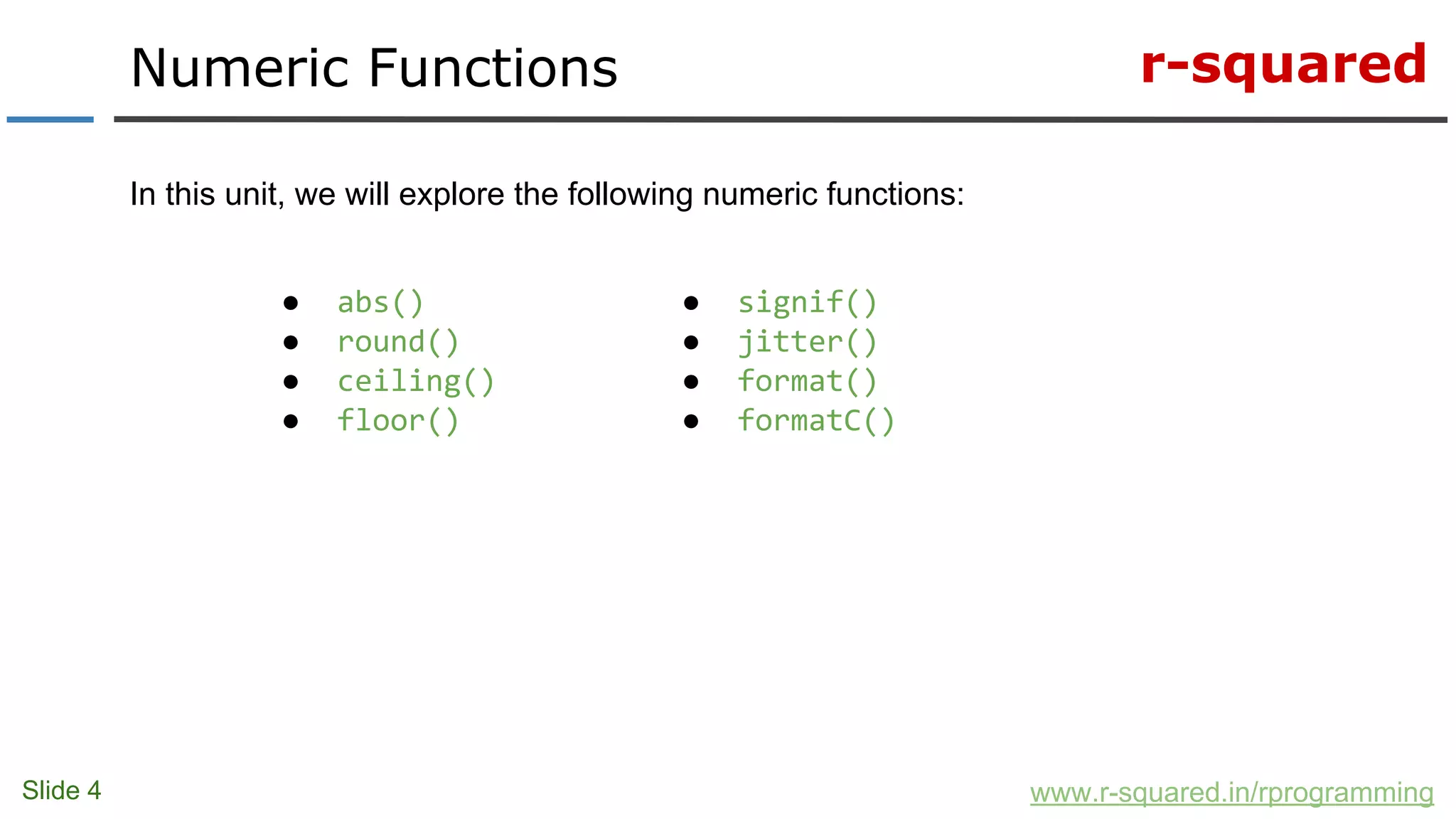
The document outlines a comprehensive R programming course focused on data analysis, covering fundamental concepts like data types, programming elements, and various numeric functions including signif(), abs(), round(), ceiling(), floor(), trunc(), and jitter(). It provides syntax, descriptions, and examples for each function, facilitating understanding through practical illustrations. Additionally, it hints at future modules on string manipulation and invites learners to connect with R-squared for further resources.

![r-squared Slide 6 abs() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 1 > x <- -5 > abs(x) [1] 5 > # example 2 > y <- 5 > abs(y) [1] 5 > # example 3 > z <- c(1, -3, 4, -7, 5, -9) > abs(z) [1] 1 3 4 7 5 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-6-2048.jpg)

![r-squared Slide 8 round() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 1 > x <- 5.3645 > round(x) # zero decimal values [1] 5 > round(x, digits = 1) # one decimal values [1] 5.4 > round(x, digits = 2) # two decimal values [1] 5.36 > round(x, digits = 3) # three decimal values [1] 5.364](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-8-2048.jpg)

![r-squared Slide 10 ceiling() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > example 1 > x <- 5.3645 > ceiling(x) [1] 6 > example 2 > x <- 3.94 > ceiling(x) [1] 4 > example 3 > x [1] 7.012865 8.148132 9.840098 2.965393 2.098276 6.139226 3.819461 8.849482 1.068249 [10] 5.105874 > ceiling(x) [1] 8 9 10 3 3 7 4 9 2 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-10-2048.jpg)

![r-squared Slide 12 floor() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 1 > x <- 5.3645 > floor(x) [1] 5 > # example 2 > x <- 3.94 > floor(x) [1] 3 > # example 3 > x <- sample(jitter(1:10)) > x [1] 6.1581438 9.9260513 0.9823364 4.1083687 4.9102557 8.1316709 7.0094556 2.8870083 [9] 2.1403249 9.0941759 > floor(x) [1] 6 9 0 4 4 8 7 2 2 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-12-2048.jpg)

![r-squared Slide 14 trunc() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 1 > x <- 5.3645 > trunc(x) [1] 5 # as we truncate the value in x towards zero, the first integer that appears is 5. > # example 2 > x <- -3.94 > trunc(x) [1] -3 > round(x) [1] -4 > floor(x) [1] -4 # as we truncate the value in x towards zero, the first integer that appears is -3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-14-2048.jpg)
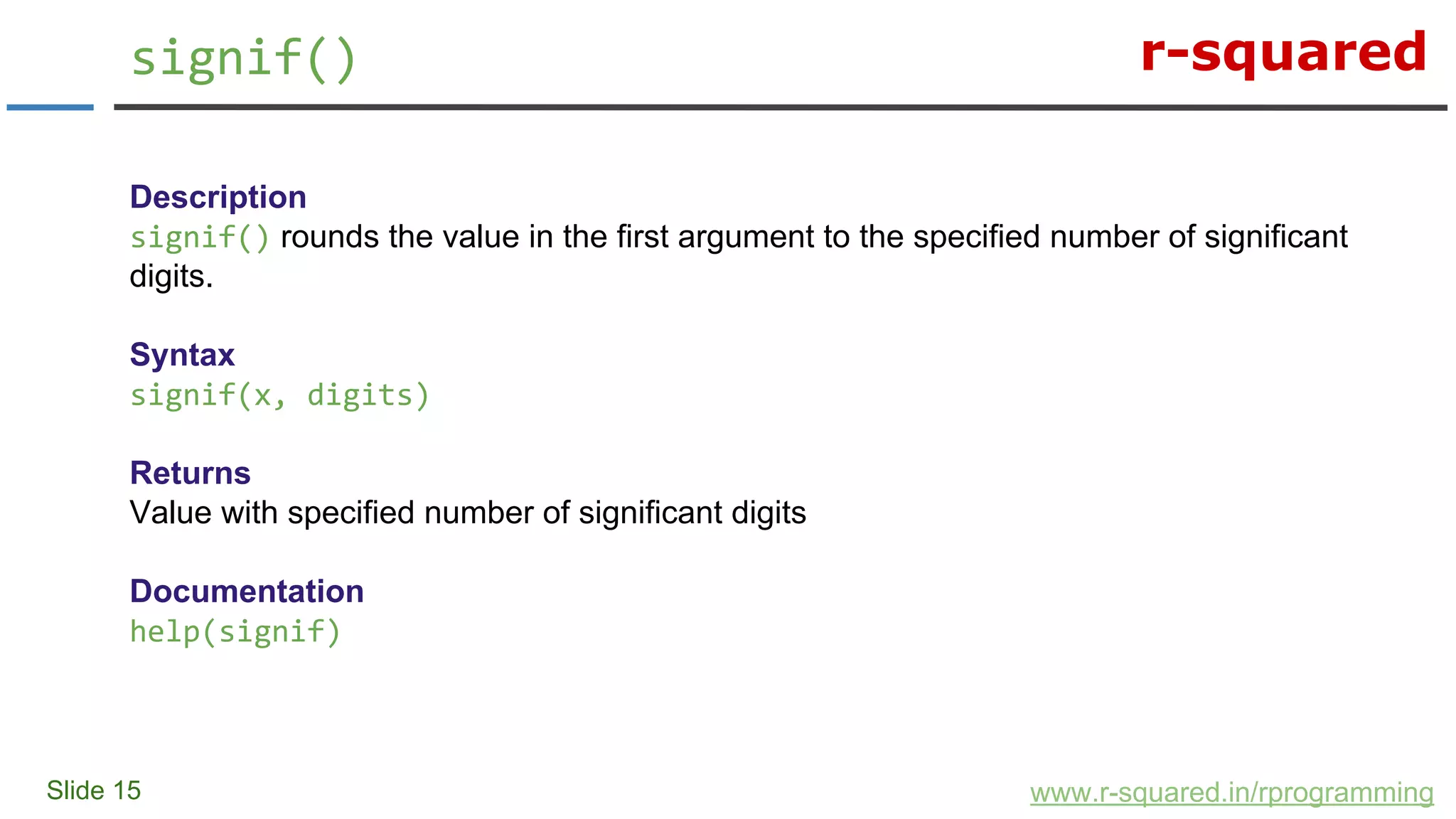
![r-squared Slide 16 signif() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example > x <- 5.3645 > signif(x, 1) [1] 5 > signif(x, 2) [1] 5.4 > signif(x, 3) [1] 5.36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-16-2048.jpg)

![r-squared Slide 18 jitter() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 1 > x <- 1:10 > x [1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 > jitter(x) [1] 1.198246 1.845626 3.171562 3.809923 5.188604 6.171728 7.022194 8.058092 [9] 9.150582 10.142704](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-18-2048.jpg)

![r-squared Slide 20 format() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 1 > x [1] 1.187272 2.080868 3.197517 4.016246 4.979482 6.163807 6.837692 8.013903 8.864735 [10] 9.939144 > format(x, digits = 3) [1] "1.19" "2.08" "3.20" "4.02" "4.98" "6.16" "6.84" "8.01" "8.86" "9.94" > # example 2 > x <- 1:10 > format(x) [1] " 1" " 2" " 3" " 4" " 5" " 6" " 7" " 8" " 9" "10" > format(x, trim = TRUE) [1] "1" "2" "3" "4" "5" "6" "7" "8" "9" "10"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-20-2048.jpg)
![r-squared Slide 21 format() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 3 > format(6.5) [1] "6.5" > format(6.5, nsmall = 3) [1] "6.500" > format(c(6.5, 15.3), digits = 2) [1] " 6.5" "15.3" > format(c(6.5, 15.3), digits = 2, nsmall = 1) [1] " 6.5" "15.3"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-21-2048.jpg)

![r-squared Slide 23 formatC() www.r-squared.in/rprogramming Examples > # example 1 > x <- 1:10 > formatC(x) [1] "1" "2" "3" "4" "5" "6" "7" "8" "9" "10" > formatC(x, width = 6) [1] " 1" " 2" " 3" " 4" " 5" " 6" " 7" " 8" " 9" [10] " 10" > # example 2 > x <- sample(jitter(1:10)) > x [1] 7.0094486 0.9592379 5.8403164 8.8848952 4.9665959 9.9507841 3.1295332 7.8283830 [9] 2.1360850 3.8991551 > formatC(x, digits = 4) [1] "7.009" "0.9592" " 5.84" "8.885" "4.967" "9.951" " 3.13" "7.828" "2.136" [10] "3.899"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericfunction-150416025456-conversion-gate02/75/R-Programming-Numeric-Functions-In-R-23-2048.jpg)

