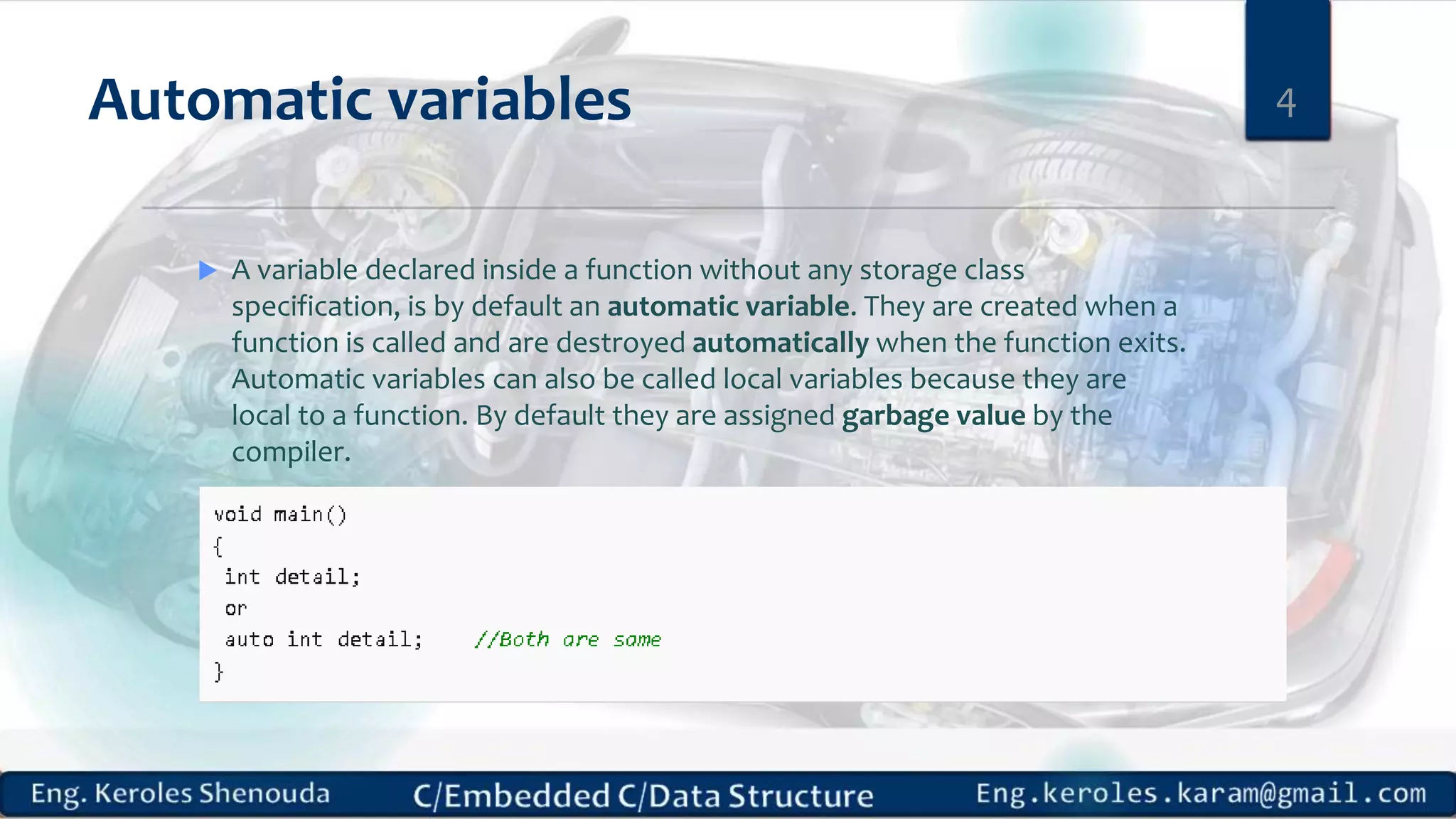
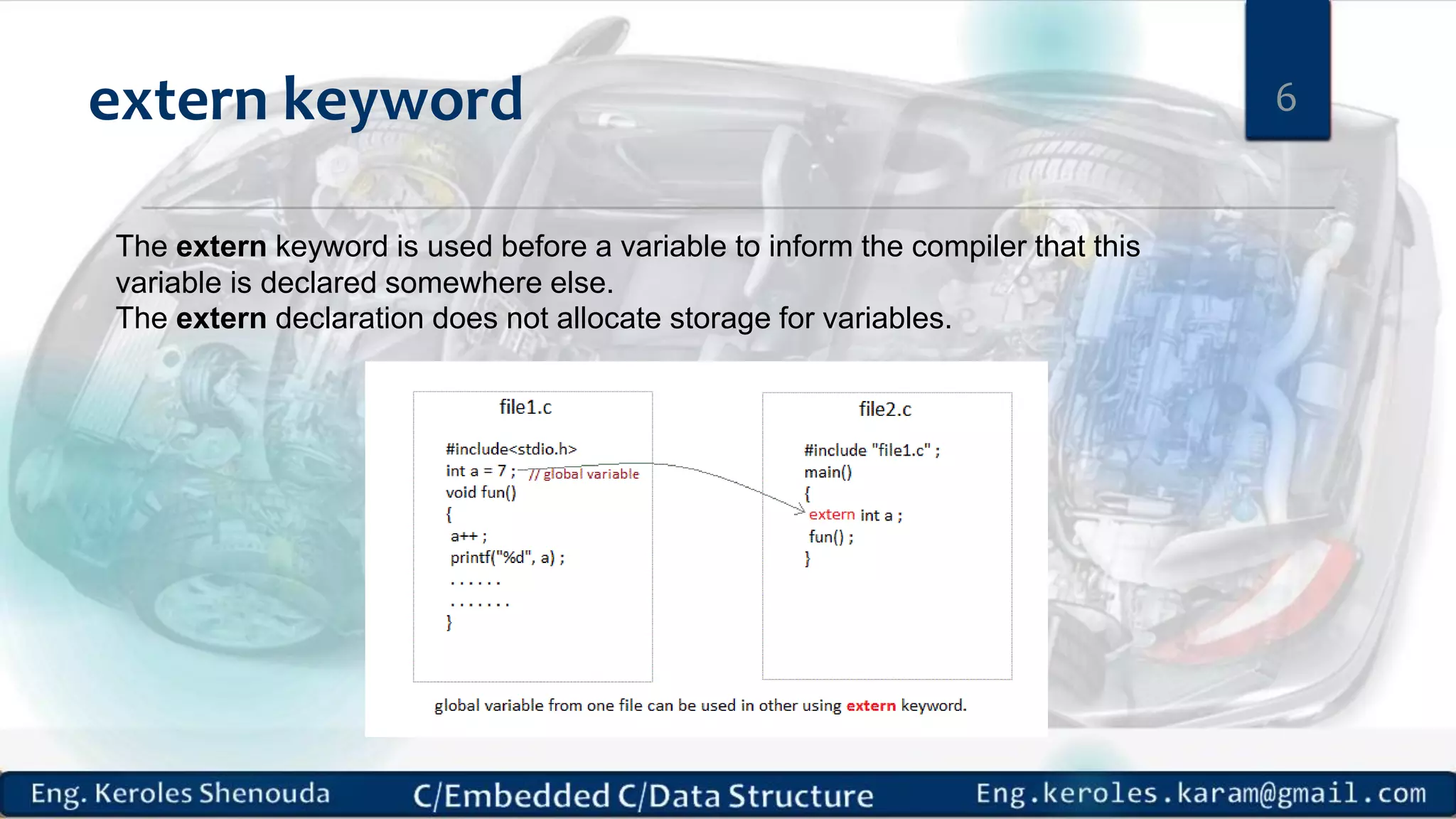
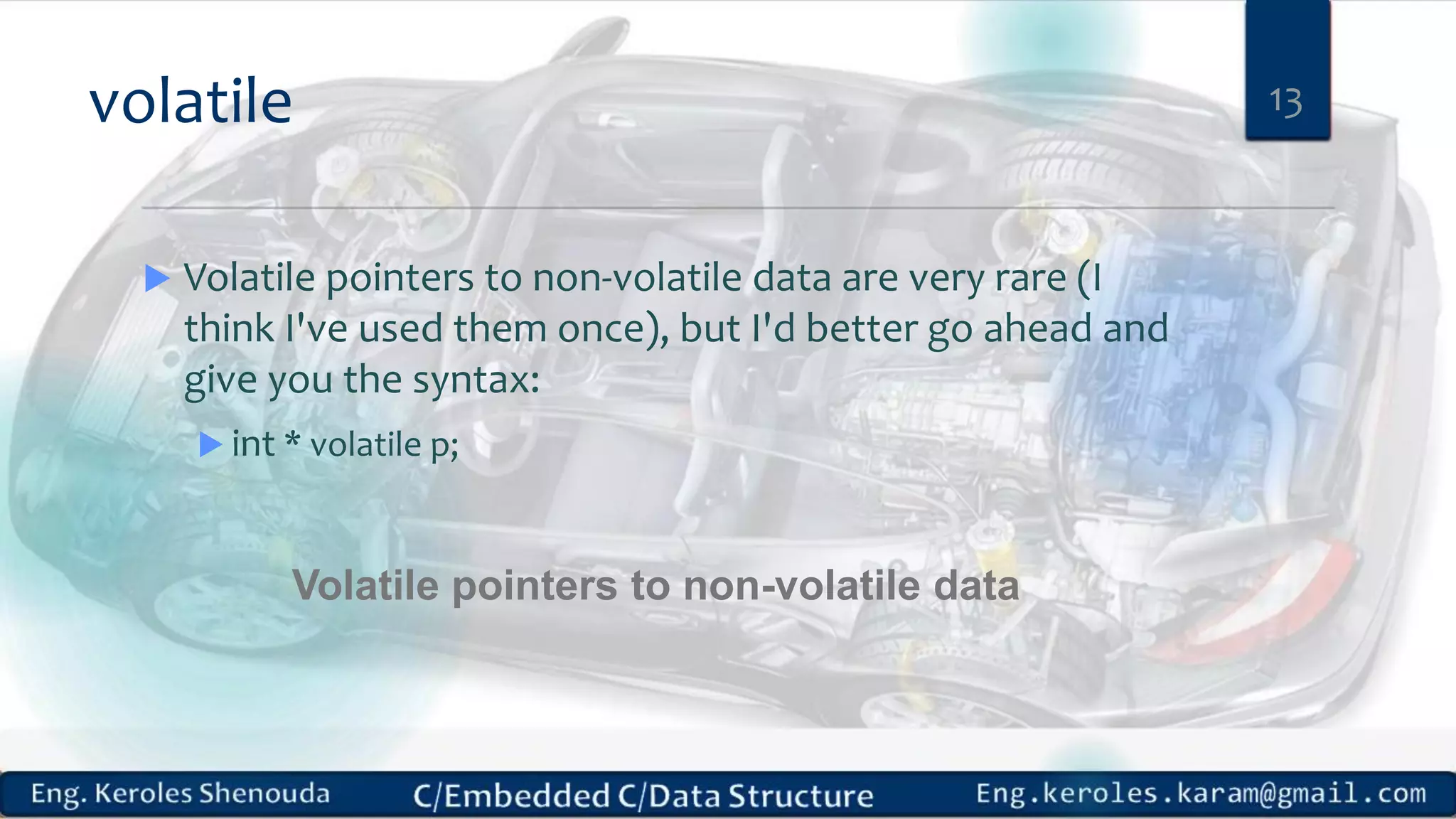
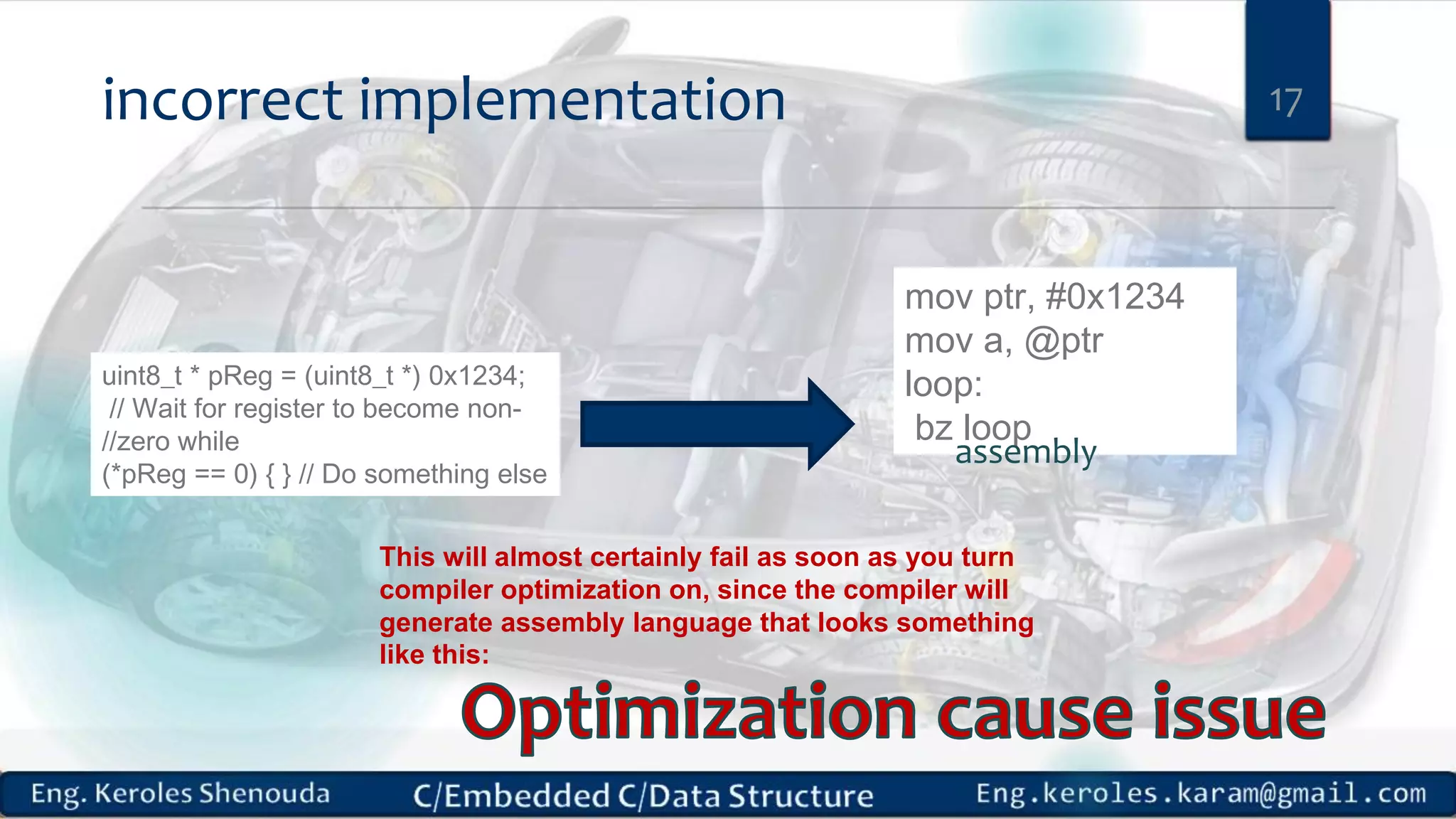
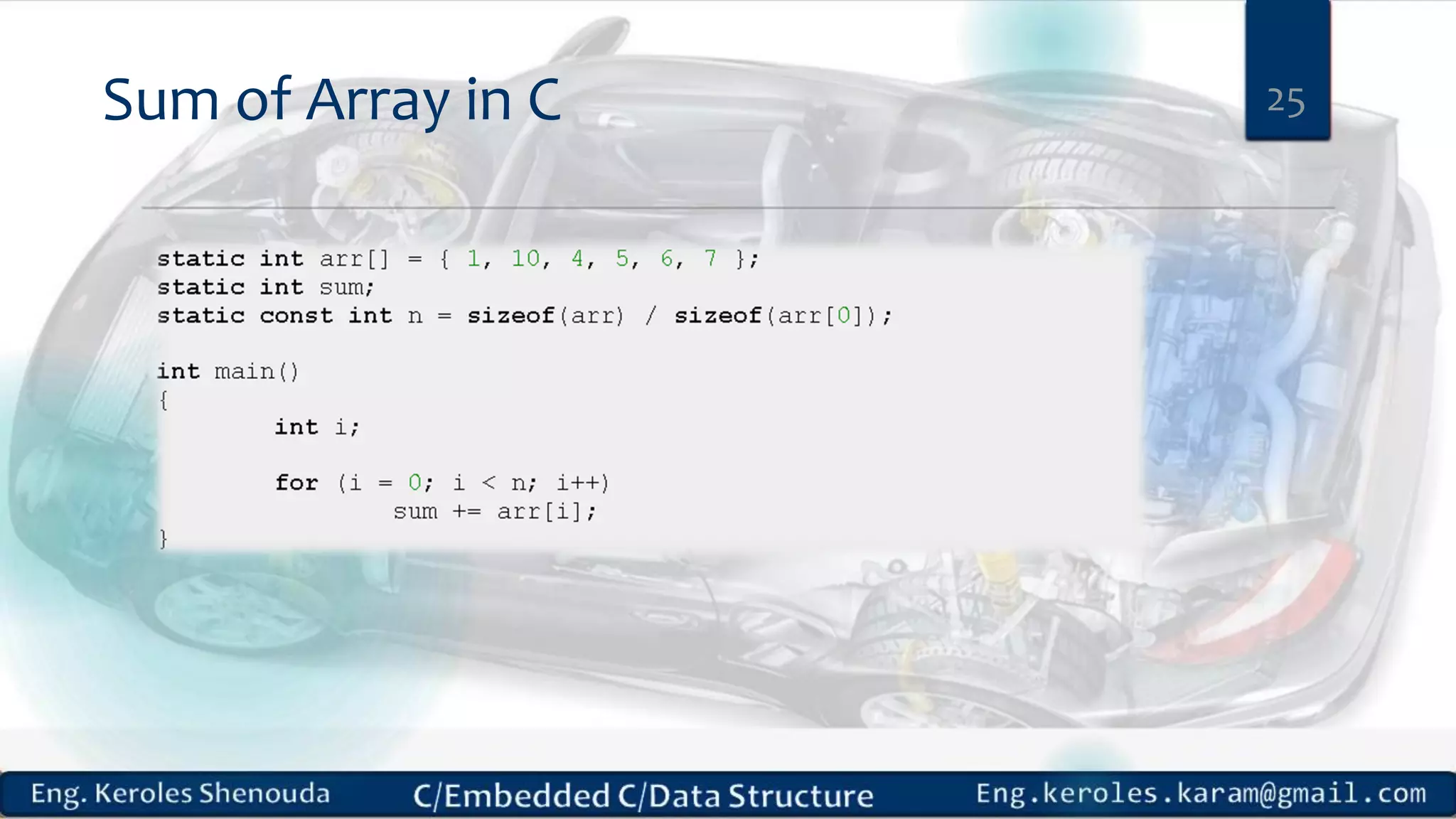
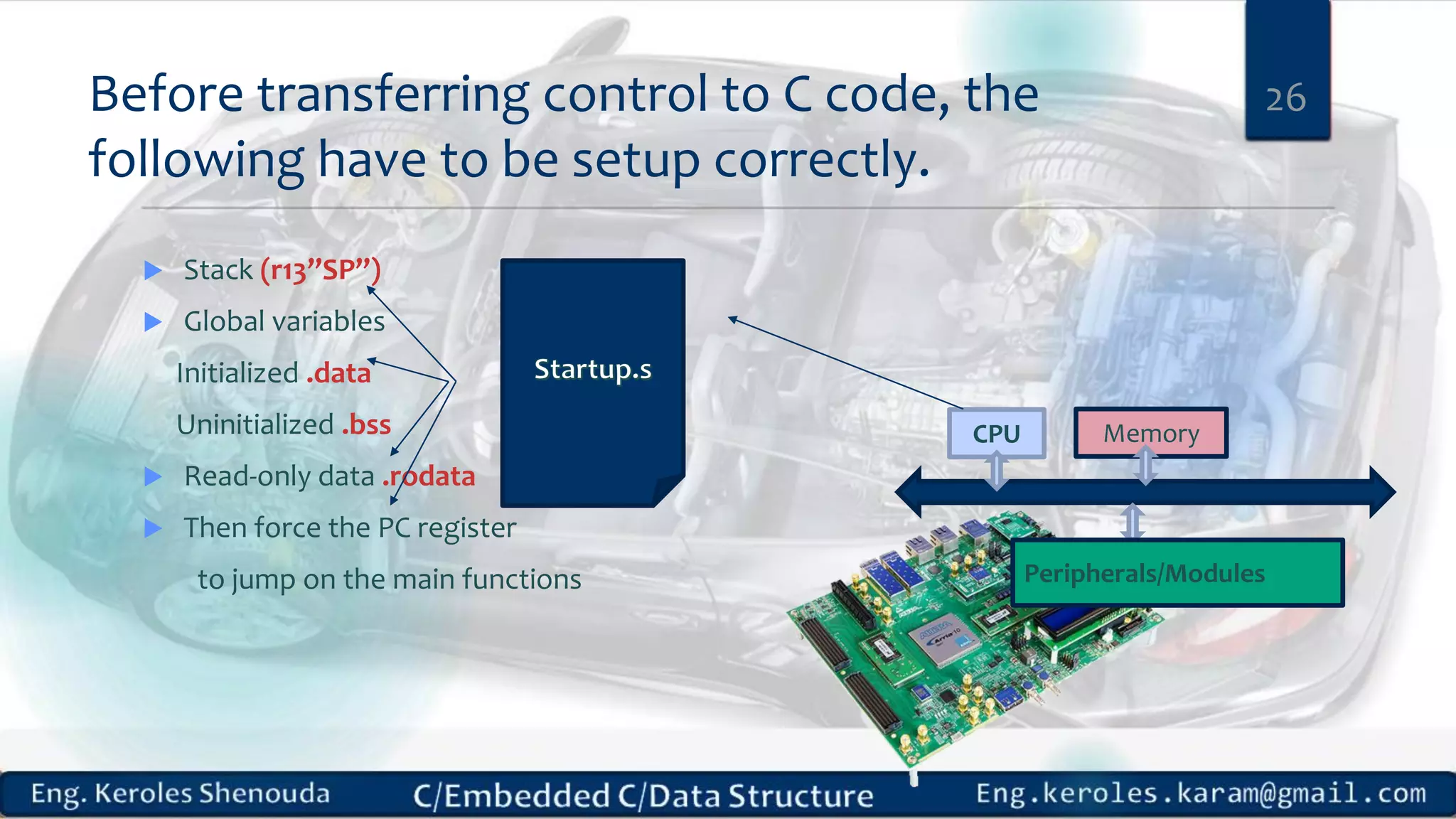
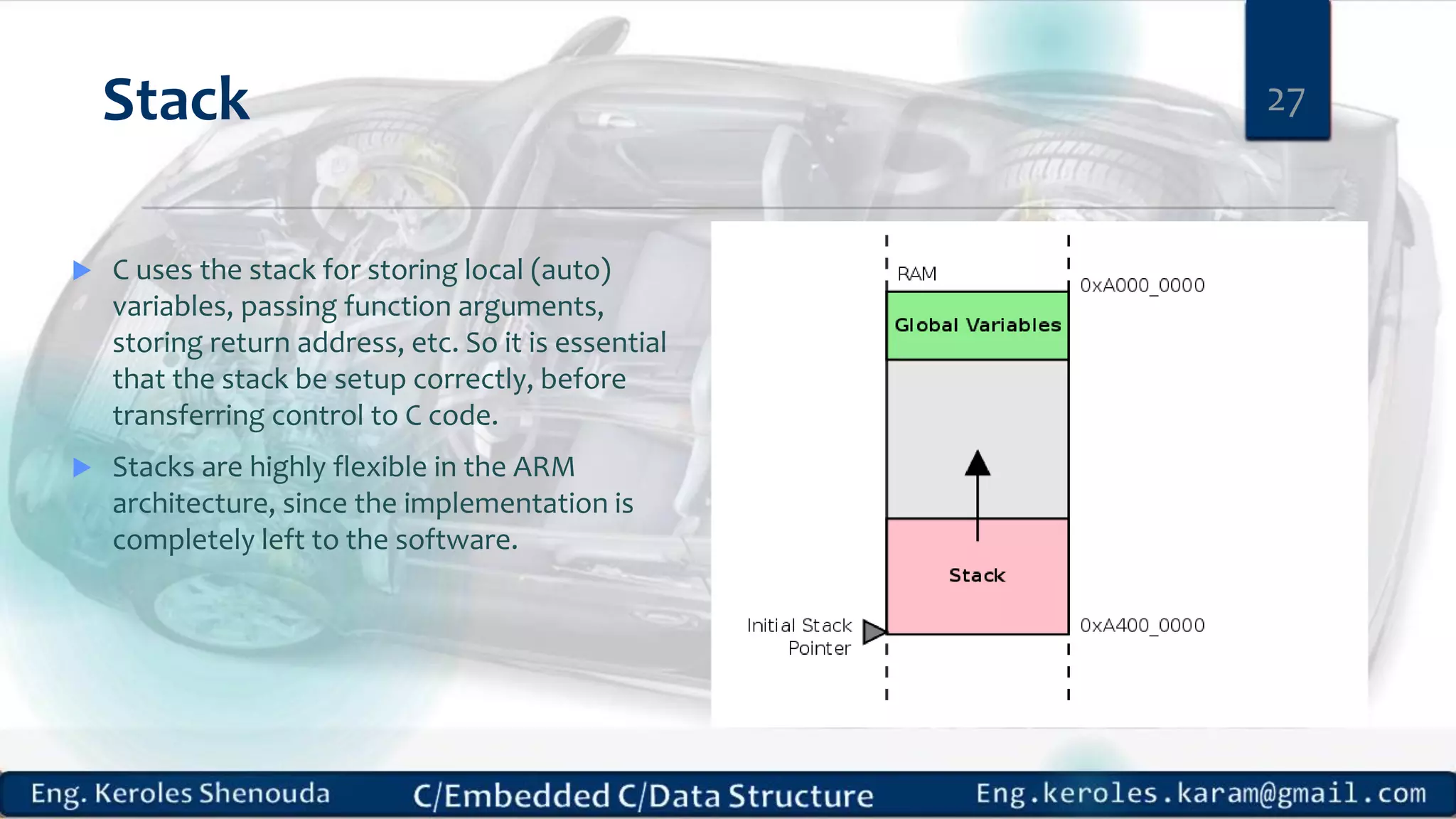
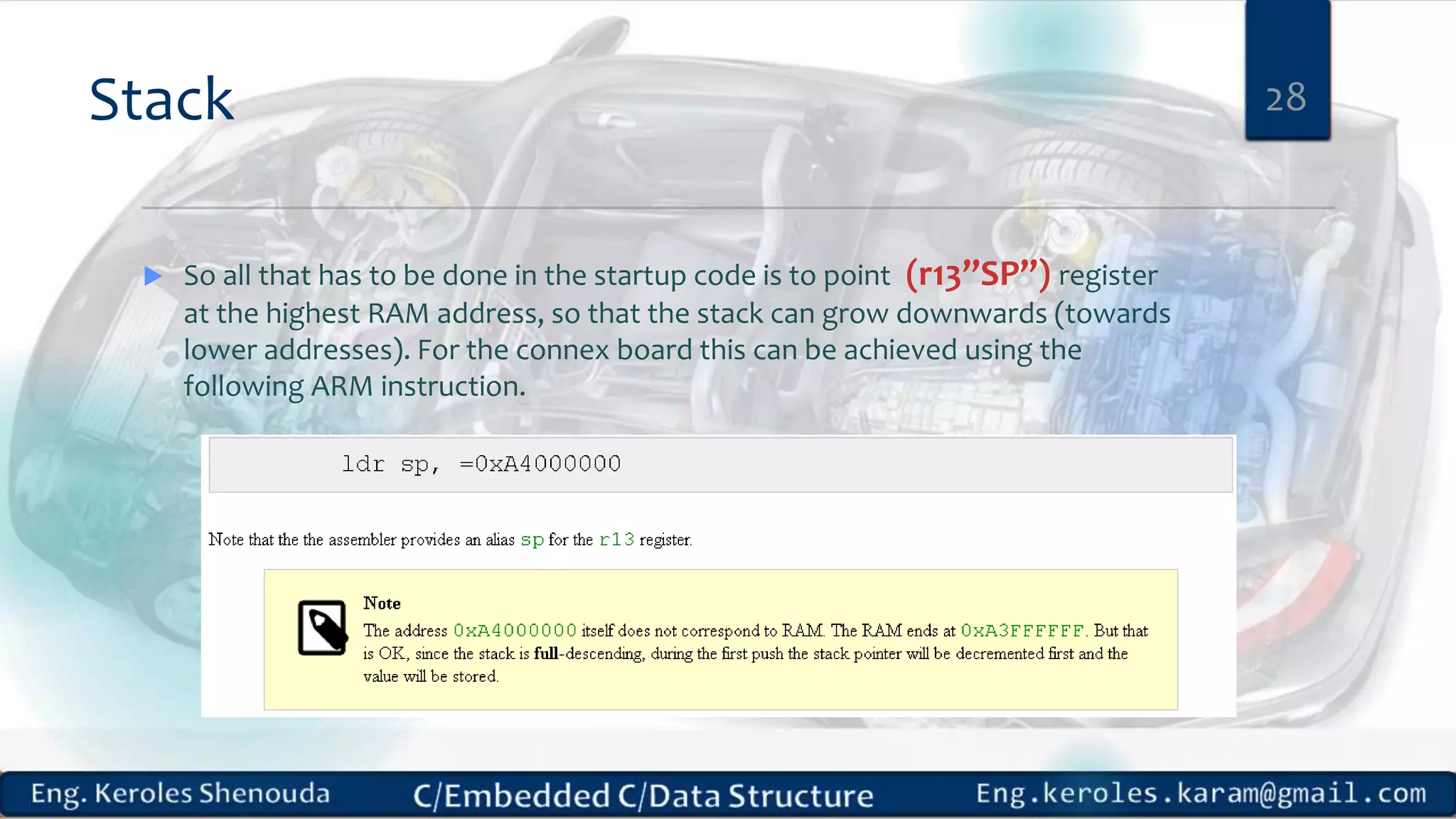
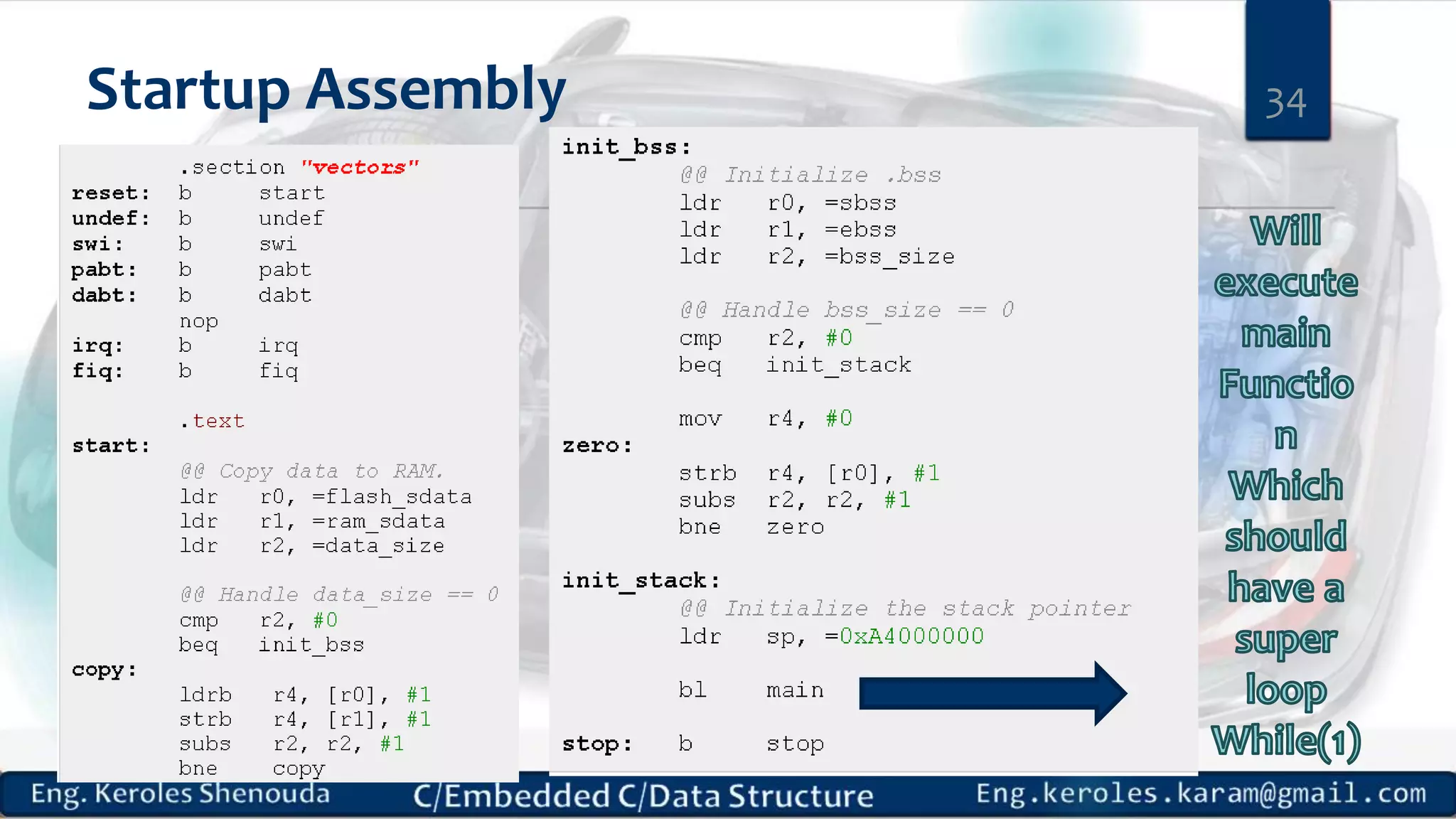
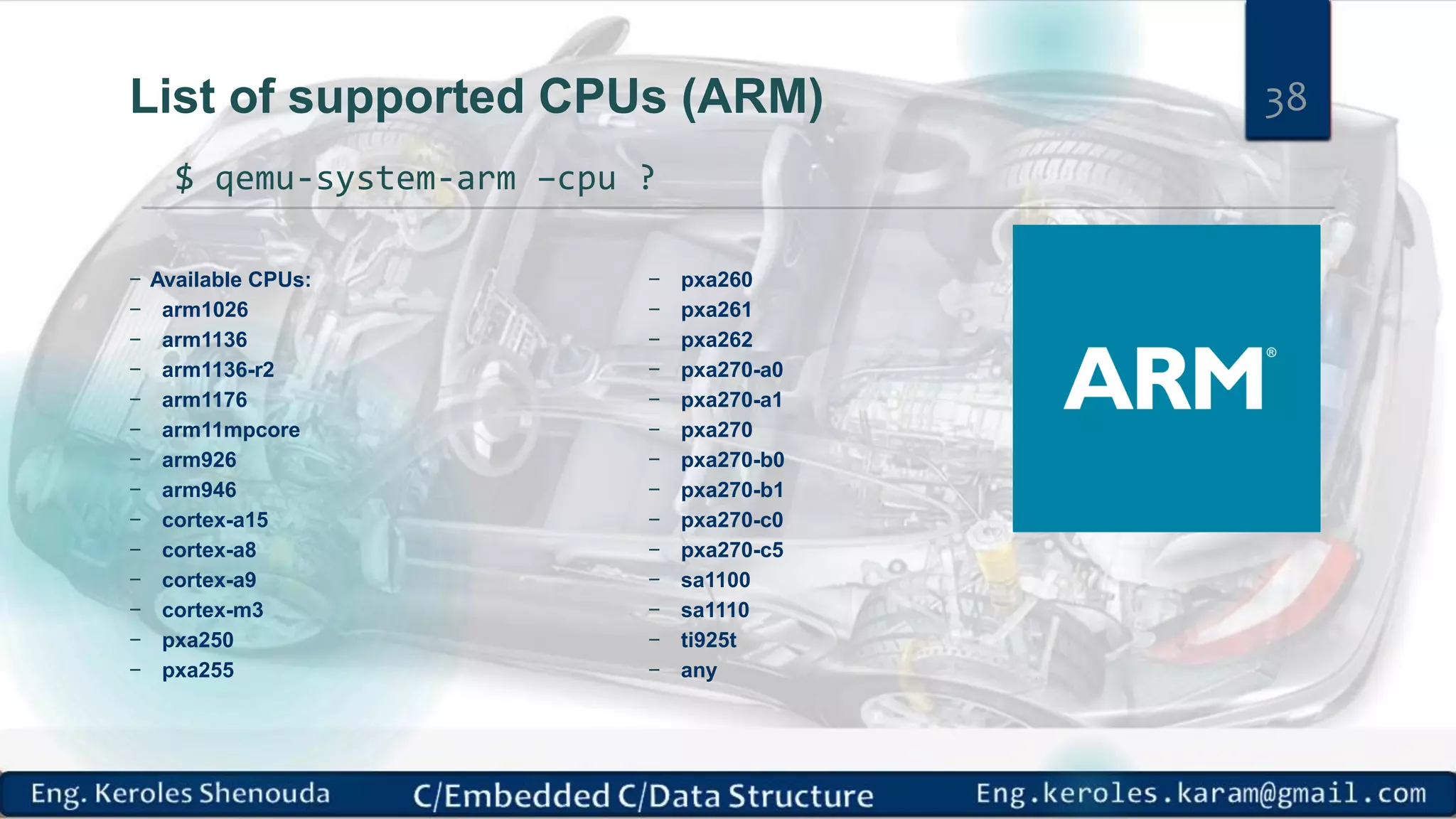
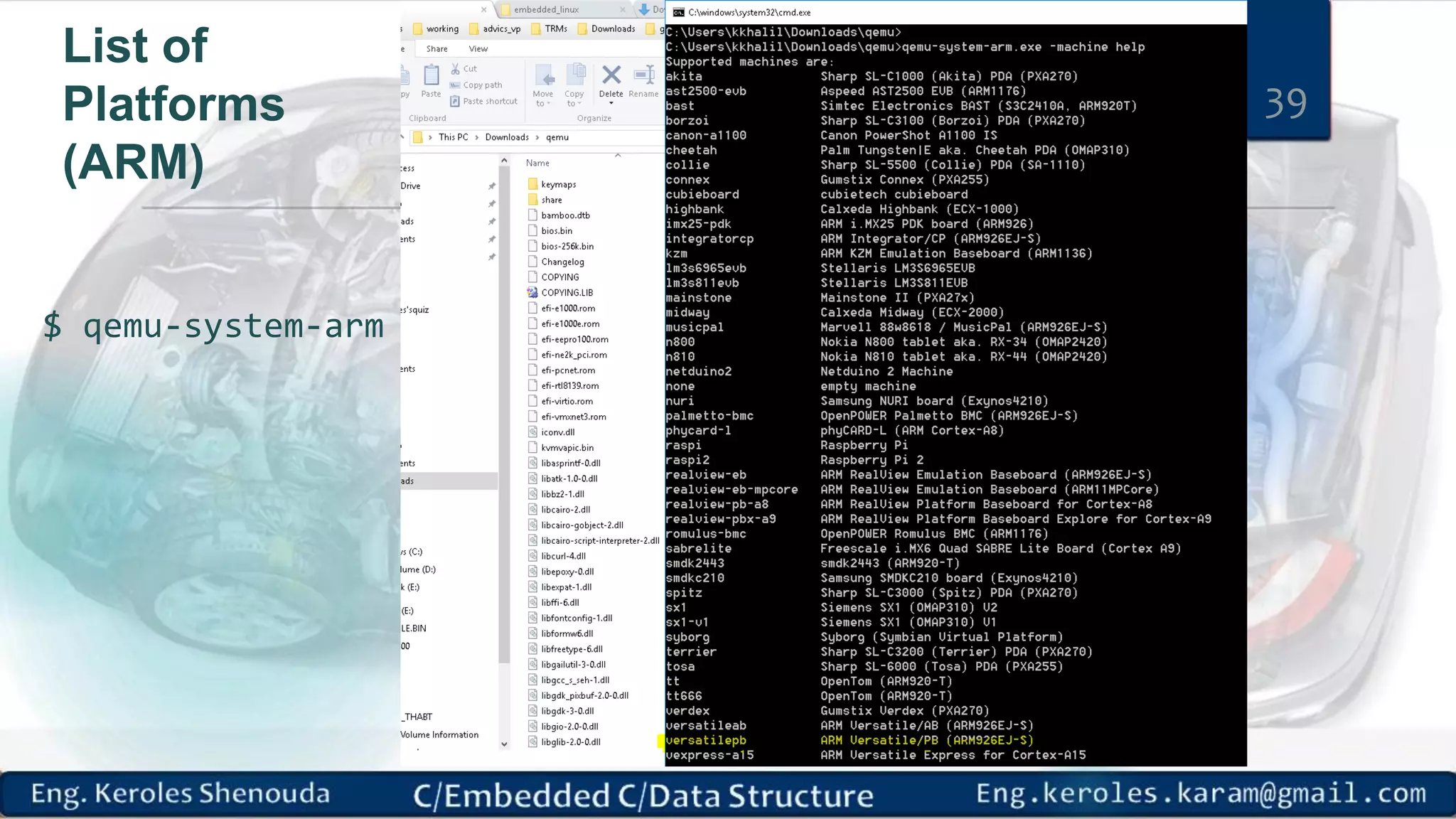
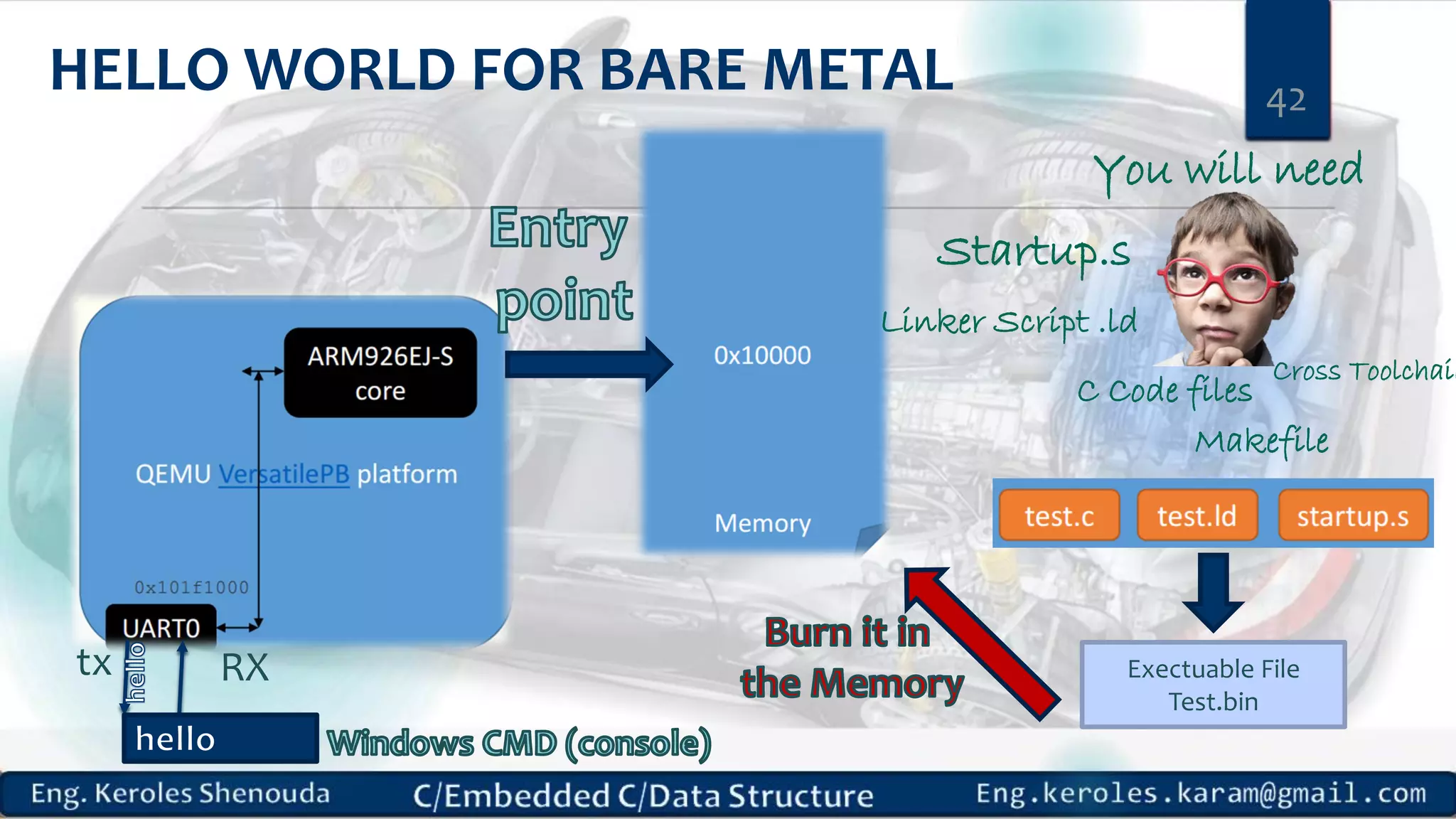
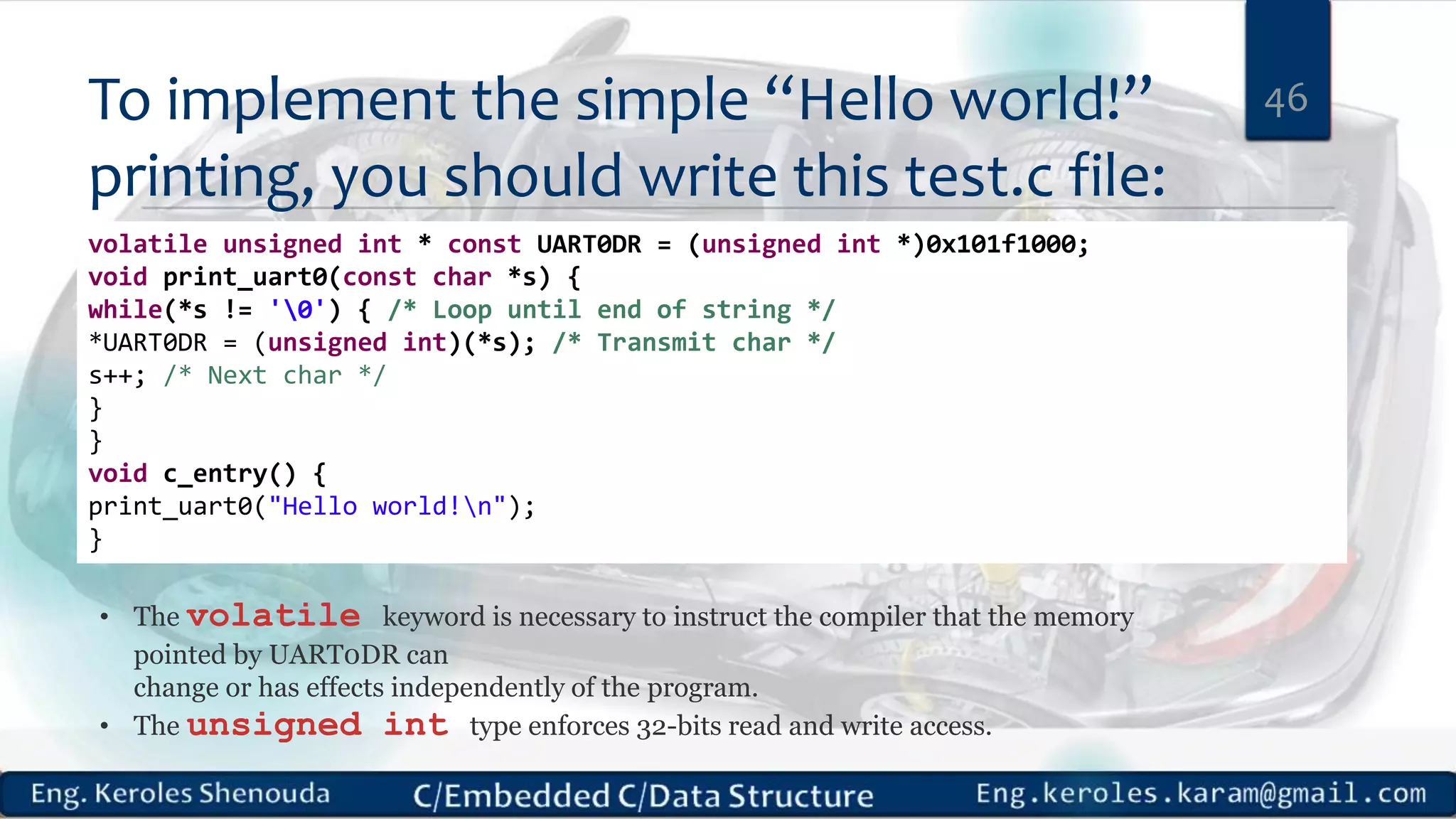
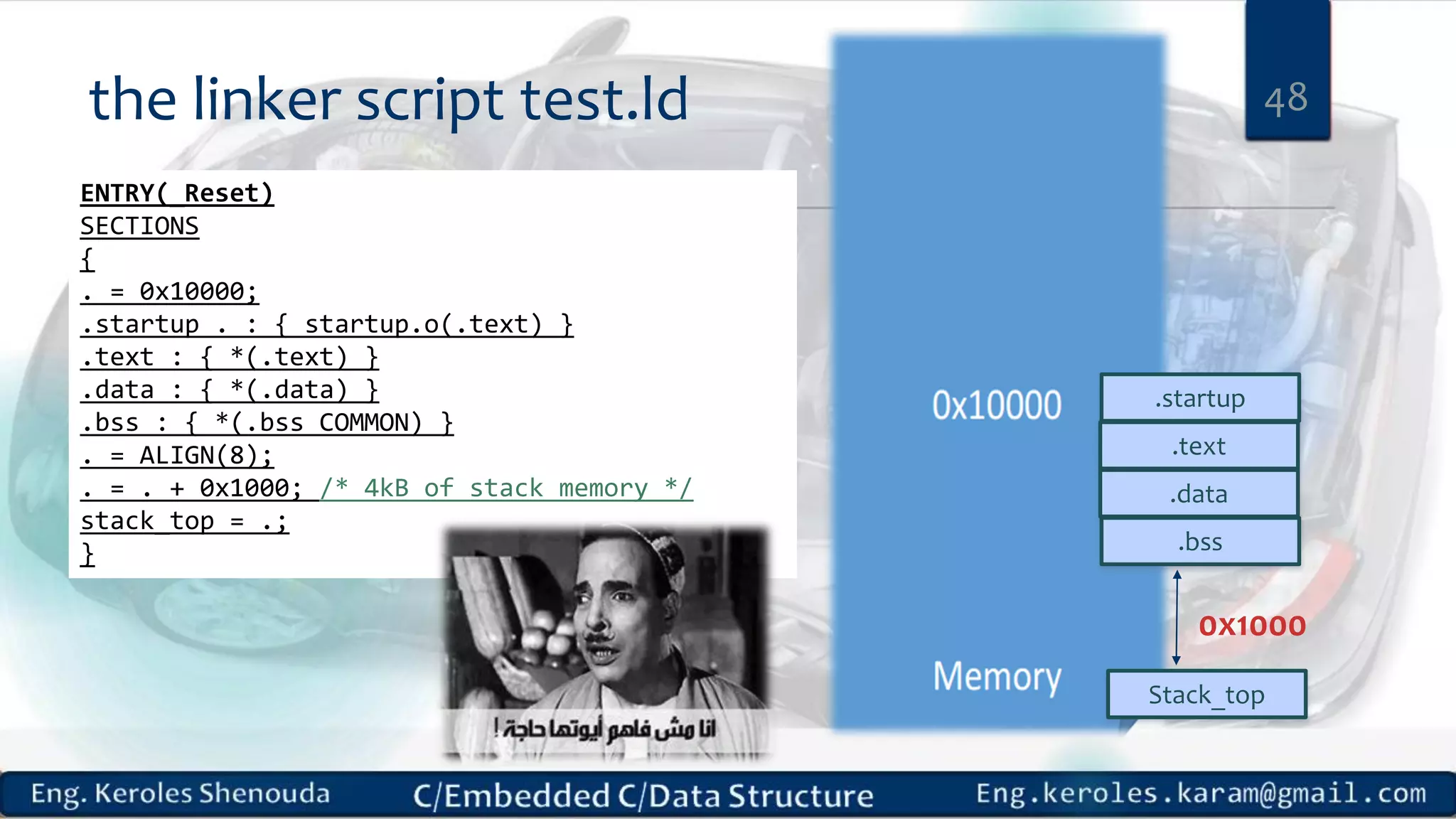
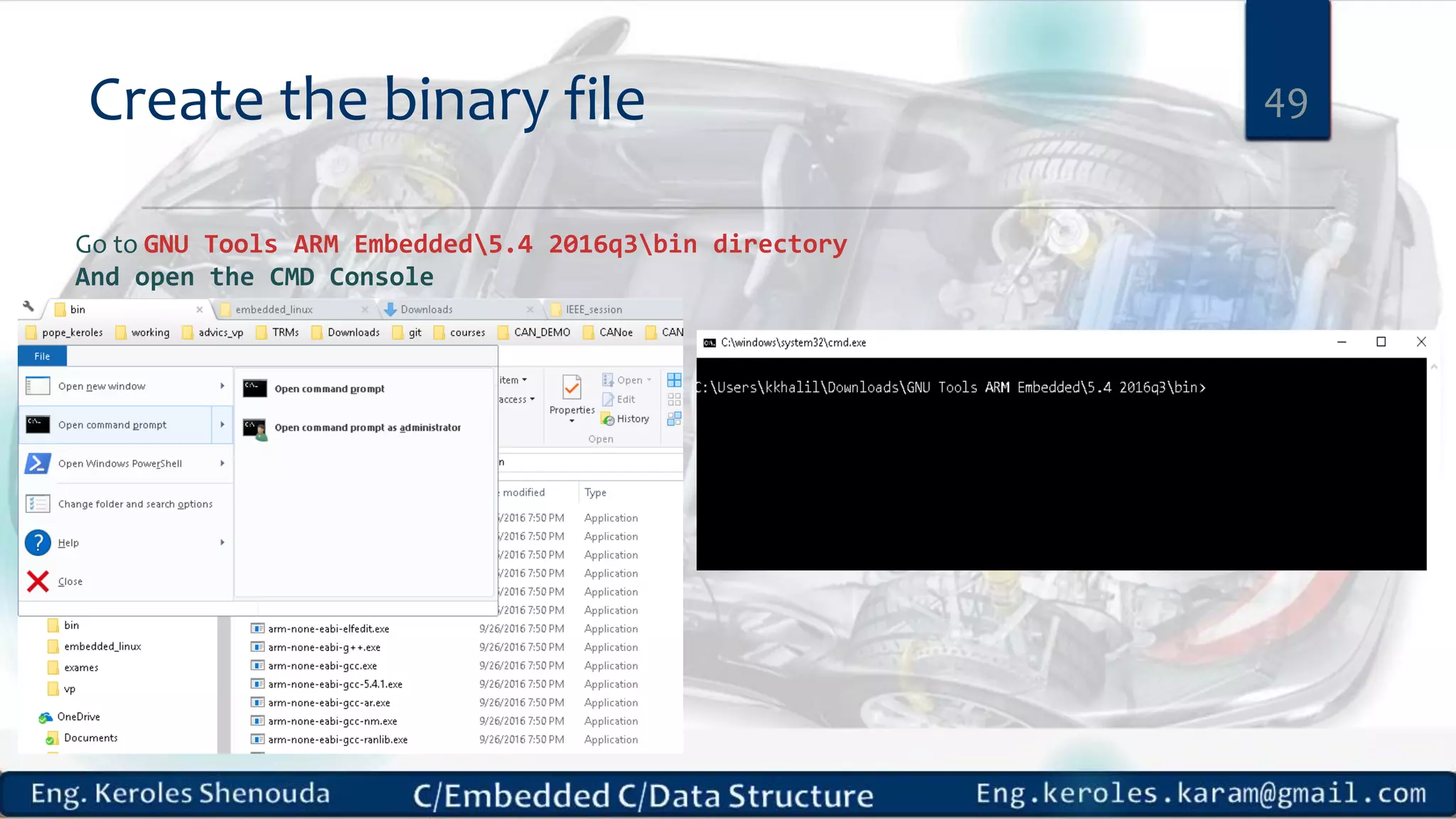
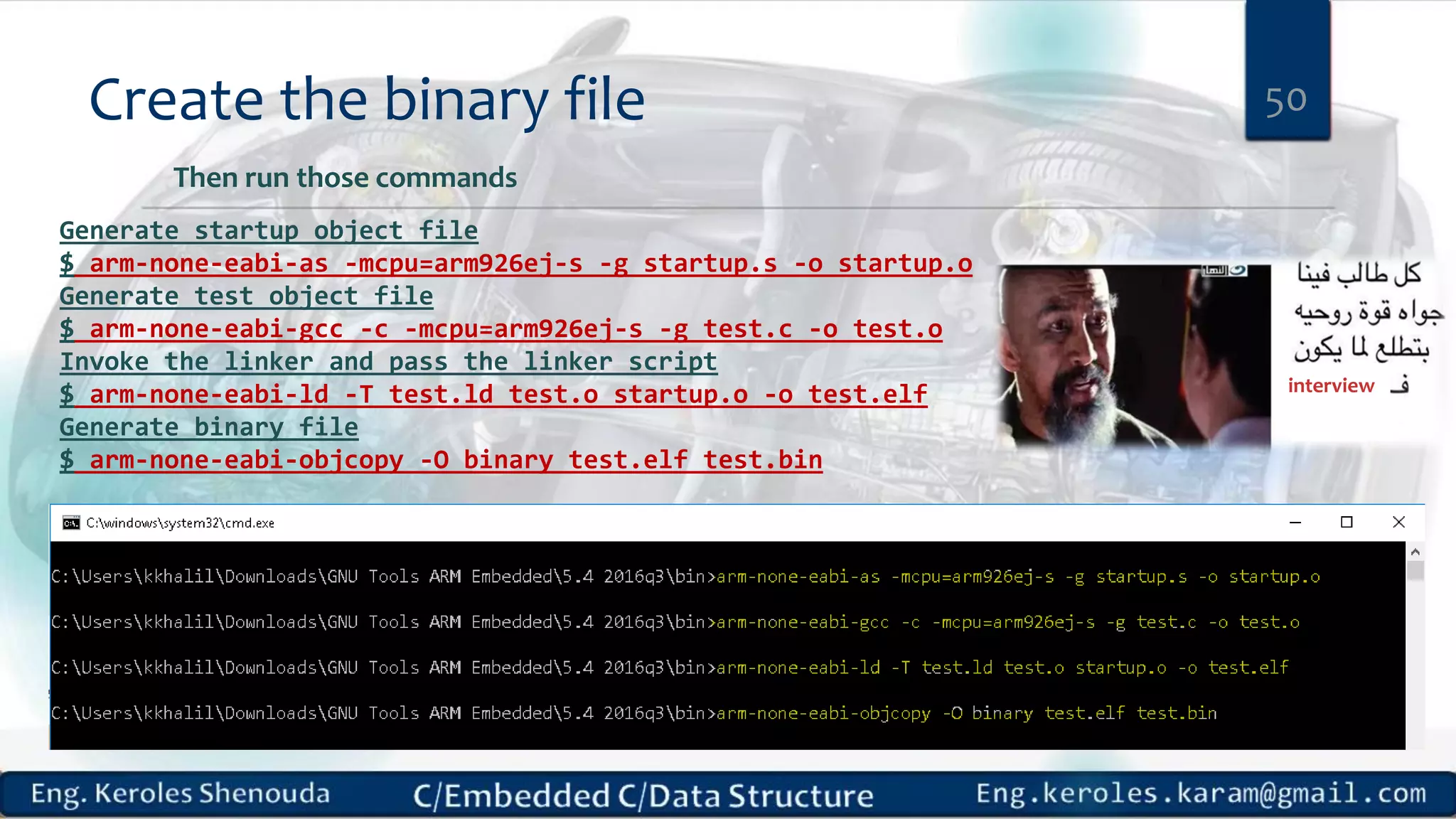
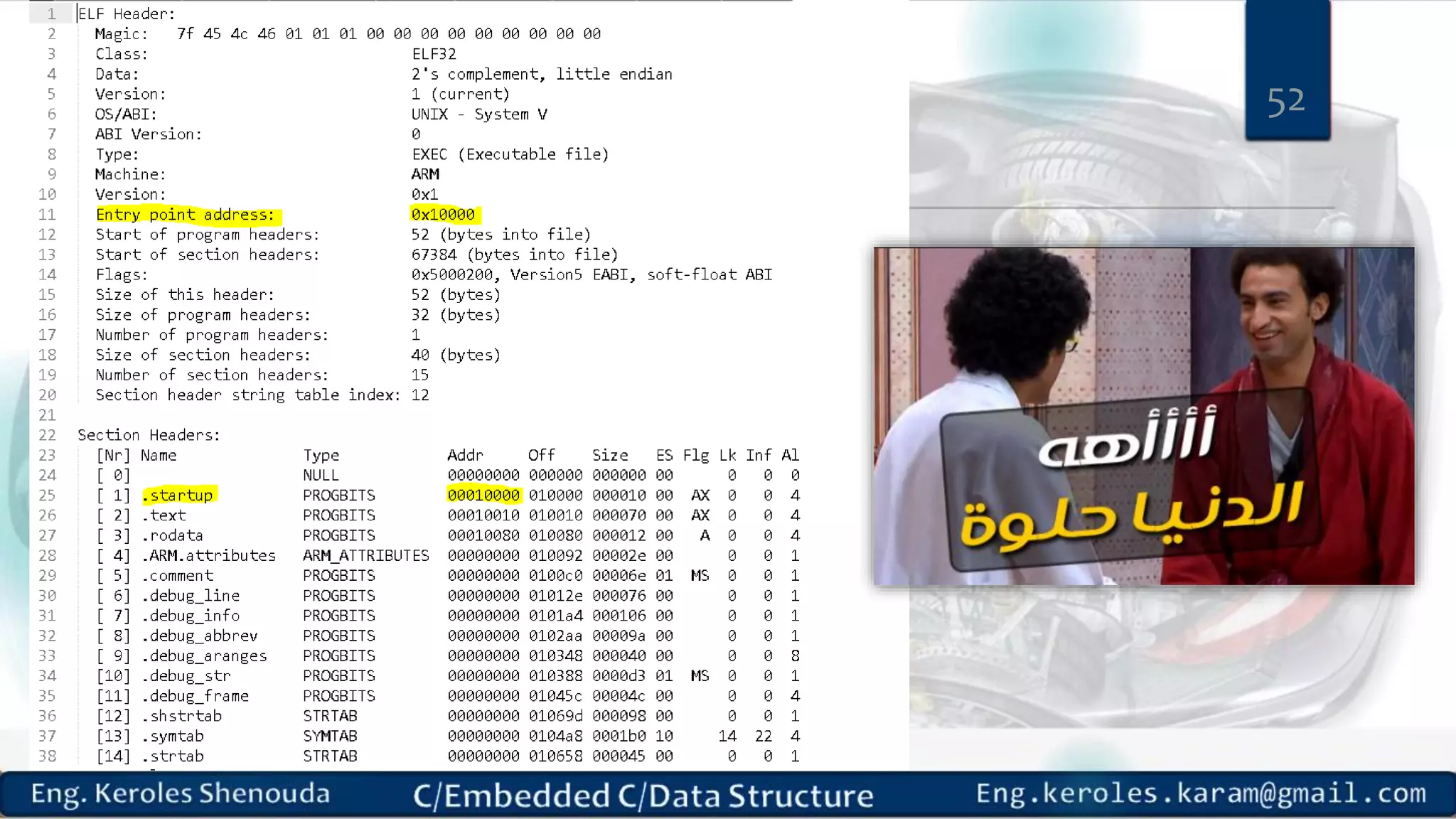
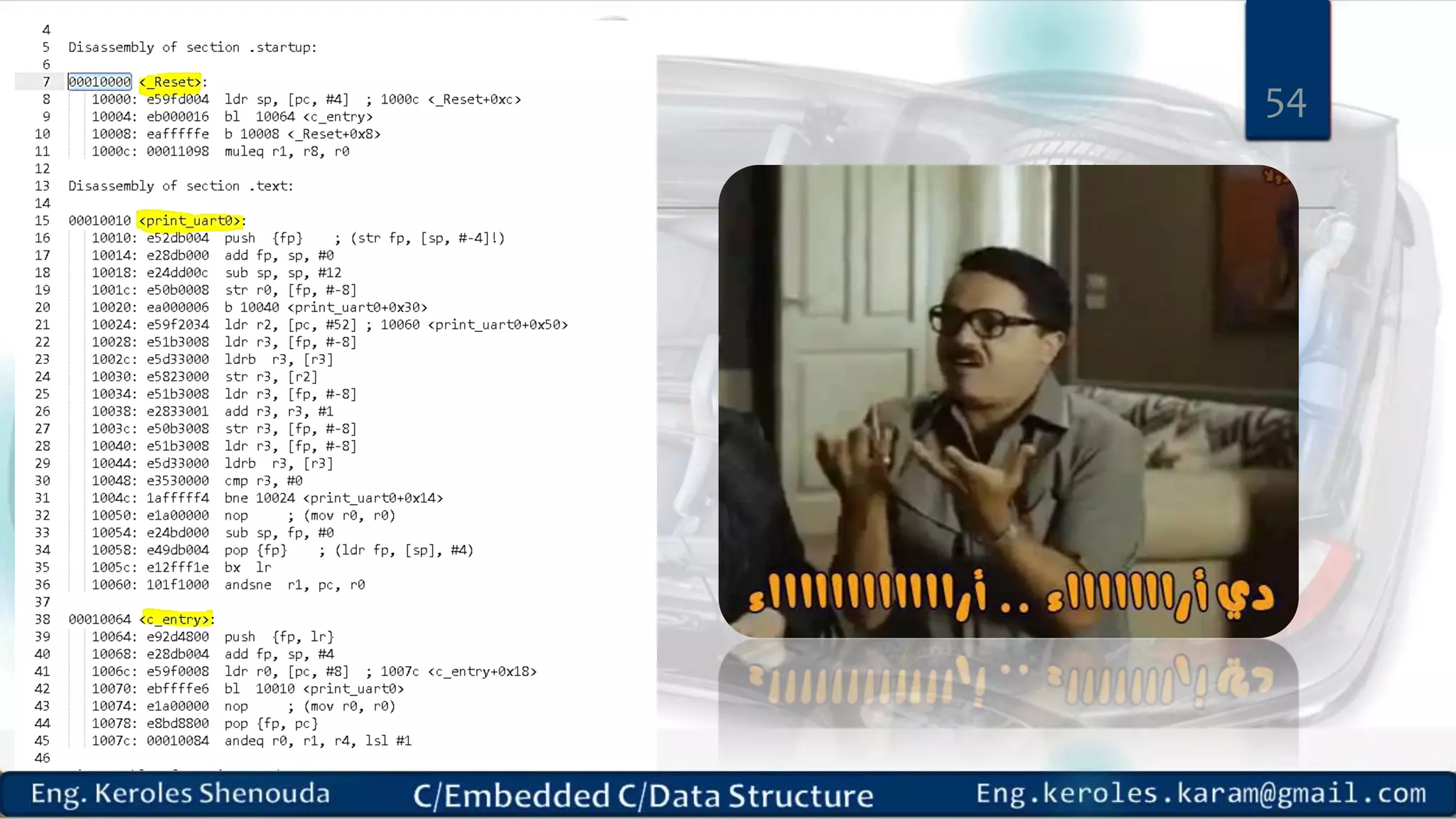
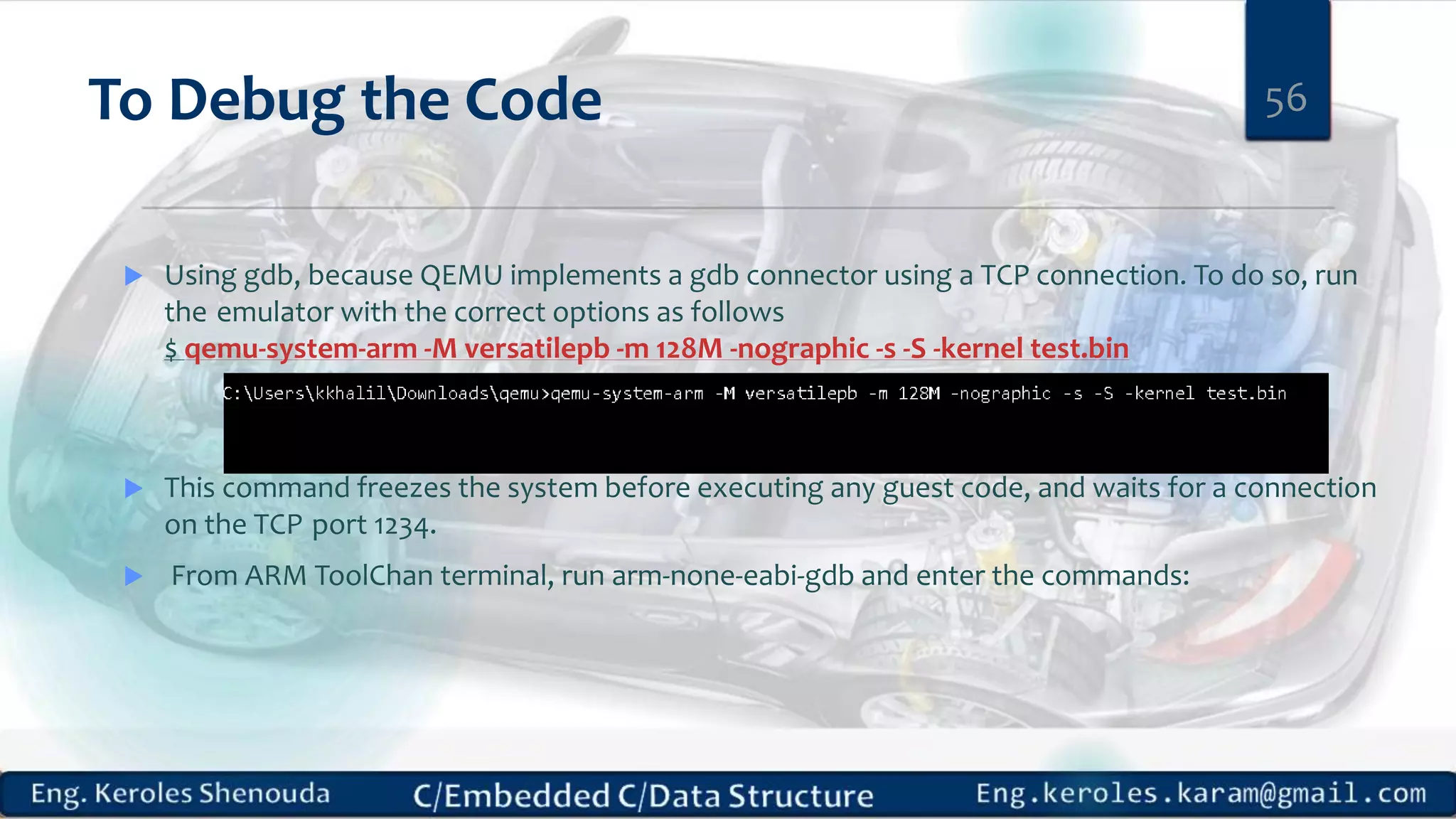
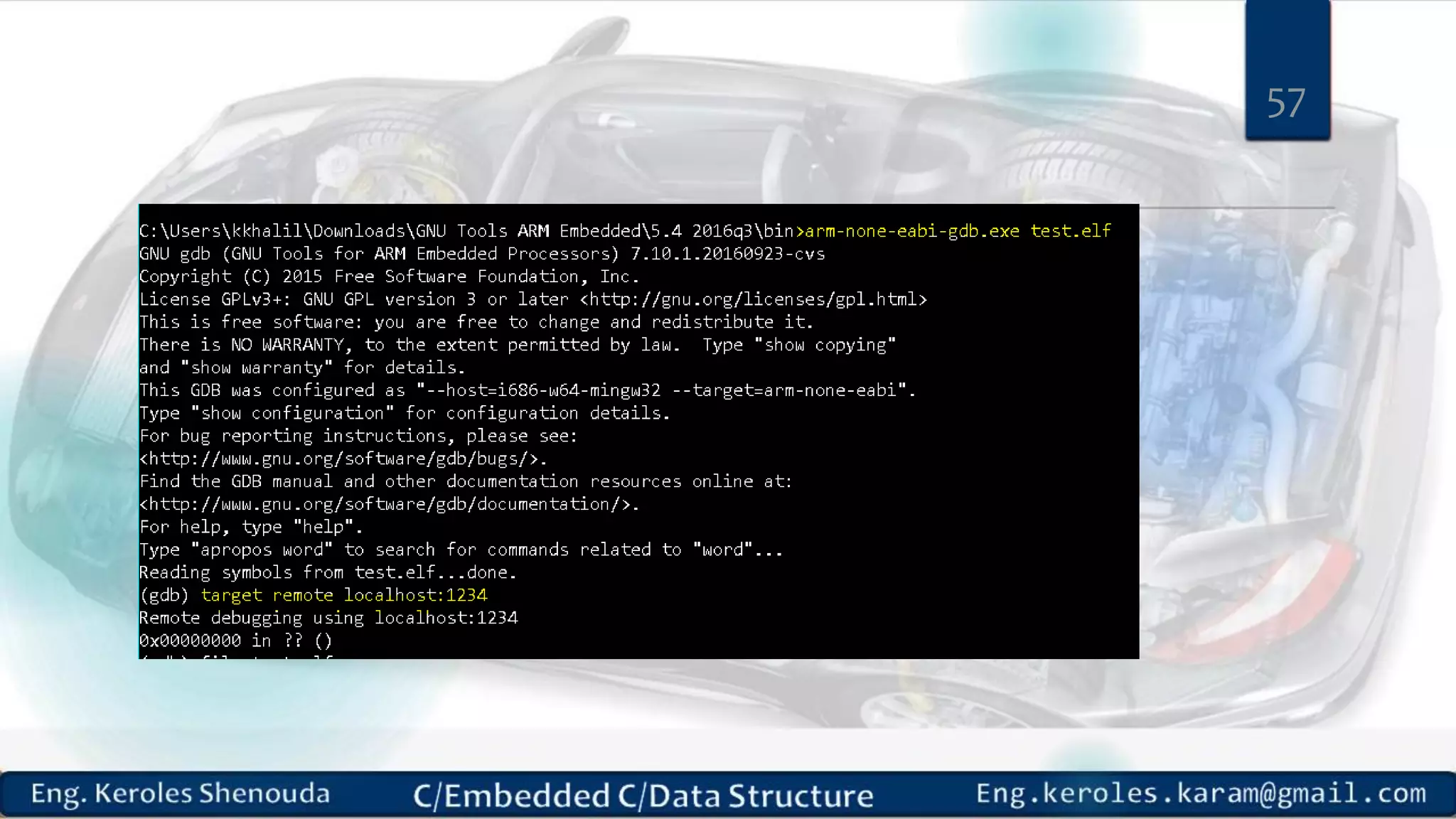
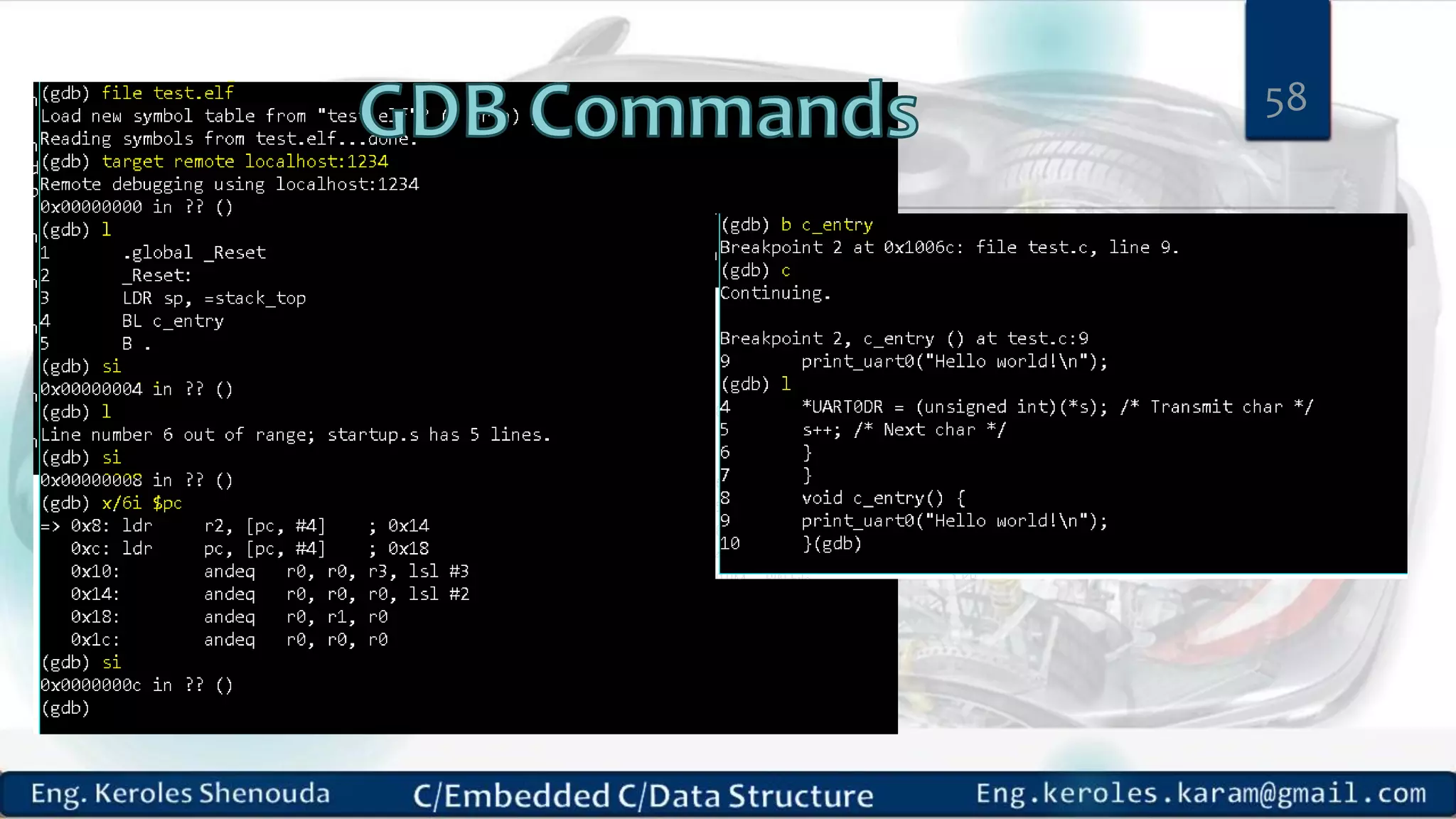
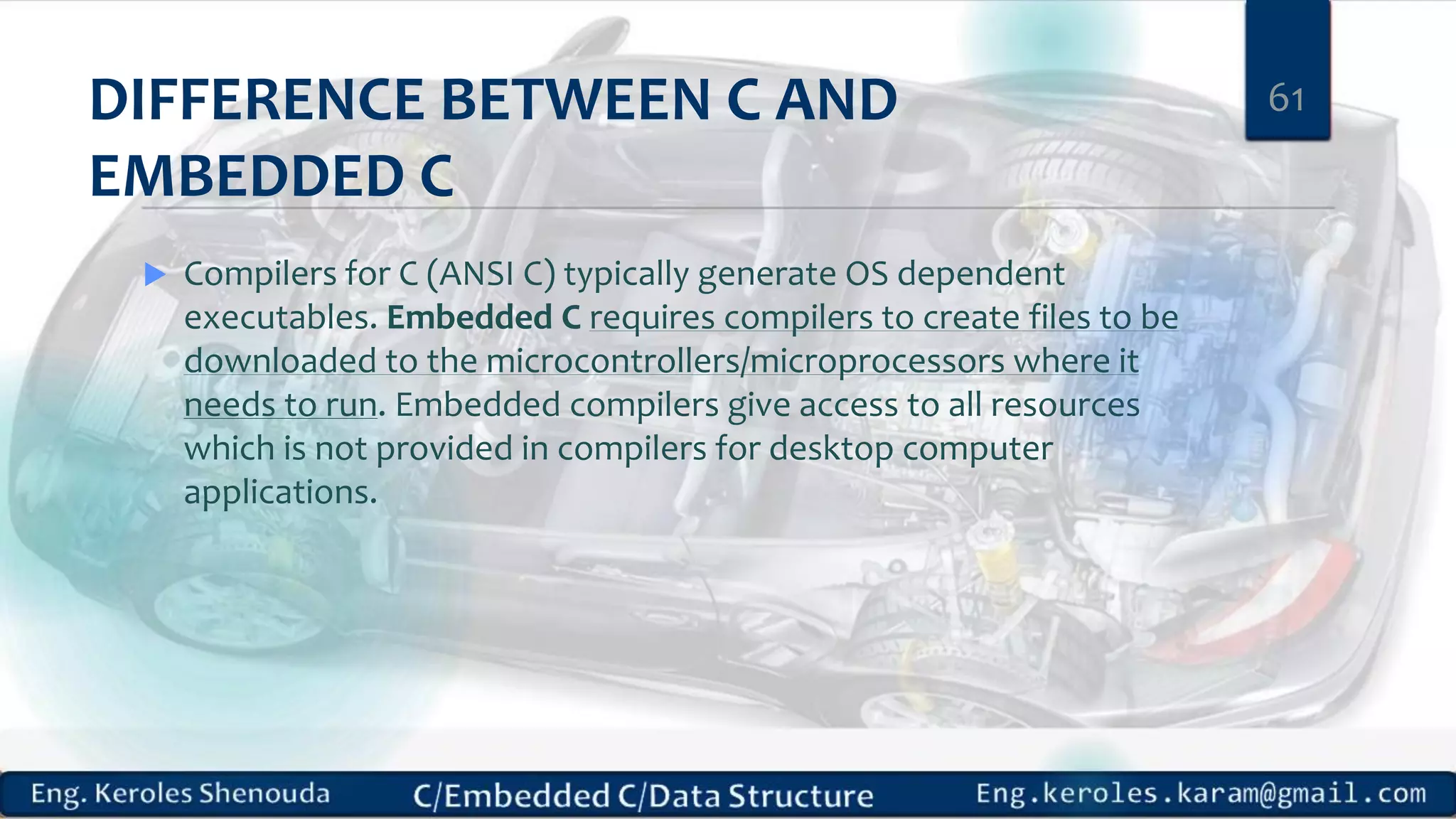
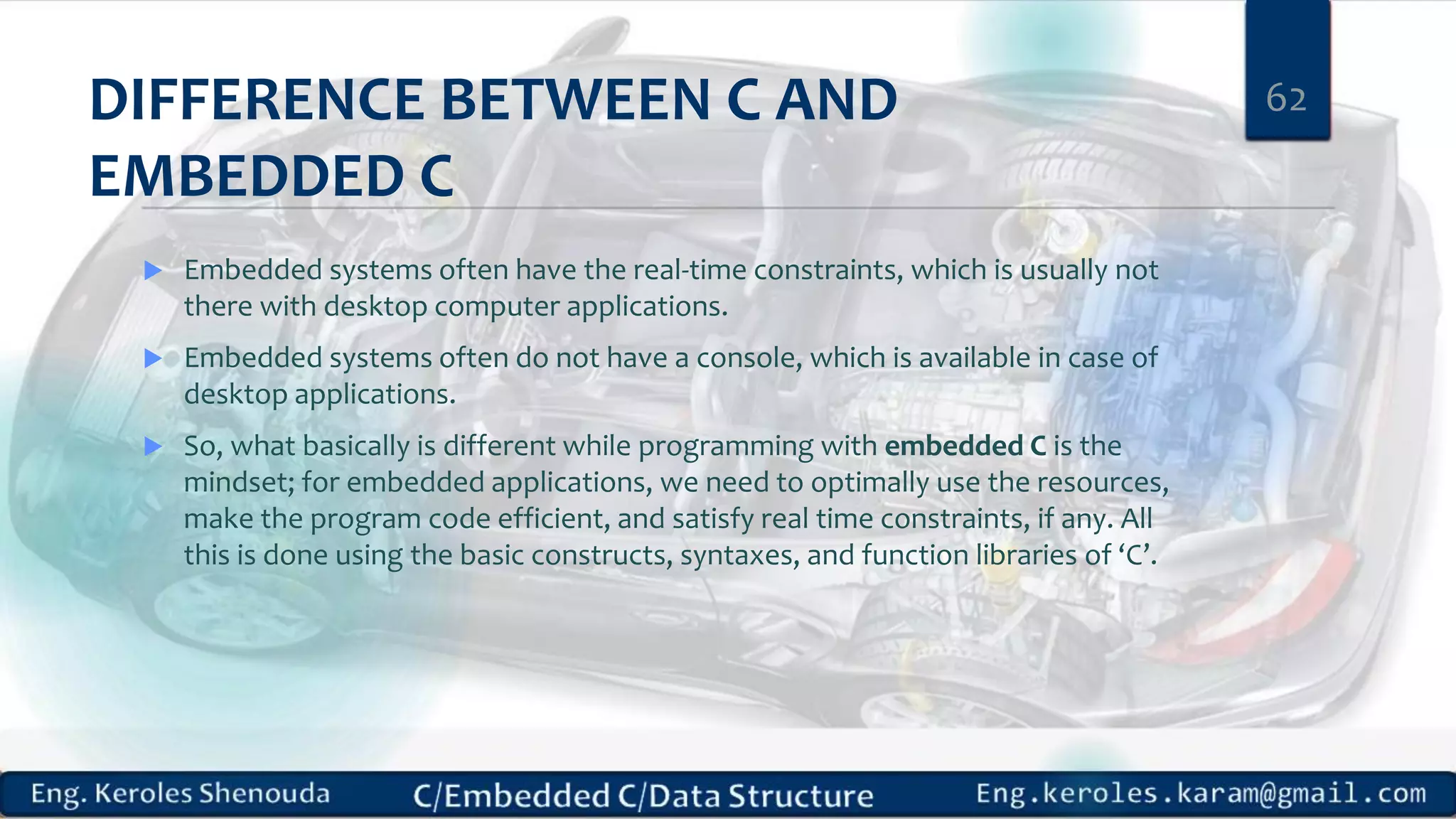
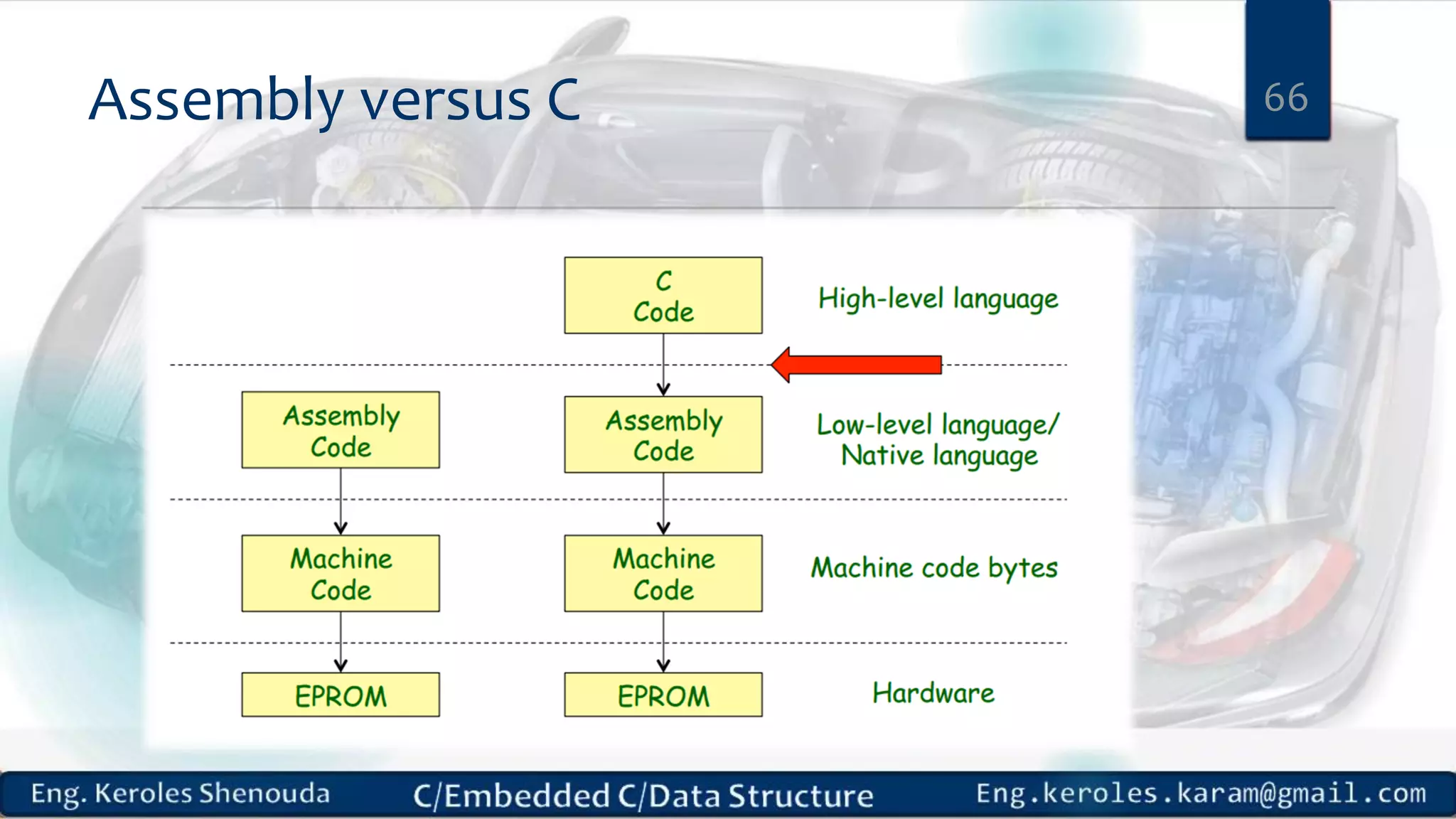
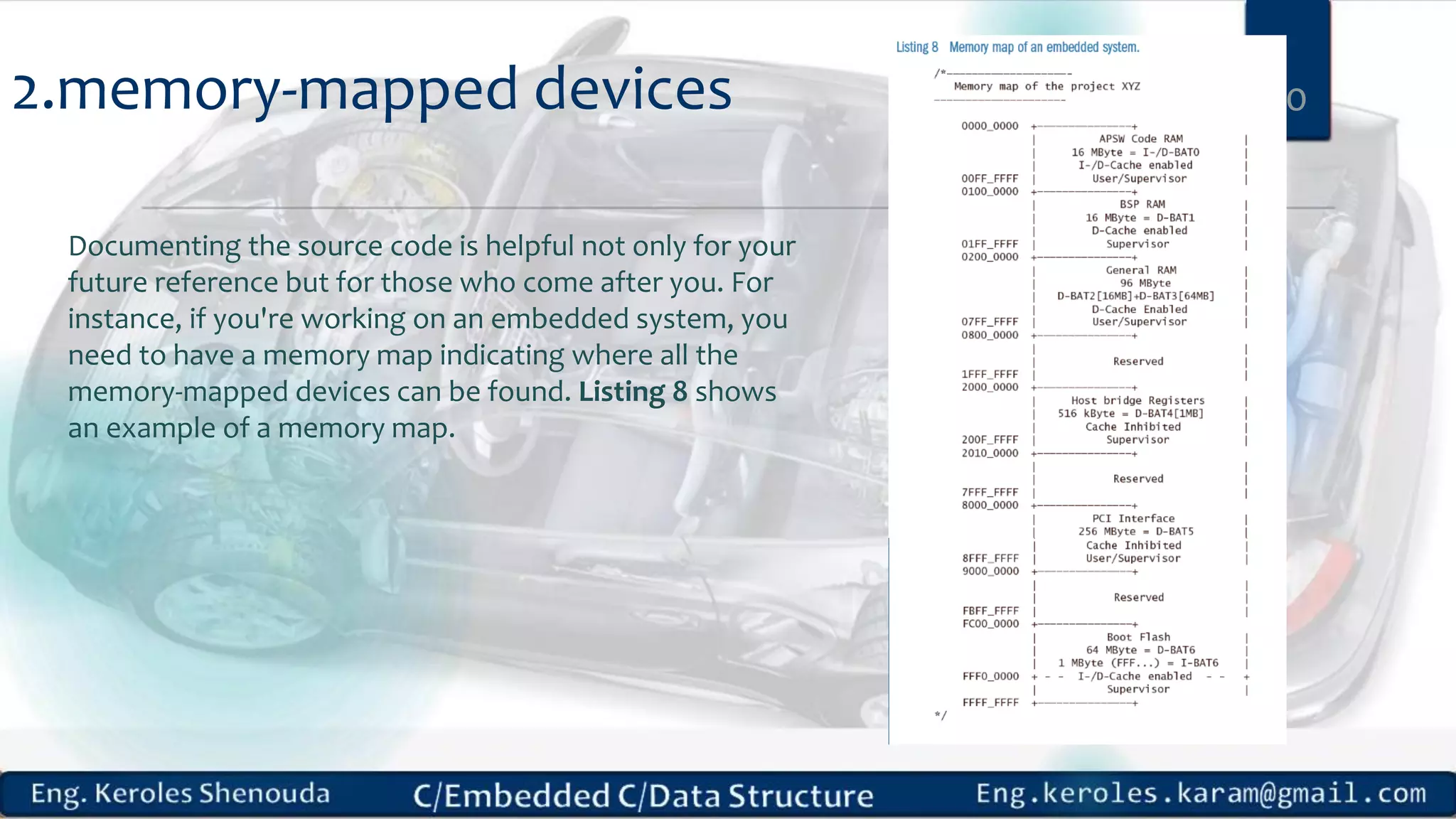
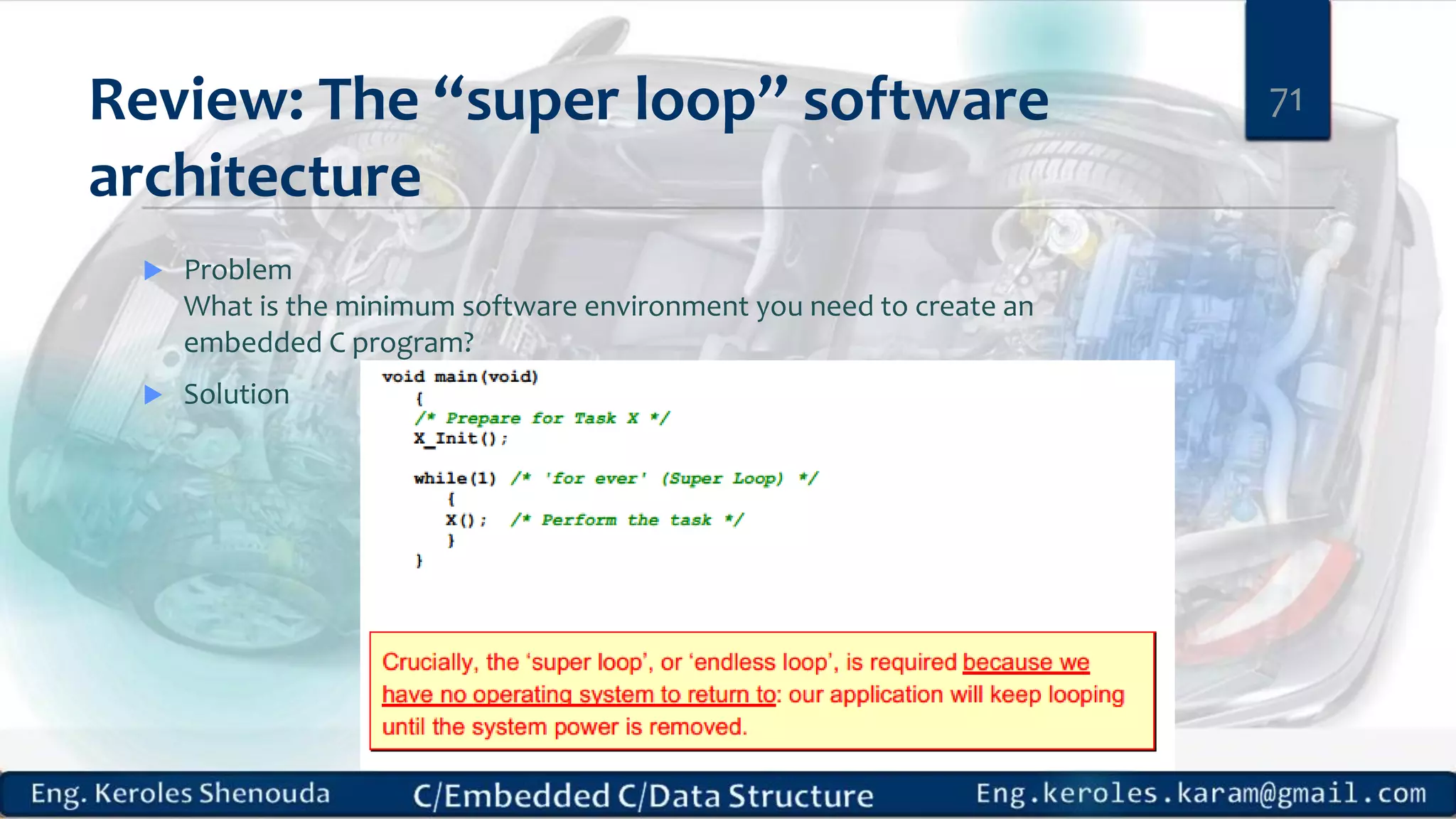
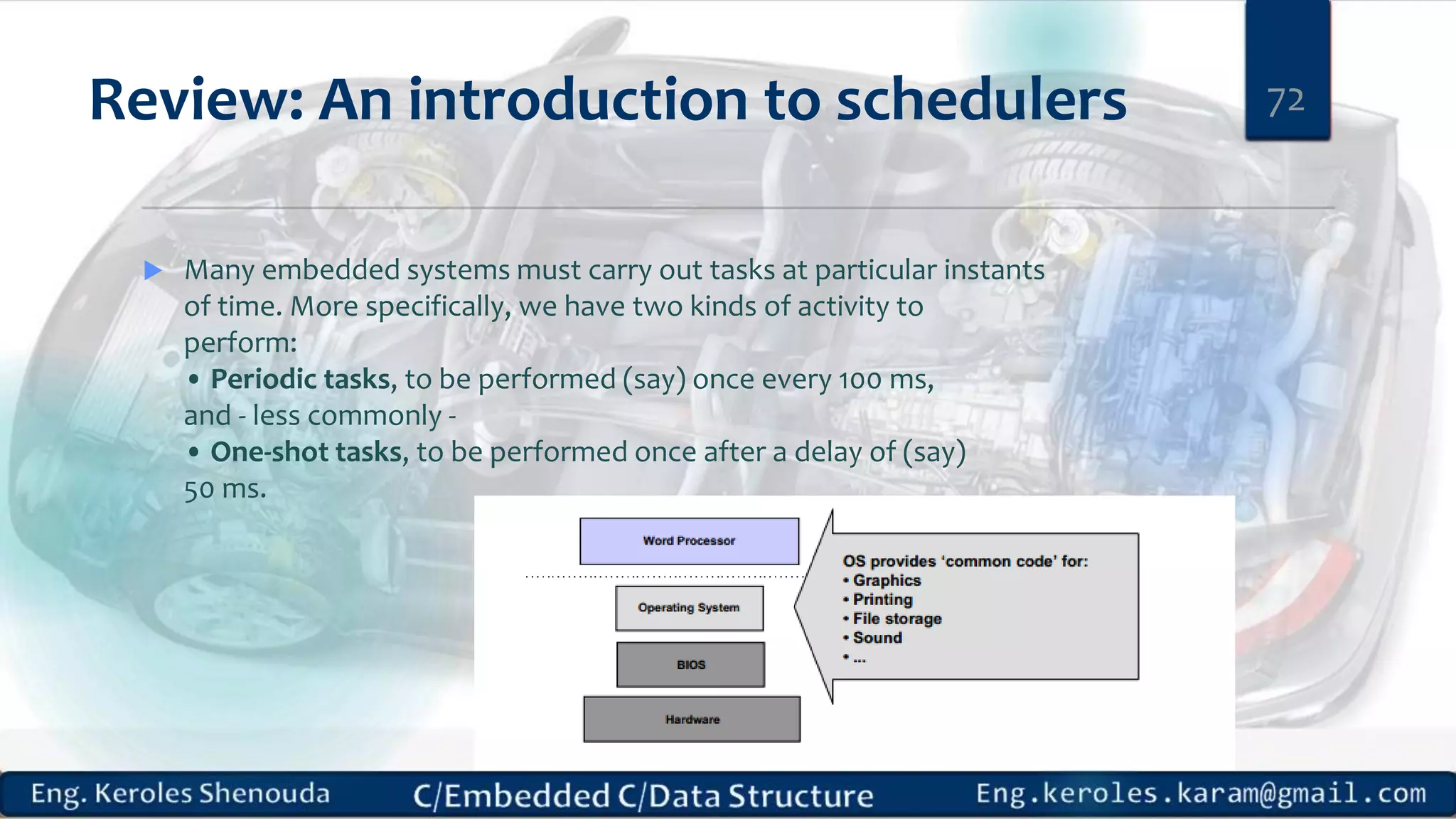
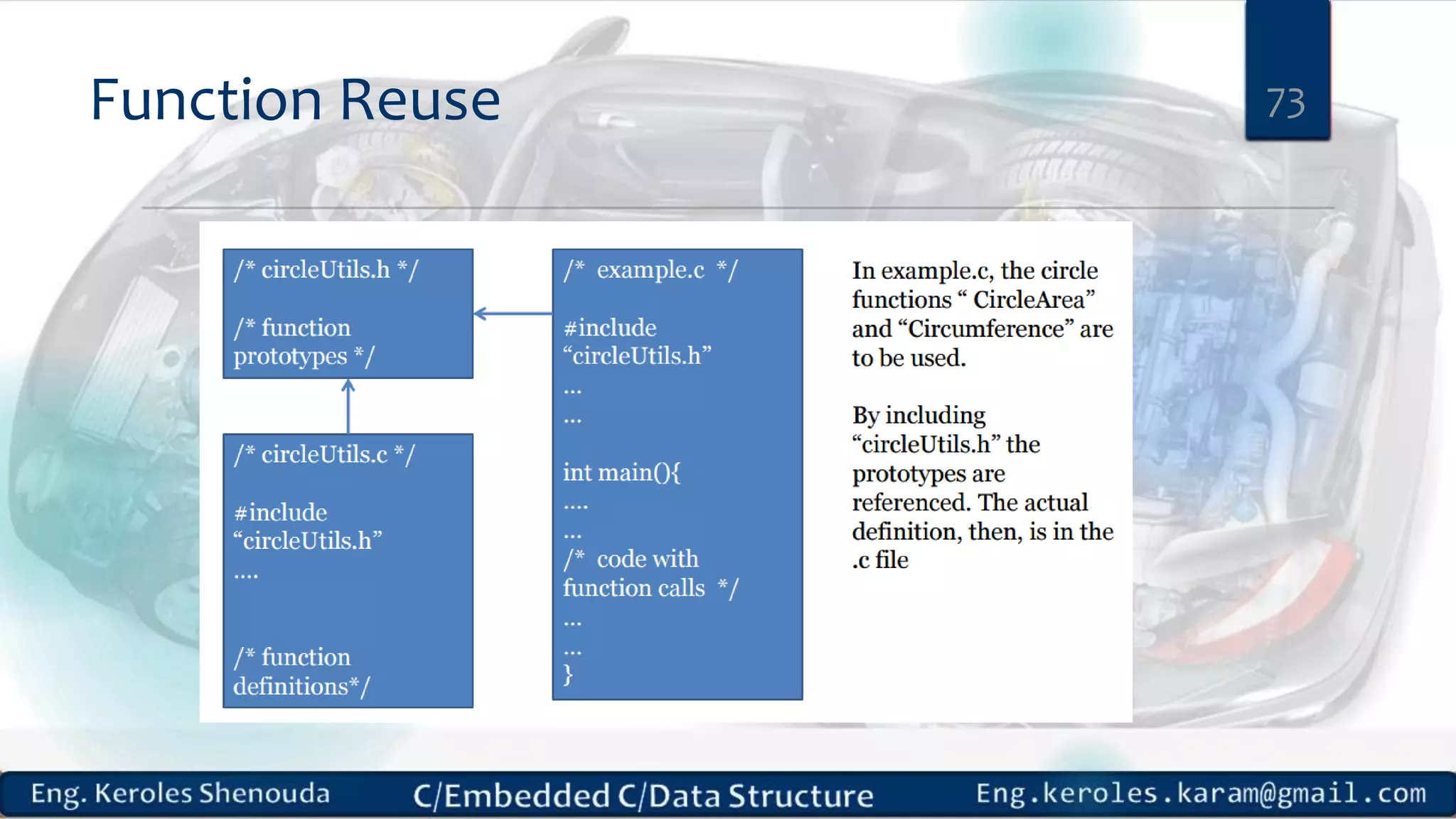
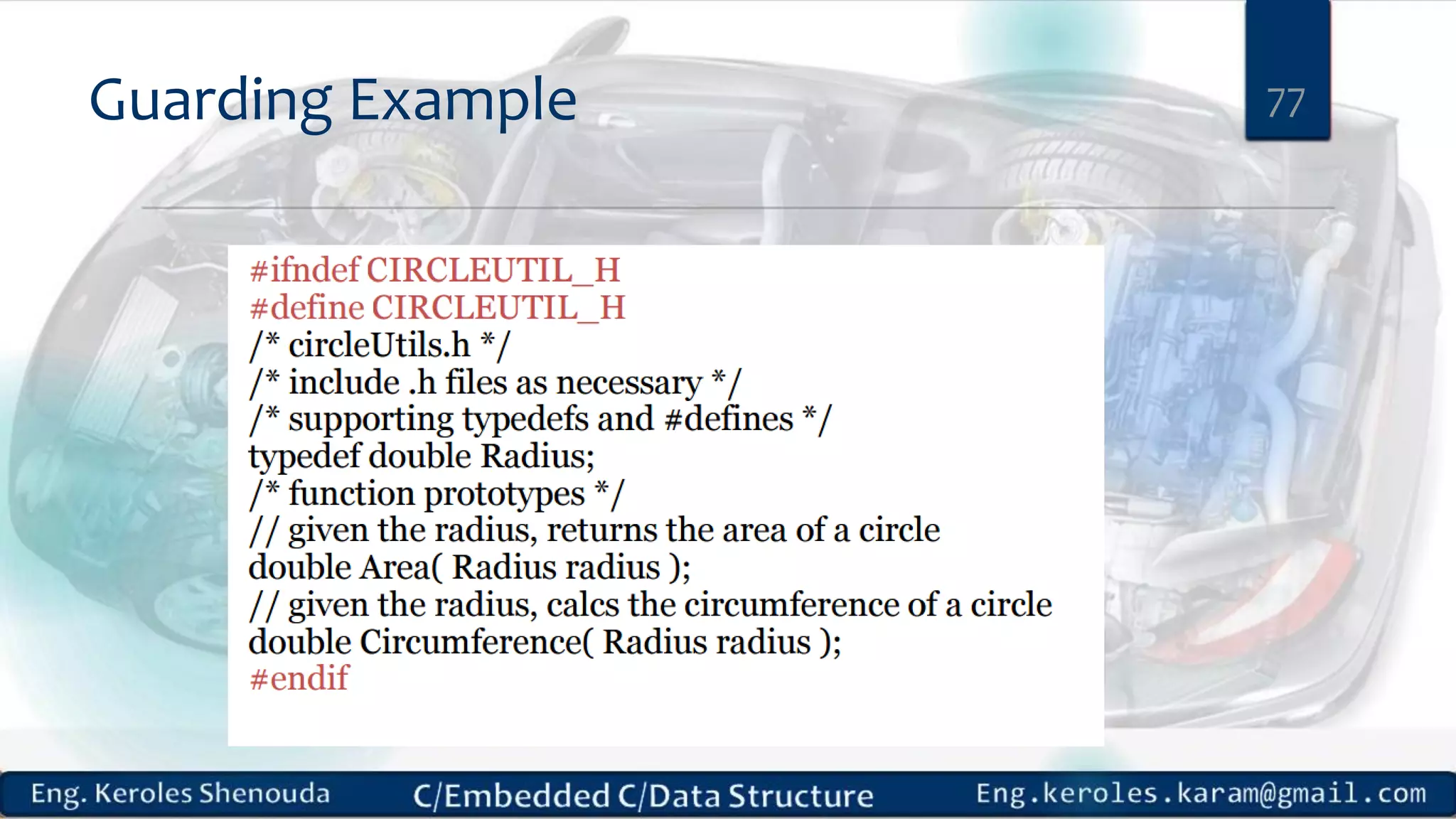
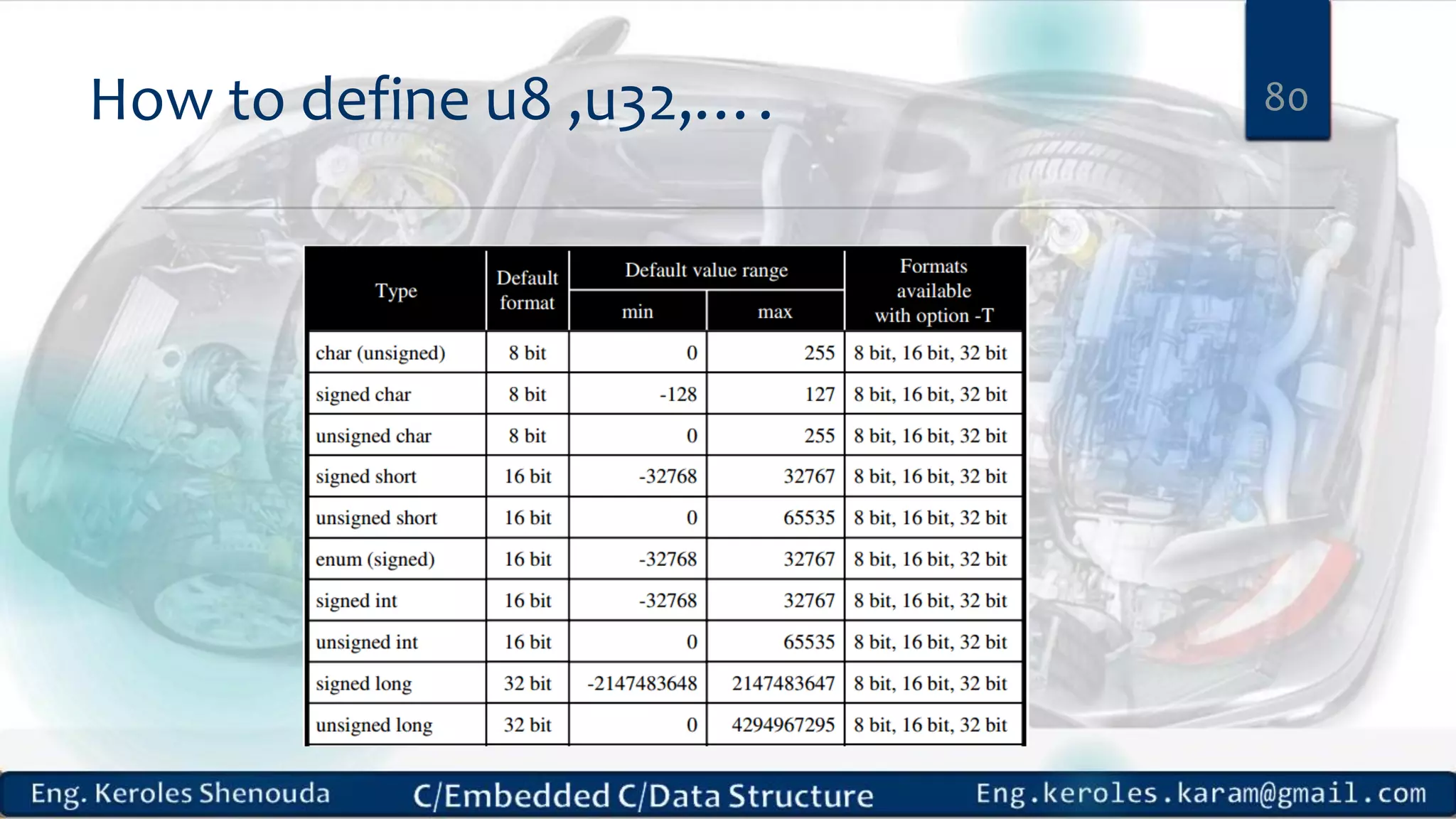
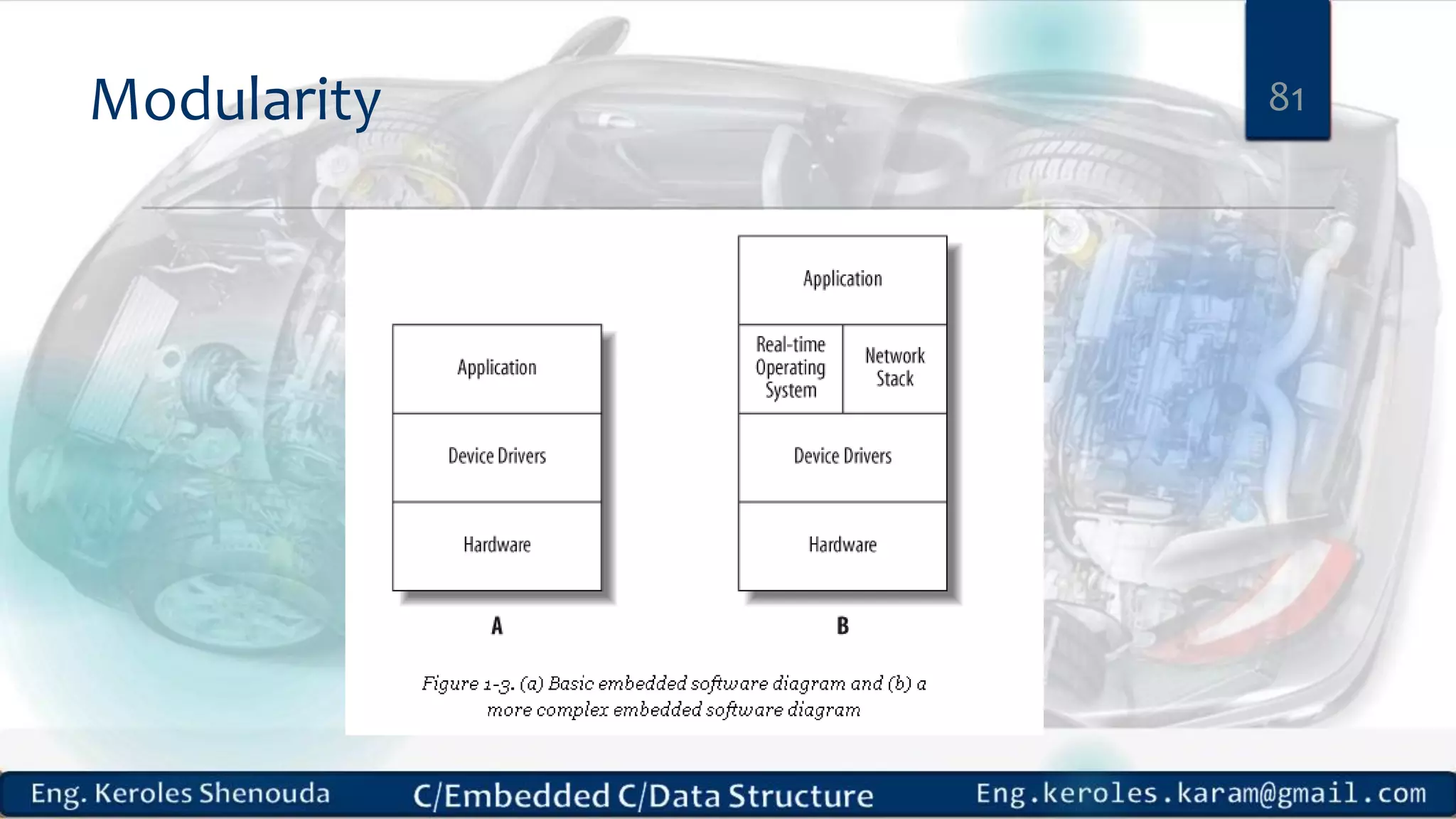
1. Embedded C requires compilers to create executable files that can be downloaded and run on microcontrollers, while C compilers typically generate code for operating systems on desktop computers. 2. Embedded systems often have real-time constraints and limited memory and other resources that require more optimization, unlike most desktop applications. 3. Programming for embedded systems focuses on optimally using limited resources and satisfying timing requirements using basic C constructs and function libraries.