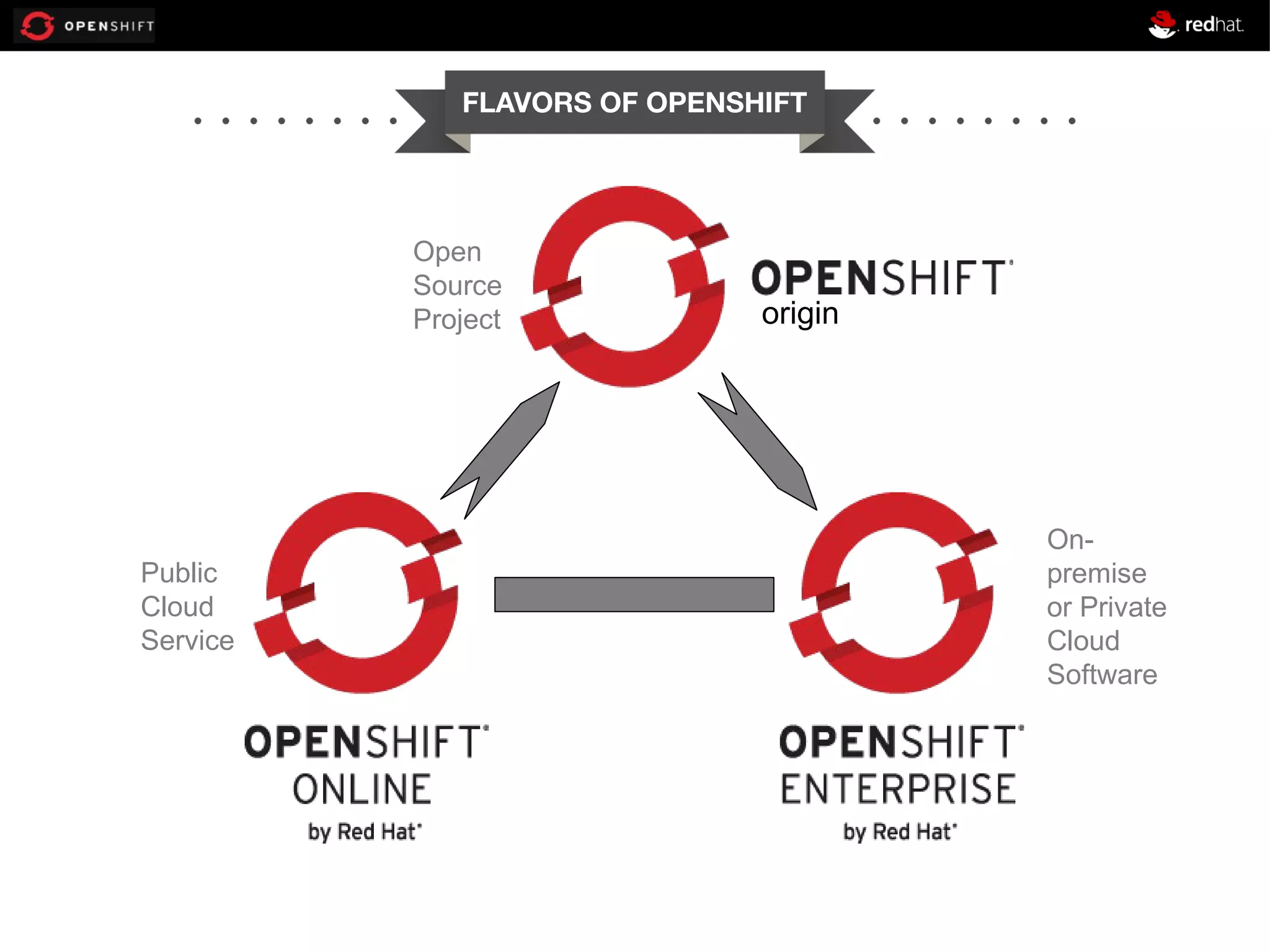
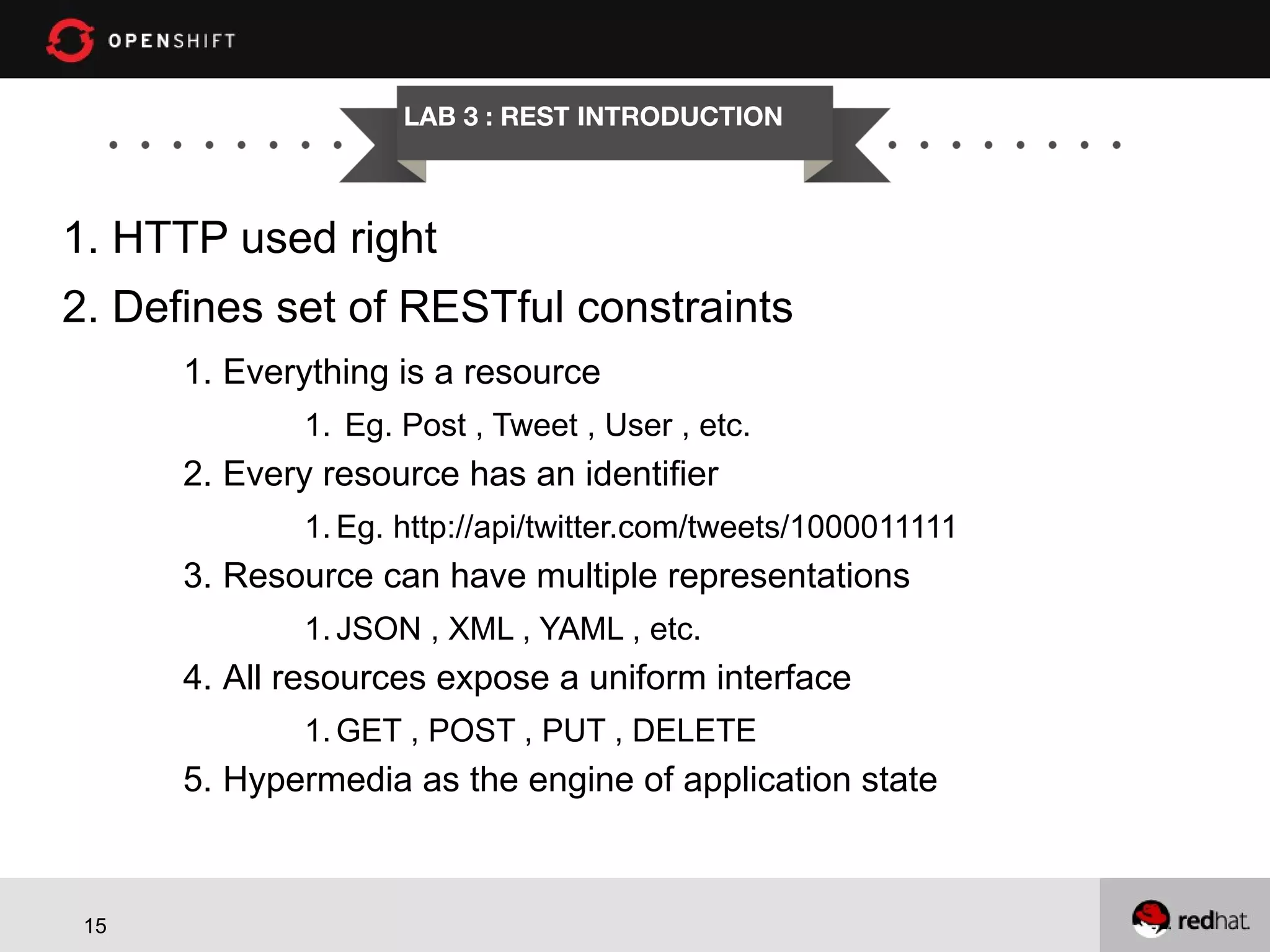
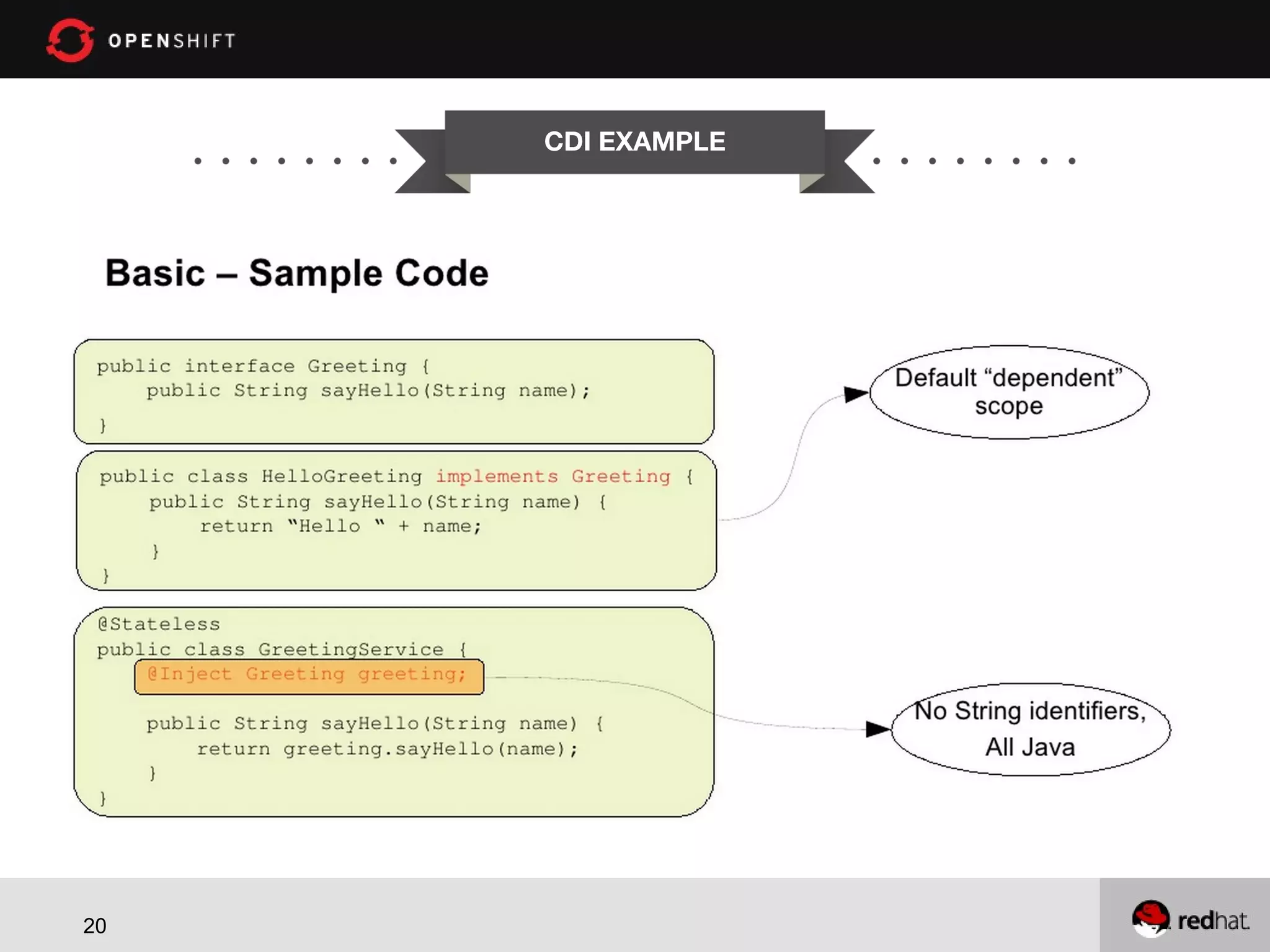
This document provides an agenda for a workshop on developing a location aware application using Java EE 6, MongoDB and OpenShift. The workshop will cover getting started with OpenShift, developing a location aware application using JAX-RS for REST web services, CDI for dependency injection and MongoDB for the database. It will also cover deploying the application to OpenShift. The agenda includes sessions on OpenShift overview, setting up JAX-RS, configuring CDI and MongoDB, implementing CRUD operations and geospatial queries. Code examples will be provided on GitHub for attendees to follow along.














![SOME QUERIES // Find all the jobs with skill as mongodb db.jobs.find({"skills":"mongodb"}) // Find all the jobs with python as skill and near to given location db.jobs.find({"lngLat":{$near : [139.69 , 35.68]}, "skills":"python"}) // Find all the python or mongodb jobs near to given location db.jobs.find({"lngLat":{$near : [139.69 , 35.68]}, "skills":{$in : ["mongodb","python"]}}) 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jee6andnosqlinthecloud-131018083553-phpapp01/75/Java-EE-6-and-NoSQL-Workshop-DevFest-Austria-24-2048.jpg)





![HOW TO MAKE IT WORK 1) Put your coordinates into an array { loc : [ 50 , 30 ] } //SUGGESTED OPTION { loc : { x : 50 , y : 30 } } { loc : { foo : 50 , y : 30 } } 1) { loc : { lon : 40.739037, lat: 73.992964 } } 2) Make a 2d index db.places.ensureIndex( { loc : "2d" } ) 3) 33 If you use latitude and longitude as your coordinate system, always store longitude first. MongoDB’s 2d spherical index operators only recognize [ longitude, latitude] ordering.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jee6andnosqlinthecloud-131018083553-phpapp01/75/Java-EE-6-and-NoSQL-Workshop-DevFest-Austria-33-2048.jpg)