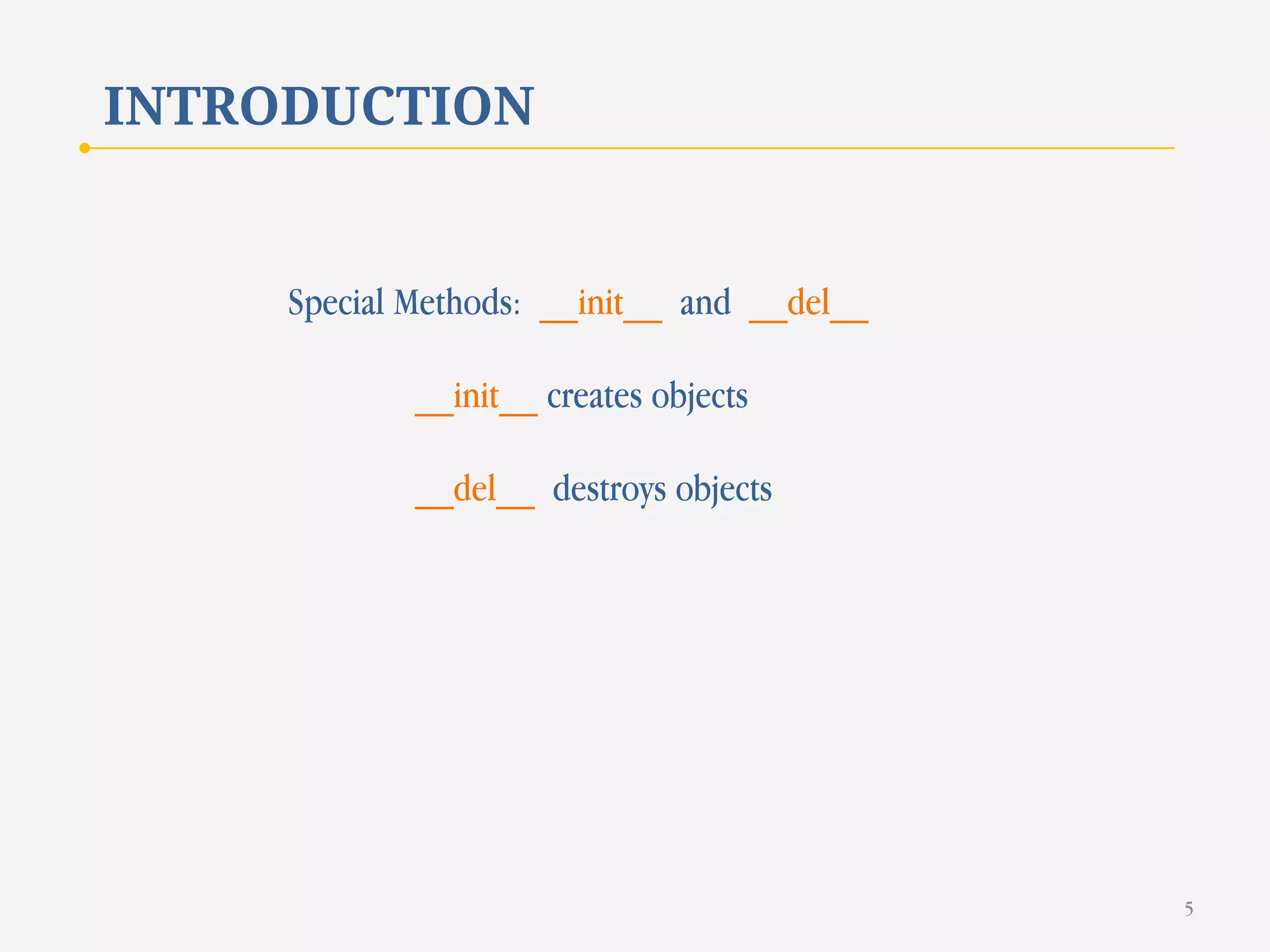
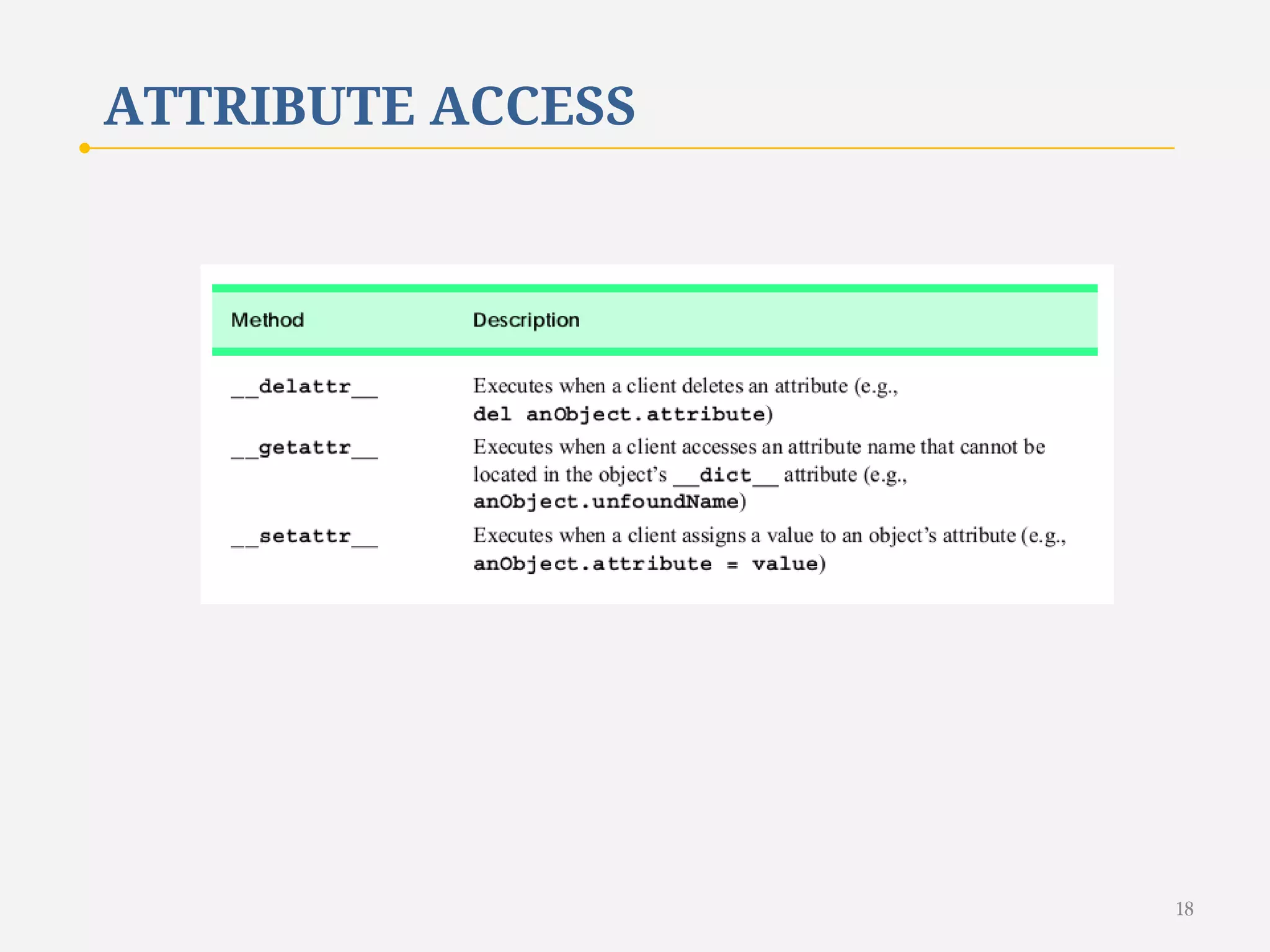
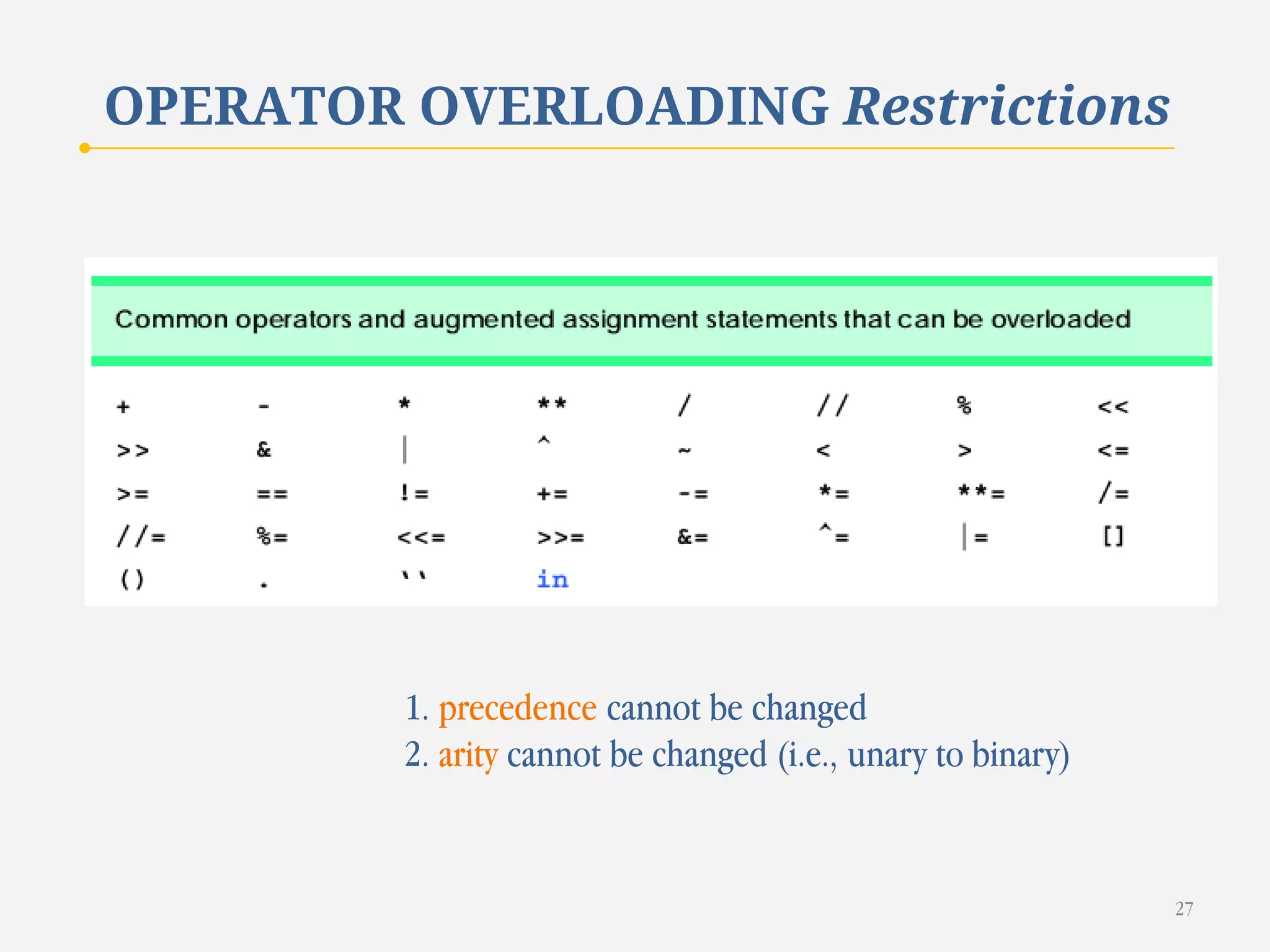
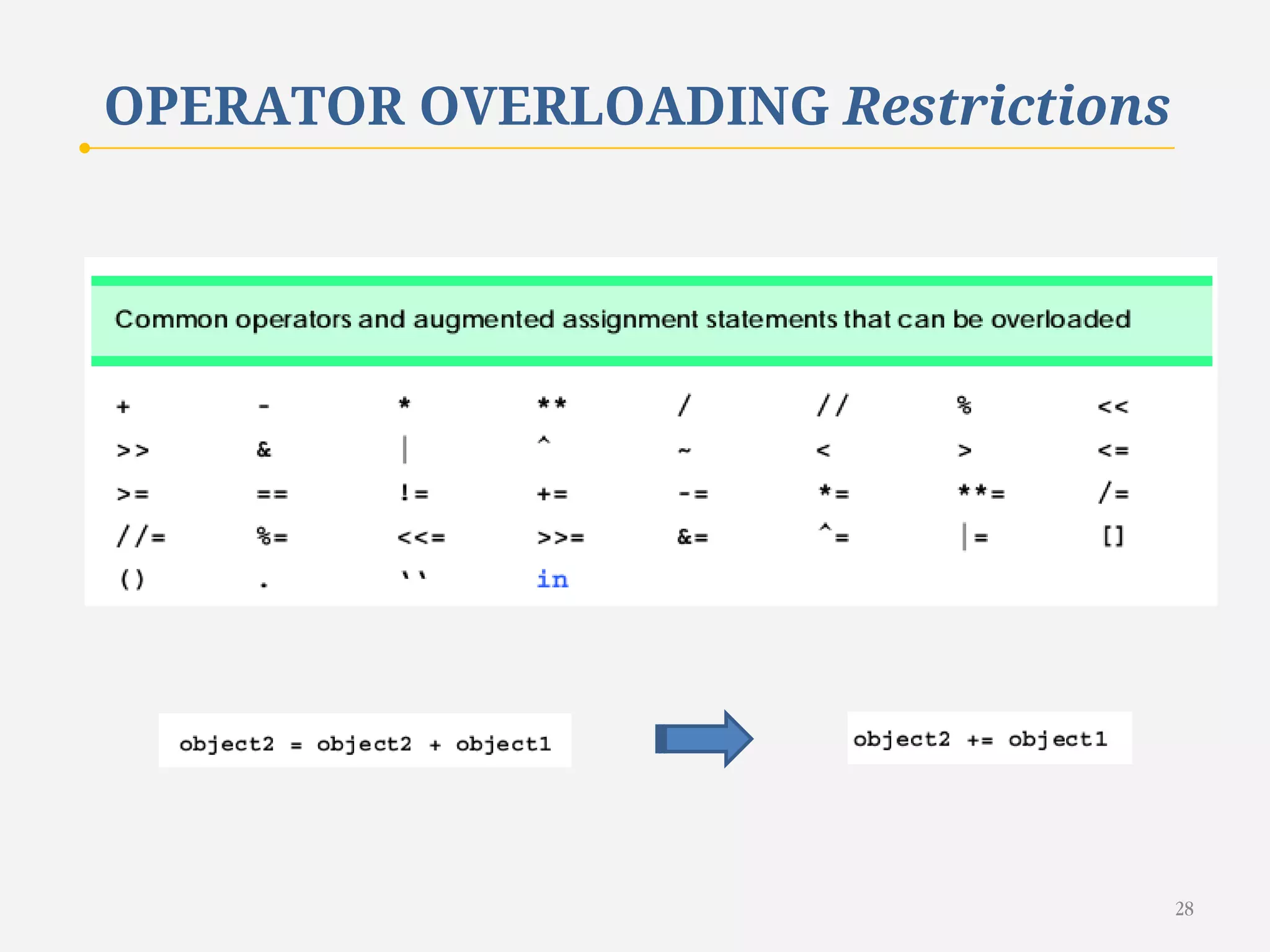
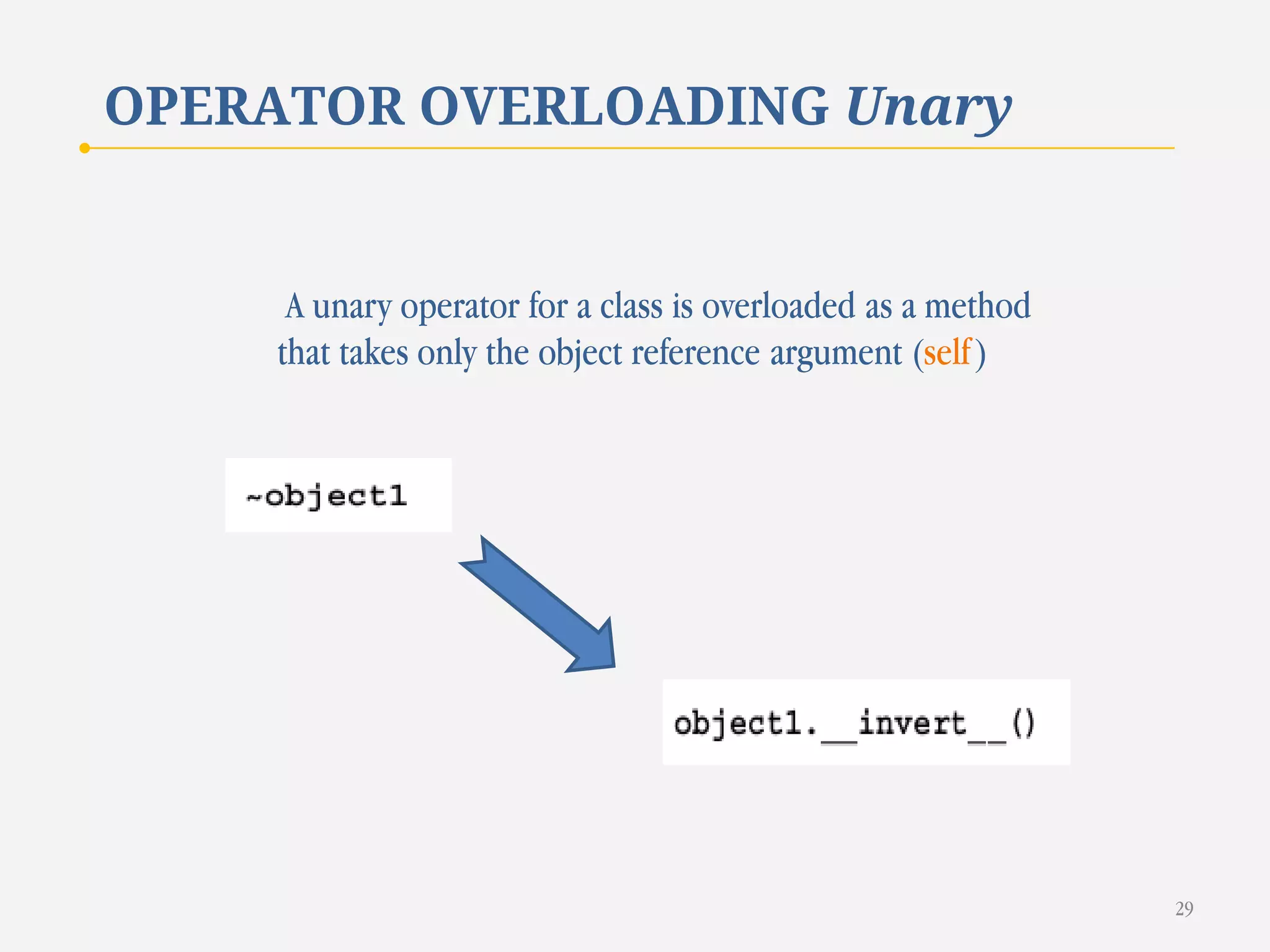
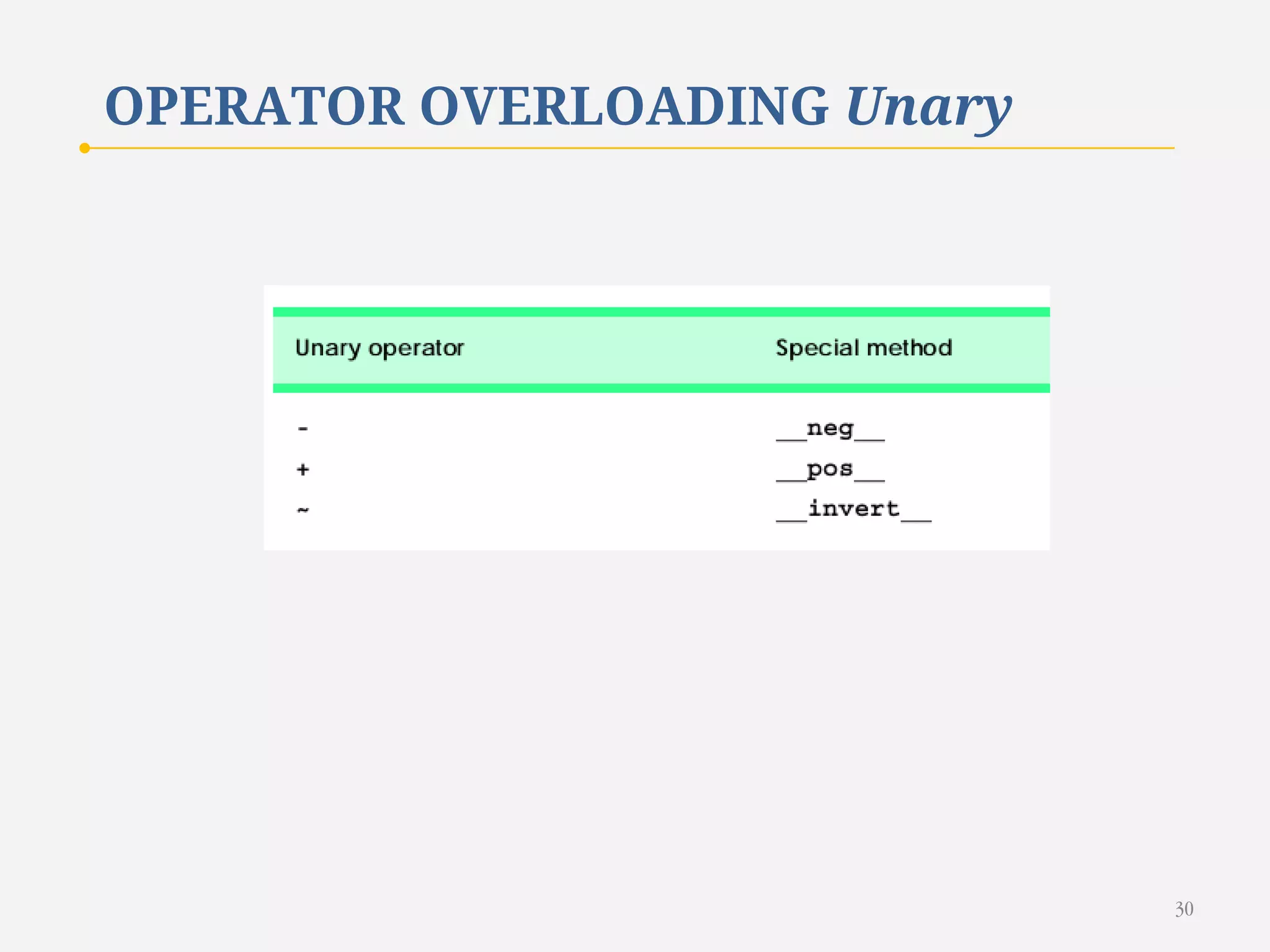
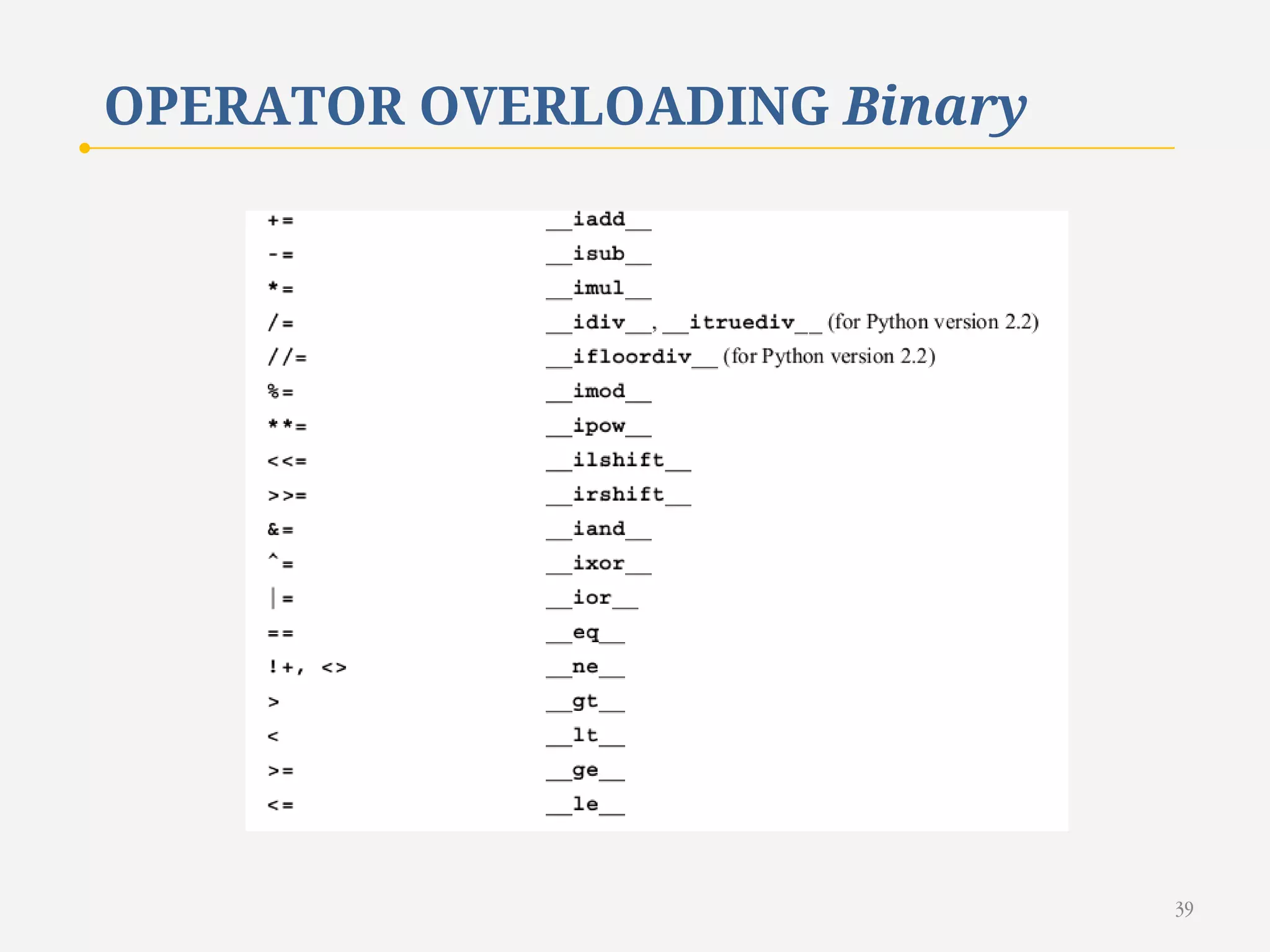
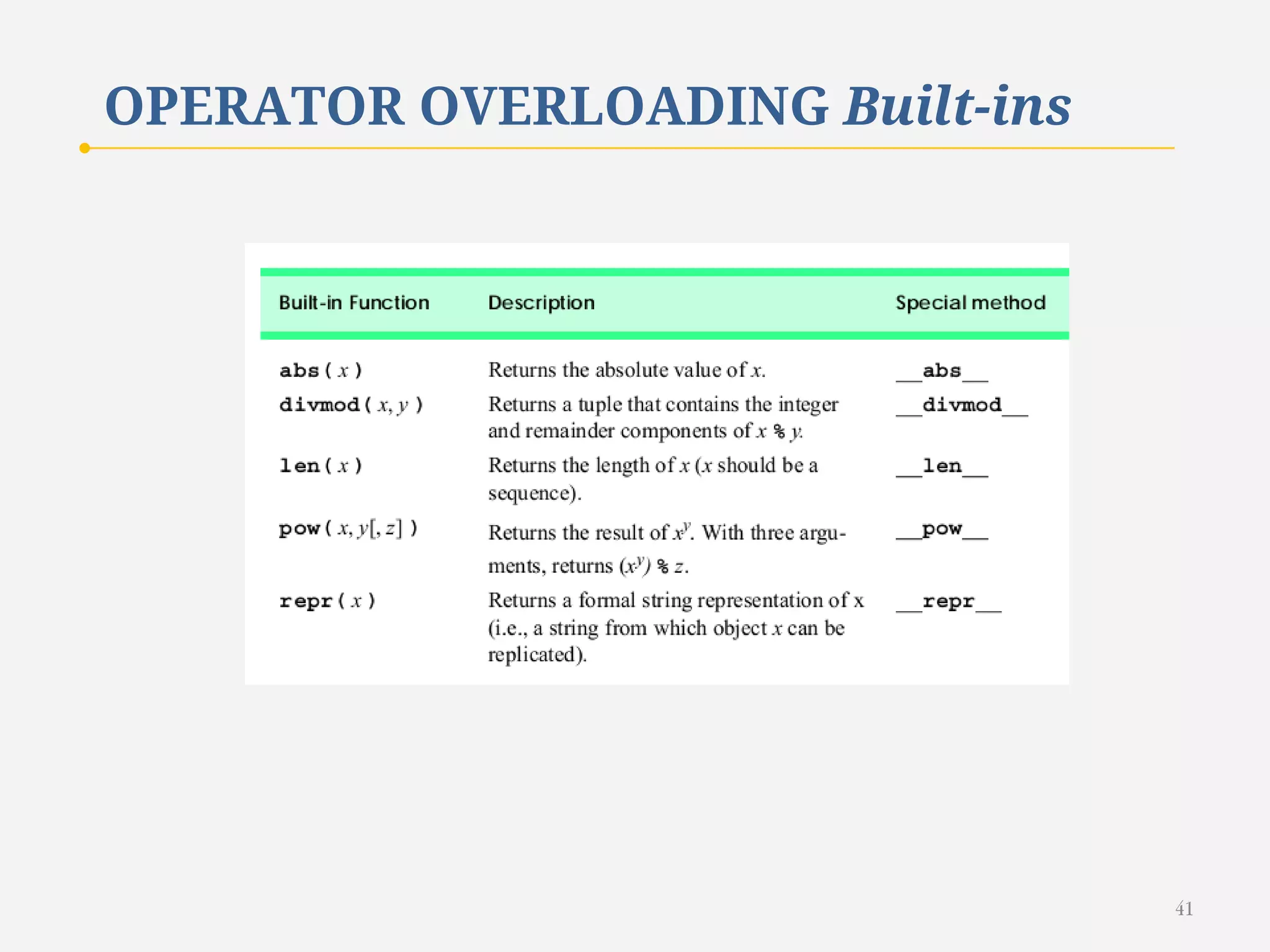
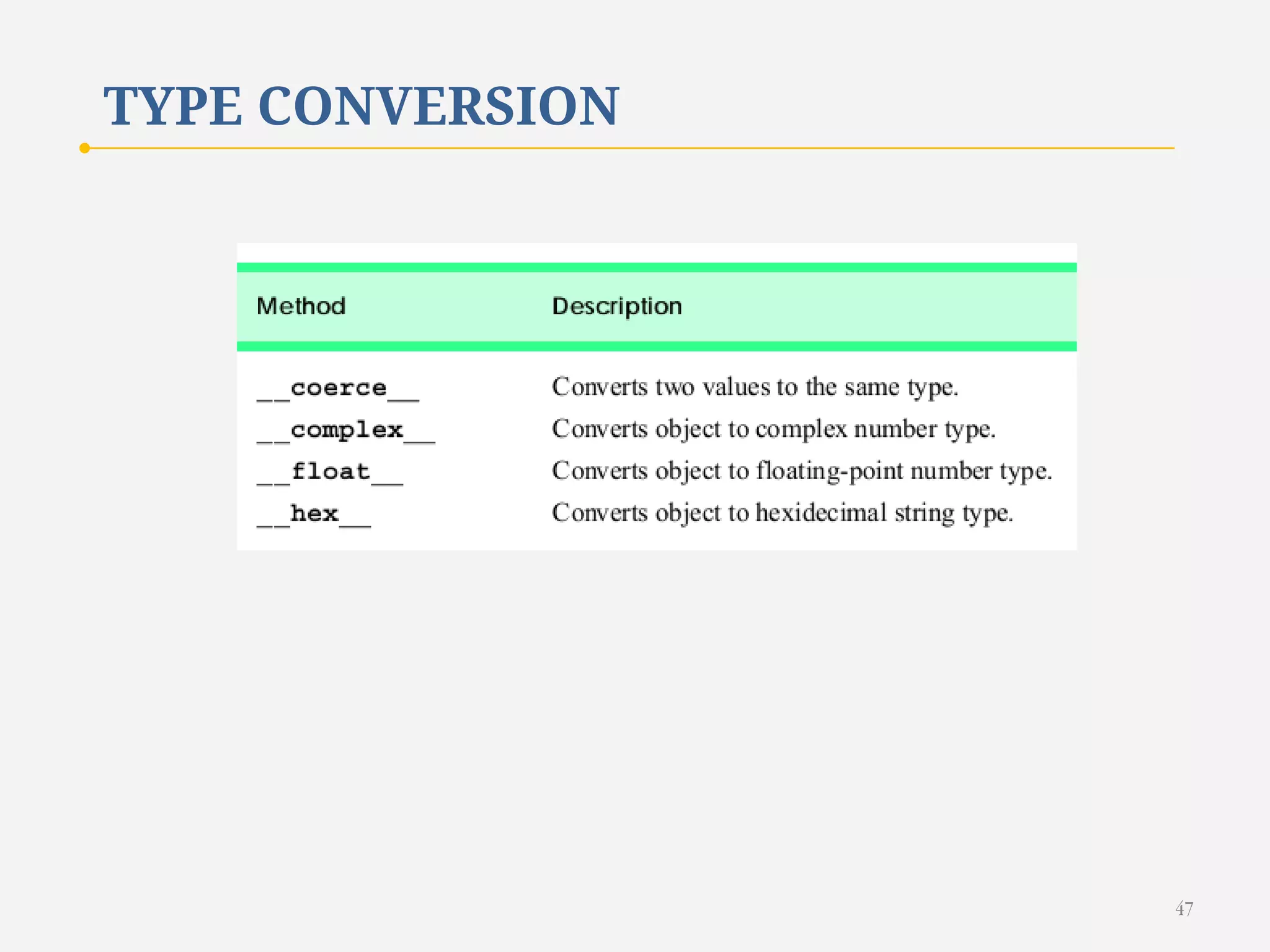
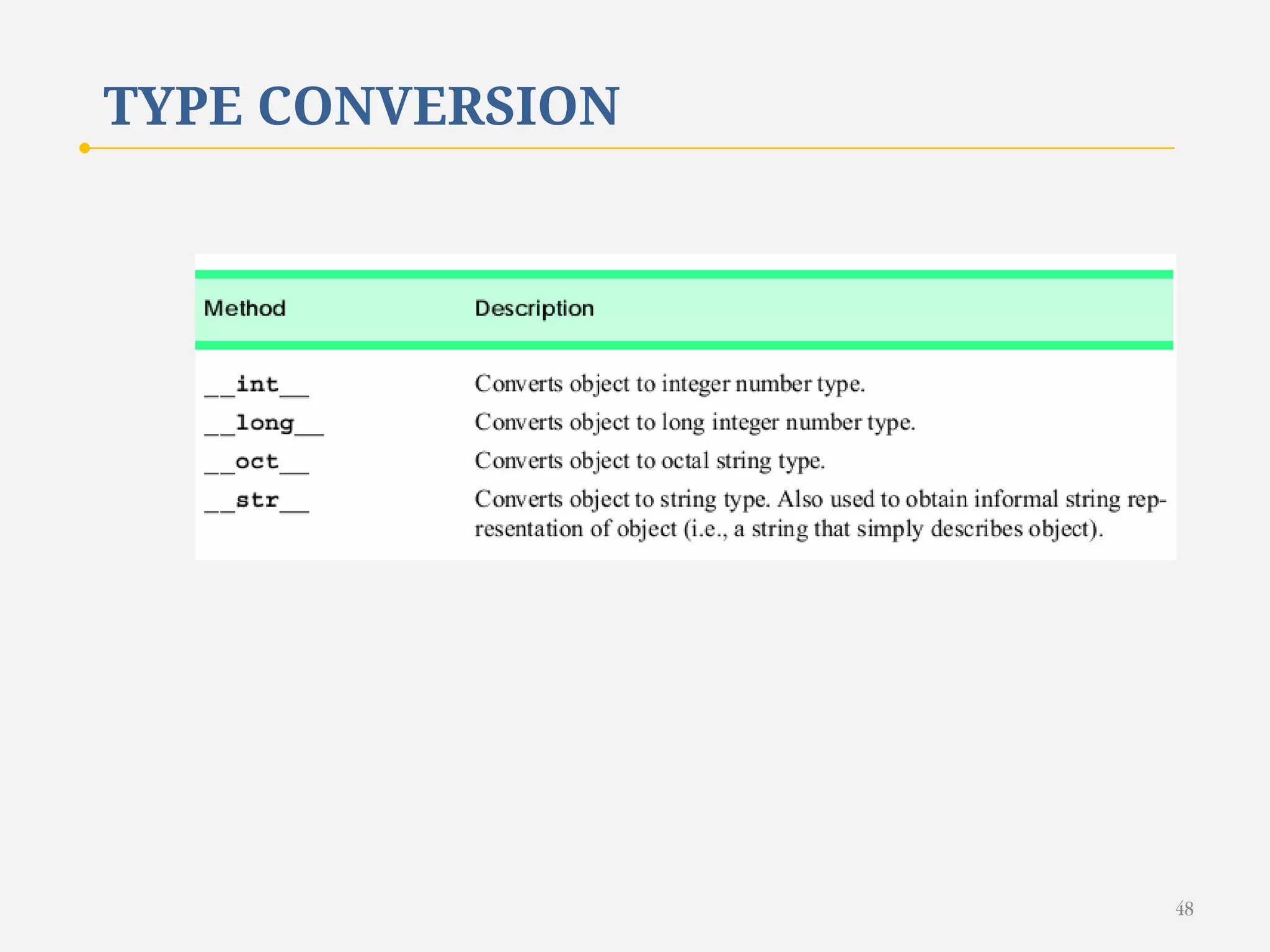
The document discusses customizing classes in Python through operator overloading. It defines operator overloading as allowing programmers to define special methods that are called when operators are used on user-defined classes. This allows operators to work with class objects in a natural way. The document provides examples of overloading operators like + and - for a Rational number class. It also discusses string representation using __str__, attribute access, type conversion, and summarizes with a case study of a Rational class that overloads various operators and functions.