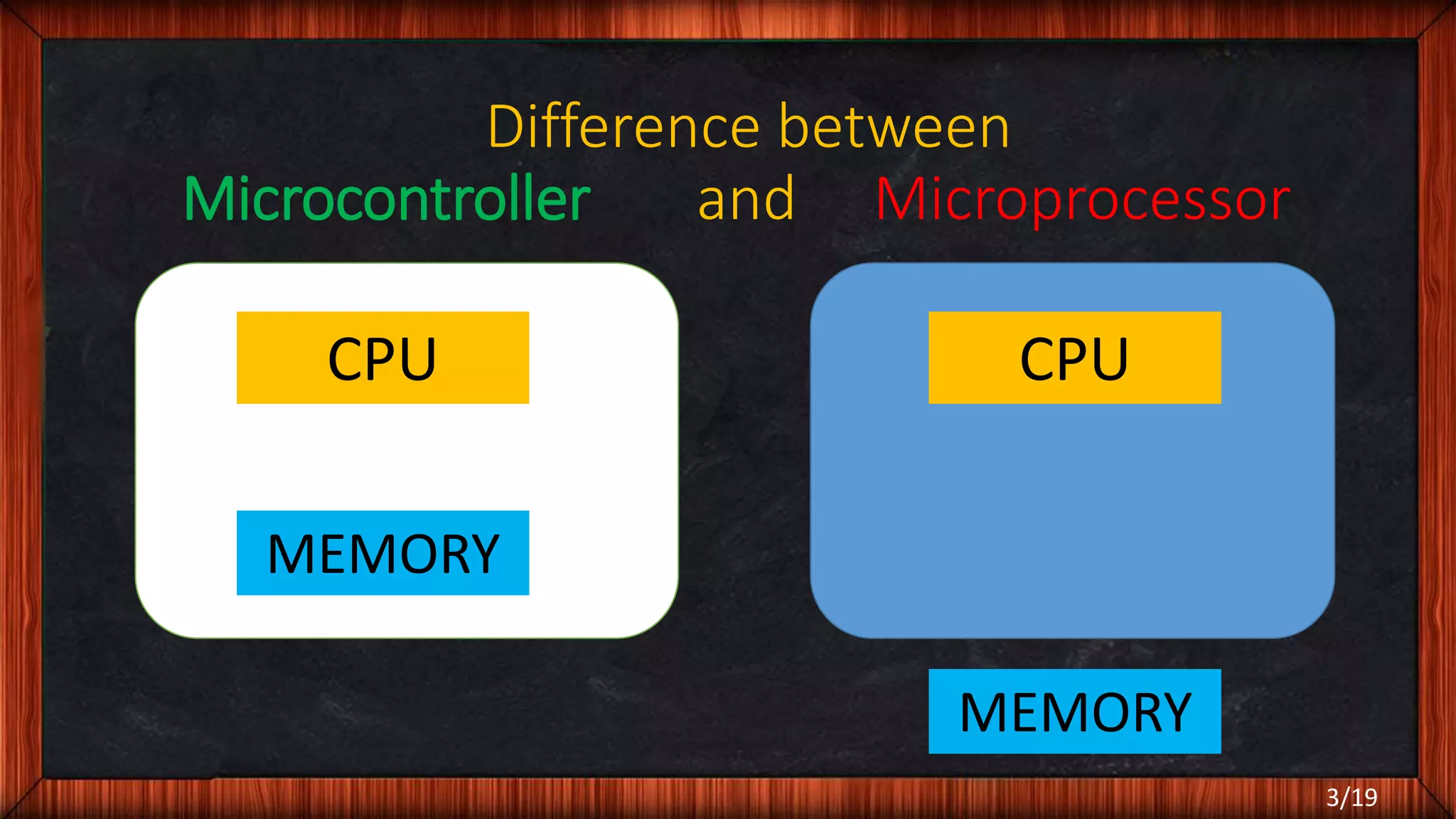
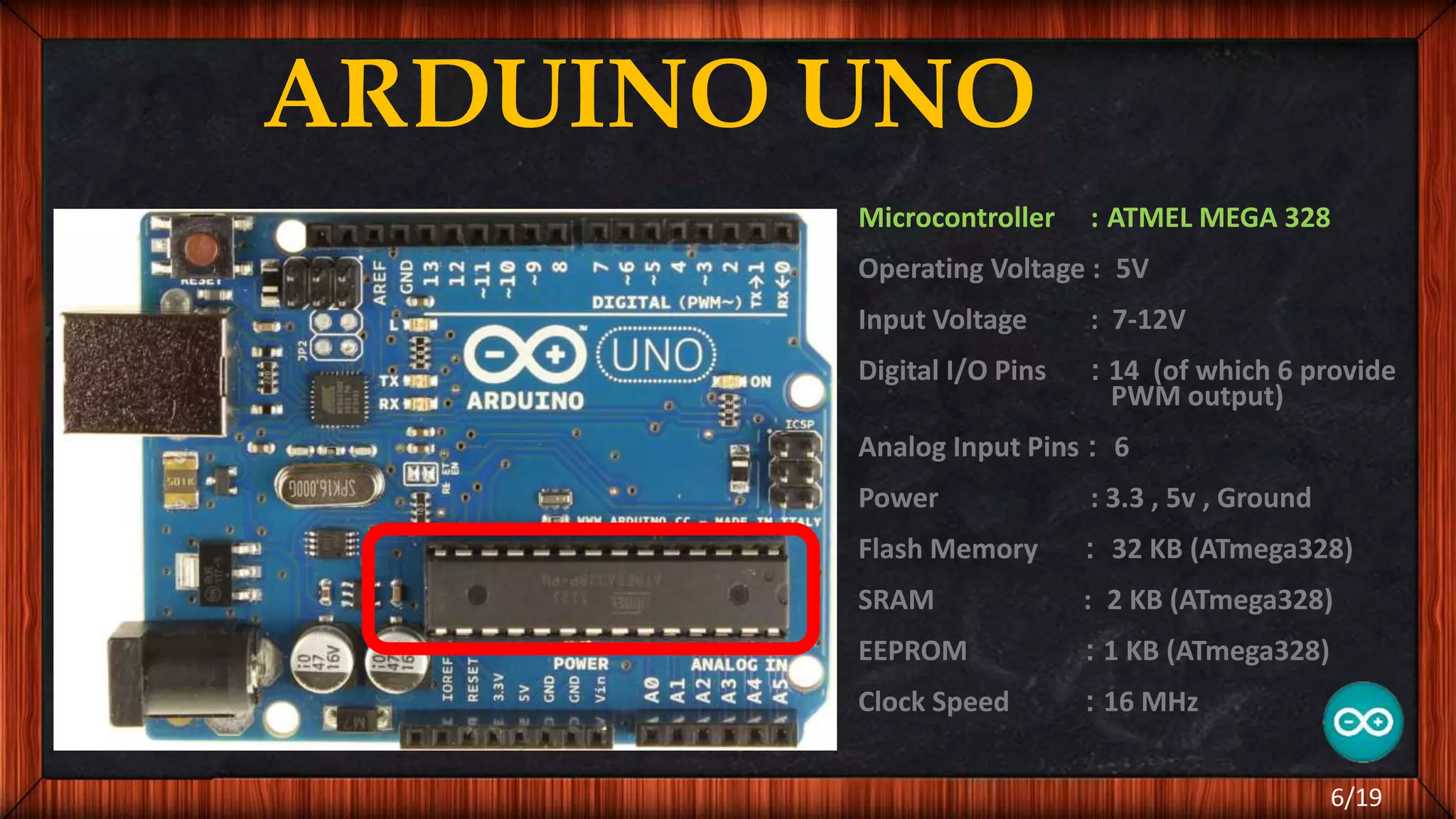
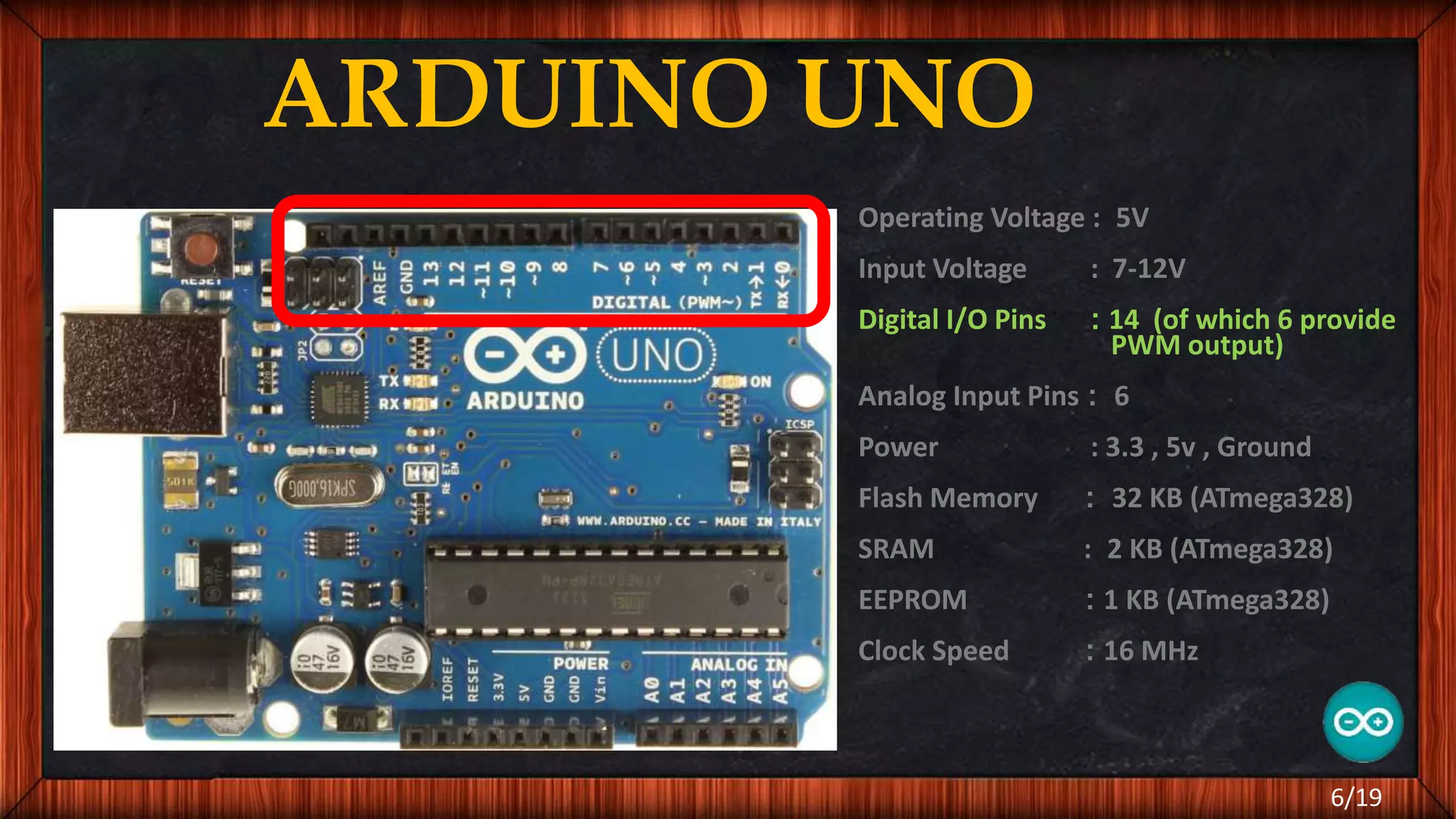
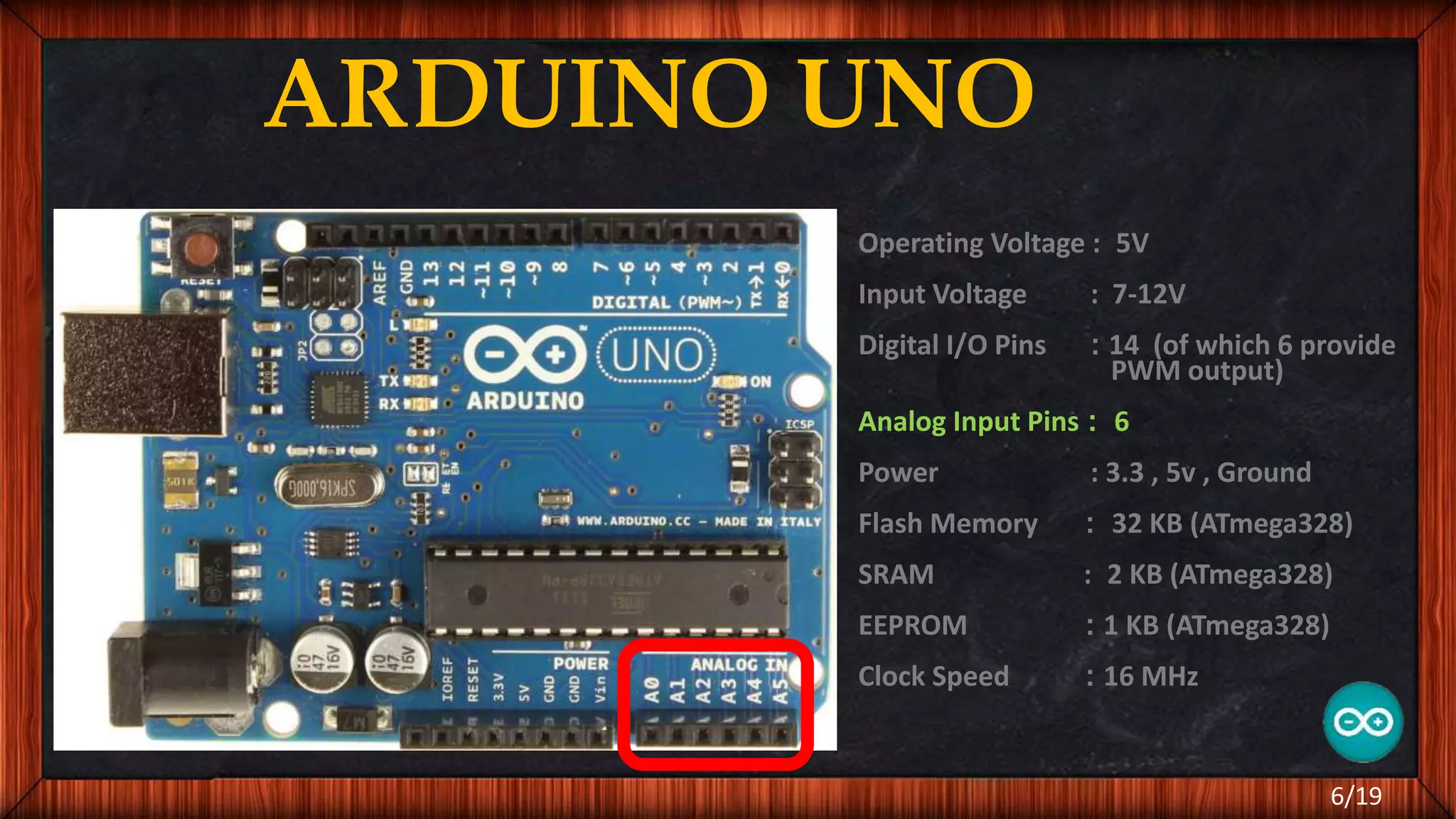
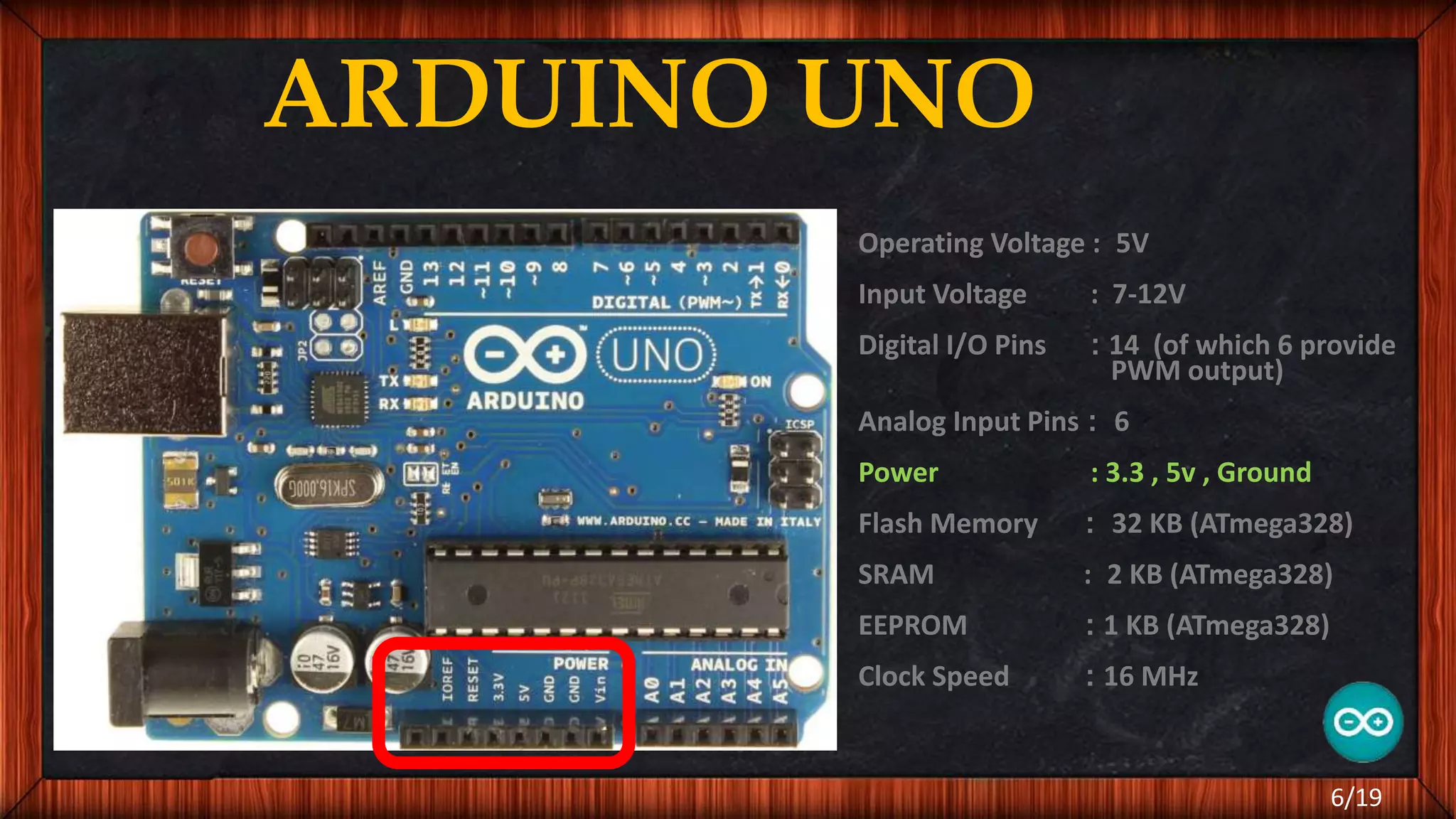
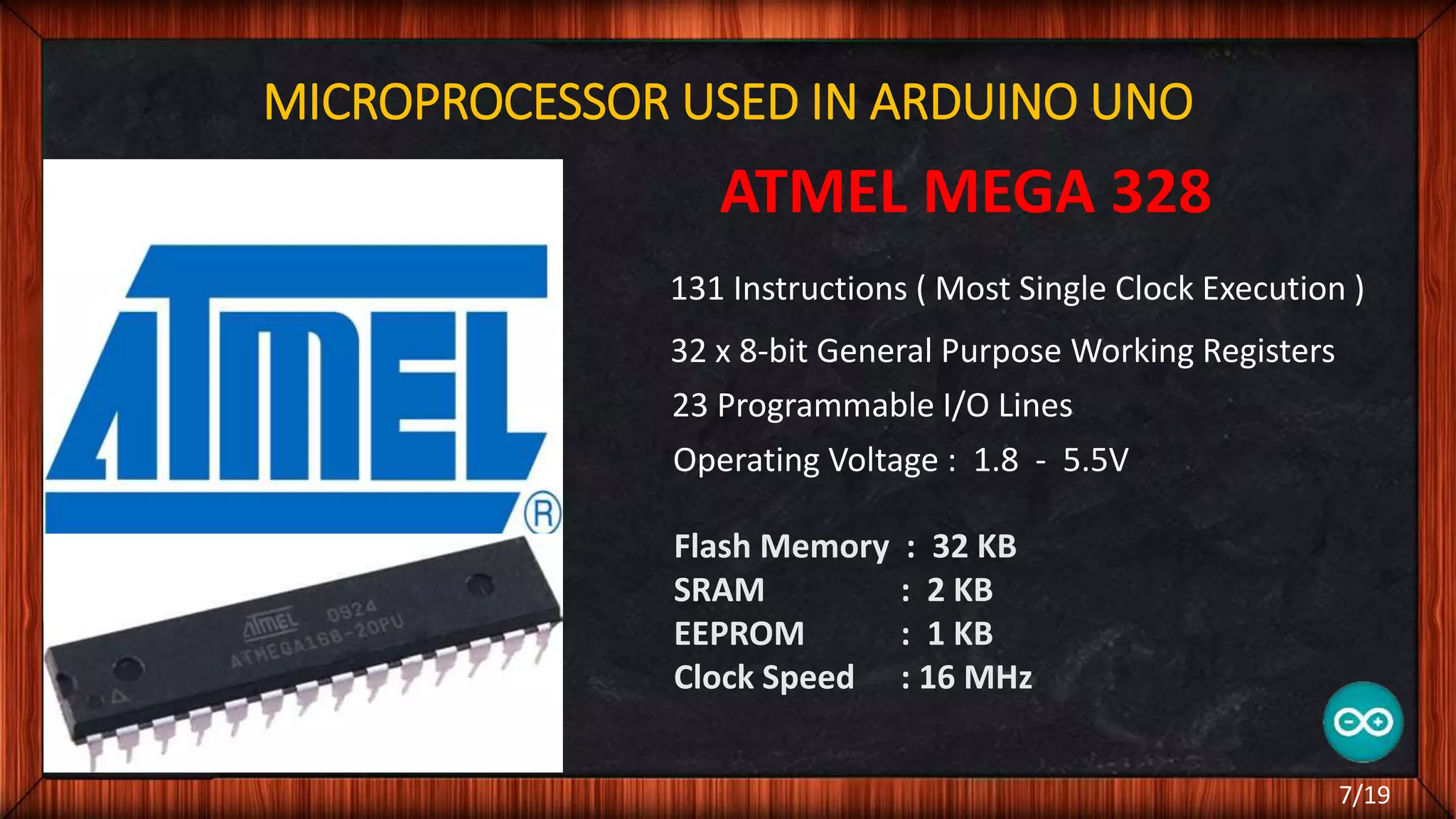
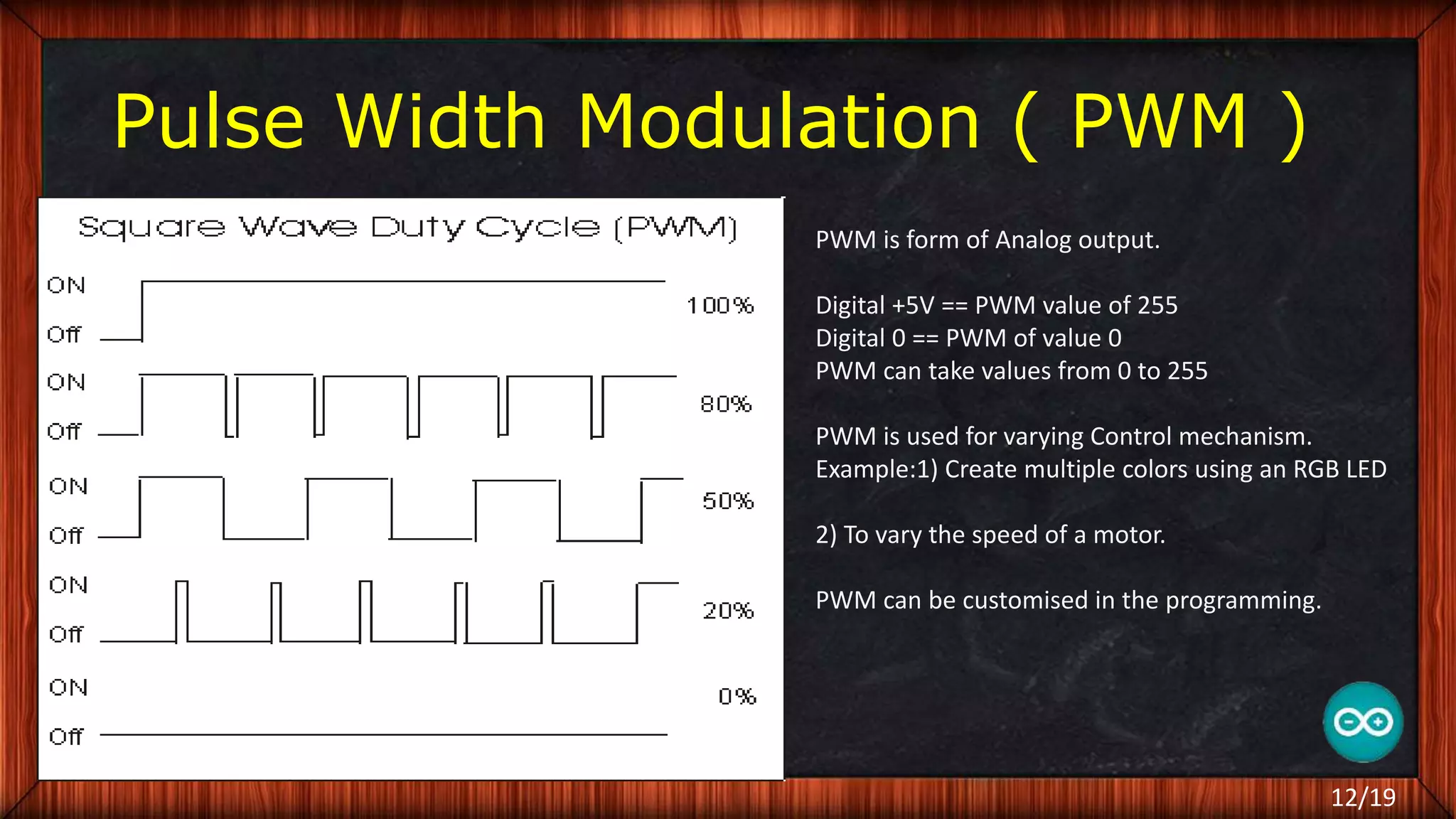
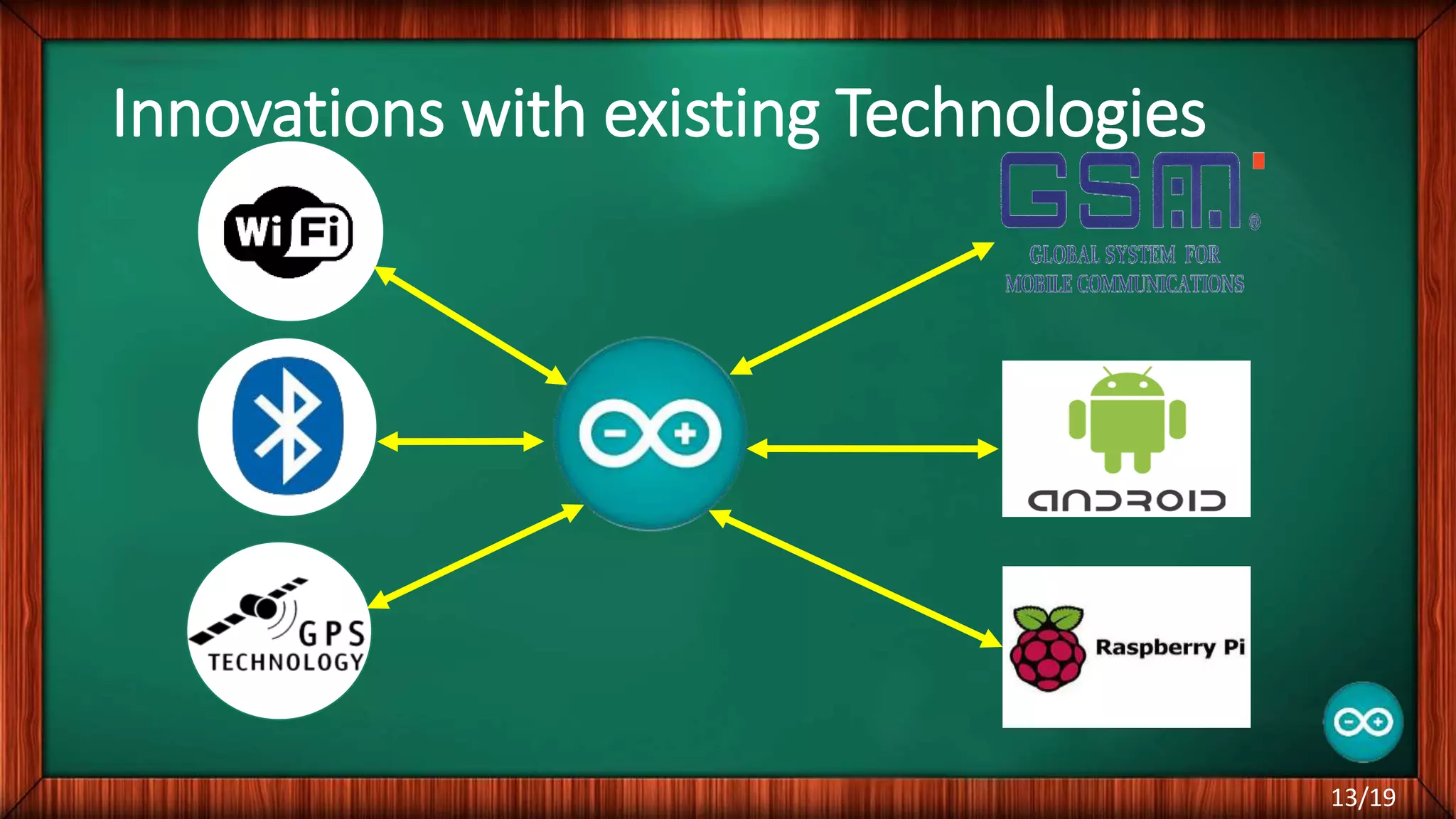
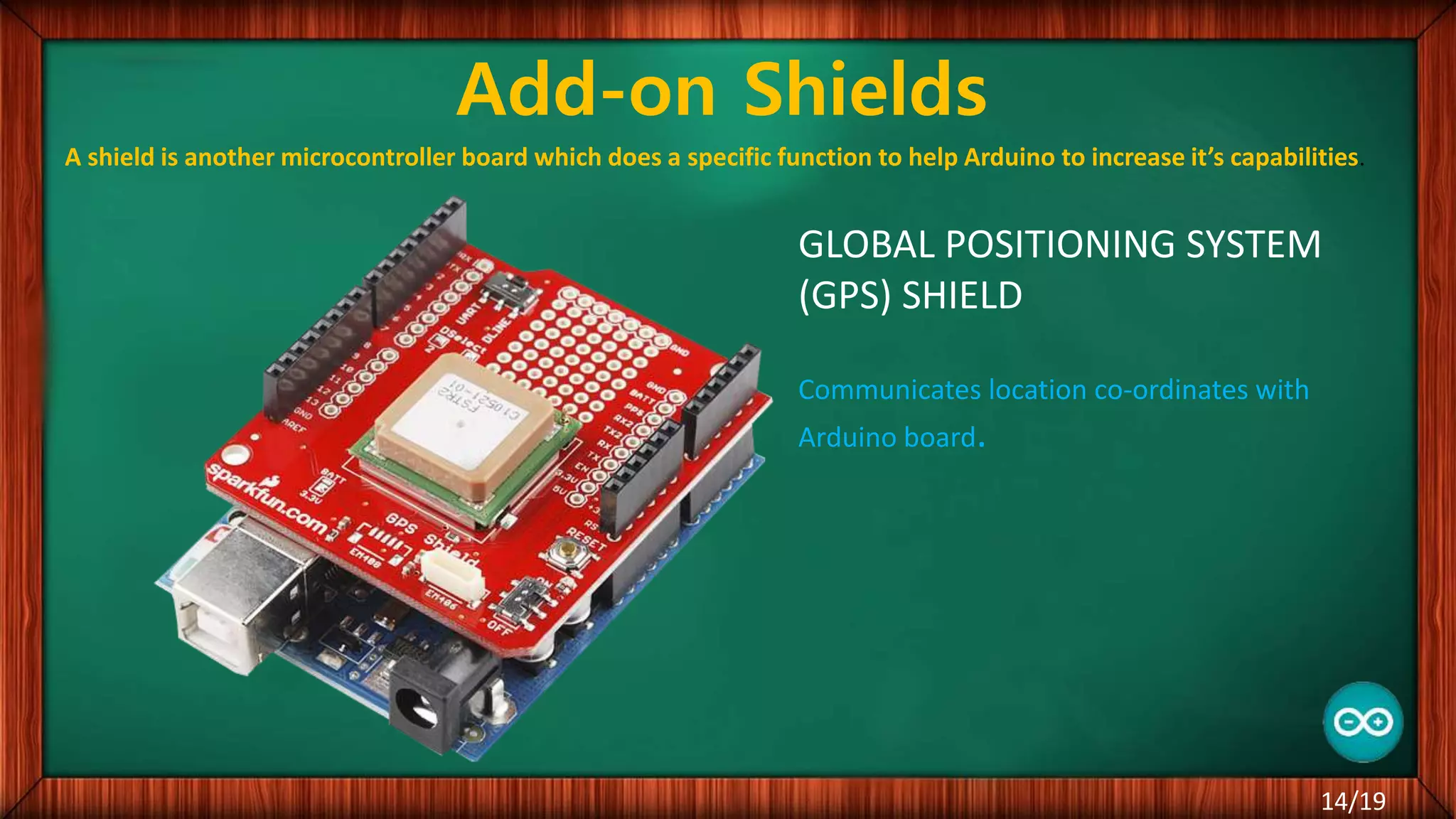
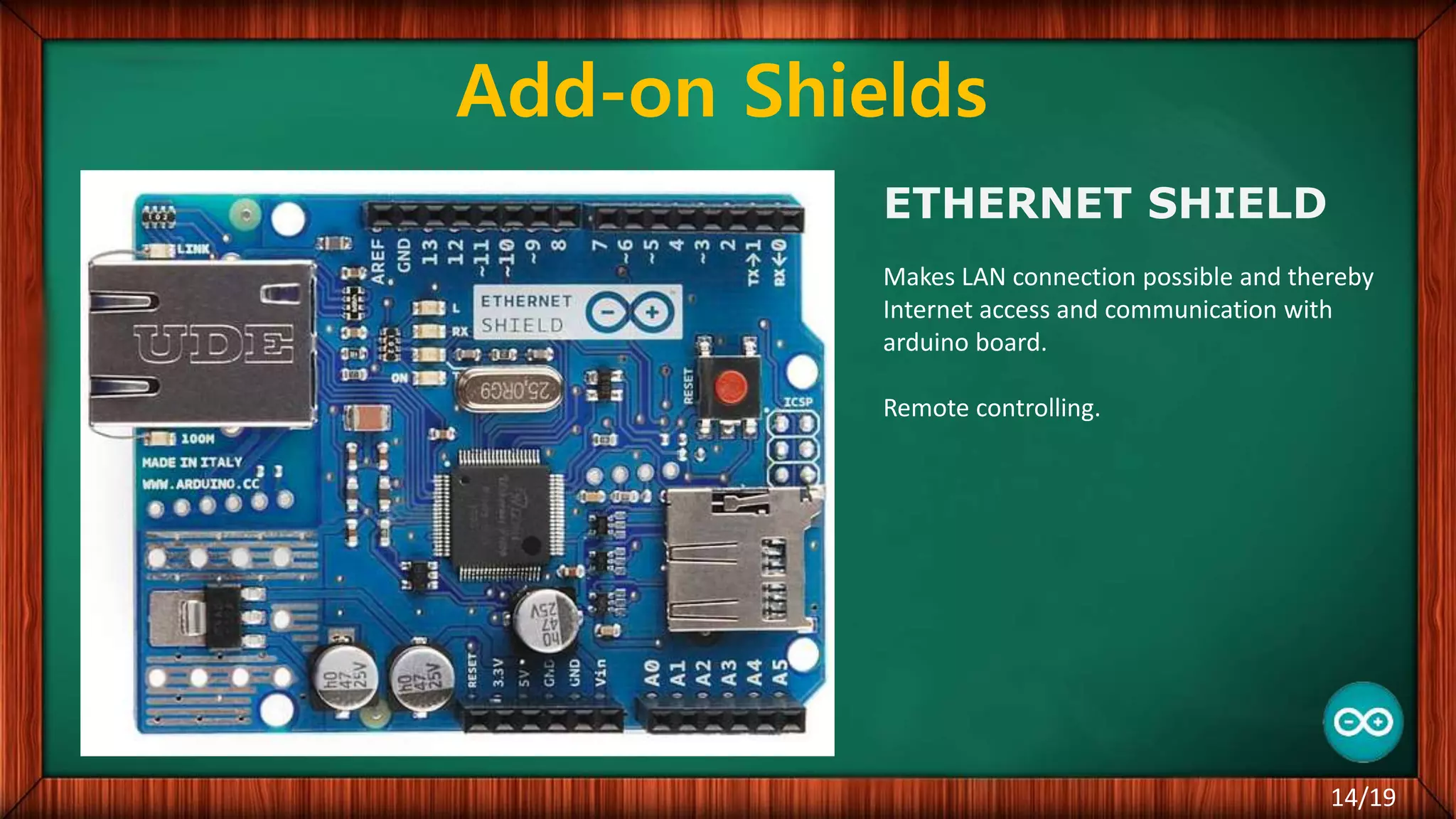
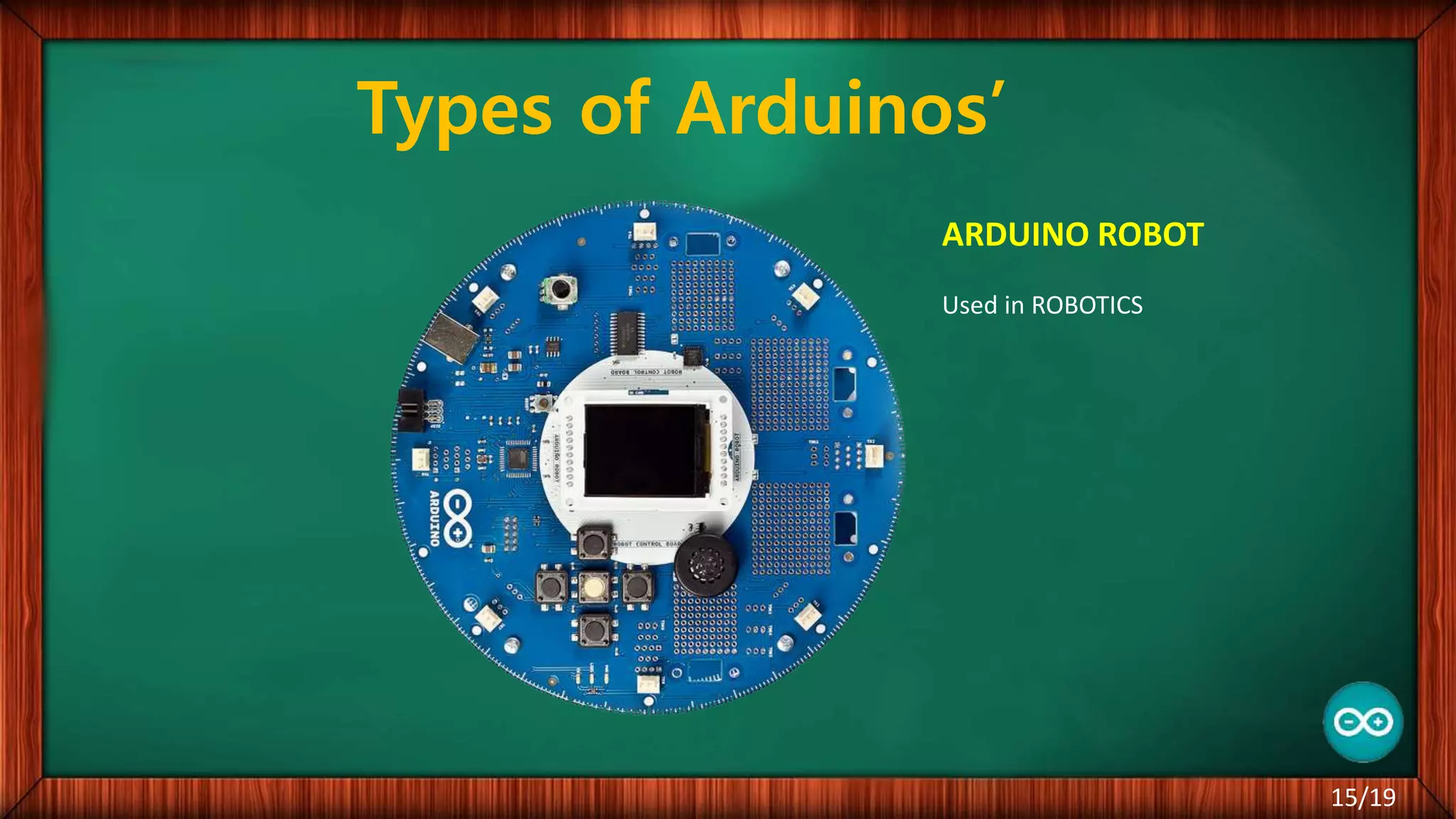
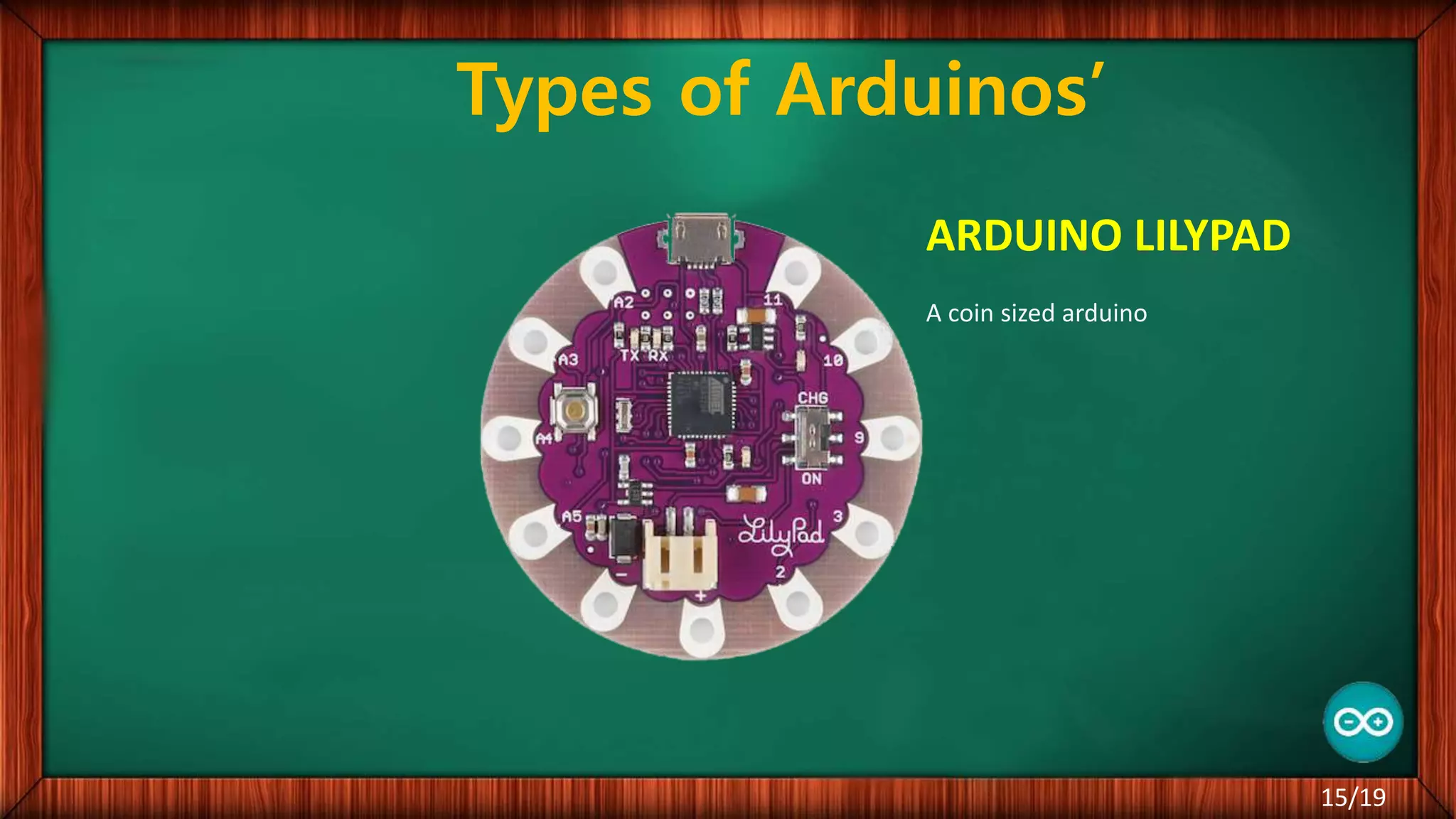
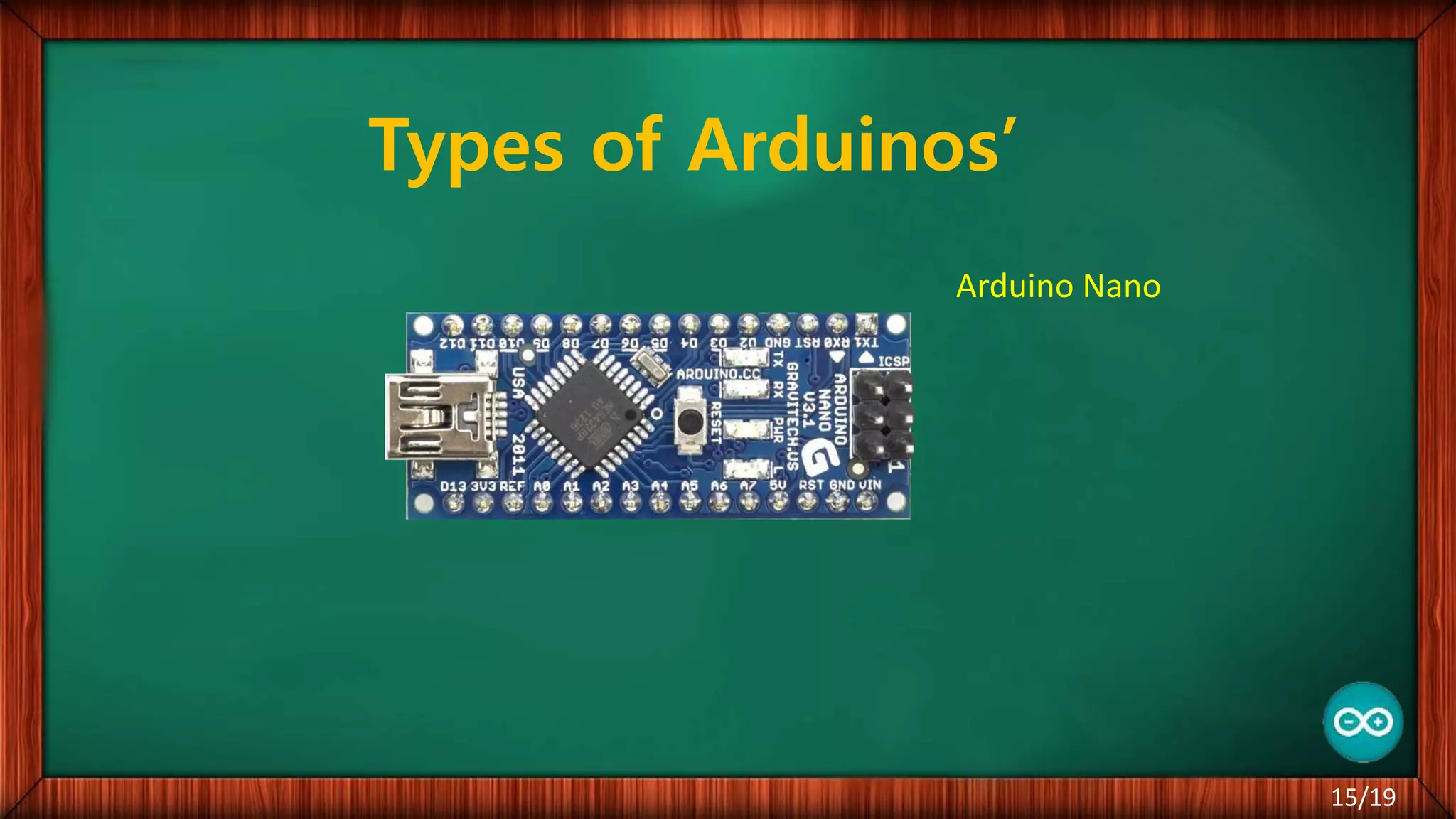
The document outlines the differences between microcontrollers and microprocessors, details on Arduino technology, specifically the Arduino Uno, and its components such as the Atmel Mega 328 microcontroller. It describes programming with the Integrated Development Environment (IDE), the use of add-on shields for enhanced functionality, and various applications including robotics and home automation. The text emphasizes Arduino's role in enabling interactive electronics projects through an open-source platform.