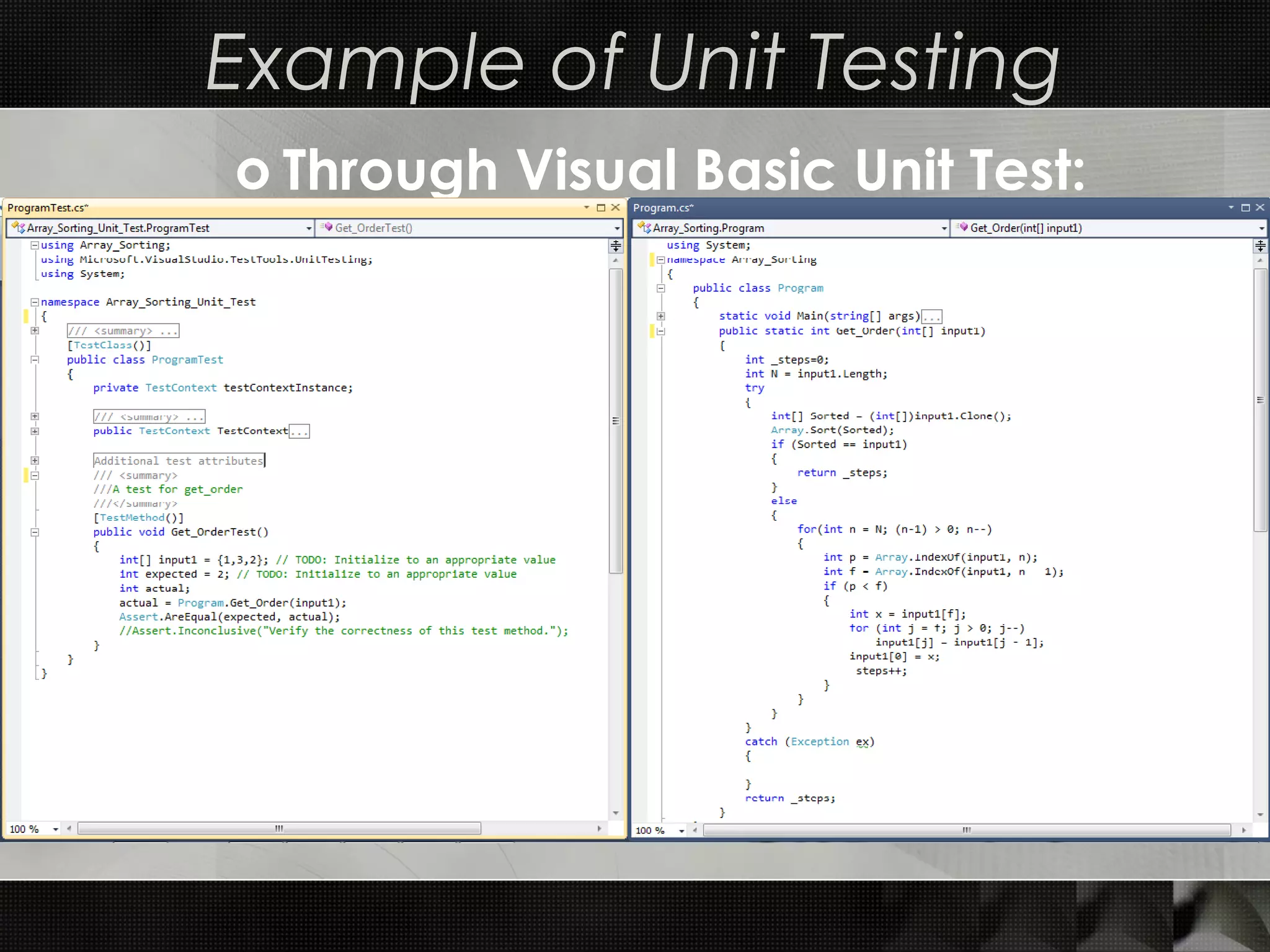
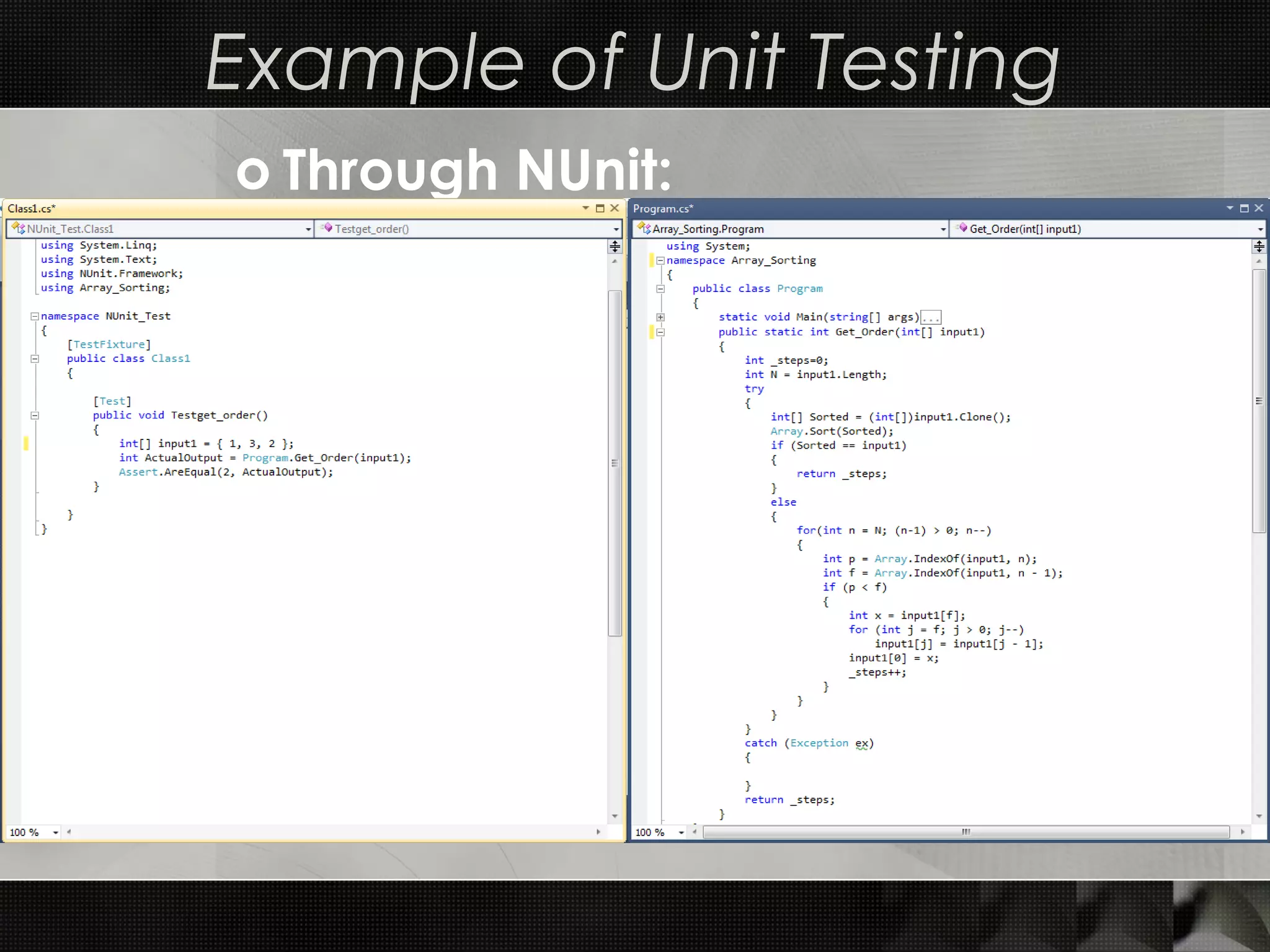
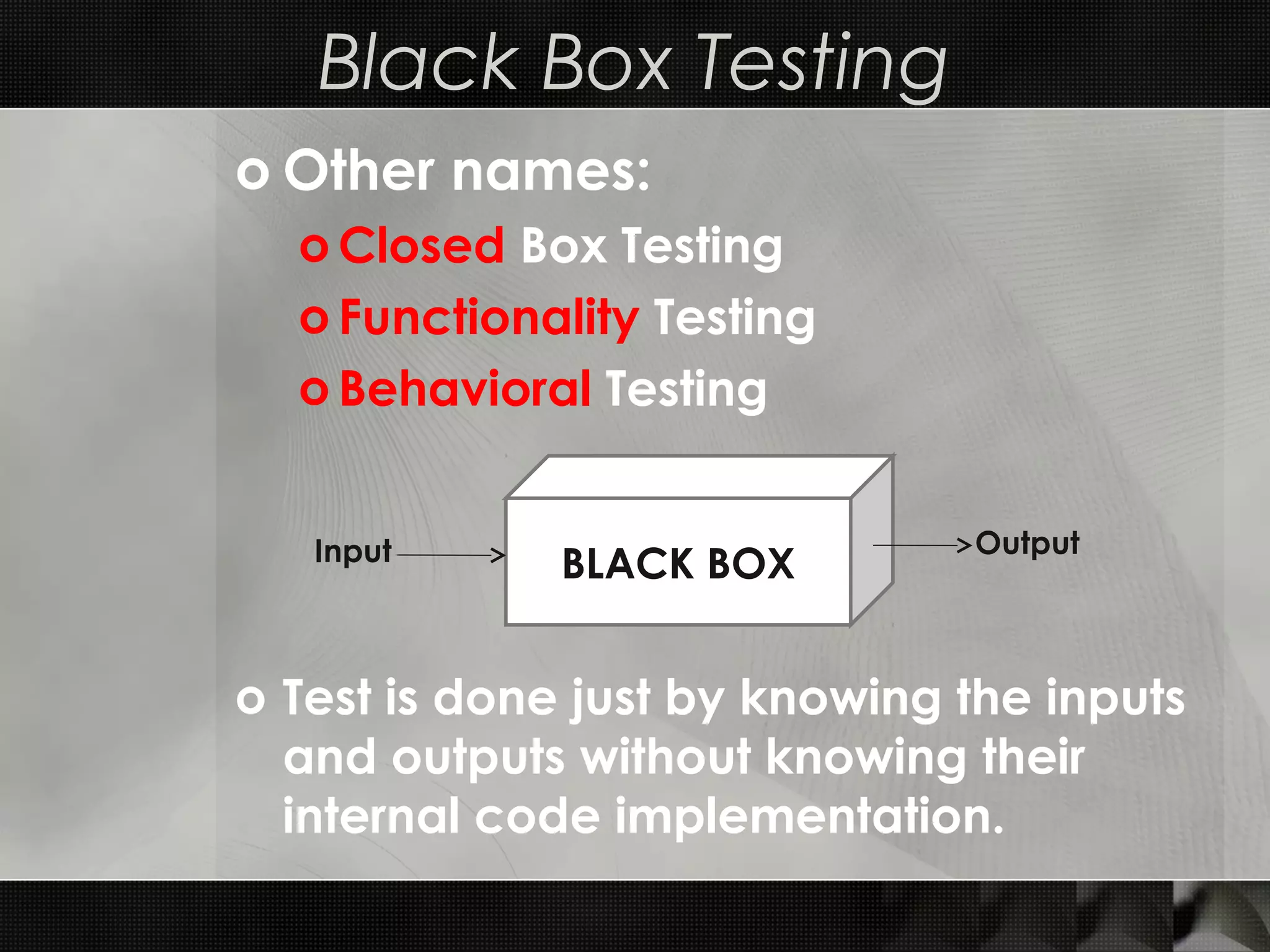
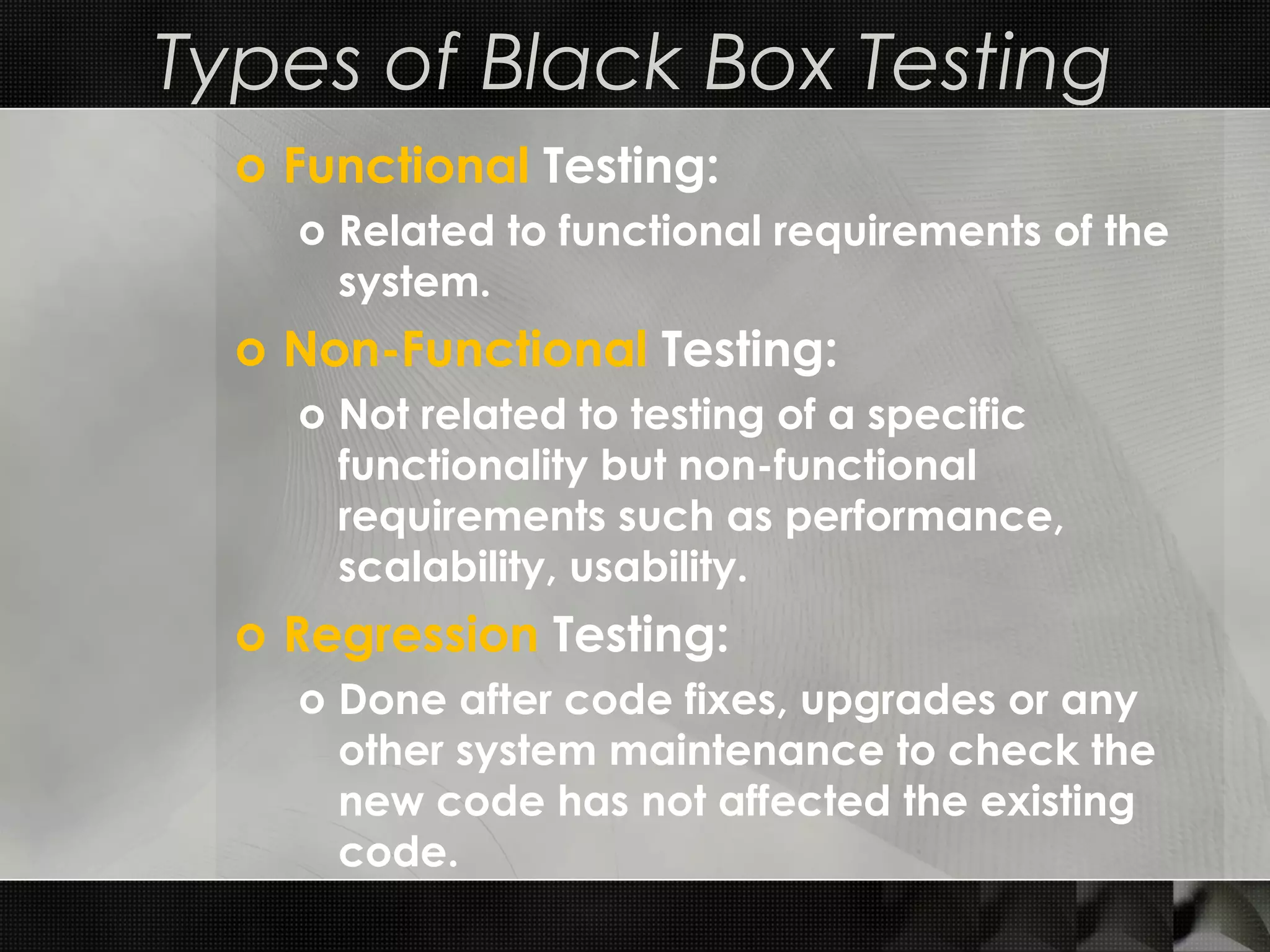
This document discusses software testing techniques, including characteristics of testable software and different types of testing. It describes white box testing which tests internal coding and structure, including unit and integration testing. Unit testing checks individual units of source code, while integration testing checks how modules work together. Black box testing checks functionality without seeing internal code, and includes functional, non-functional, and regression testing. The document provides examples of unit testing in Visual Studio and NUnit and describes top-down and bottom-up approaches to integration testing.