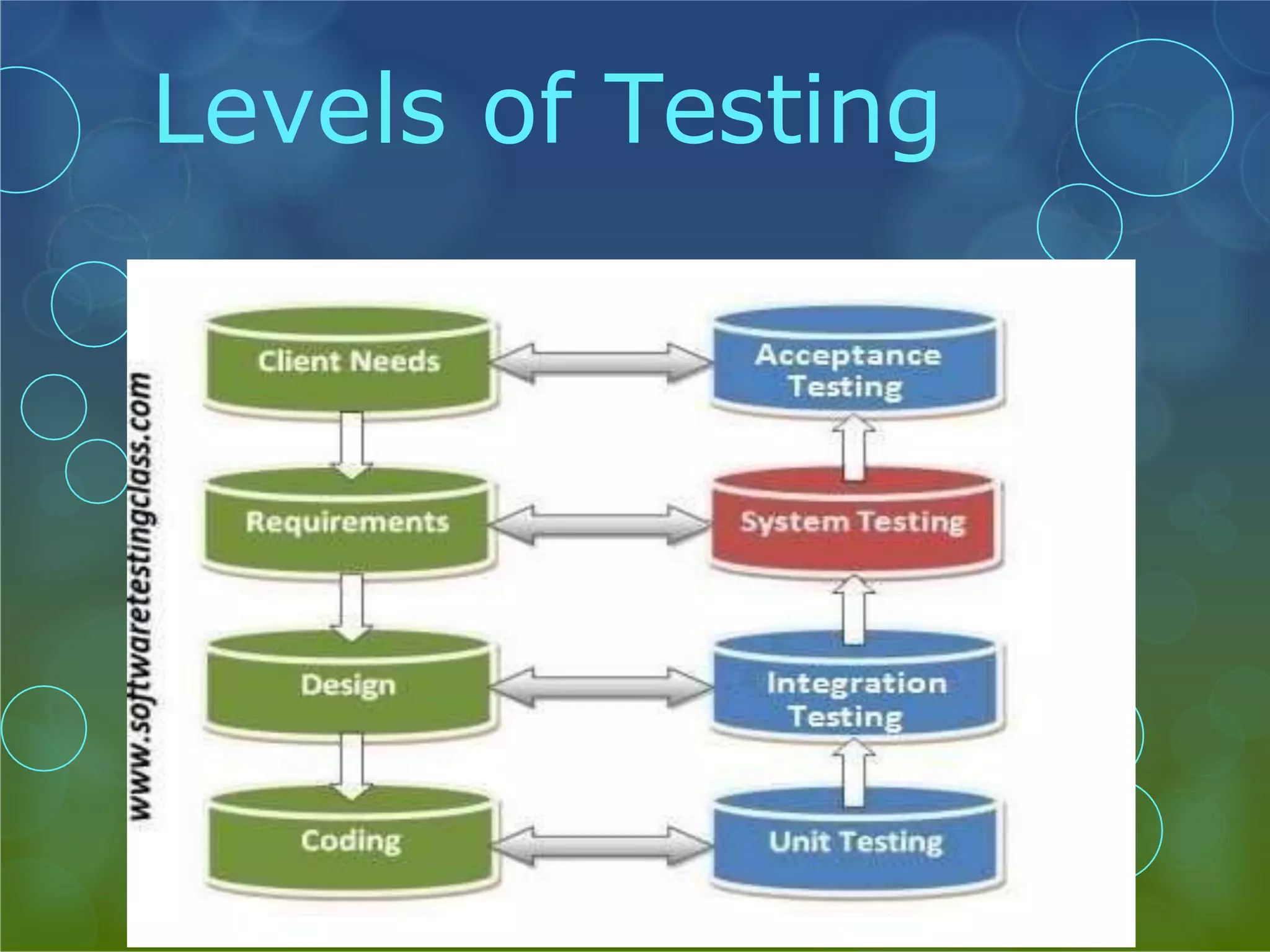
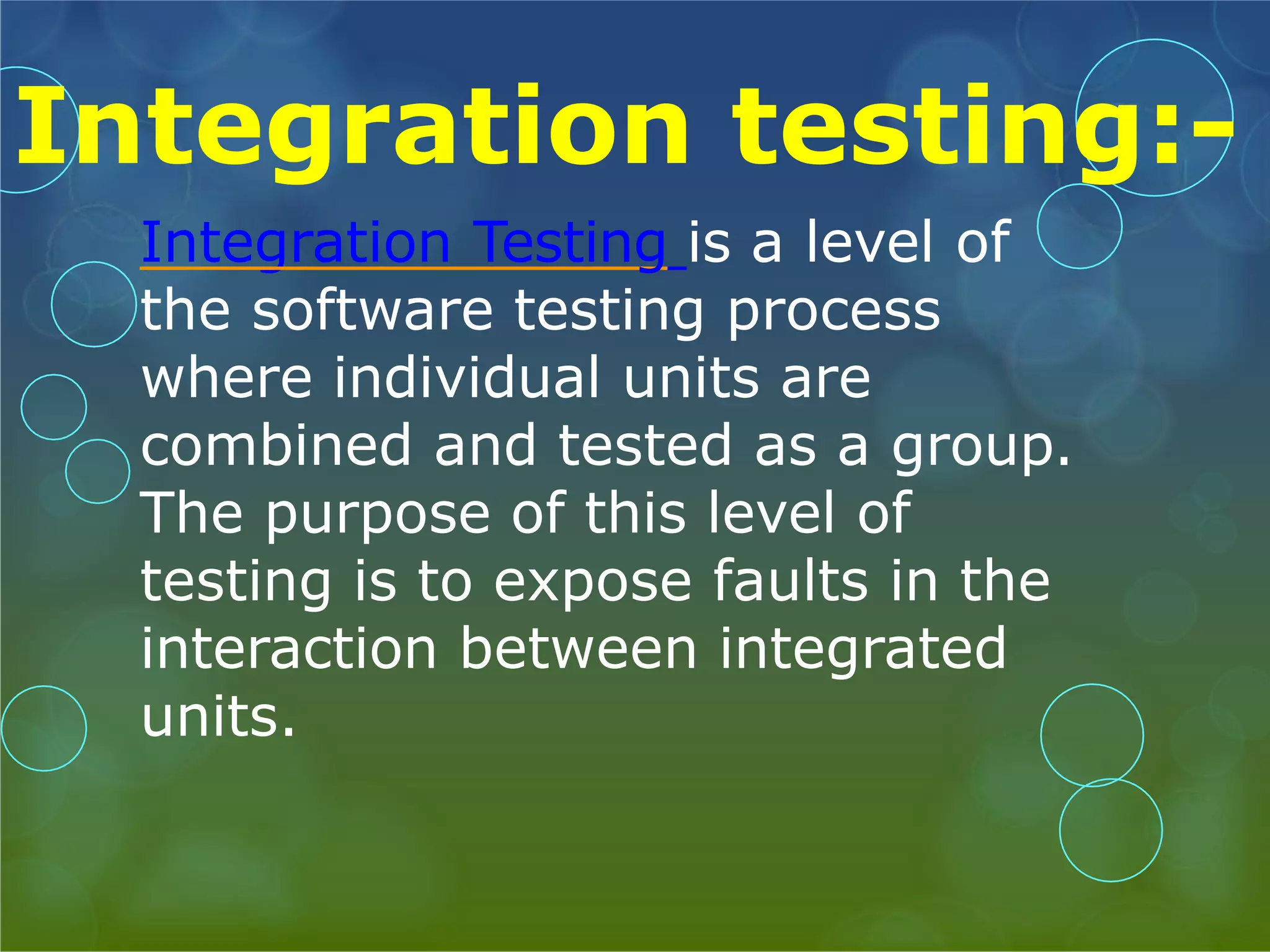
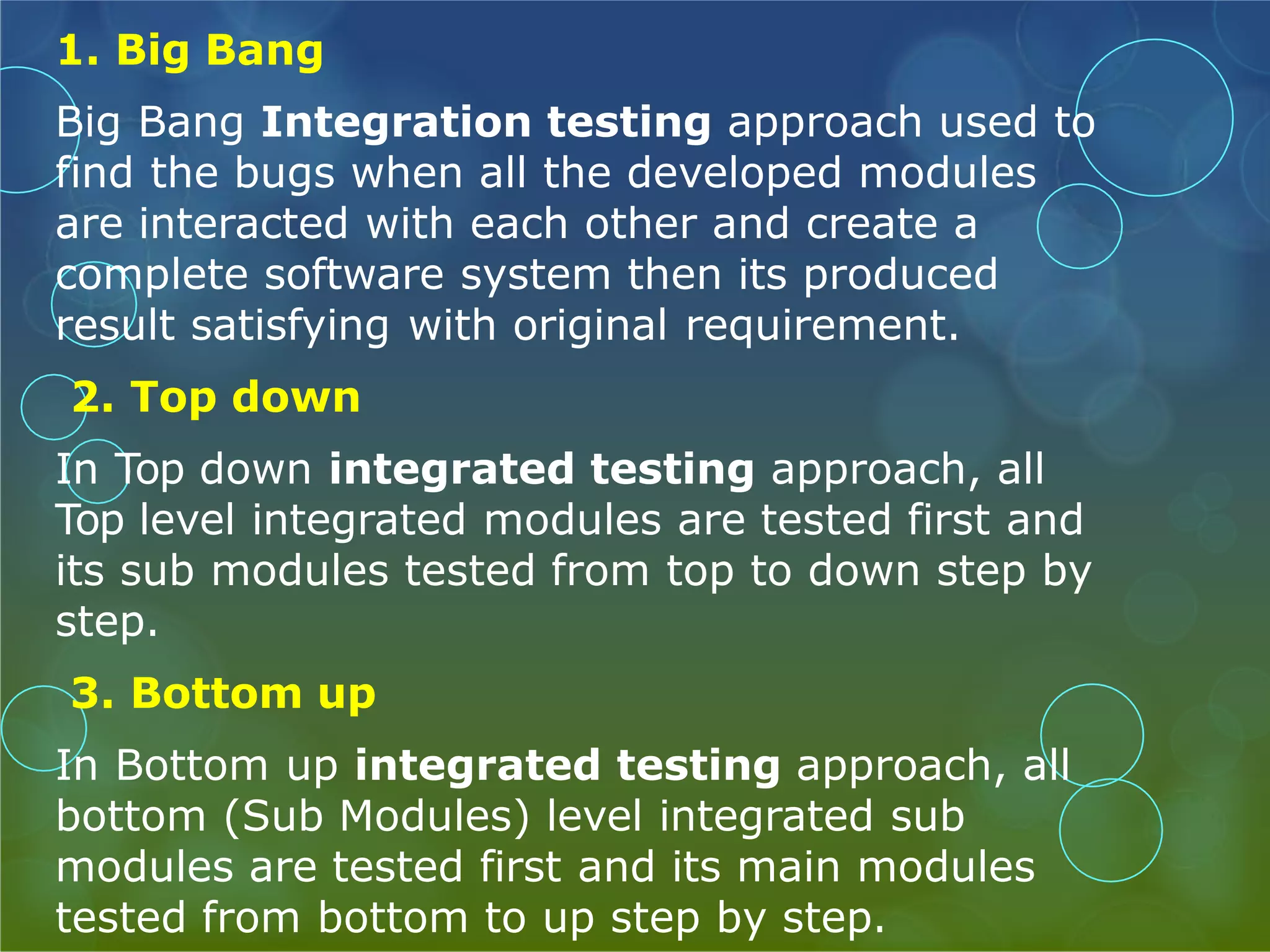
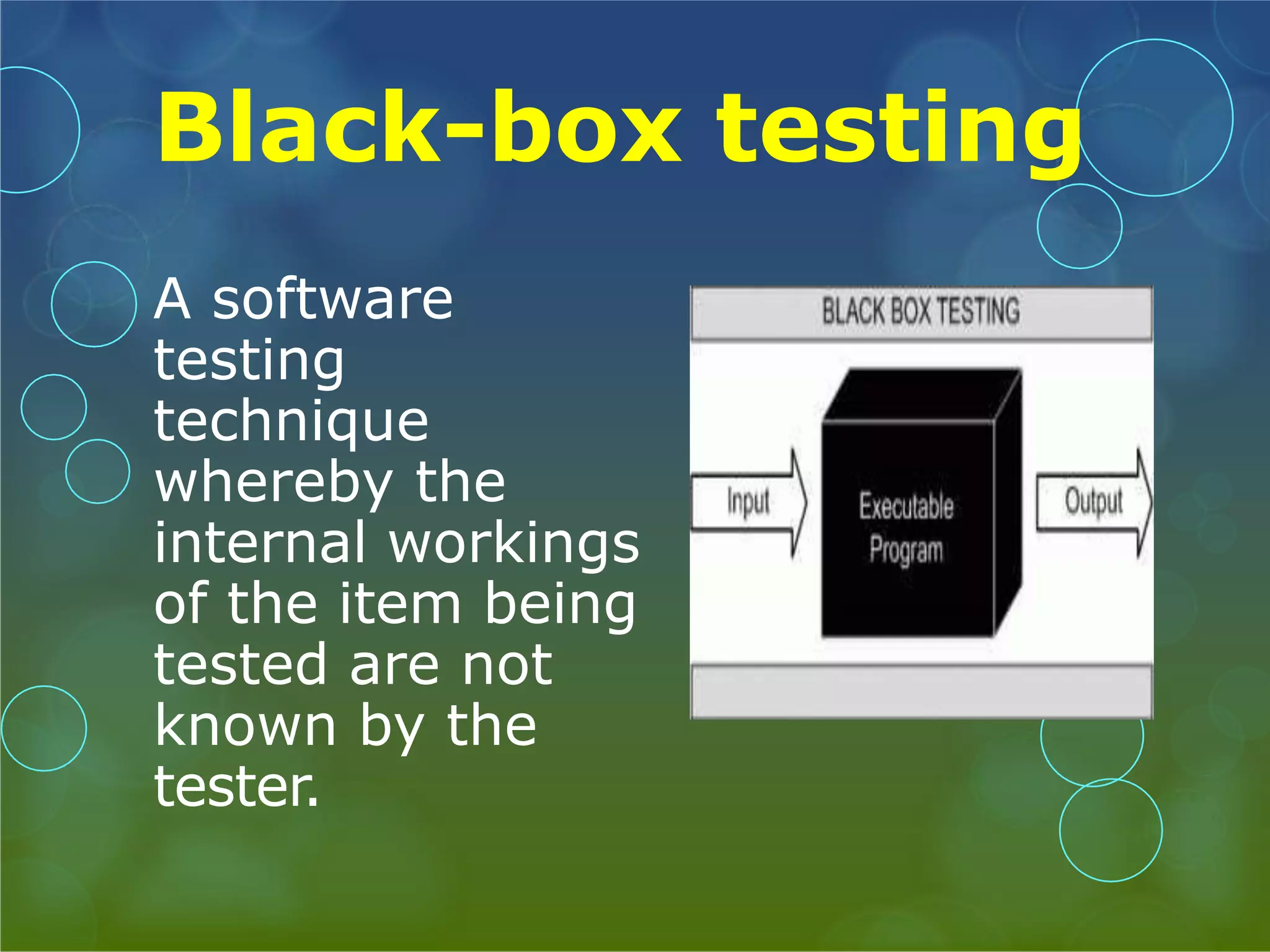
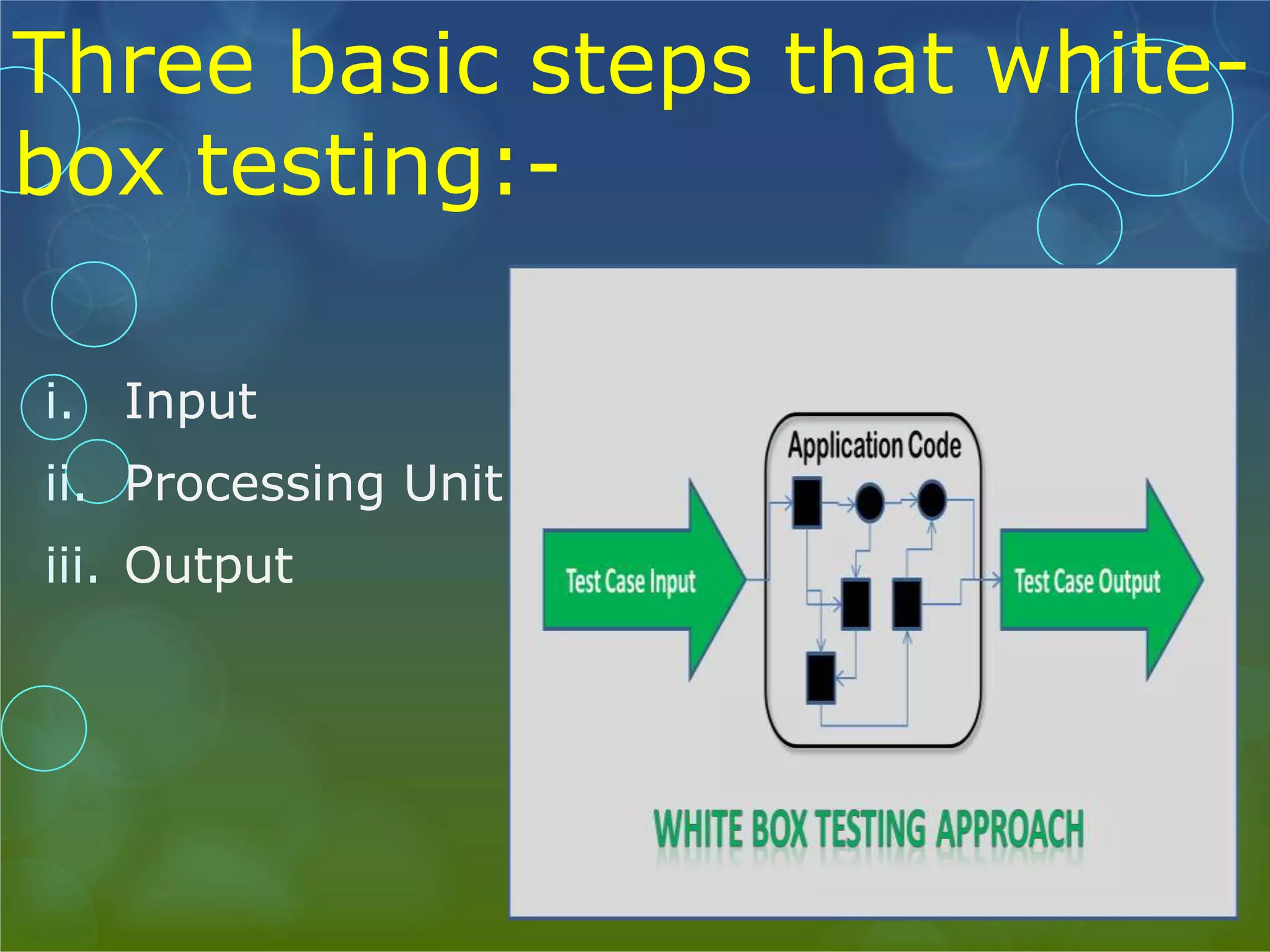
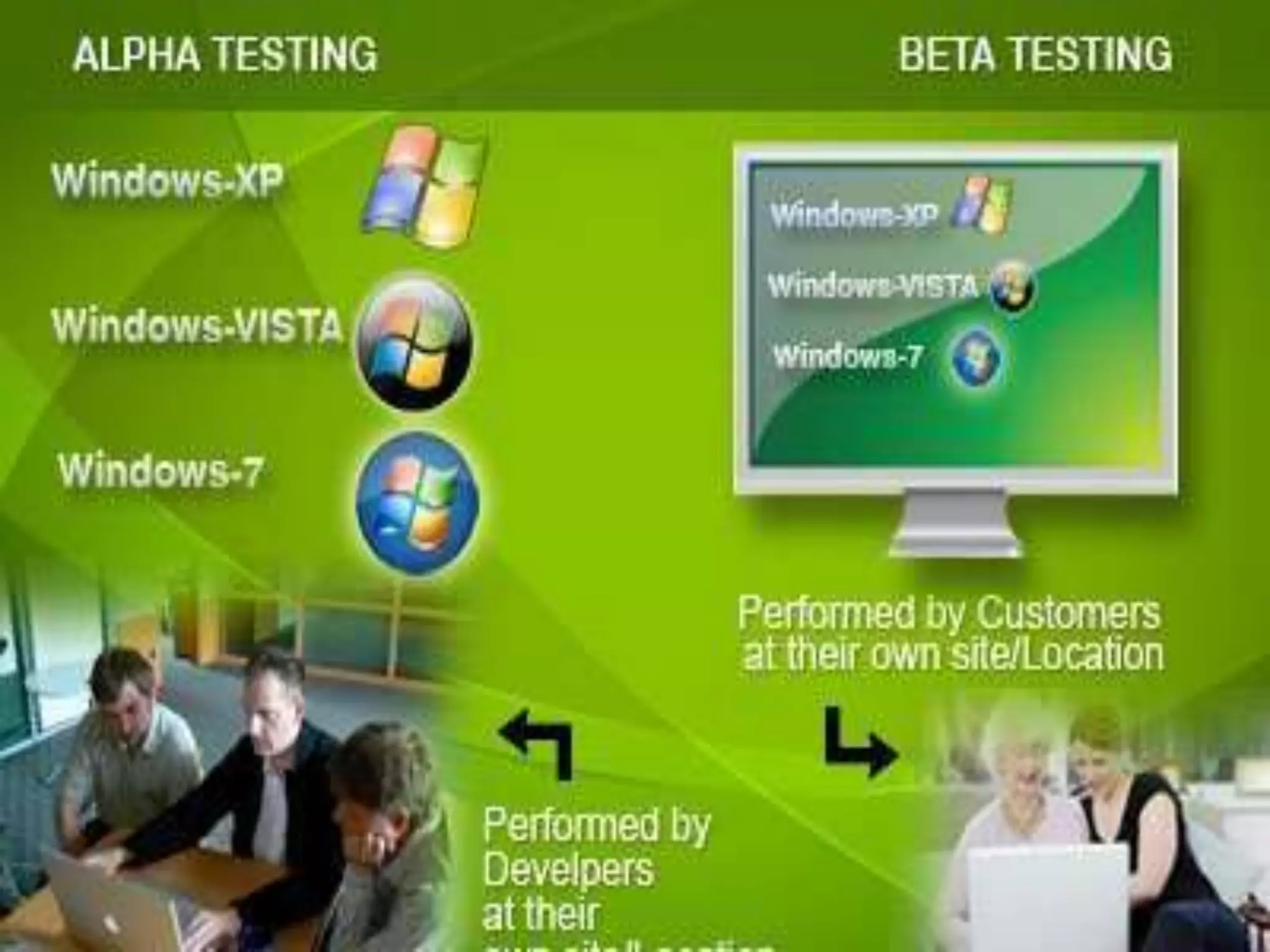
This presentation provides an overview of different types of software testing, including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing, black-box testing, and white-box testing. It discusses the principles and goals of testing at each level. Key points covered include how unit testing validates individual components, integration testing exposes faults in component interaction, system testing evaluates compliance of the full system, and acceptance testing assesses if requirements are met before user delivery. Black-box and white-box testing approaches are also summarized.