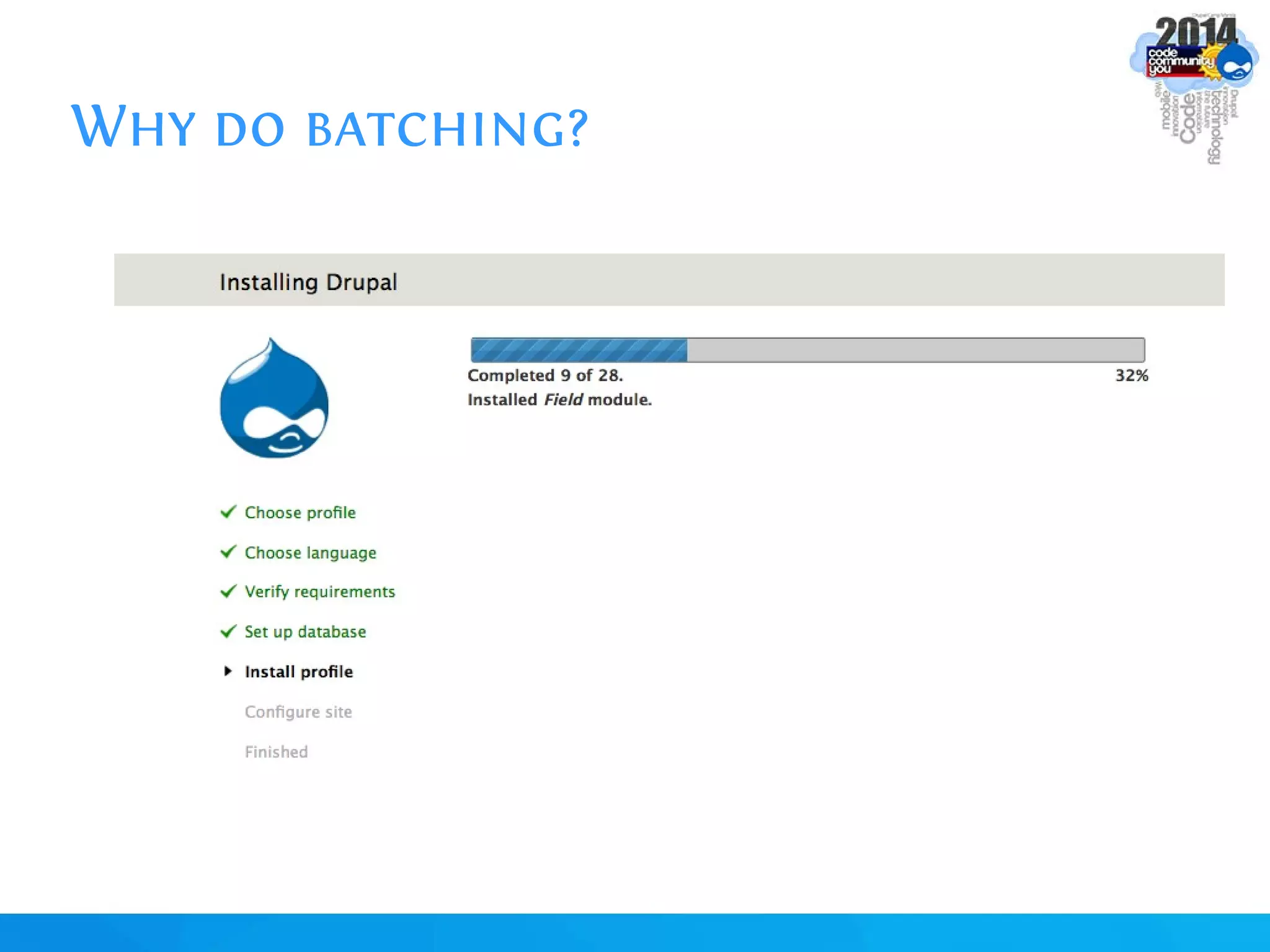
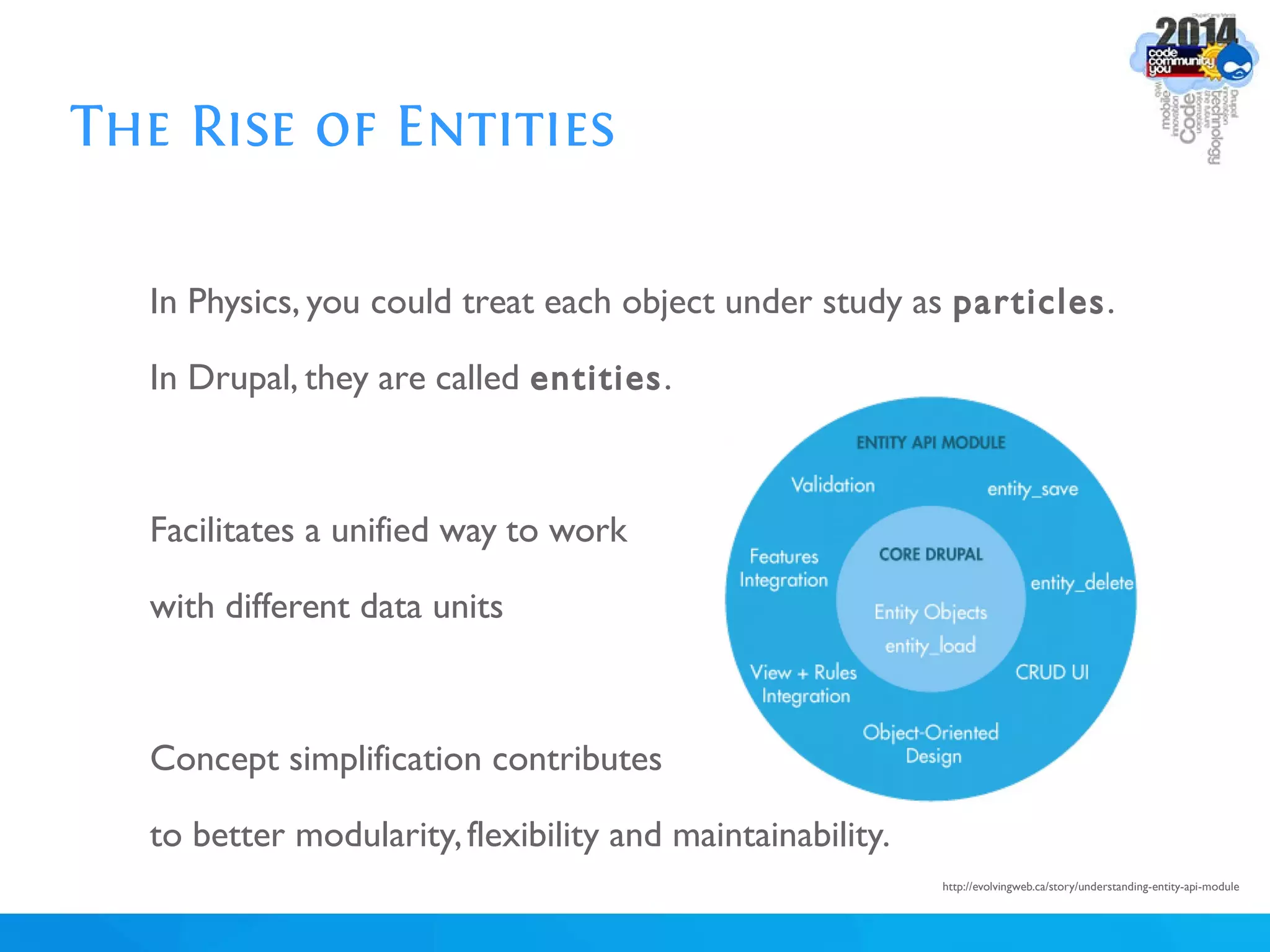
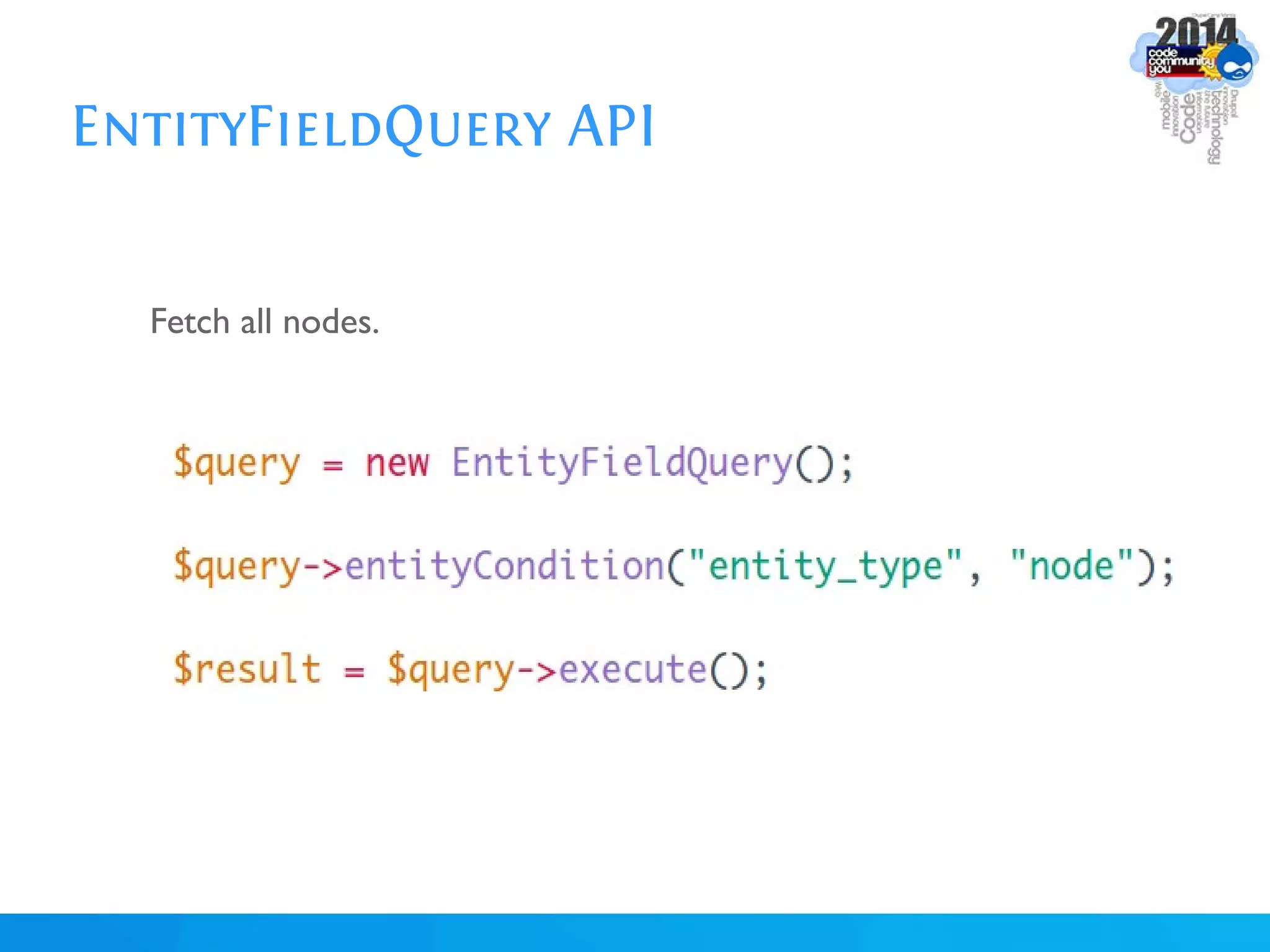
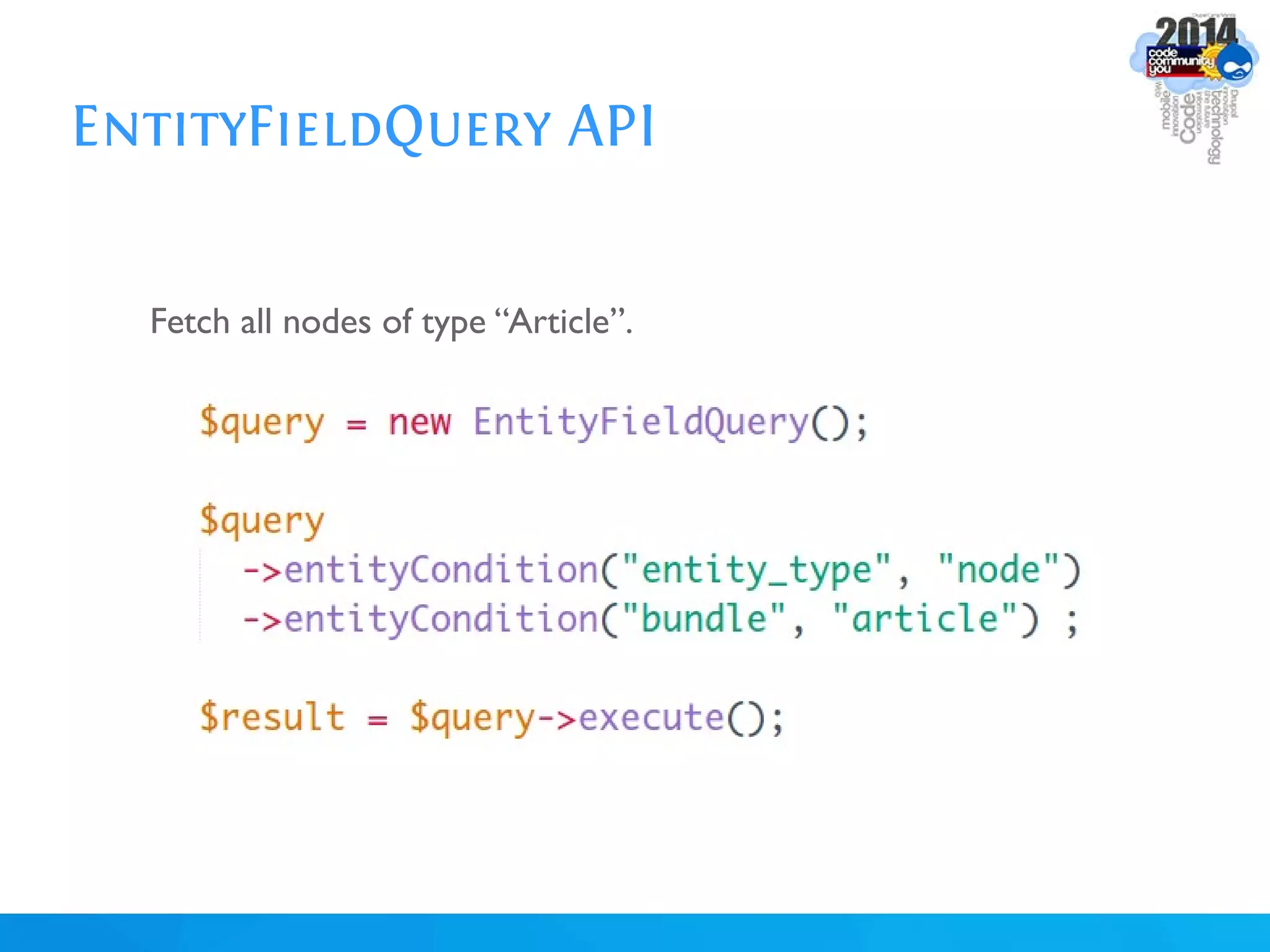
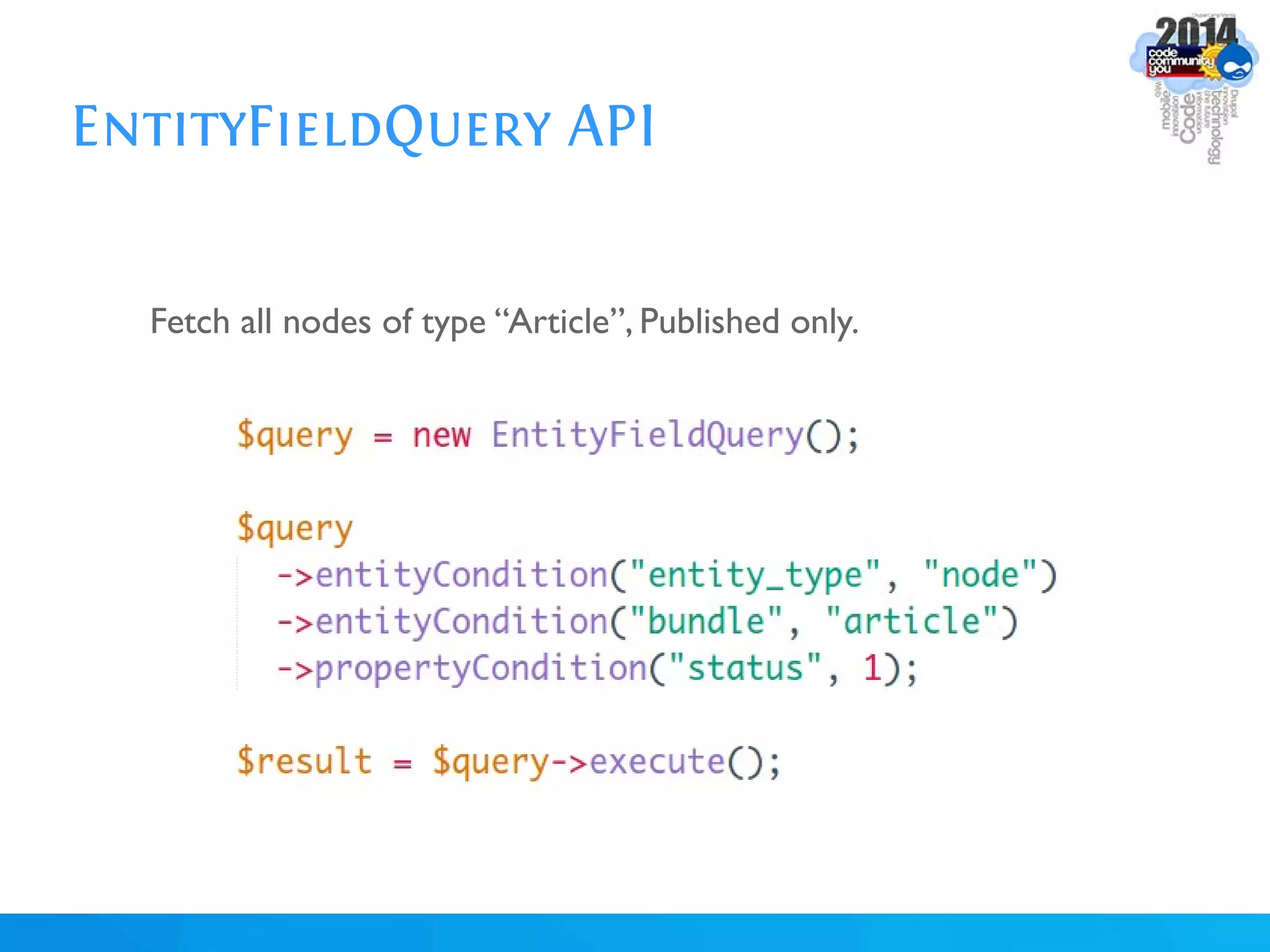
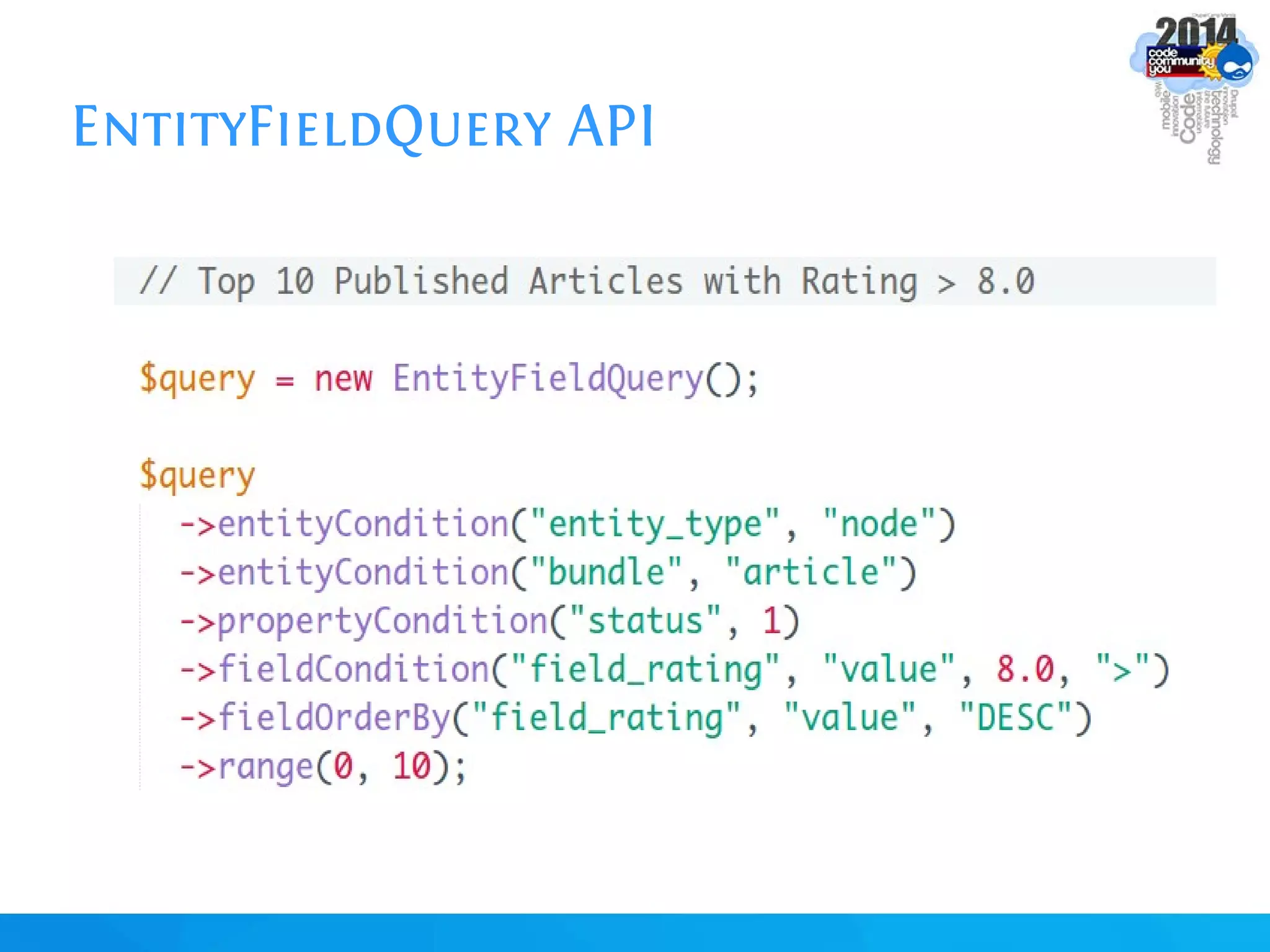
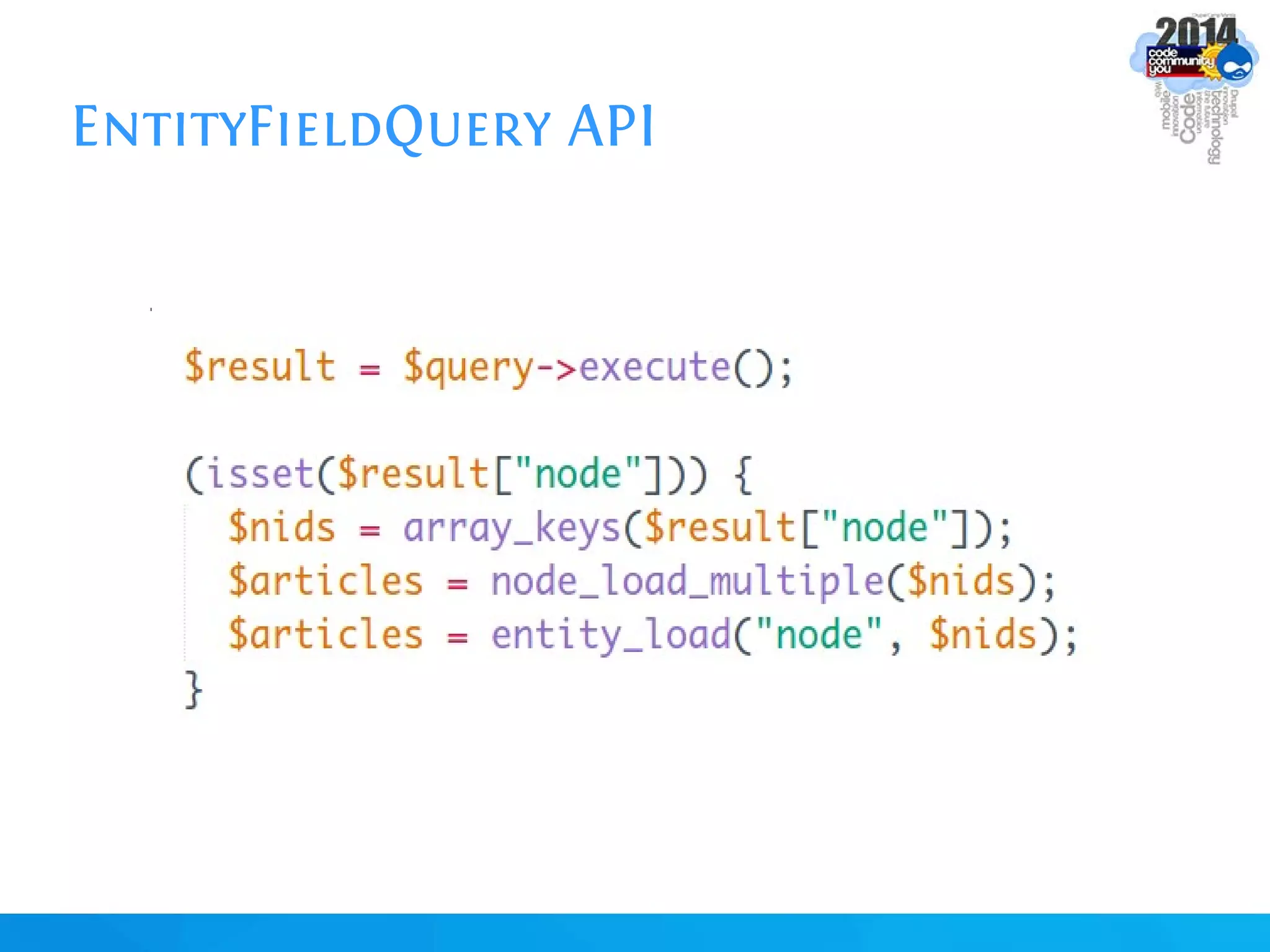
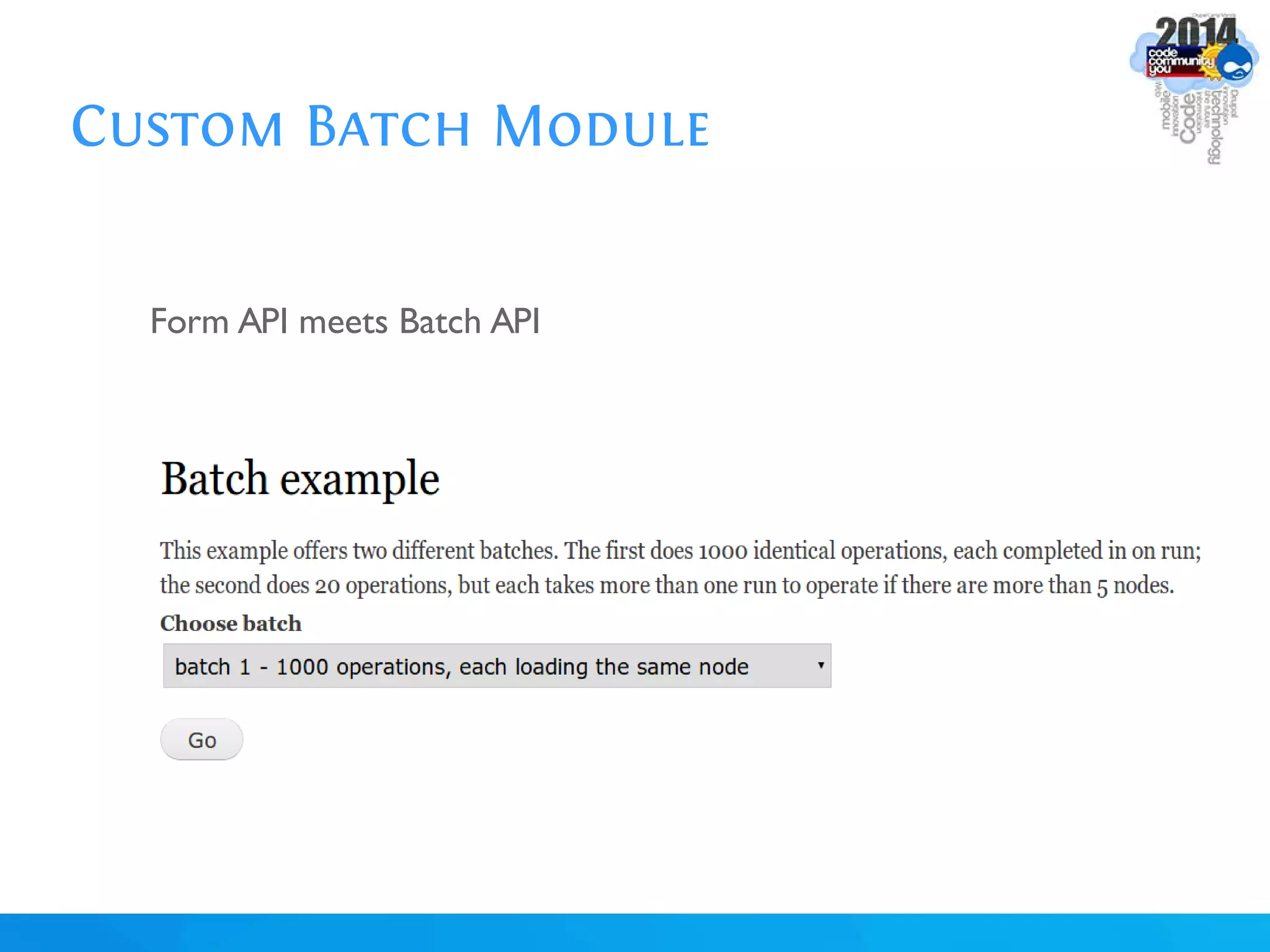
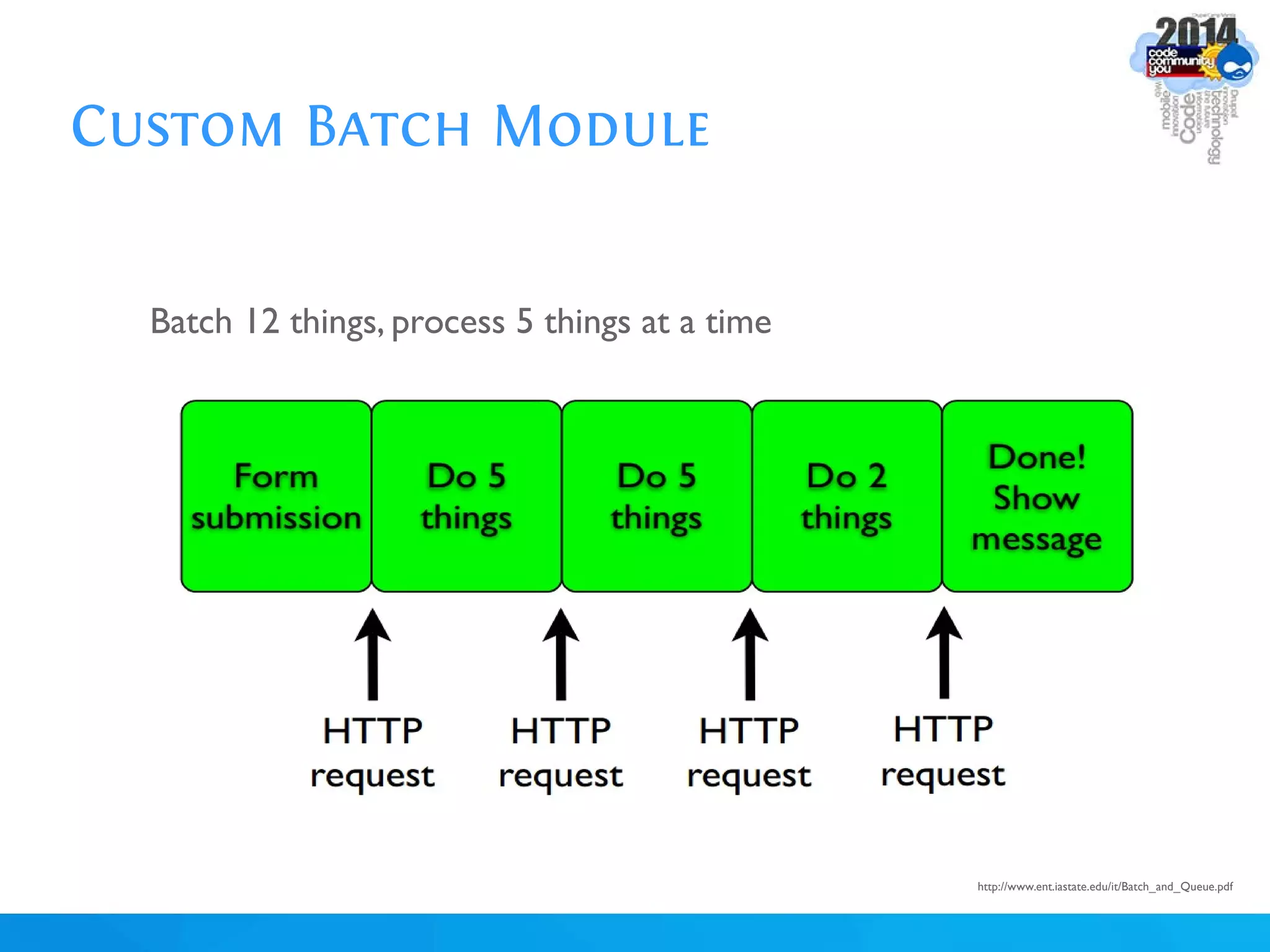
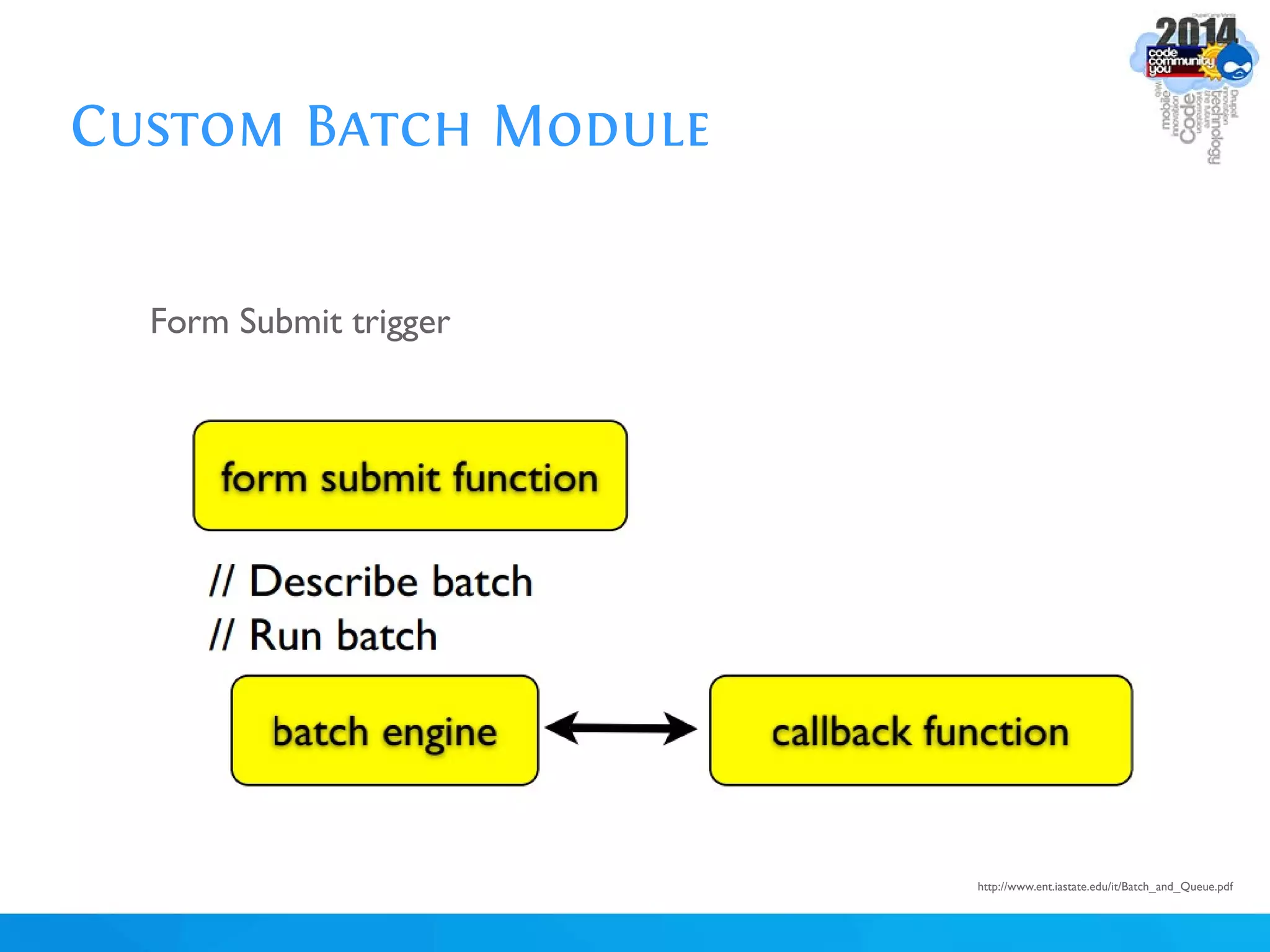
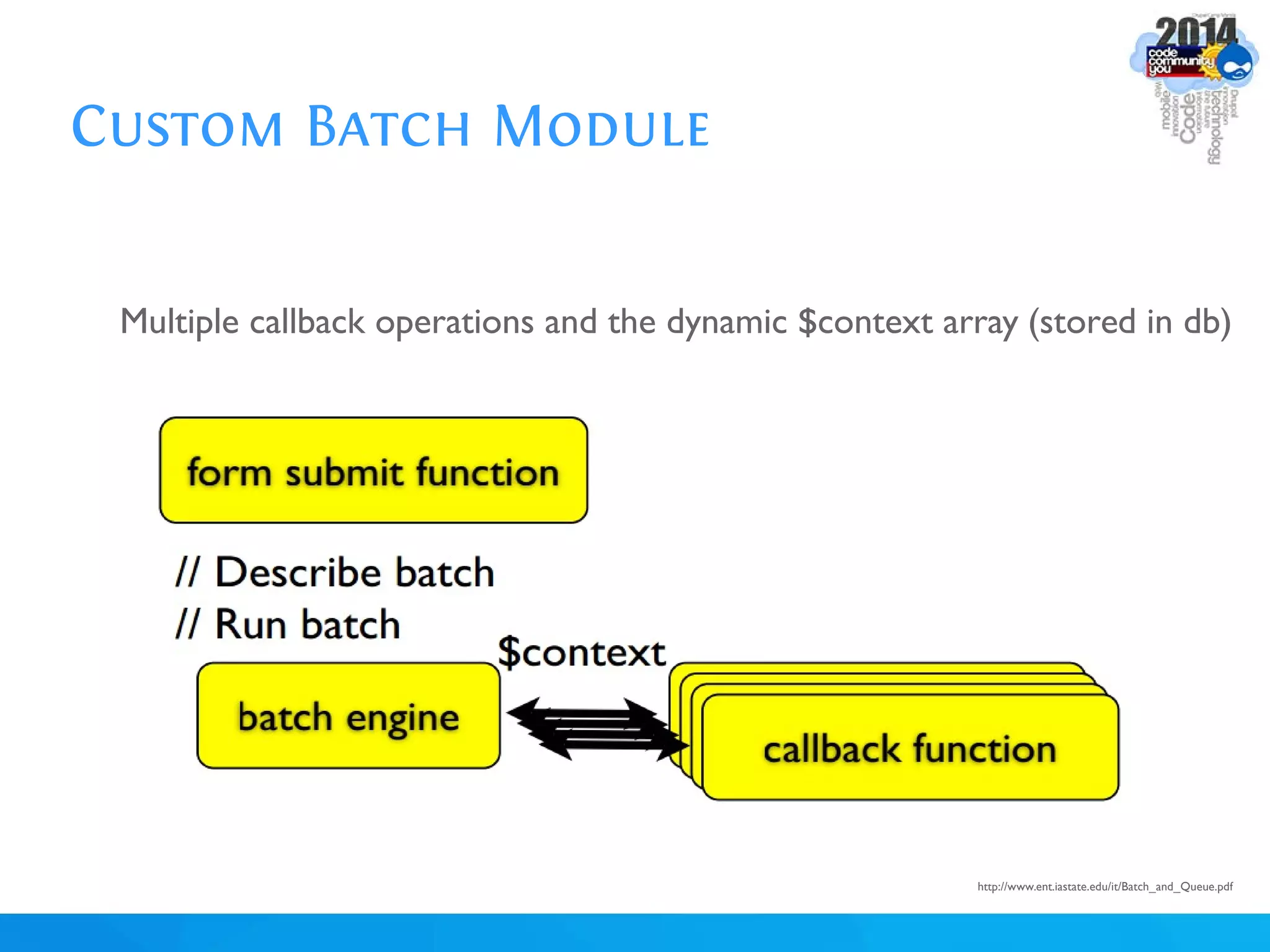
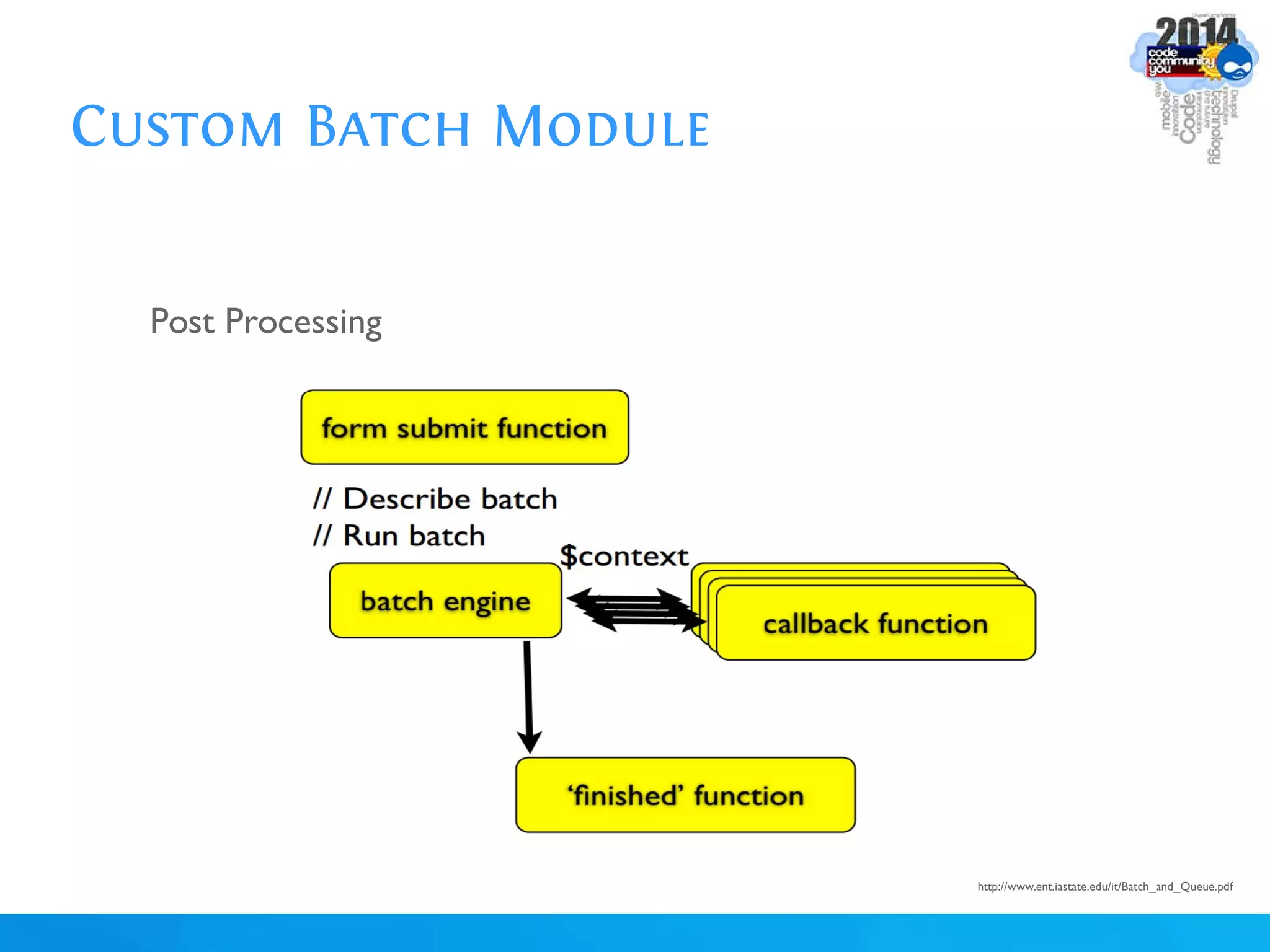
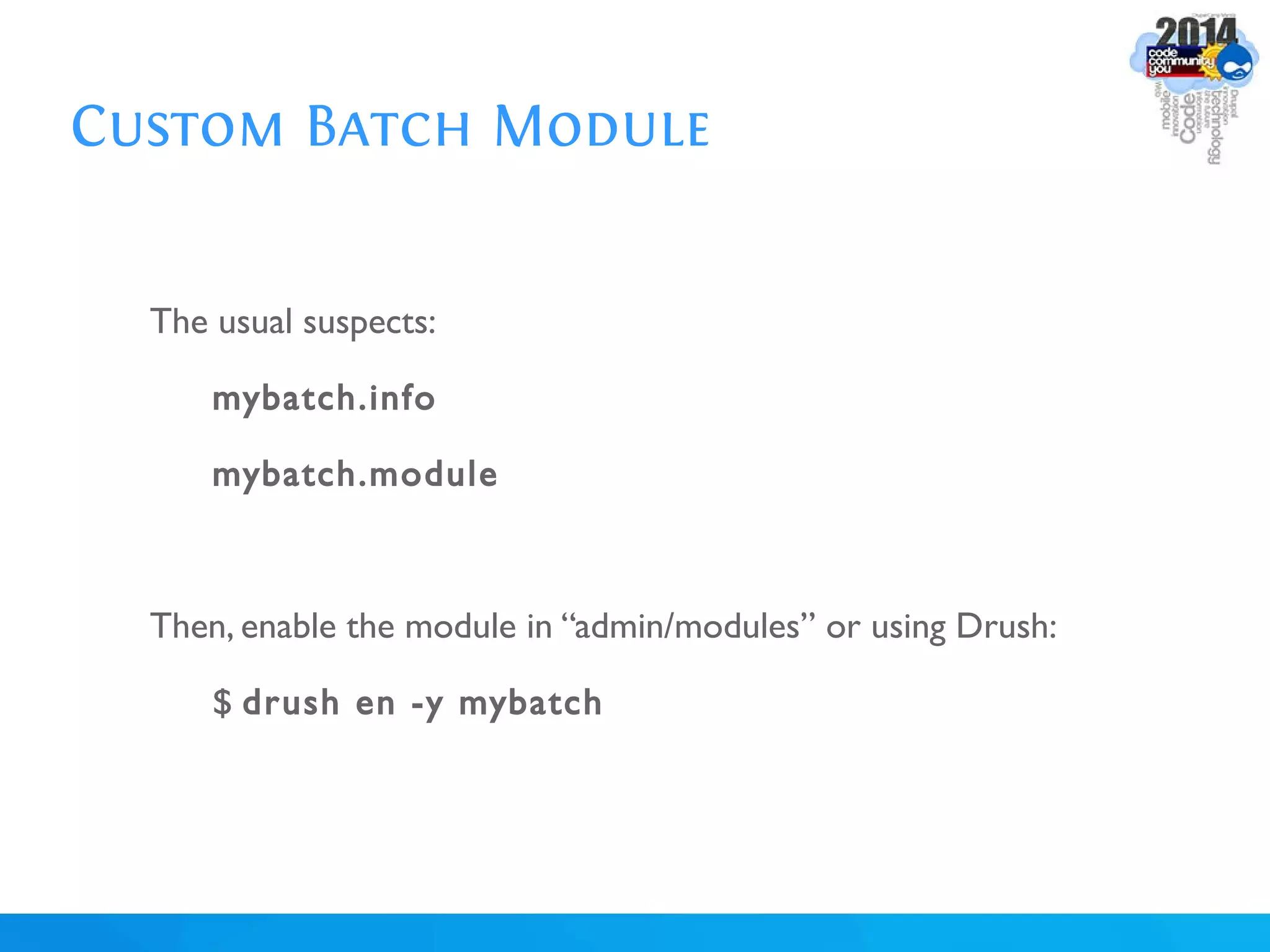
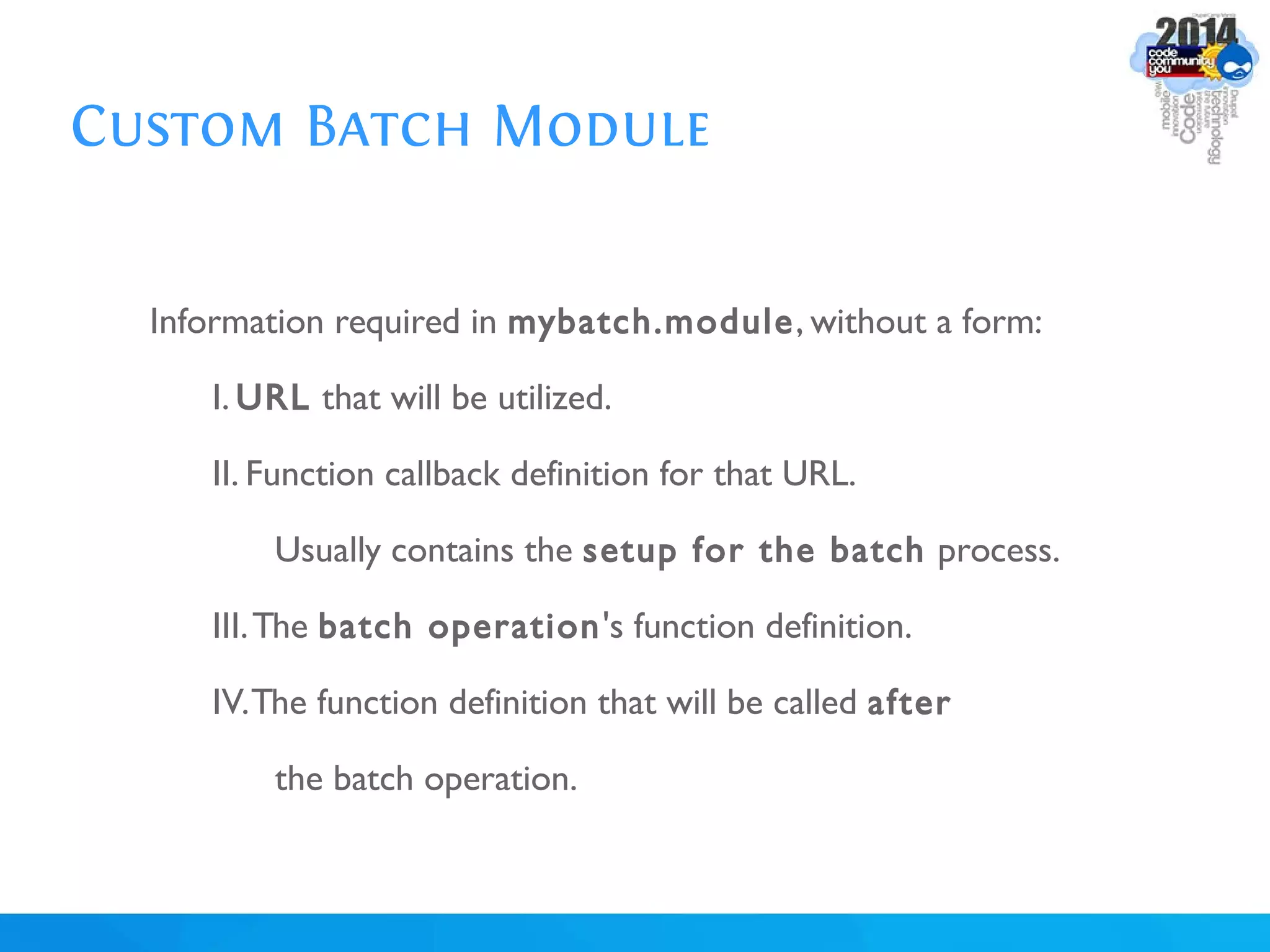
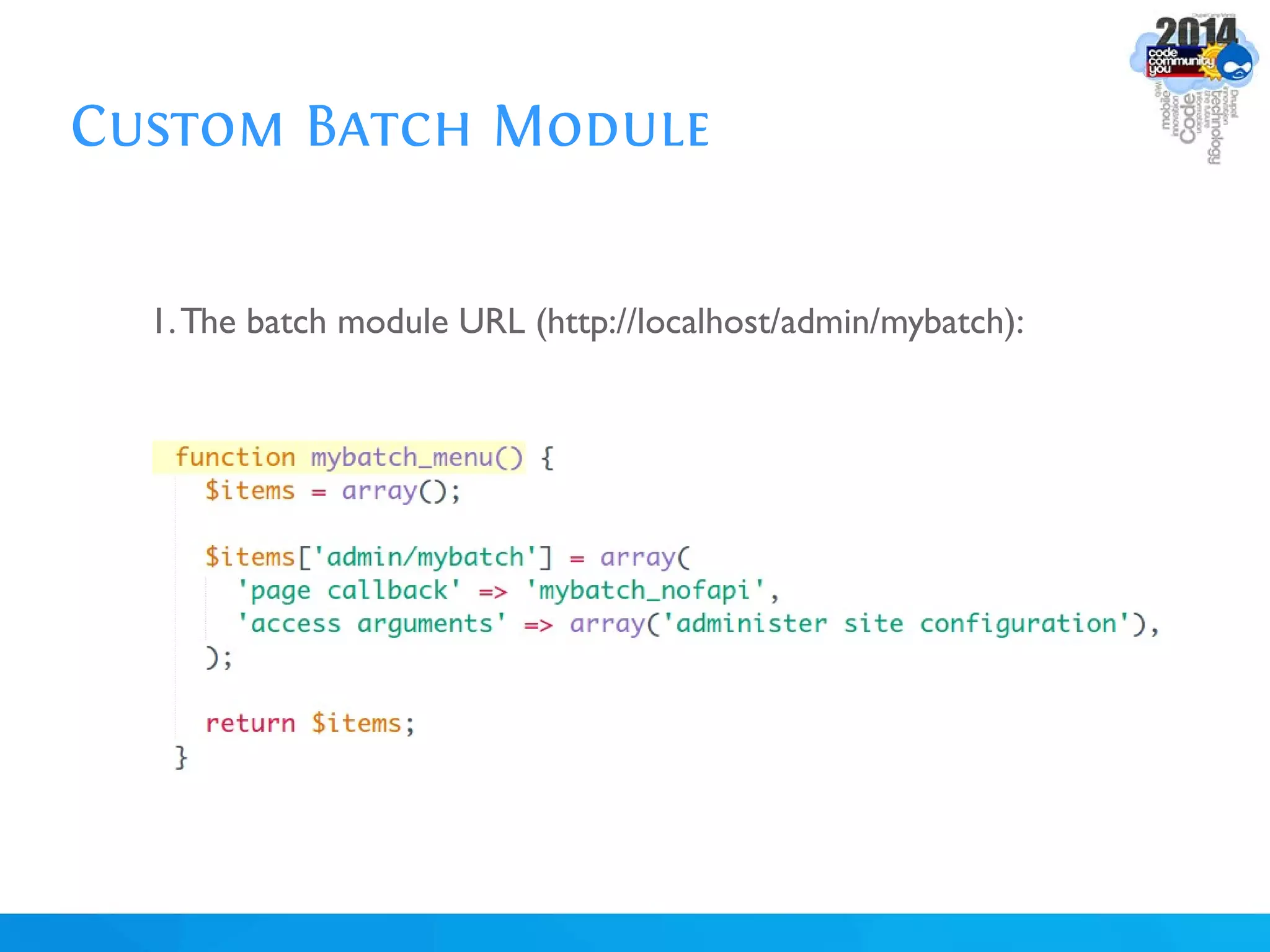
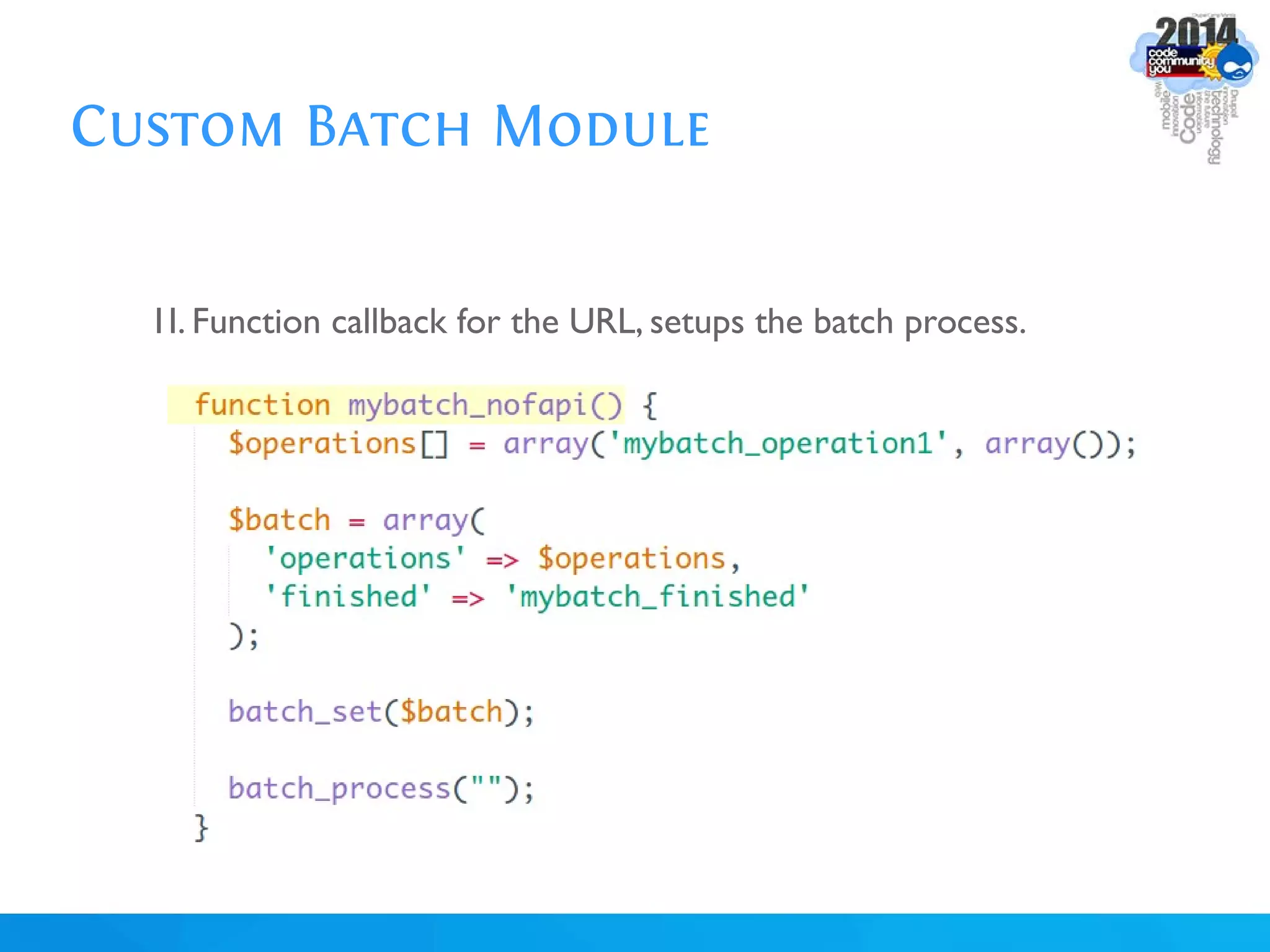
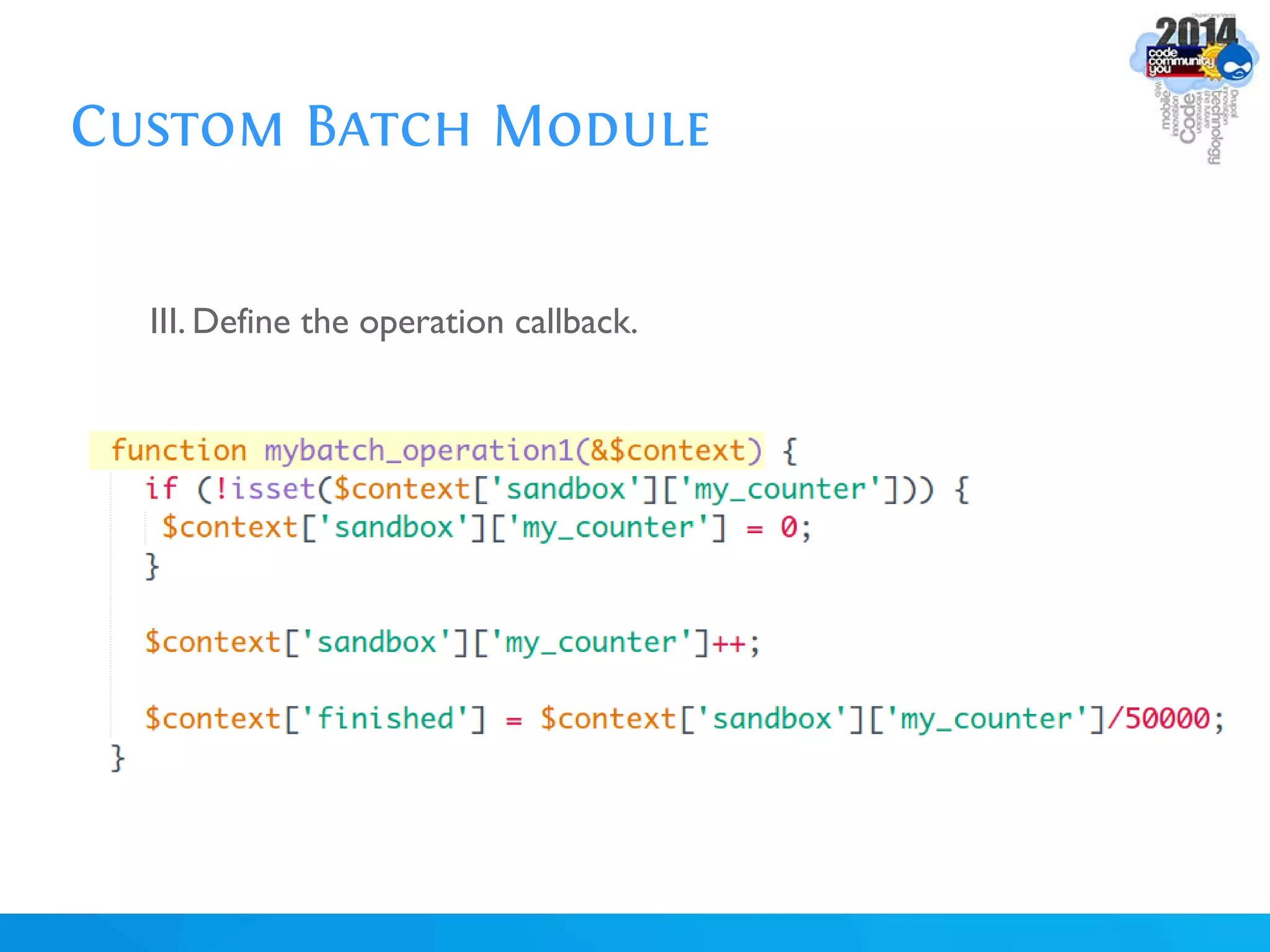
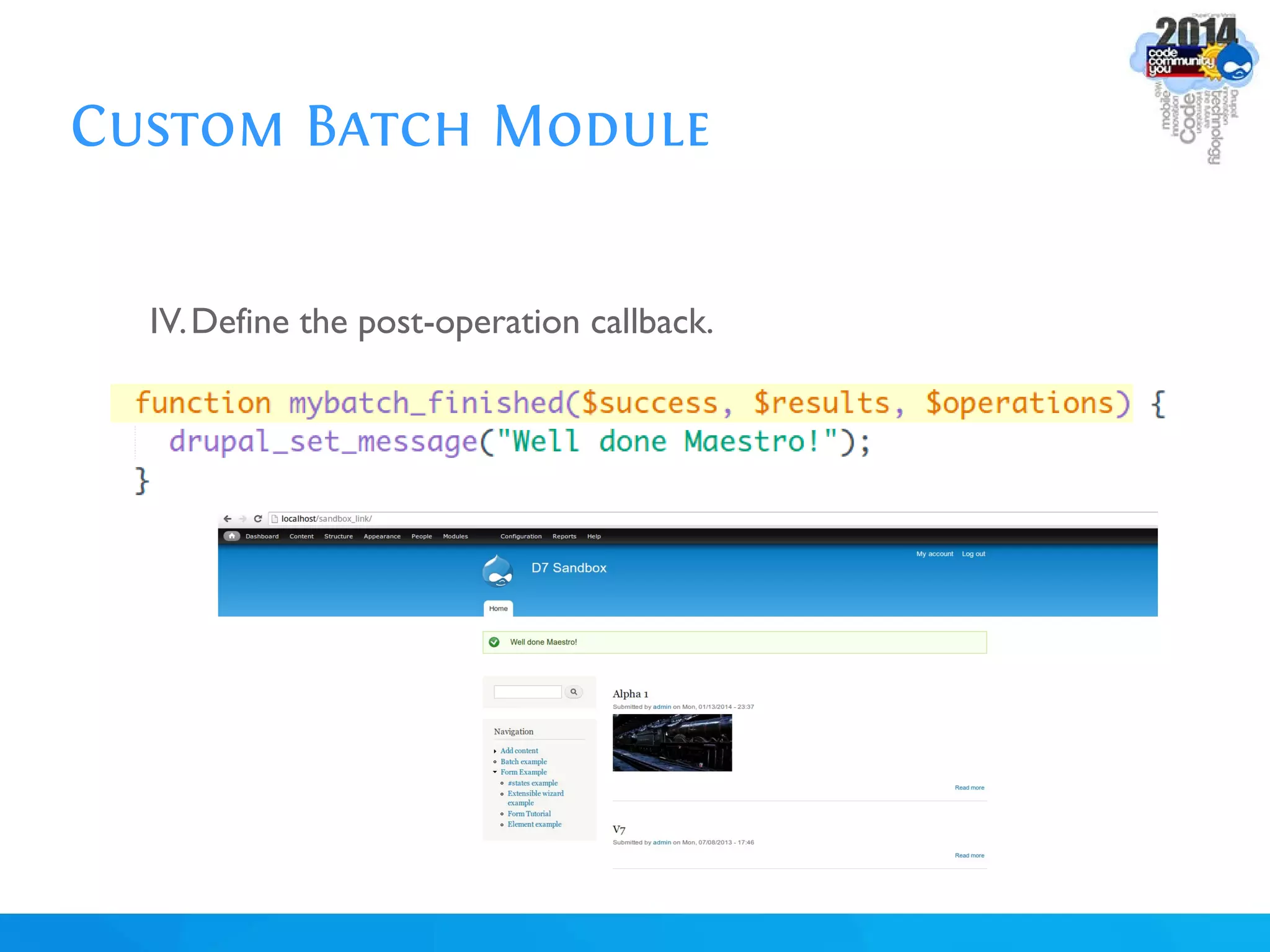
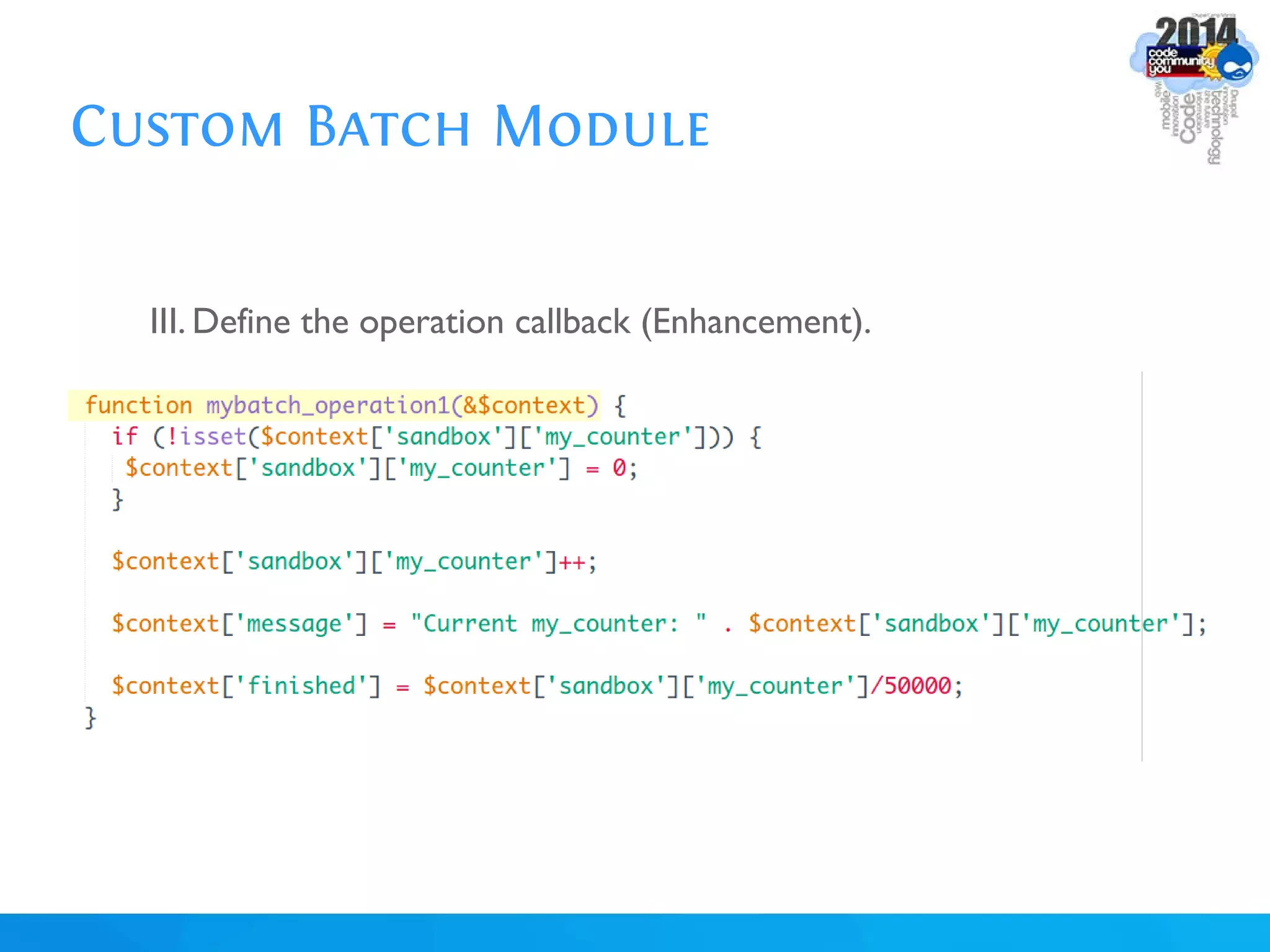
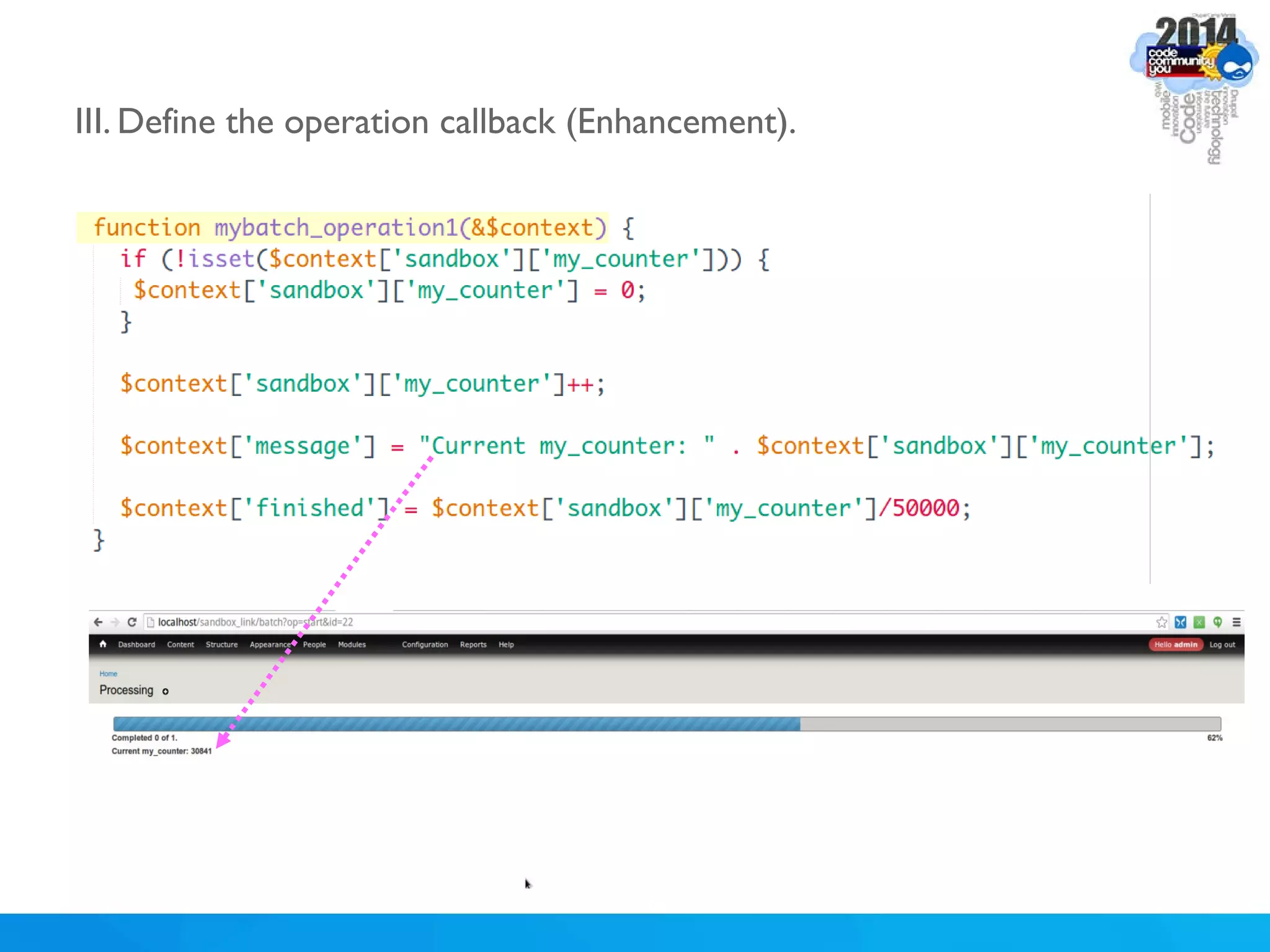
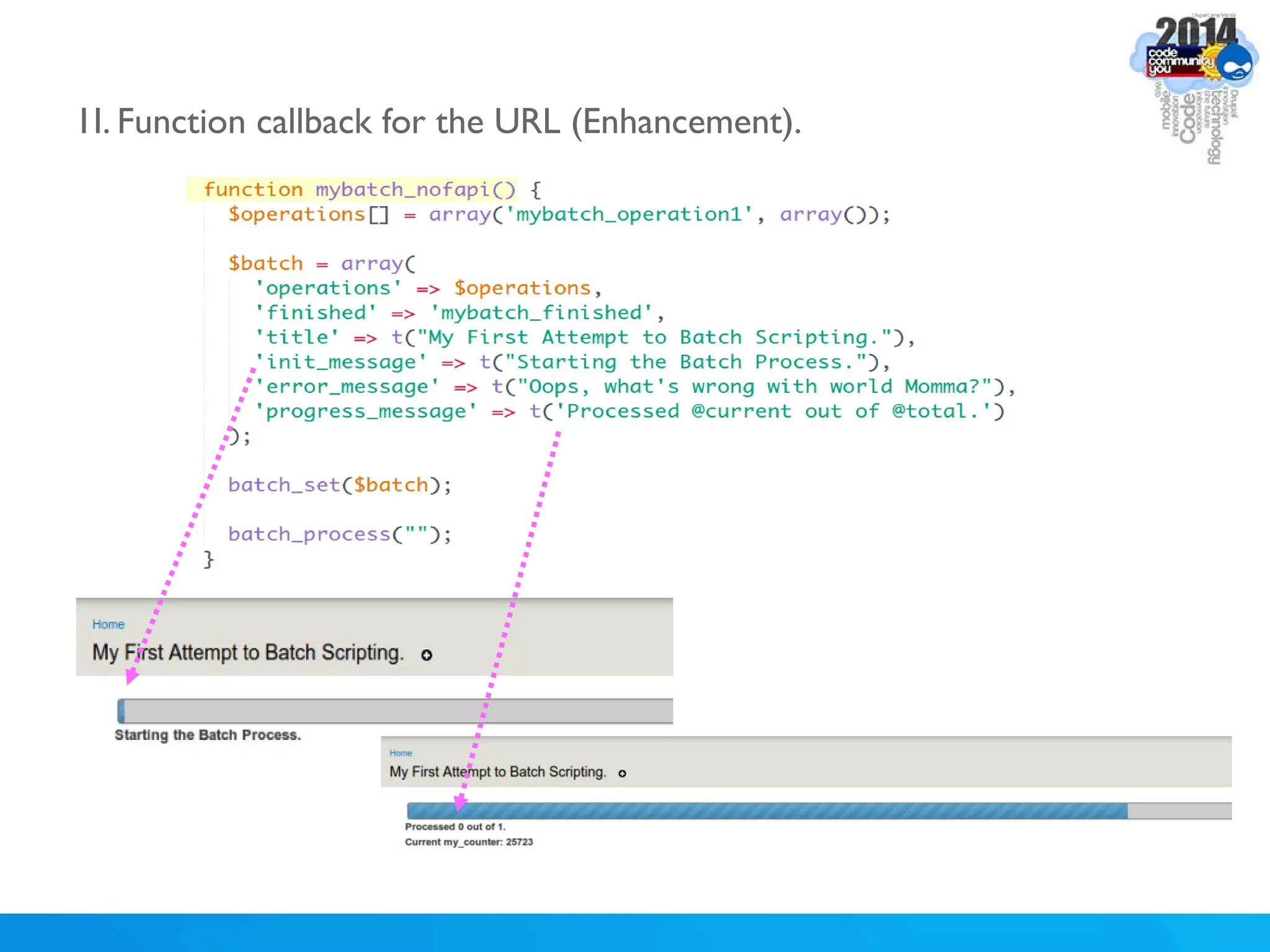
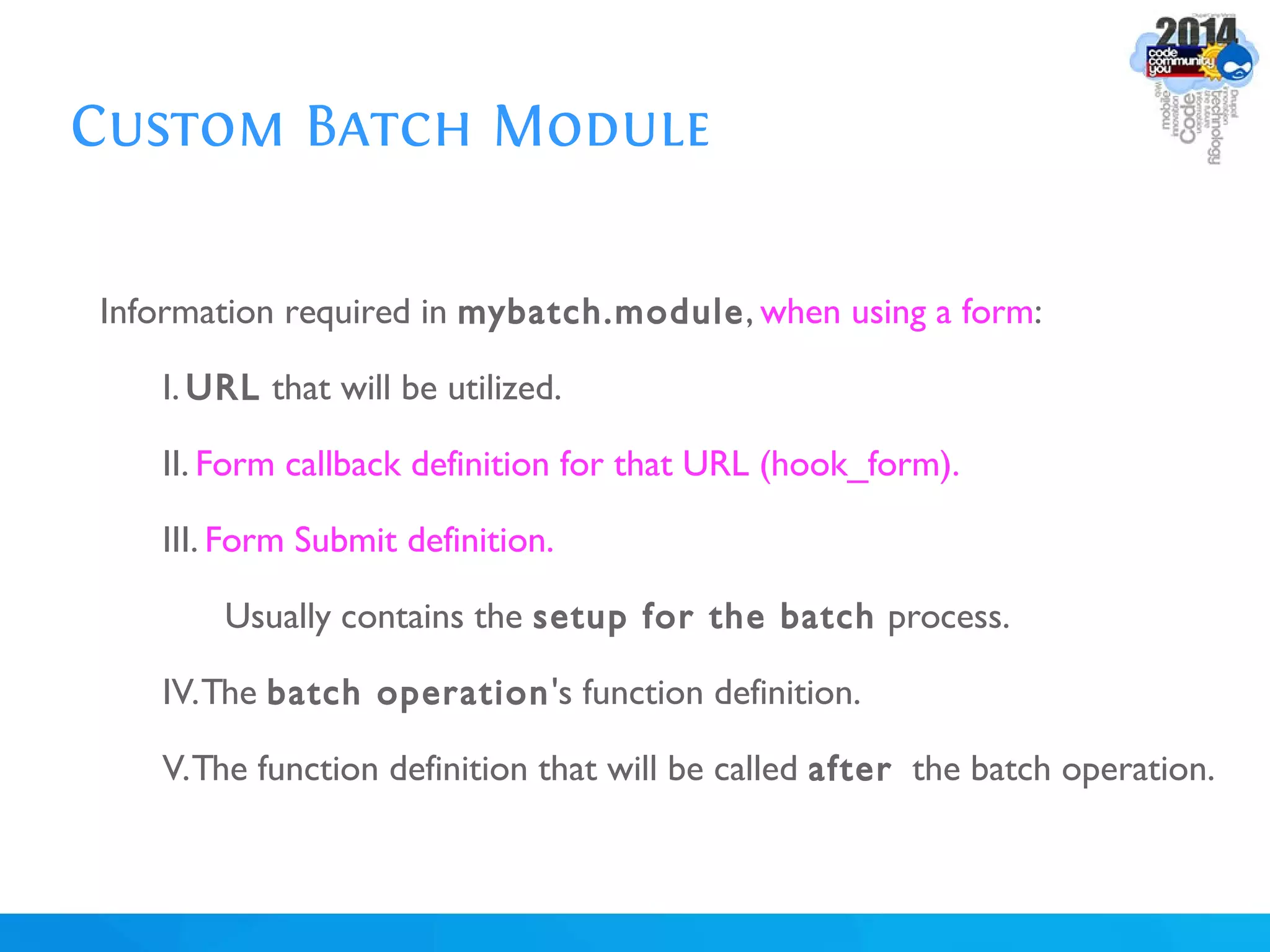
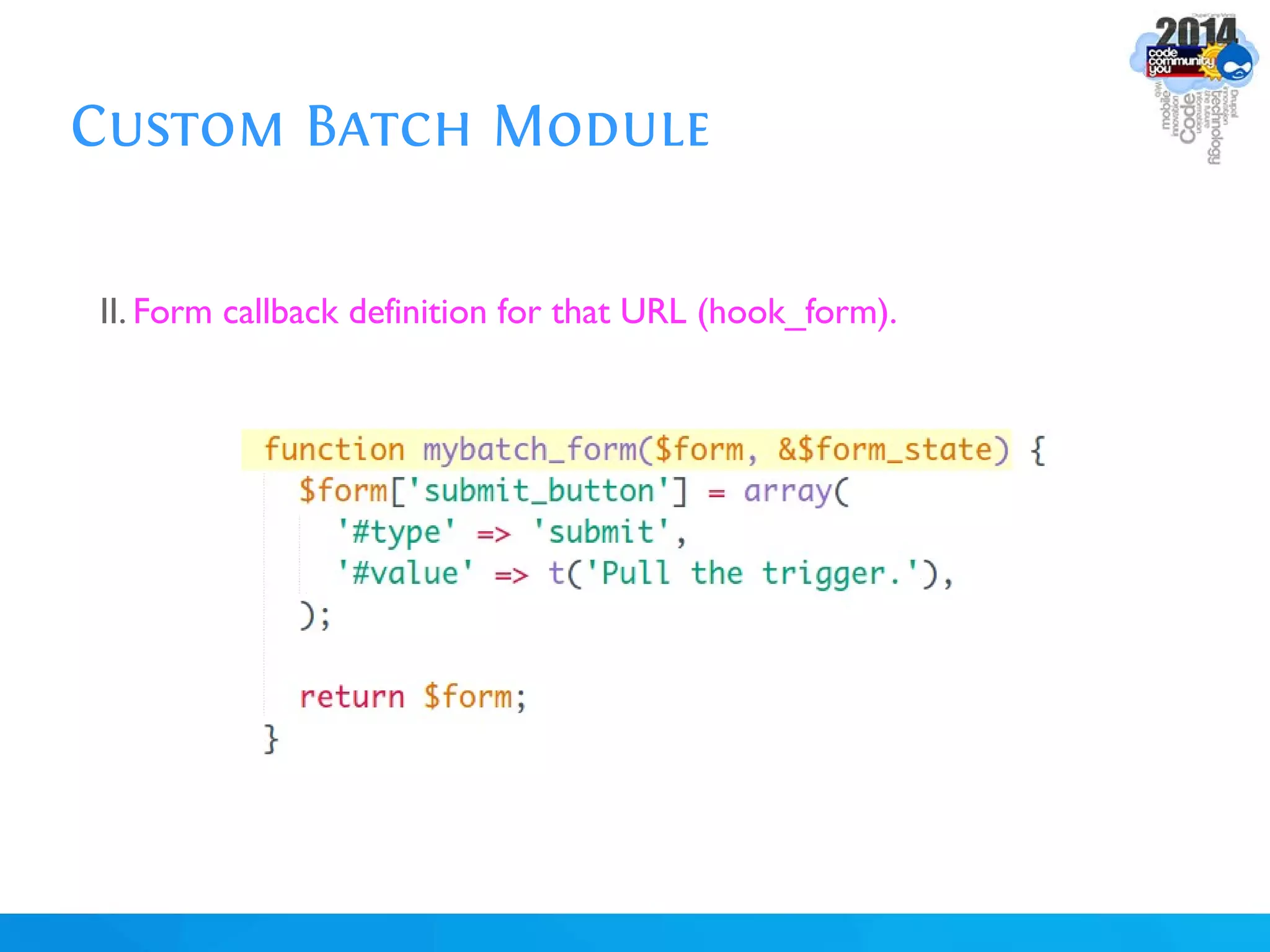
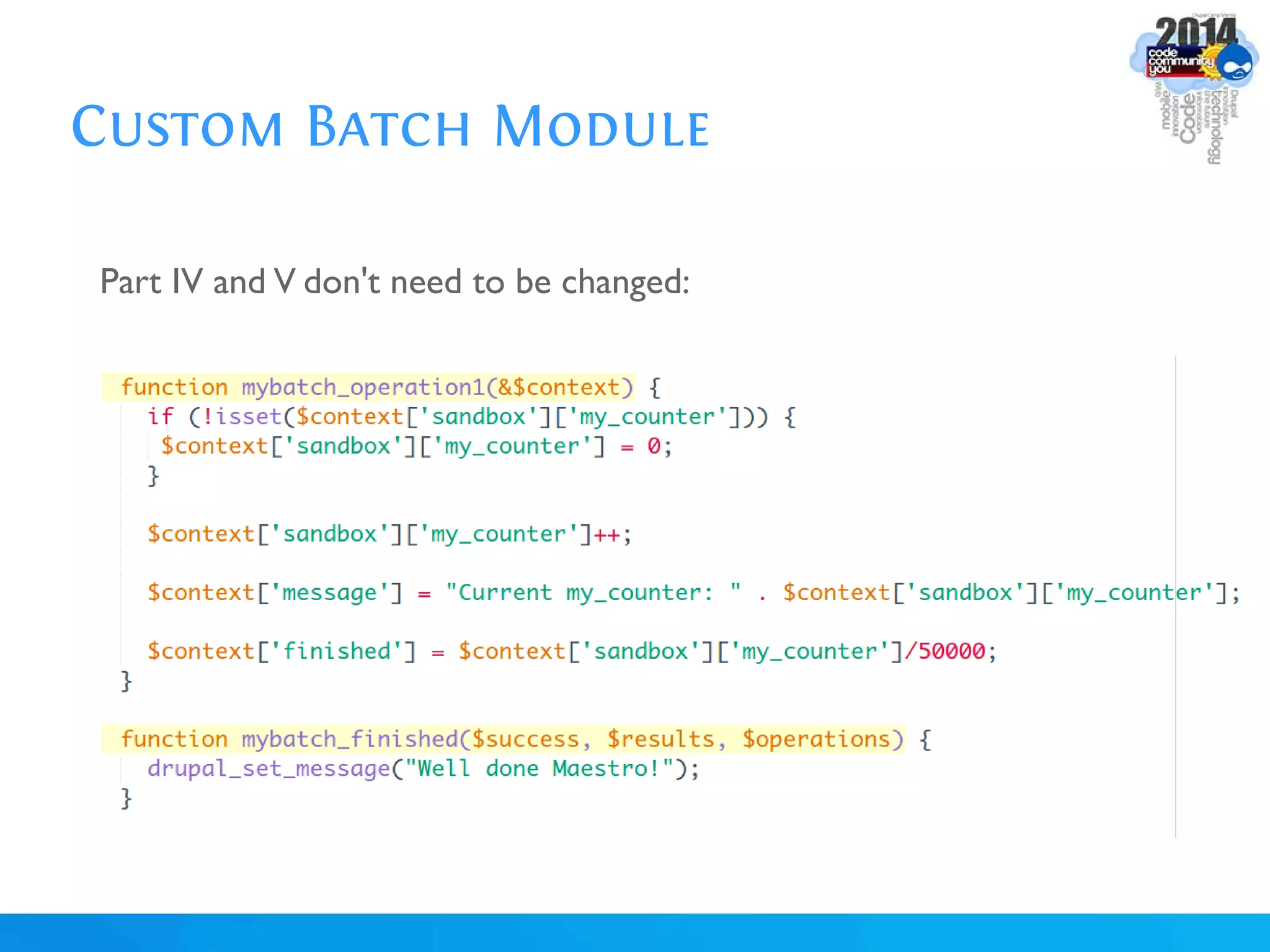
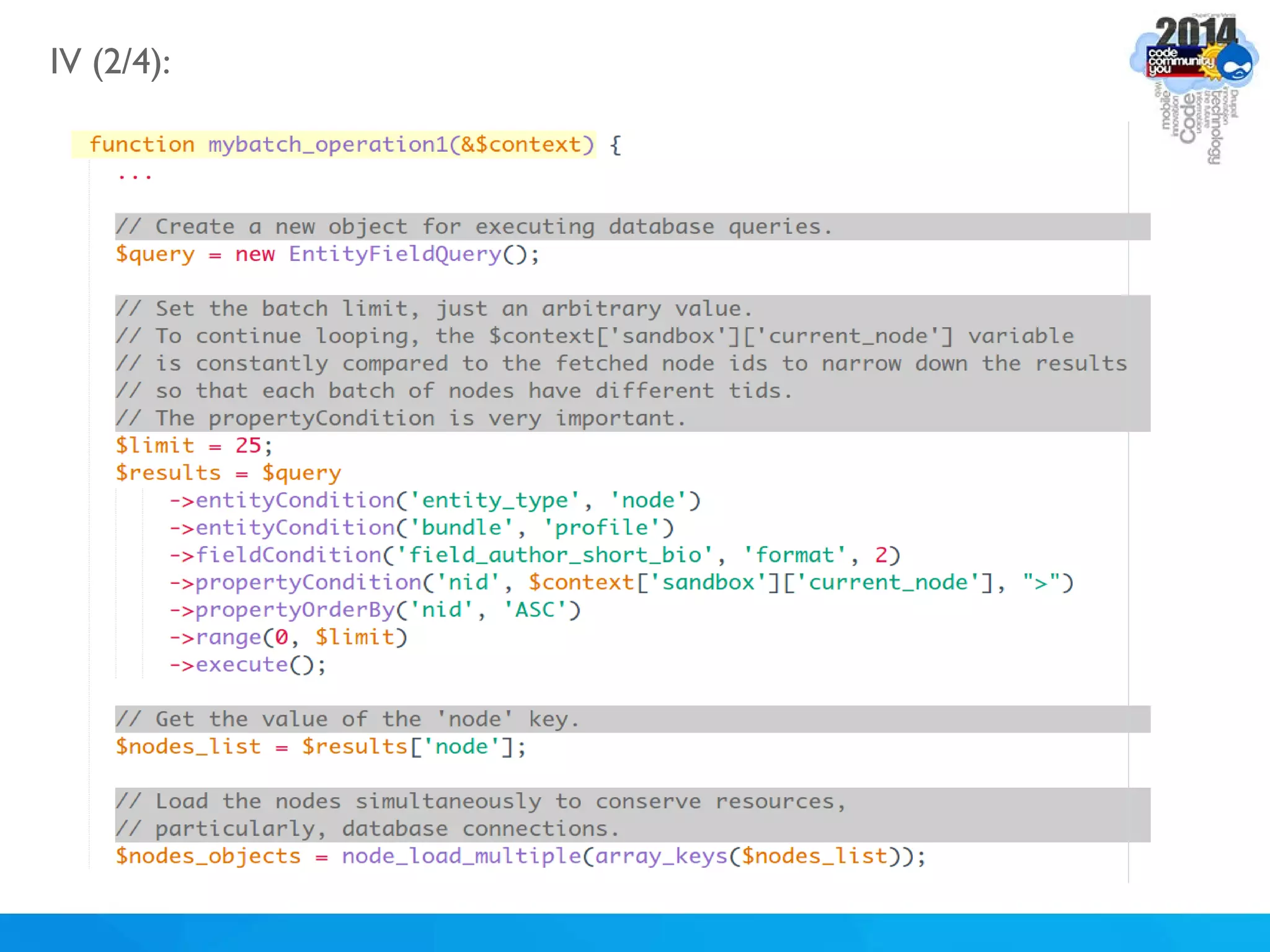
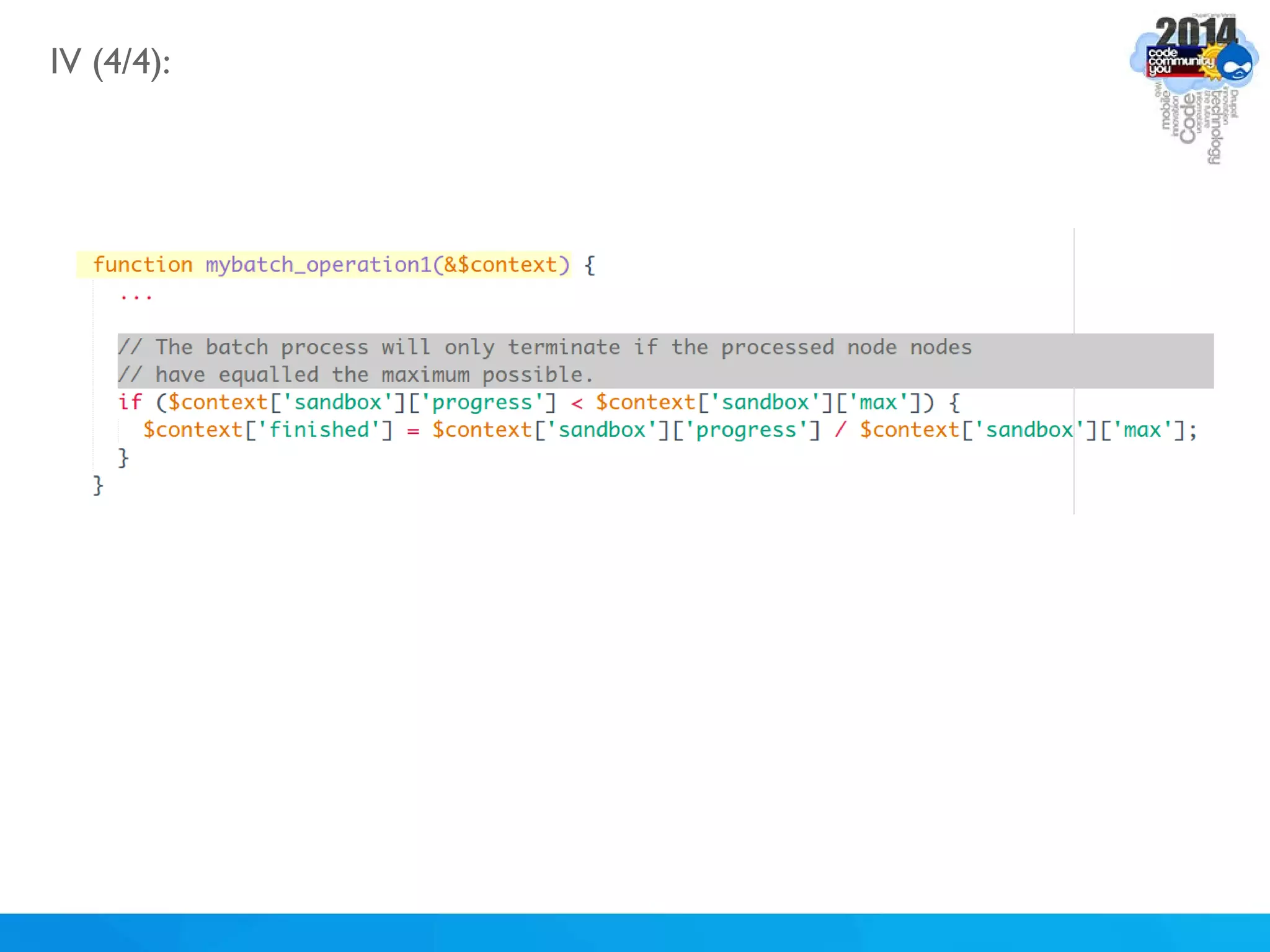
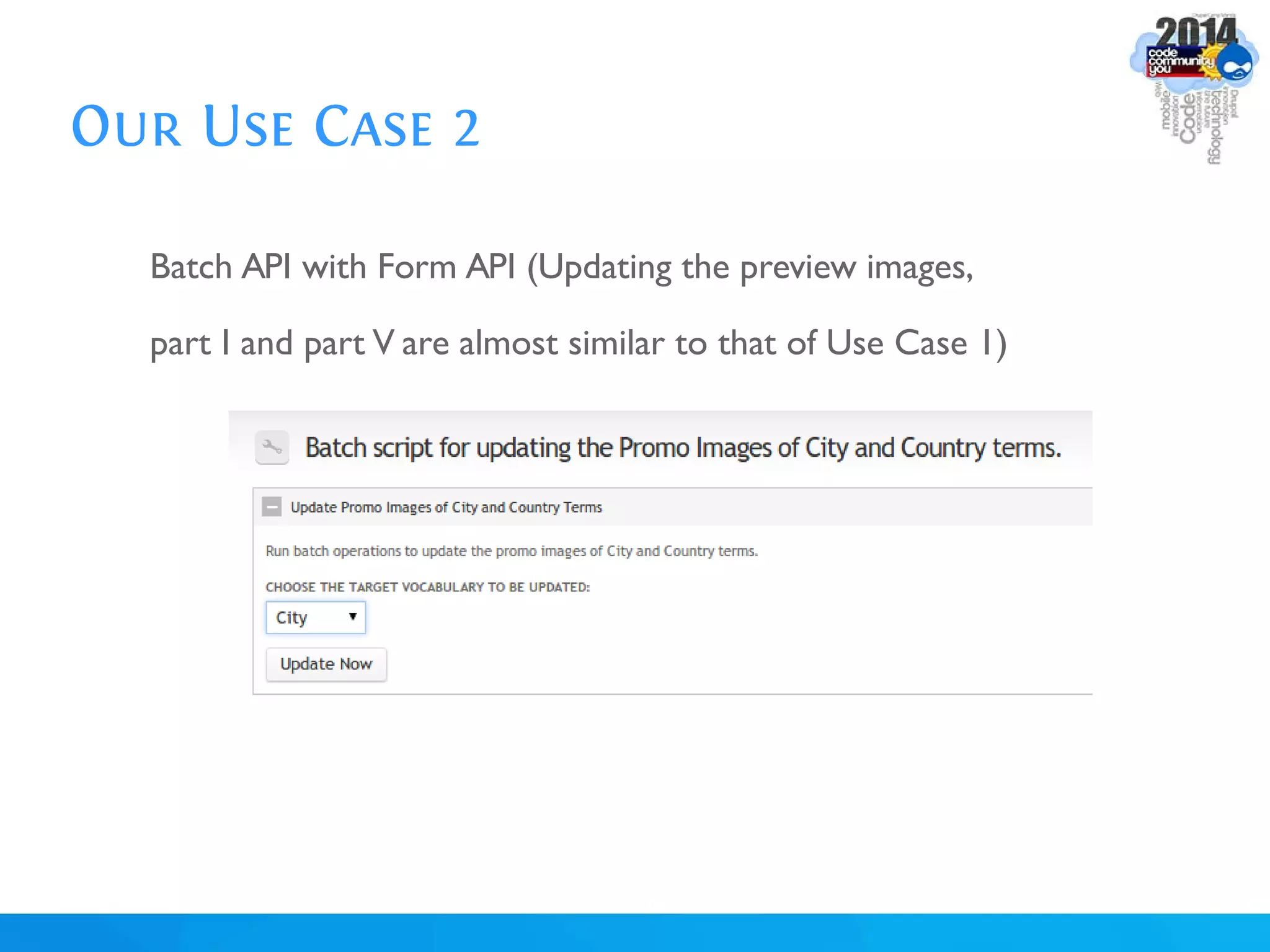
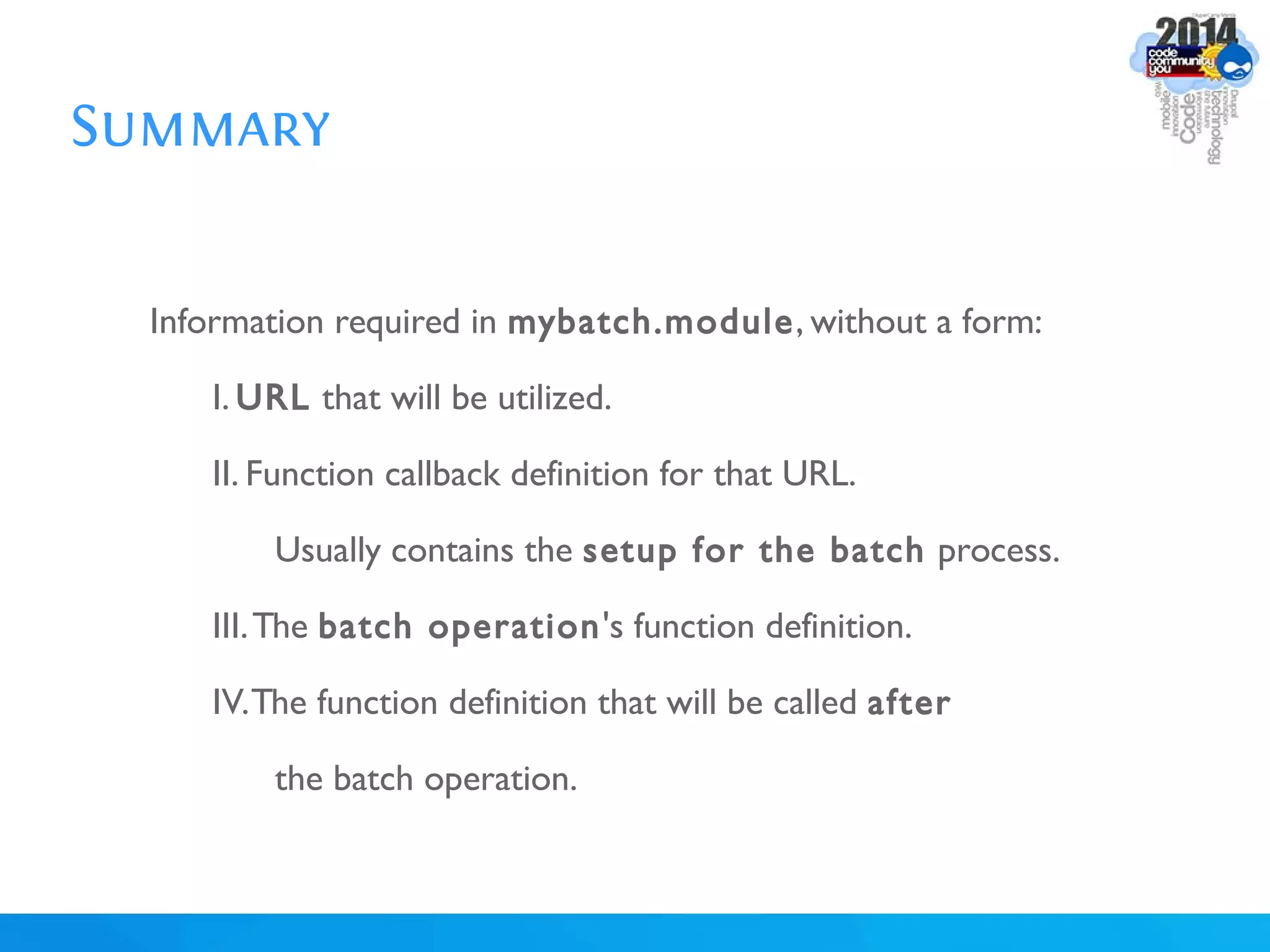
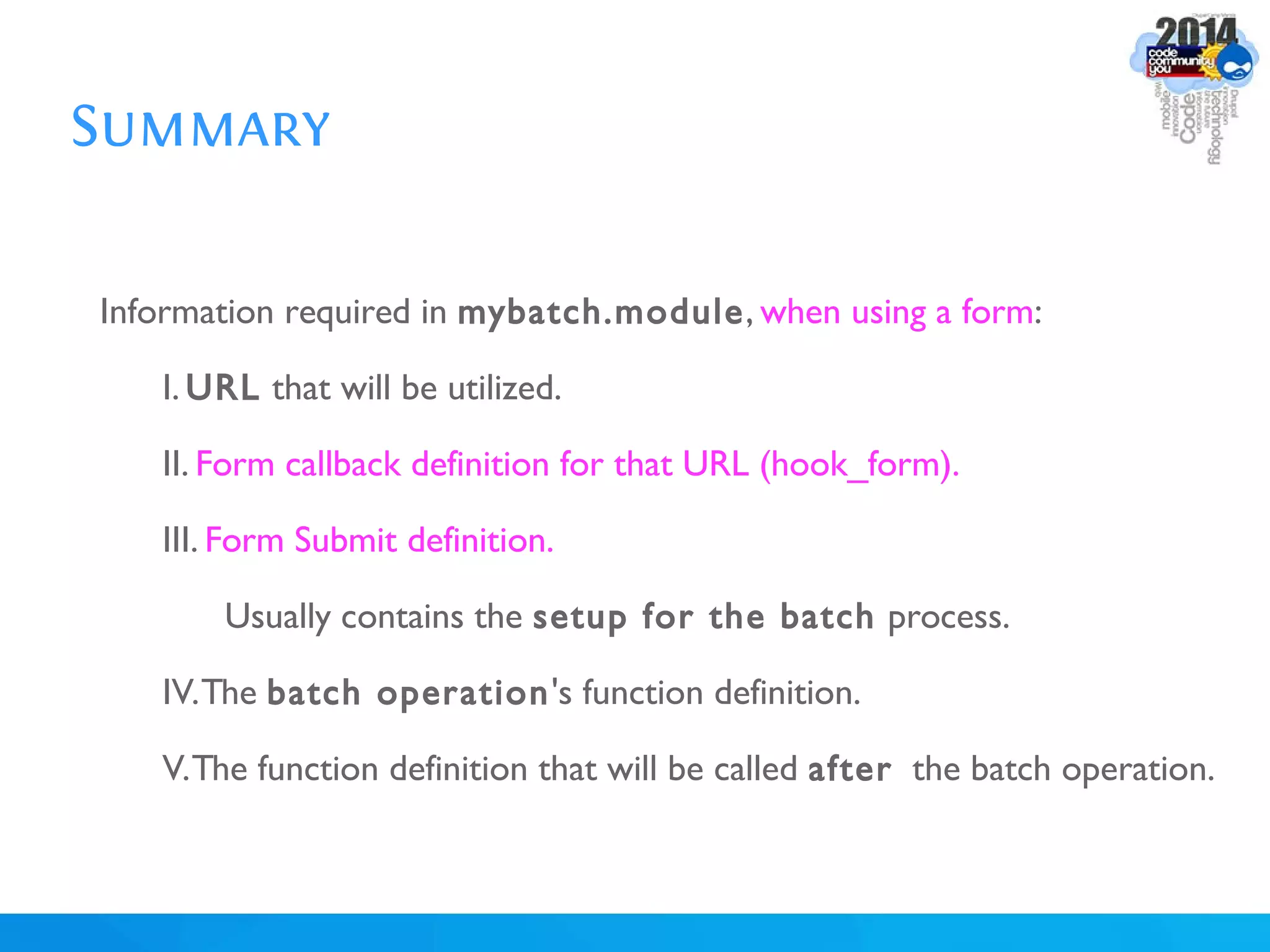
The document discusses using batch scripting with Drupal and the EntityFieldQuery API. It explains why batch processing is useful, such as avoiding PHP timeouts and integrating with installation profiles. The EntityFieldQuery API allows querying entity properties and fields across entity types in a database-agnostic way. The document also provides details on implementing a custom batch module, including using the Form and Batch APIs, and defining callbacks. Two use cases are presented: updating user profile field formats in batches, and setting preview images for taxonomy terms. The summary recommends links for additional resources on batch processing and the EntityFieldQuery API.