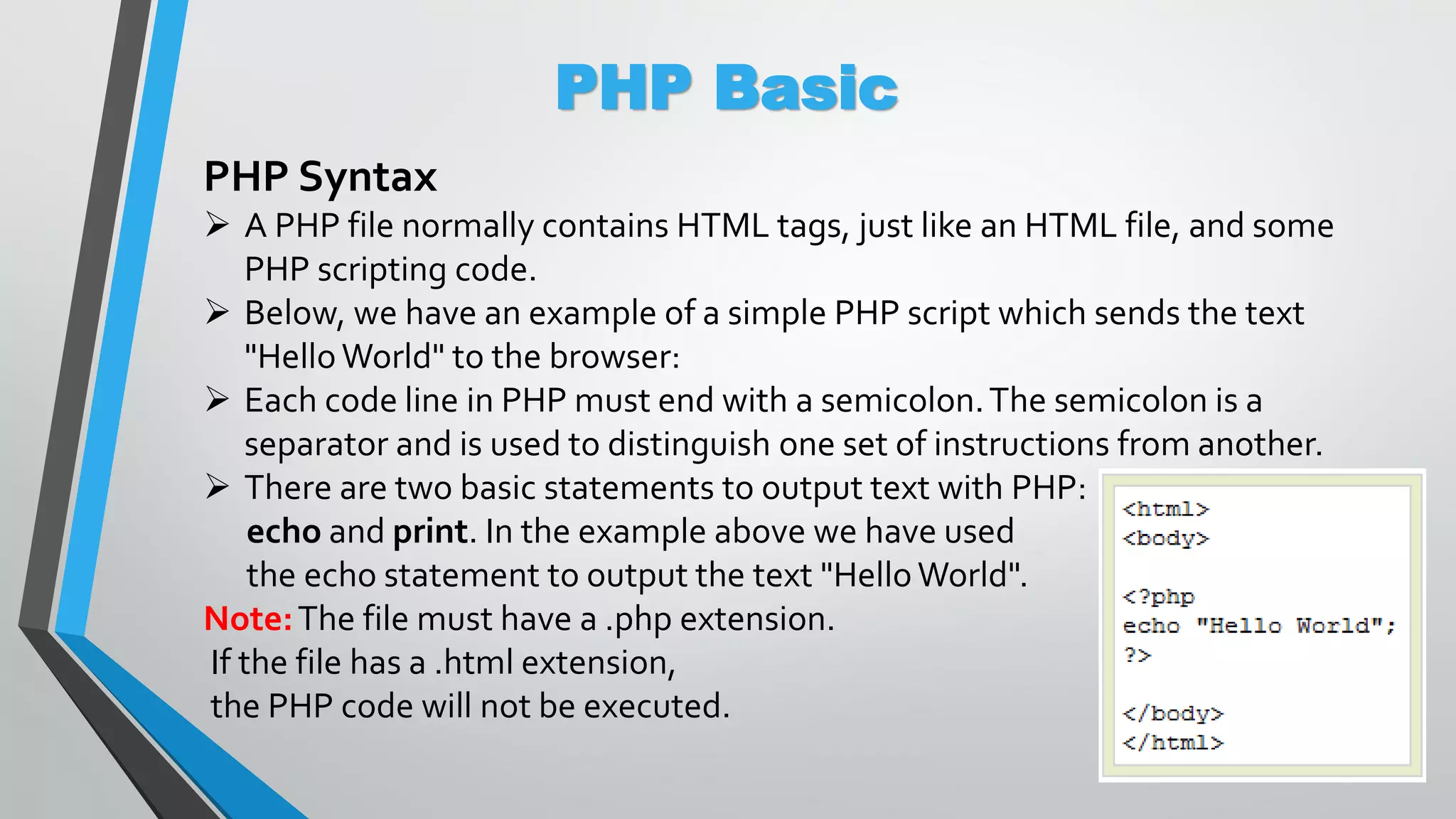
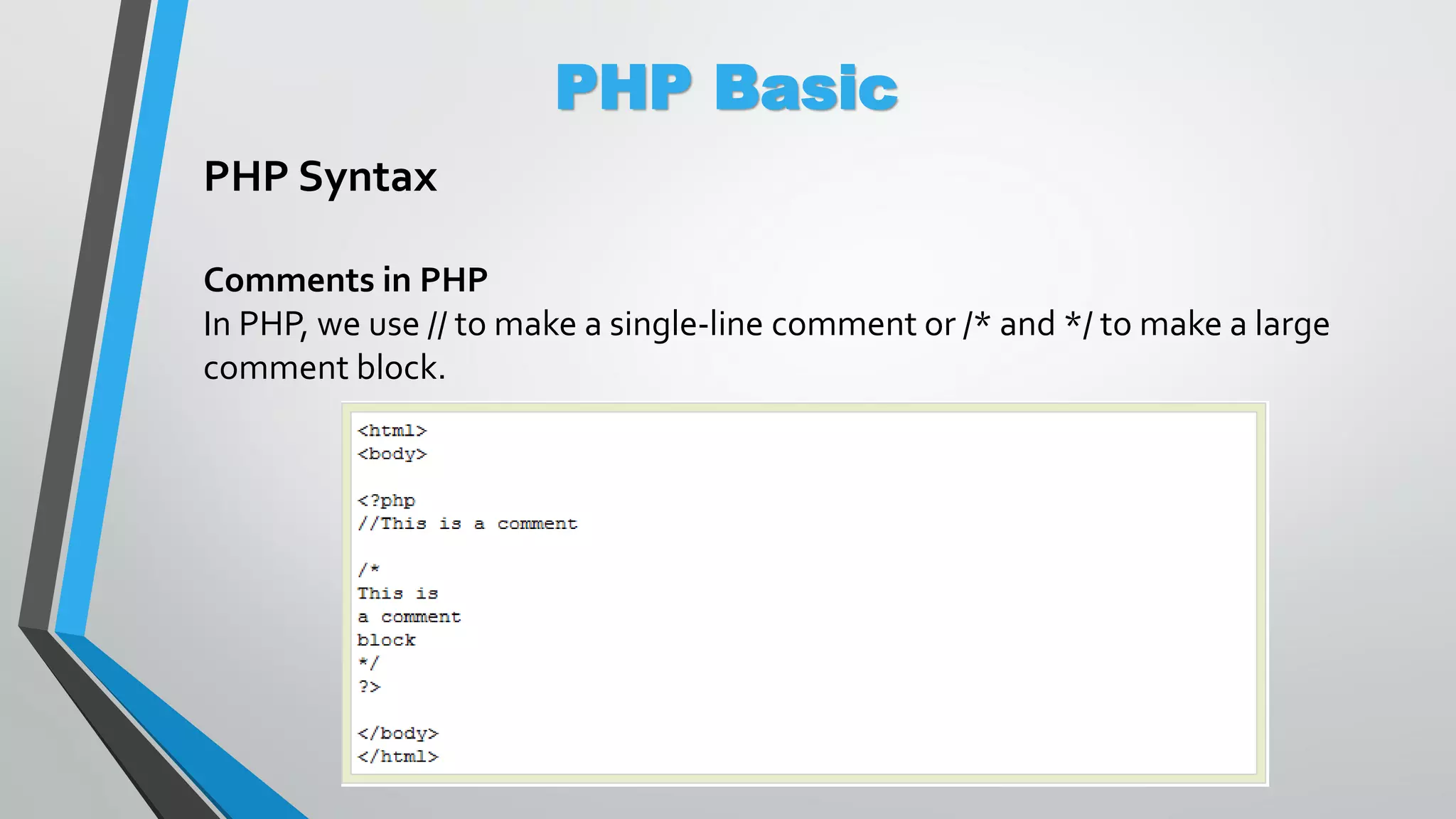
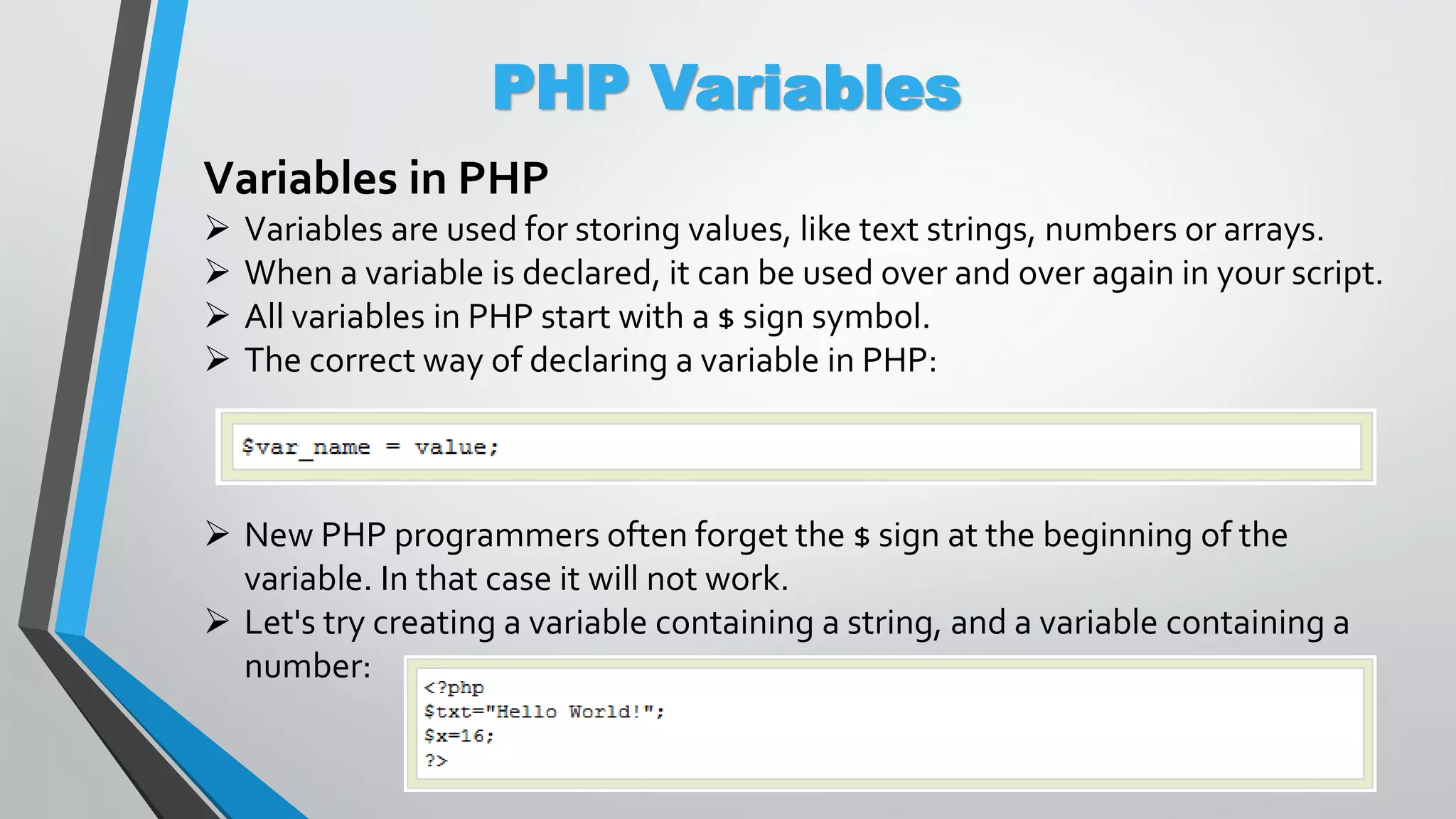
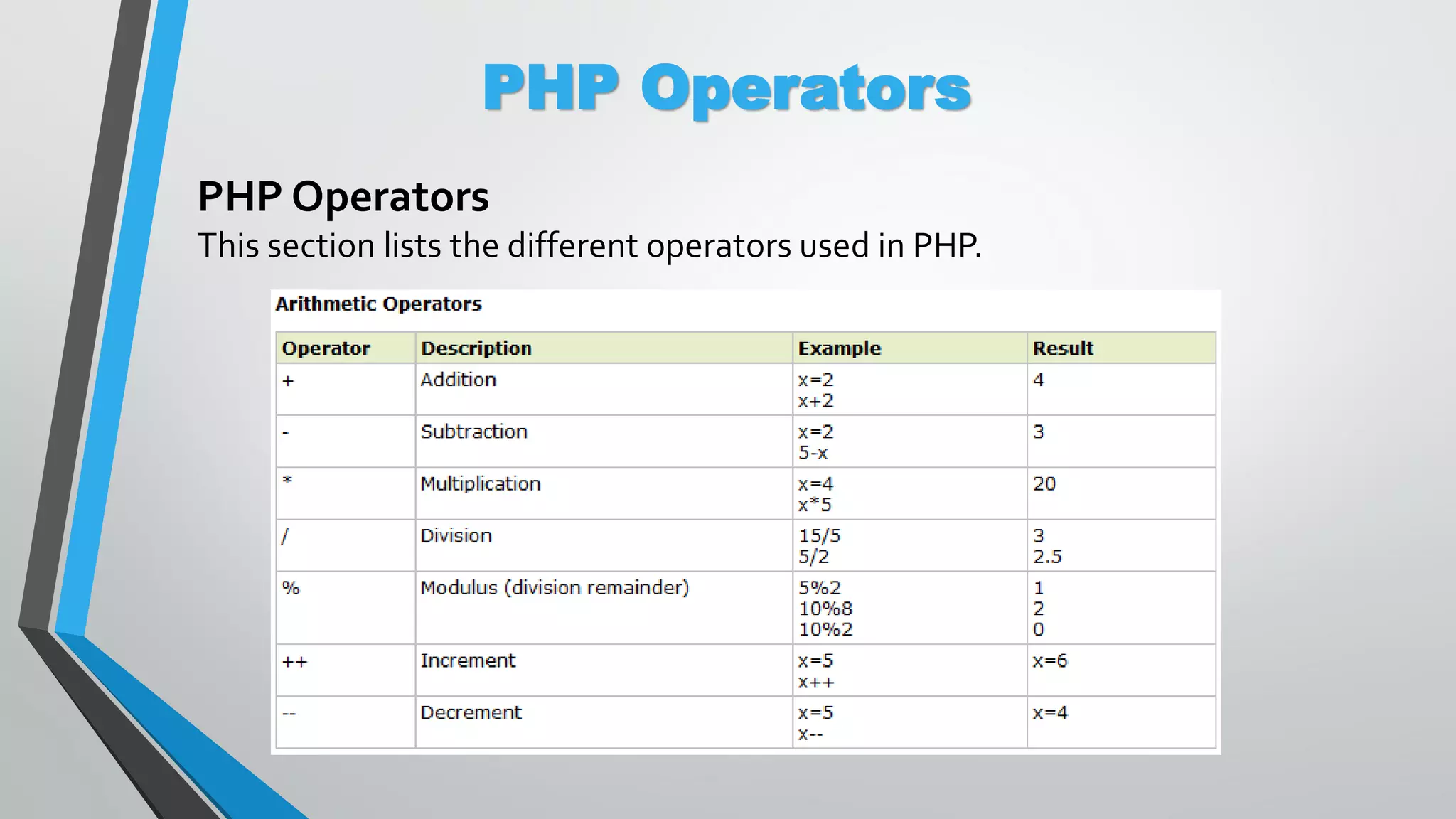
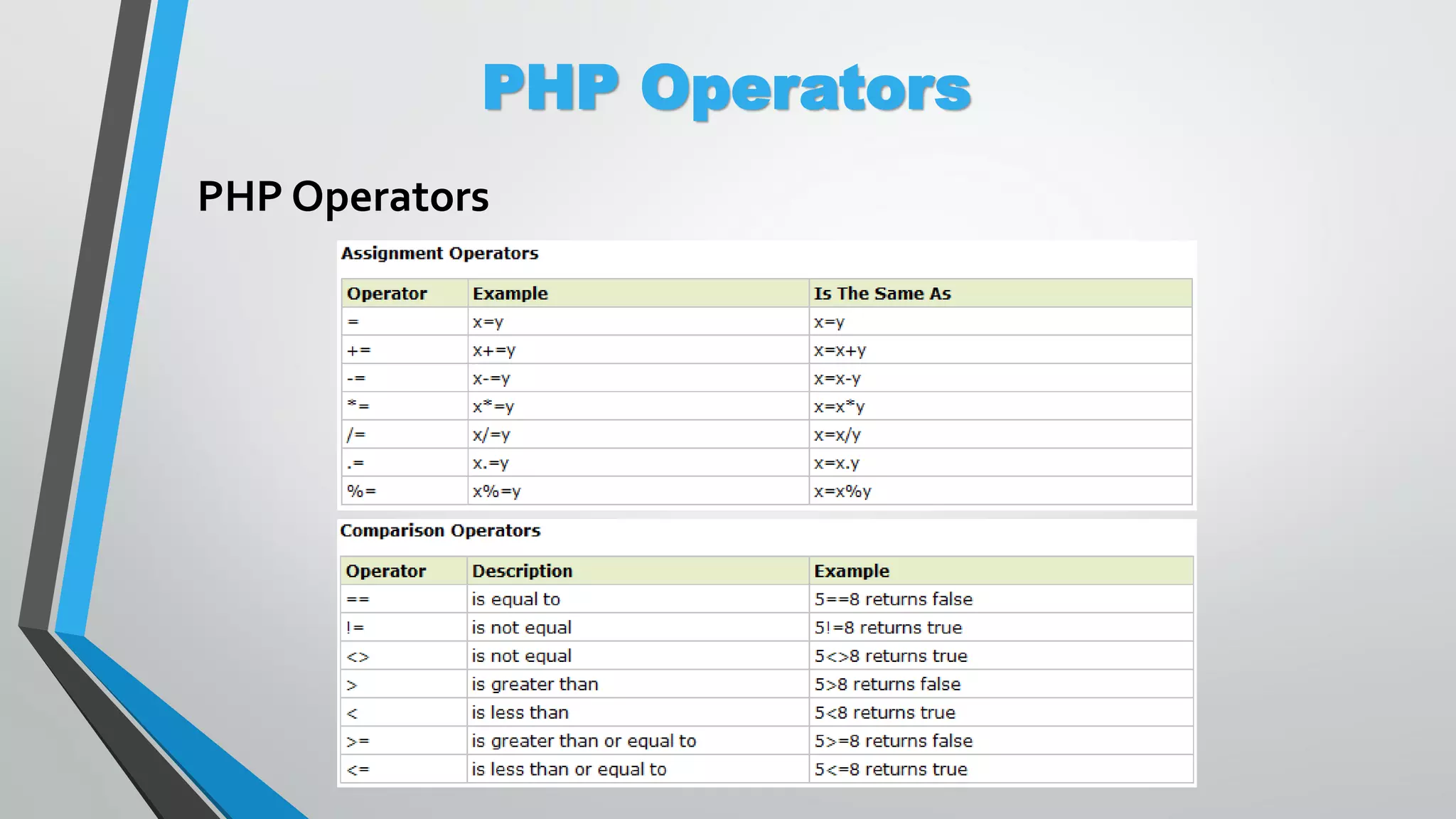
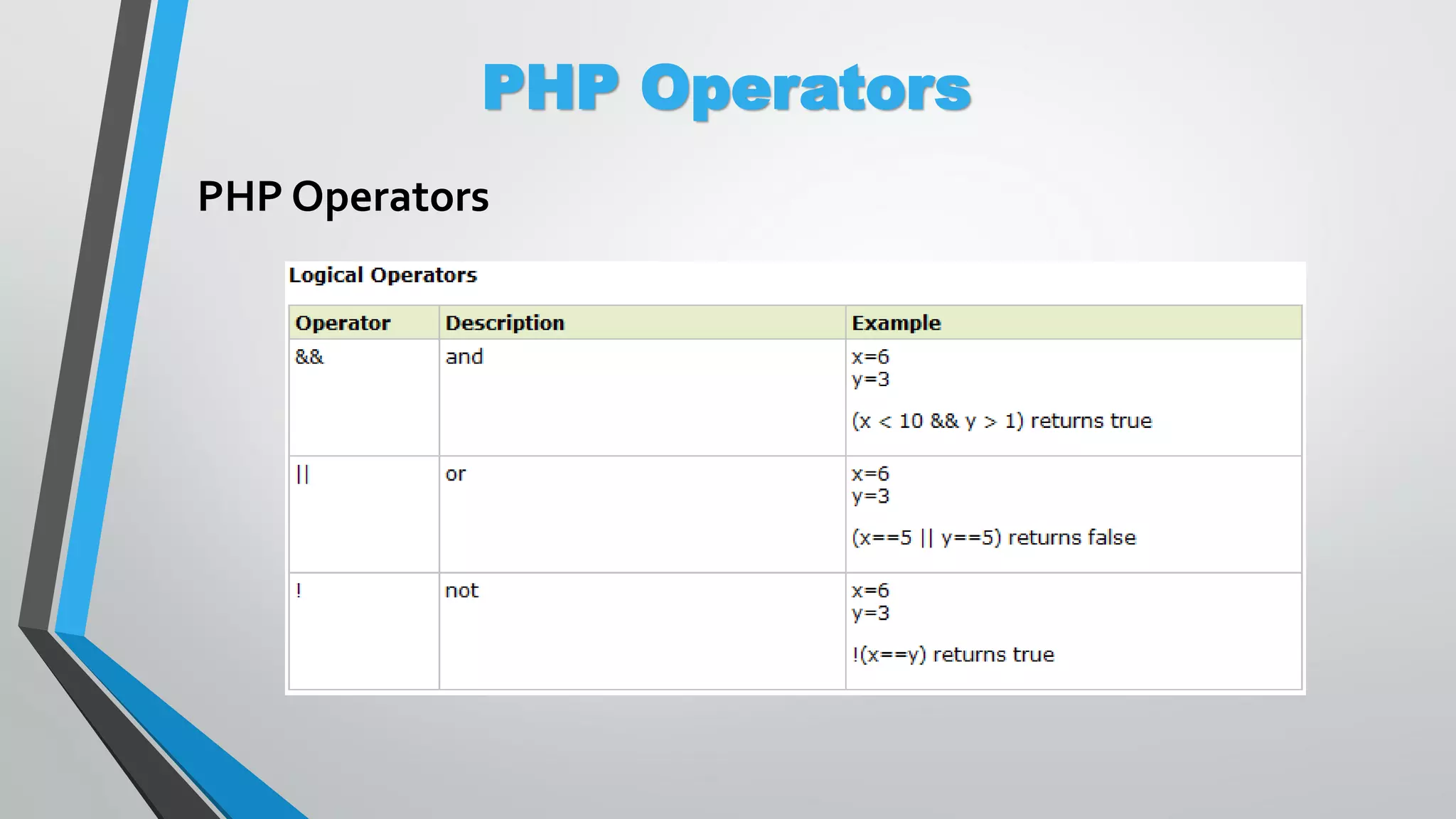
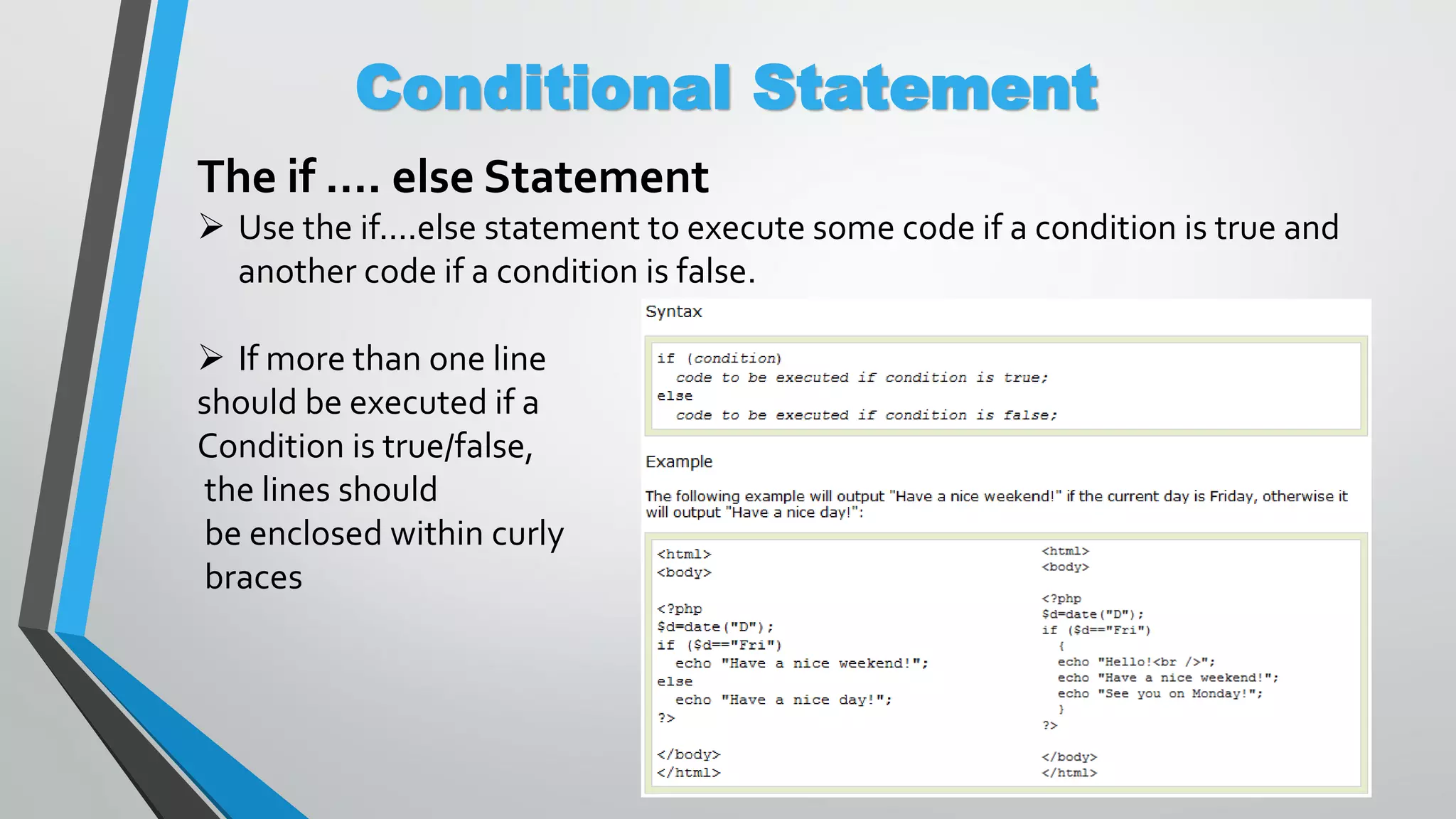
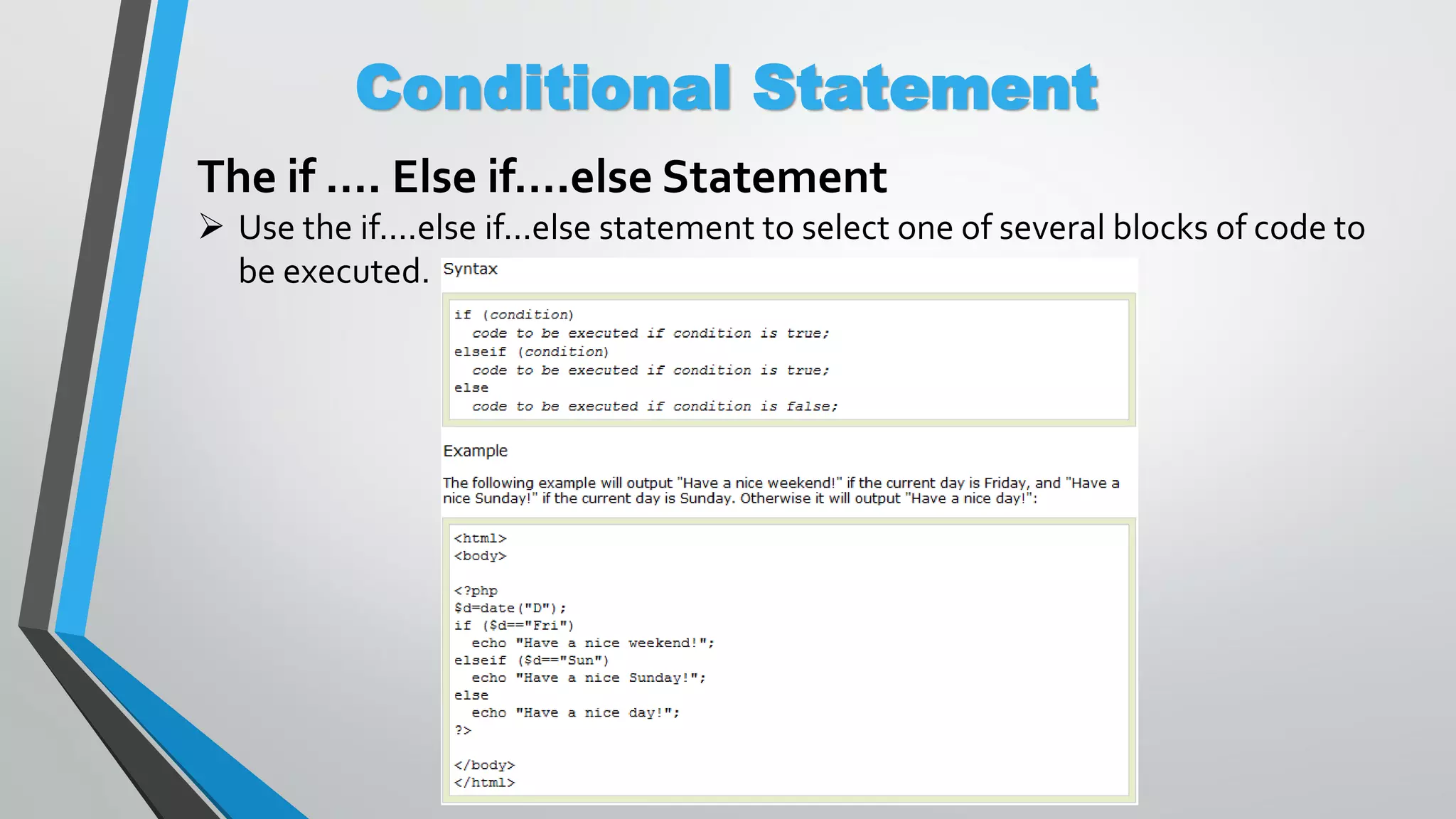
The document provides an overview of PHP, a server-side scripting language, including its capabilities, compatibility with databases like MySQL, and basic syntax. It covers fundamental concepts such as variables, conditional statements, and the structure of PHP files. Additionally, it outlines how to get started with PHP by setting up a web server or using a hosting plan.