - Different types of Arduino boards like Uno, Mega, LilyPad, and DIY boards. - How to code for Arduino using the Arduino IDE software, by selecting the correct board and port and uploading programs. - Key concepts like digital and analog I/O, if-statements, and serial communication.