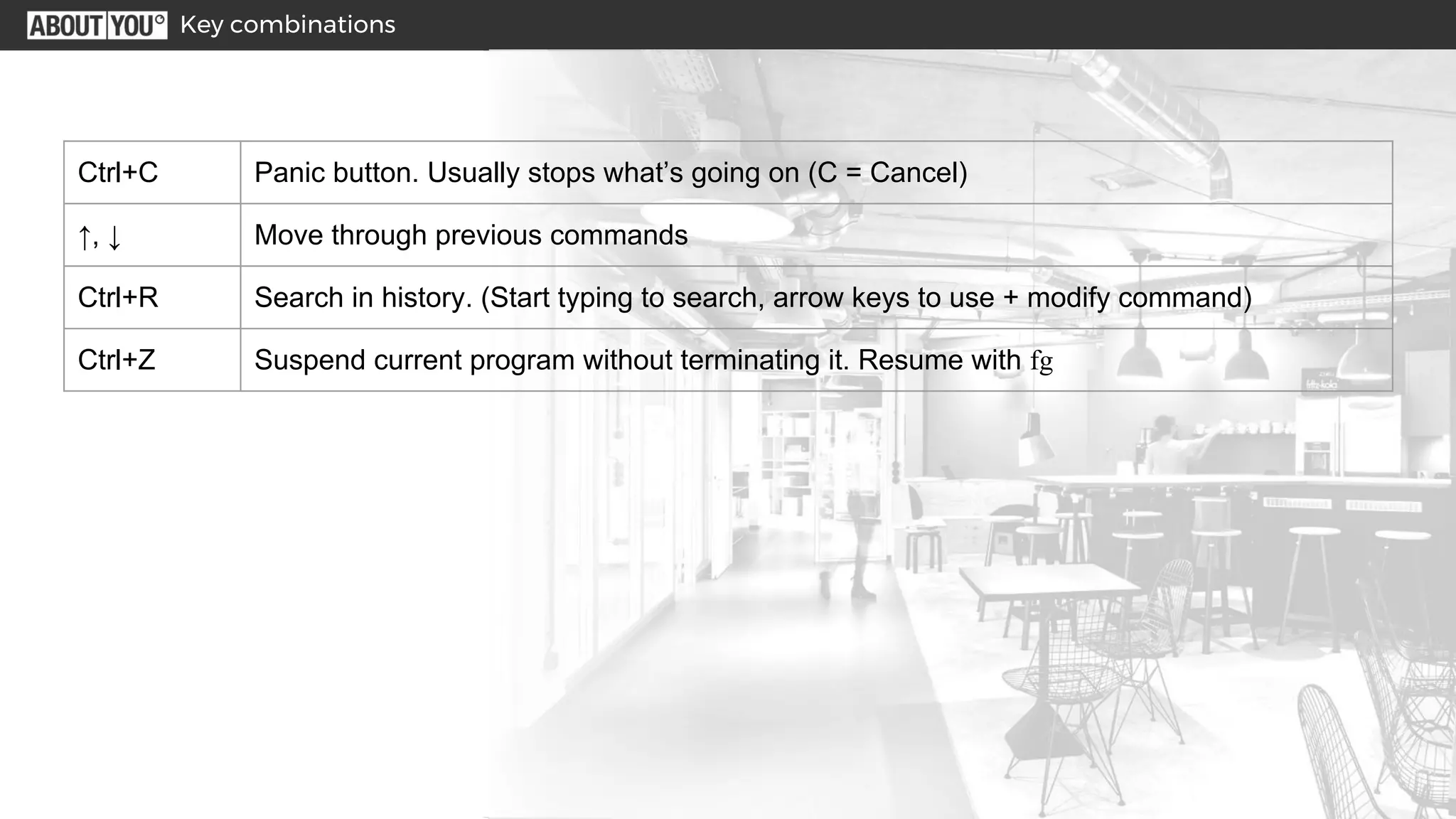
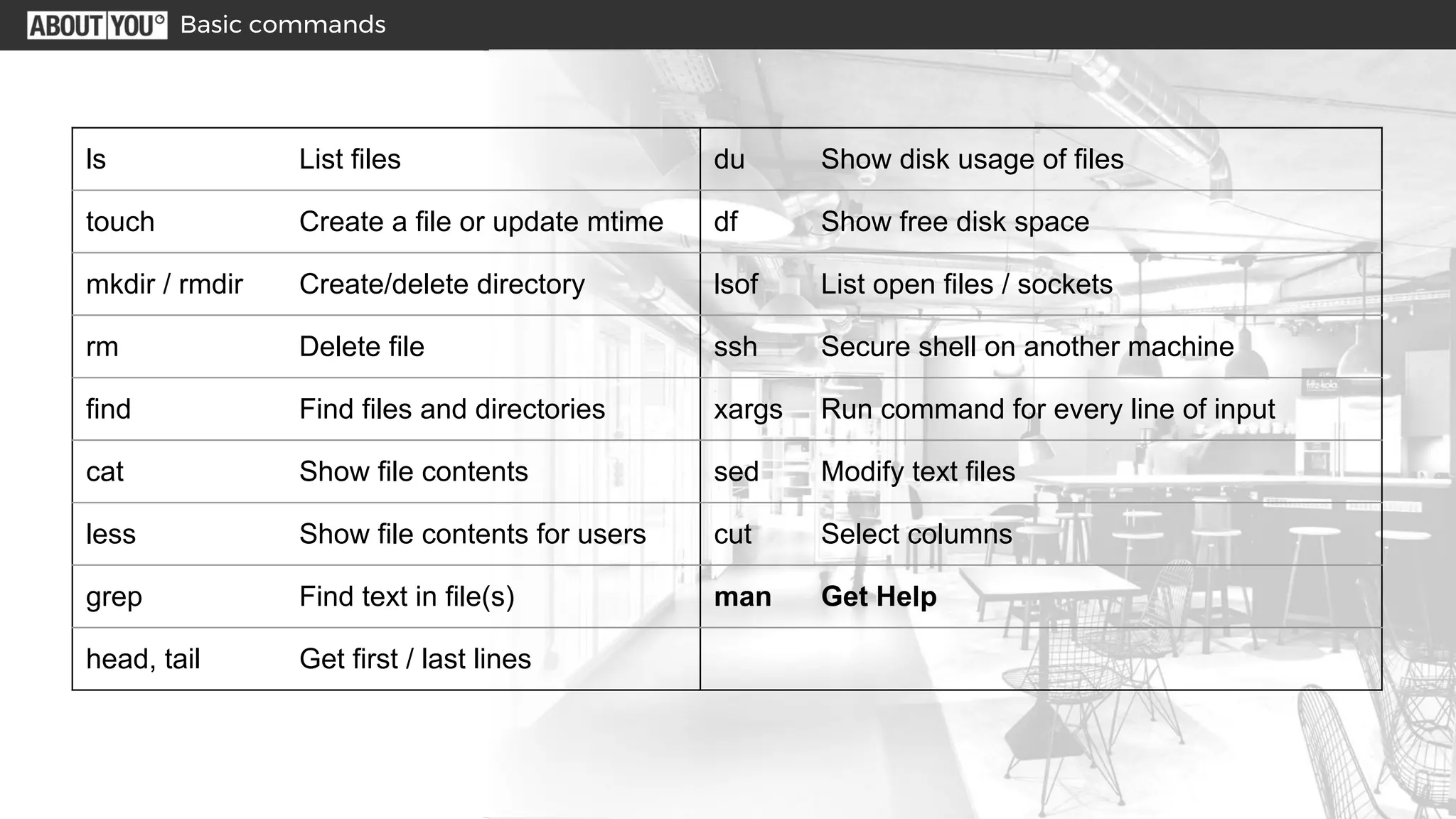
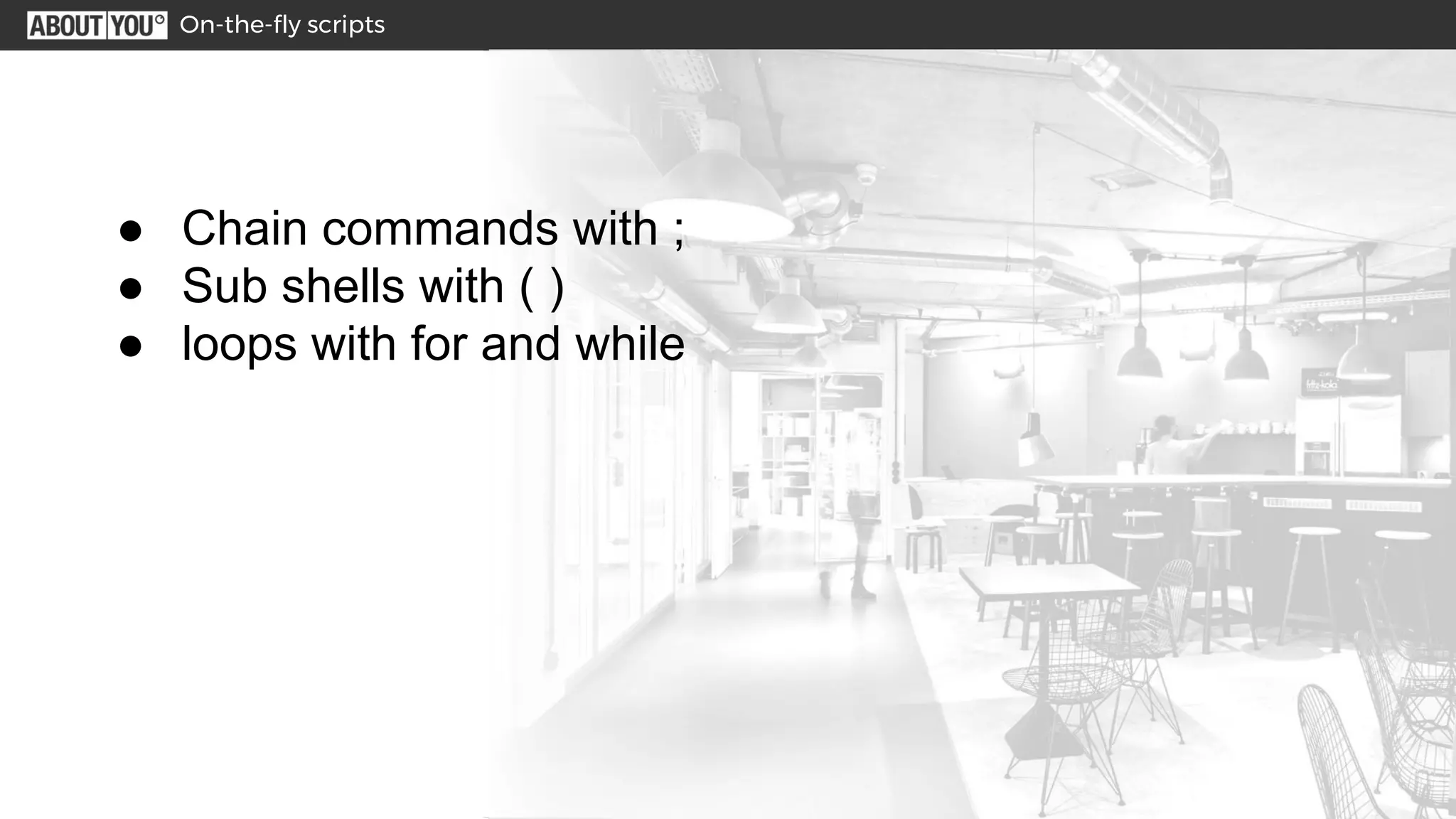
The document outlines various Linux shell tricks and commands, including useful key combinations, basic commands for file management and system information, special shell expressions using wildcards and braces, pipes and redirects to connect commands, examples of on-the-fly scripts using semicolons and parentheses, a vim survival guide for basic text editing, and ways to customize the shell. It also provides hands-on examples of processing log files to count HTTP status codes and find customer IDs that were denied refunds.