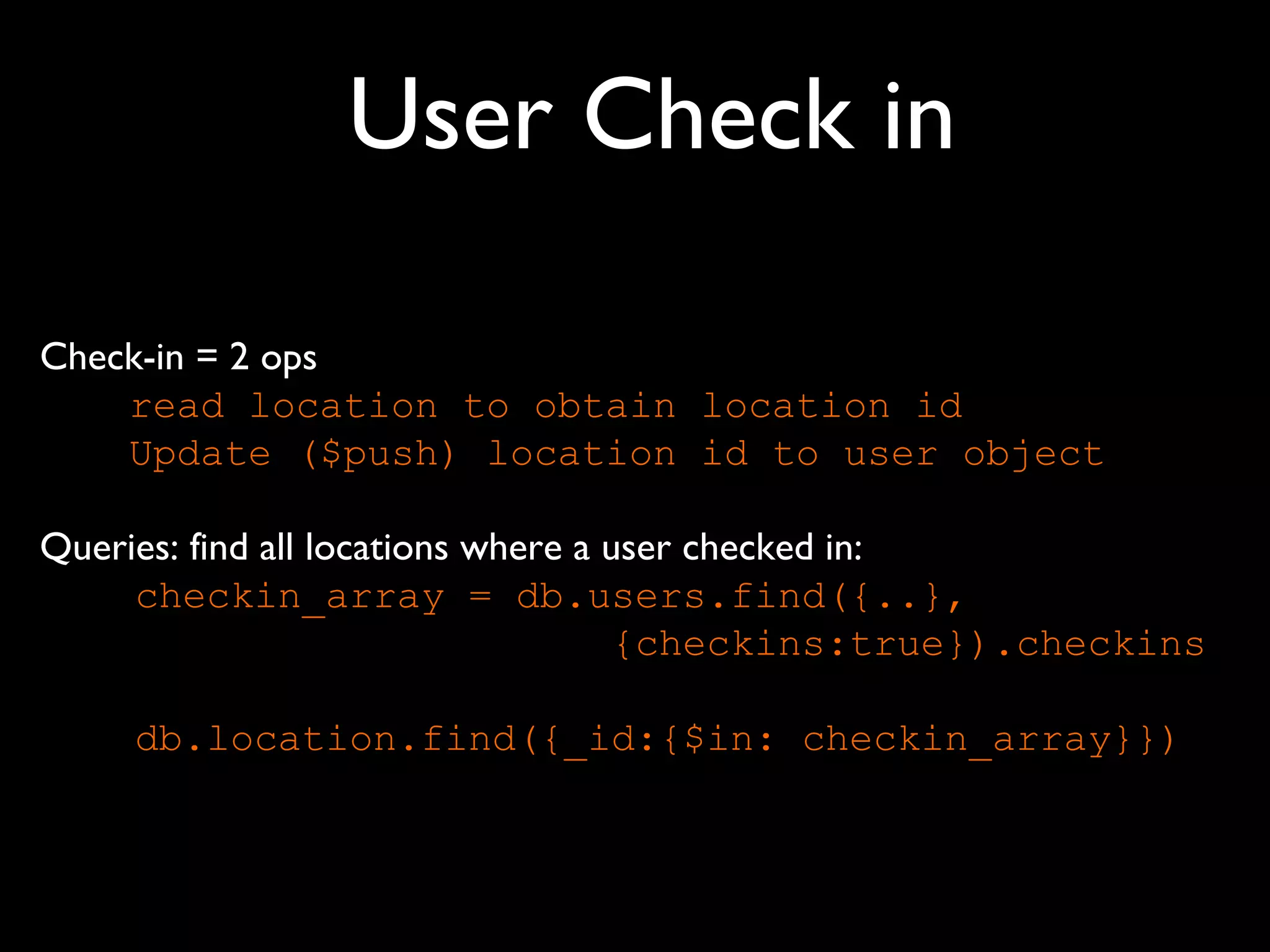
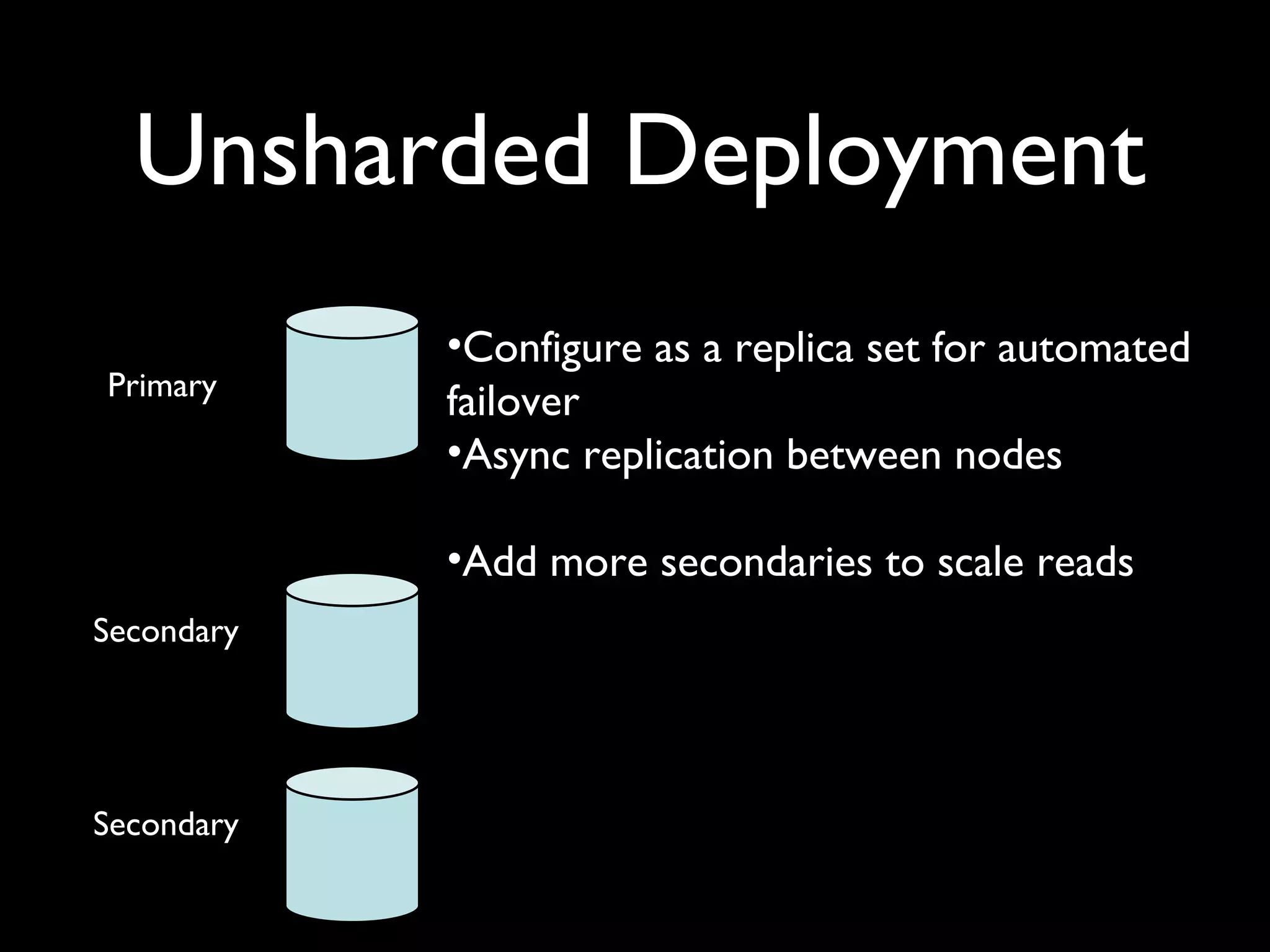
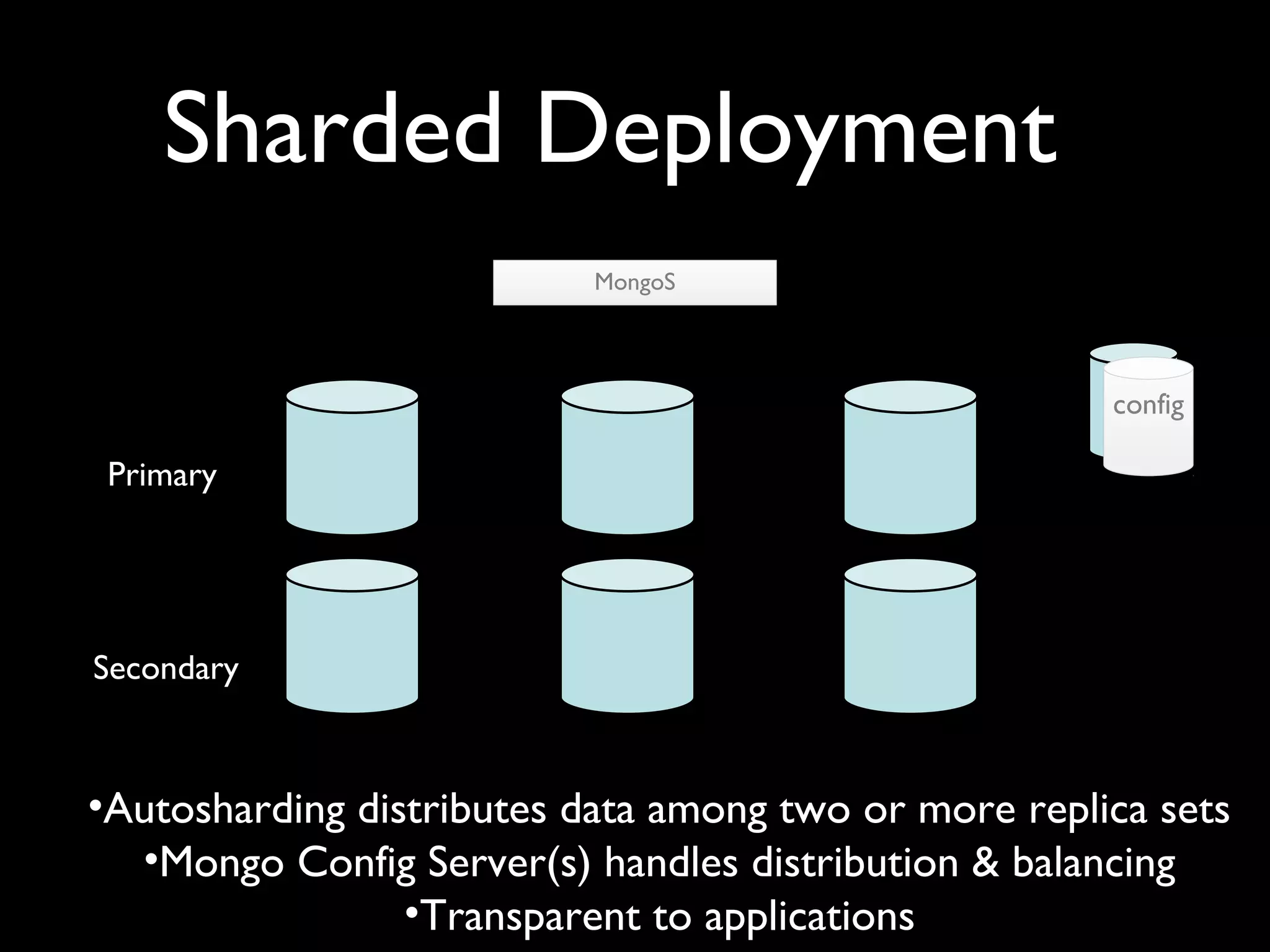
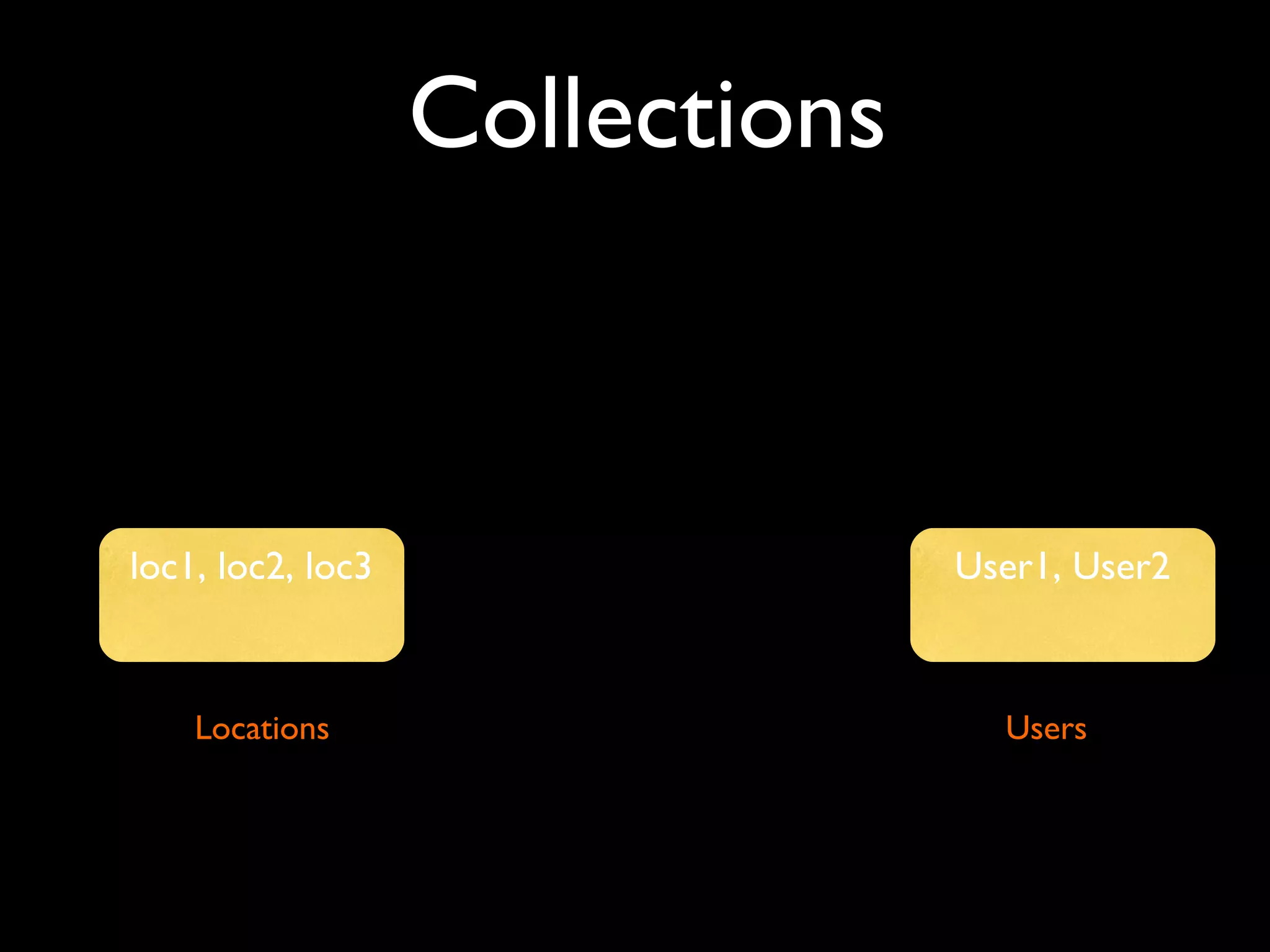
The document introduces building web applications using MongoDB, a document-oriented database. It discusses MongoDB's data modeling and querying capabilities, including examples of modeling user and location data for a check-in application. The document also covers indexing, insertion, updating, and analytics queries for the sample location and user data models.







![JSON Sample Doc { _id : ObjectId("4c4ba5c0672c685e5e8aabf3"), author : "roger", date : "Sat Jul 24 2010 19:47:11 GMT-0700 (PDT)", text : ”MongoSF", tags : [ ”San Francisco", ”MongoDB" ] } Notes: - _id is unique, but can be anything you’d like](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-10-2048.jpg)



![Places v2 location1 = { name: "10gen East Coast”, address: "17 West 18th Street 8th Floor”, city: "New York”, zip: "10011”, tags: [“business”, “mongodb”] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-14-2048.jpg)
![Places v2 location1 = { name: "10gen East Coast”, address: "17 West 18th Street 8th Floor”, city: "New York”, zip: "10011”, tags: [“business”, “mongodb”] } db.locations.find({zip:”10011”, tags:”business”})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-15-2048.jpg)
![Places v3 location1 = { name: "10gen East Coast”, address: "17 West 18th Street 8th Floor”, city: "New York”, zip: "10011”, tags: [“business”, “mongodb”], latlong: [40.0,72.0] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-16-2048.jpg)
![Places v3 location1 = { name: "10gen East Coast”, address: "17 West 18th Street 8th Floor”, city: "New York”, zip: "10011”, tags: [“business”, “cool place”], latlong: [40.0,72.0] } db.locations.ensureIndex({latlong:”2d”})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-17-2048.jpg)
![location1 = { Places v3 name: "10gen HQ”, address: "17 West 18th Street 8th Floor”, city: "New York”, zip: "10011”, tags: [“business”, “cool place”], latlong: [40.0,72.0] } db.locations.ensureIndex({latlong:”2d”}) db.locations.find({latlong:{$near:[40,70]}})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-18-2048.jpg)
![location1 = { Places v4 name: "10gen HQ”, address: "17 West 18th Street 8th Floor”, city: "New York”, zip: "10011”, latlong: [40.0,72.0], tags: [“business”, “cool place”], tips: [ {user:"nosh", time:6/26/2010, tip:"stop by for office hours on Wednesdays from 4-6pm"}, {.....}, ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-19-2048.jpg)
![Querying your Places Creating your indexes db.locations.ensureIndex({tags:1}) db.locations.ensureIndex({name:1}) db.locations.ensureIndex({latlong:”2d”}) Finding places: db.locations.find({latlong:{$near:[40,70]}}) With regular expressions: db.locations.find({name: /^typeaheadstring/) By tag: db.locations.find({tags: “business”})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-20-2048.jpg)


![Users user1 = { name: “nosh” email: “nosh@10gen.com”, . . . checkins: [{ location: “10gen HQ”, ts: 9/20/2010 10:12:00, …}, … ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-23-2048.jpg)

![Alternative user1 = { name: “nosh” email: “nosh@10gen.com”, . . . checkins: [4b97e62bf1d8c7152c9ccb74, 5a20e62bf1d8c736ab] } checkins [] = ObjectId reference to locations collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingwebapplicationswithmongodbpresentation-121230160430-phpapp01/75/Building-web-applications-with-mongo-db-presentation-25-2048.jpg)