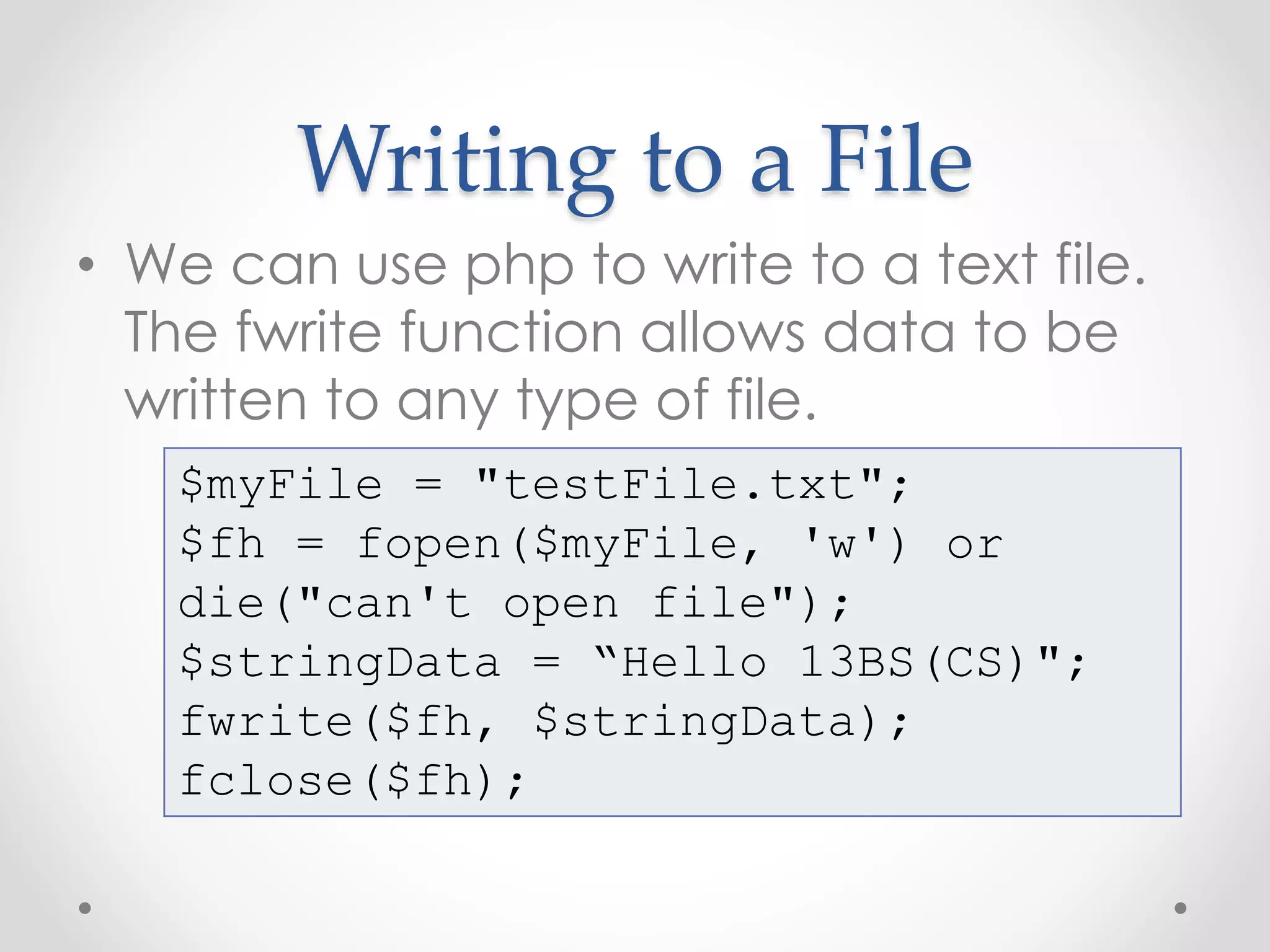
This document discusses file manipulation using PHP. It covers creating, opening, reading from, writing to, appending to, and removing files. The key functions covered are fopen() for opening files, fgets() for reading single lines, fwrite() for writing data, and unlink() for removing files. Modes like read, write, and append are discussed for manipulating files in different ways.