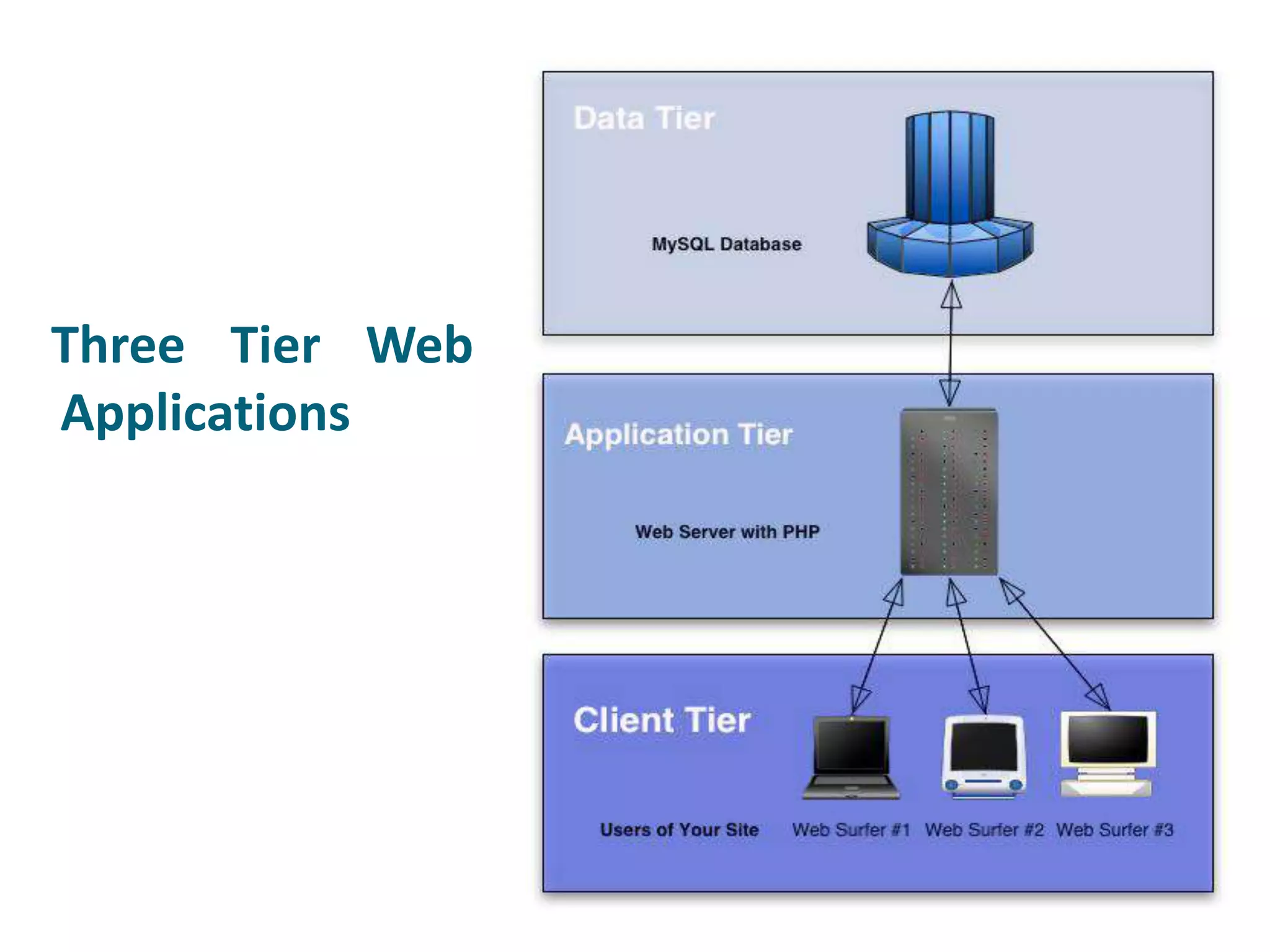
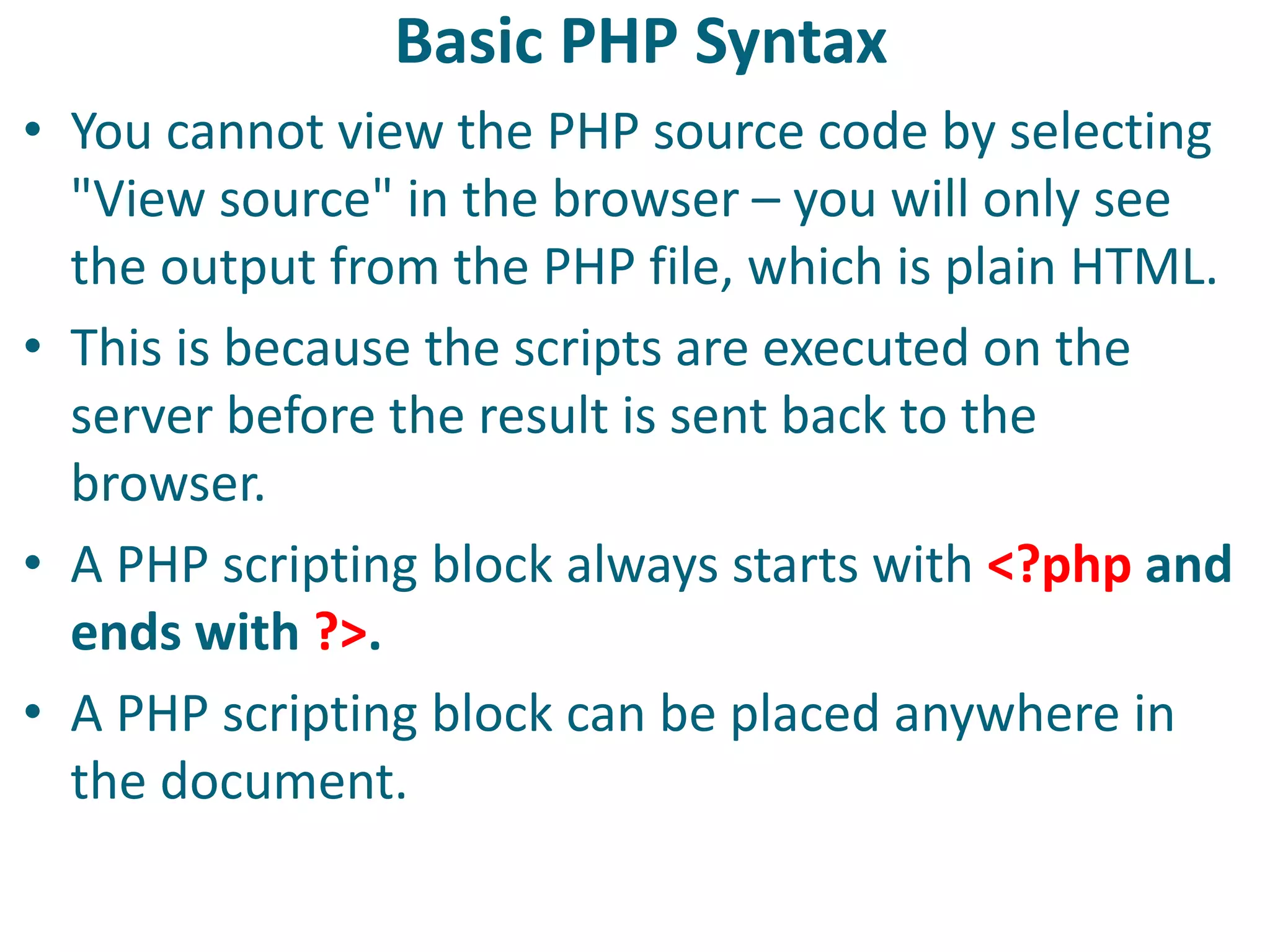
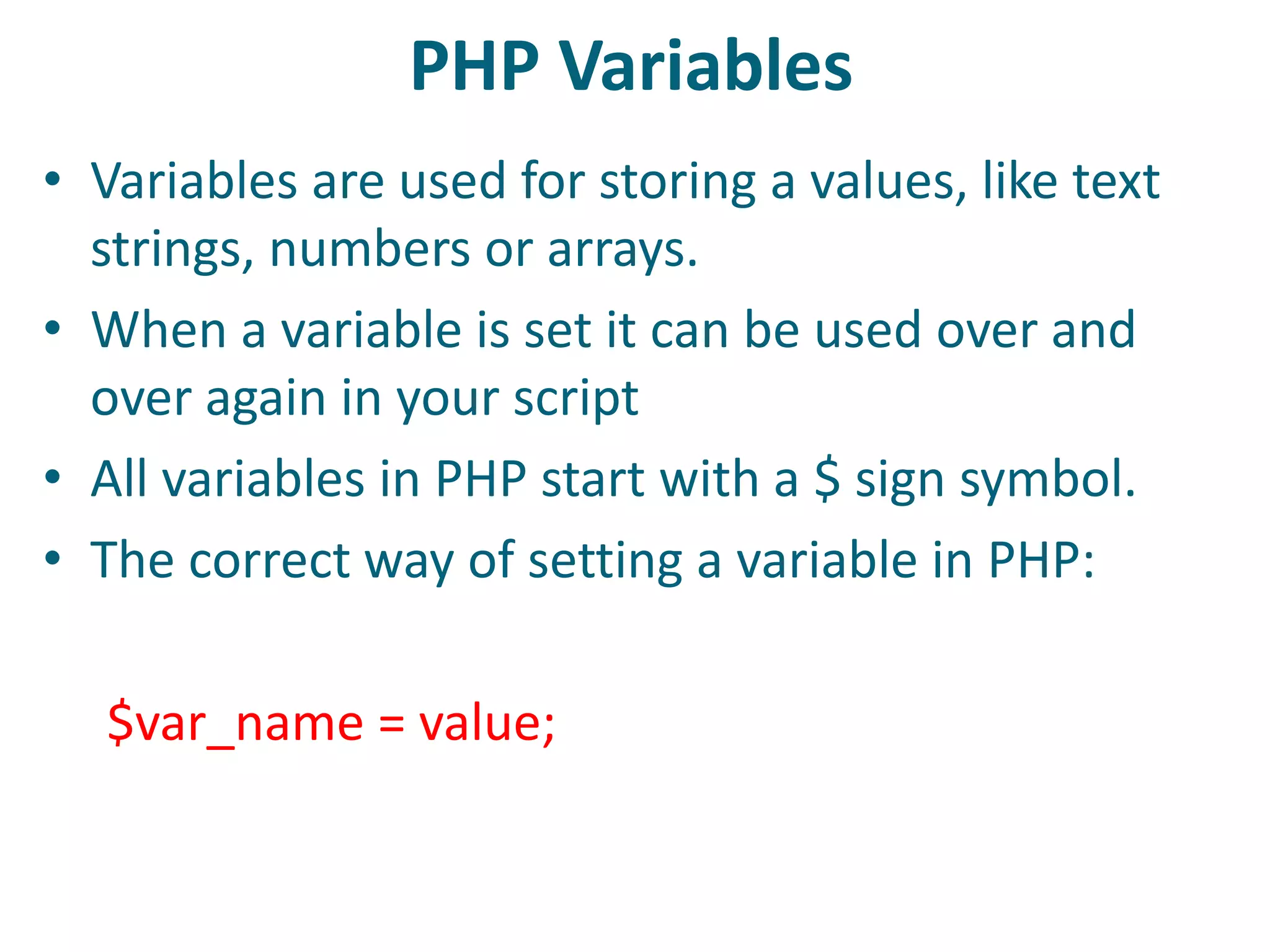
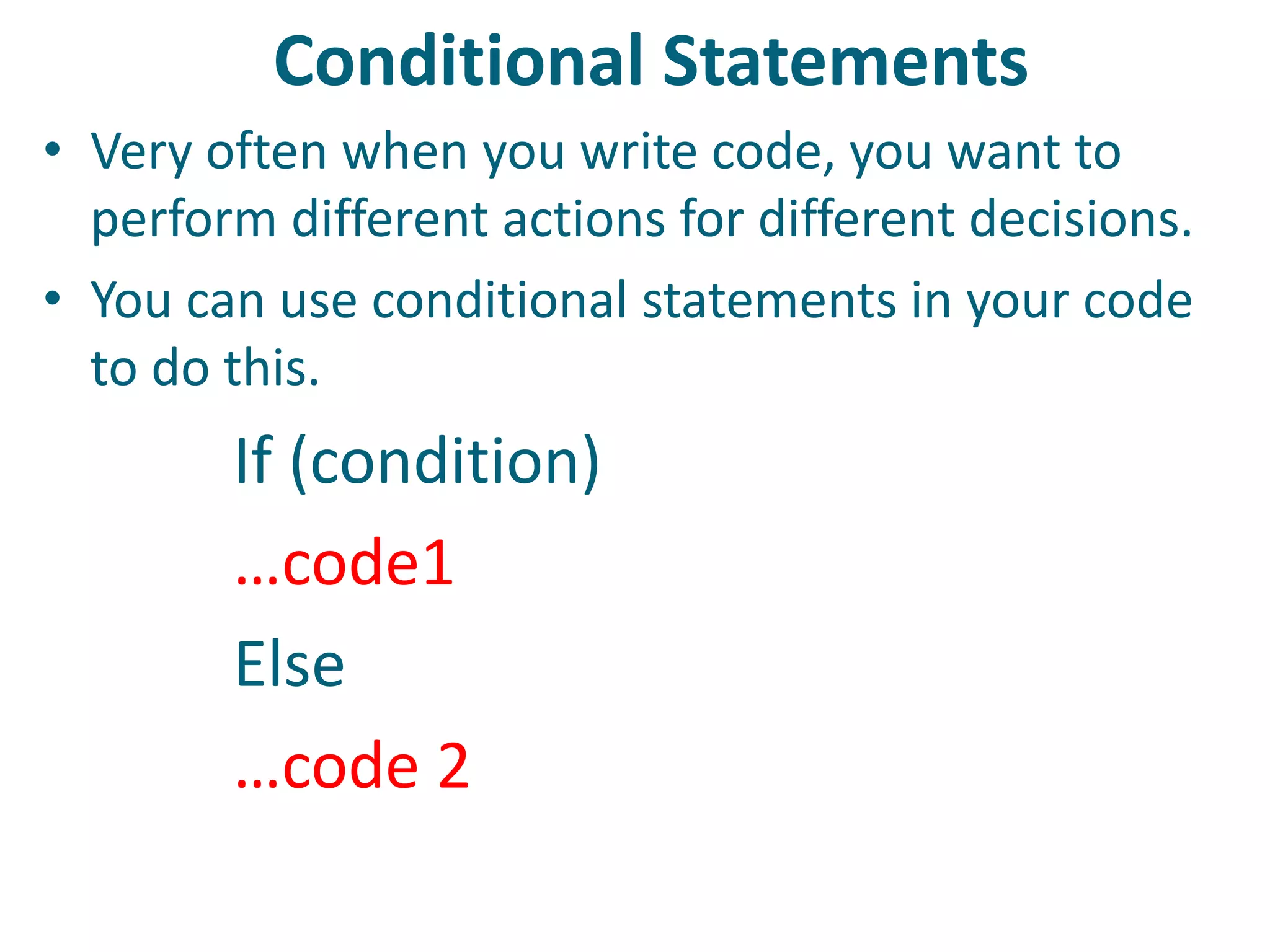
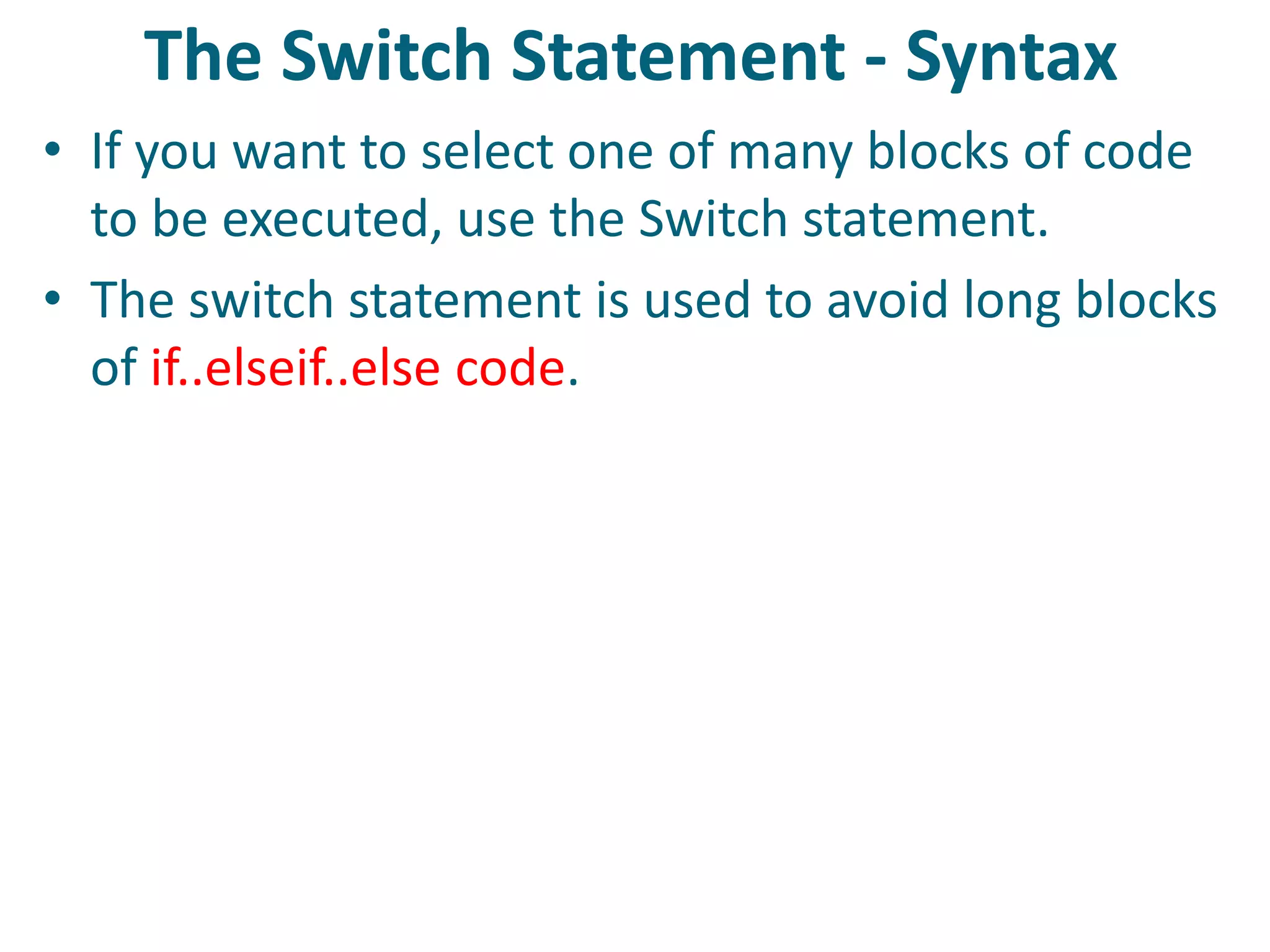
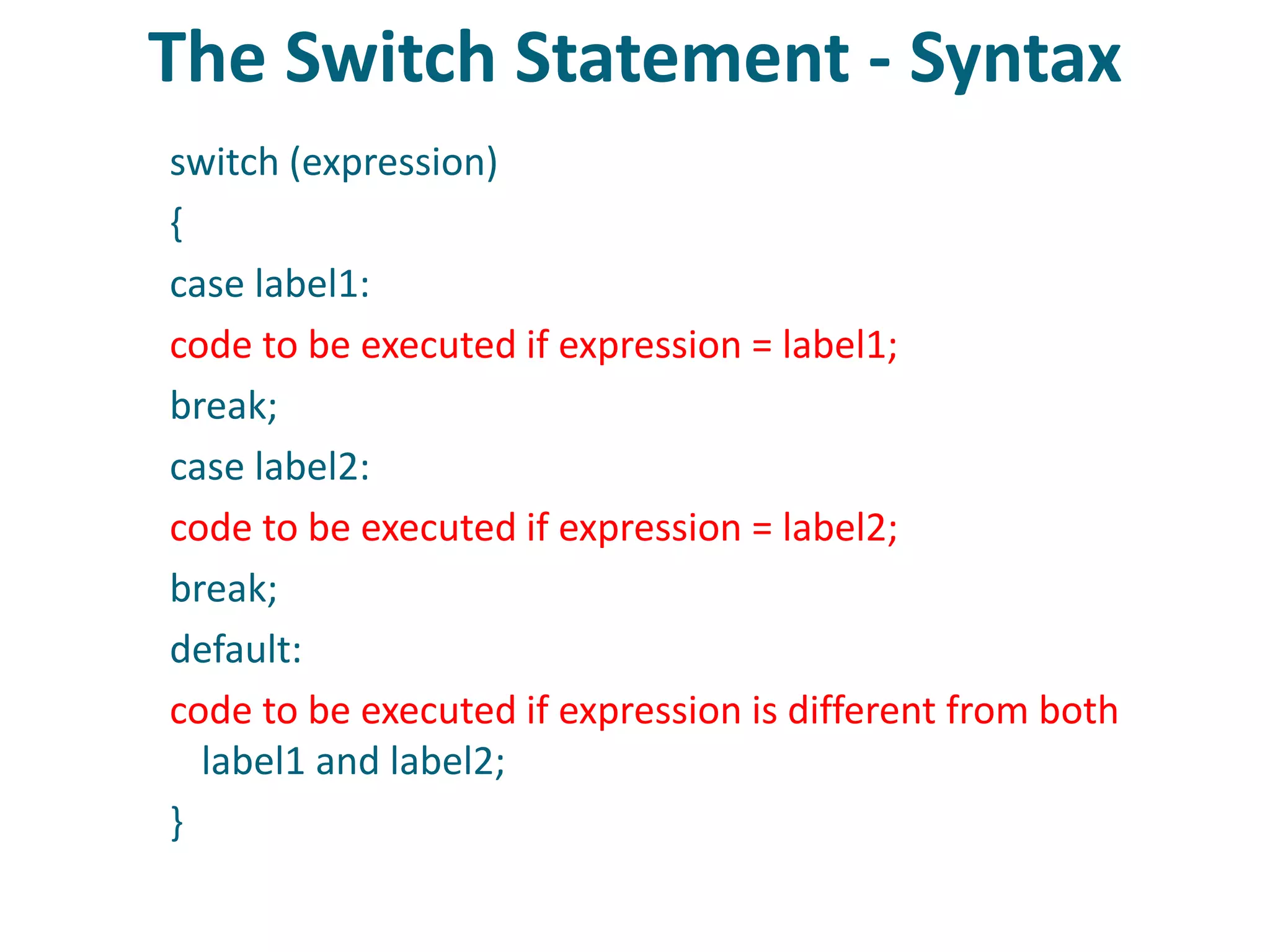
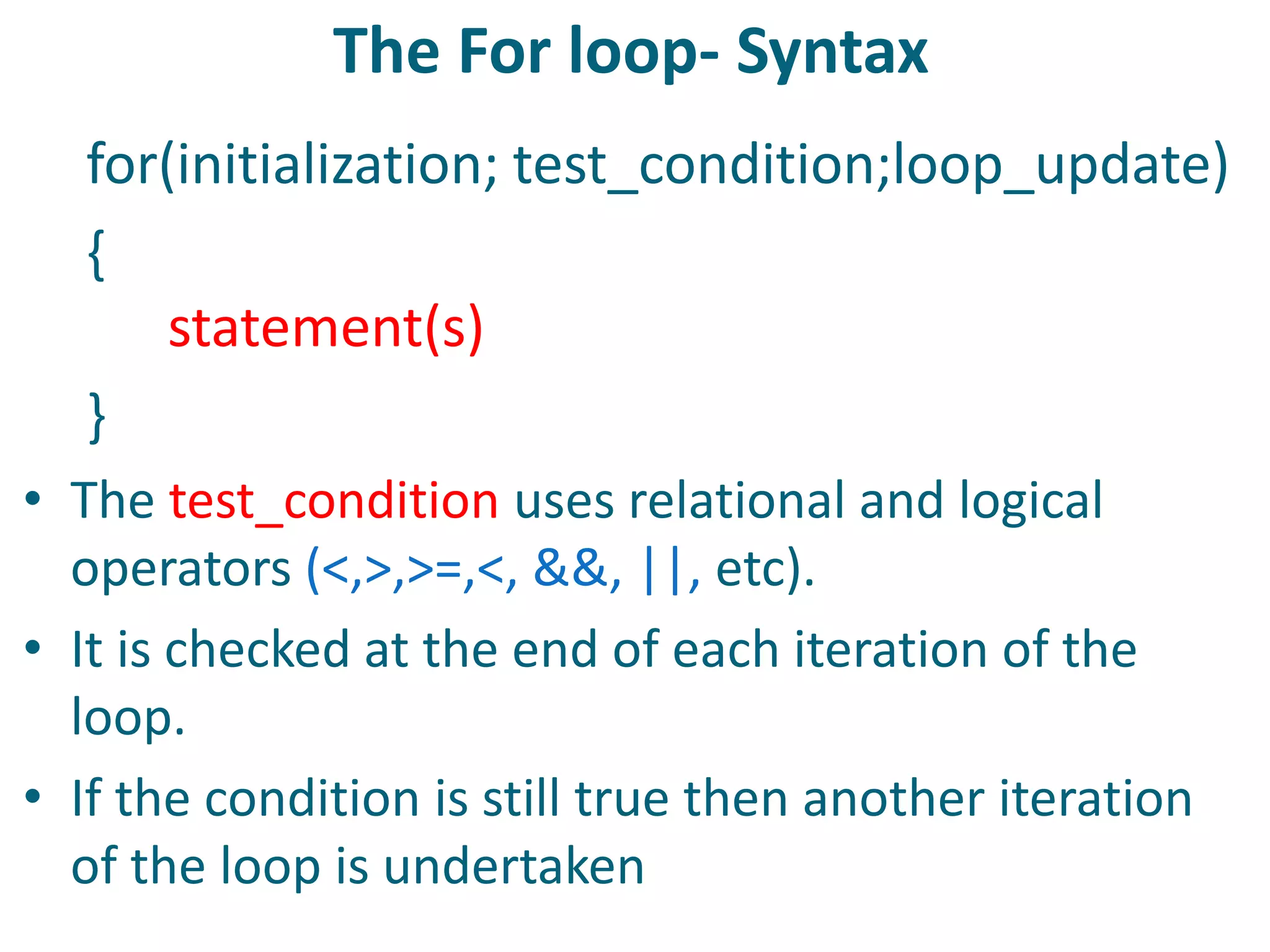
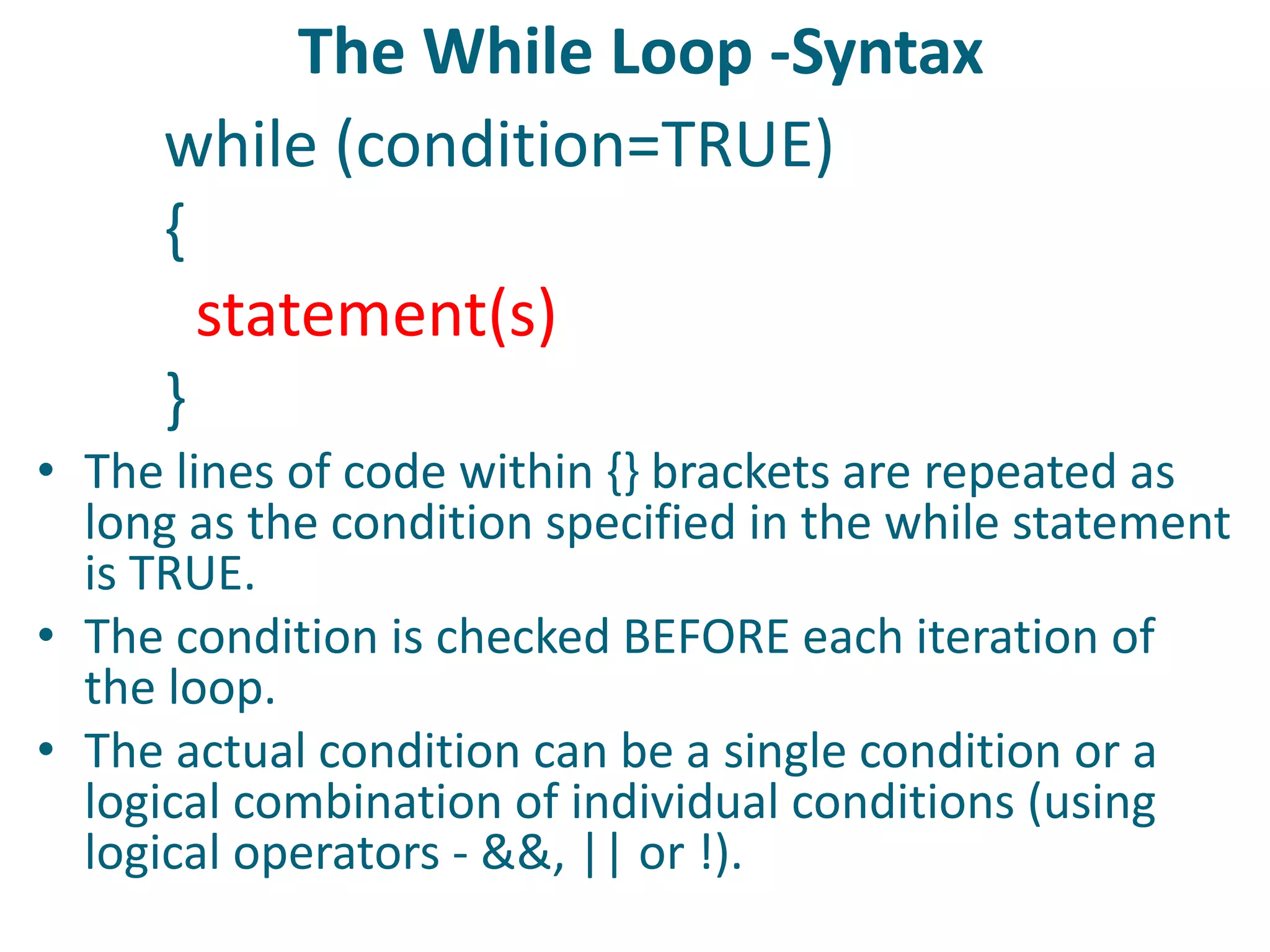
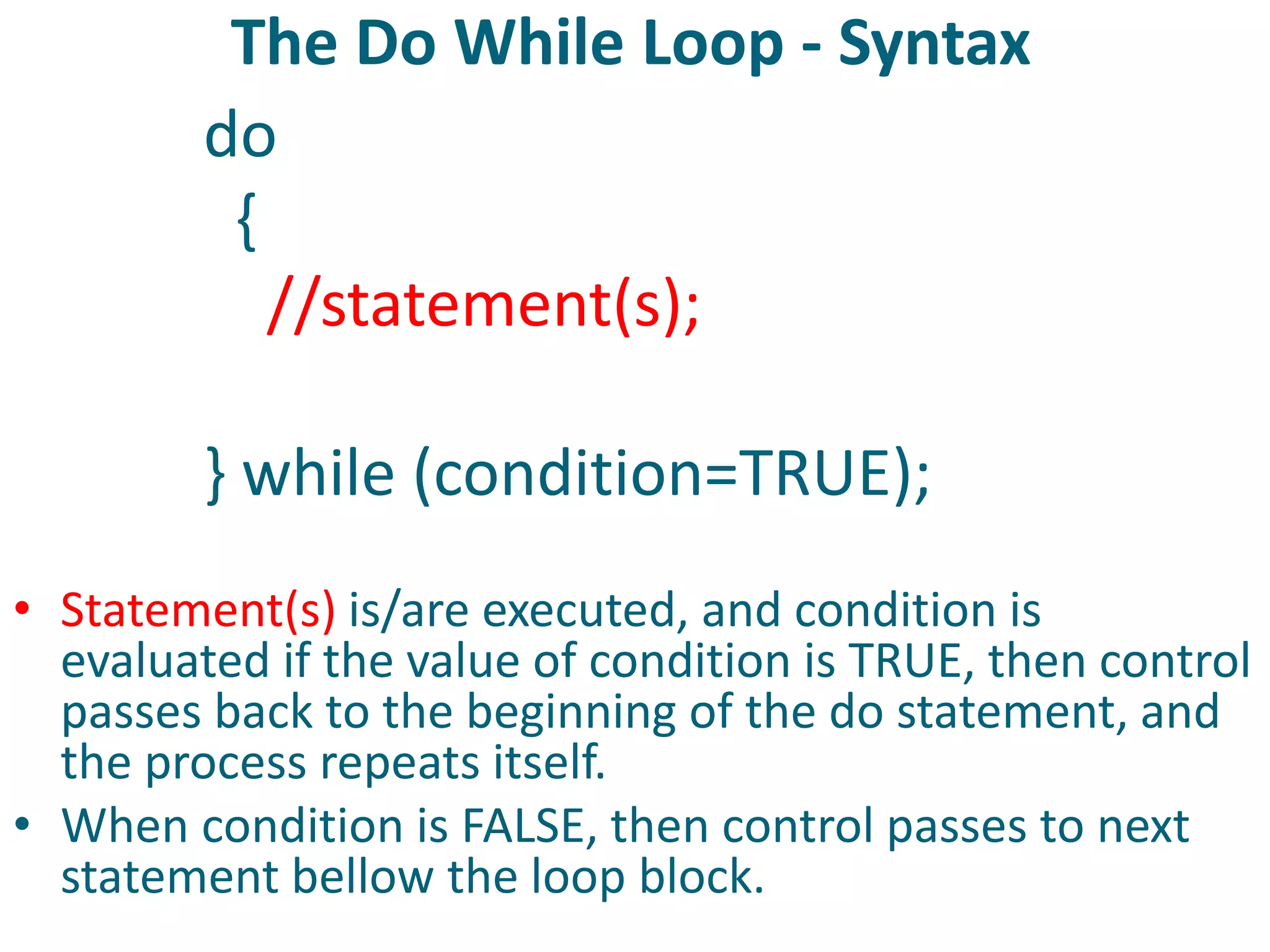
This document discusses server-side scripting and provides examples using PHP. It introduces server-side scripting languages like PHP, ASP, and JSP that generate dynamic web pages using scripts interpreted by applications on the web server. It also describes basic PHP syntax including variables, conditional statements, loops and communicating with databases to store and retrieve information.