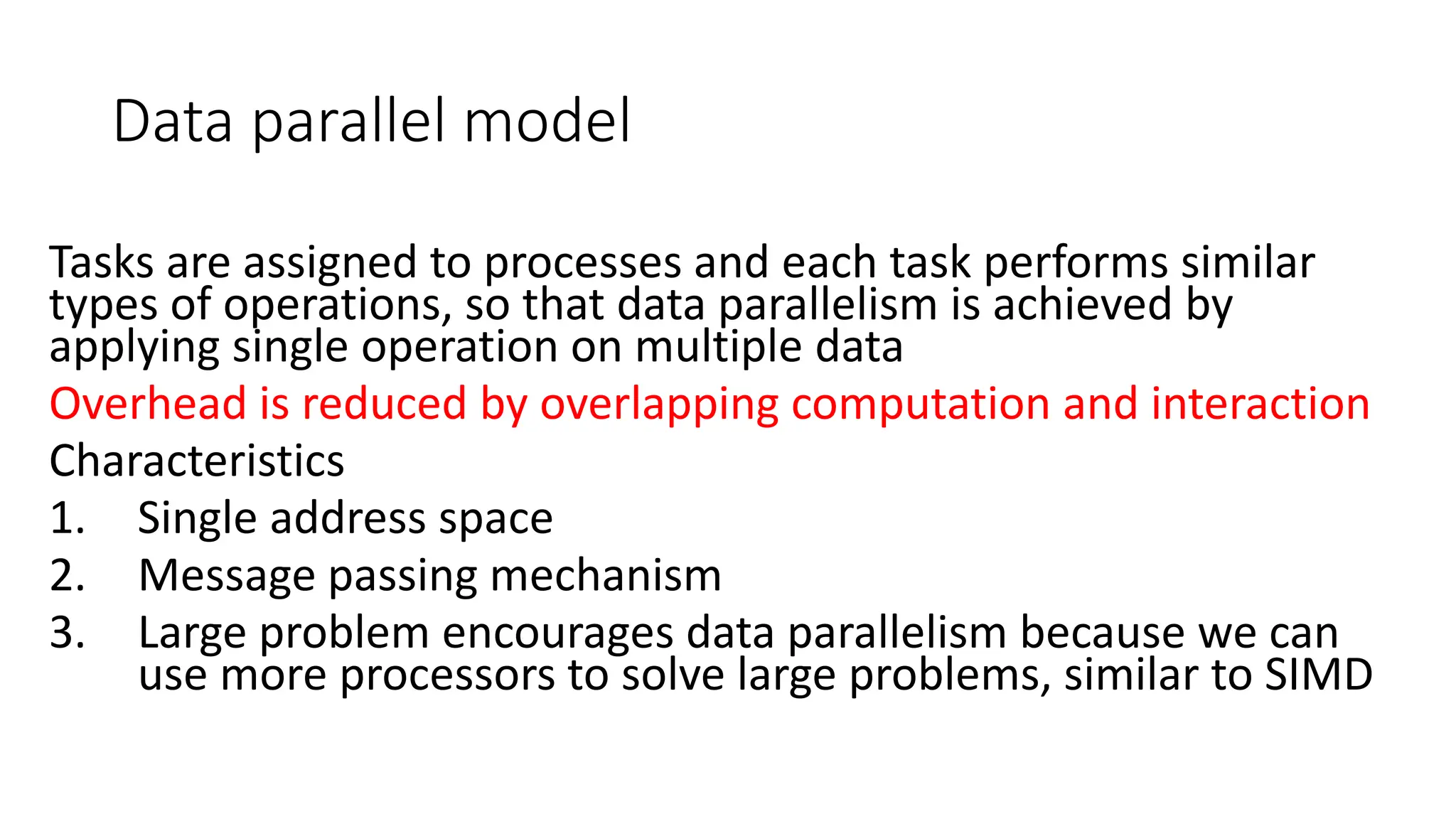
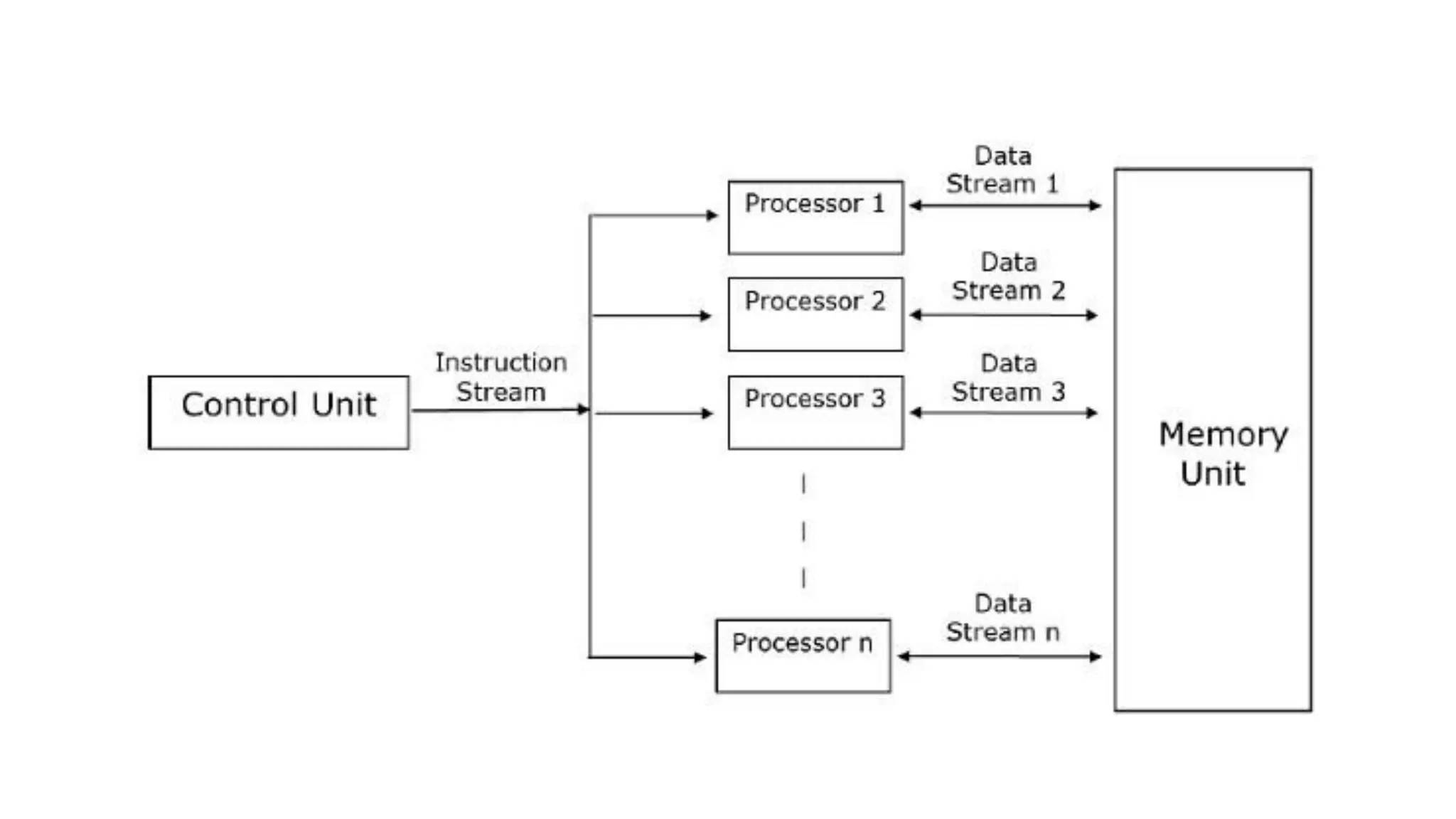
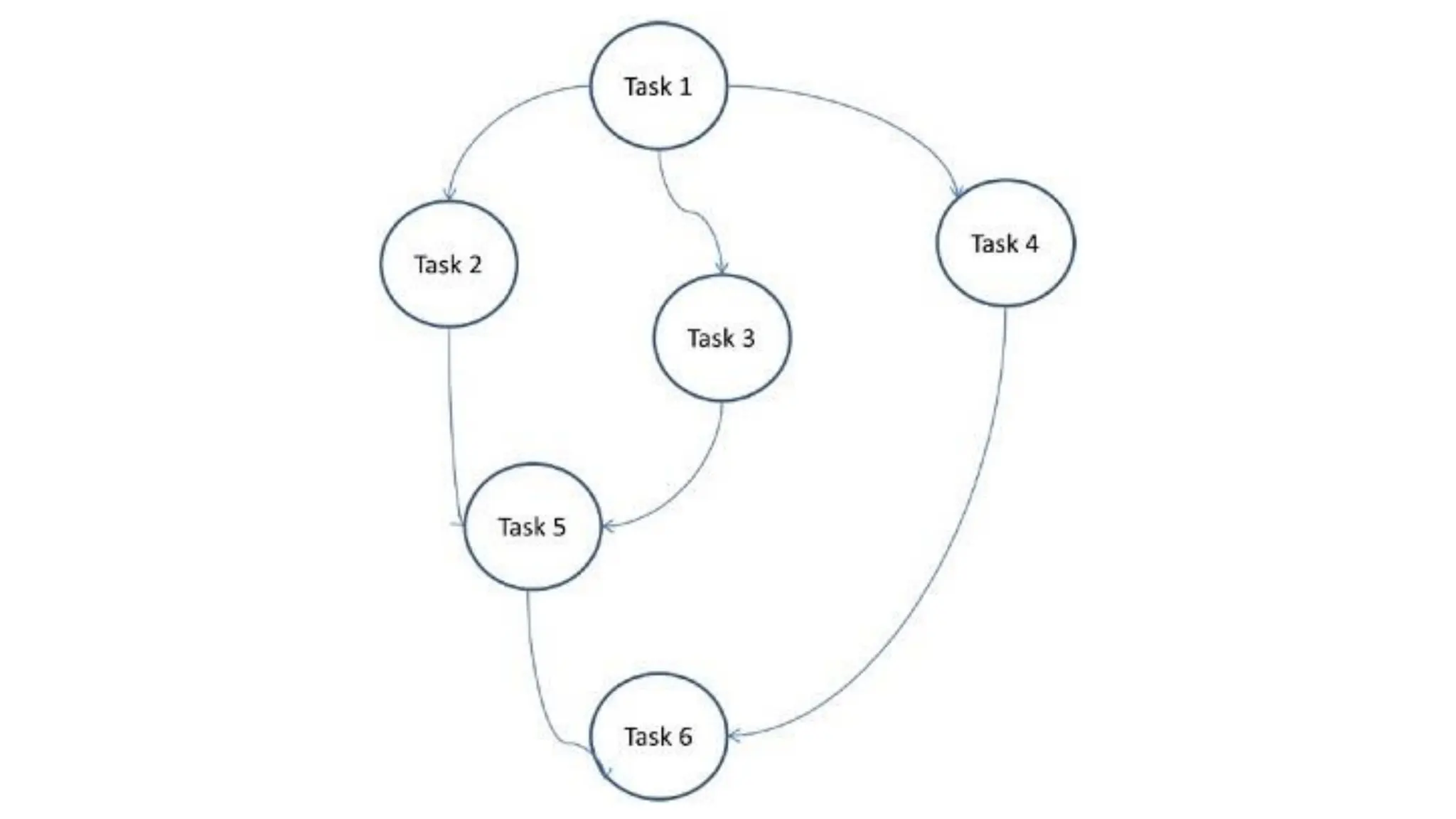
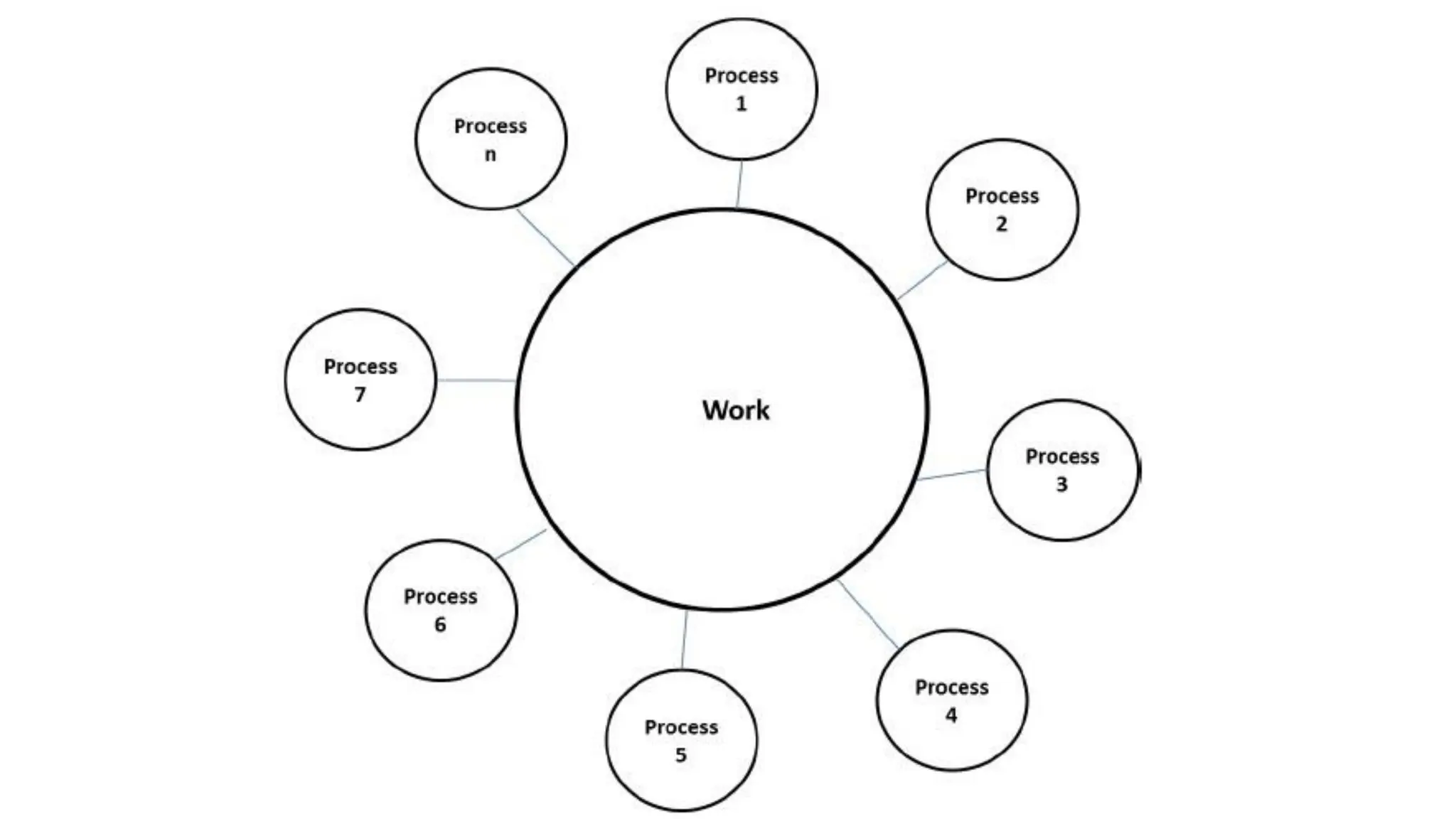
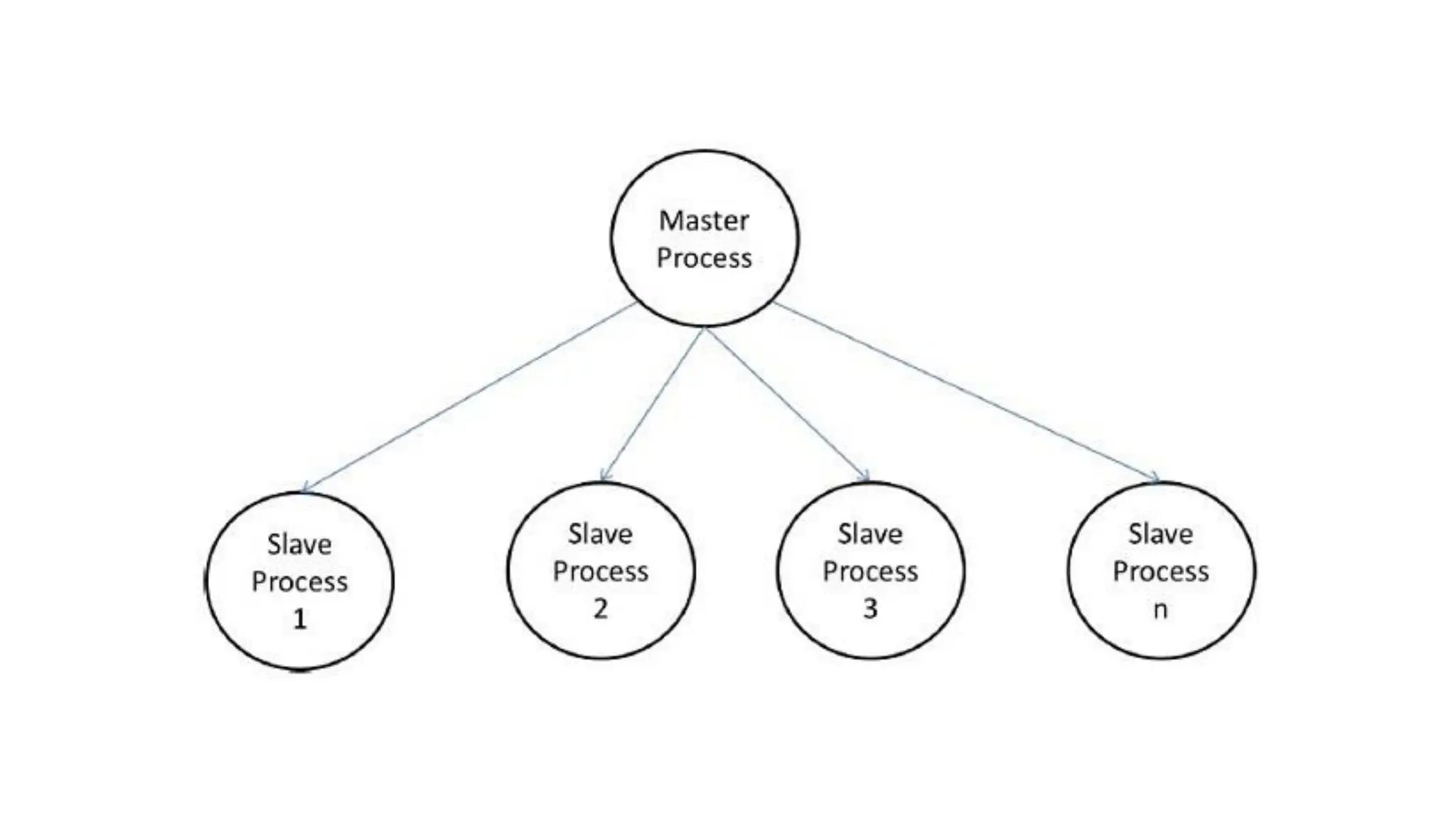
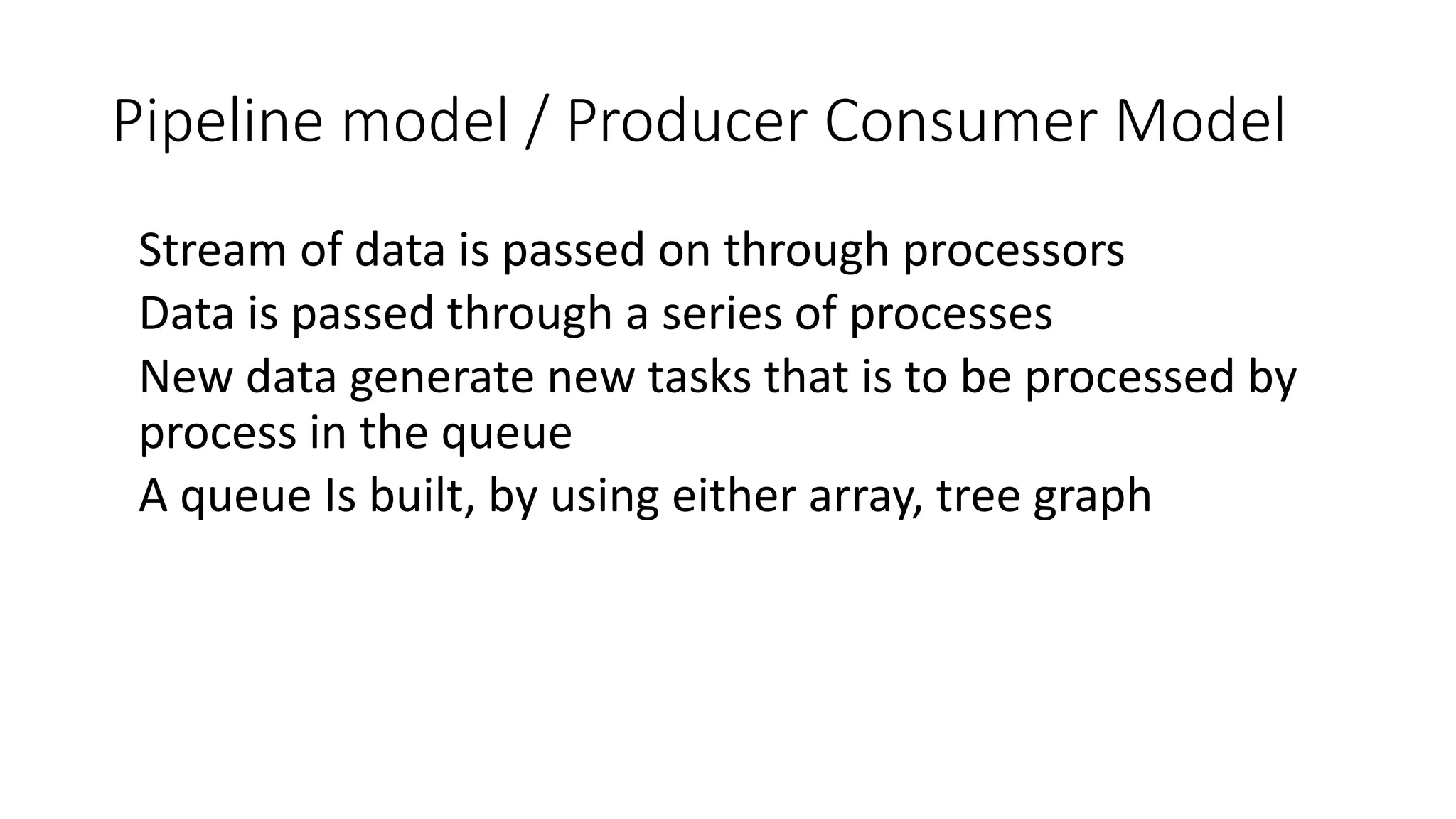
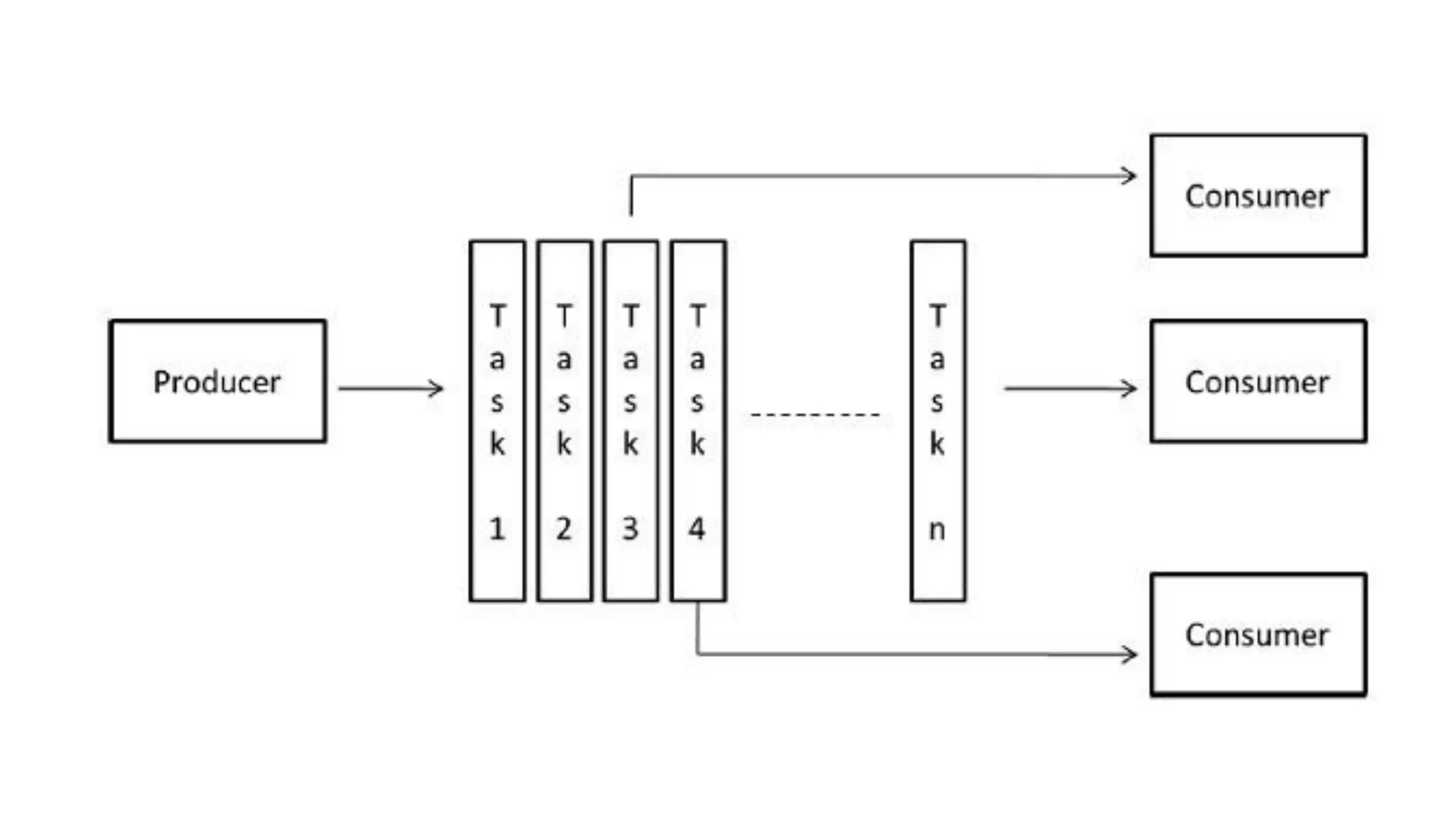
This document outlines several parallel algorithm models: 1) Data parallel models divide data among processes that perform similar operations to achieve parallelism. They have low overhead through overlapping computation and communication. 2) The task graph model expresses parallelism through a task graph and is suitable when there is a large amount of data but less computation. 3) The work pool model assigns tasks dynamically among processes to balance load. It is suitable when operations are large but data is small.