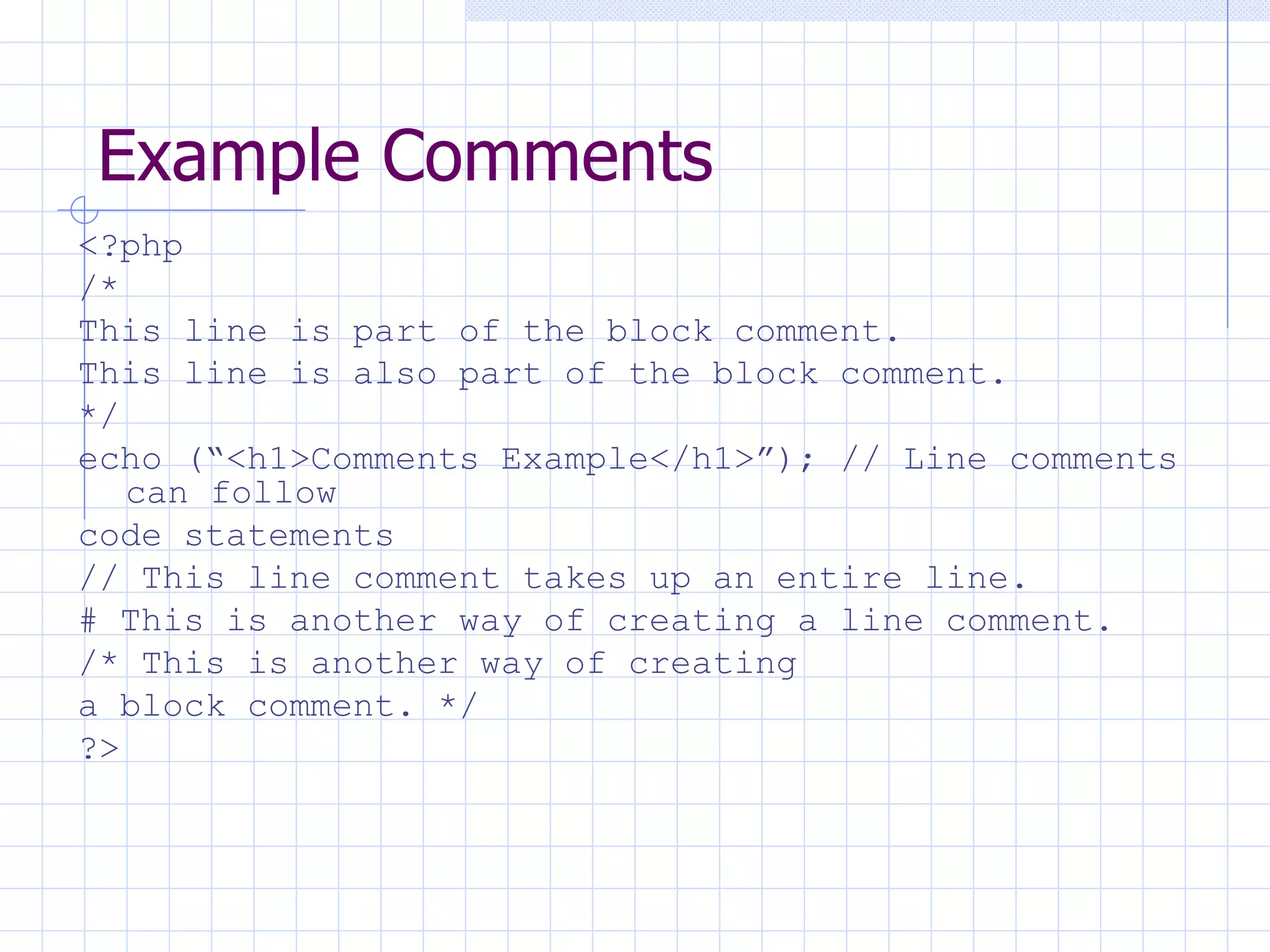
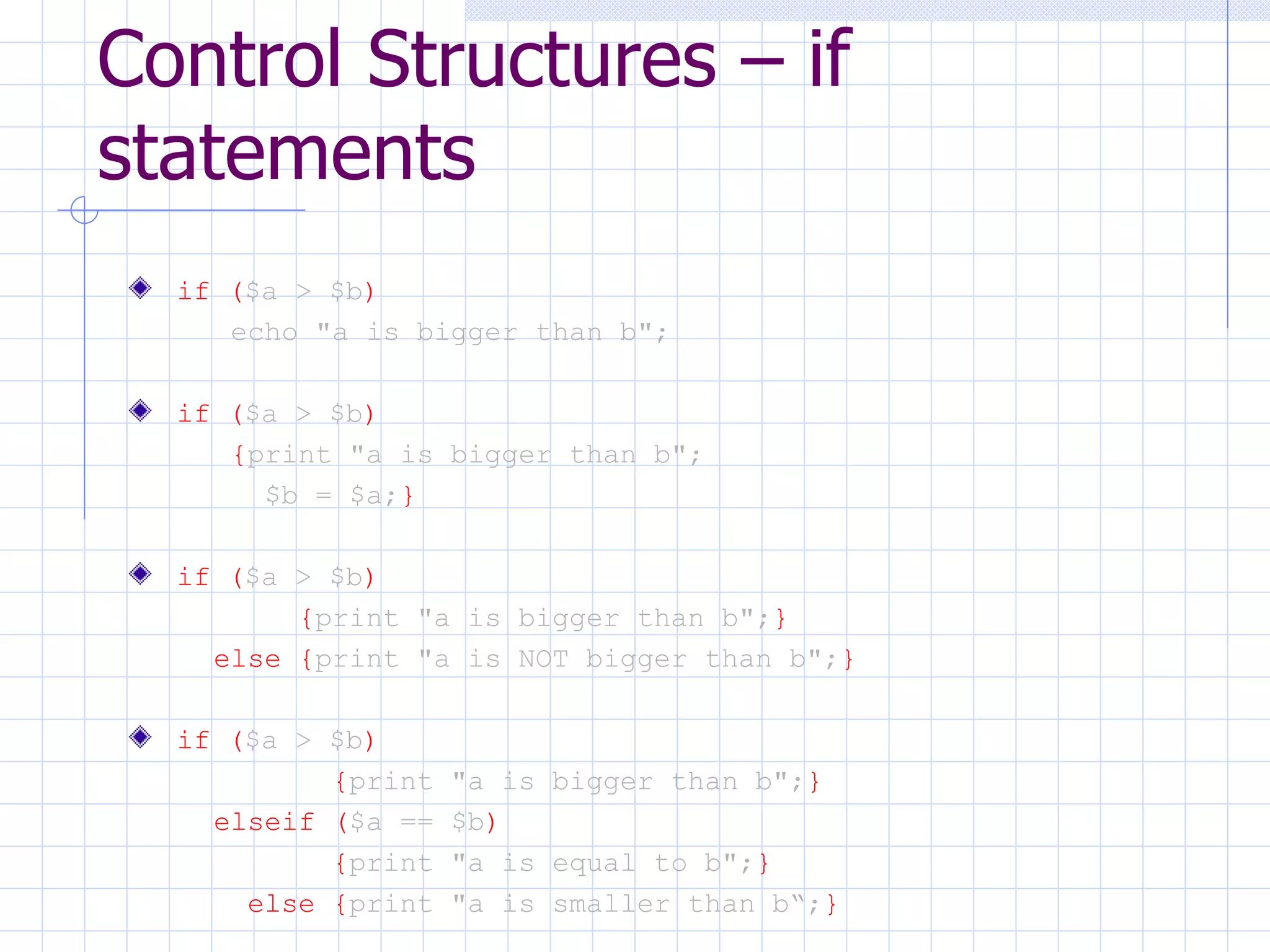
The document discusses various control structures in PHP including if/else statements, loops (while, do/while, for, foreach), and jumping in and out of PHP mode. It provides examples of how to use each control structure and also discusses adding comments to PHP scripts.






![A FORM and its handler in one <html> <head> <title>Application Handler</title> </head> <body> <?php if (! $_POST["surname"] or !$_POST["address"]){ ?> <form method="post" action="<?php echo $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'];?>"> <p>Your surname: <input type="text" name="surname"></p> <p>Your address: <input type="text" name="address"></p> <input button type="submit" value= "Please send me the brochure."> </form> <?php } else{ $sn = $_REQUEST['surname']; echo "<p>Thank you, $sn.</p>"; $addr = $_REQUEST['address']; echo "<p> We will write to you at $addr .</p>"; } ?> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/control-structures-in-php2-1233508083629550-3/75/Control-Structures-In-Php-2-9-2048.jpg)