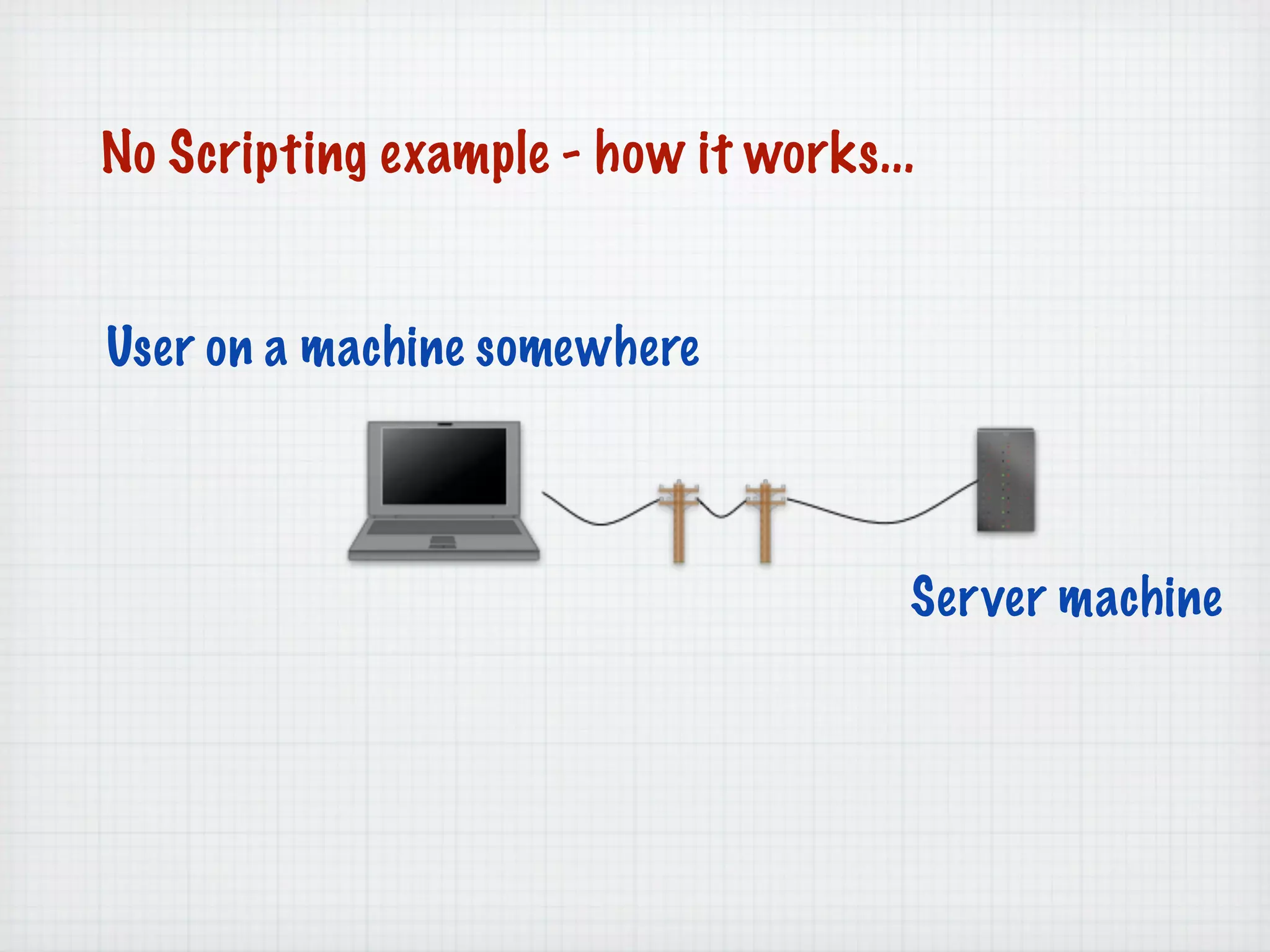
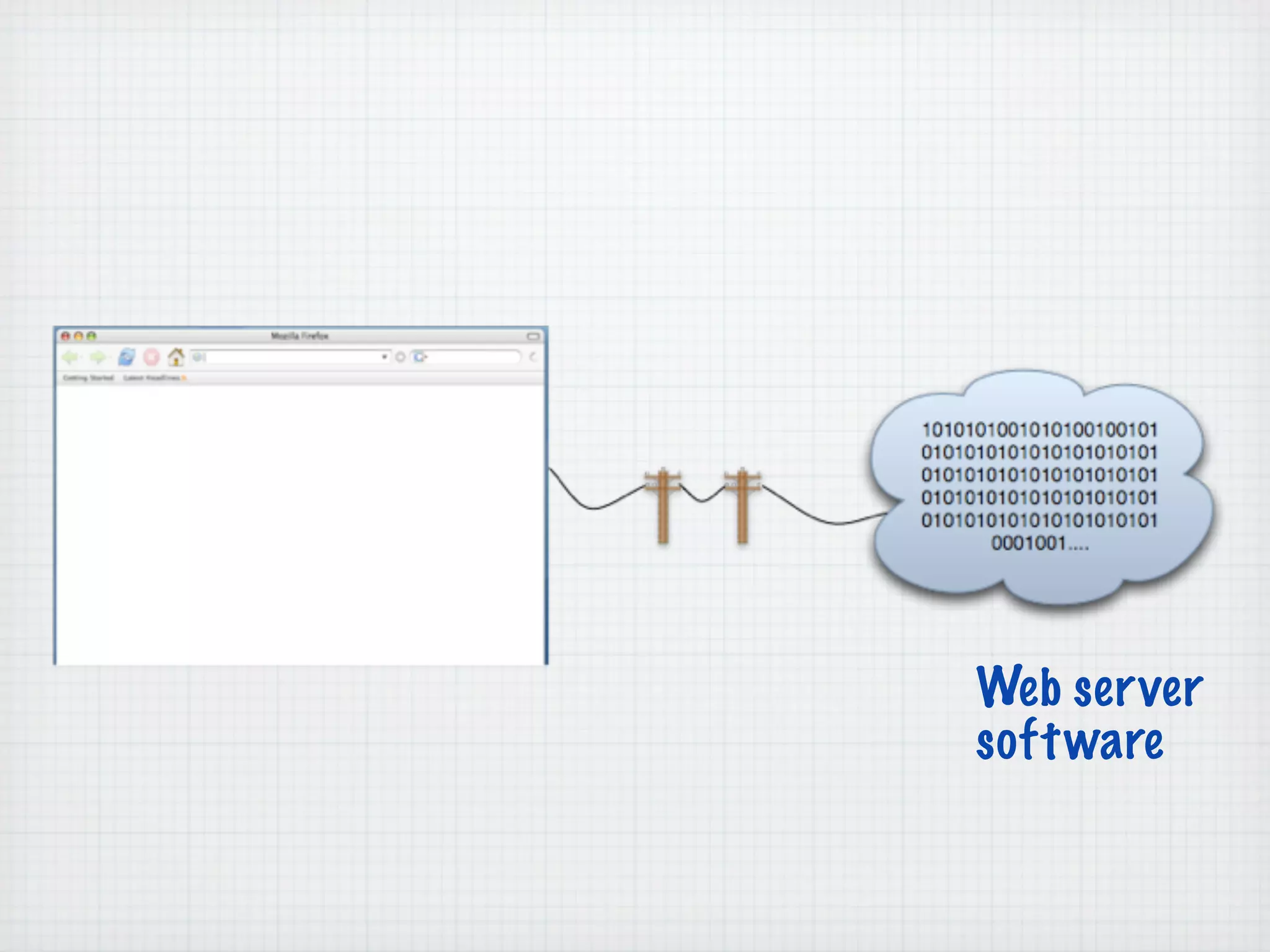
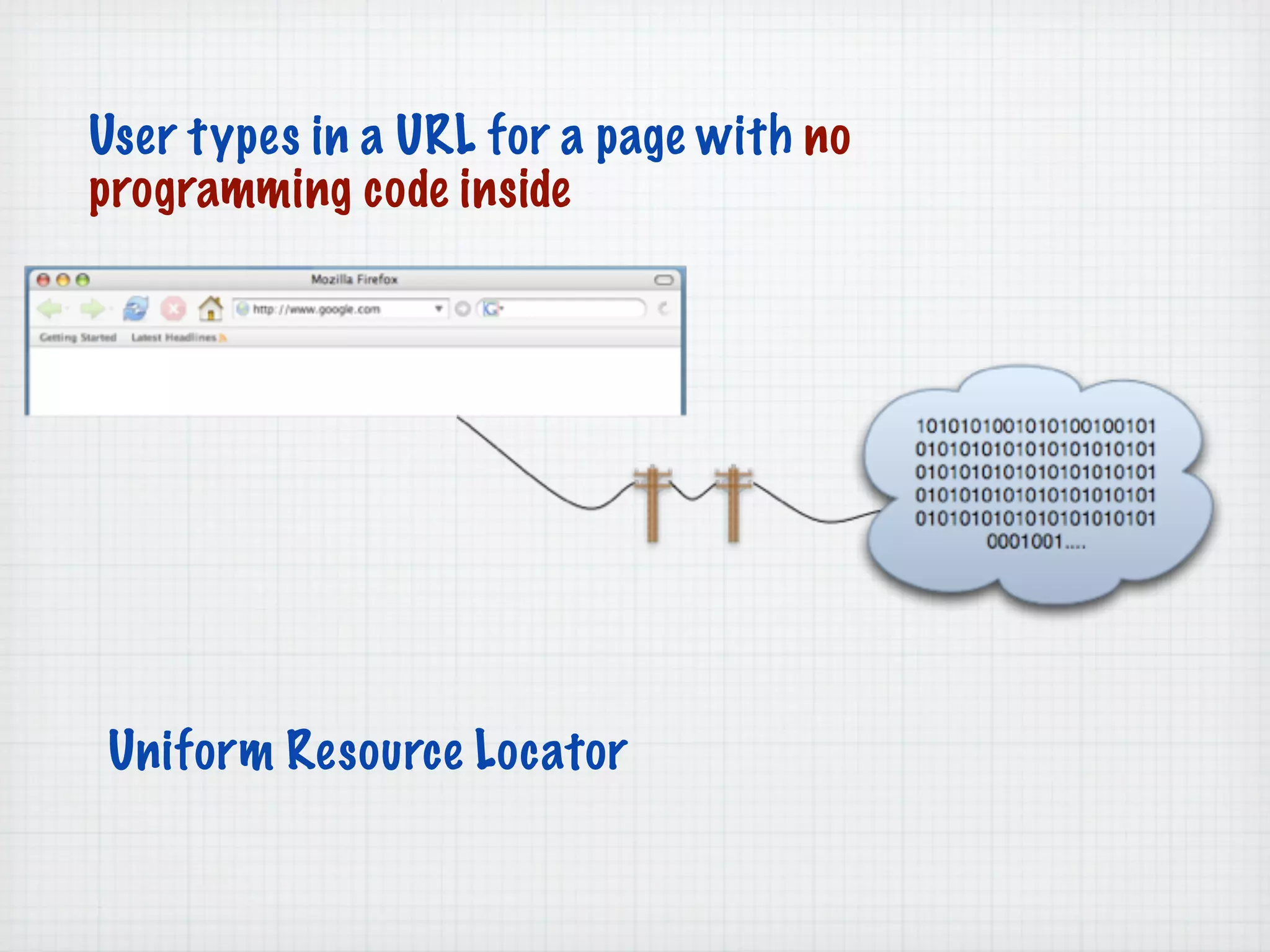
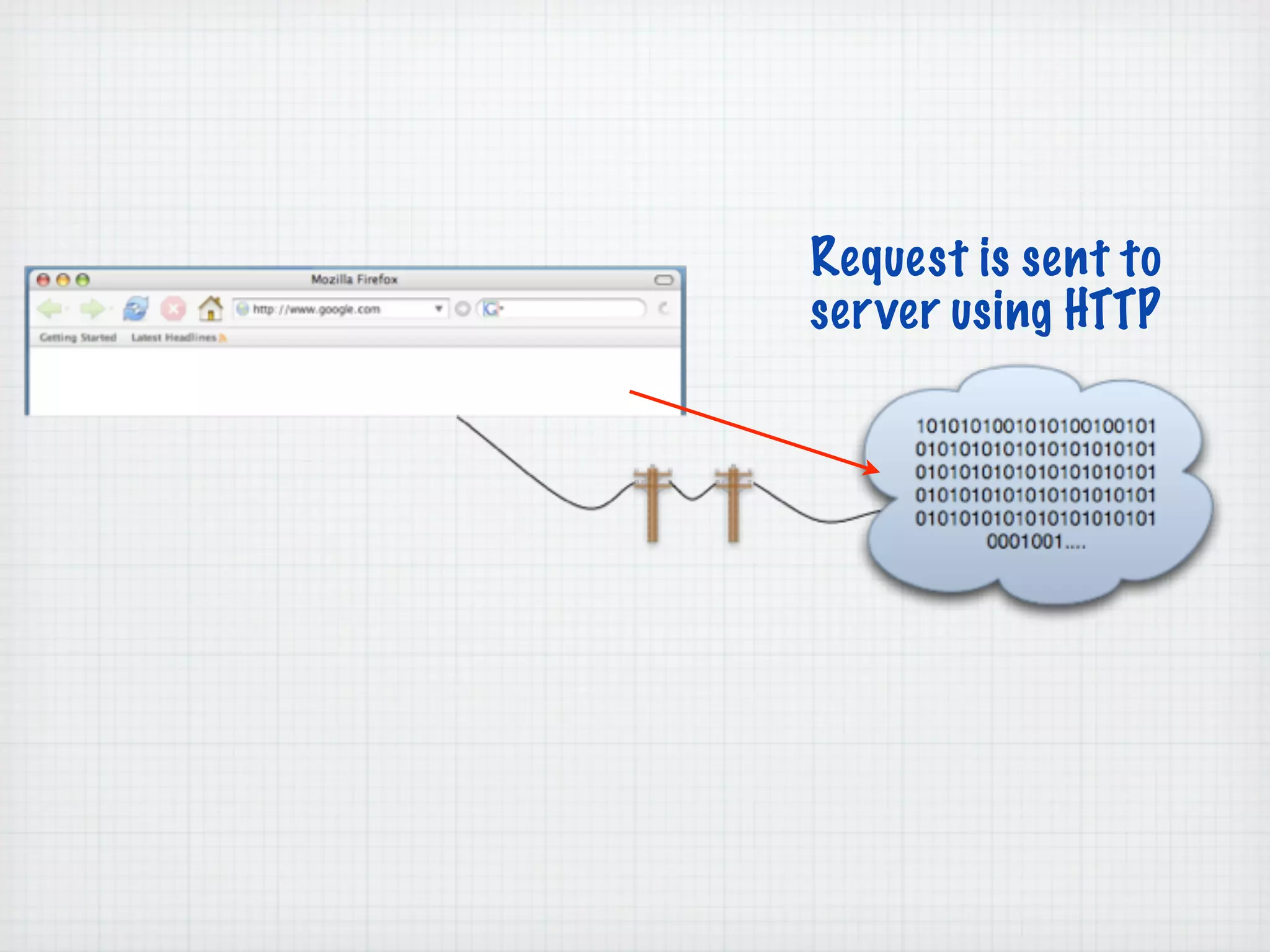
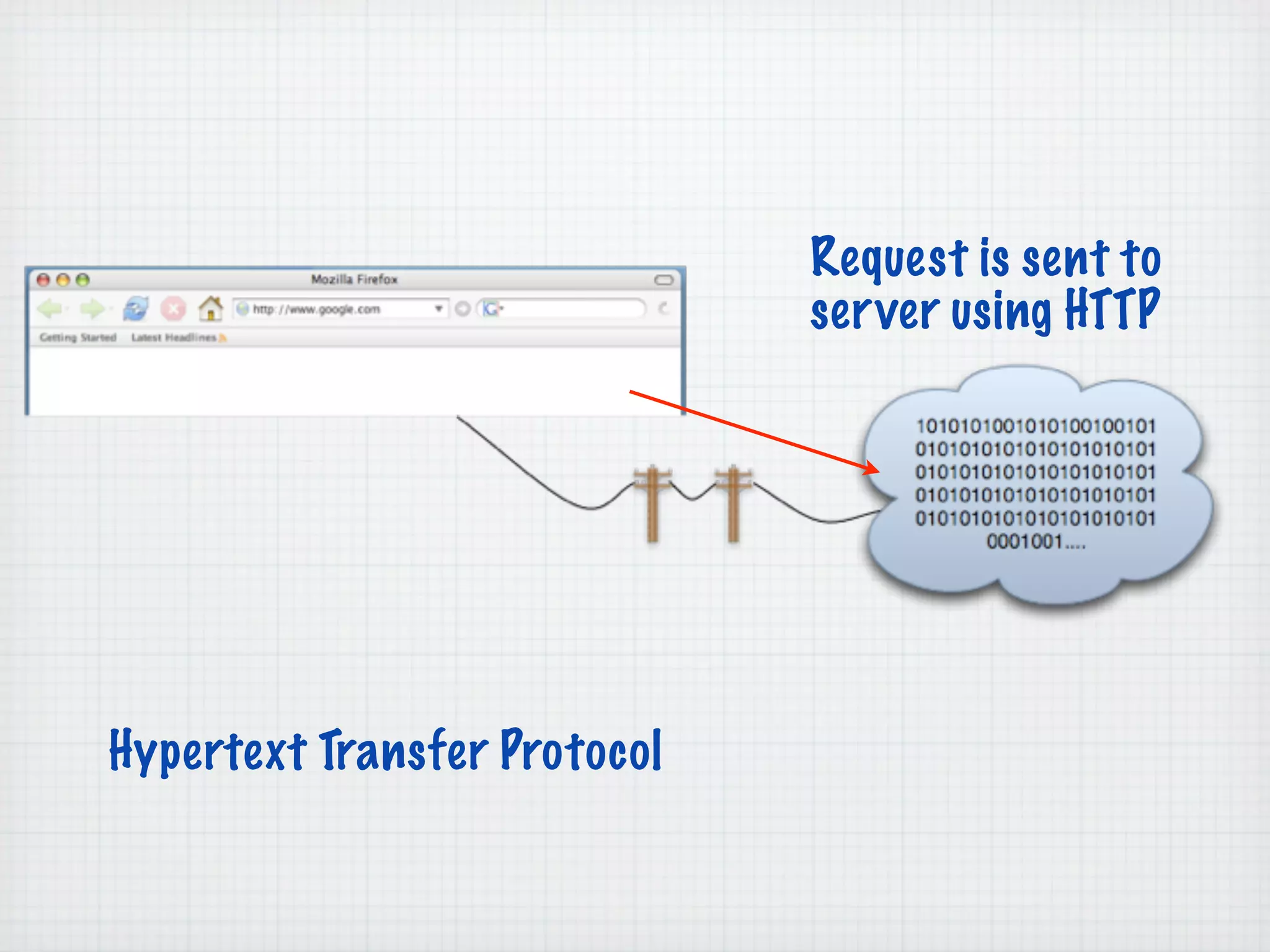
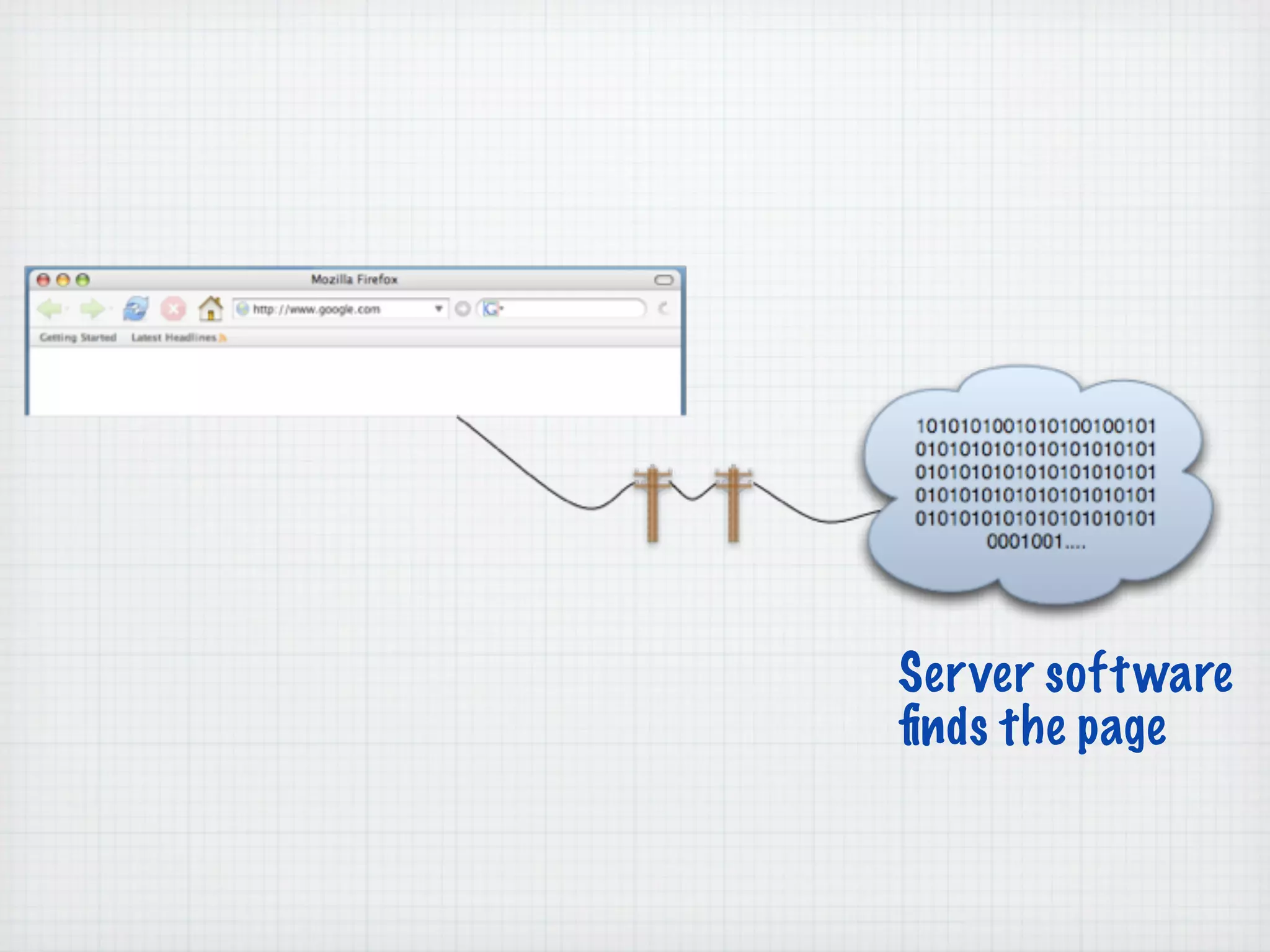
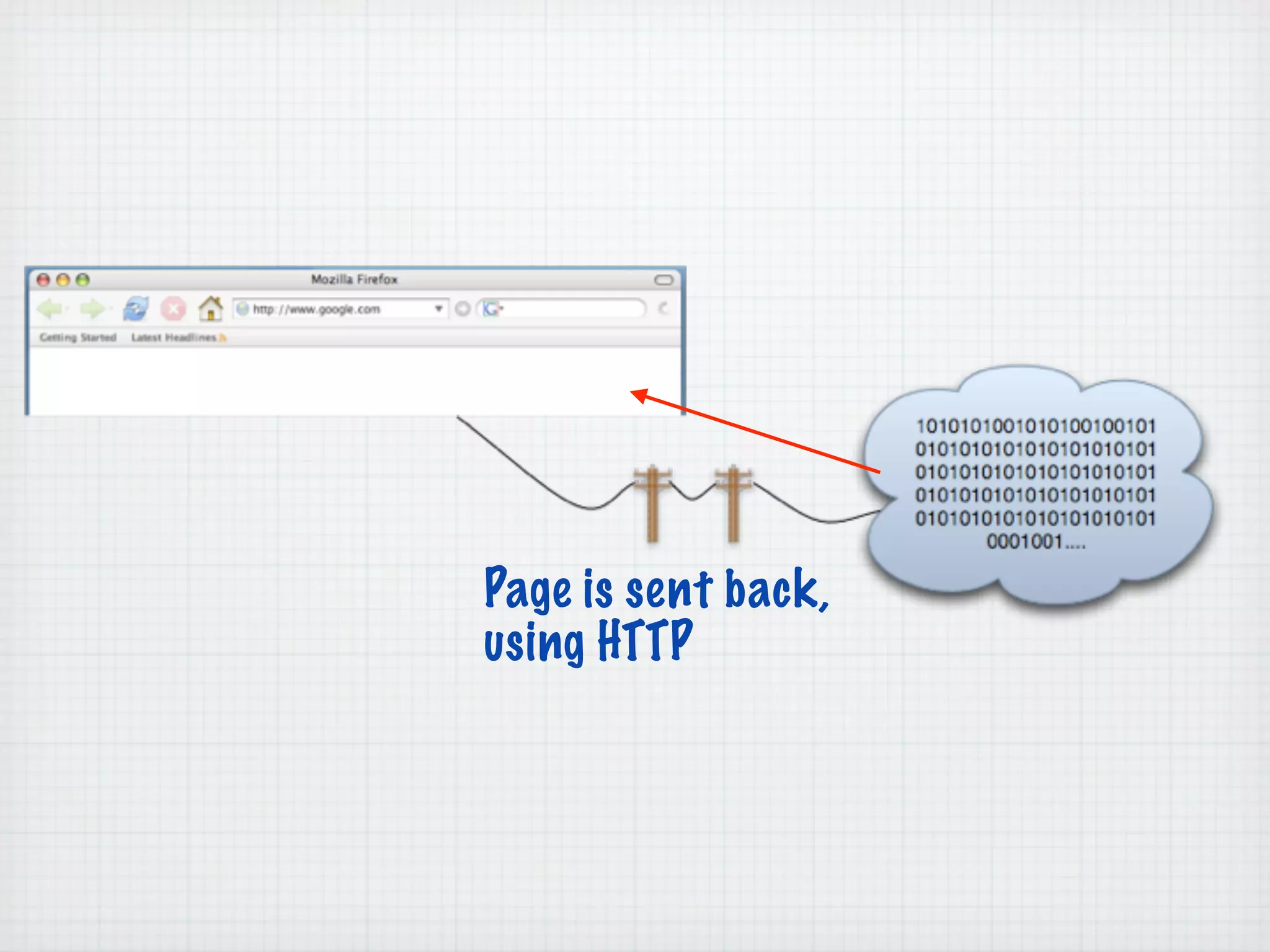
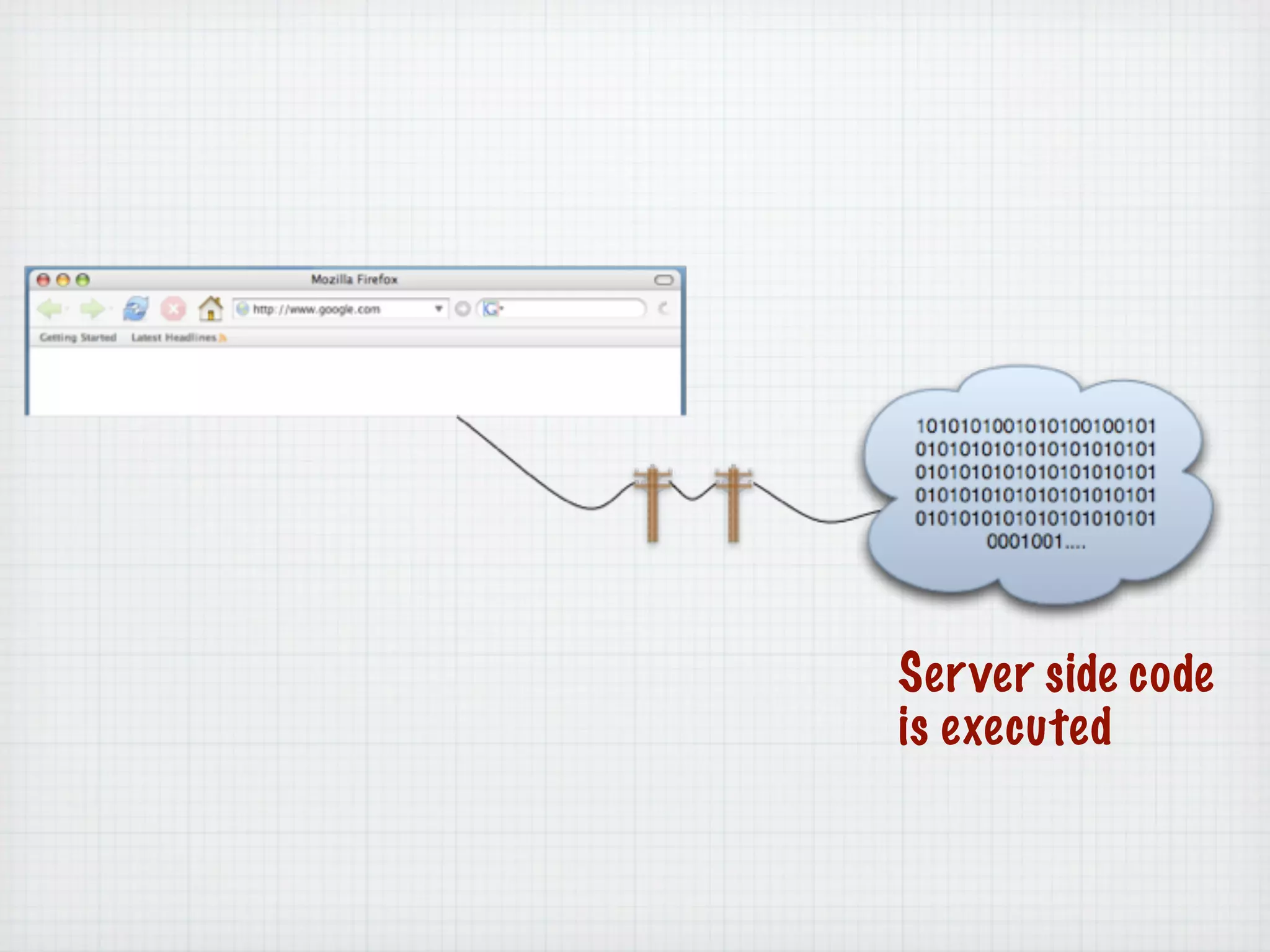
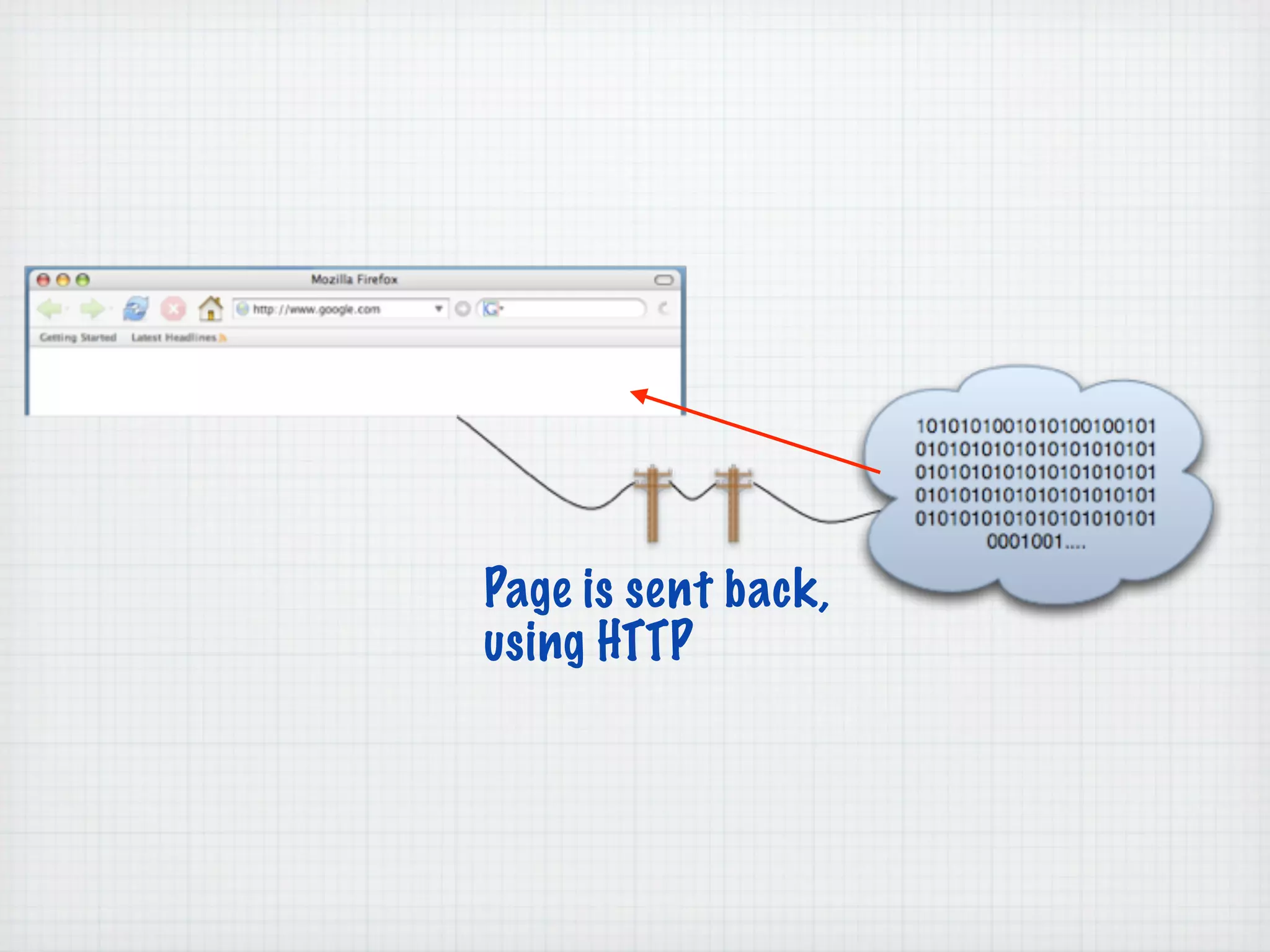
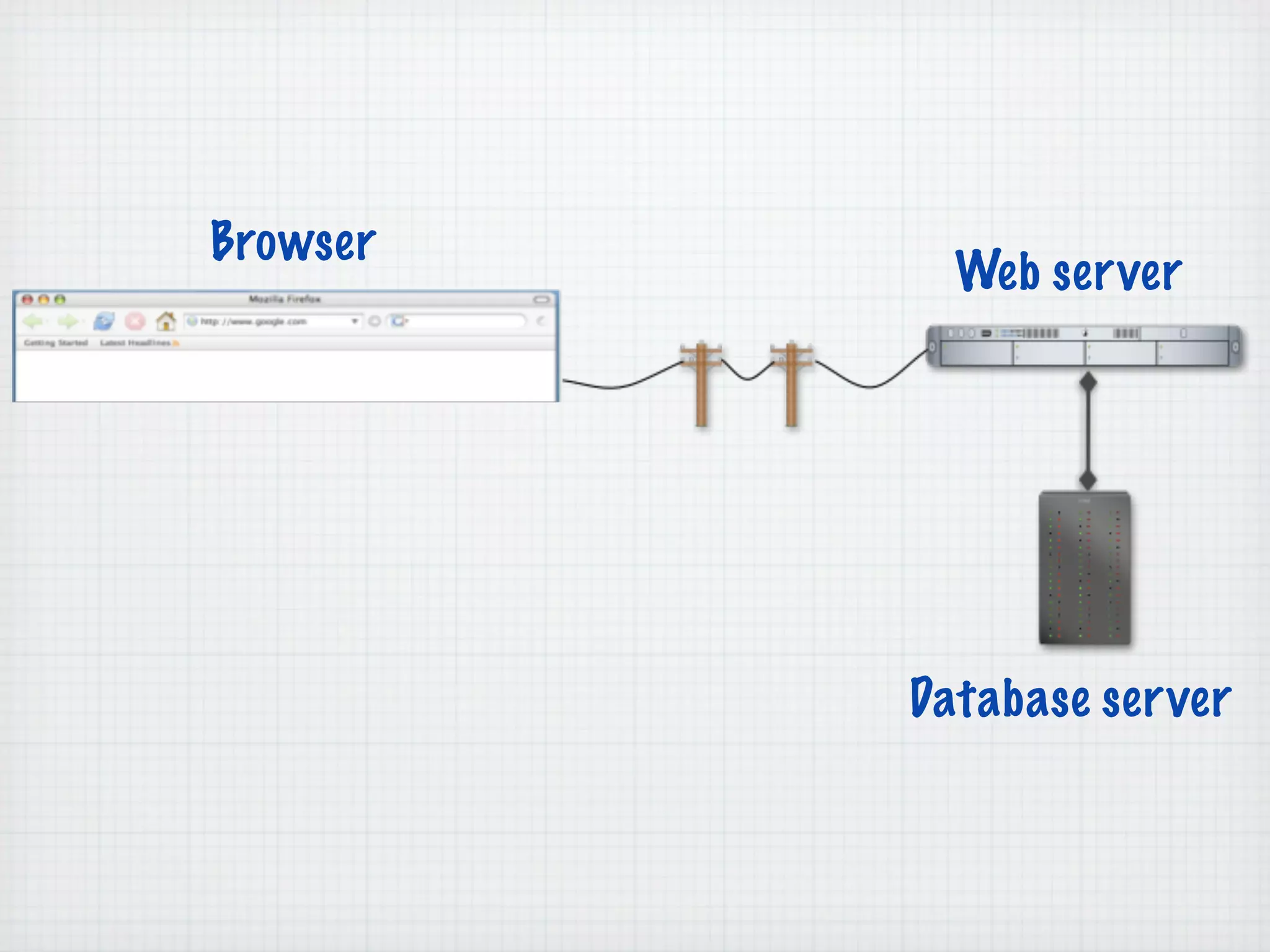
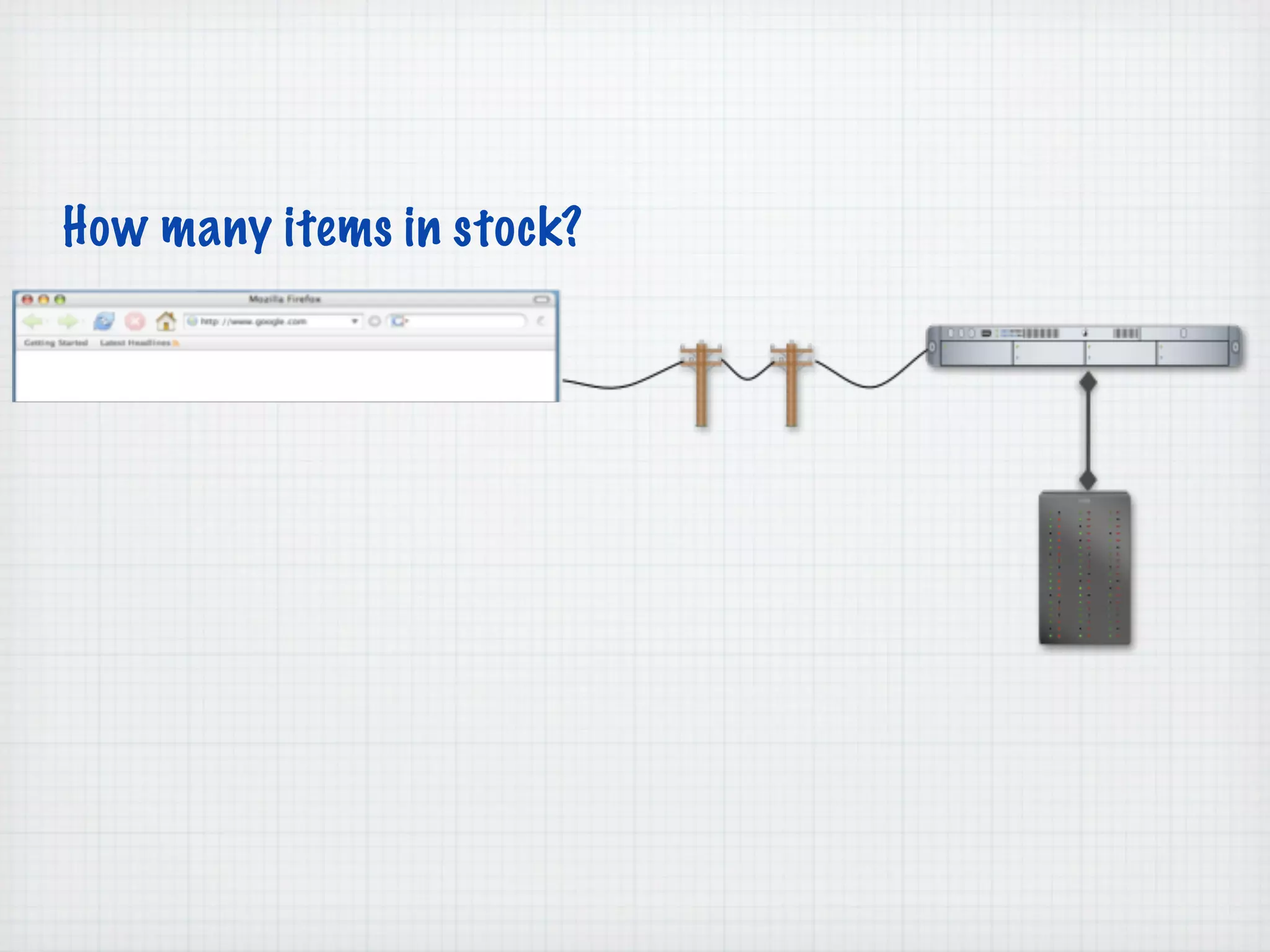
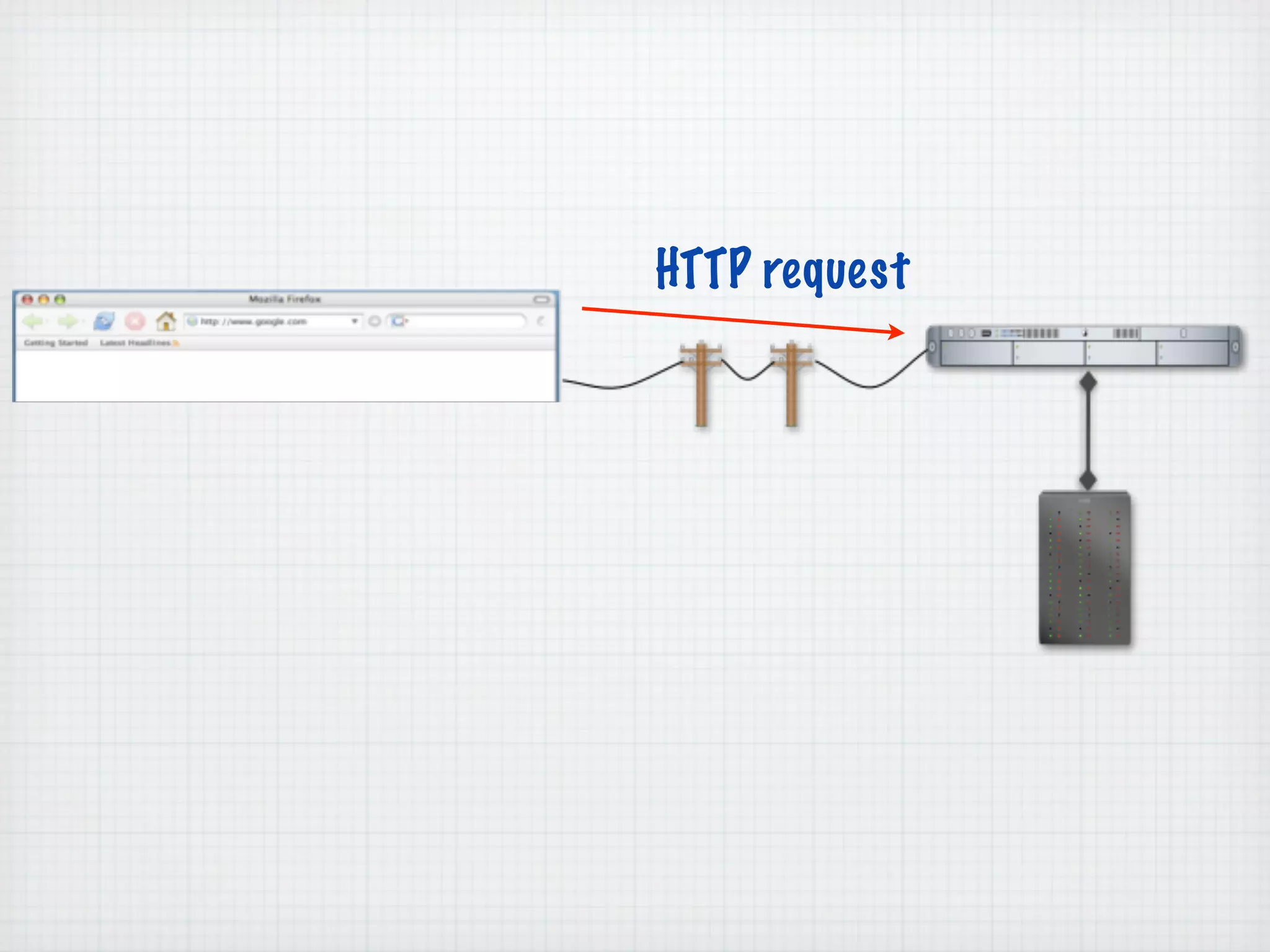
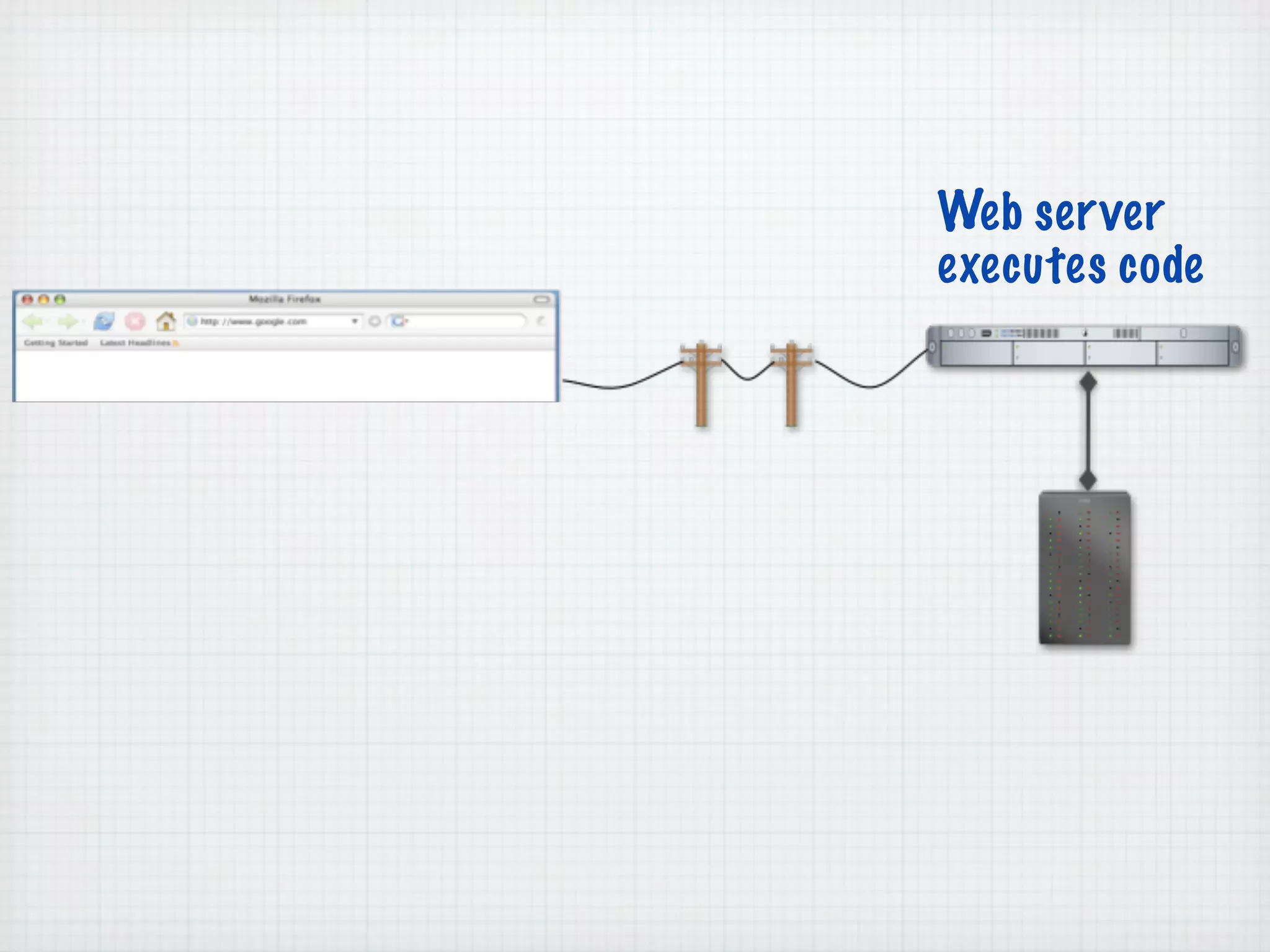
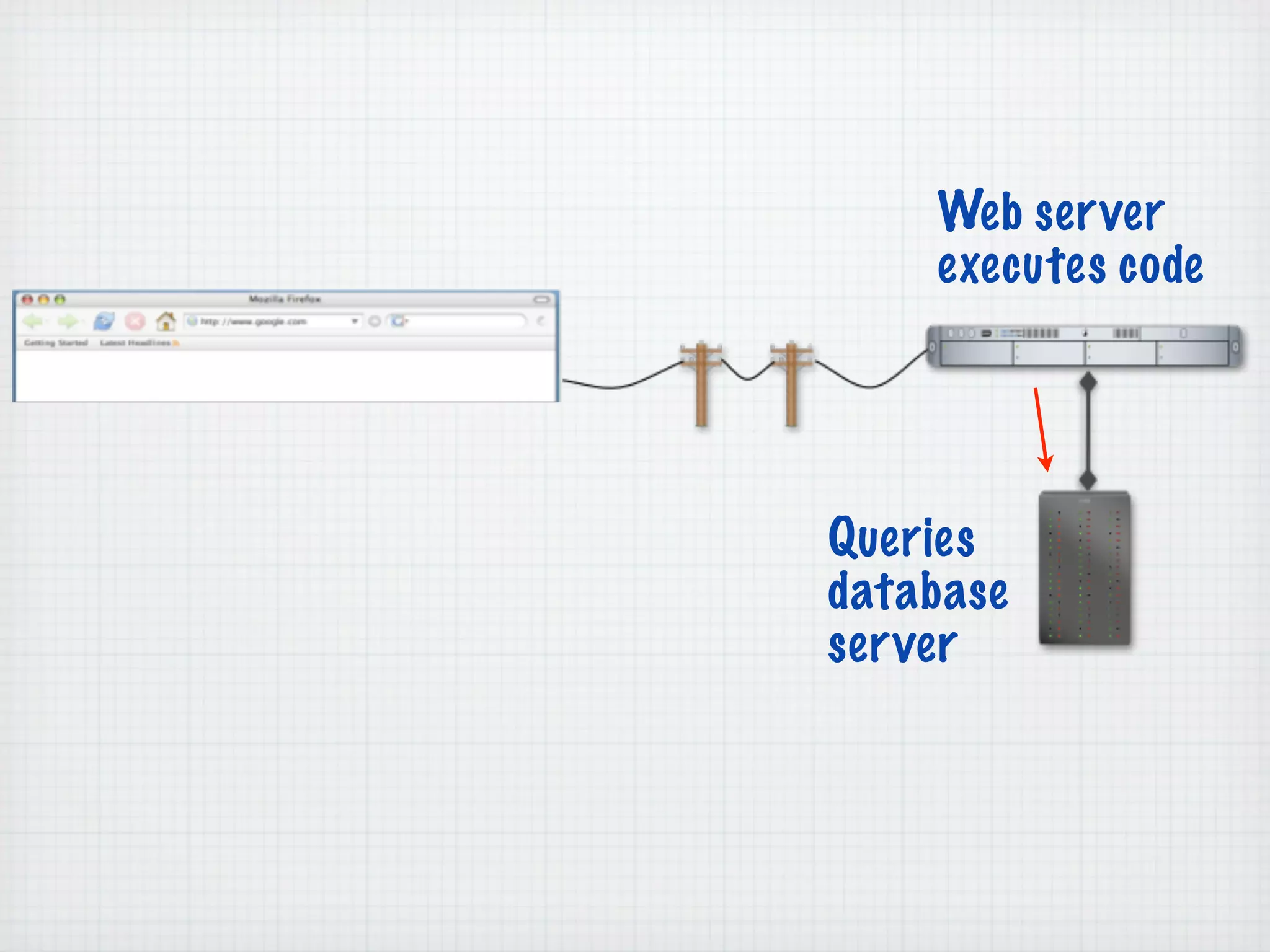
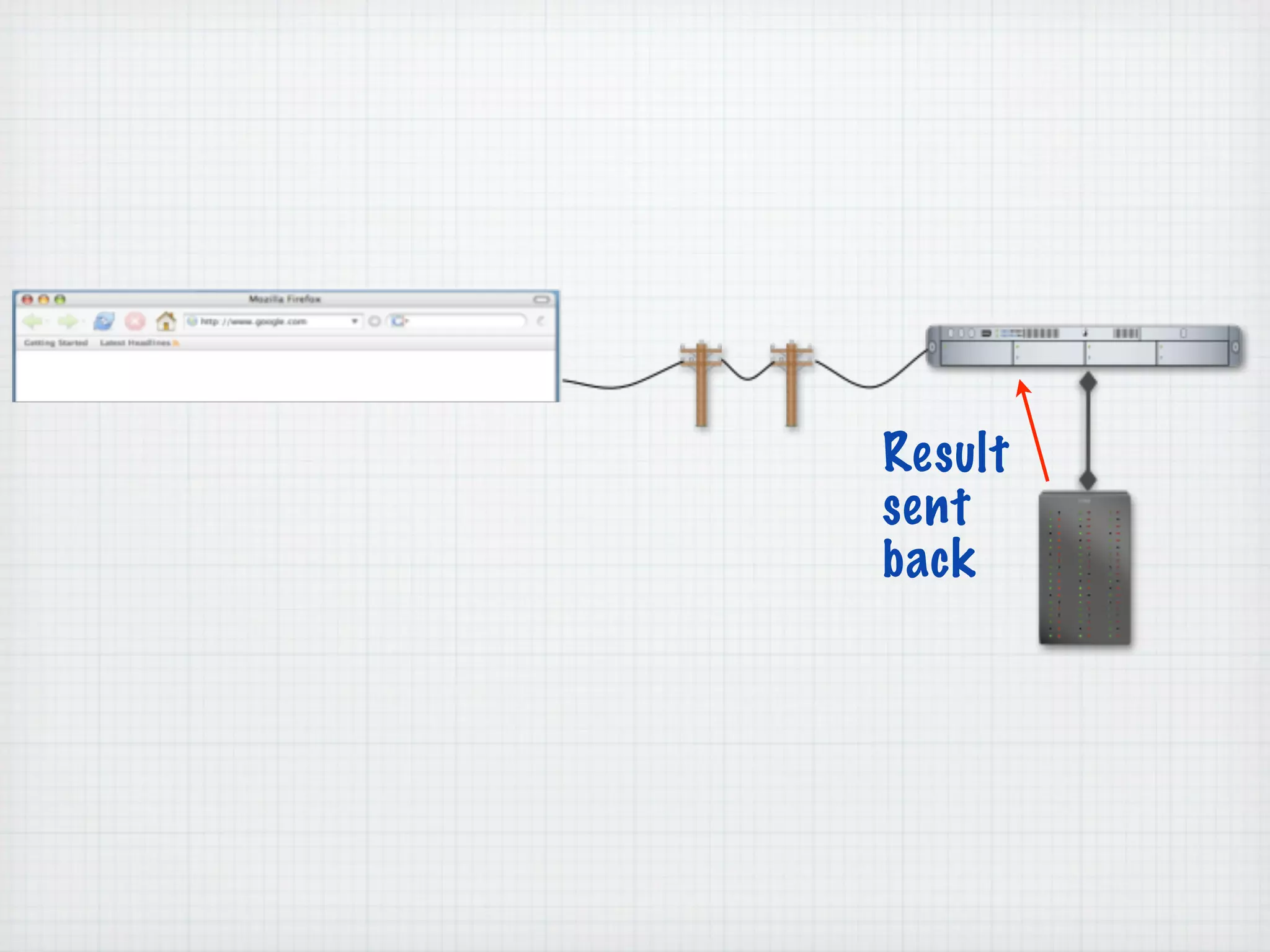
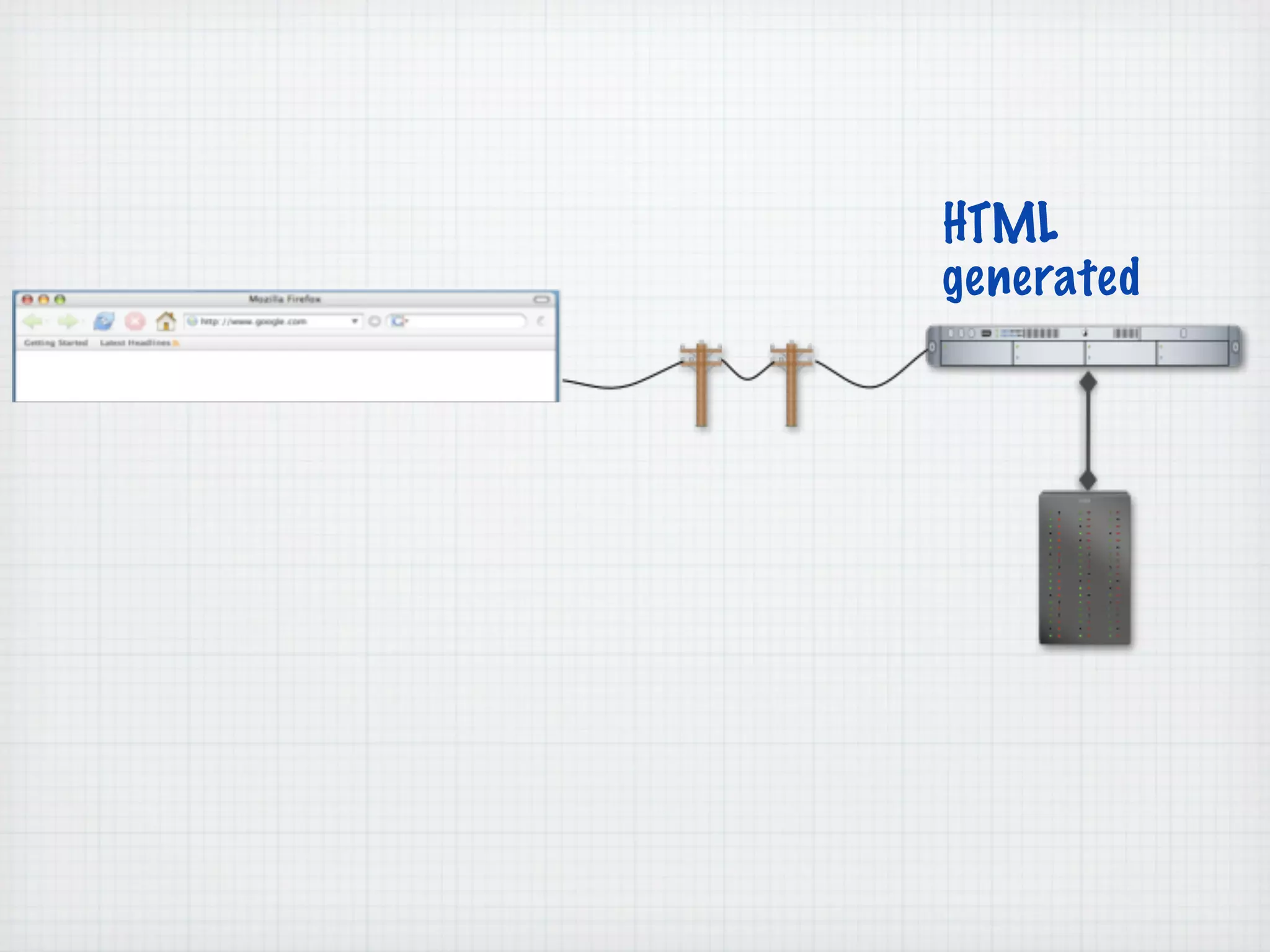
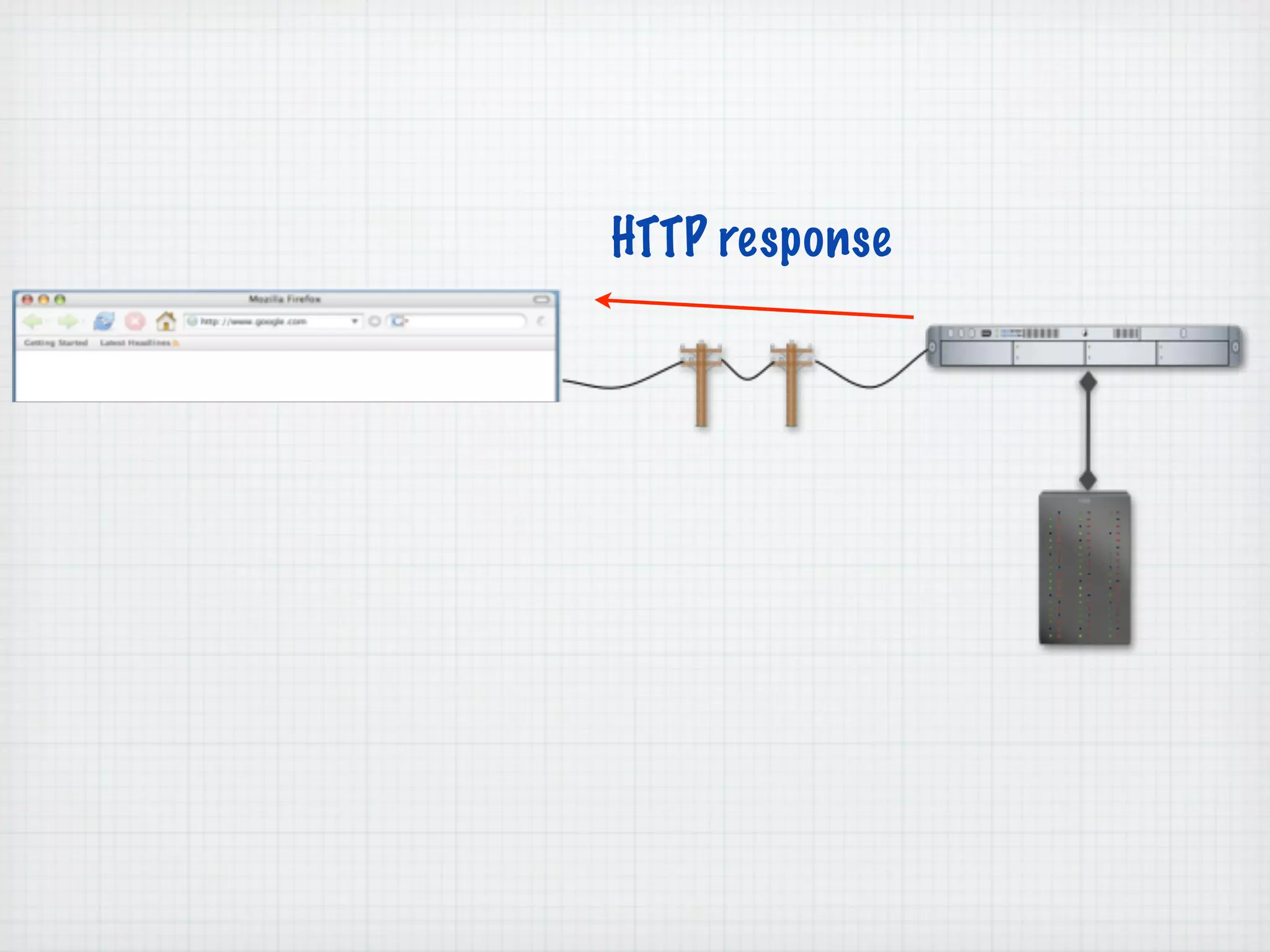
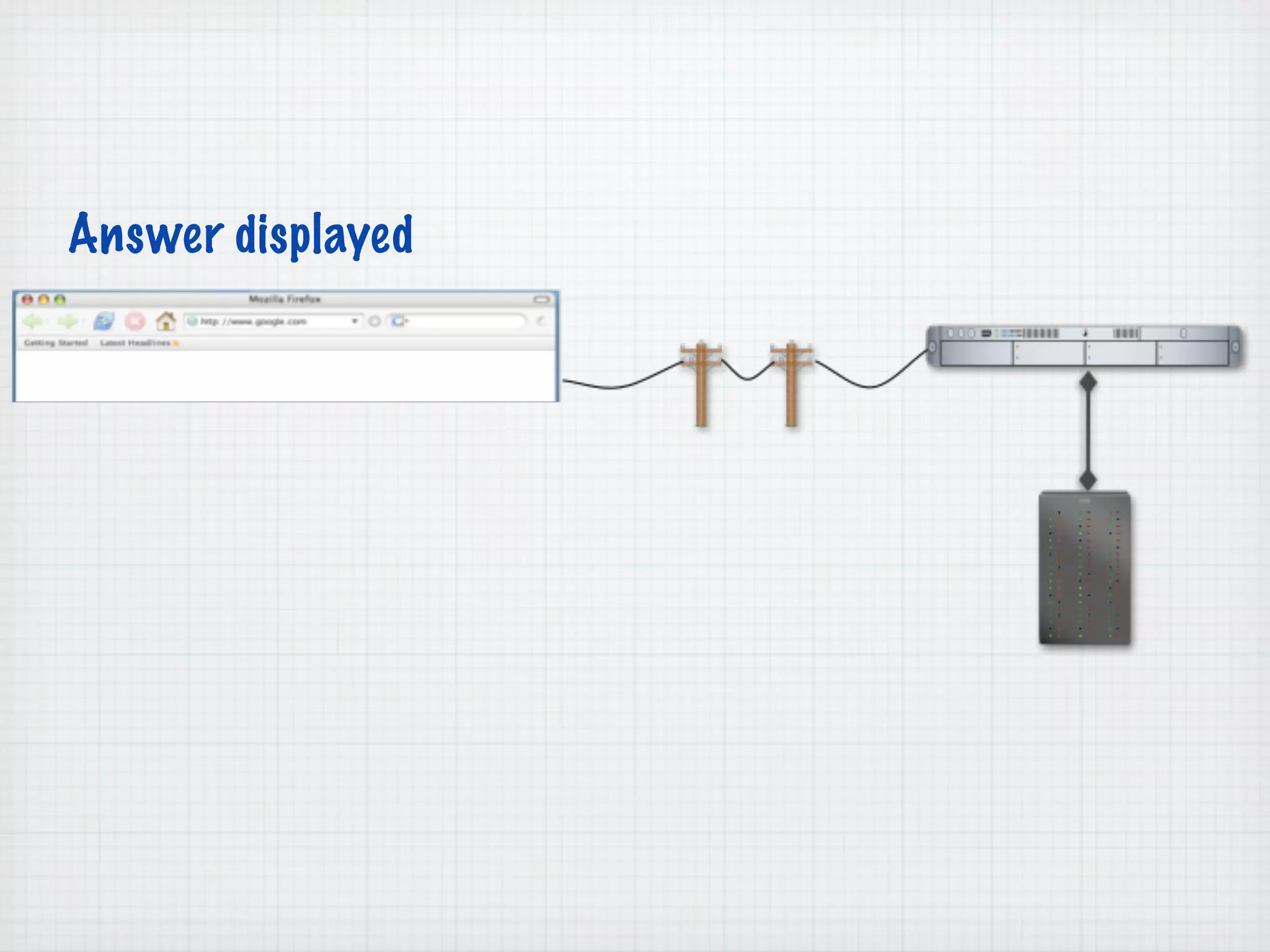
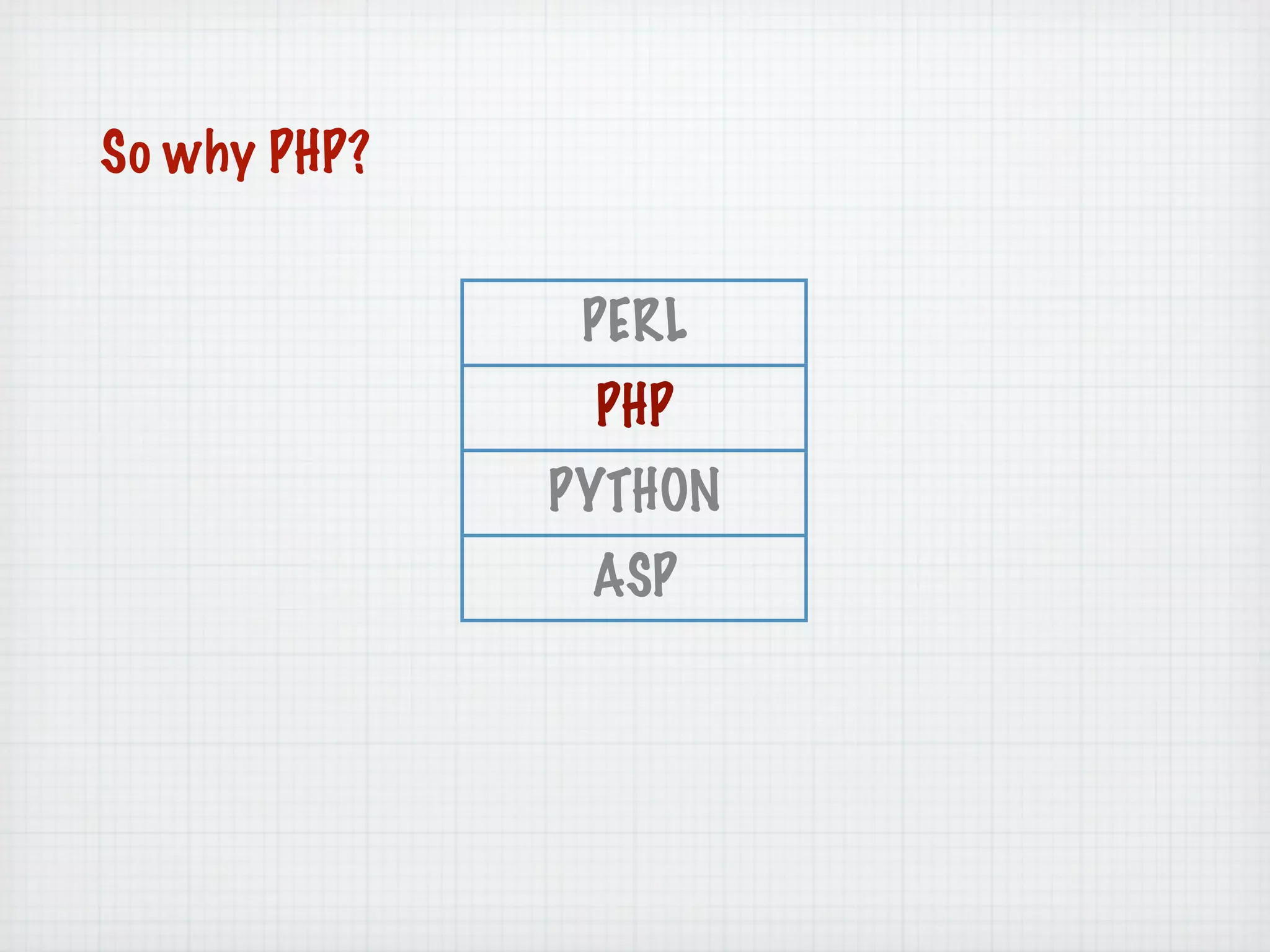
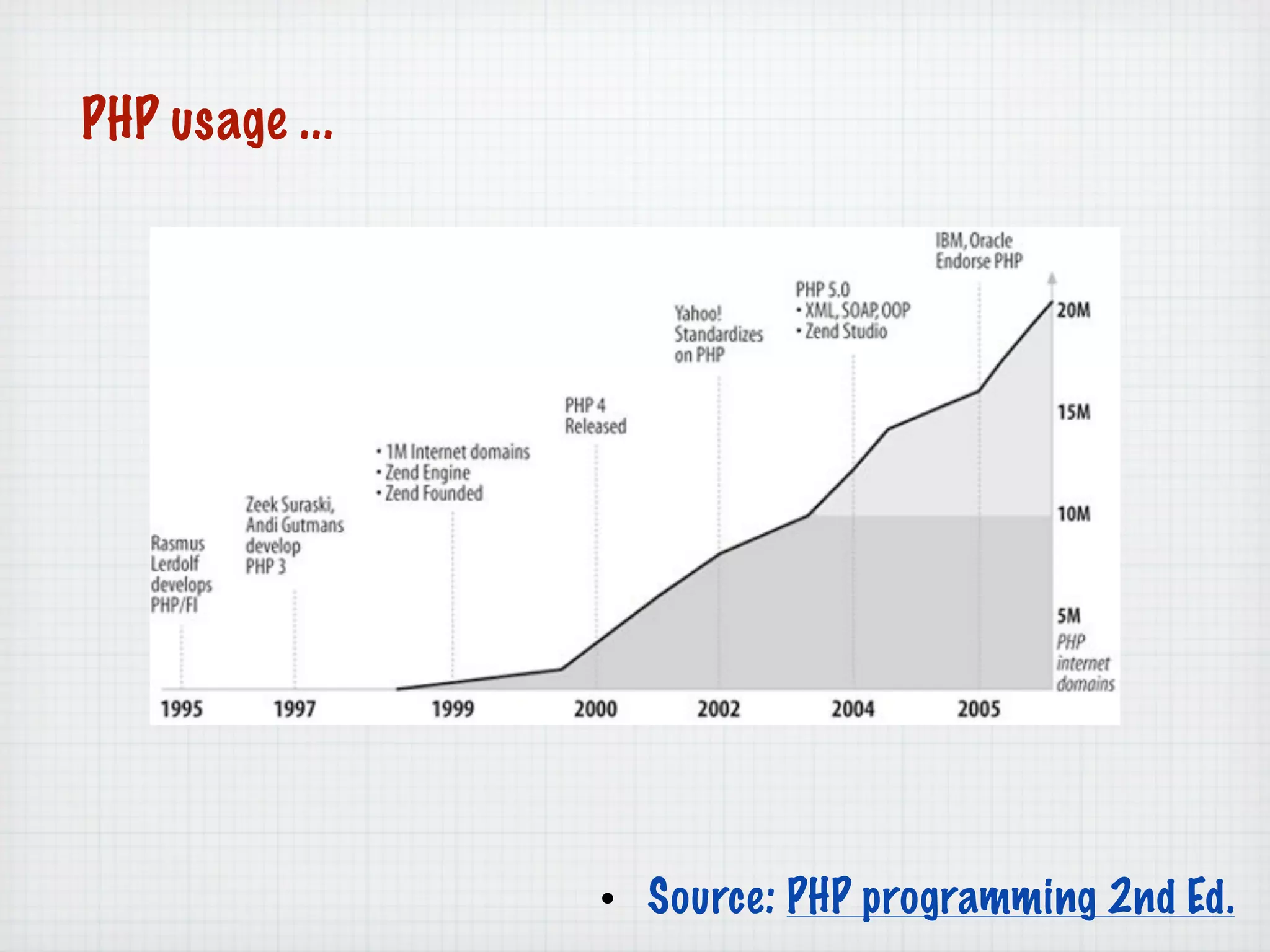
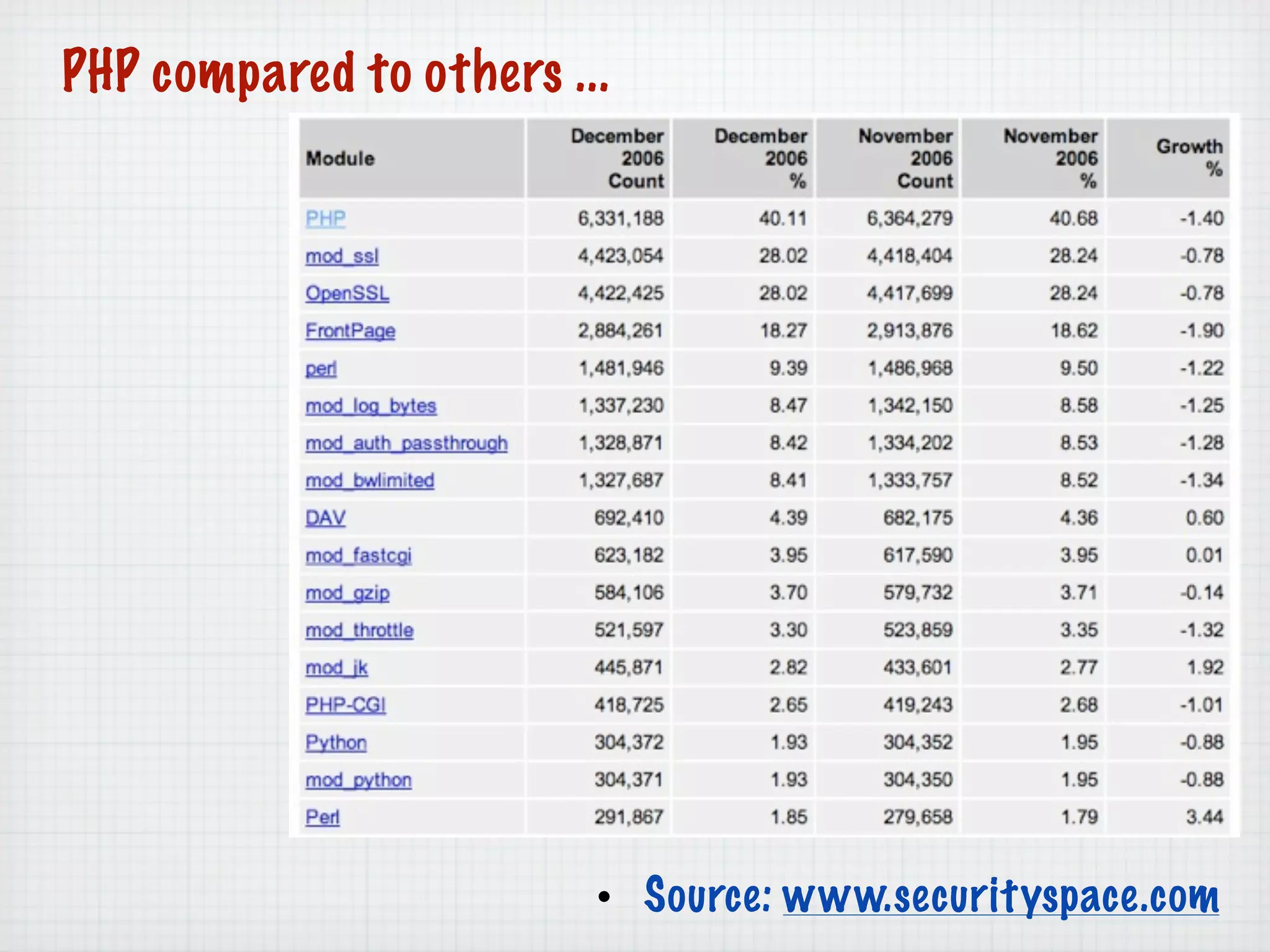
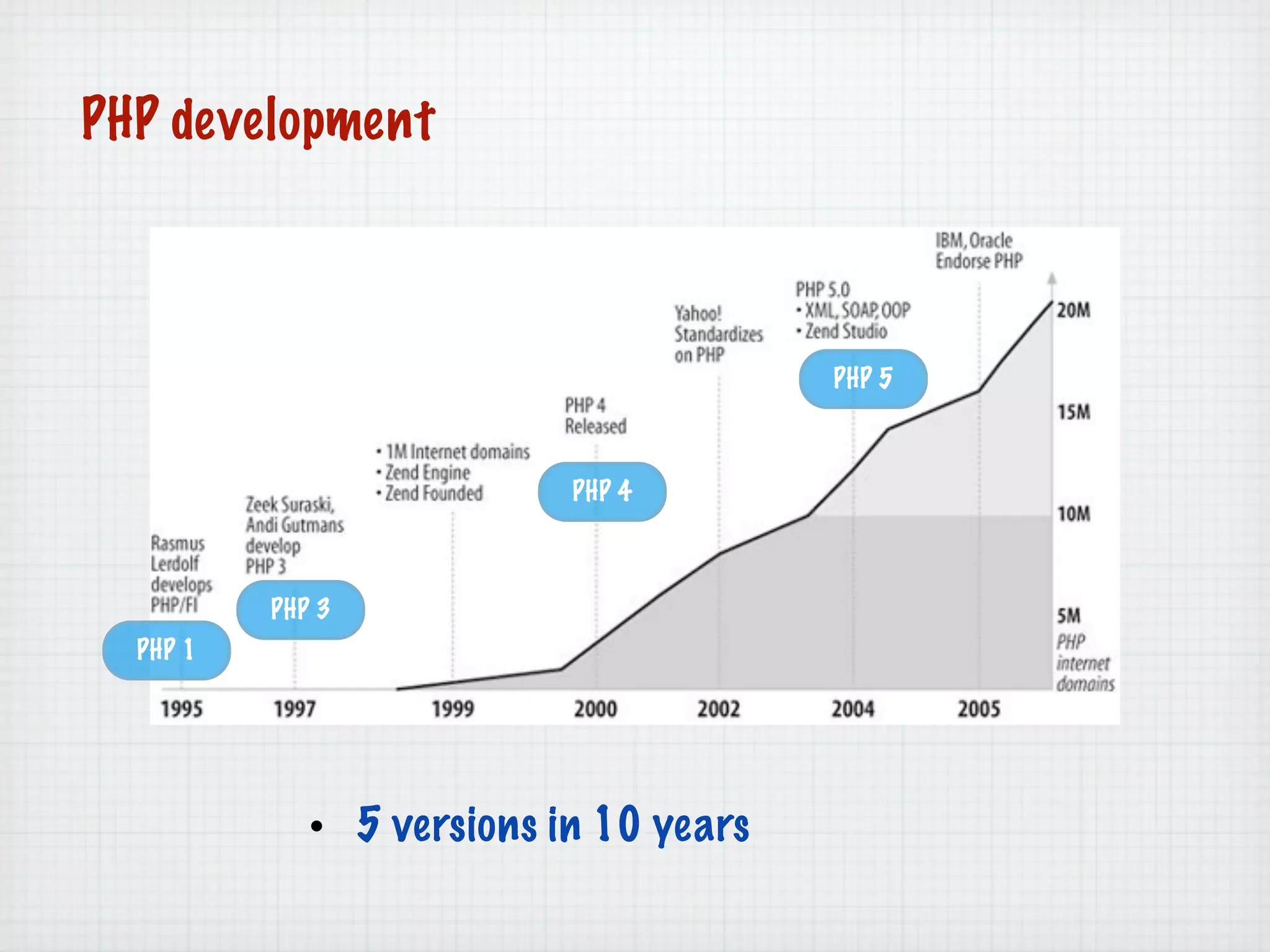
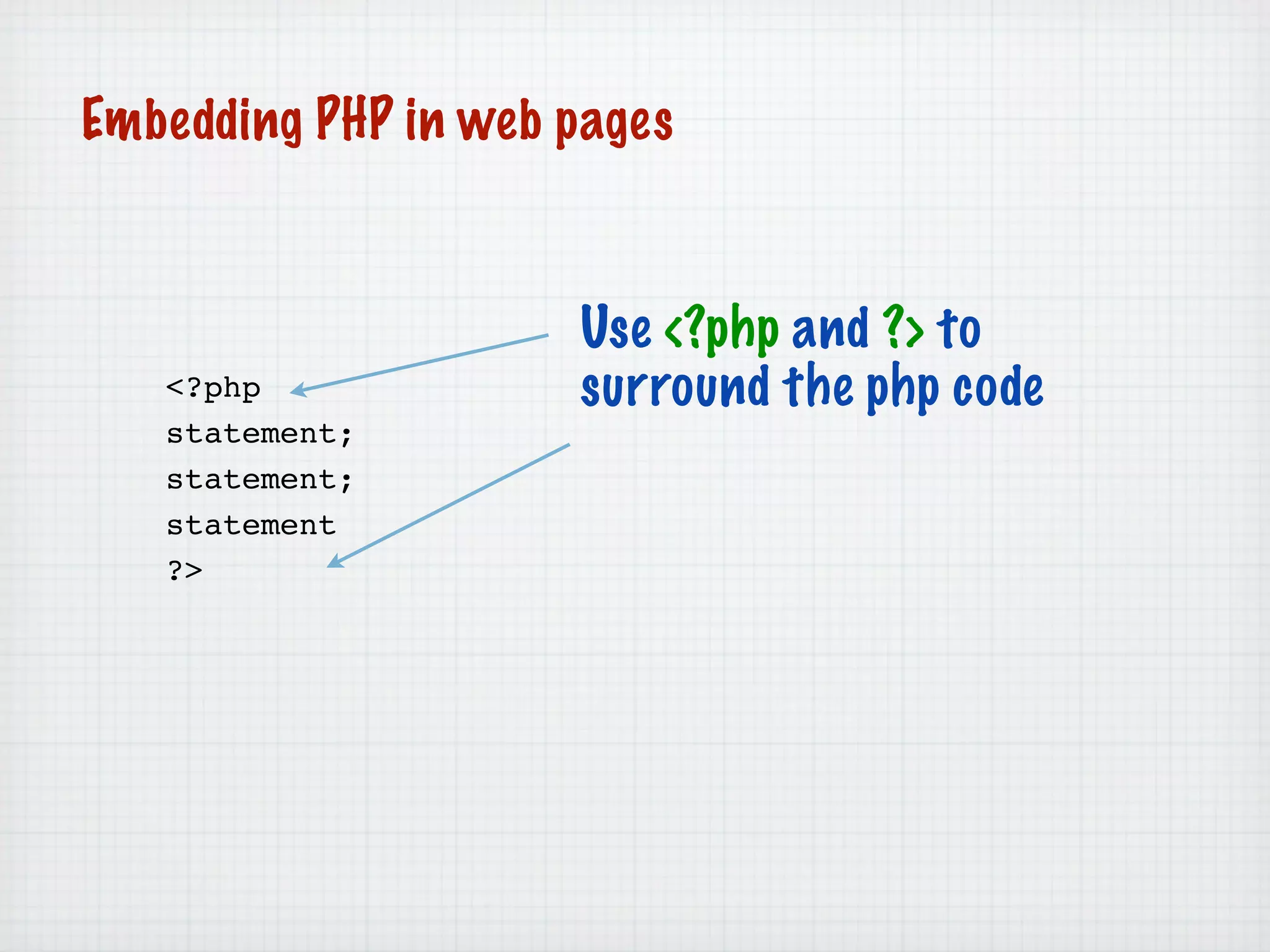
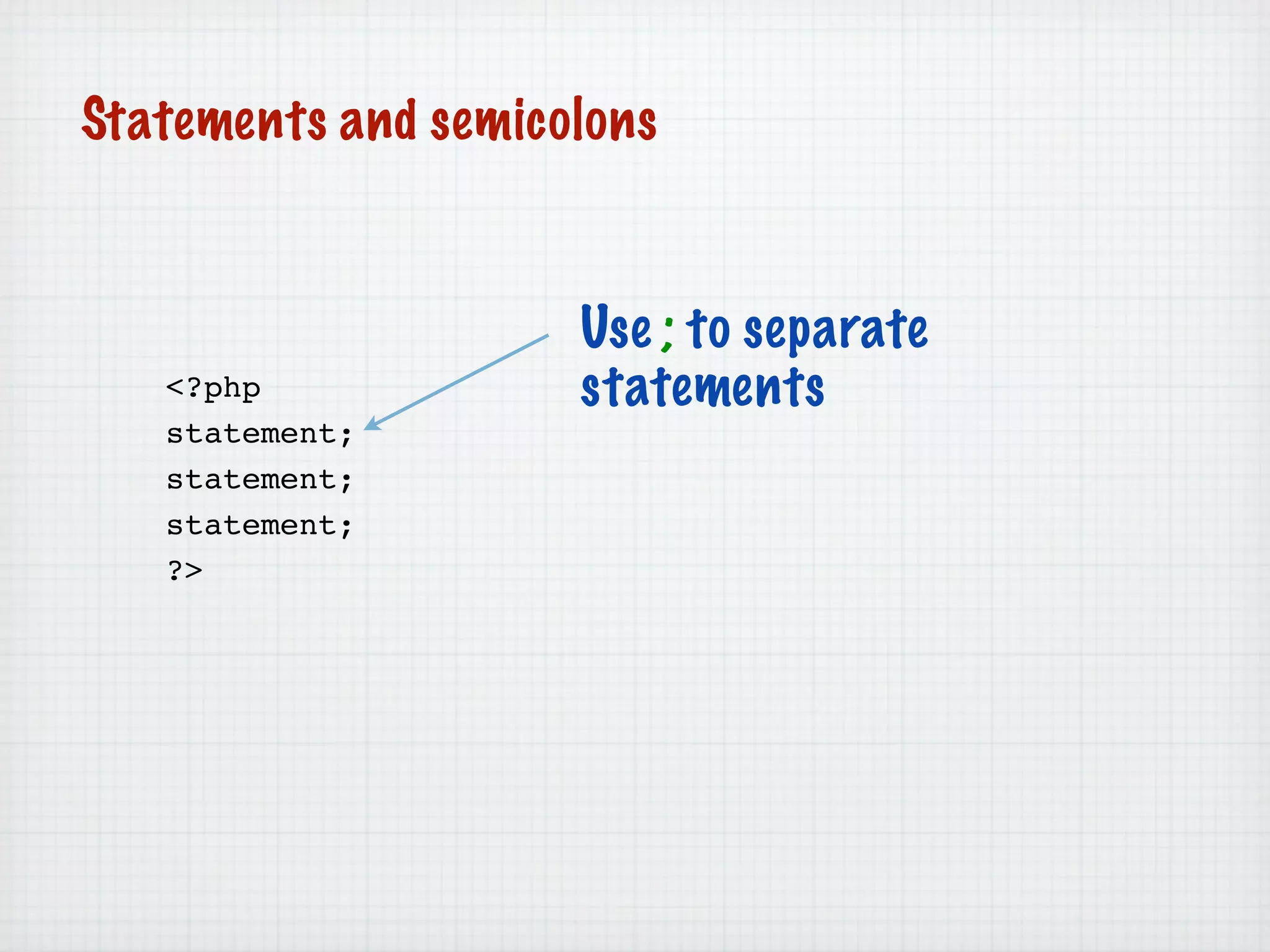
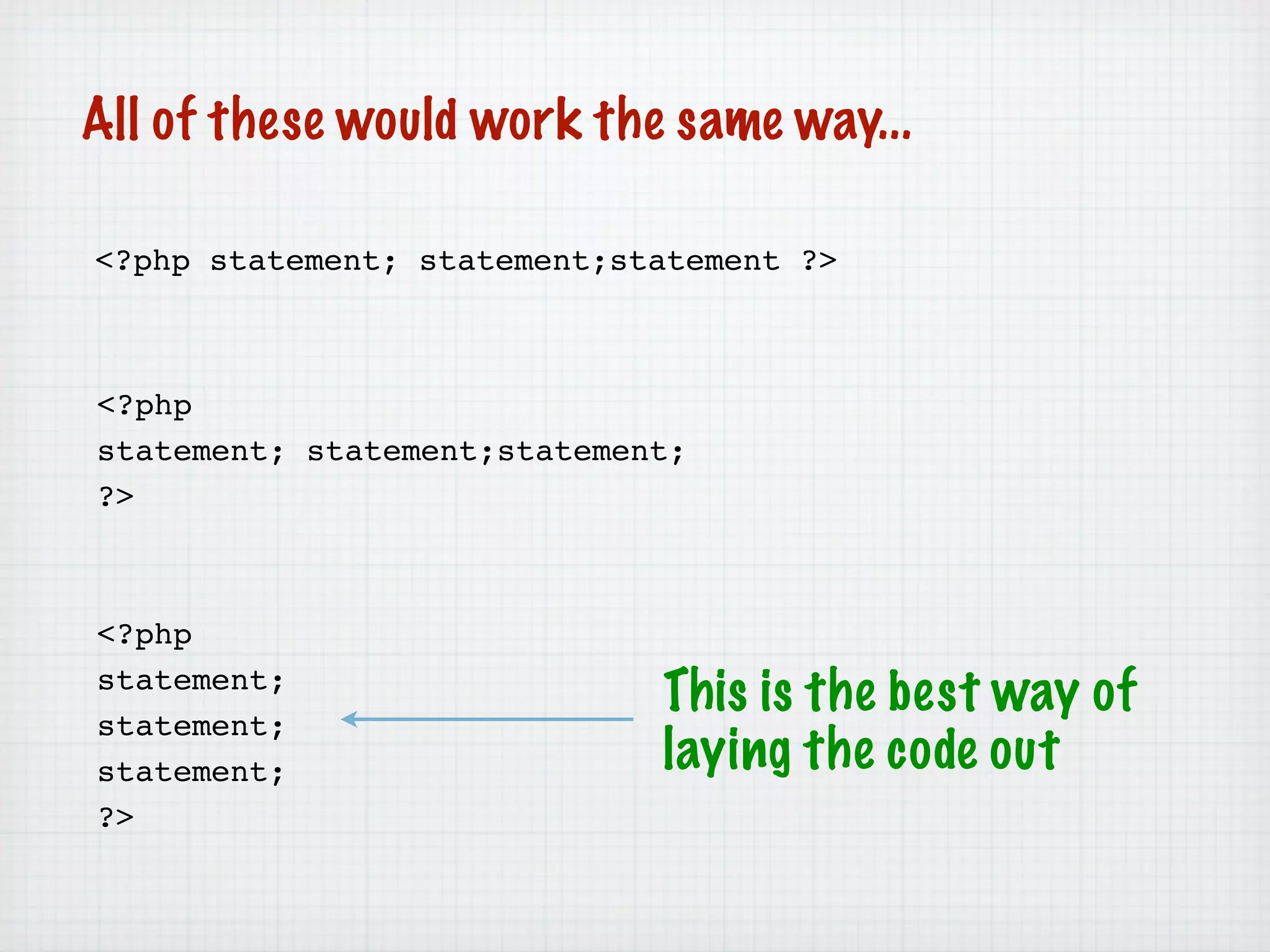
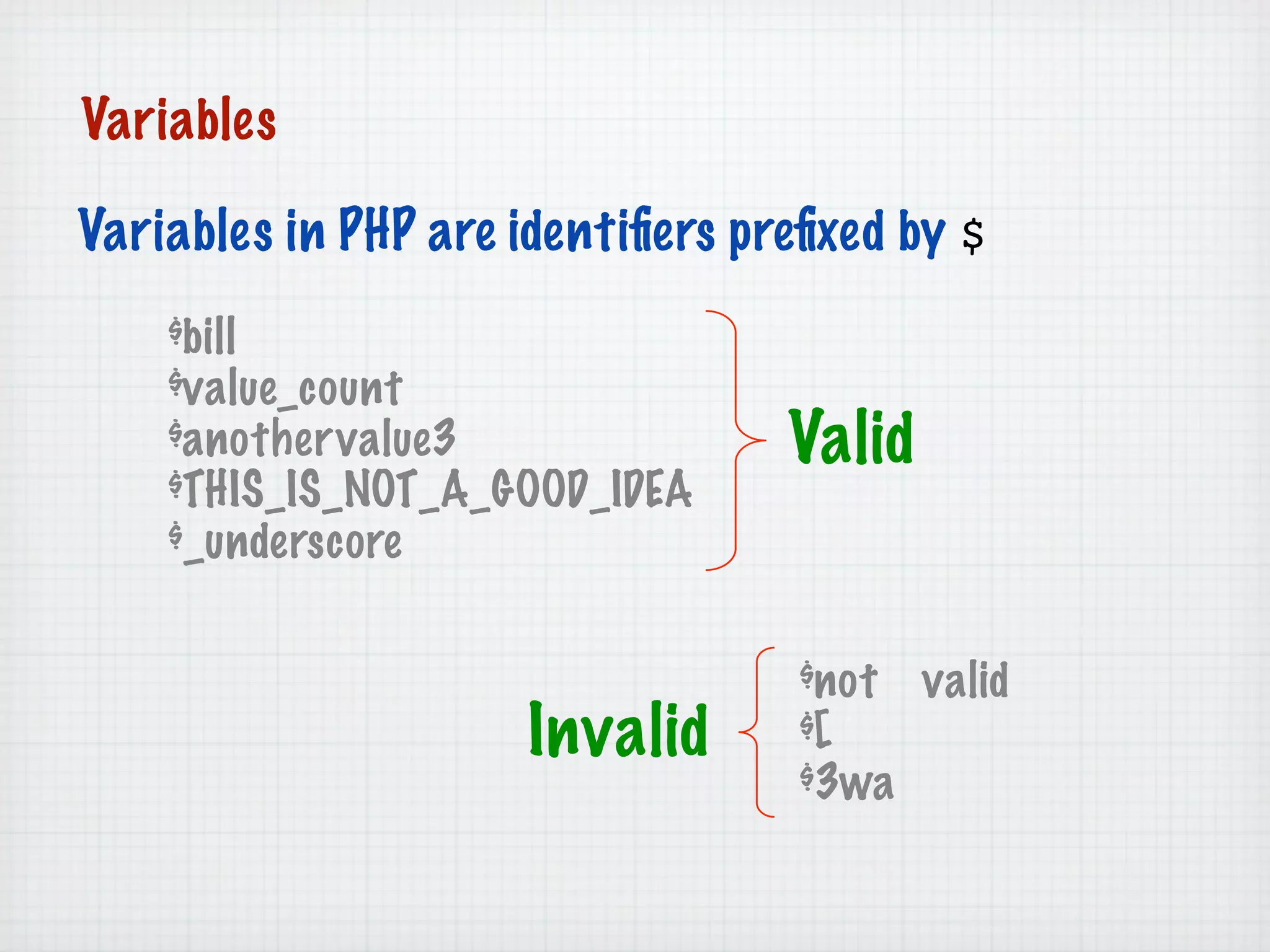
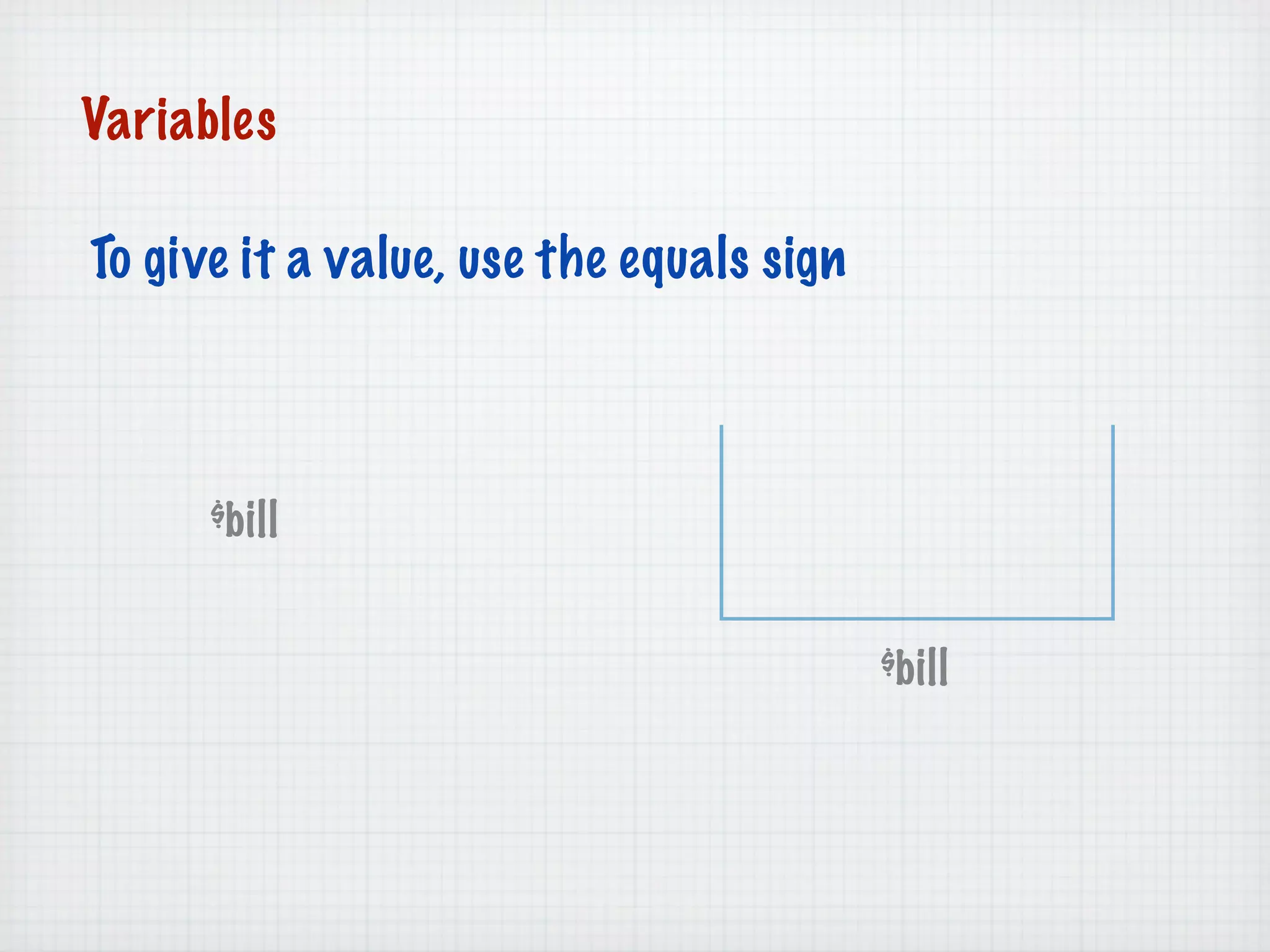
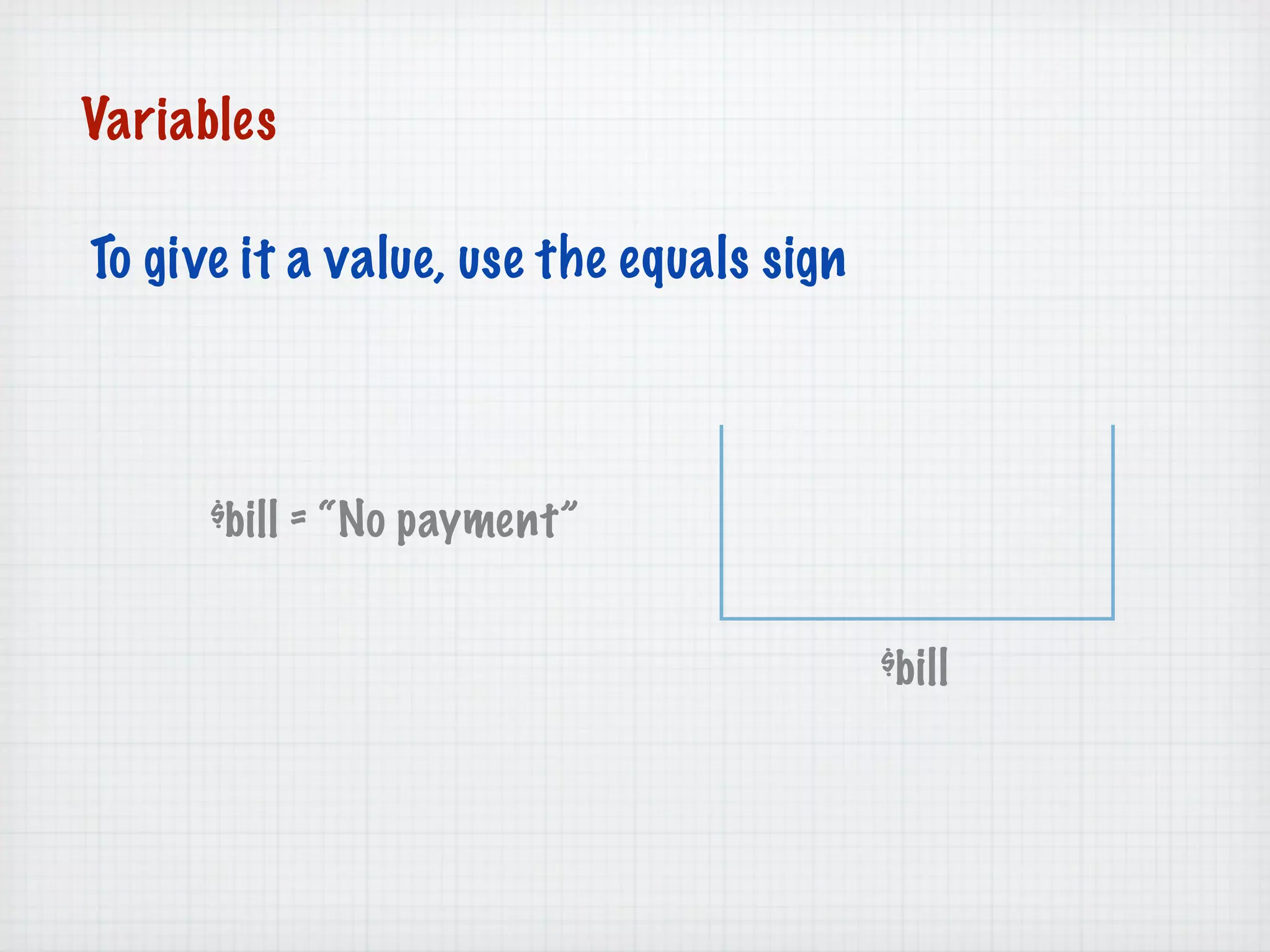
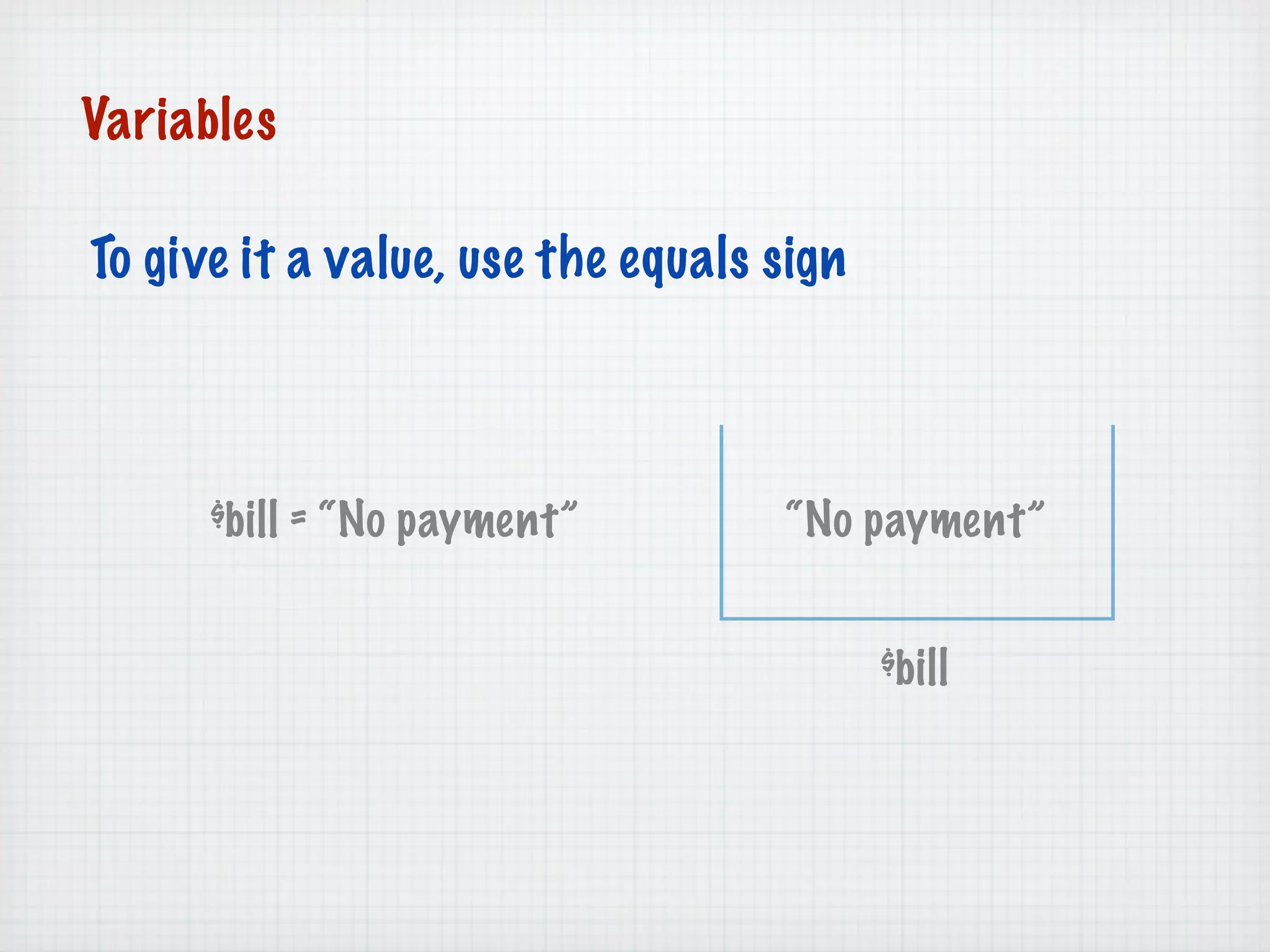
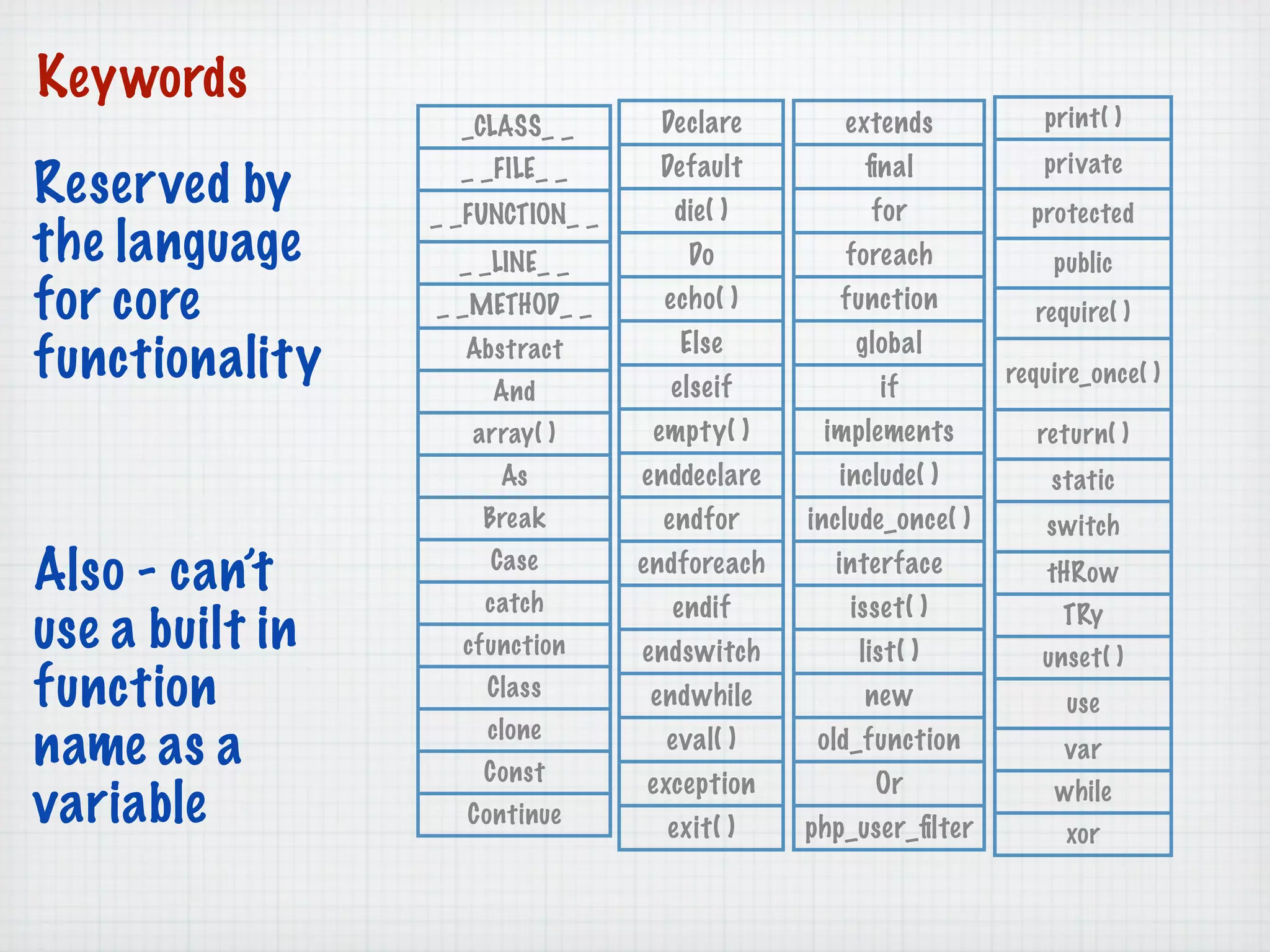
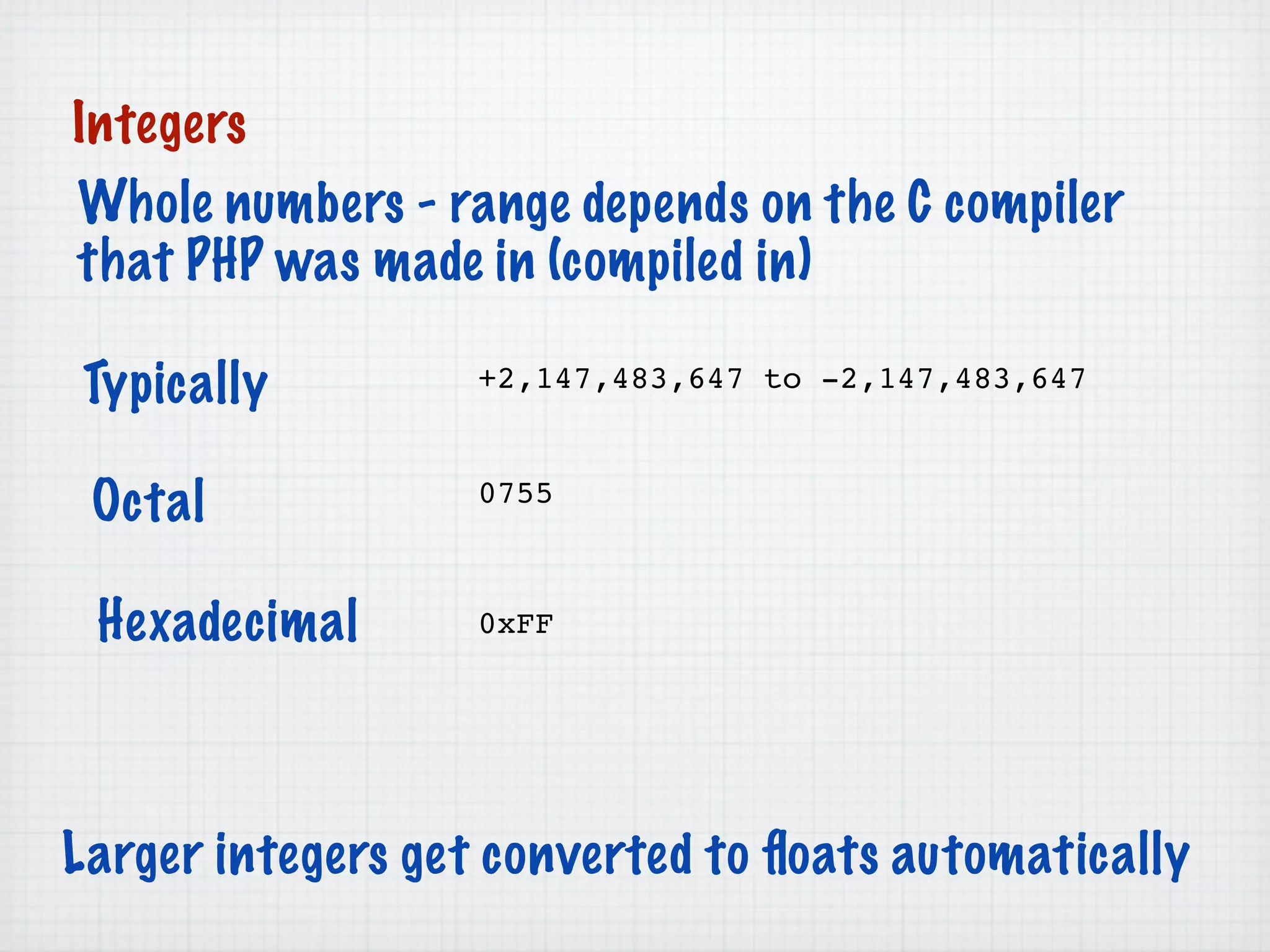
Web Scripting using PHP discusses server-side scripting languages like PHP. Server-side scripts are embedded in web pages and executed by the server before the page is sent to the browser. PHP code is executed by the web server, allowing it to access server-side resources and generate dynamic web page content. The document provides examples of basic PHP code structure and syntax, including embedding PHP in HTML, using statements, comments, variables, and data types.