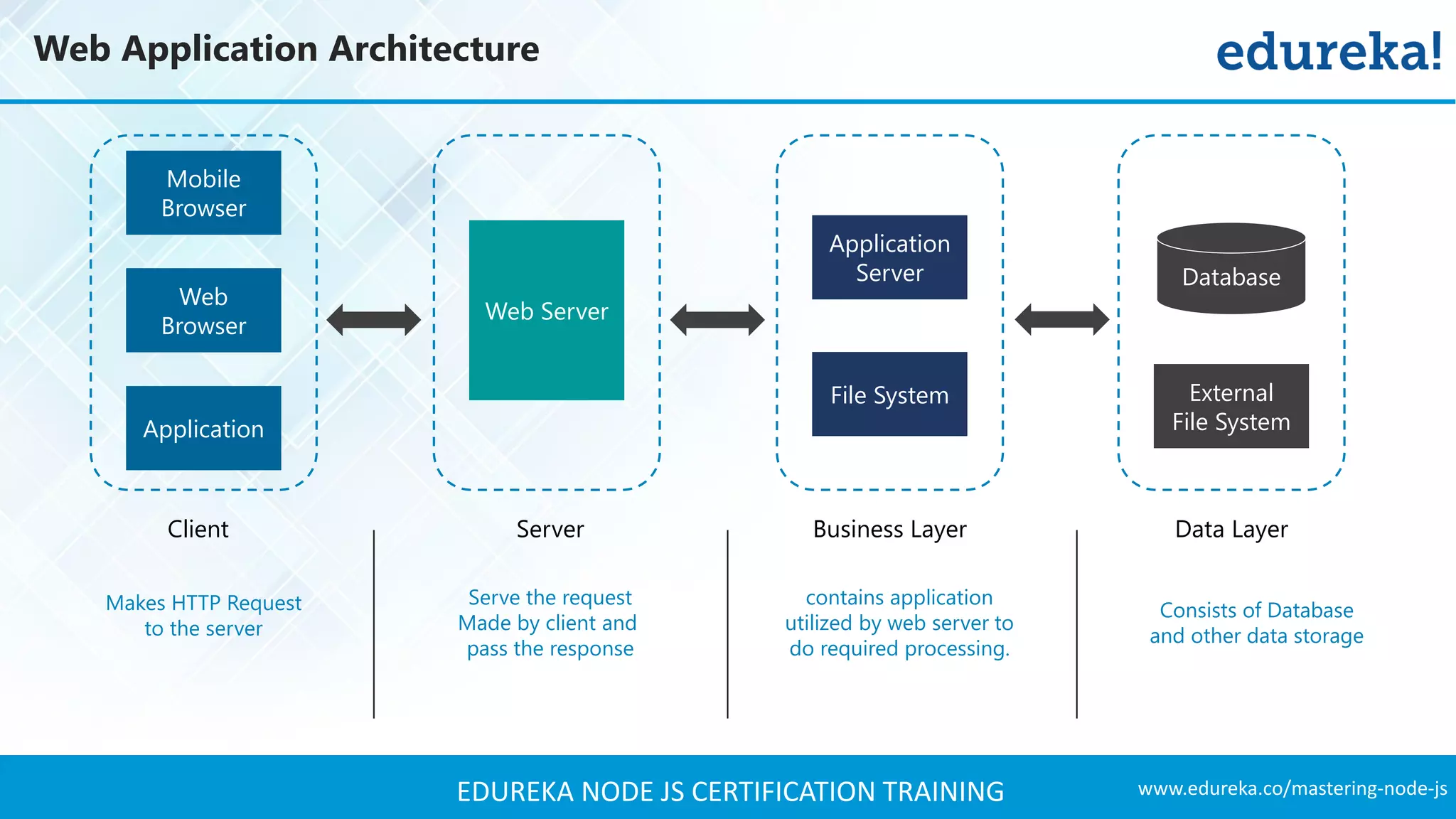
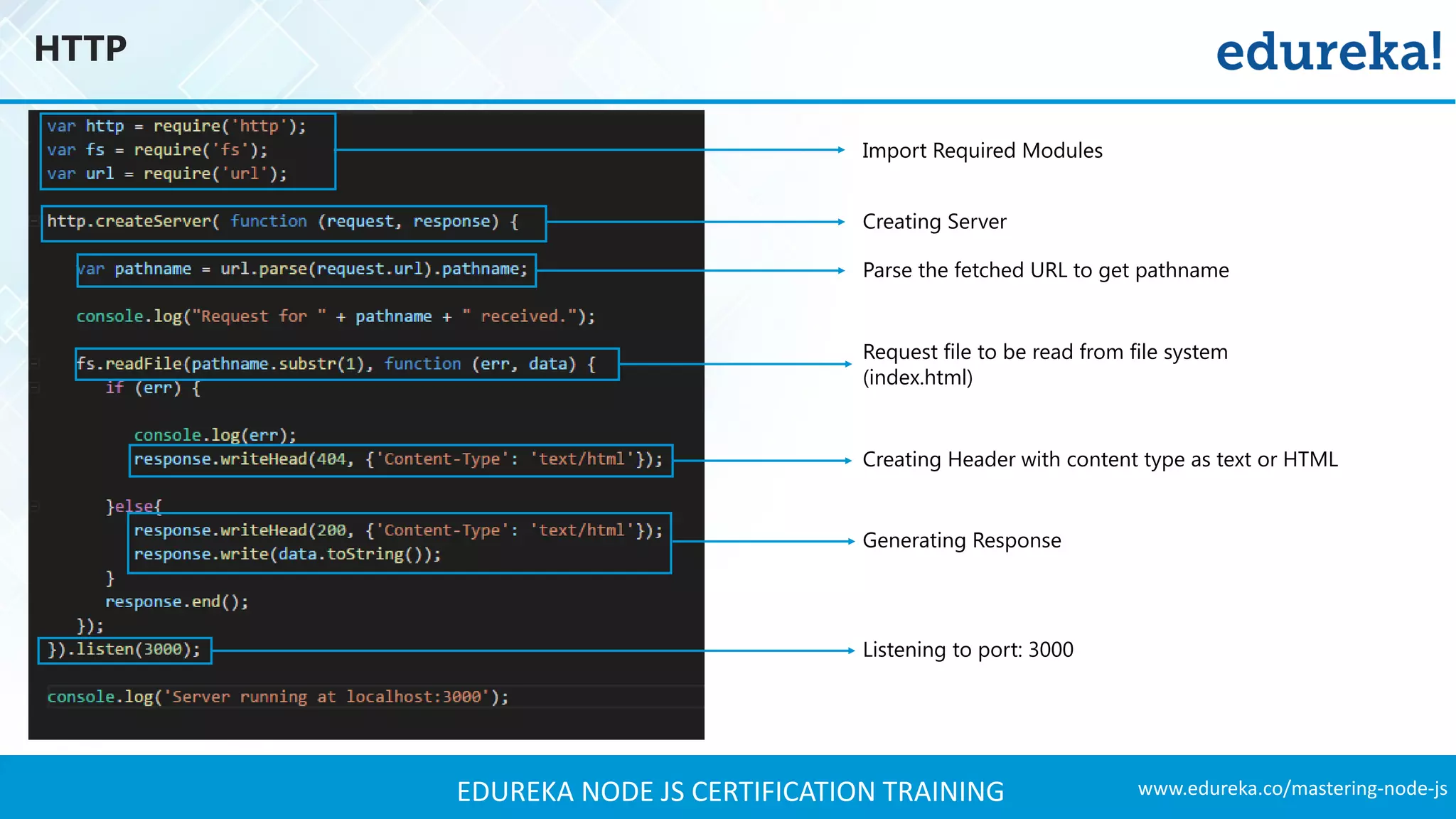
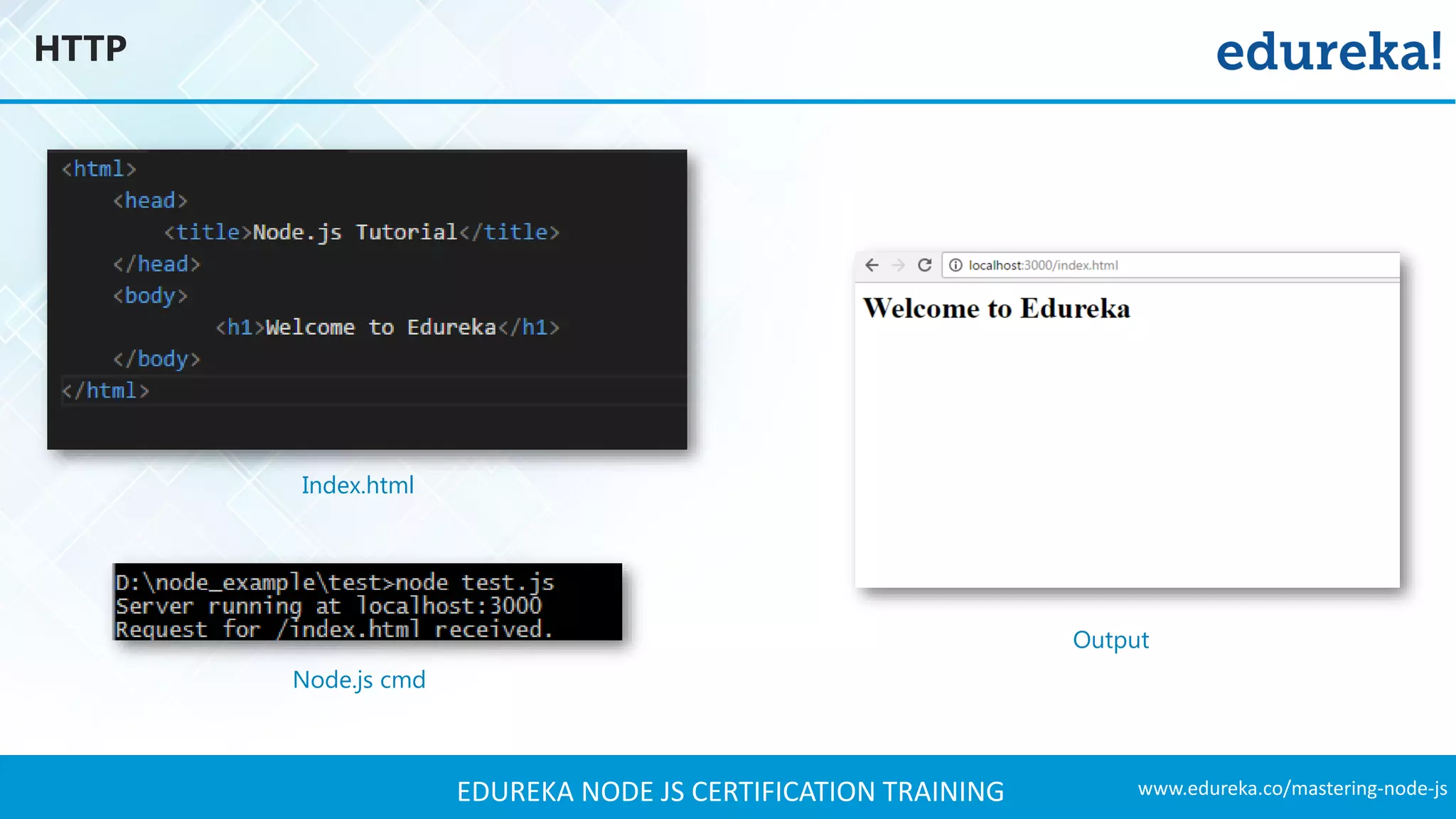
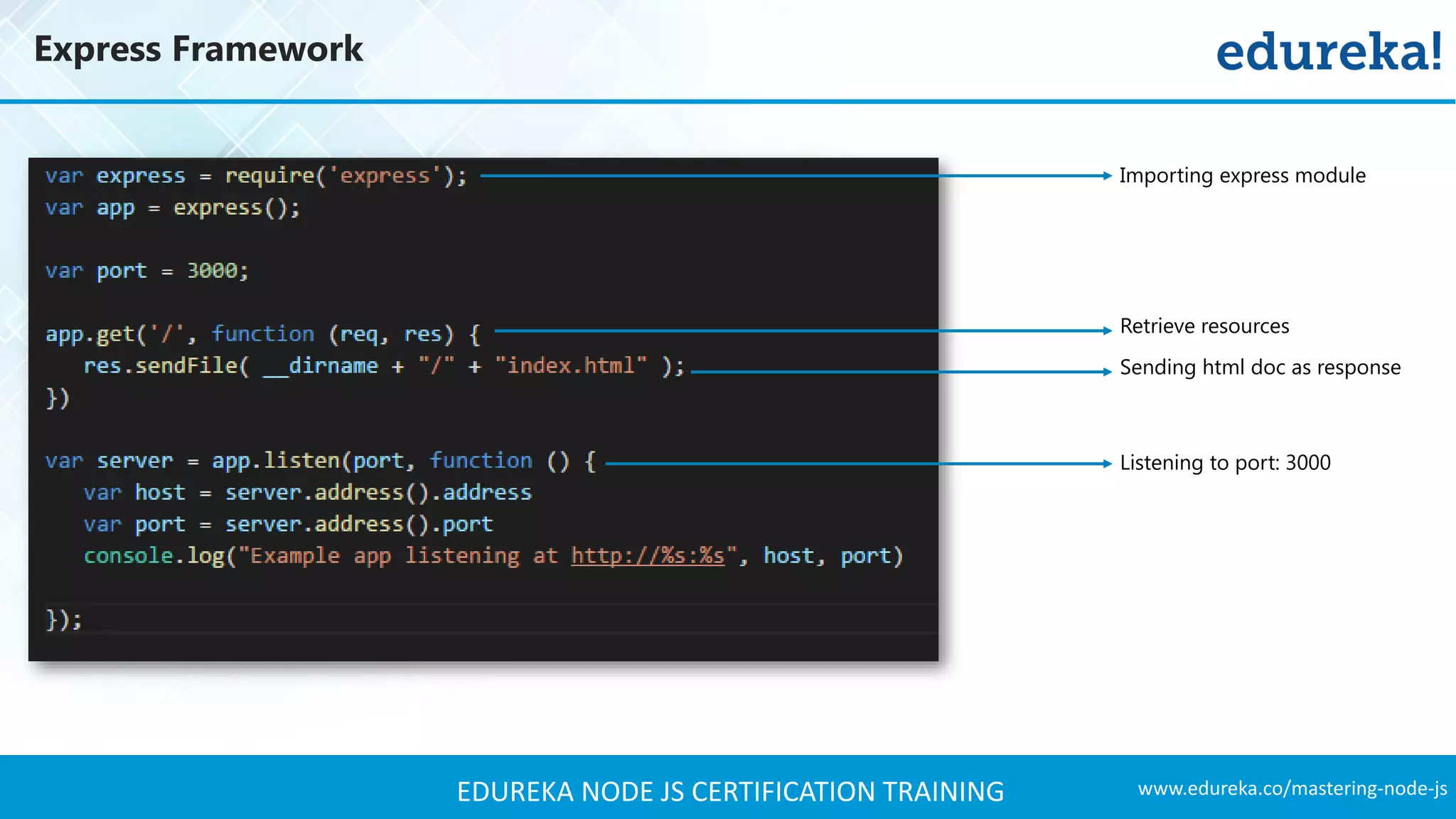
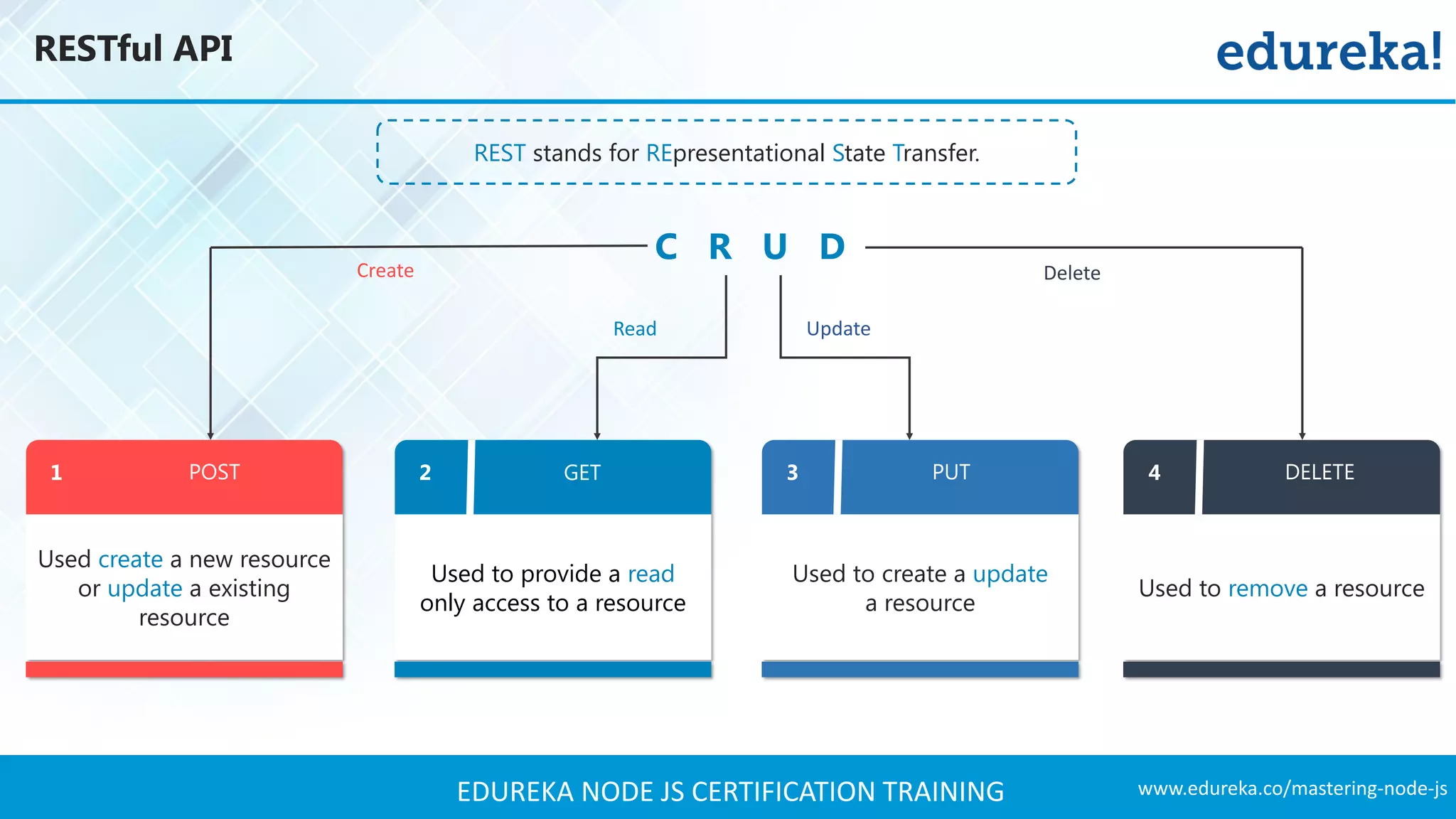
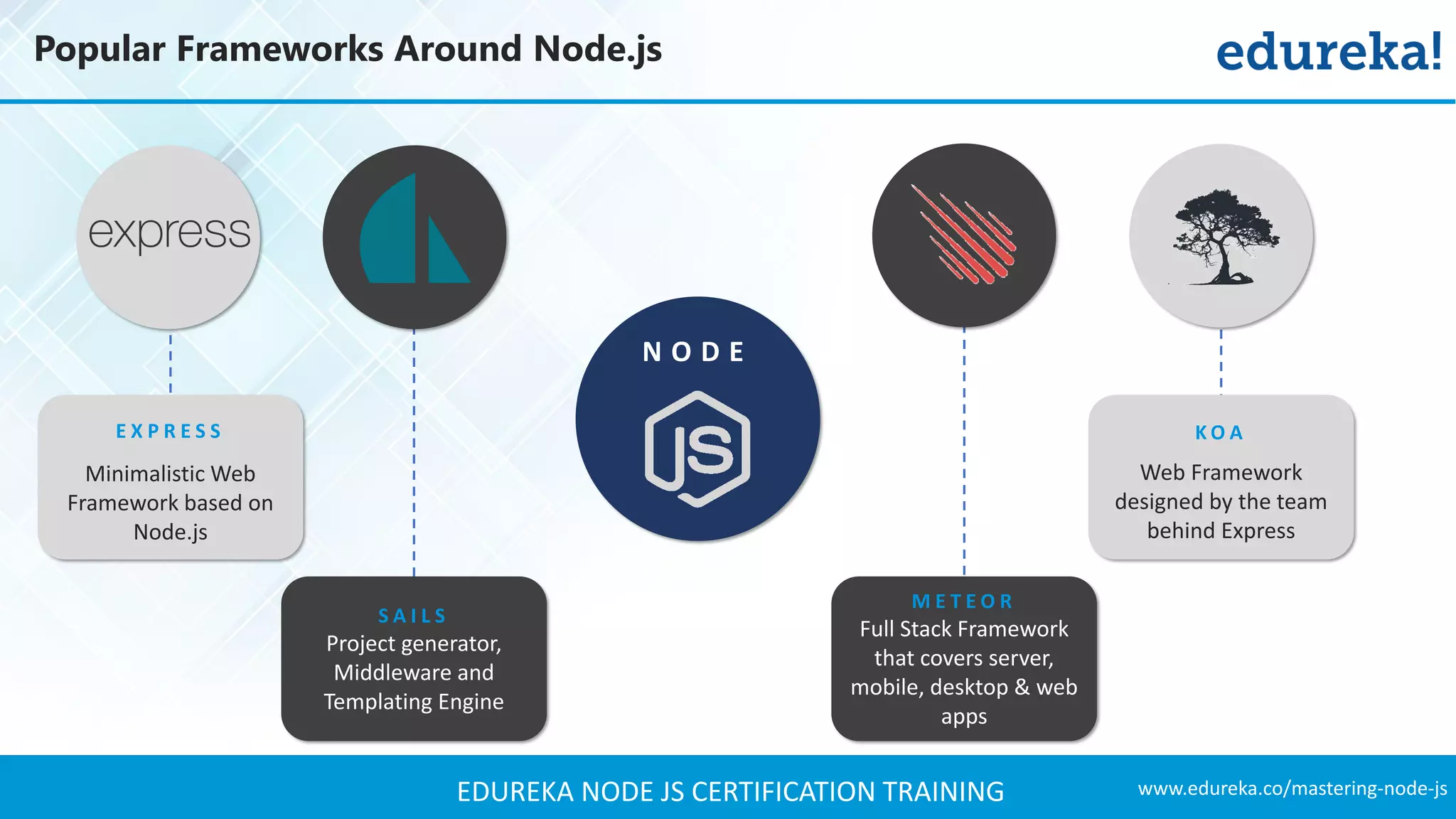
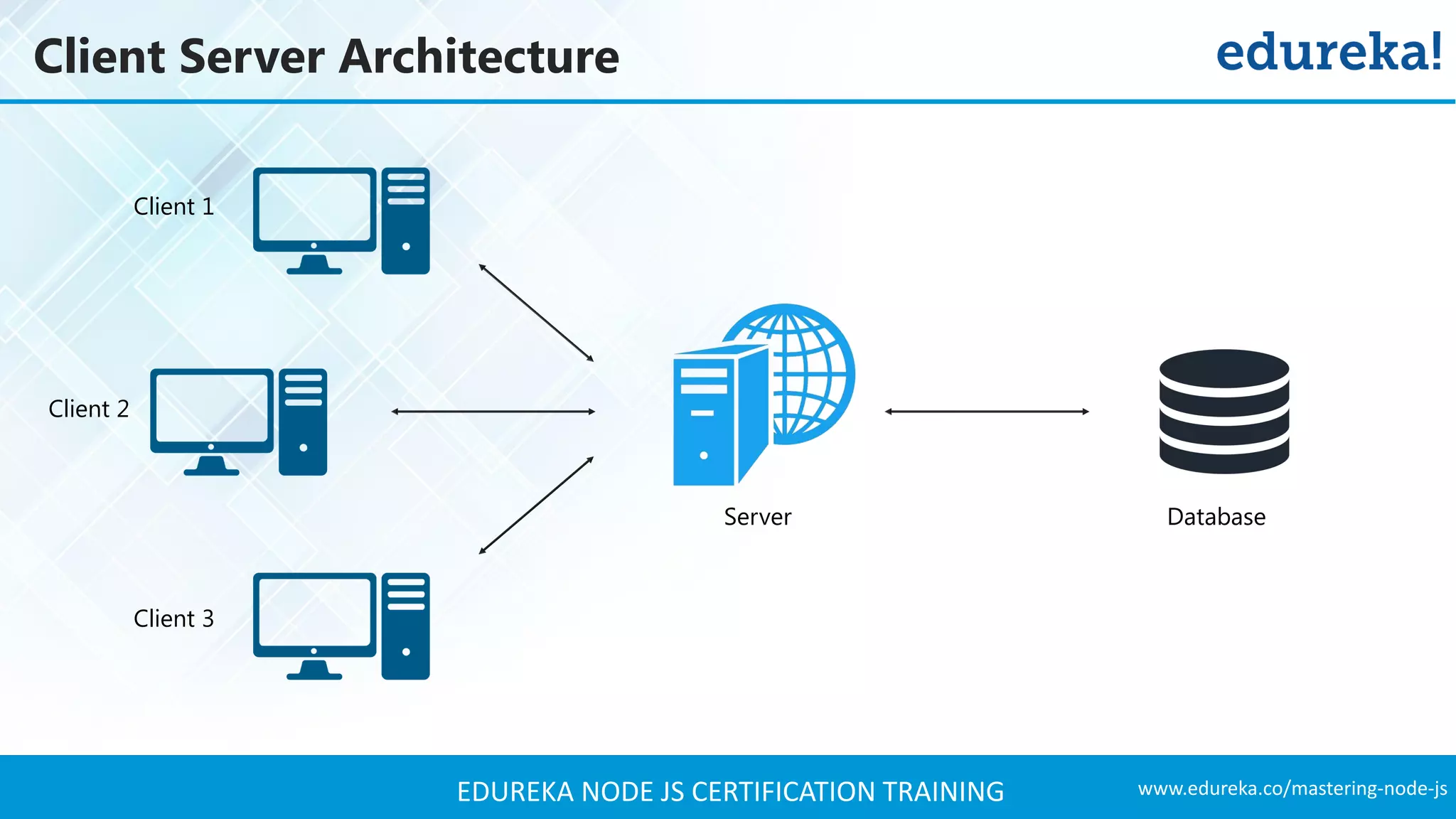
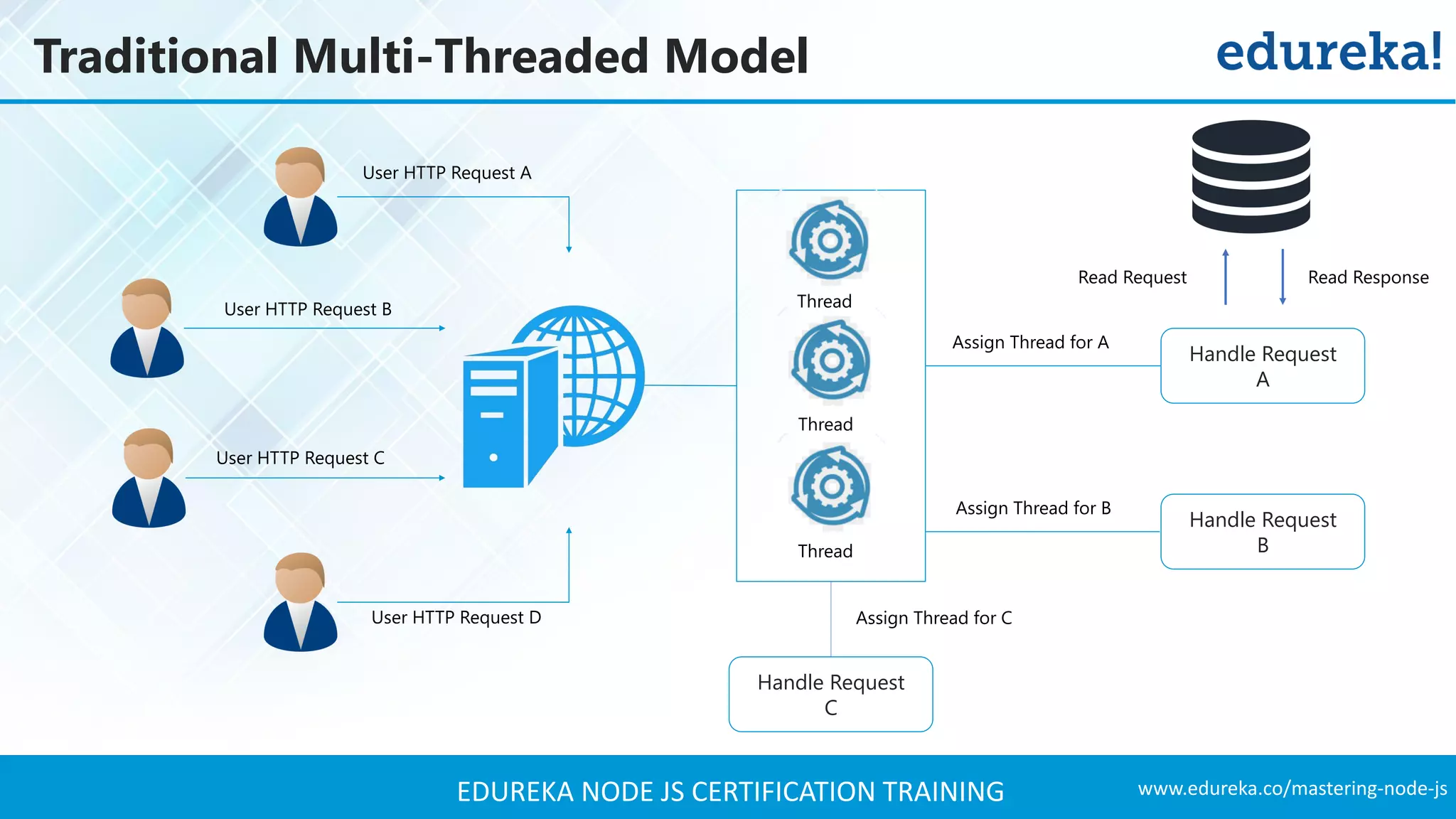
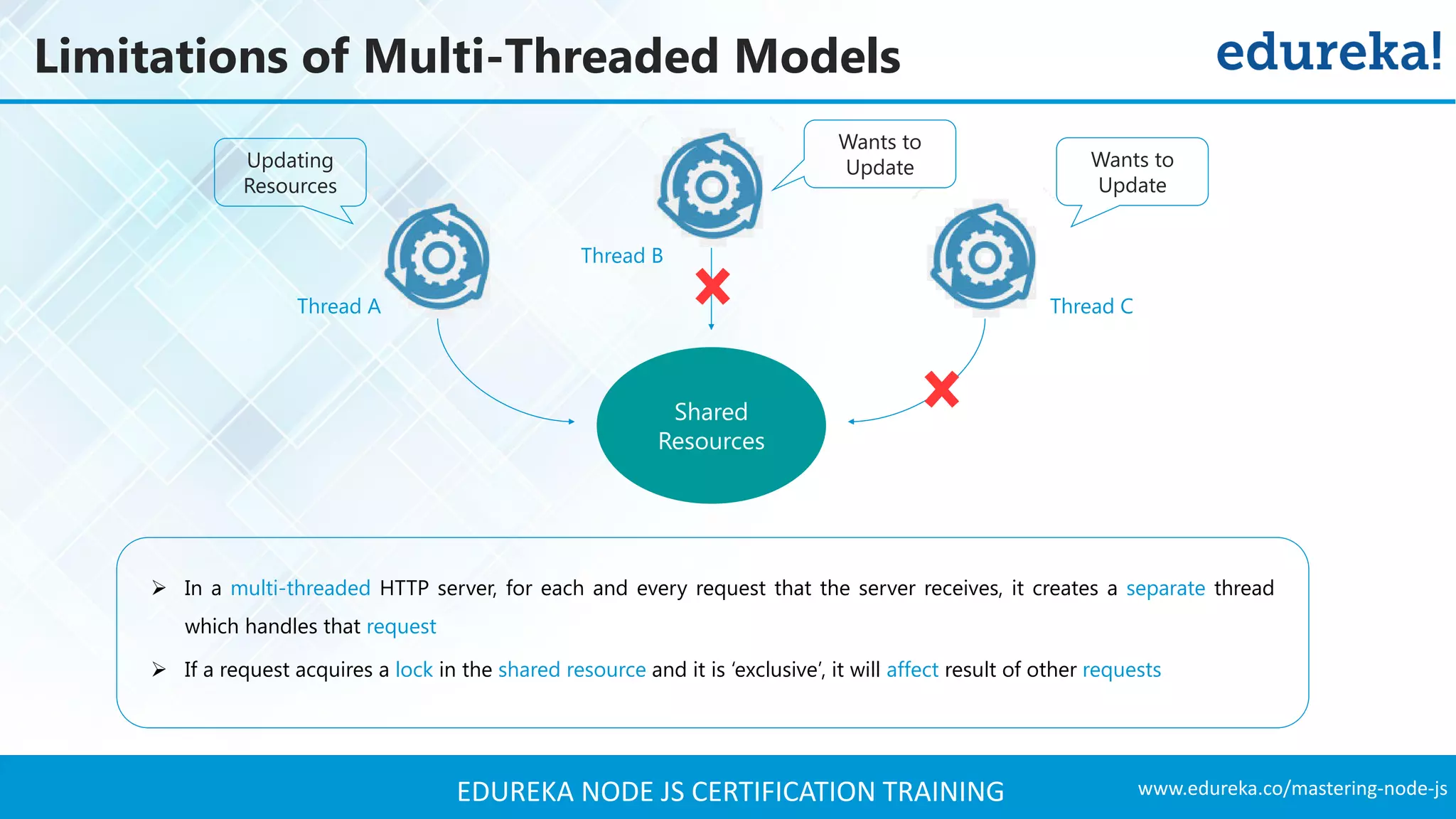
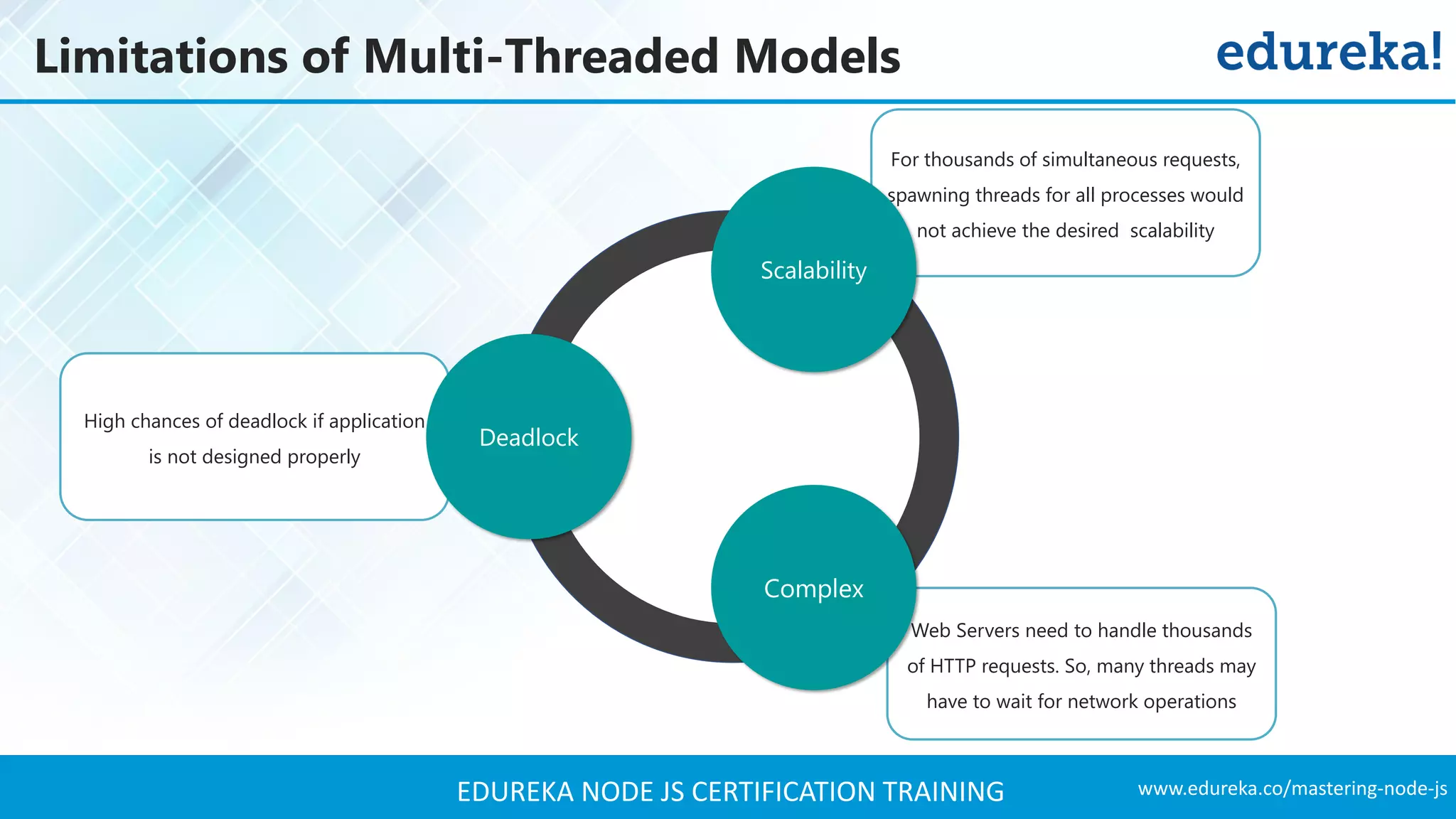
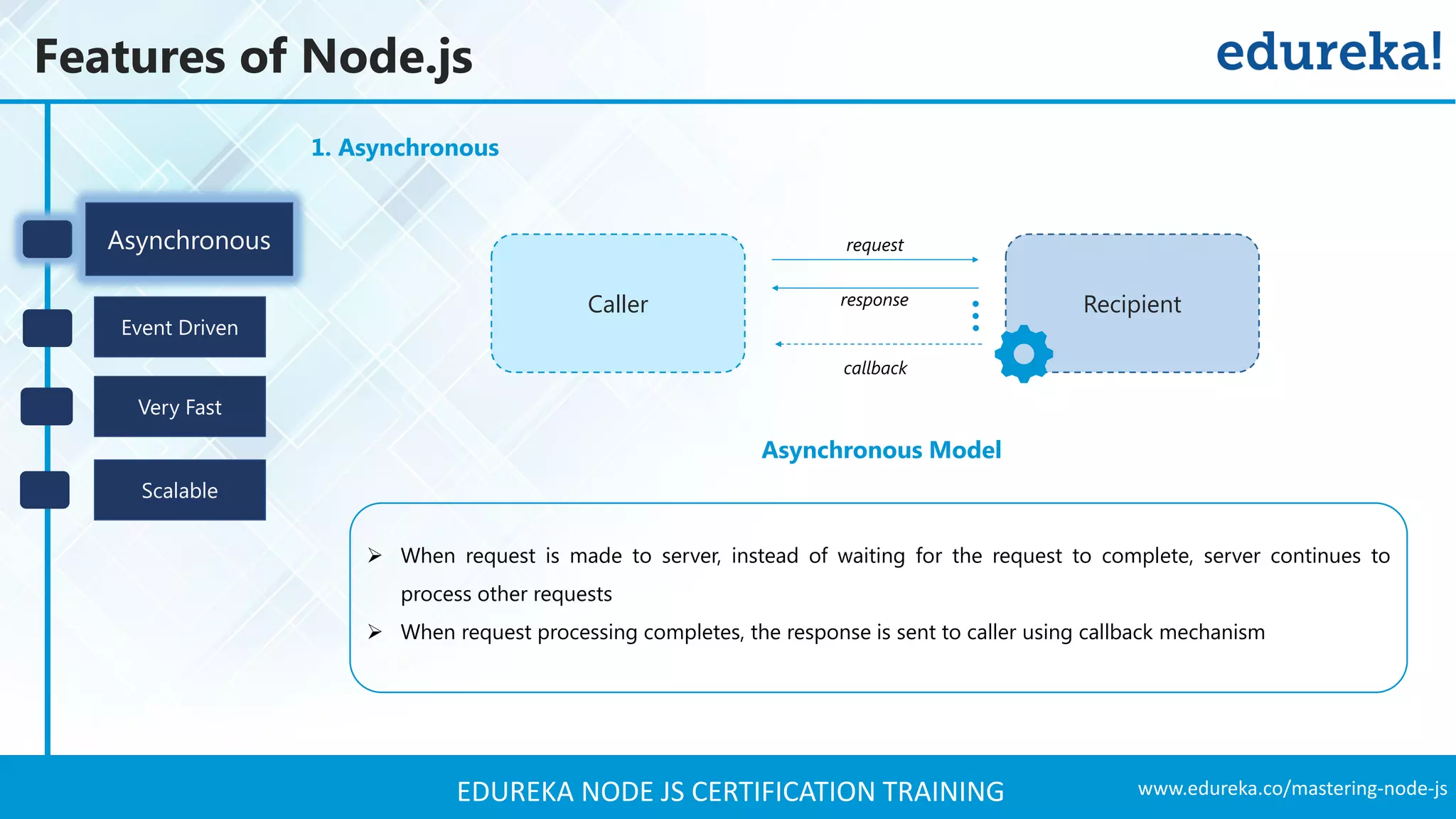
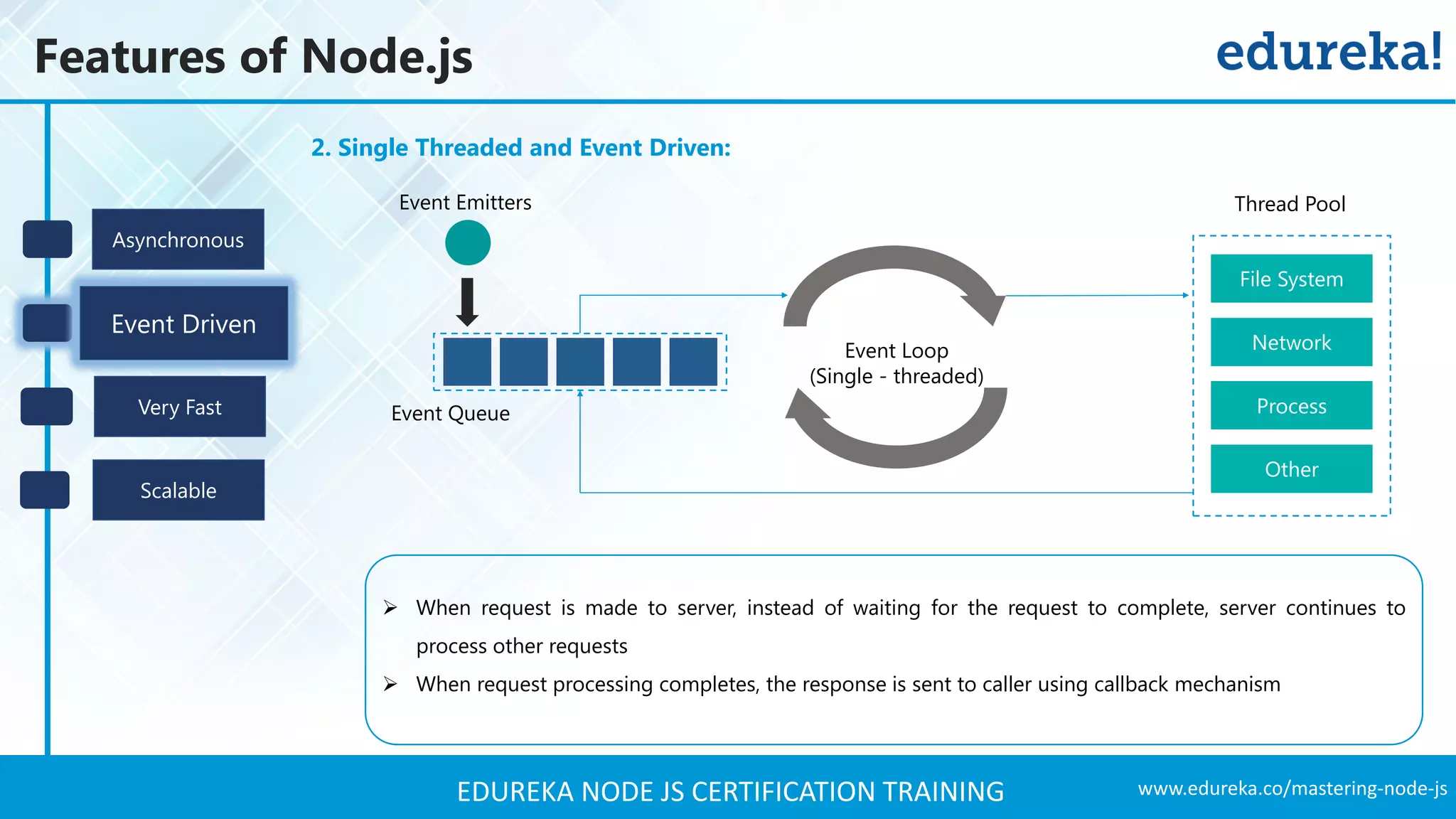
The document provides an overview of Node.js, including its architecture, features, and installation process. It discusses asynchronous vs. blocking I/O, introduces basic modules, and delves into the event-driven architecture that enables scalability. Additionally, it highlights the Express framework for building web applications and explains RESTful APIs for handling resources.










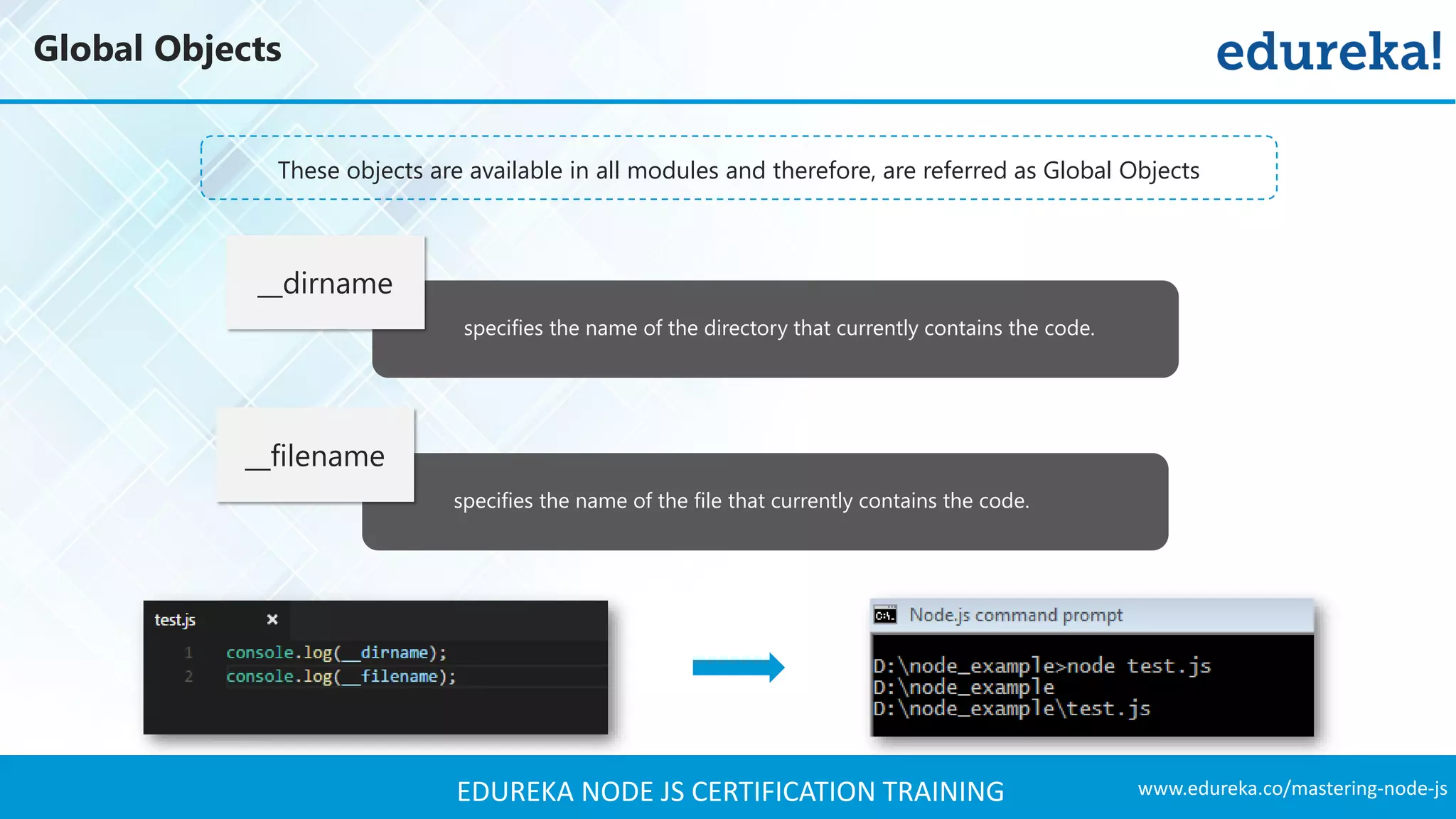
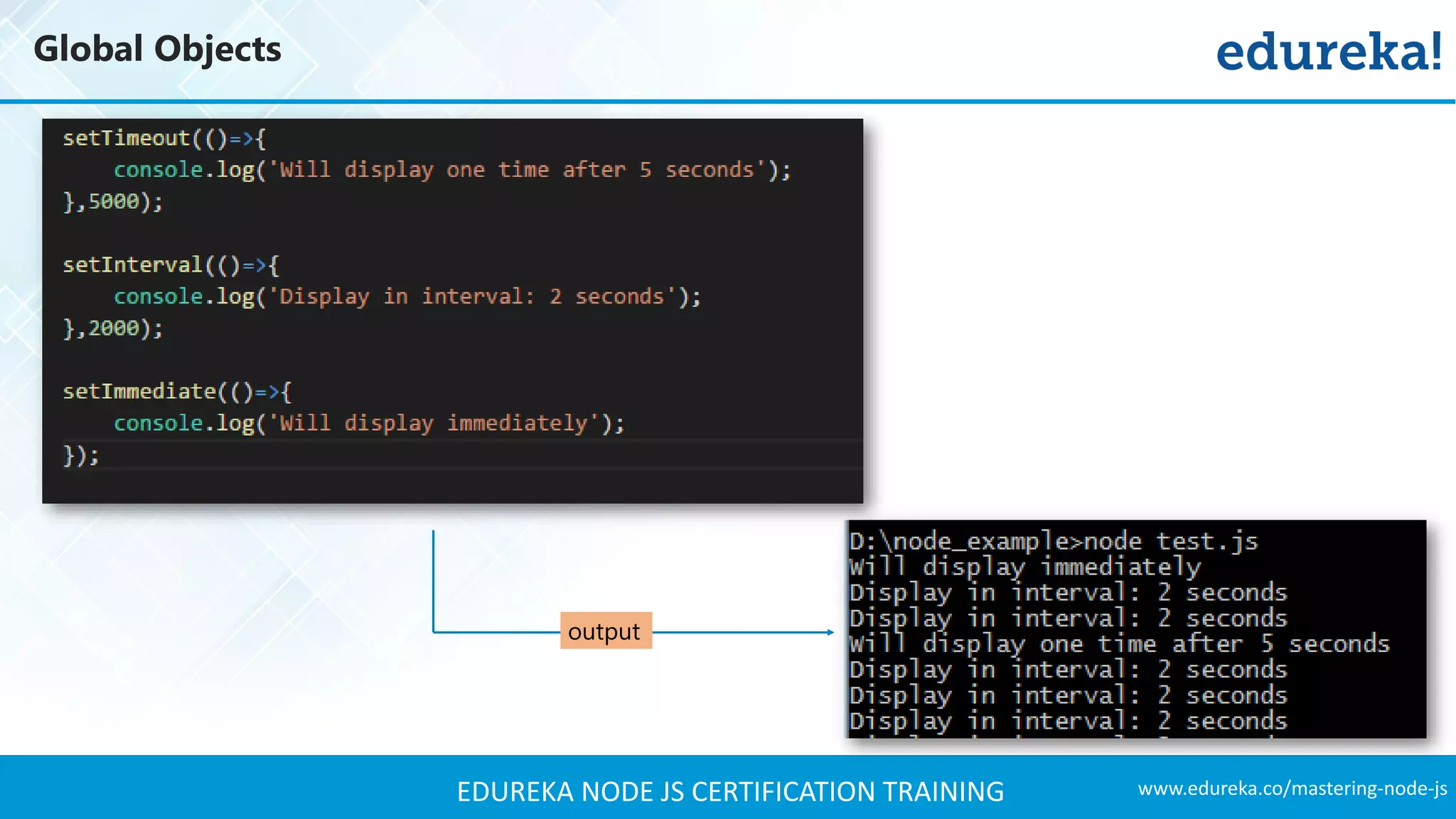
![www.edureka.co/mastering-node-jsEDUREKA NODE JS CERTIFICATION TRAINING Global Objects A timer in Node.js is an internal construct that calls a given function after a certain period of time. setTimeout(callback, delay[, ...args]) ➢ Schedules execution of a one-time callback after delay milliseconds ➢ Returns a Timeout for use with clearTimeout( ) setInterval(callback, delay[, ...args]) ➢ Schedules repeated execution of callback every delay milliseconds. ➢ Returns a Timeout for use with clearTimeout( ) setImmediate(callback, [,..args]) ➢ Schedules an immediate execution of the callback after I/O events' callbacks but before setTimeout() and setInterval() timers are triggered. ➢ Returns an Immediate for use with clearImmediate().](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nodejstutorial-edureka-170718091811/75/Node-js-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Node-js-Web-Application-Tutorial-Node-js-Training-Edureka-33-2048.jpg)
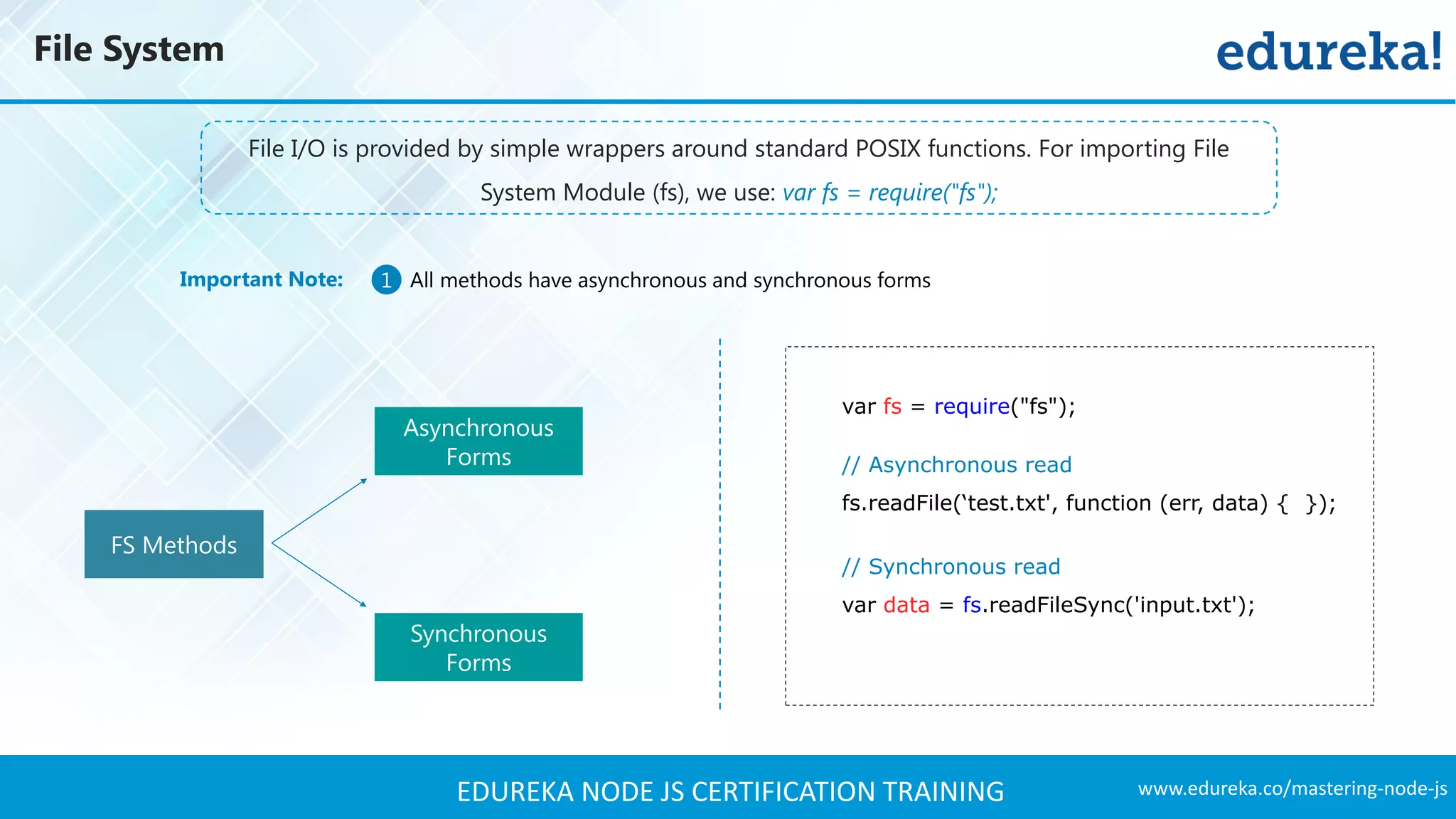
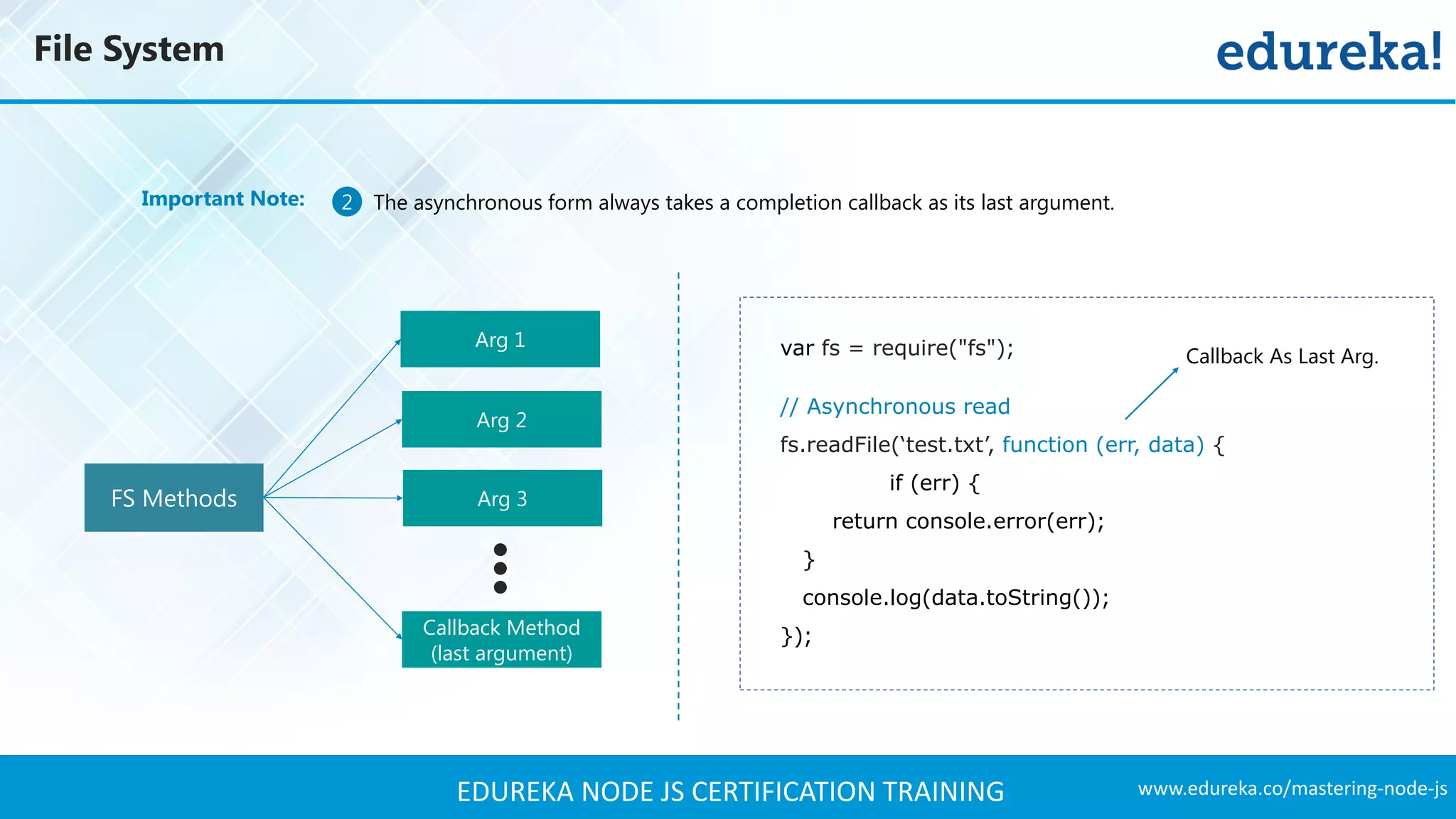
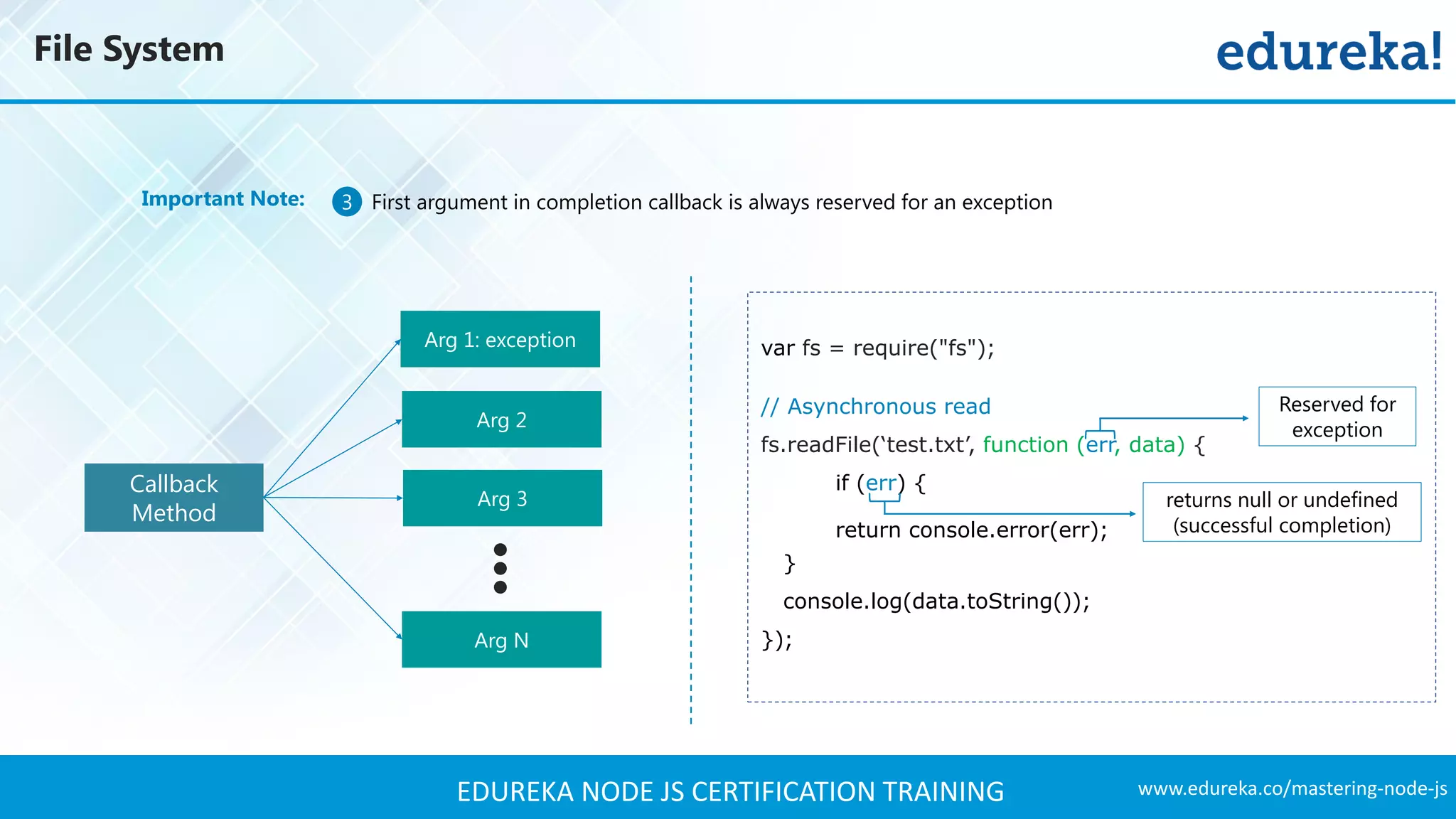
![www.edureka.co/mastering-node-jsEDUREKA NODE JS CERTIFICATION TRAINING Some Methods in File System Module – Open() fs.open( path, flags[, mode], callback ) fs.openSync( path, flags[, mode] ) fs.close( fd, callback ) ➢ var fs = require(‘fs’); Open File Asynchronously Open File Synchronously Closing File Arguments Description Path < string > Path of the file Flags < string > Access Modifiers Mode < integer > sets the permission and sticky bits, but only if the file was created Callback < function > Callback signature - function(err, fd)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nodejstutorial-edureka-170718091811/75/Node-js-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Node-js-Web-Application-Tutorial-Node-js-Training-Edureka-39-2048.jpg)

![www.edureka.co/mastering-node-jsEDUREKA NODE JS CERTIFICATION TRAINING Some Methods in File System Module – Read() read(fd, buffer, offset, length, position, callback) readFile(file[, options], callback) readFileSync(file[, options]) Read Content of a File into Buffer Reads File Asynchronously Arguments Description fd < integer > File Descriptor buffer <string | Buffer | Unit8Array > The buffer that the data will be written to. offset < integer > Offset in the buffer to start writing at. length < integer > Specifies the number of bytes to read. position < integer > Specifies where to begin reading from in the file Callback < function > Read Callback signature - function(err, bytesRead, buffer) Reads File Synchronously](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nodejstutorial-edureka-170718091811/75/Node-js-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Node-js-Web-Application-Tutorial-Node-js-Training-Edureka-41-2048.jpg)
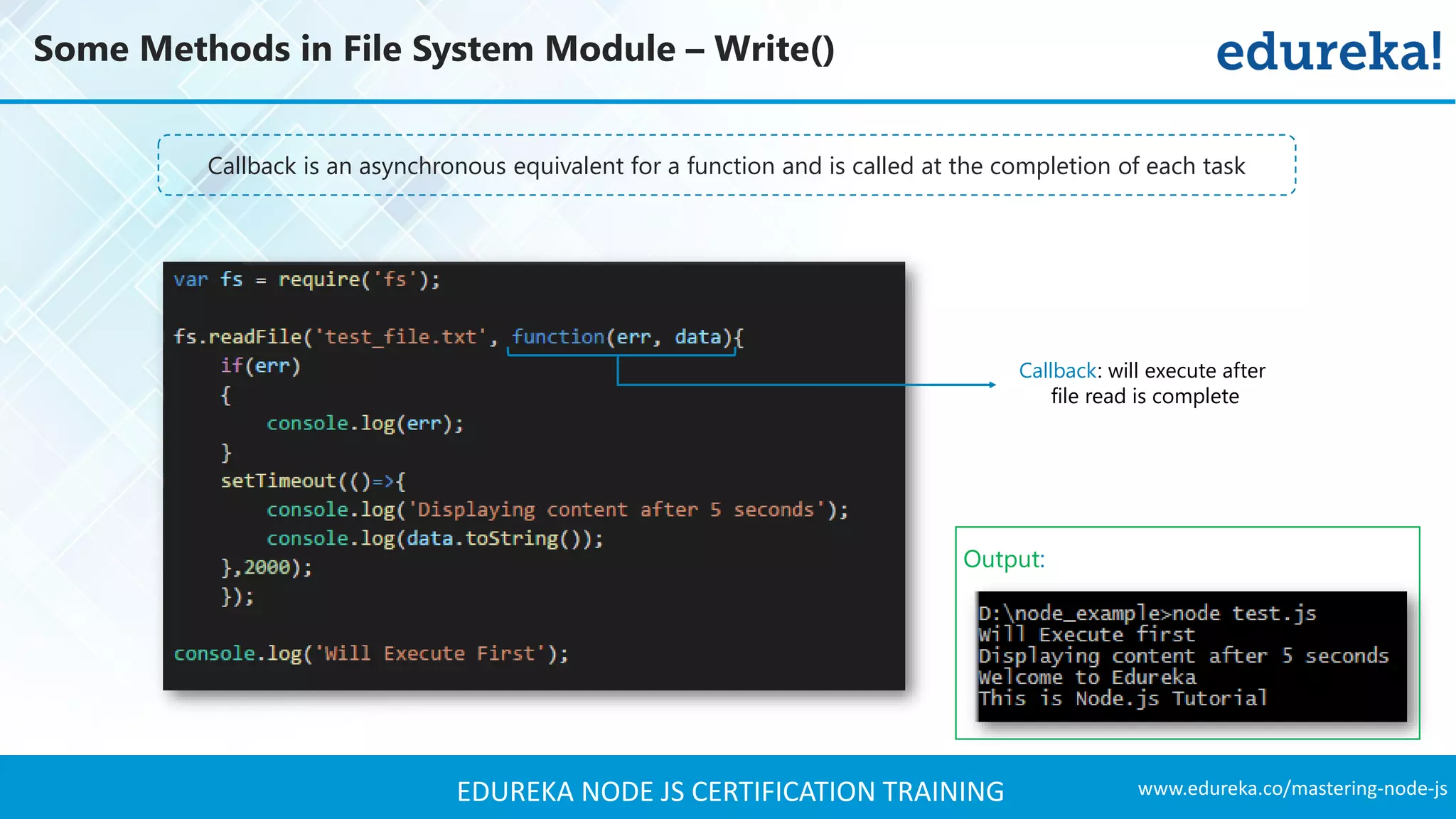
![www.edureka.co/mastering-node-jsEDUREKA NODE JS CERTIFICATION TRAINING Some Methods in File System Module – Write() writeFile(file, data[, options], callback) writeFileSync(file, data[, options]) Writes into a File Asynchronously Arguments Description File Filename or File Descriptor Data The buffer that the data will be written to. Options: Encoding, Mode or flag Callback < function > Callback signature - function(err, bytesRead, buffer) Writes into a File Synchronously](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nodejstutorial-edureka-170718091811/75/Node-js-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Node-js-Web-Application-Tutorial-Node-js-Training-Edureka-42-2048.jpg)