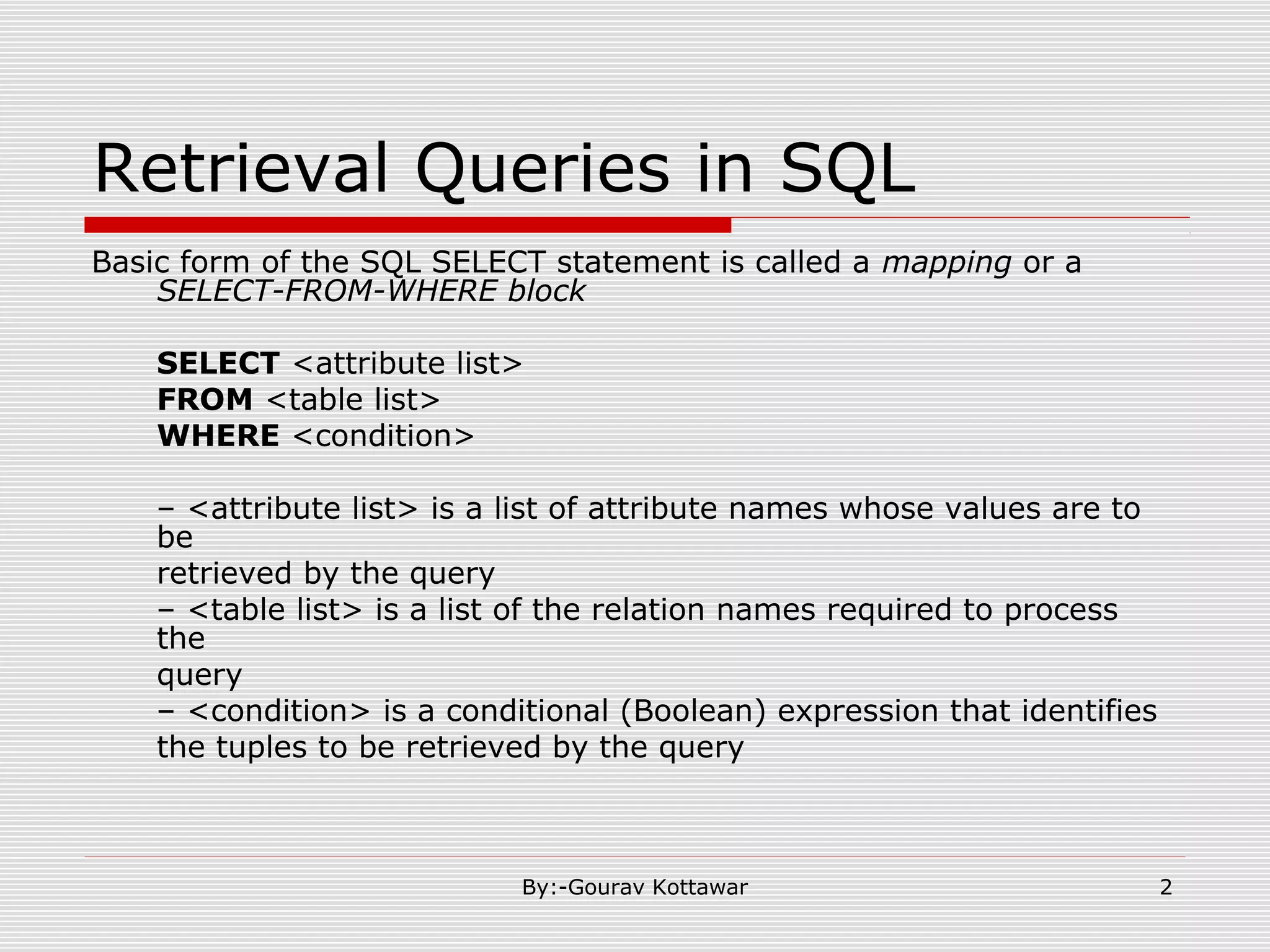
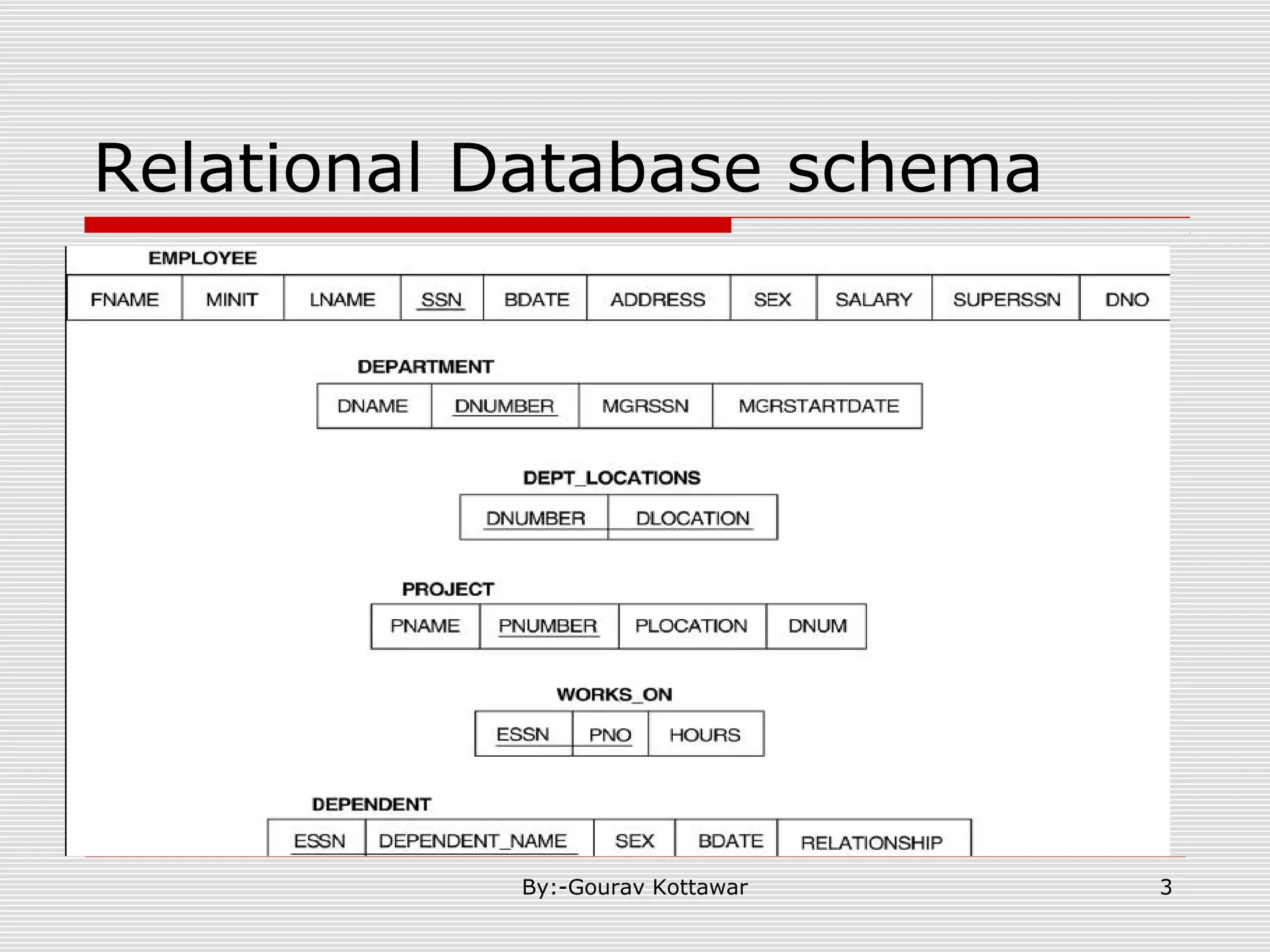
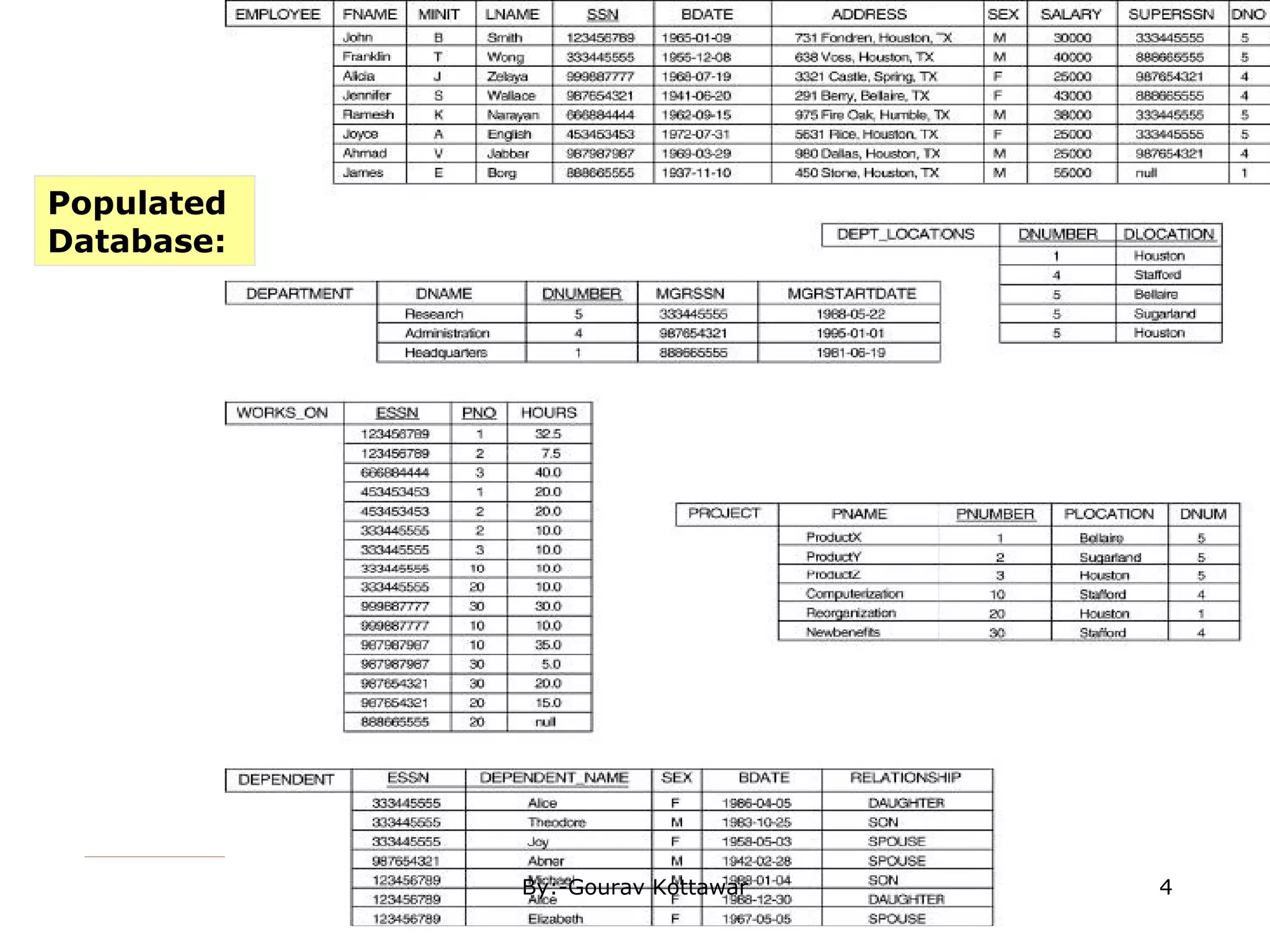
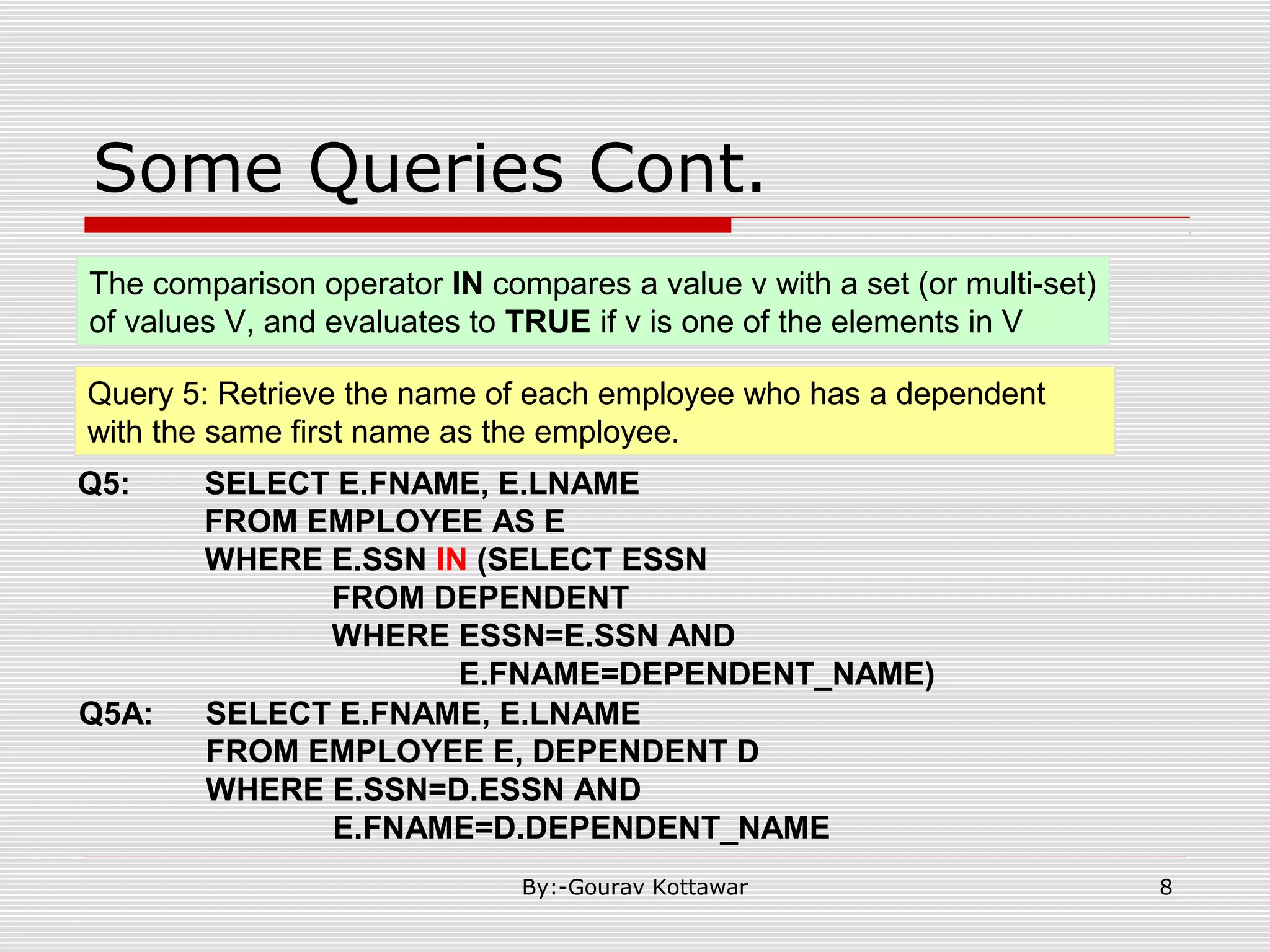
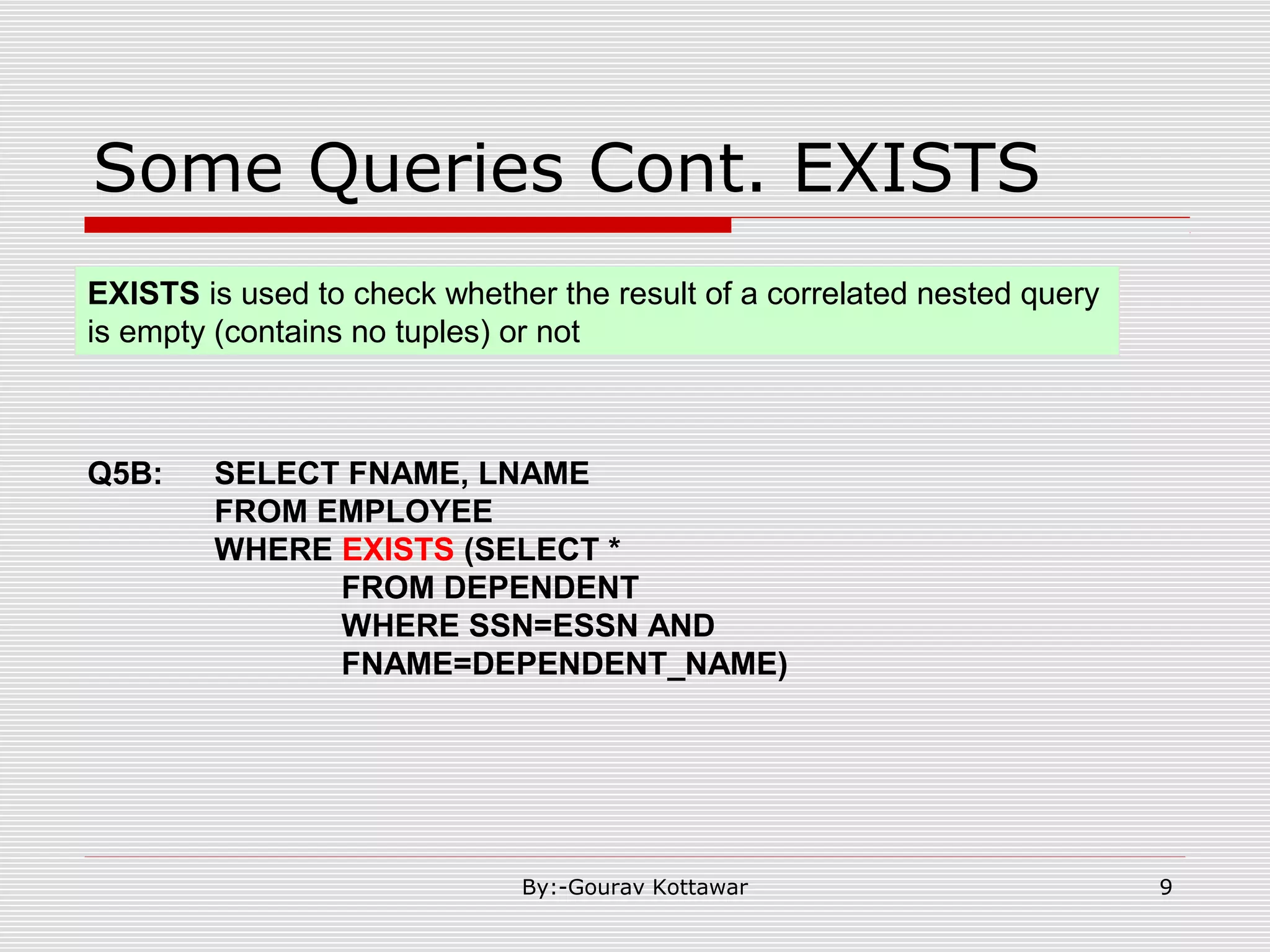
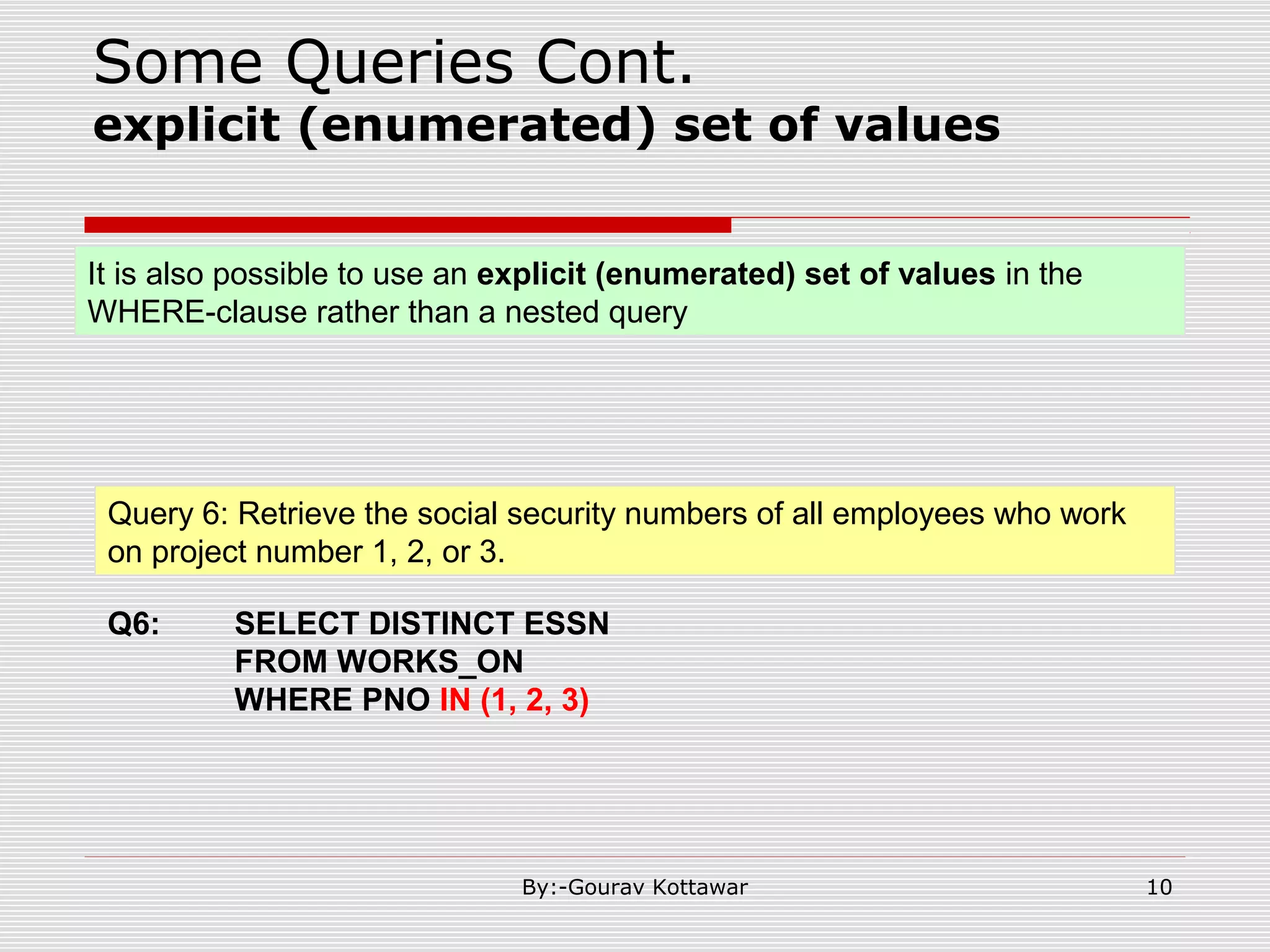
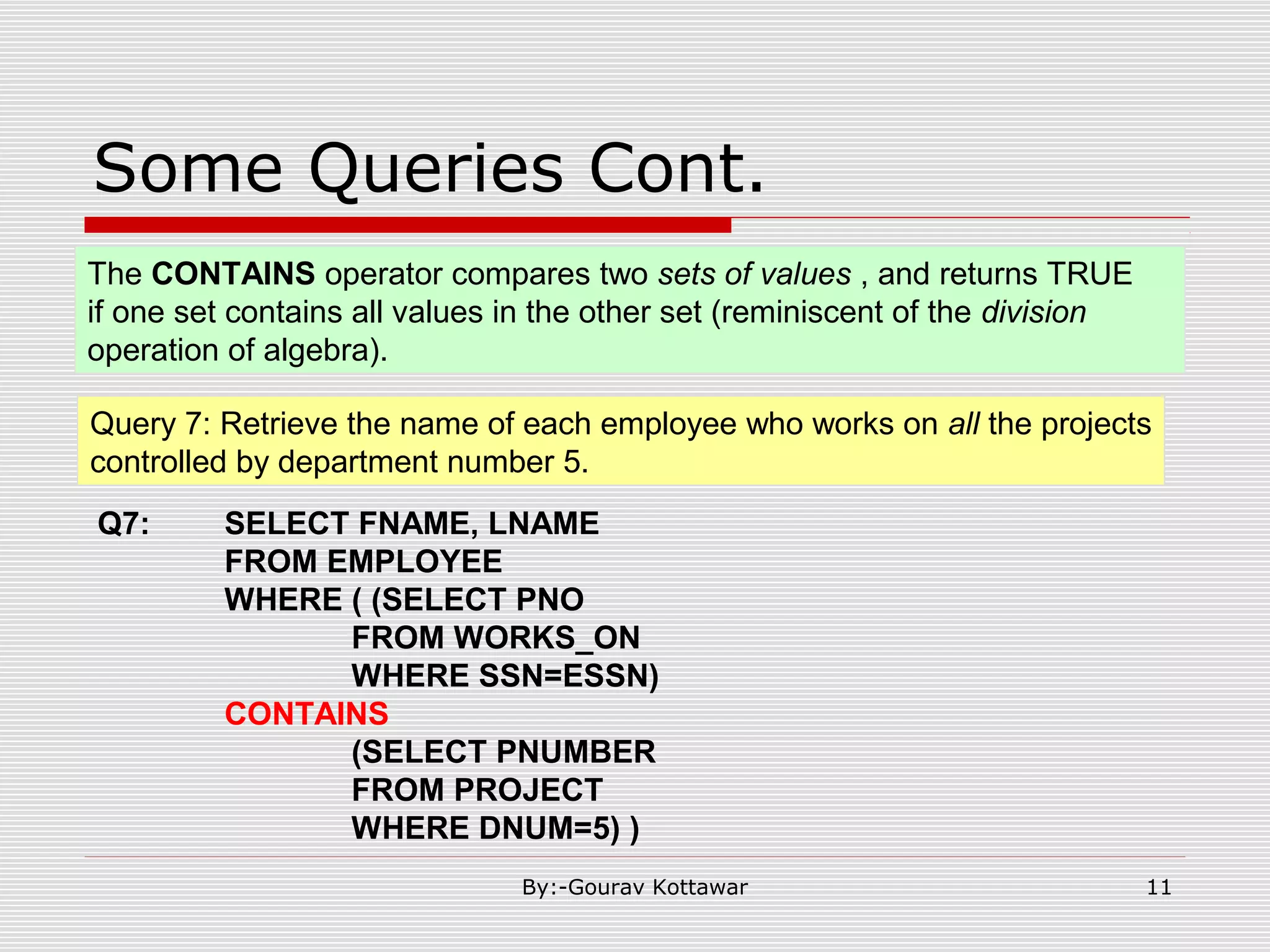
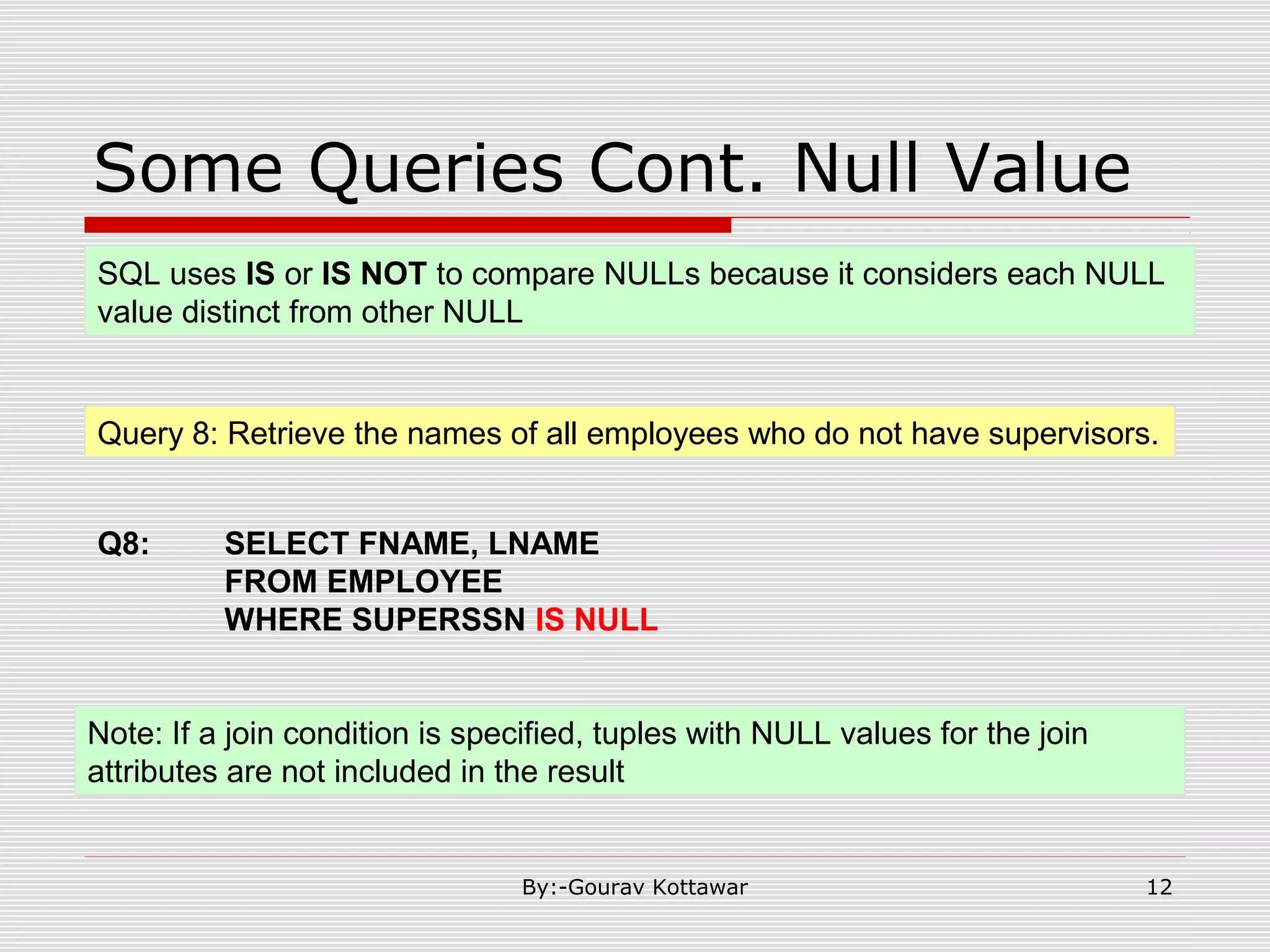
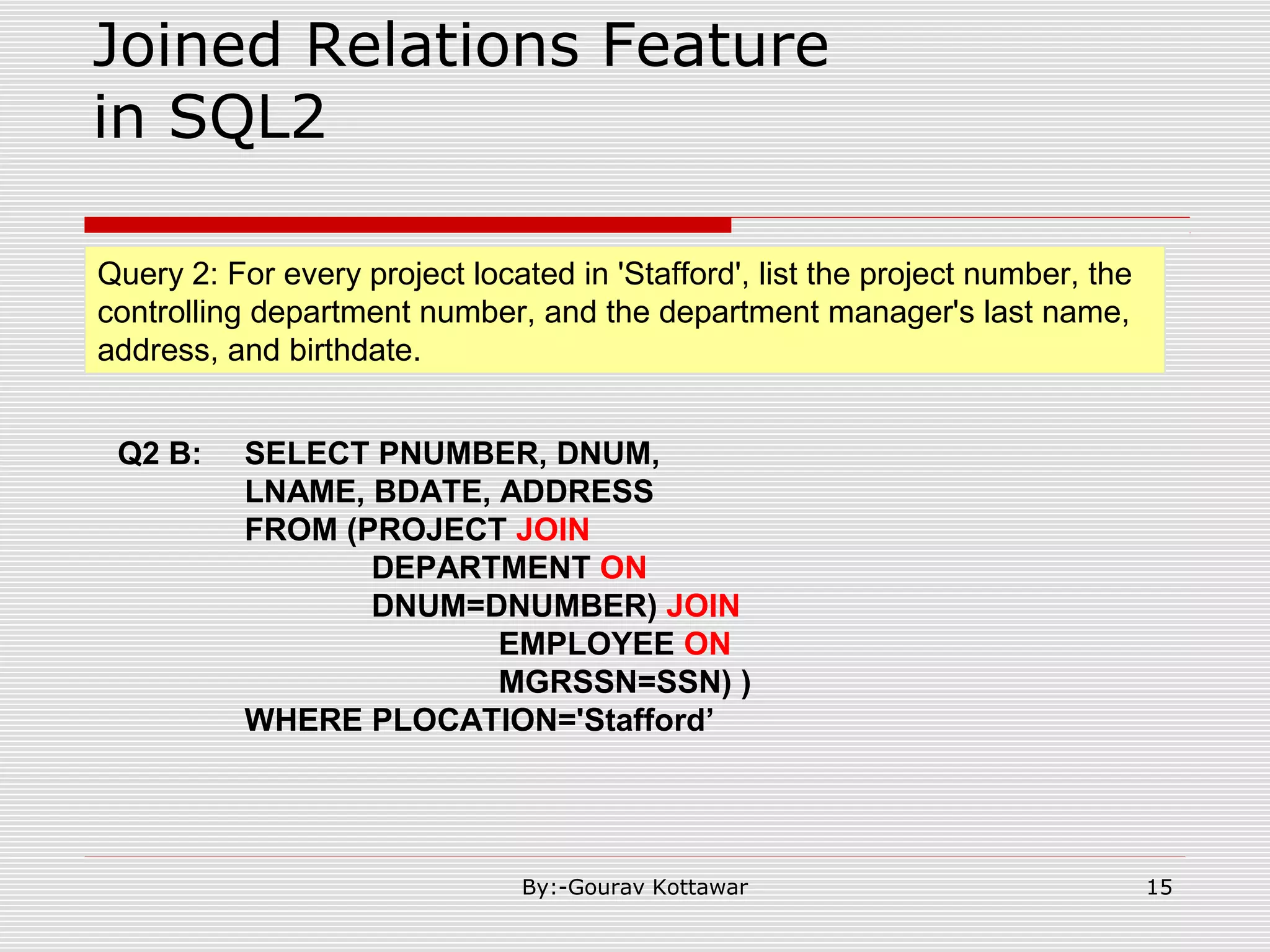
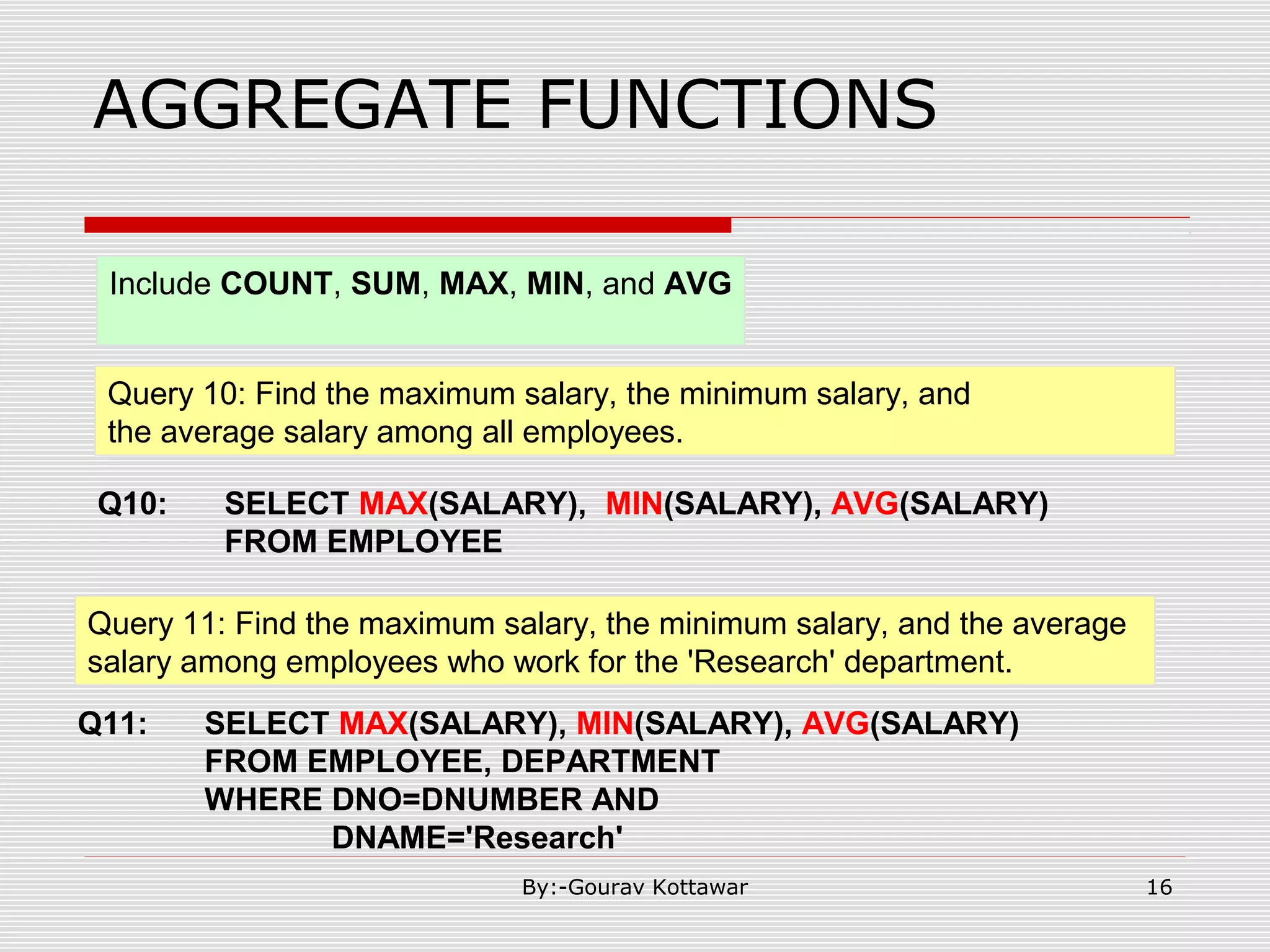
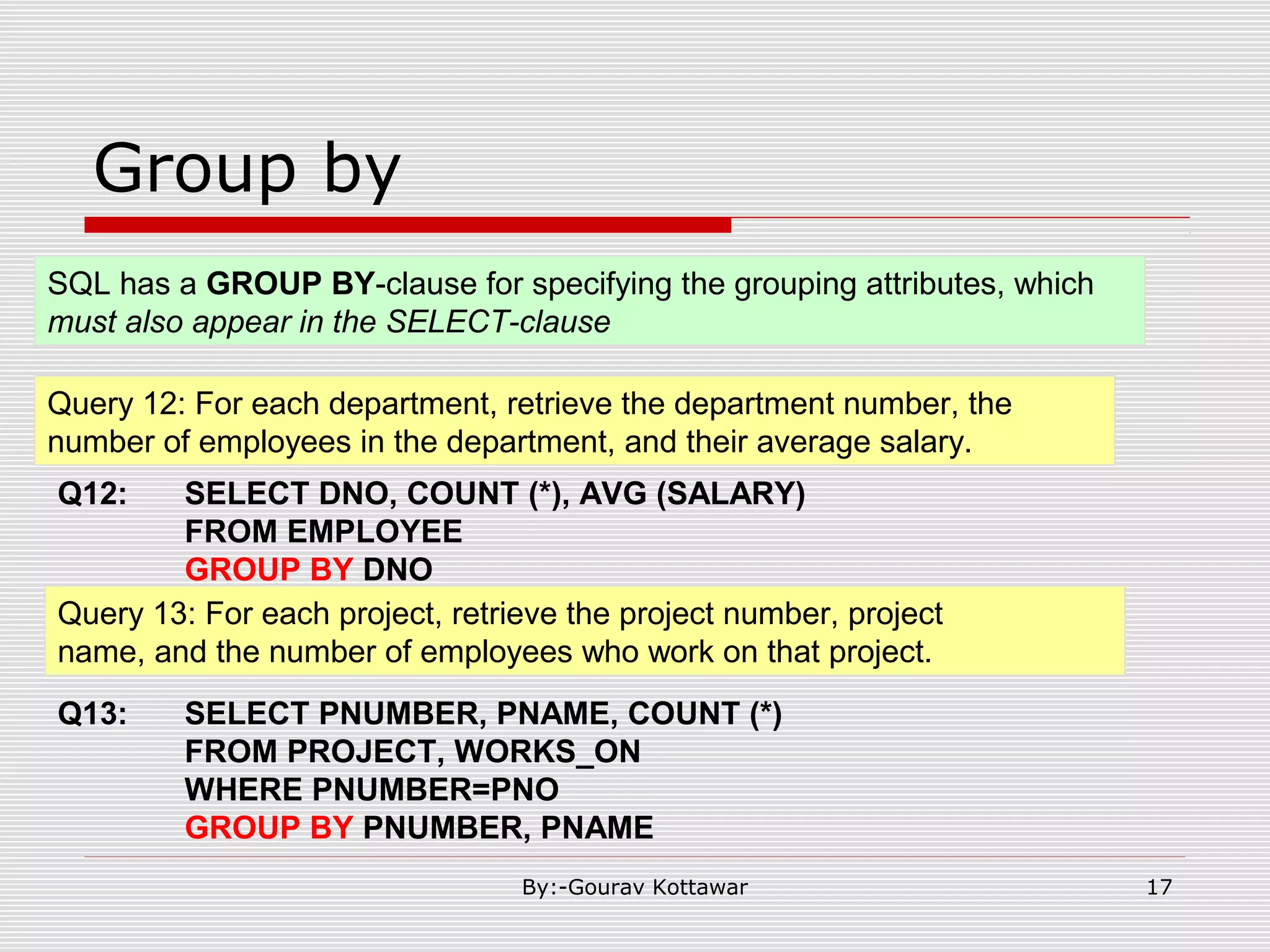
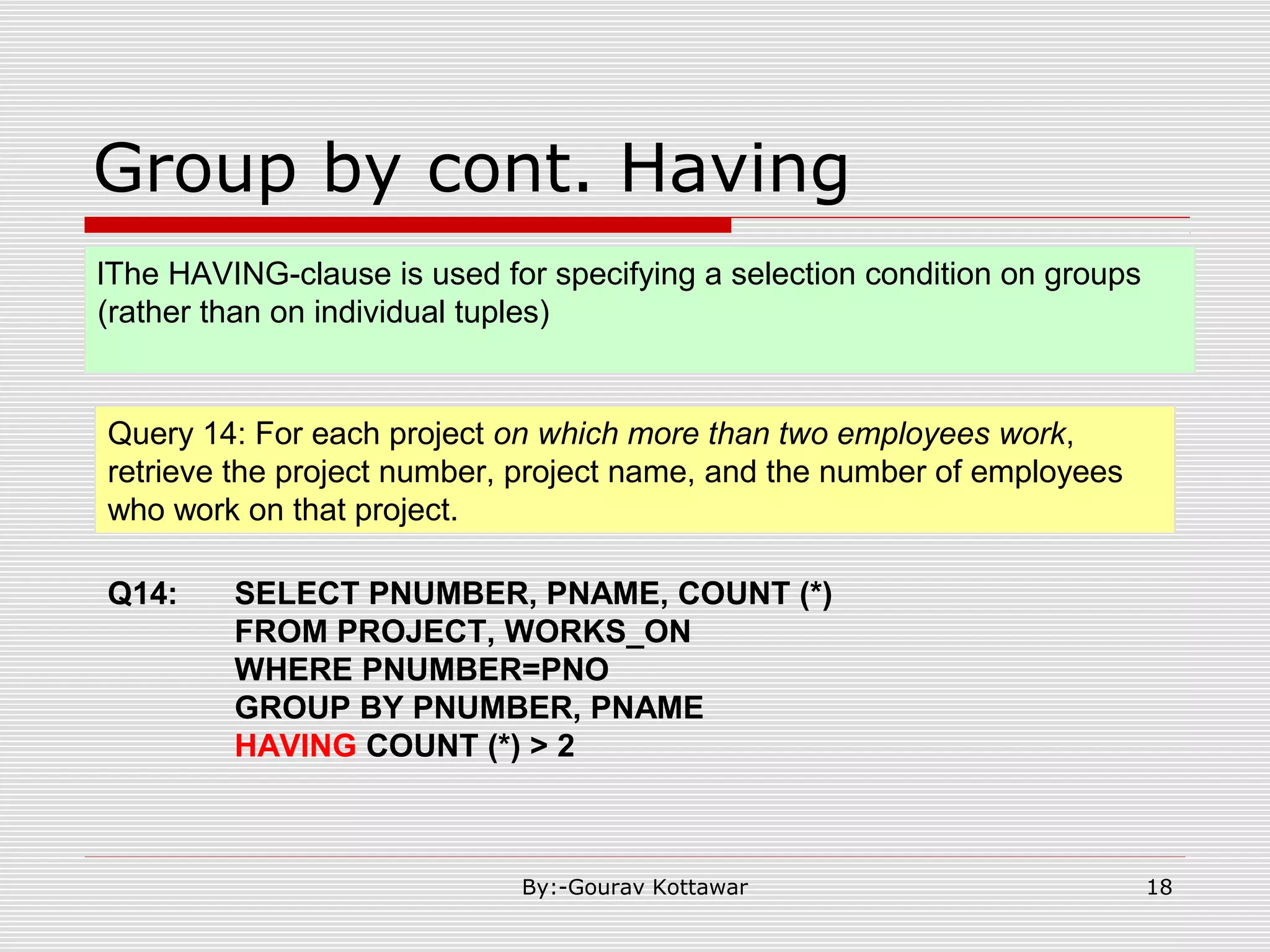
The document discusses SQL queries and concepts like SELECT statements, FROM and WHERE clauses, JOINs, aggregation functions, GROUP BY and HAVING clauses. It provides examples of 14 queries with the corresponding SQL code to retrieve employee and department information from sample tables. The key concepts covered include SELECTing columns, filtering rows with WHERE, JOINs between tables, aggregation with functions like COUNT and AVG, and grouping query results with GROUP BY.






![Summary of SQL Queries A query in SQL can consist of up to six clauses, but only the first two, SELECT and FROM, are mandatory. The clauses are specified in the following order: SELECT <attribute list> FROM <table list> [WHERE <condition>] [GROUP BY <grouping attribute(s)>] [HAVING <group condition>] [ORDER BY <attribute list>] 19By:-Gourav Kottawar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlrbmsppt-160311141023/75/SQL-querys-in-detail-Sql-query-slides-19-2048.jpg)

![More complex Select “SQL Server” SELECT [ ALL | DISTINCT ] [ TOP n [ PERCENT ] [ WITH TIES ] ] < select_list > < select_list > ::= { * | { table_name | view_name | table_alias }.* | { column_name | expression | IDENTITYCOL | ROWGUIDCOL } [ [ AS ] column_alias ] | column_alias = expression } [ ,...n ] SELECT select_list [ INTO new_table ] FROM table_source [ WHERE search_condition ] [ GROUP BY group_by_expression ] [ HAVING search_condition ] [ ORDER BY order_expression [ ASC | DESC ] ] Select Clause: From Clause: [ FROM { < table_source > } [ ,...n ] ] < table_source > ::= table_name [ [ AS ] table_alias ] [ WITH ( < table_hint > [ ,...n ] ) ] | view_name [ [ AS ] table_alias ] | rowset_function [ [ AS ] table_alias ] | OPENXML | derived_table [ AS ] table_alias [ ( column_alias [ ,...n ] ) ] | < joined_table > < joined_table > ::= < table_source > < join_type > < table_source > ON < search_condition > | < table_source > CROSS JOIN < table_source > | < joined_table > < join_type > ::= [ INNER | { { LEFT | RIGHT | FULL } [ OUTER ] } ] [ < join_hint > ] JOIN Arguments < table_source > 21By:-Gourav Kottawar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlrbmsppt-160311141023/75/SQL-querys-in-detail-Sql-query-slides-21-2048.jpg)
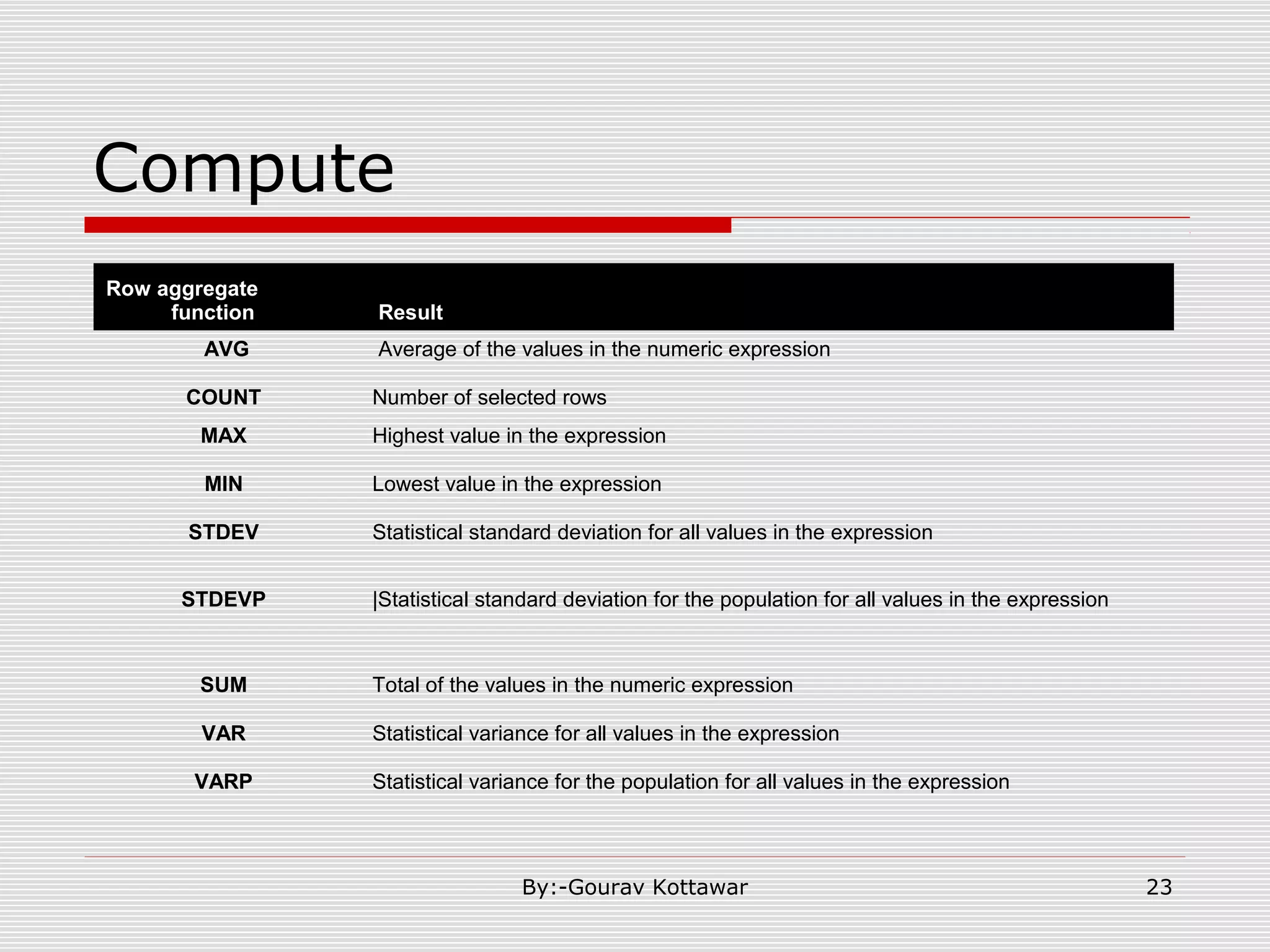
![More complex Select “SQL Server” Cont. Where Clause: [ WHERE < search_condition > | < old_outer_join > ] < old_outer_join > ::= column_name { * = | = * } column_name Group by clause: [ GROUP BY [ ALL ] group_by_expression [ ,...n ] [ WITH { CUBE | ROLLUP } ] ] Having: [ HAVING < search_condition > ] Order By Clause: [ ORDER BY { order_by_expression [ ASC | DESC ] } [ ,...n] ] Compute Clause: [ COMPUTE { { AVG | COUNT | MAX | MIN | STDEV | STDEVP | VAR | VARP | SUM } ( expression ) } [ ,...n ] [ BY expression [ ,...n ] ] ] 22By:-Gourav Kottawar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlrbmsppt-160311141023/75/SQL-querys-in-detail-Sql-query-slides-22-2048.jpg)