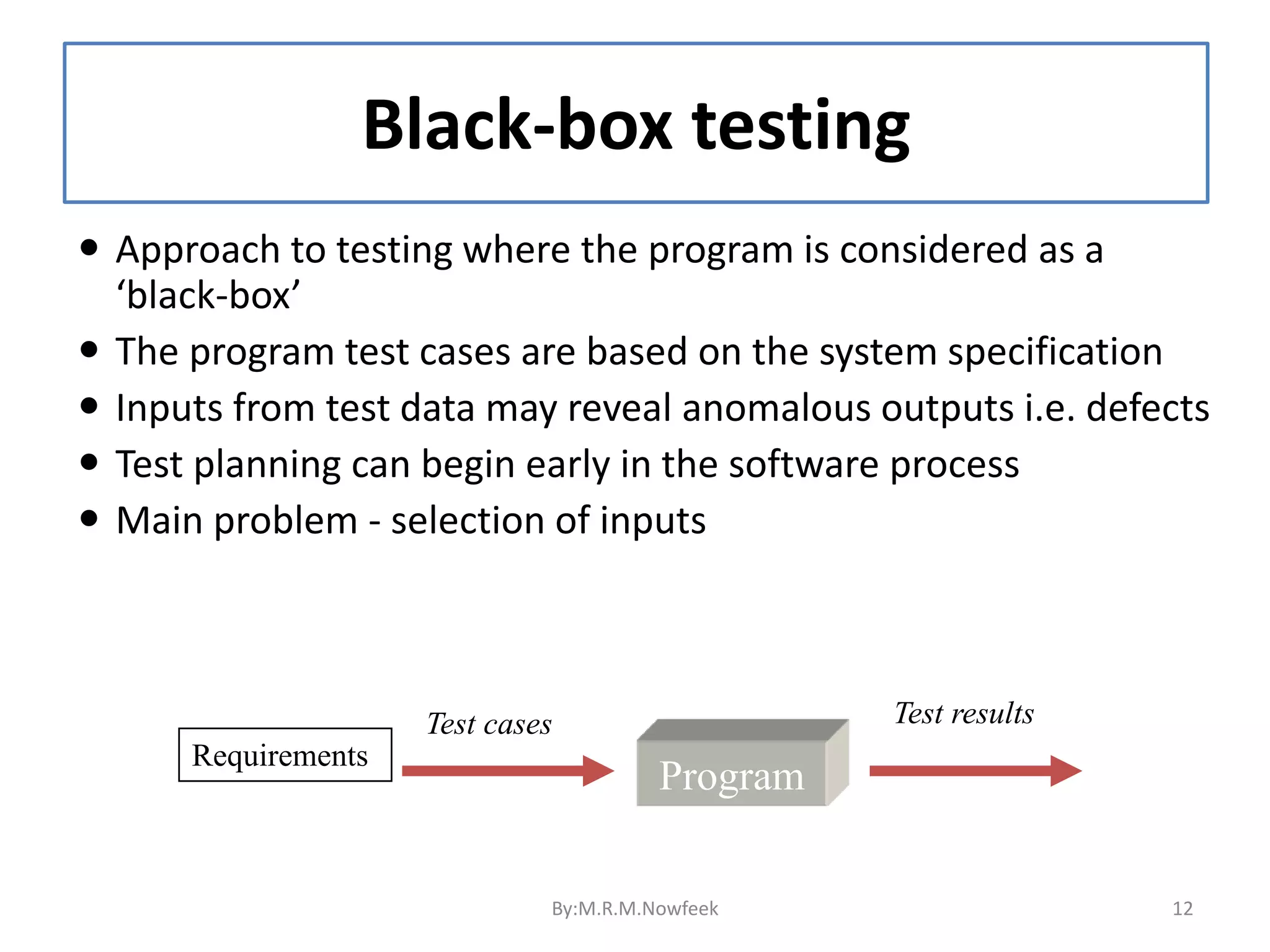
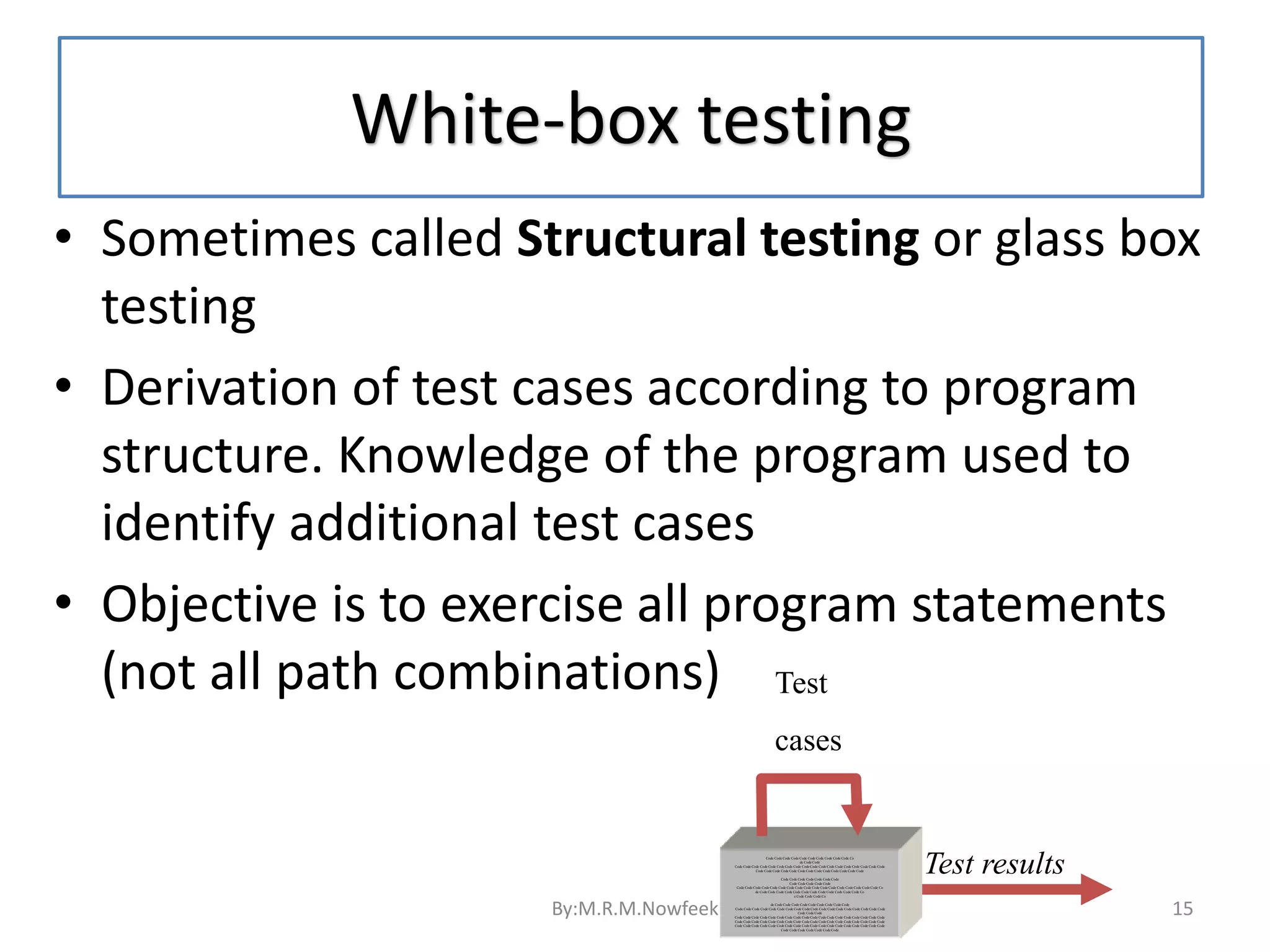
1. Software testing is the process of evaluating software to identify differences between expected and actual results. It assesses the quality and identifies defects. 2. There are different types of testing including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing. Unit testing is done by developers, while later tests involve independent testers. 3. Test automation uses software to control tests and compare results to reduce manual effort in repetitive testing. It helps test changes through regression testing.