PHP and MySQL are open-source languages that allow for the creation of dynamic web pages; PHP is a server-side scripting language that is often used with MySQL to access and manipulate databases. The document provides an overview of PHP and how it can be used to connect to MySQL databases, retrieve and display data, handle forms, and write scripts with variables, functions, and control structures.
![PHP and MySQL Prepared By: Md. Sirajus Salayhin Assistant Programmer Nanosoft Email: [email_address] Web: http://nanoit.biz](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysqlsalayhin-110801023449-phpapp01/75/PHP-MySQL-1-2048.jpg)



![Array Arrays can be created with integers or strings as keys. <?php $arr = array("UK" => "London", 12 => 56); echo $arr["UK"]; // London echo $arr[12]; // 56 ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysqlsalayhin-110801023449-phpapp01/75/PHP-MySQL-8-2048.jpg)

![String Functions There are a lot of string functions in PHP that you can use. For example: int strlen(string str) string strtoupper(string str) string strtolower(string str) int strcmp(string str1, string str2) int strcasecmp(string str1, string str2) string strstr(string src, string target) int strpos(string src, string target [, int offset]) You can find them in the PHP manual: http://www.php.net/manual/en/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysqlsalayhin-110801023449-phpapp01/75/PHP-MySQL-12-2048.jpg)


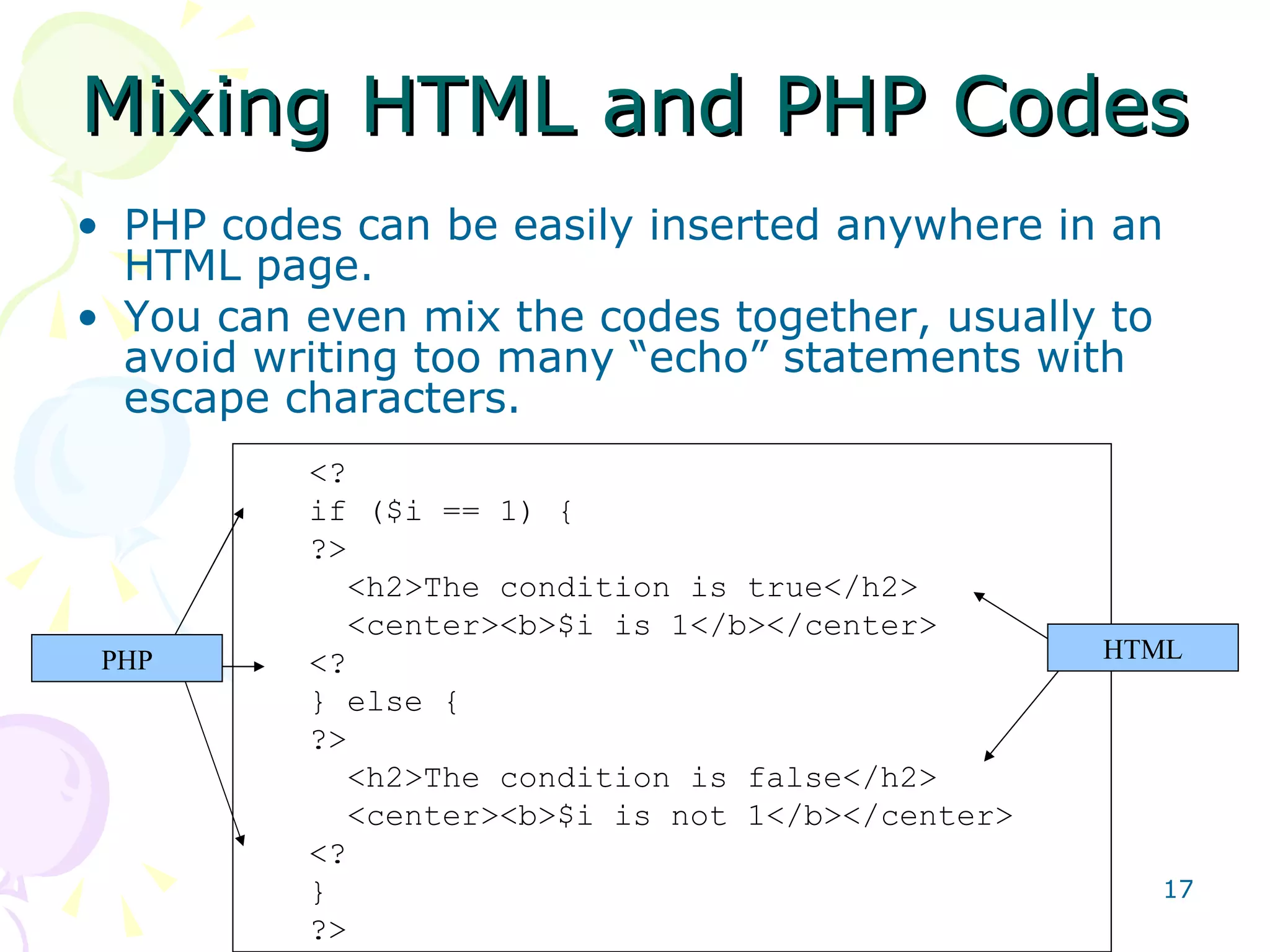

![Working with HTML Forms You can easily get the variables submitted by an HTML form using the following (assume the form input is called “name”: $_POST['name'] // post method $_GET['name'] // get method $name /* easier, but Register Globals must be set to ON in PHP config */](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysqlsalayhin-110801023449-phpapp01/75/PHP-MySQL-19-2048.jpg)
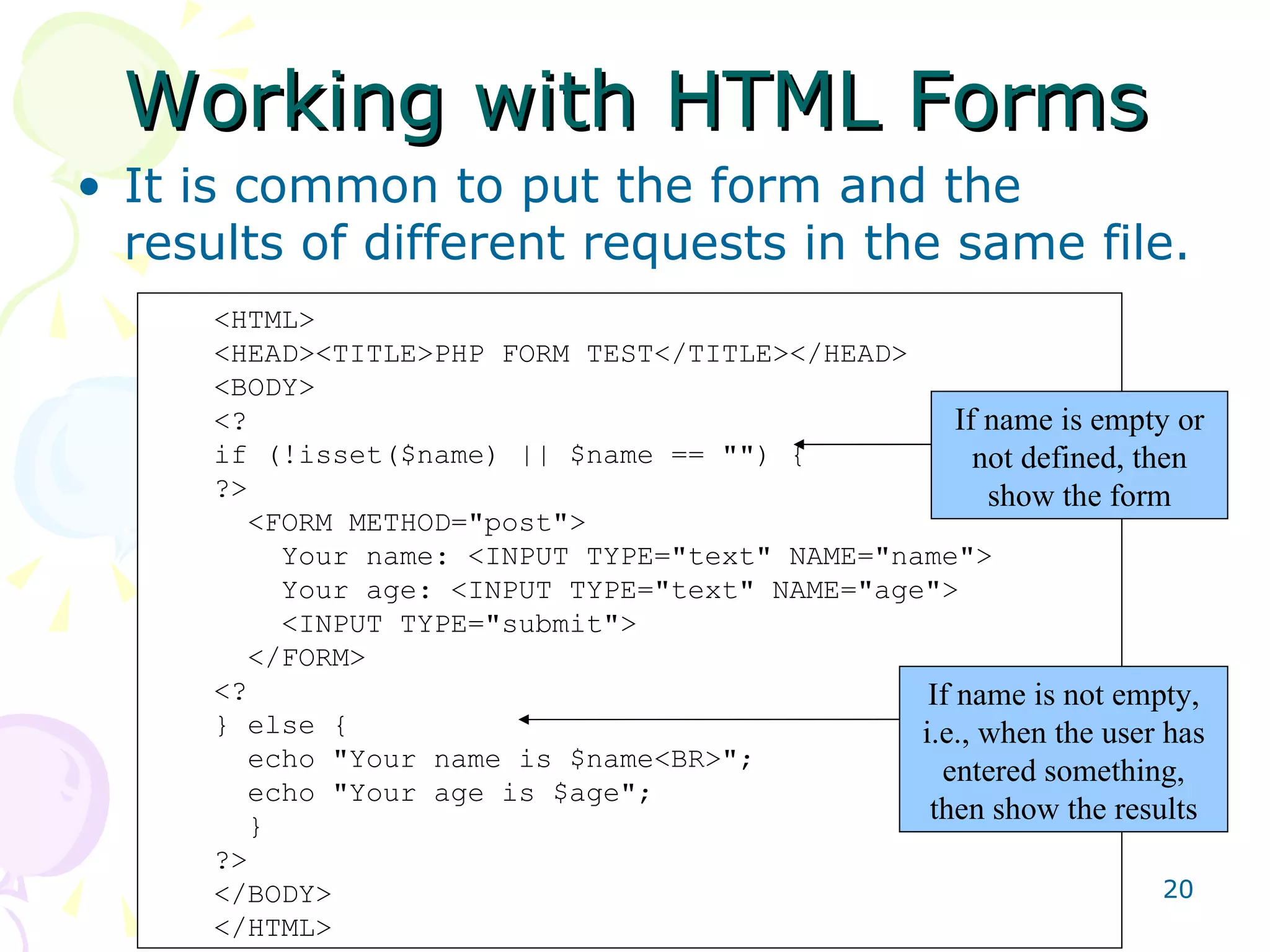

![Useful PHP Functions for MySQL mysql_connect(host, username [,password]); Connects to a MySQL server on the specified host using the given username and/or password. Returns a MySQL link identifier on success, or FALSE on failure. mysql_select_db(db_name [,resource]) Selects a database from the database server.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysqlsalayhin-110801023449-phpapp01/75/PHP-MySQL-23-2048.jpg)
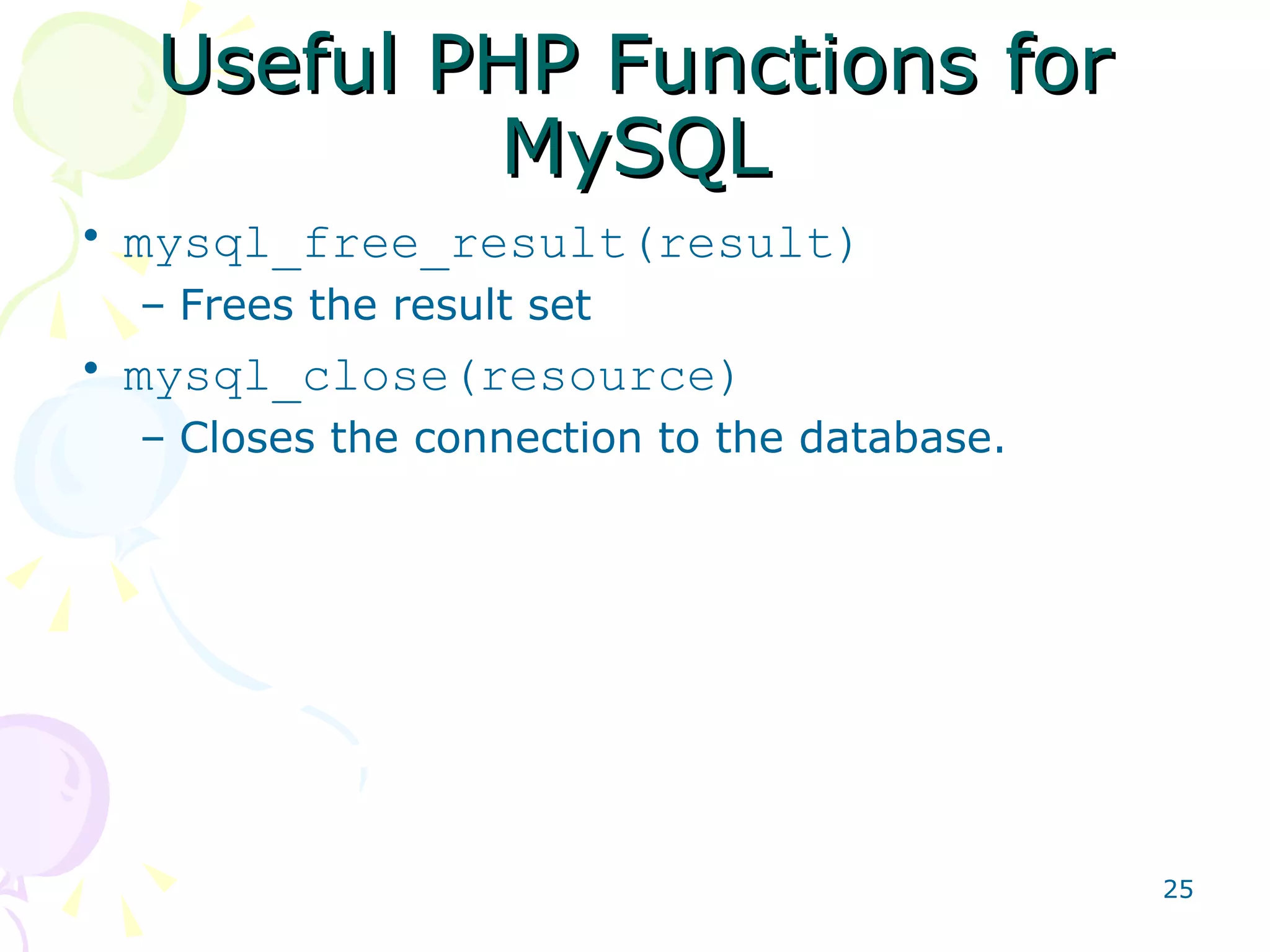
![Useful PHP Functions for MySQL mysql_query(SQL, resource); Sends the specified SQL query to the database specified by the resource identifier. The retrieved data are returned by the function as a MySQL result set. mysql_result(result, row [,field]); Returns the contents of one cell from a MySQL result set. The field argument can be the field name or the field’s offset. mysql_fetch_array(result [,result_type]) Fetch a result row as an associative array, a numeric array, or both. The result type can take the constants MYSQL_ASSOC, MYSQL_NUM, and MYSQL_BOTH.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpmysqlsalayhin-110801023449-phpapp01/75/PHP-MySQL-24-2048.jpg)