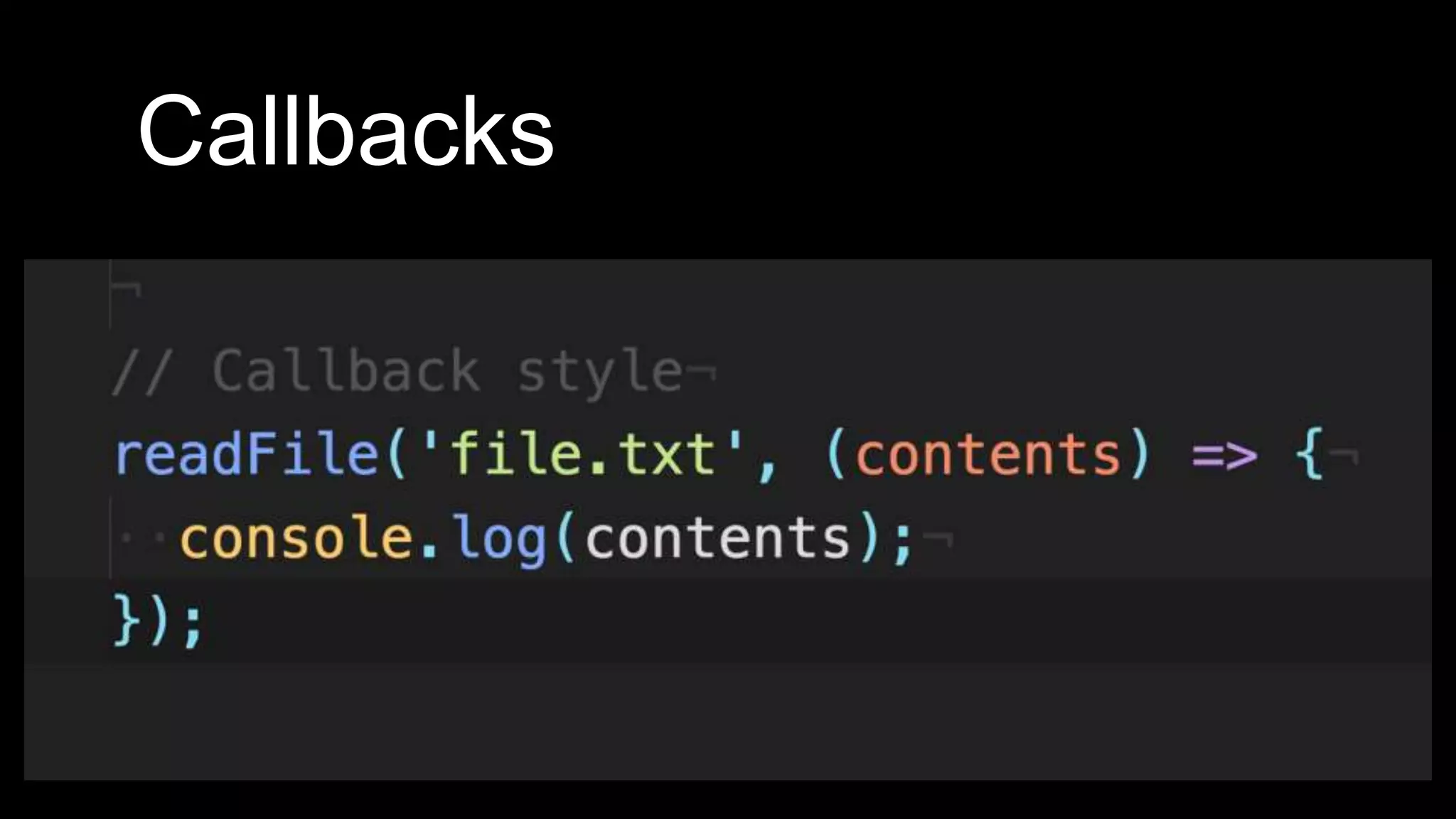
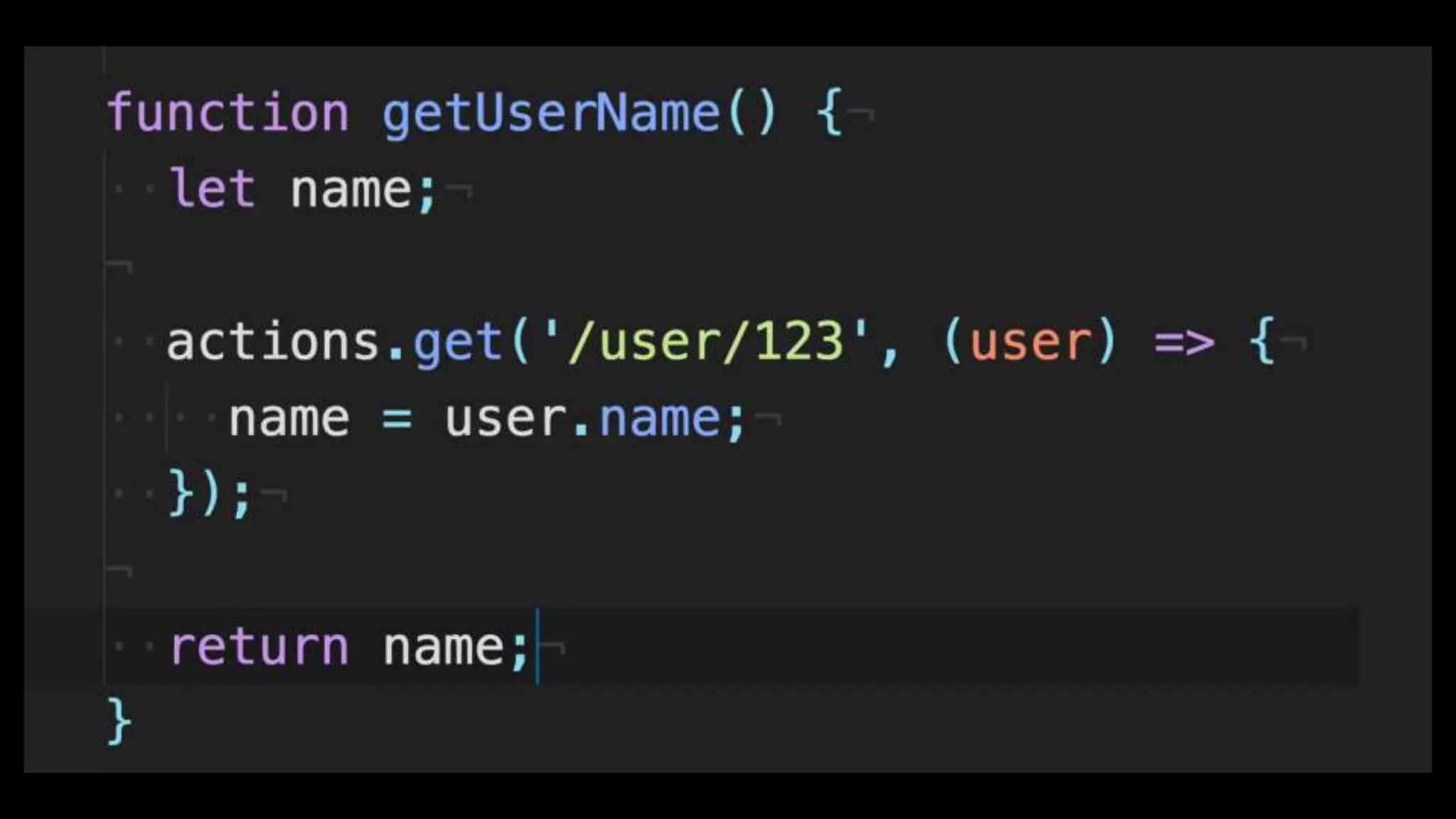
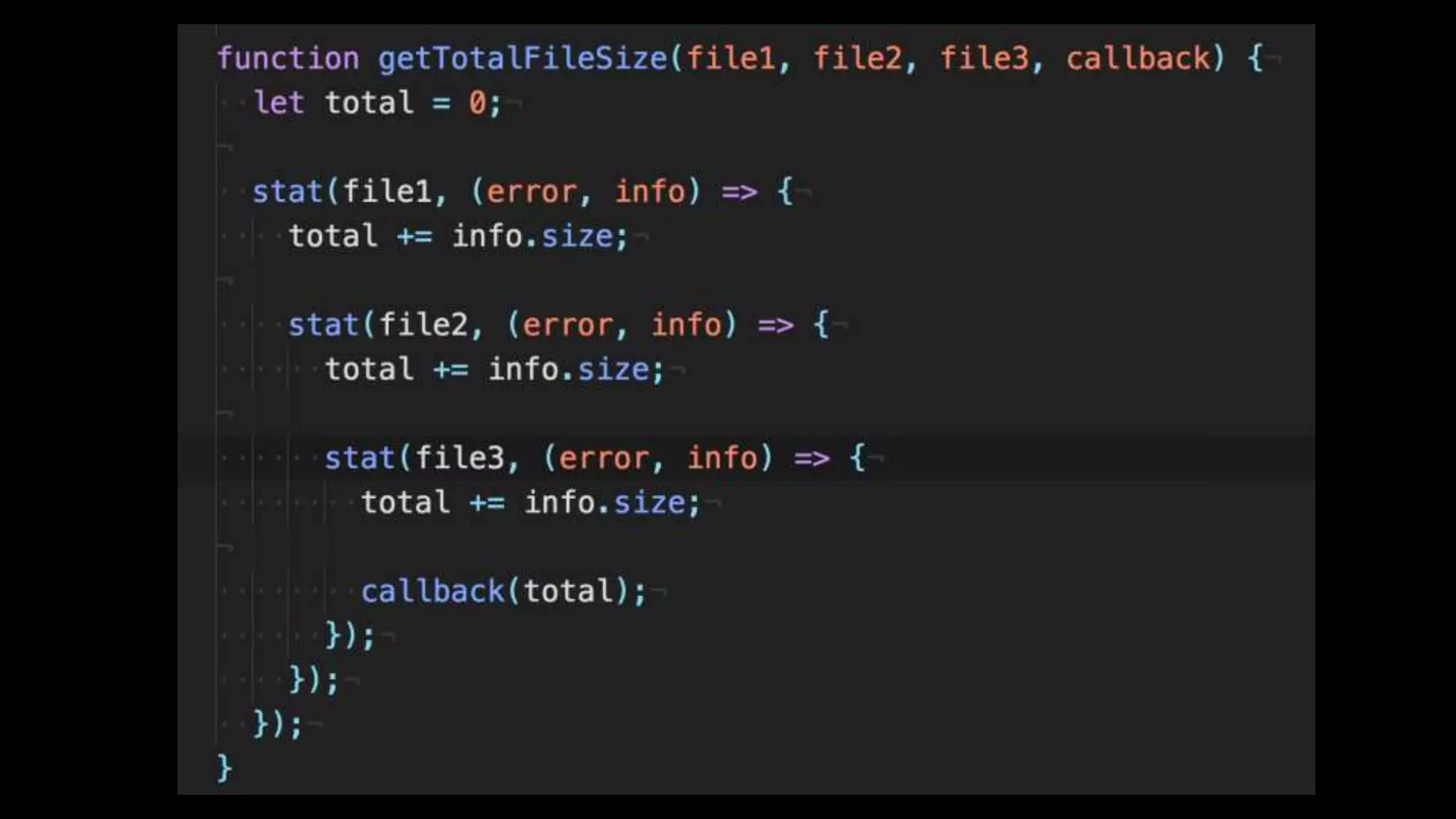
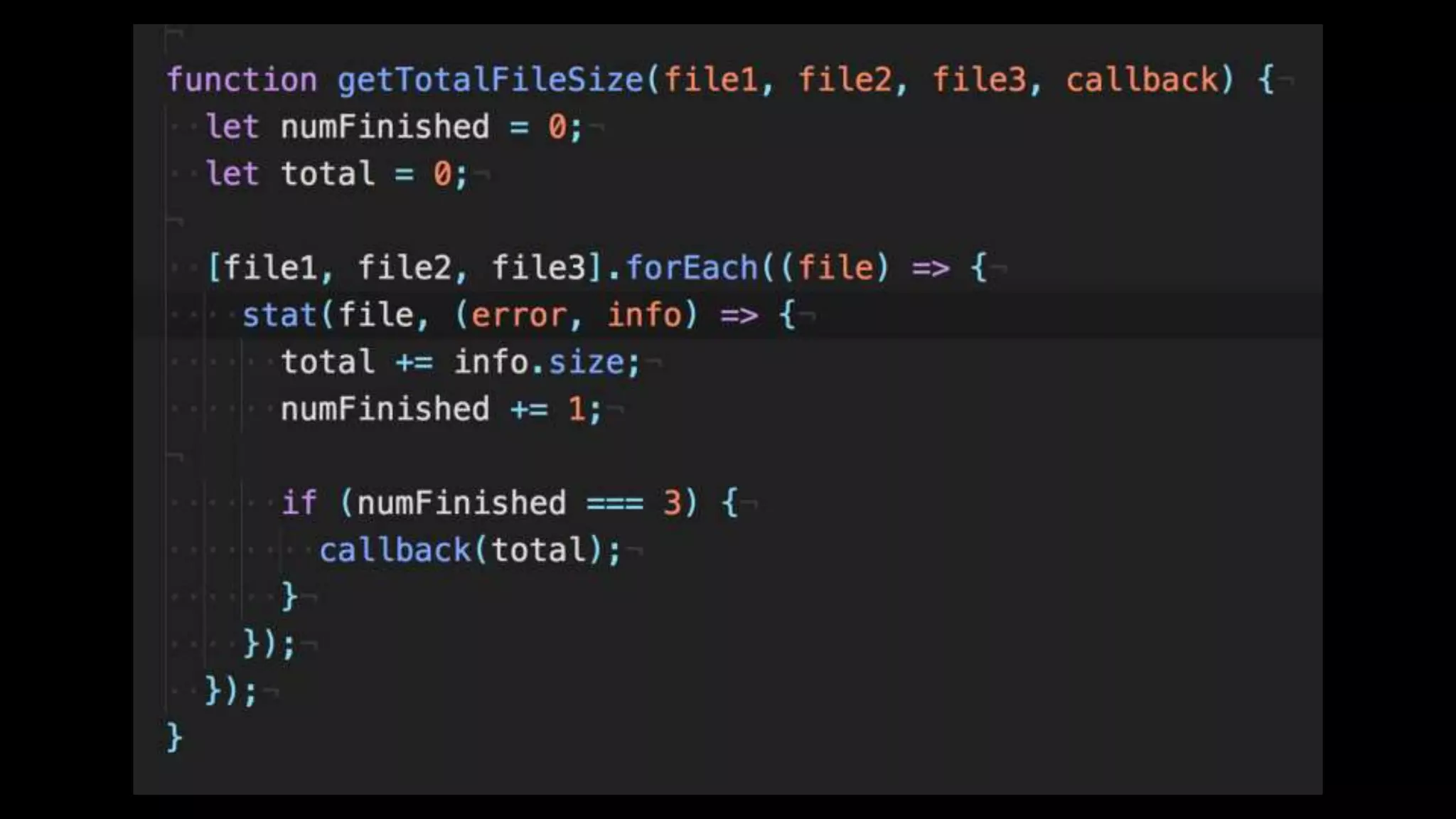
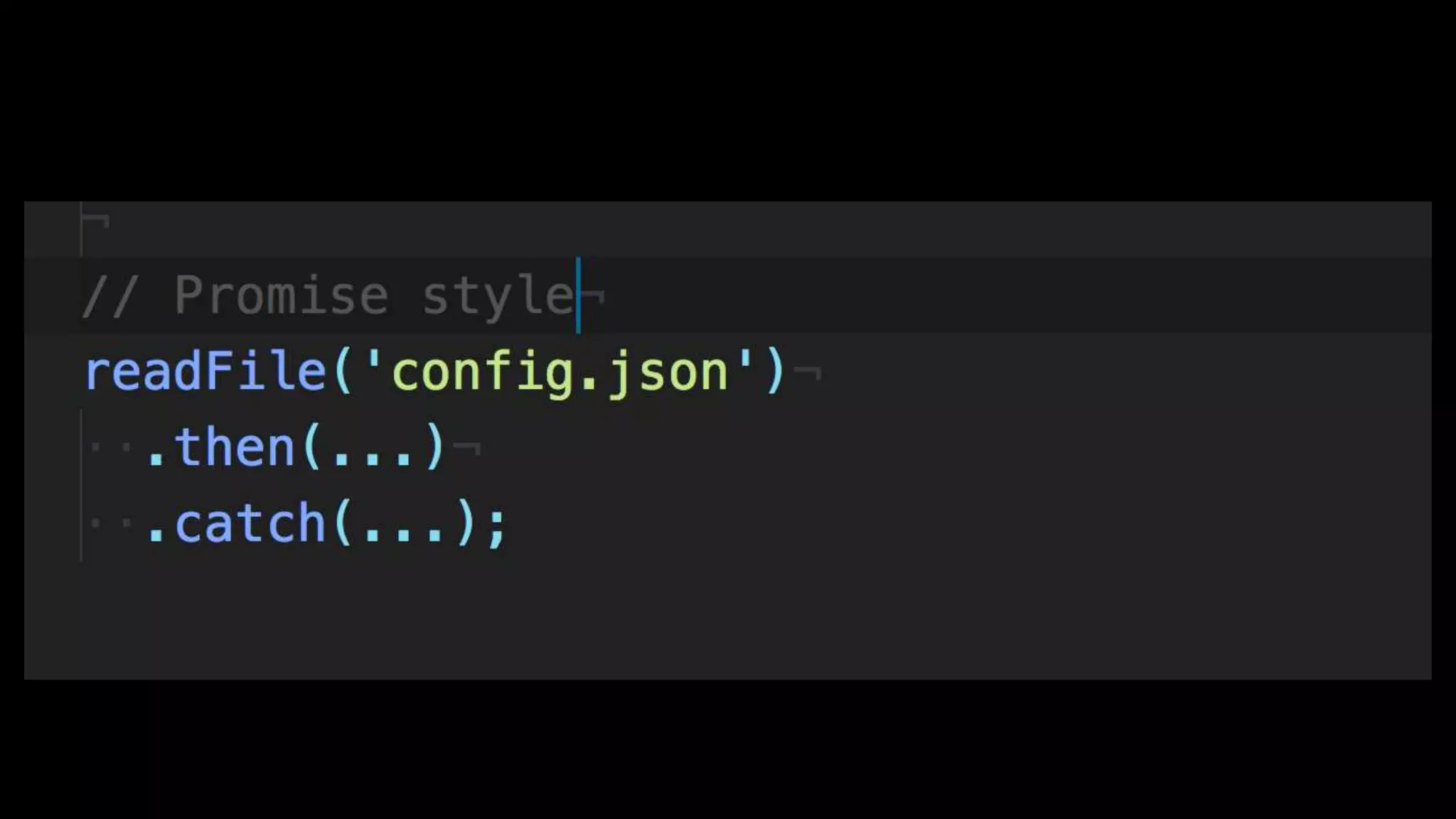
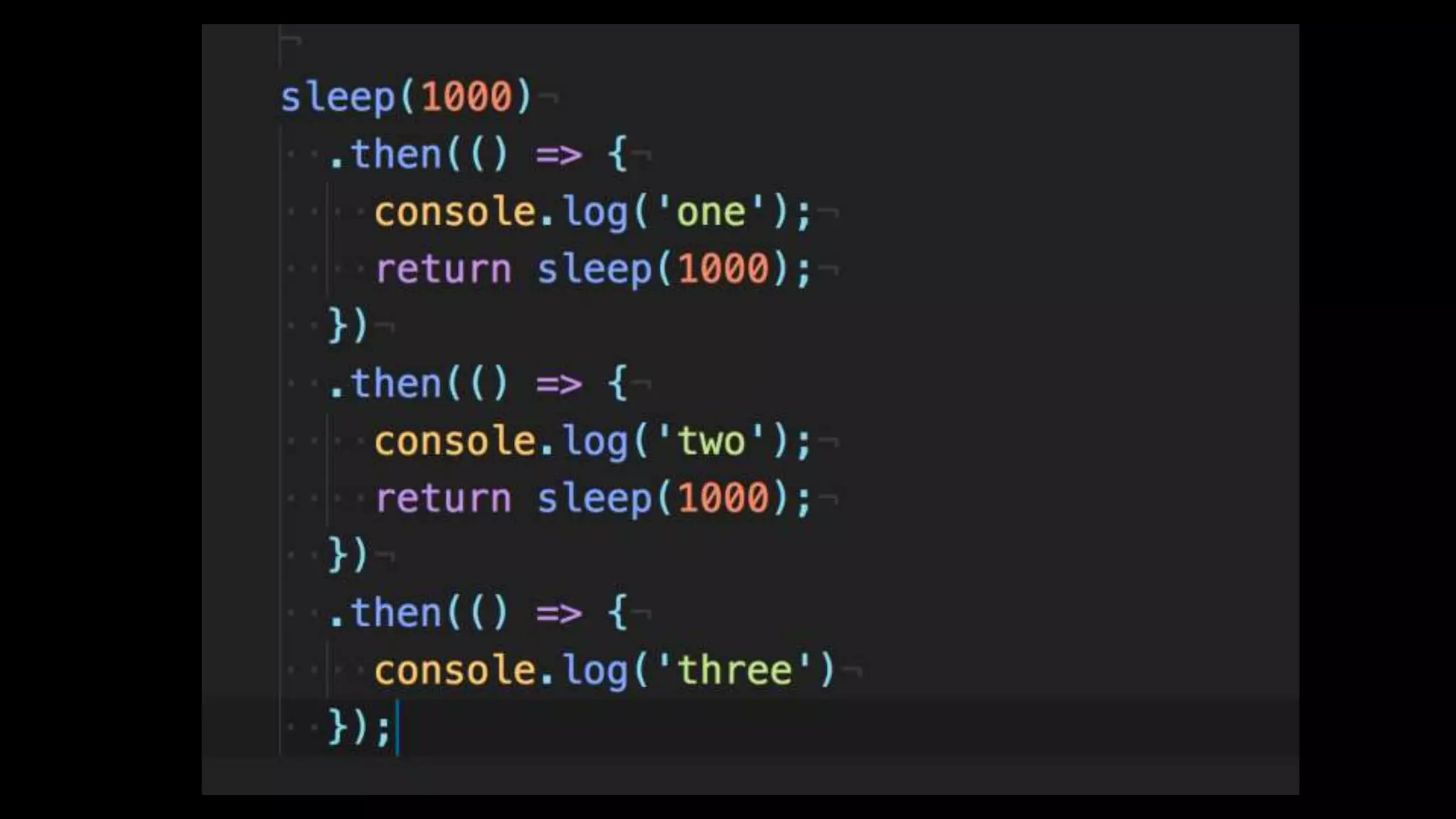
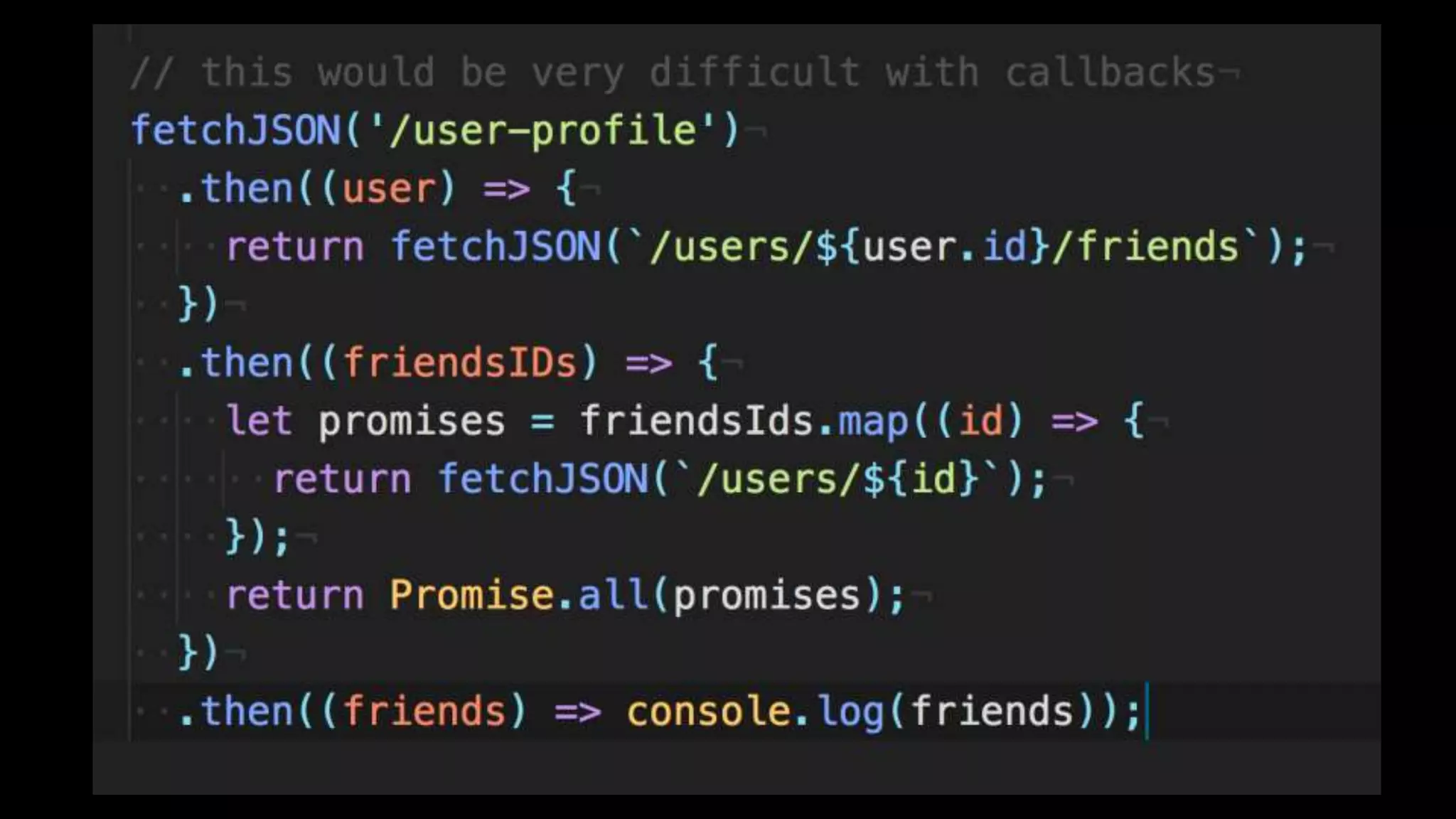
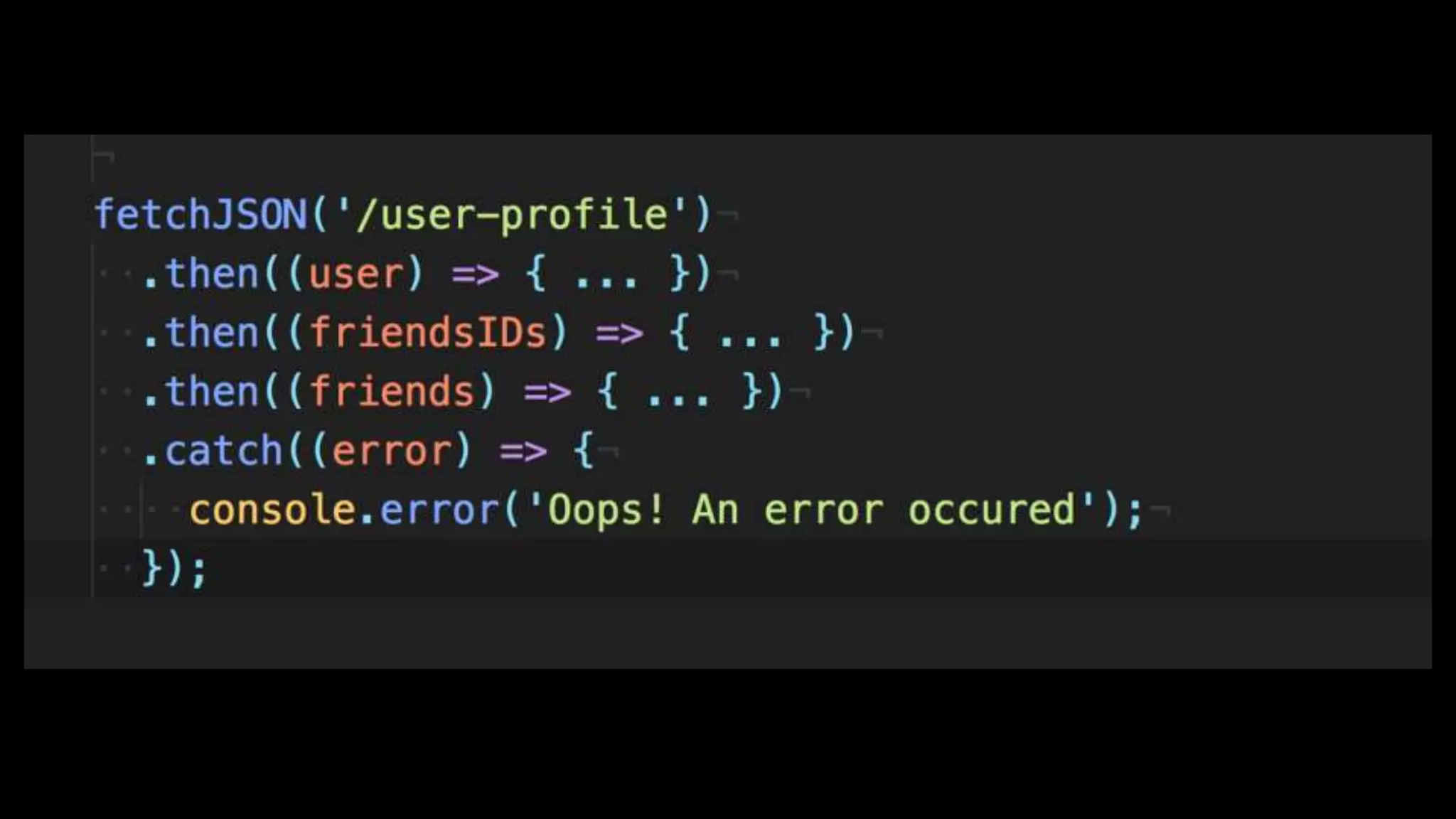
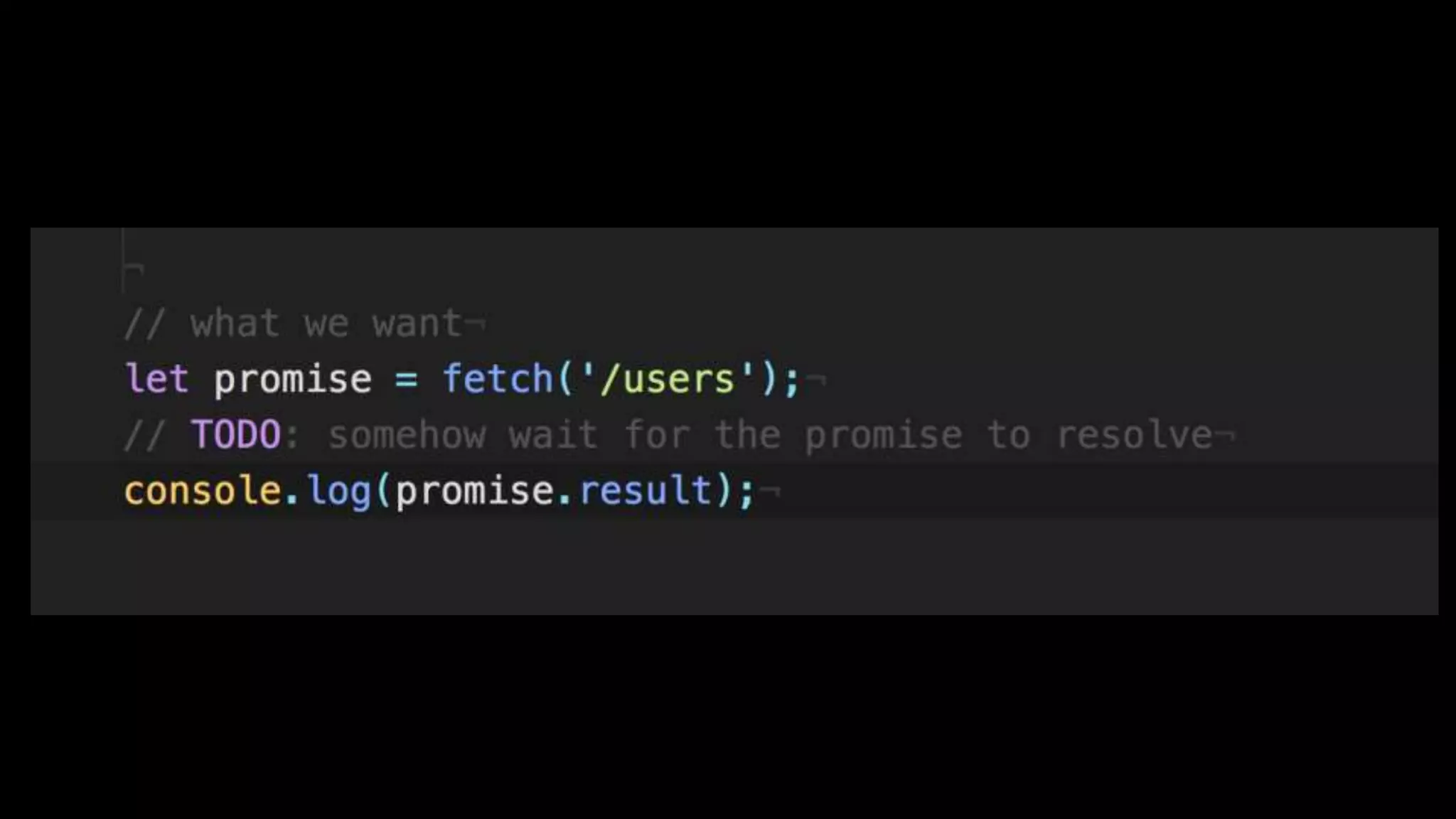
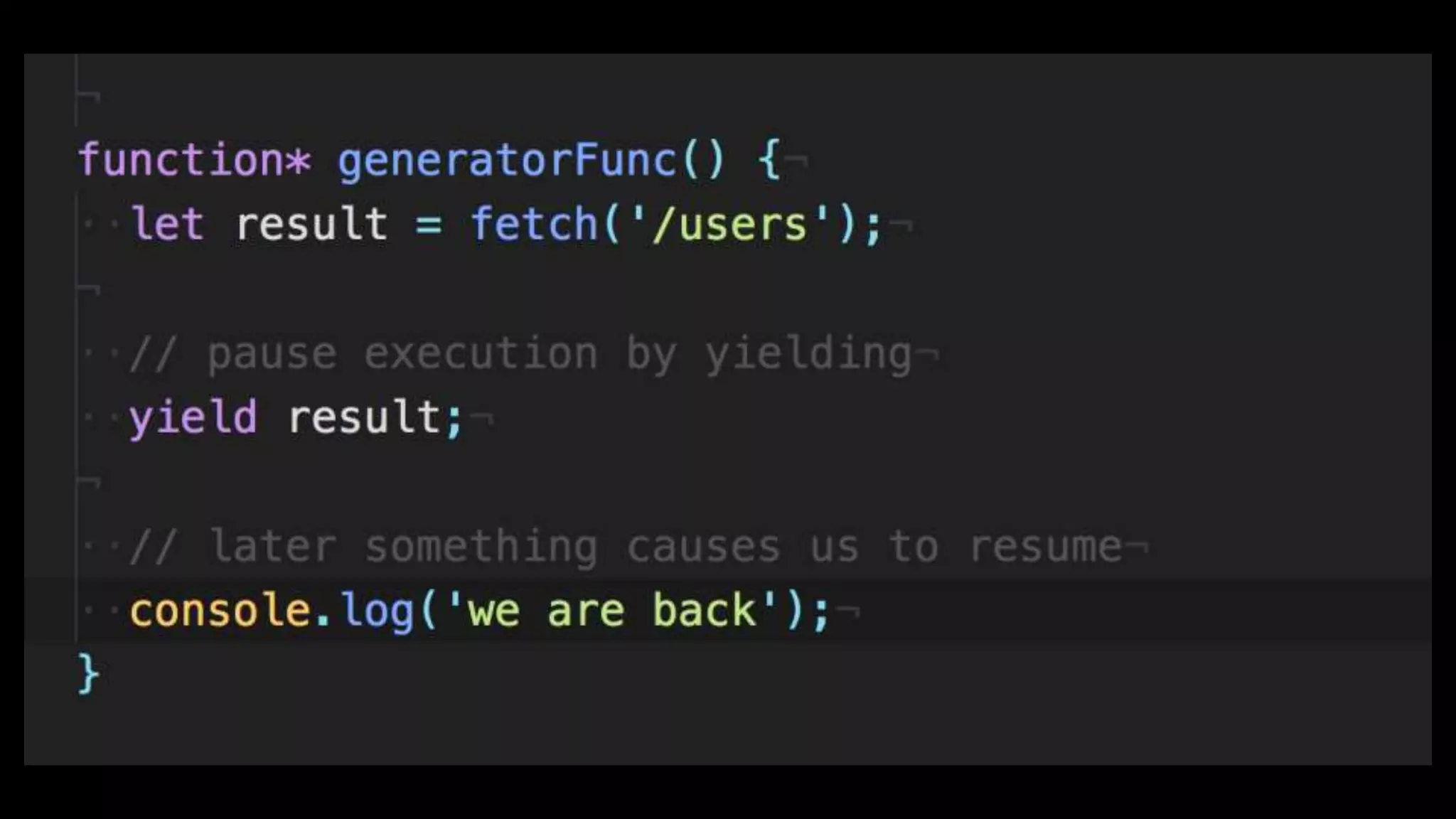
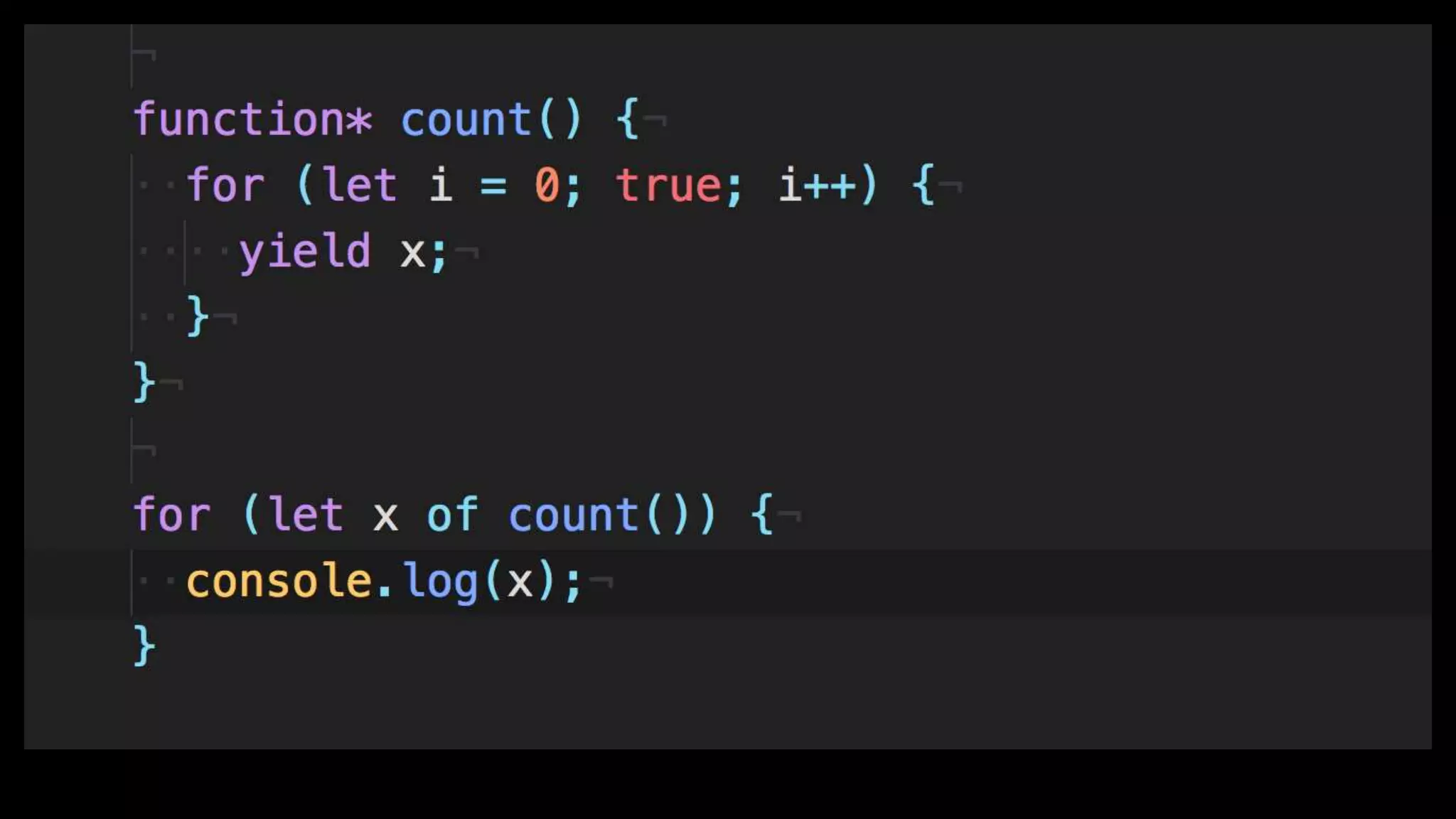
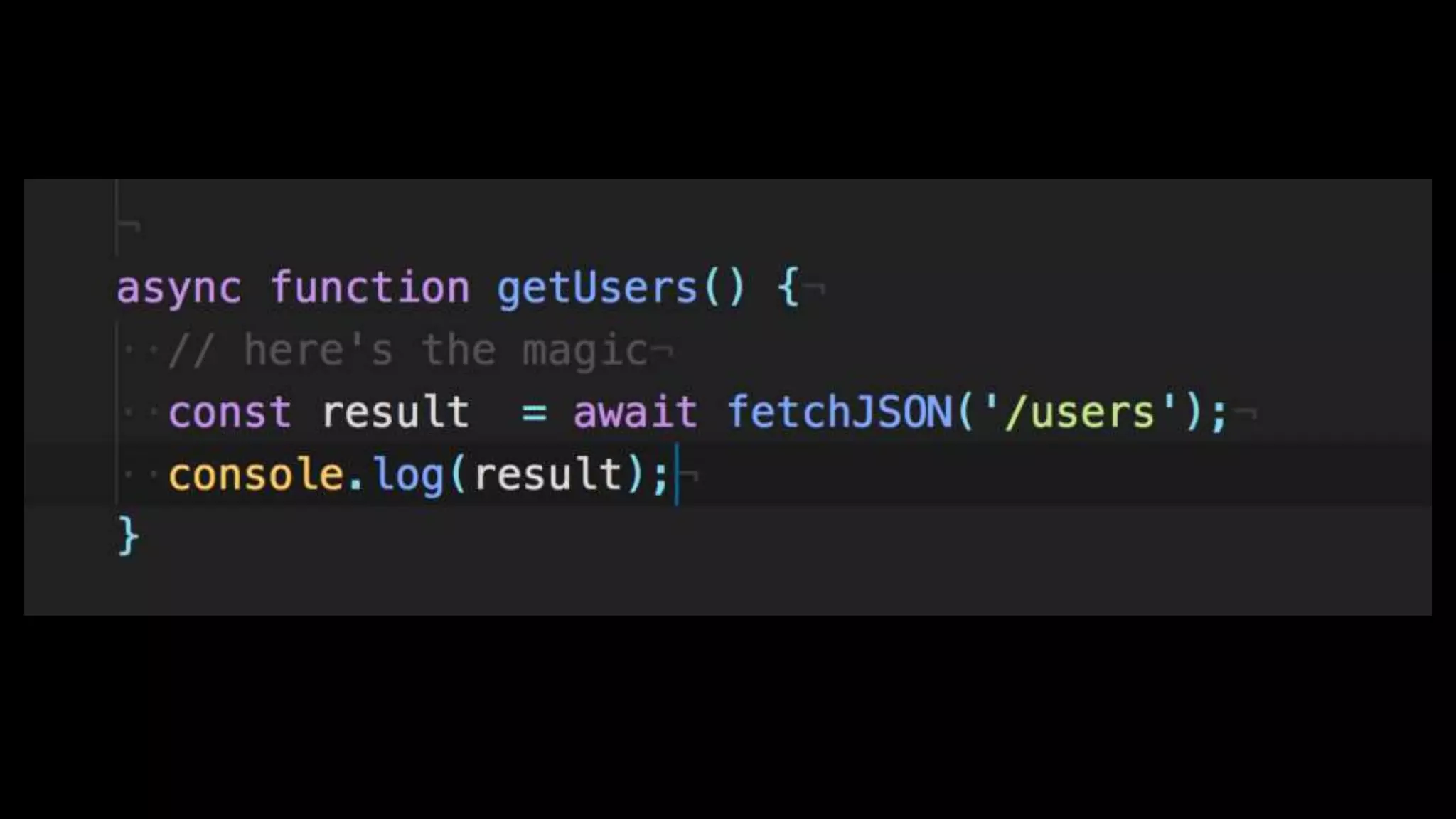
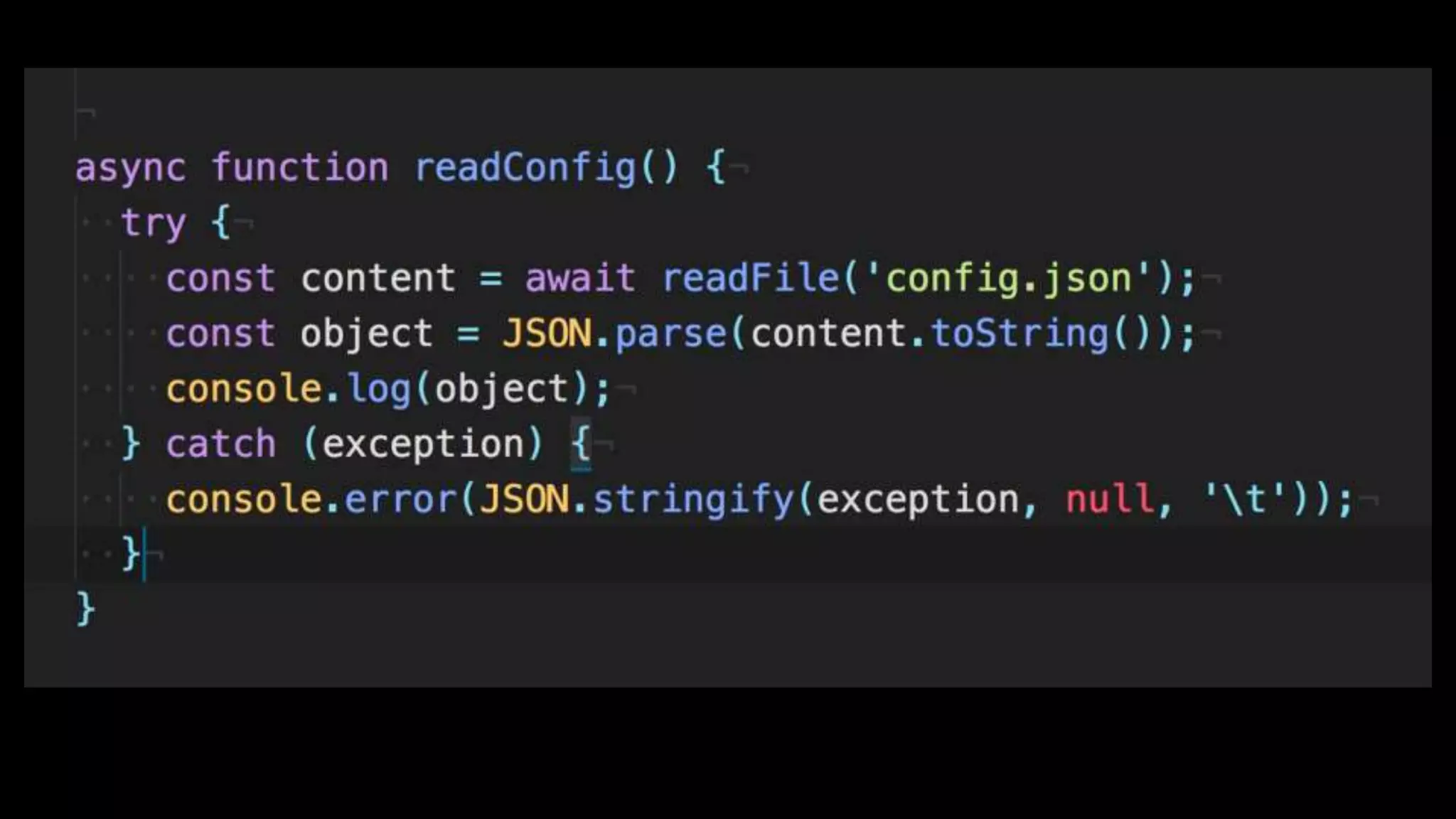
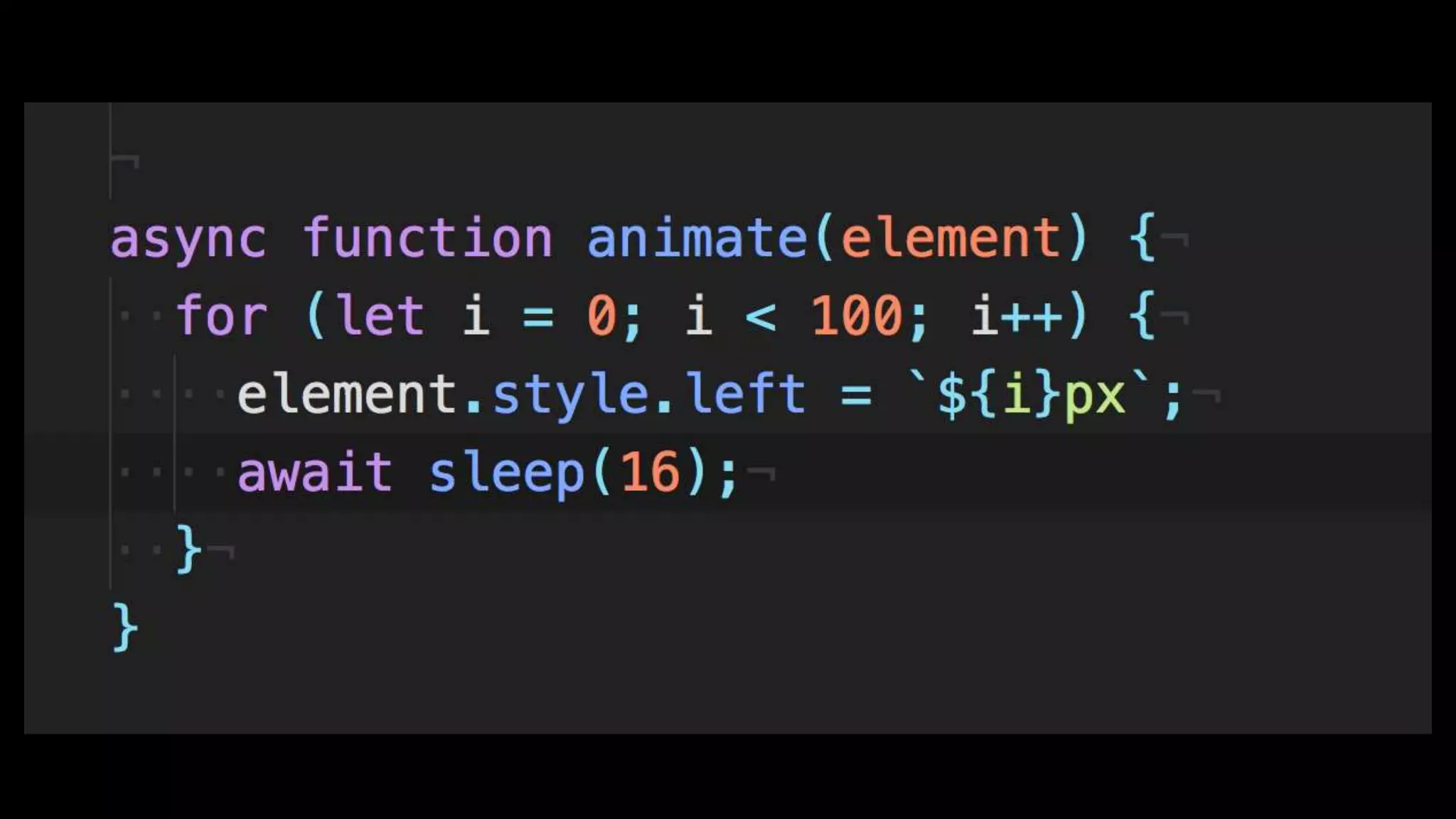
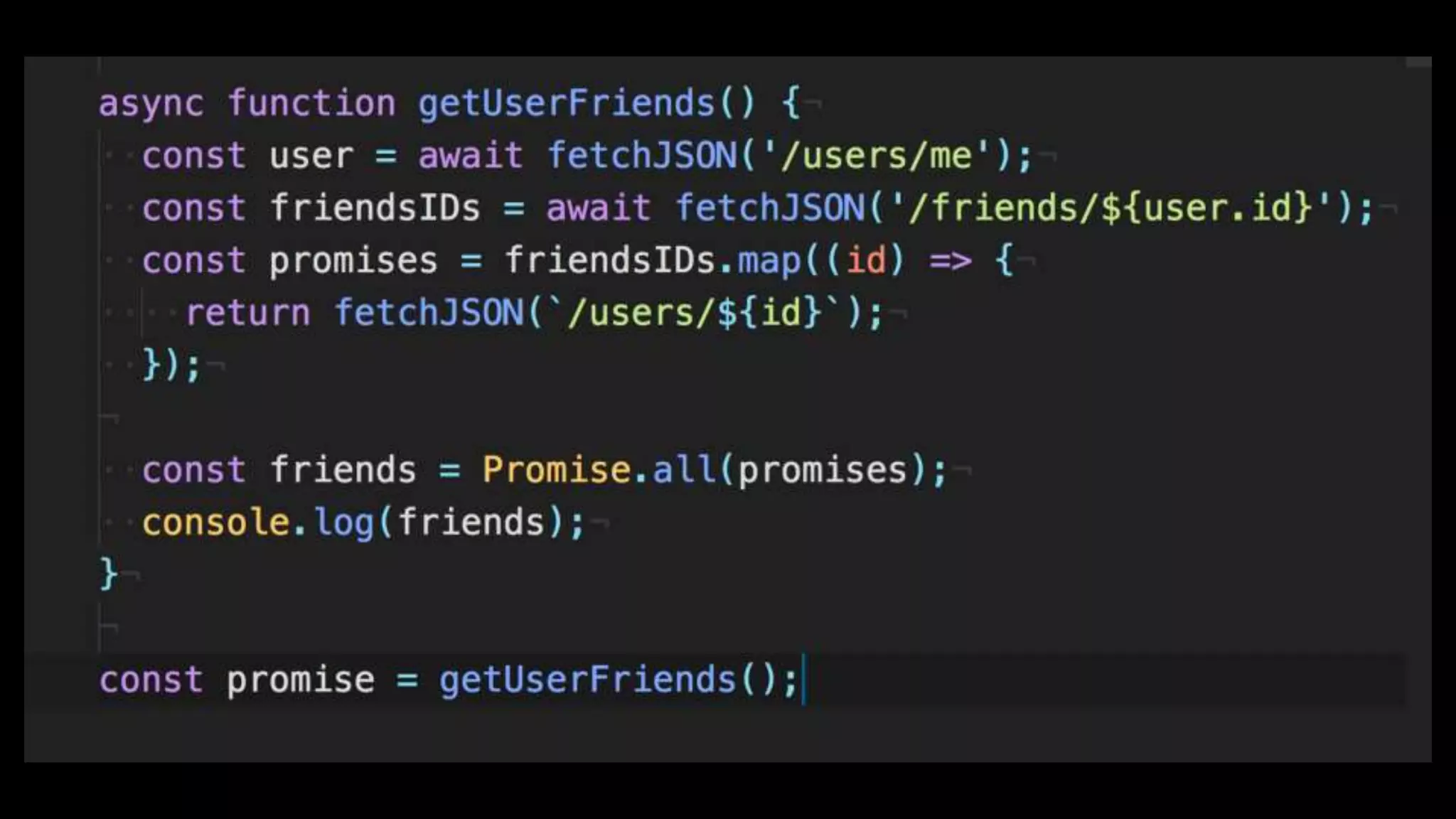
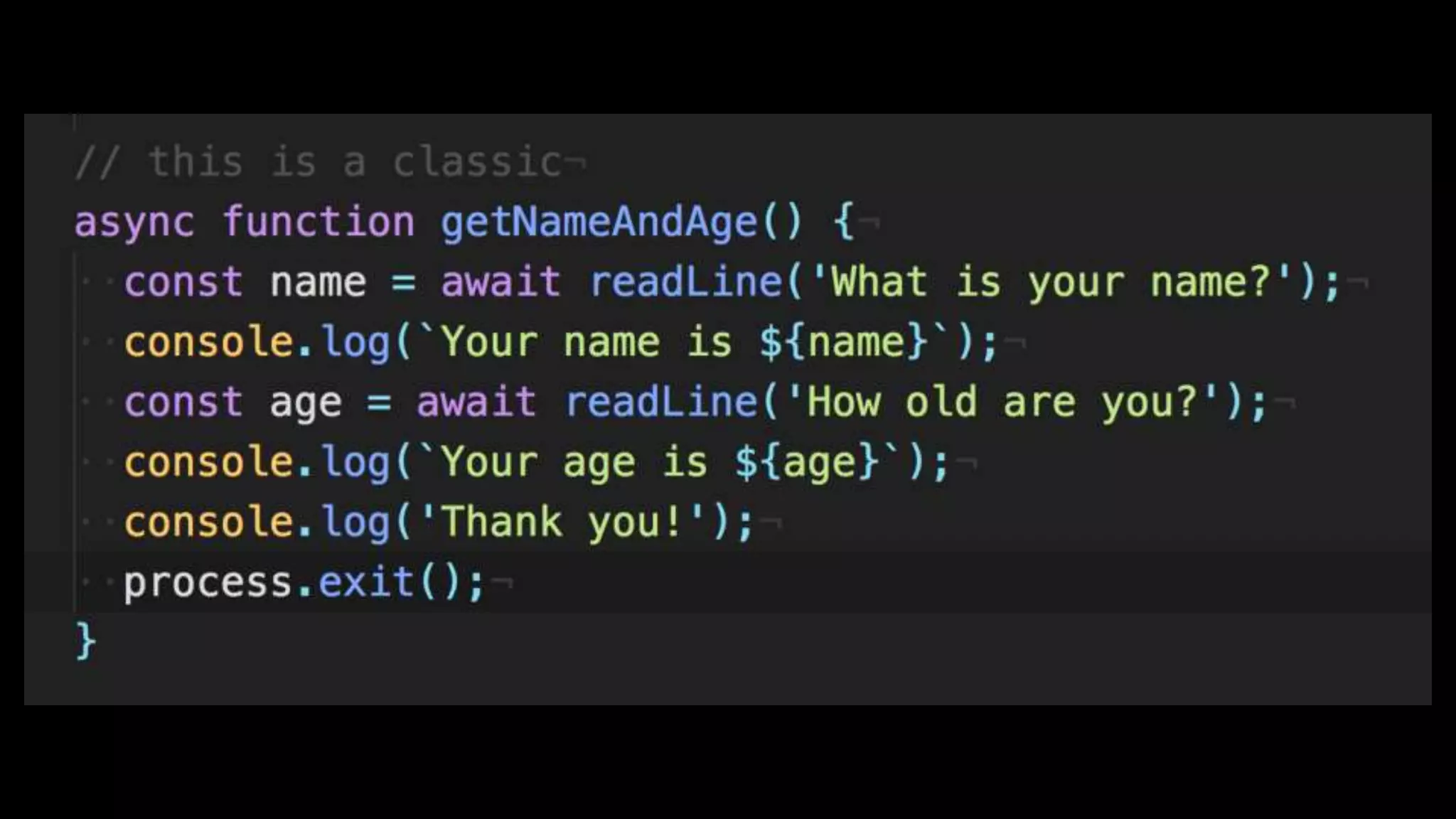
This document discusses concurrency in JavaScript and how async/await helps improve asynchronous code. It covers: - Concurrency involves doing multiple tasks over time in order or partially ordered ways. JavaScript uses non-blocking I/O with an event loop. - Blocking code can halt everything, so JavaScript uses callbacks for asynchronous operations like network requests. - Promises help solve issues with callbacks but still require callback functions. Async/await allows writing asynchronous code that looks synchronous using generators and promises under the hood. It provides better readability and error handling than callbacks or promises alone. Developers must still be careful about parallelism and await usage.