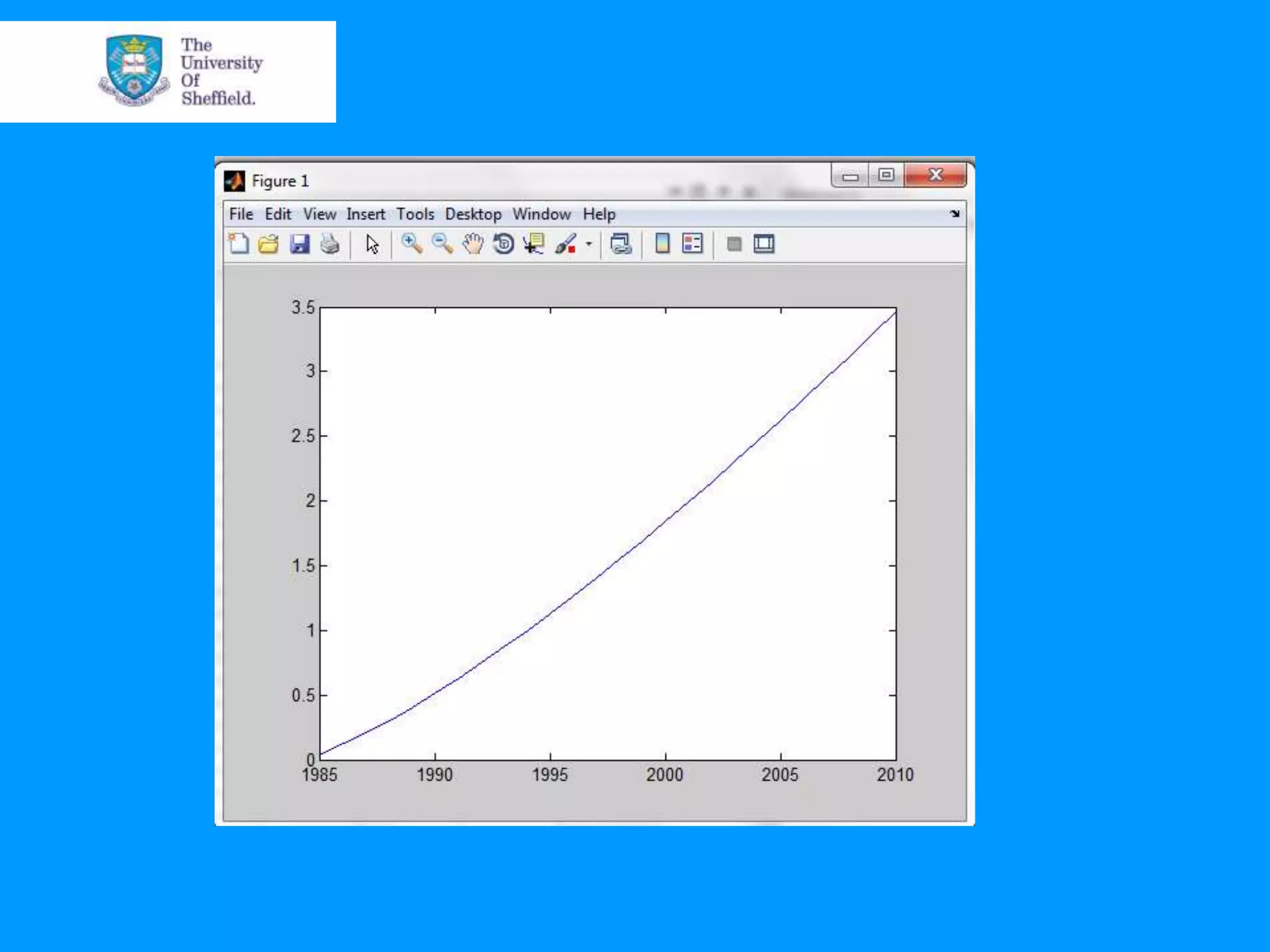
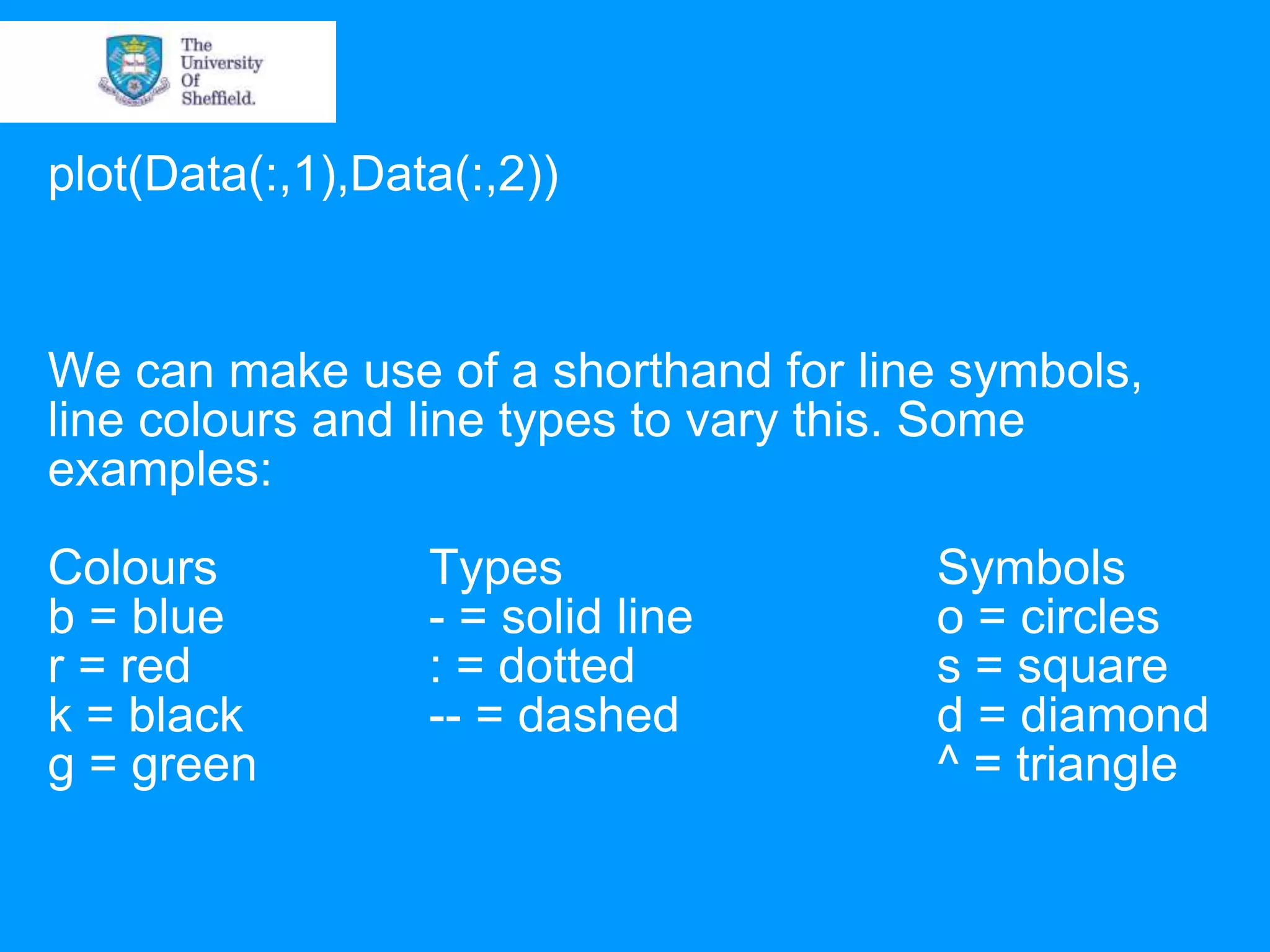
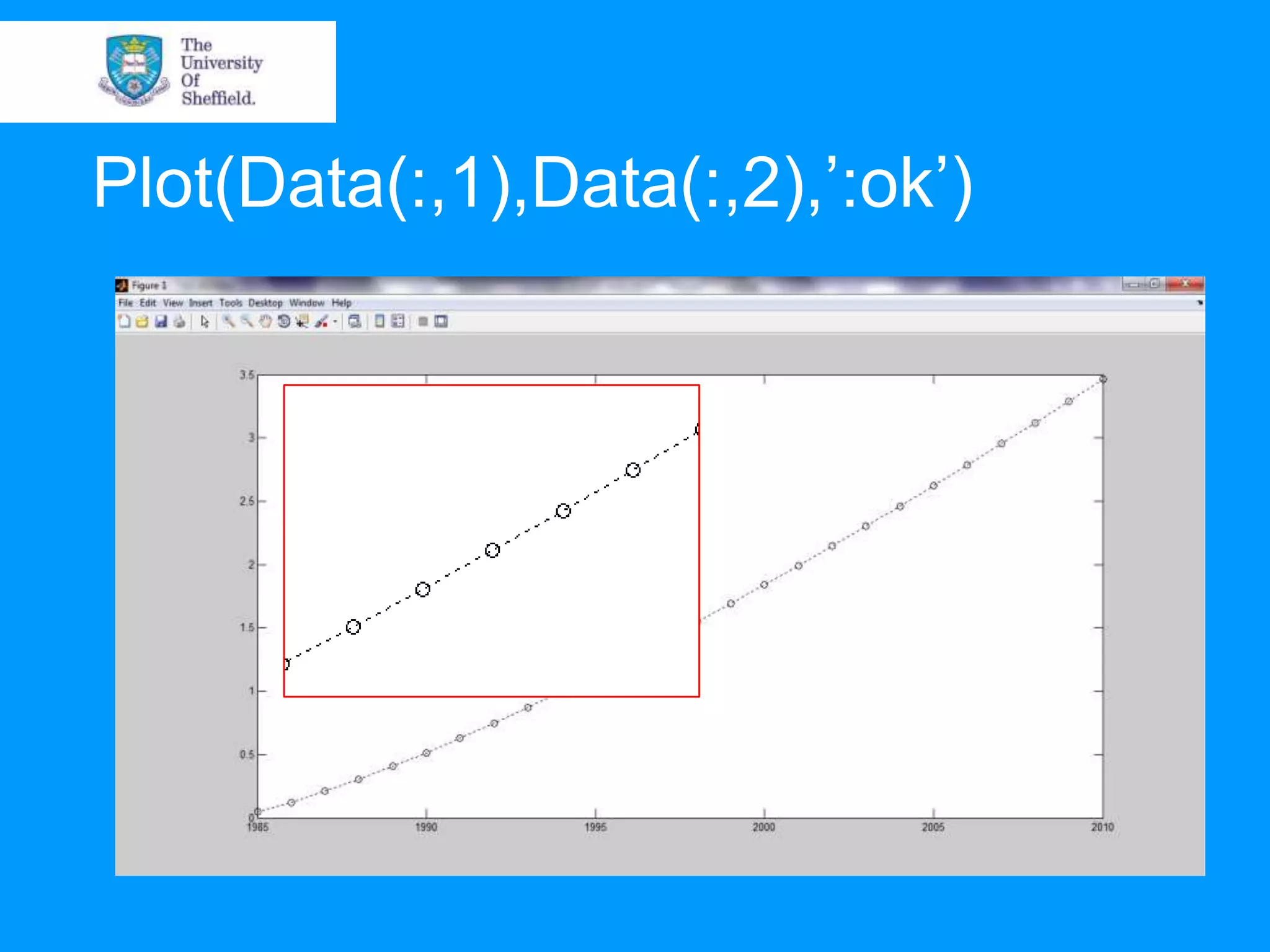
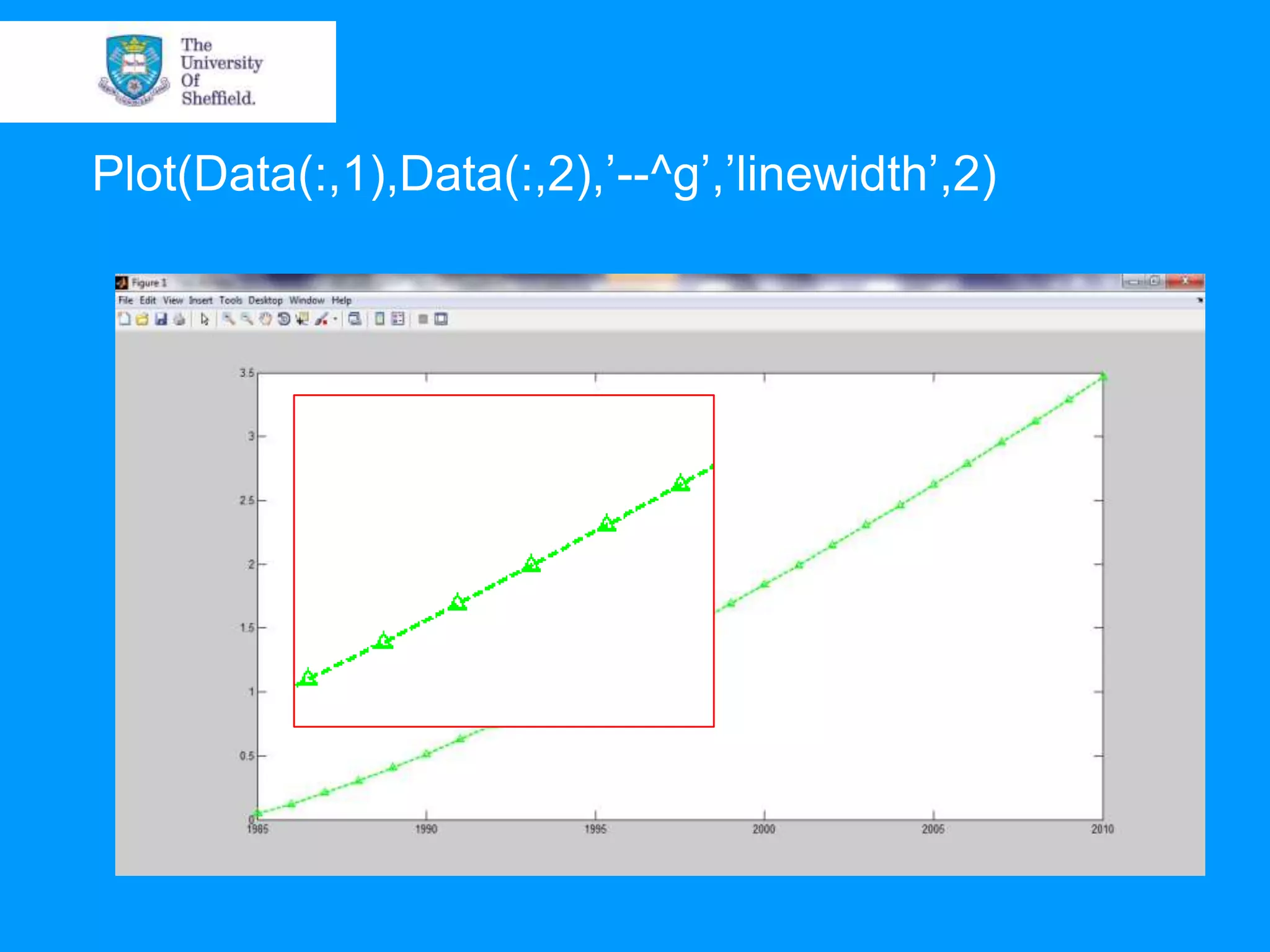
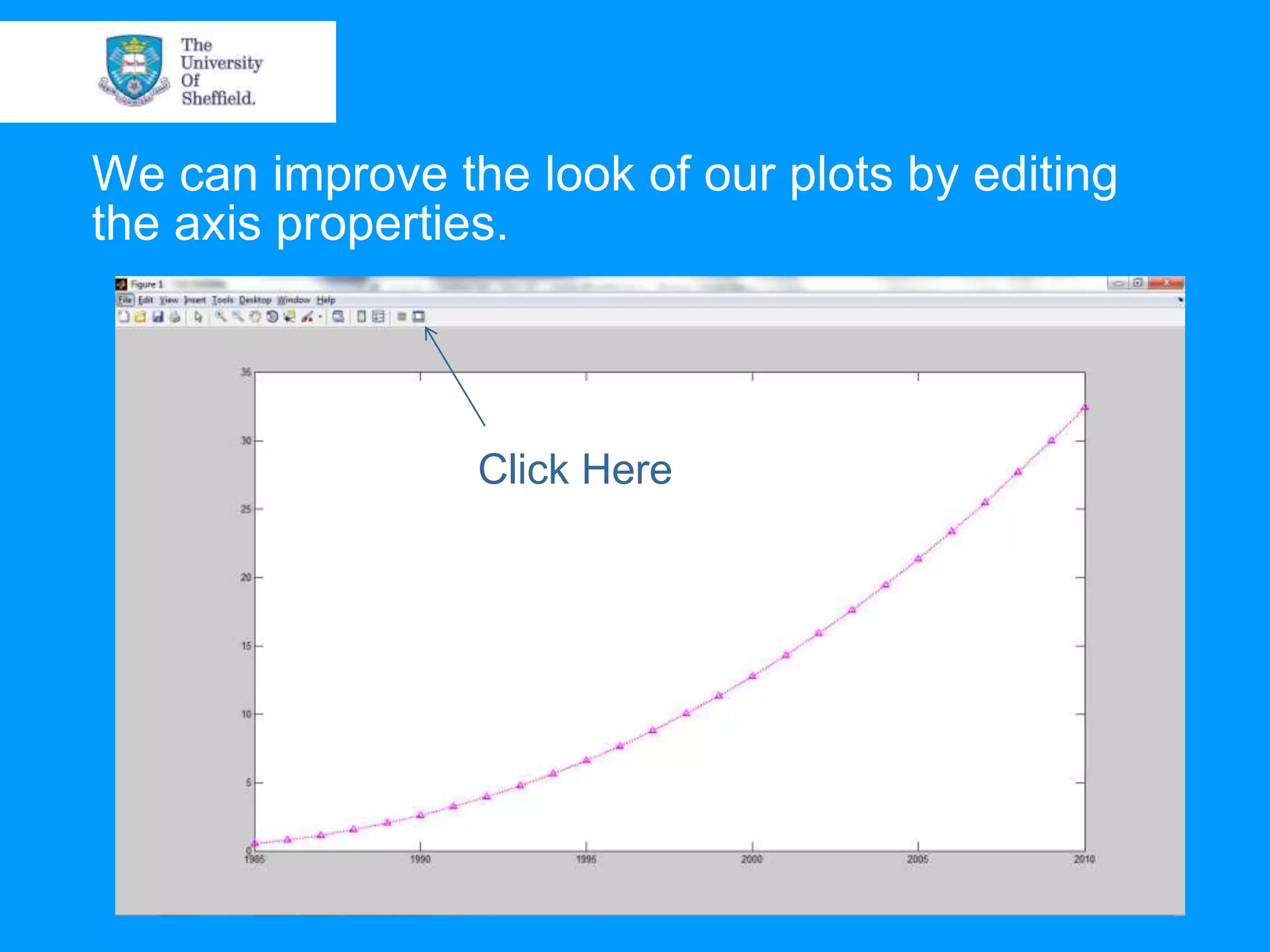
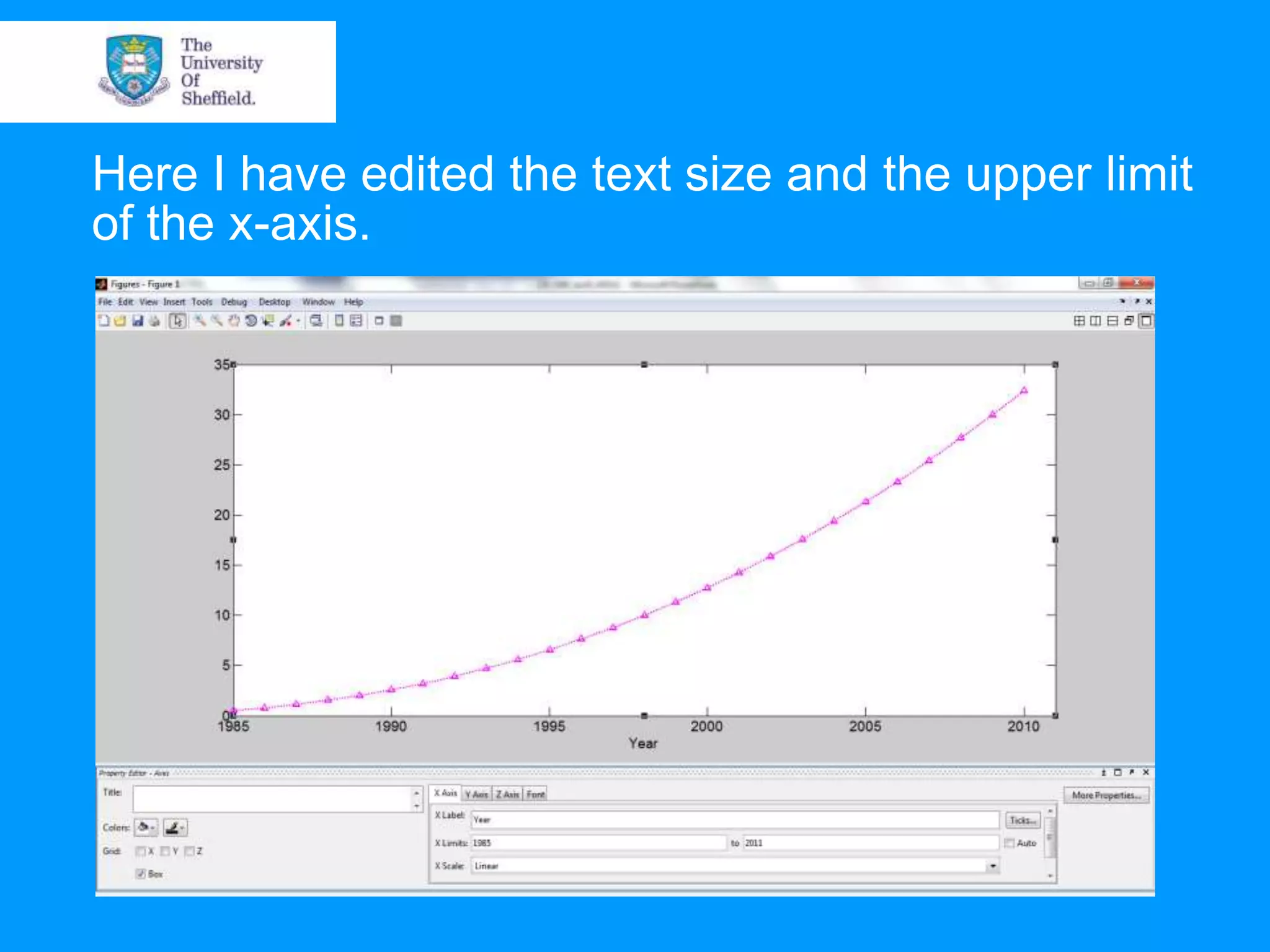
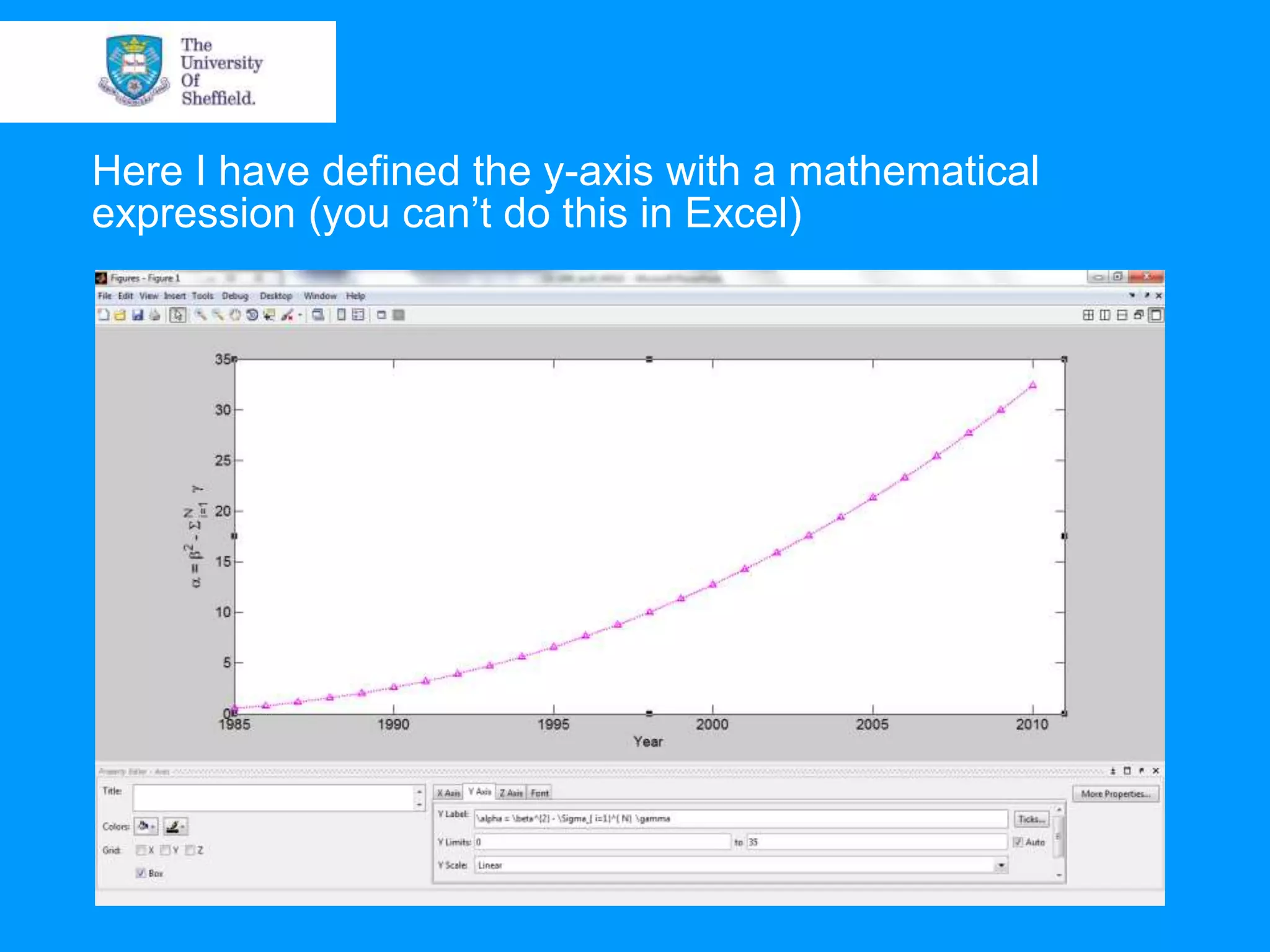
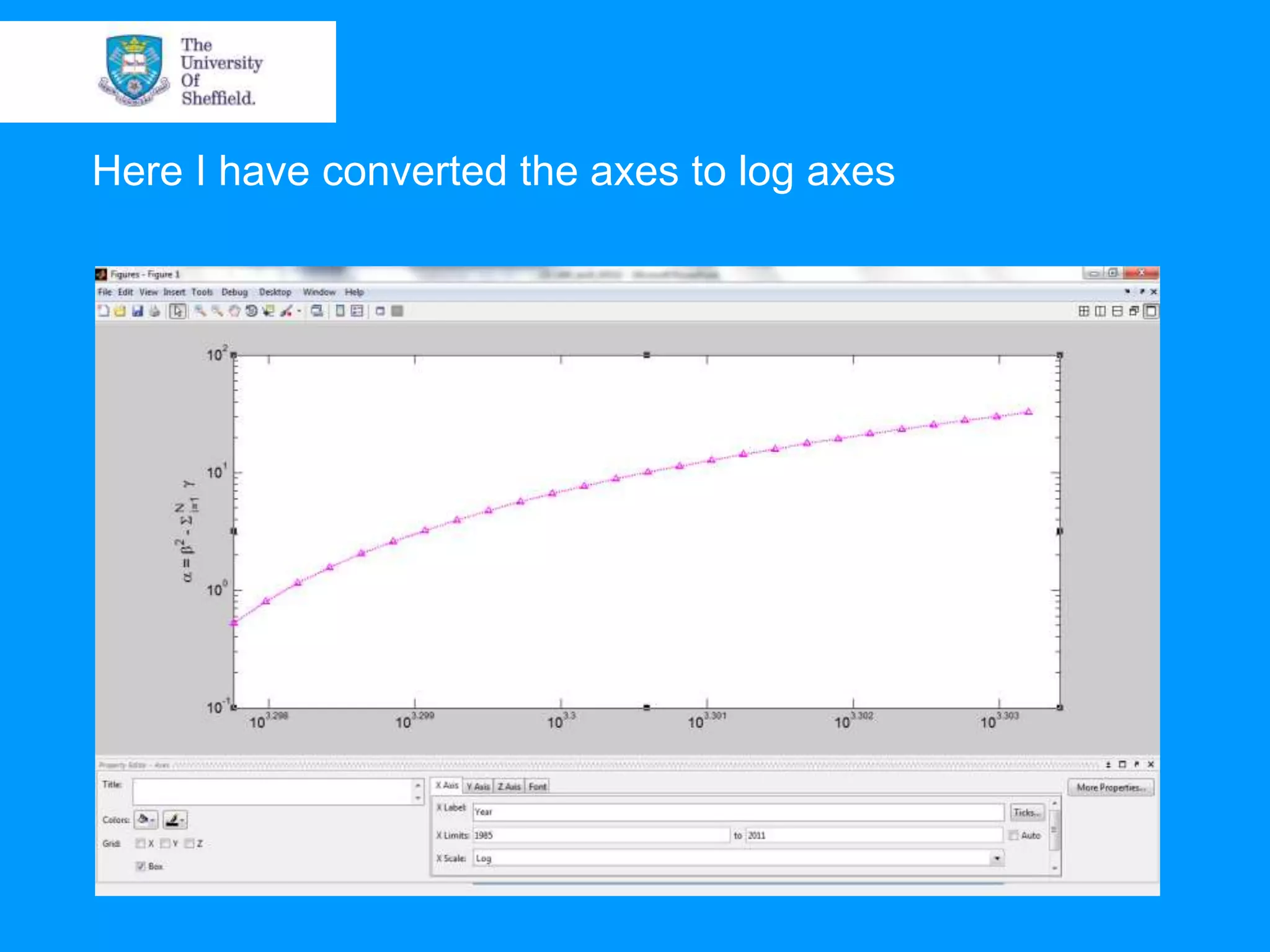
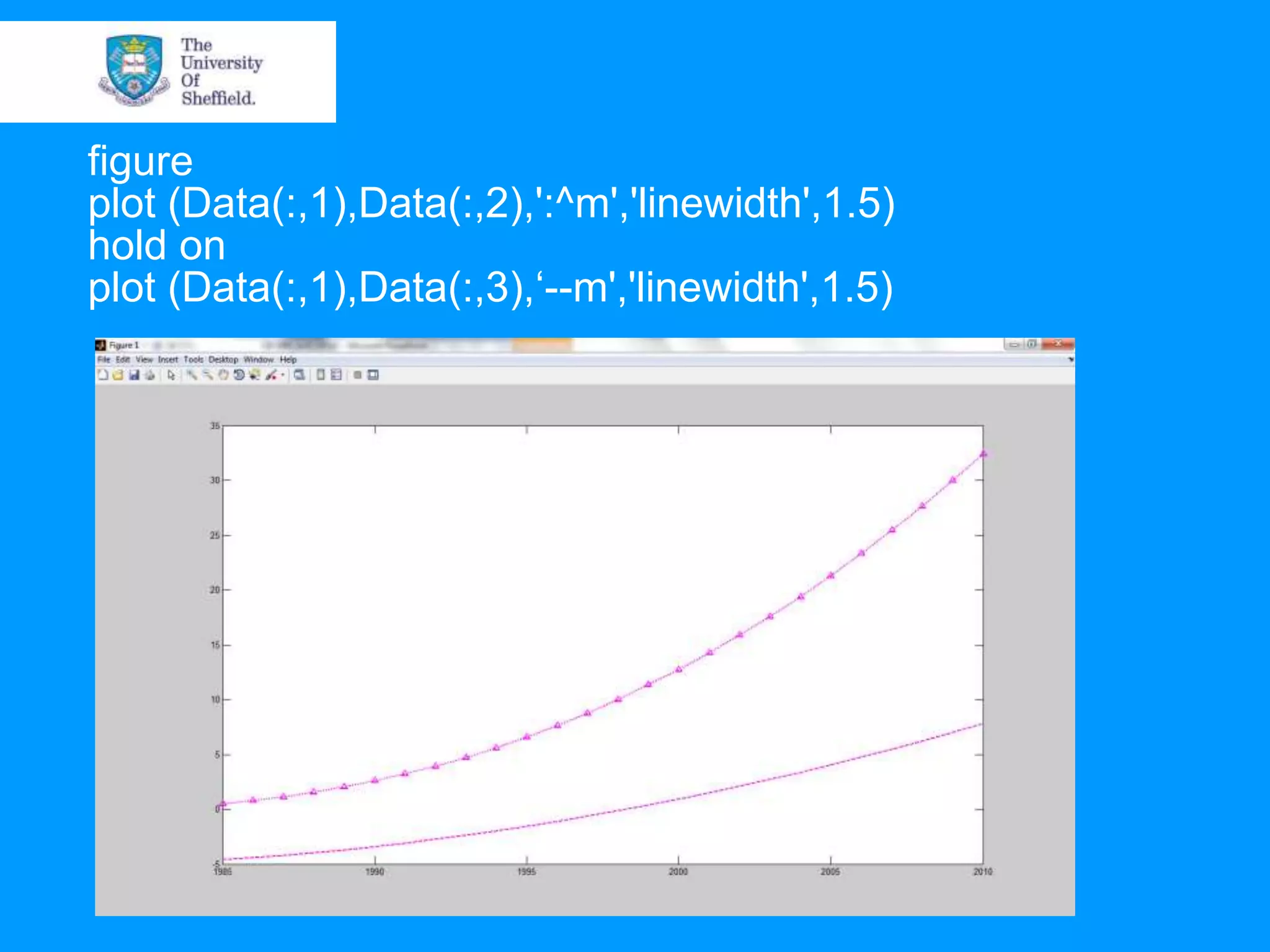
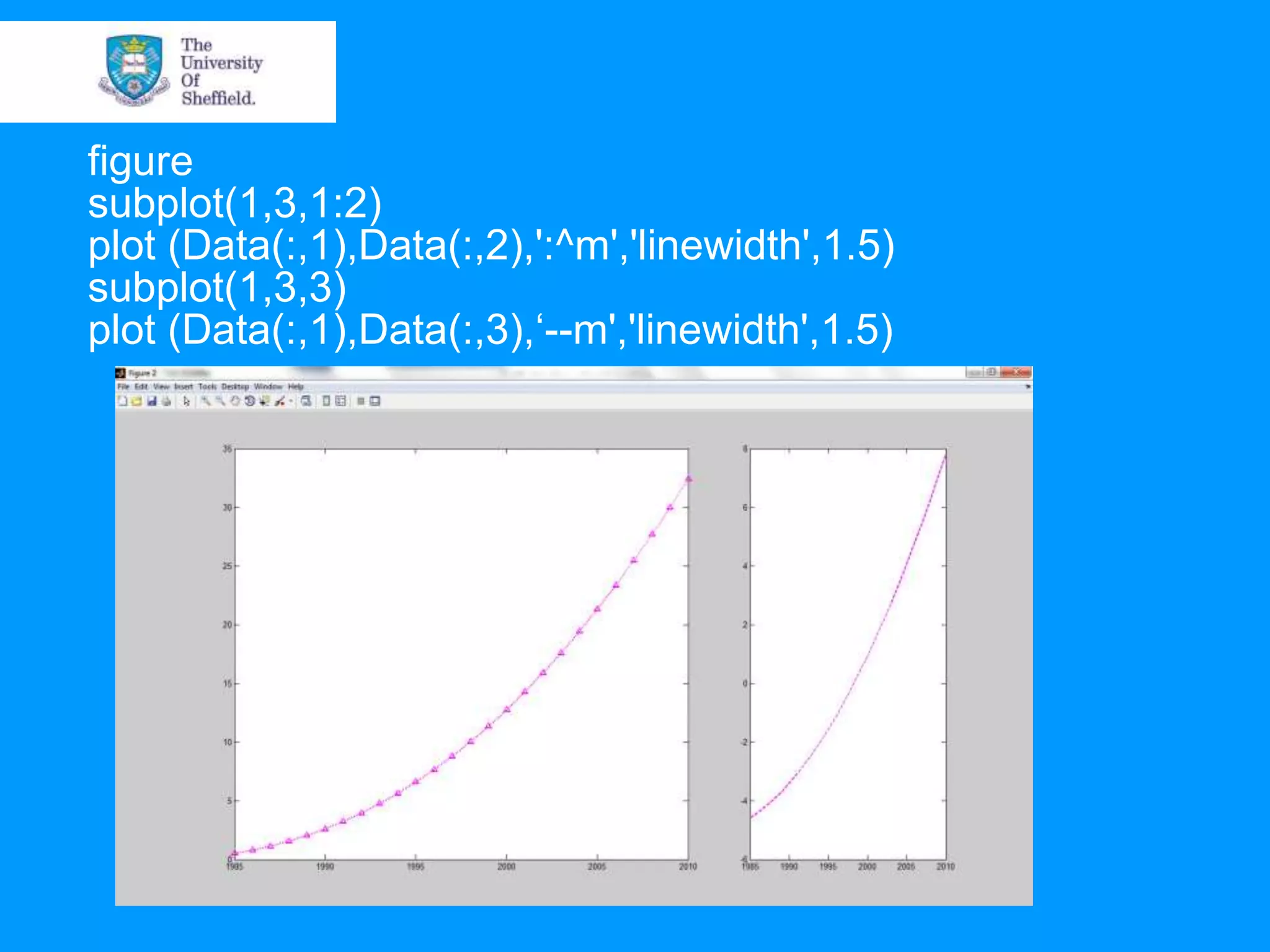
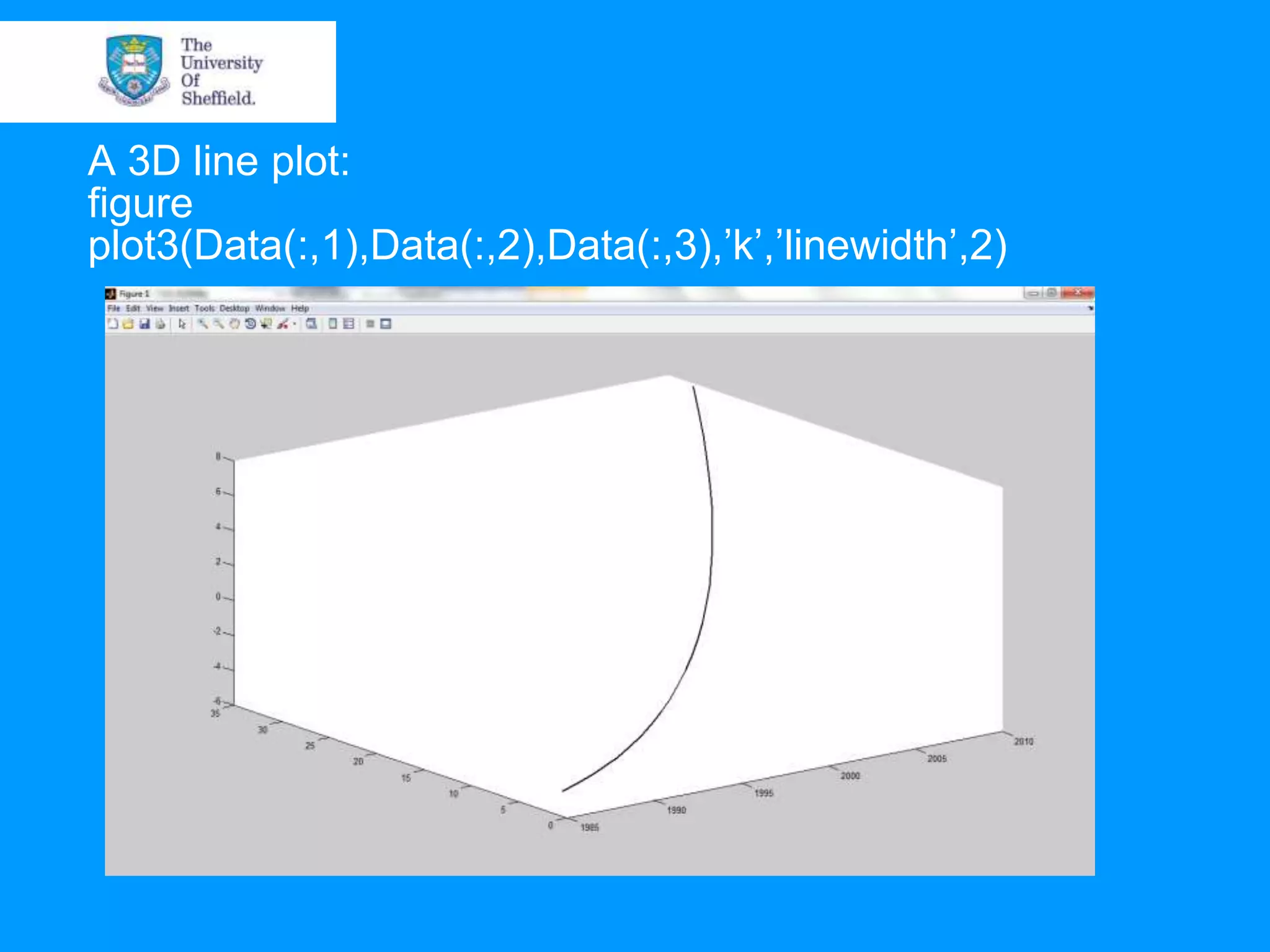
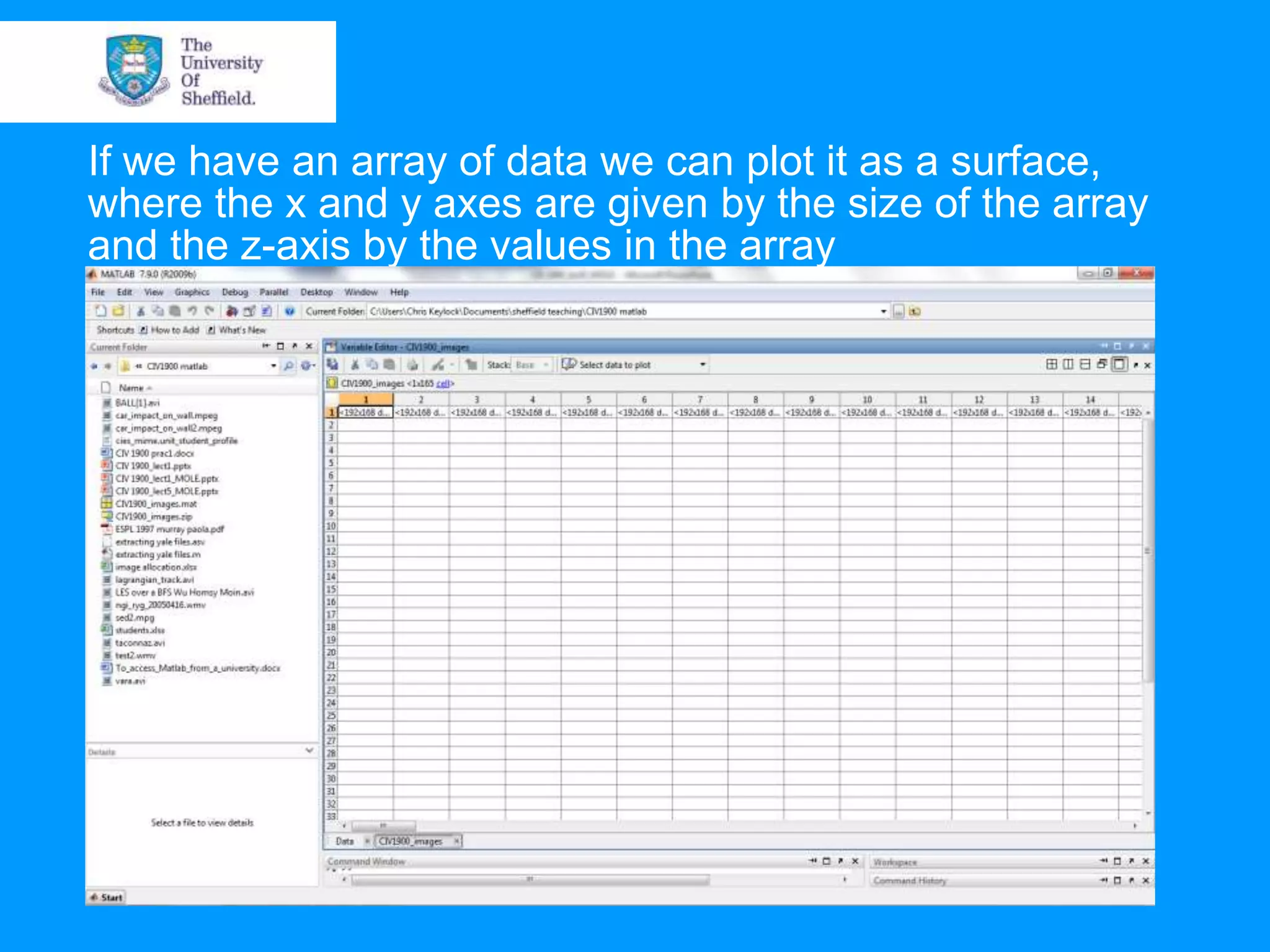
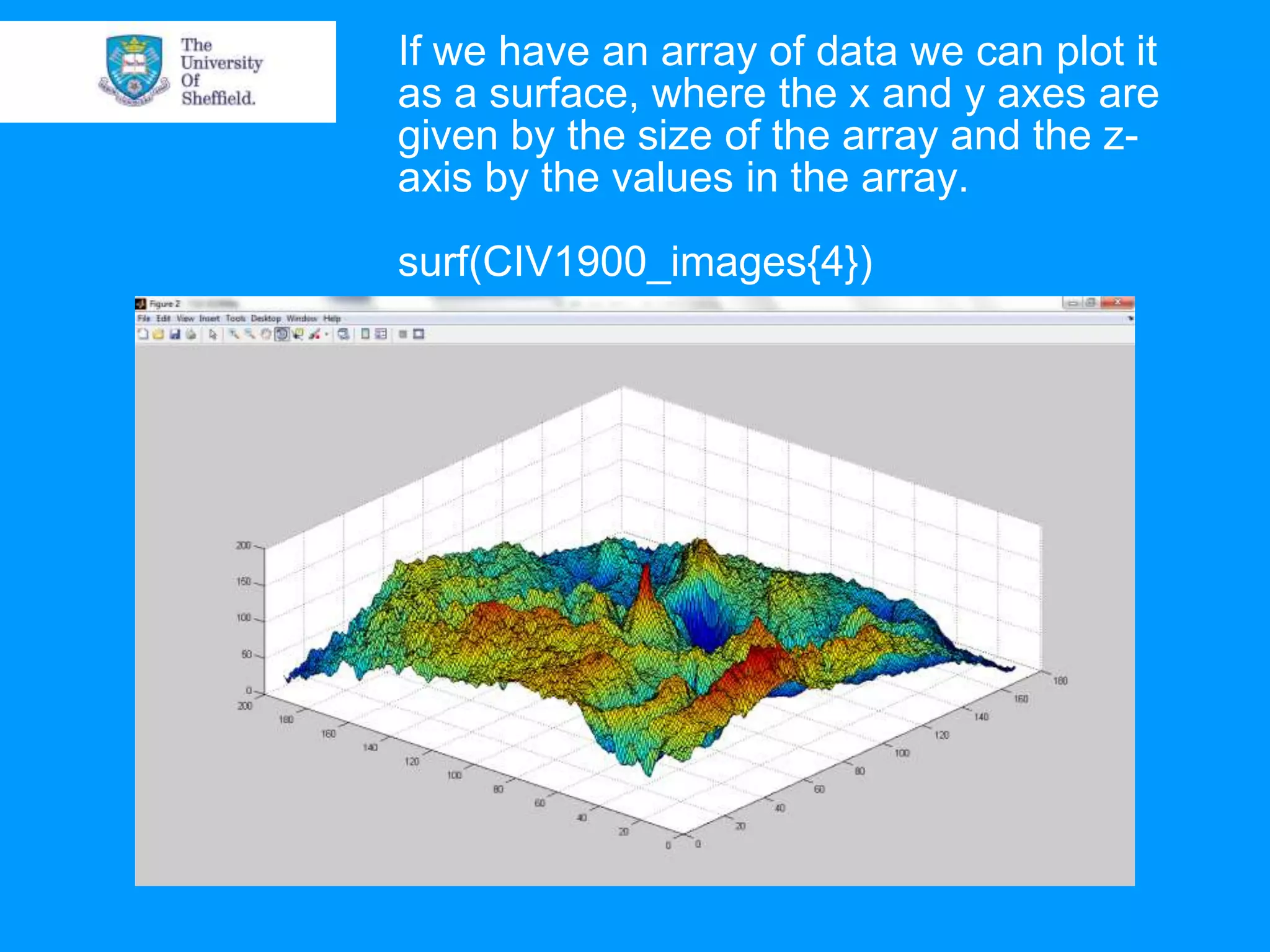
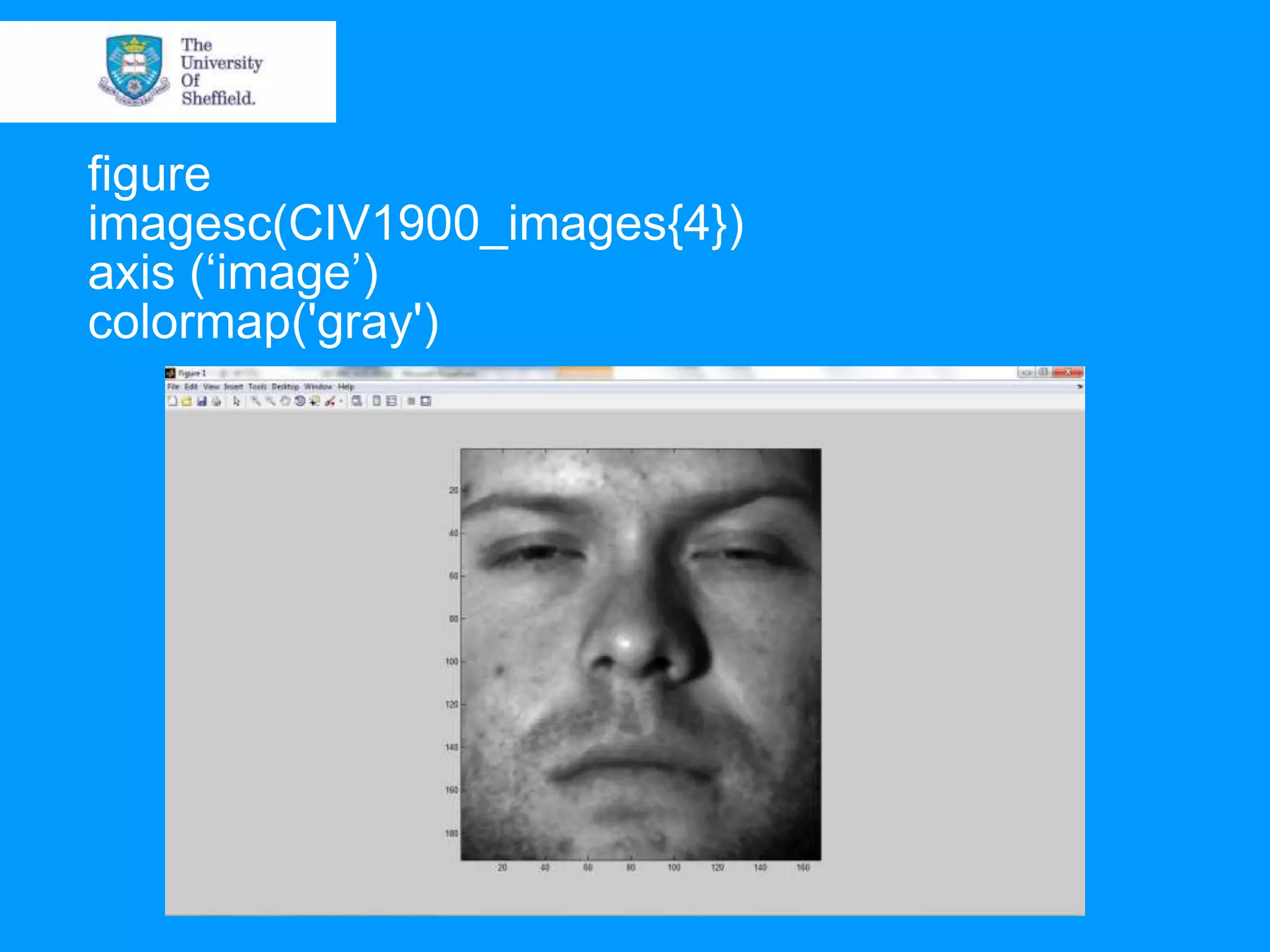
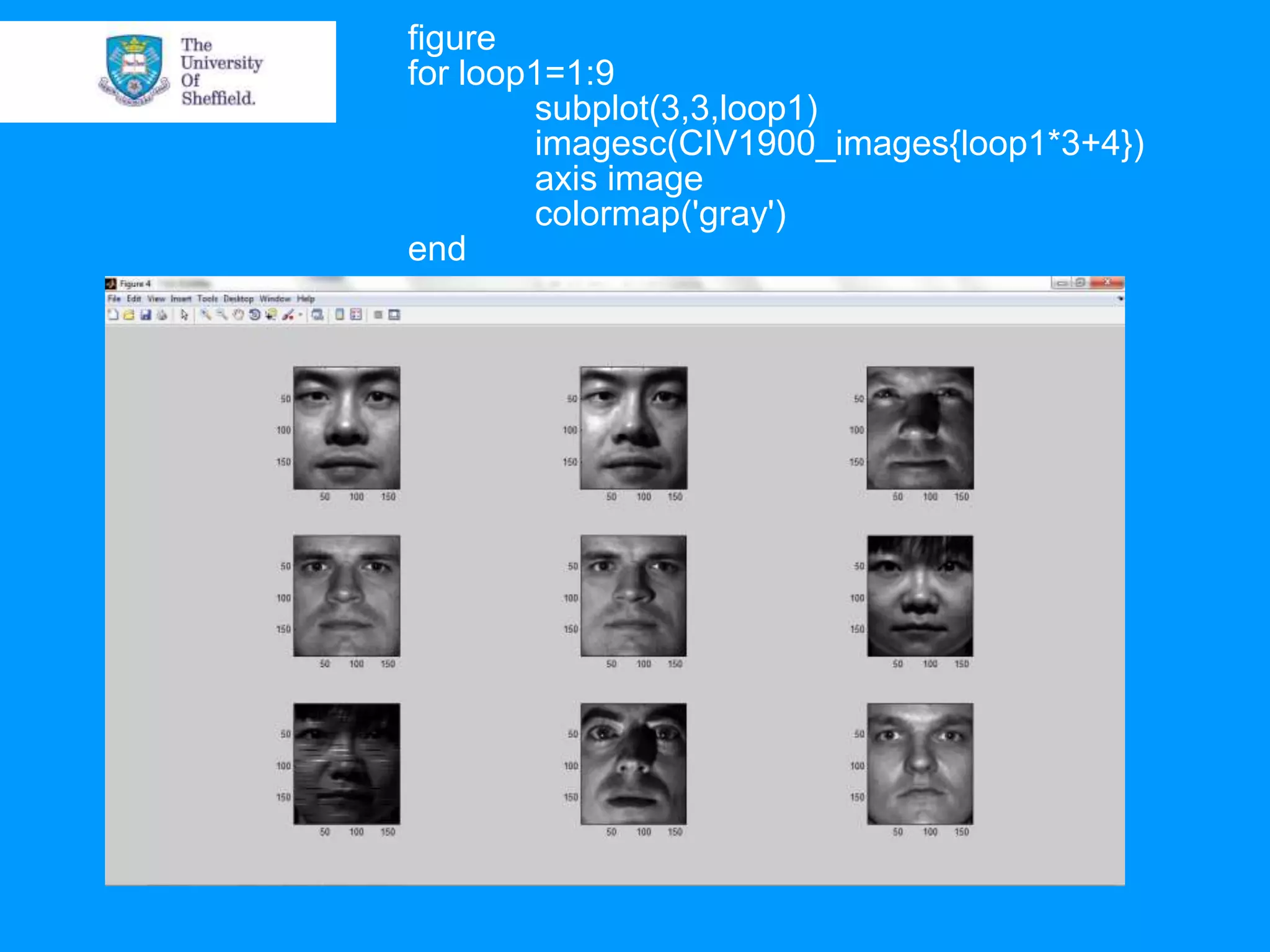
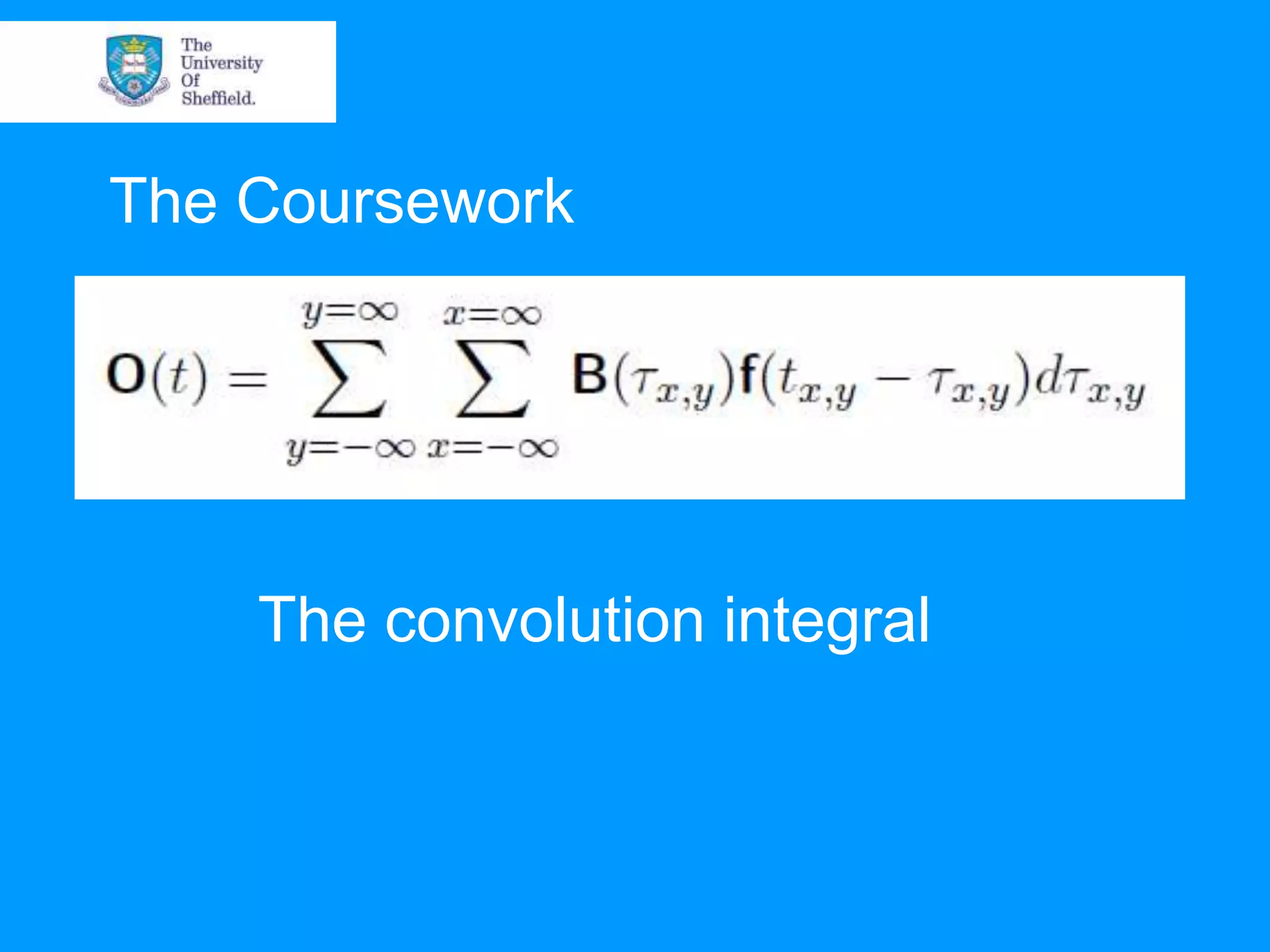
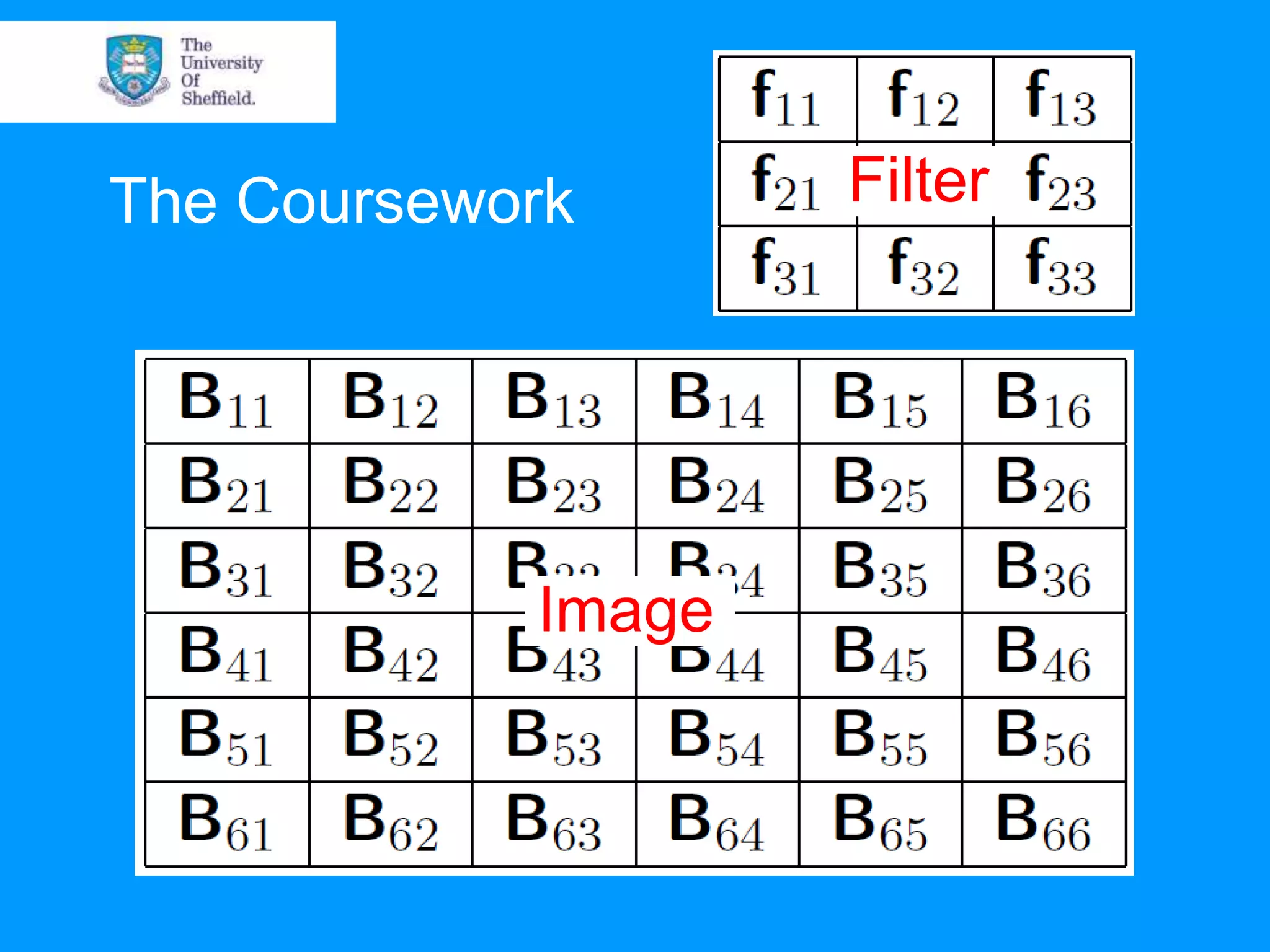
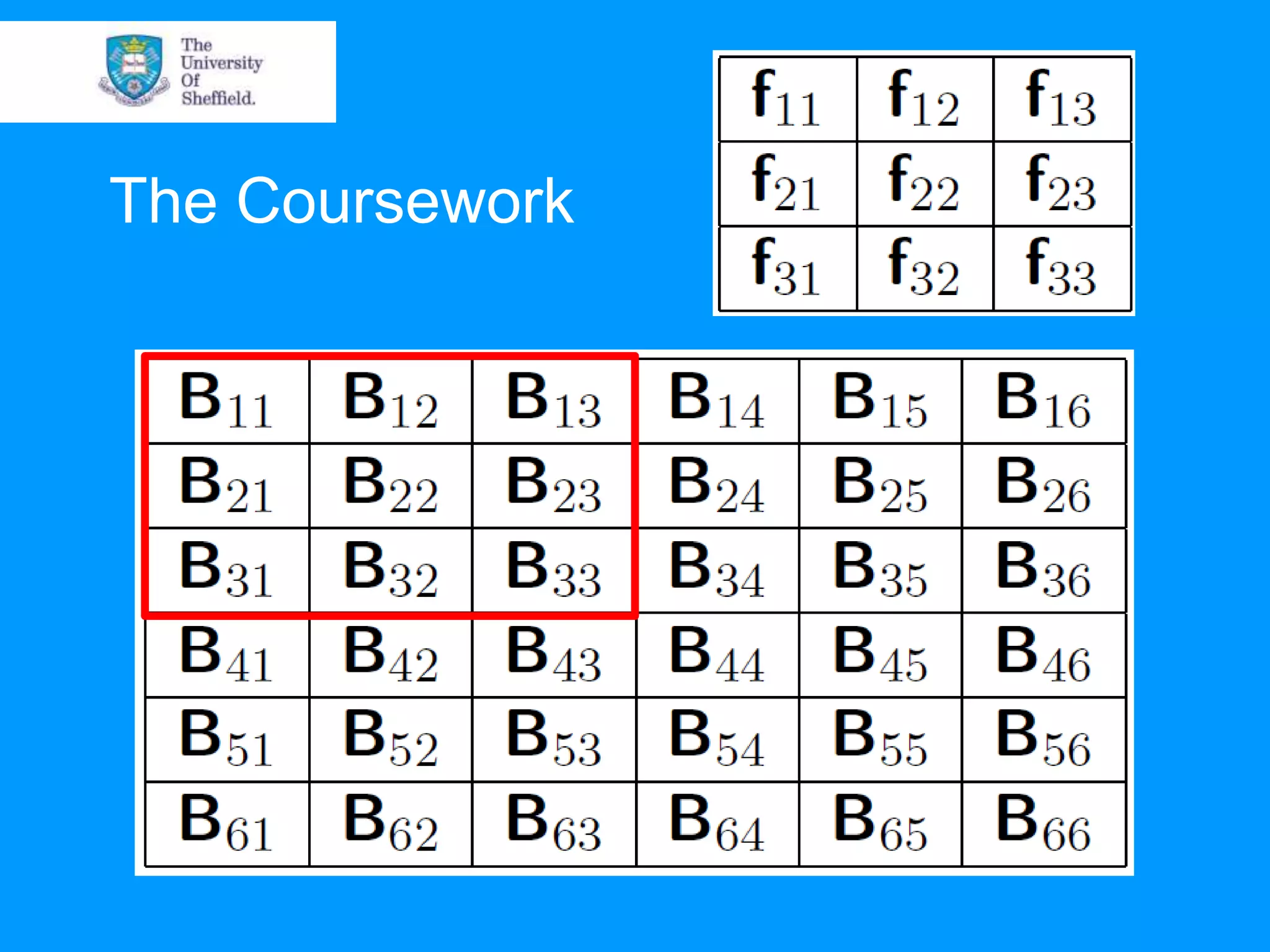
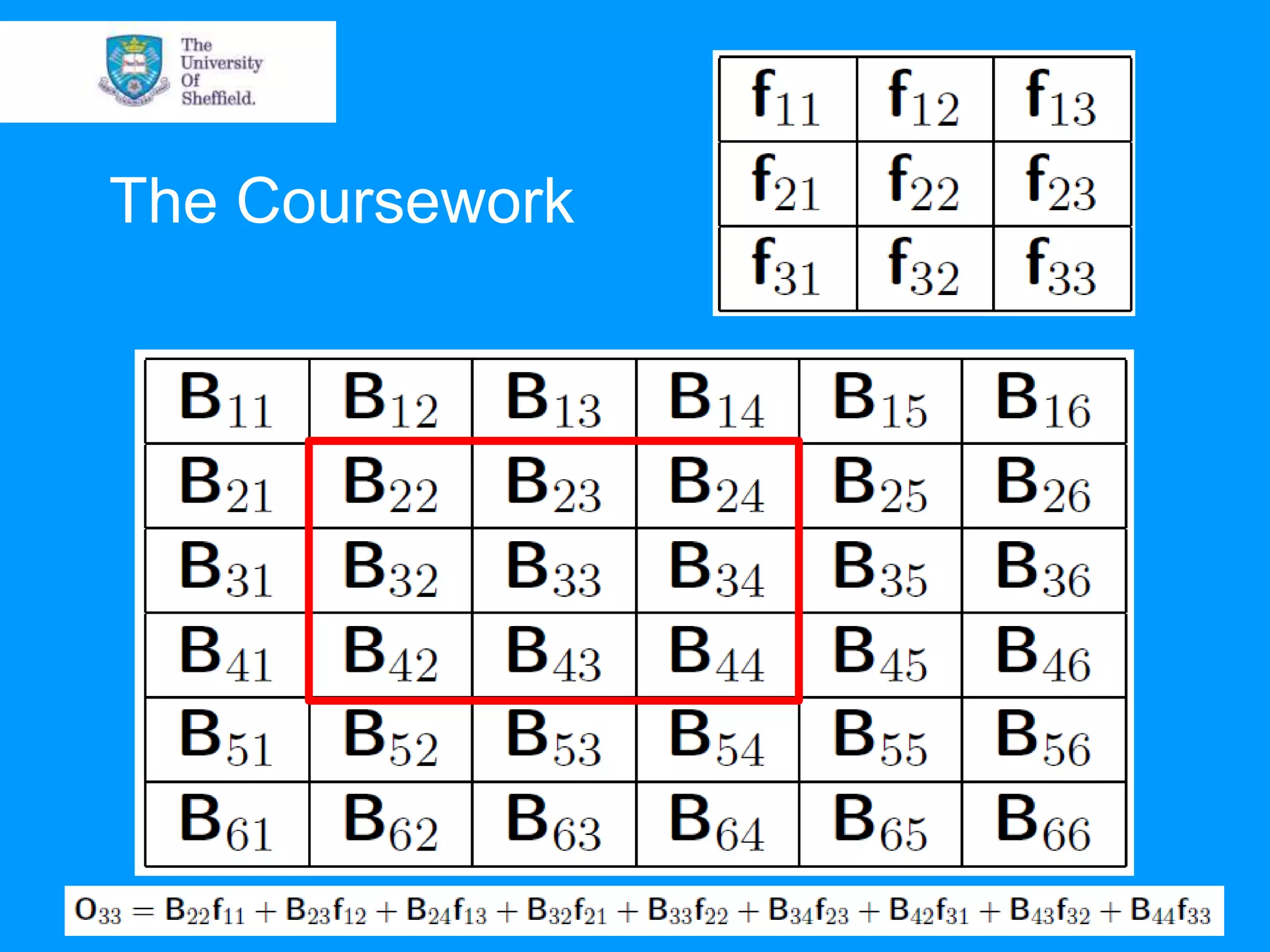
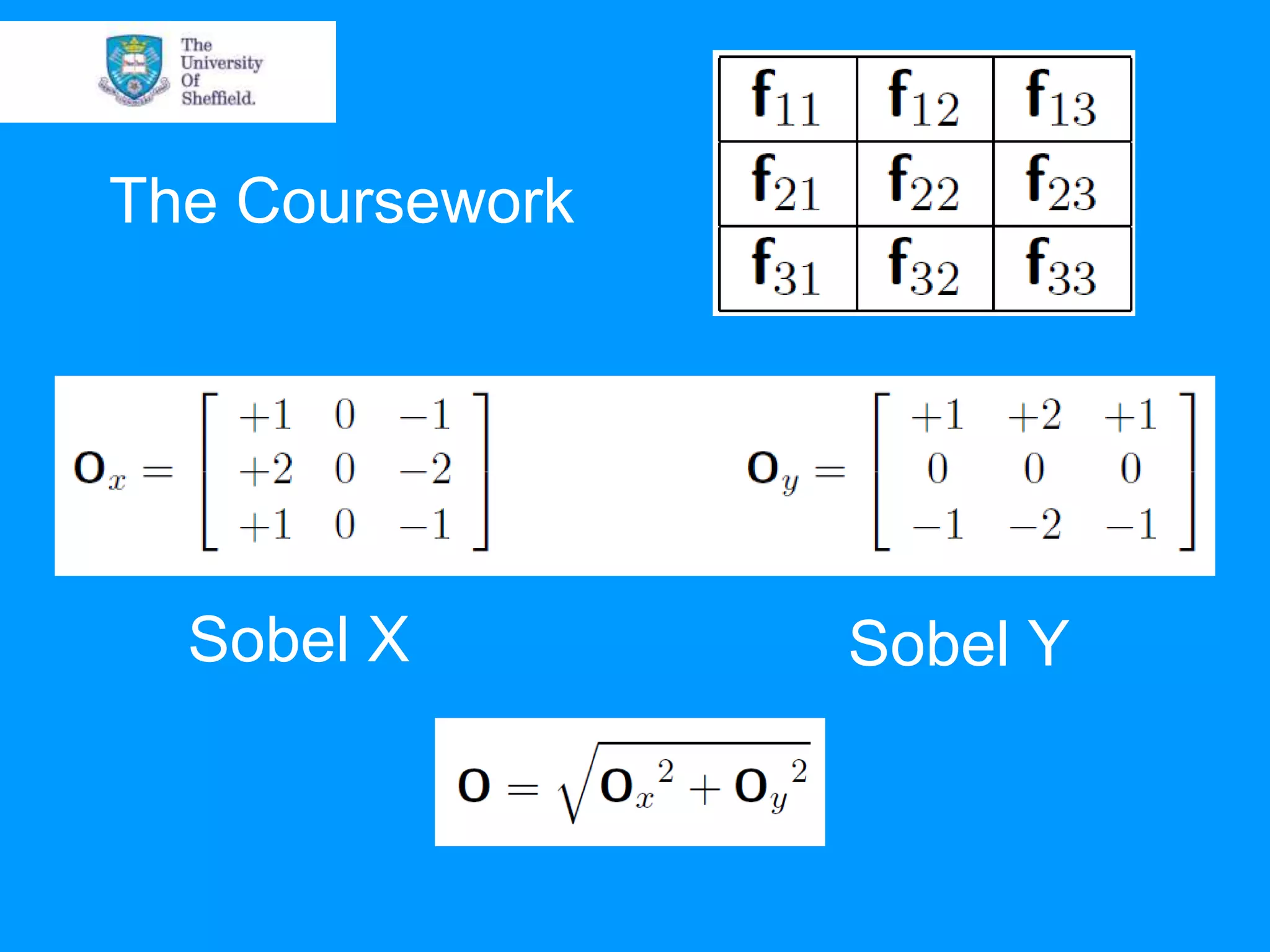
This document provides an overview of plotting and image processing capabilities in Matlab. It discusses how to generate basic scatter plots and customize axis properties. It also explains how digital images are constructed as arrays and can be displayed, rotated, and converted to grayscale using commands like plot, surf, image, and imagesc. The document demonstrates plotting multiple lines and images on the same figure. It describes how image processing techniques like Sobel filtering can be used to detect edges in an image.