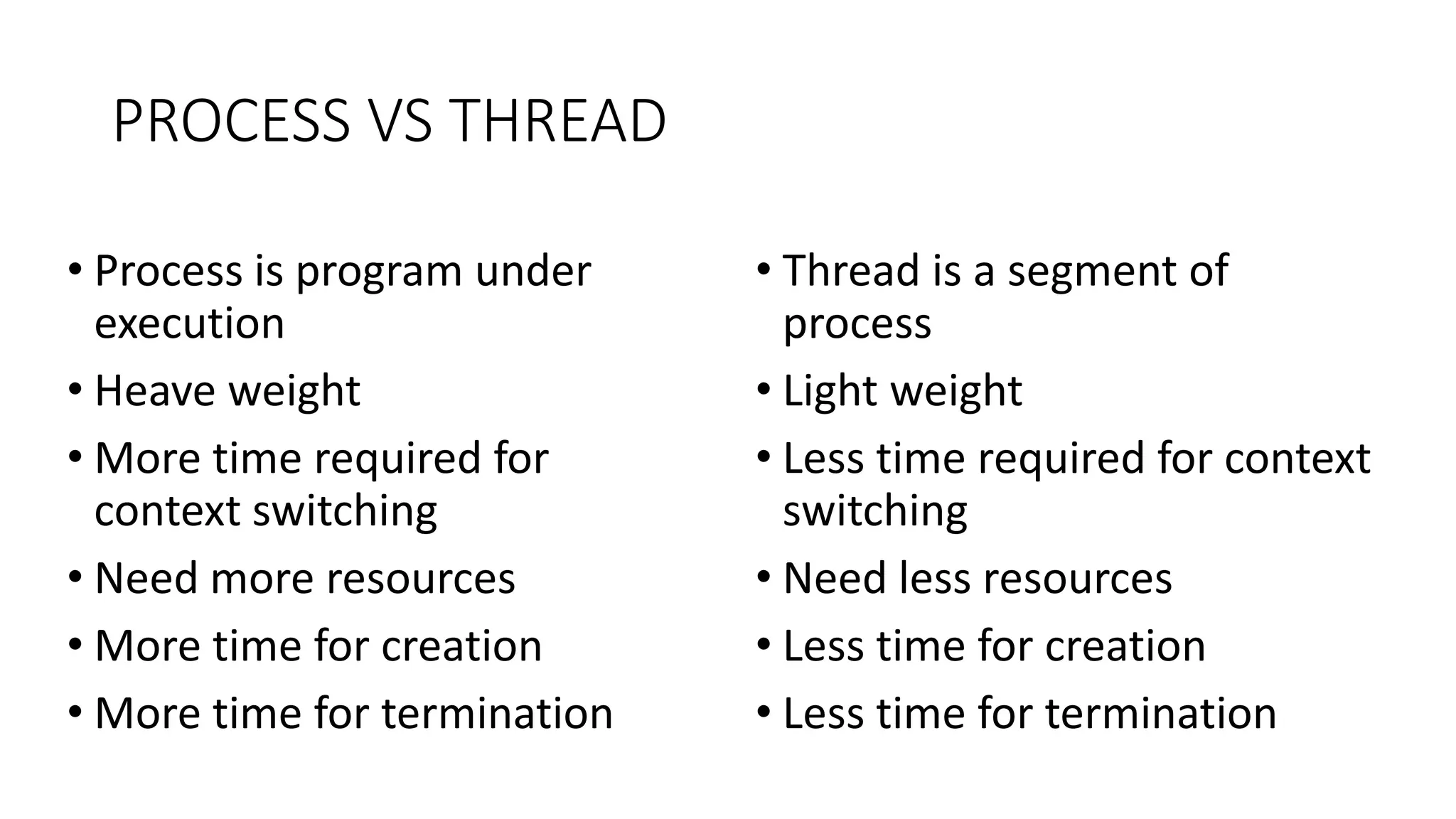
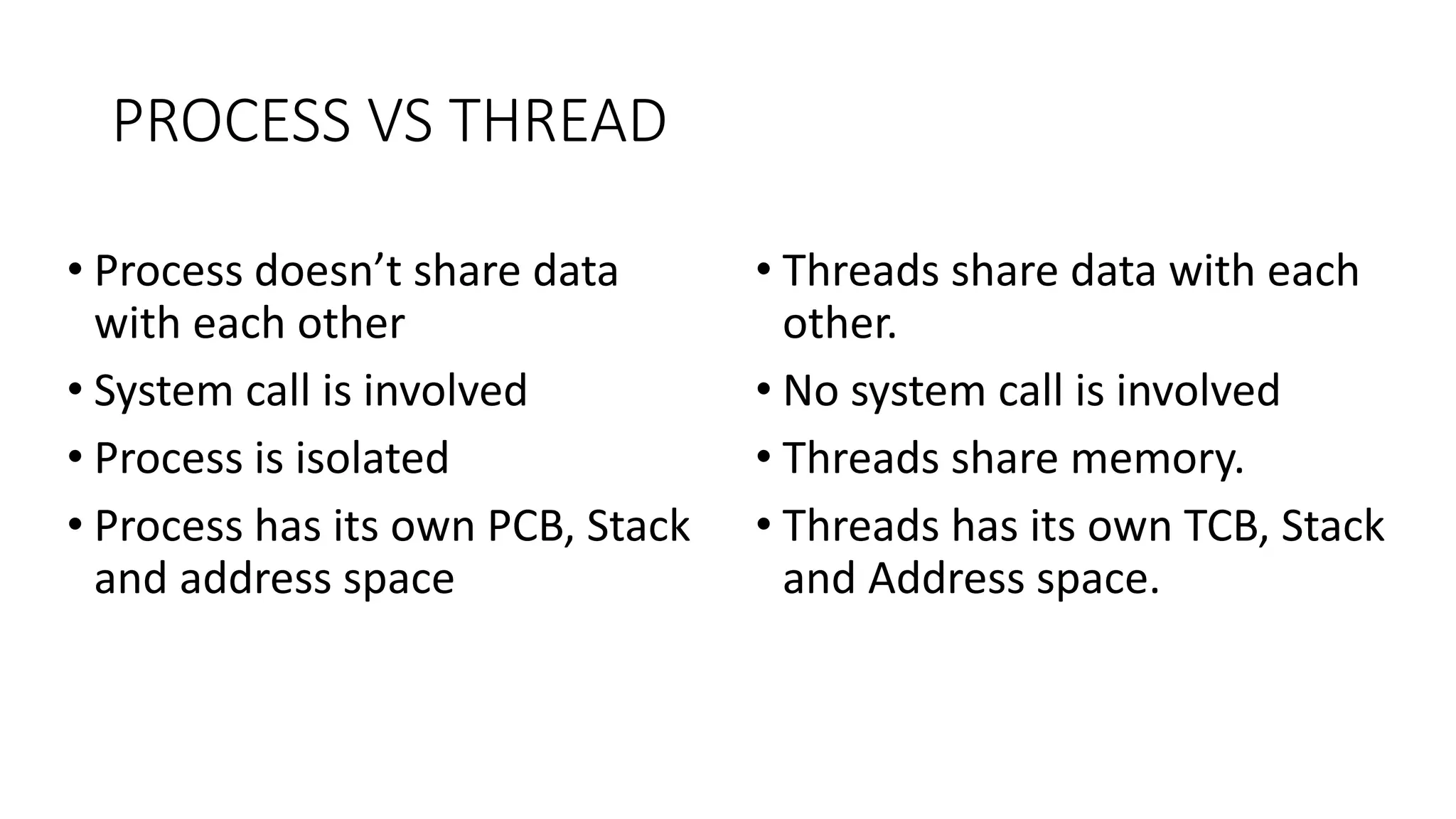
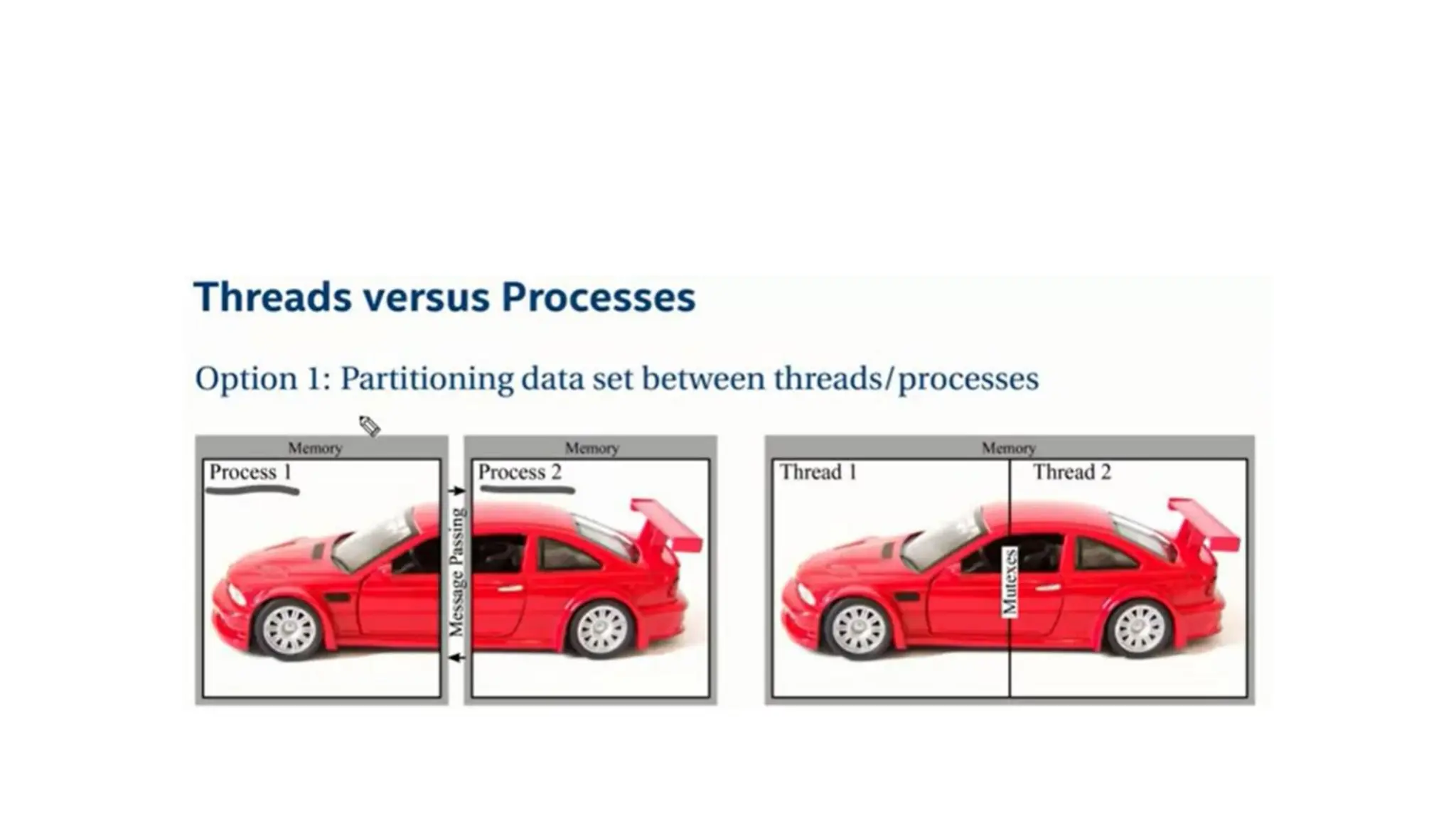
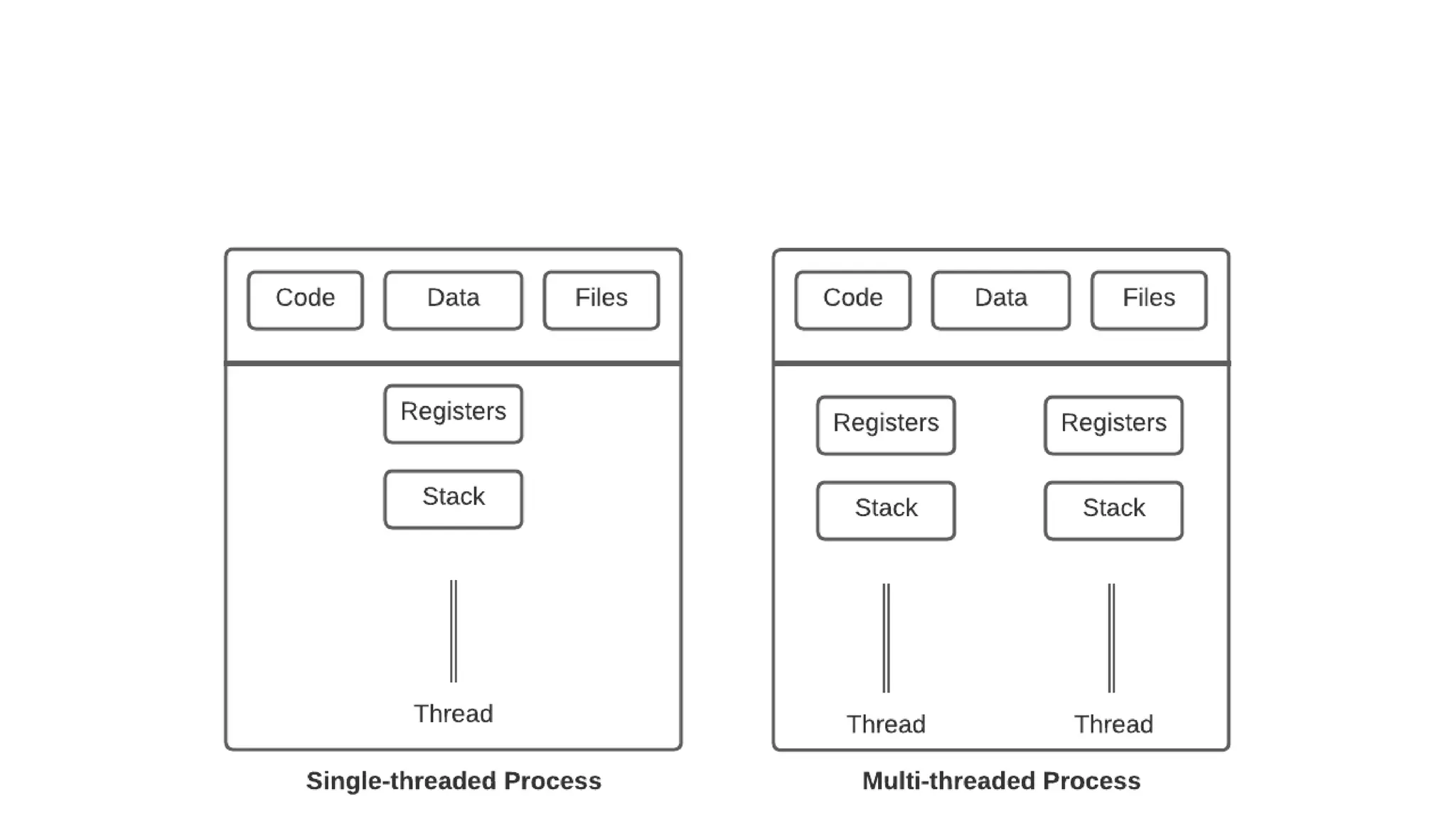
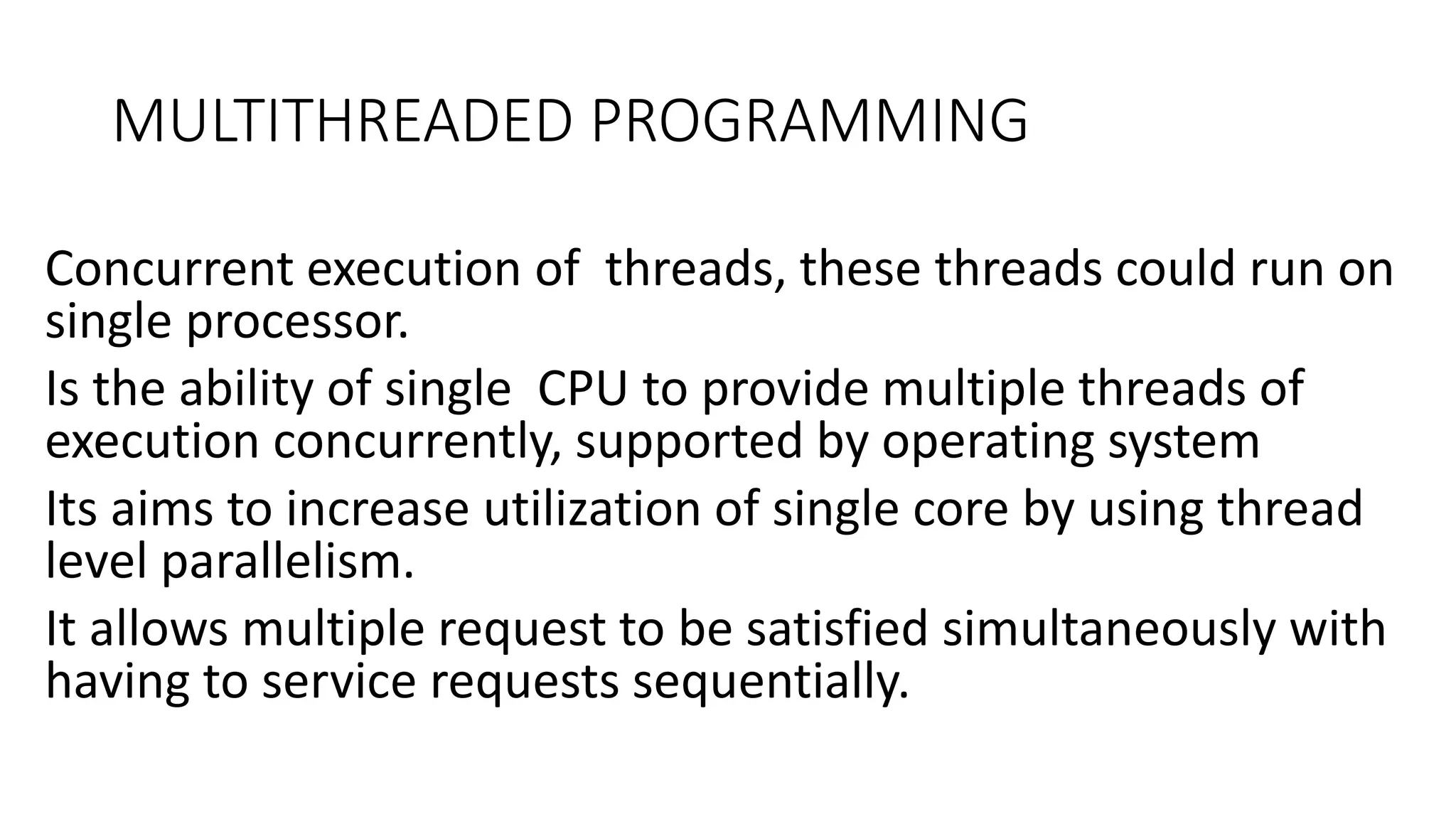
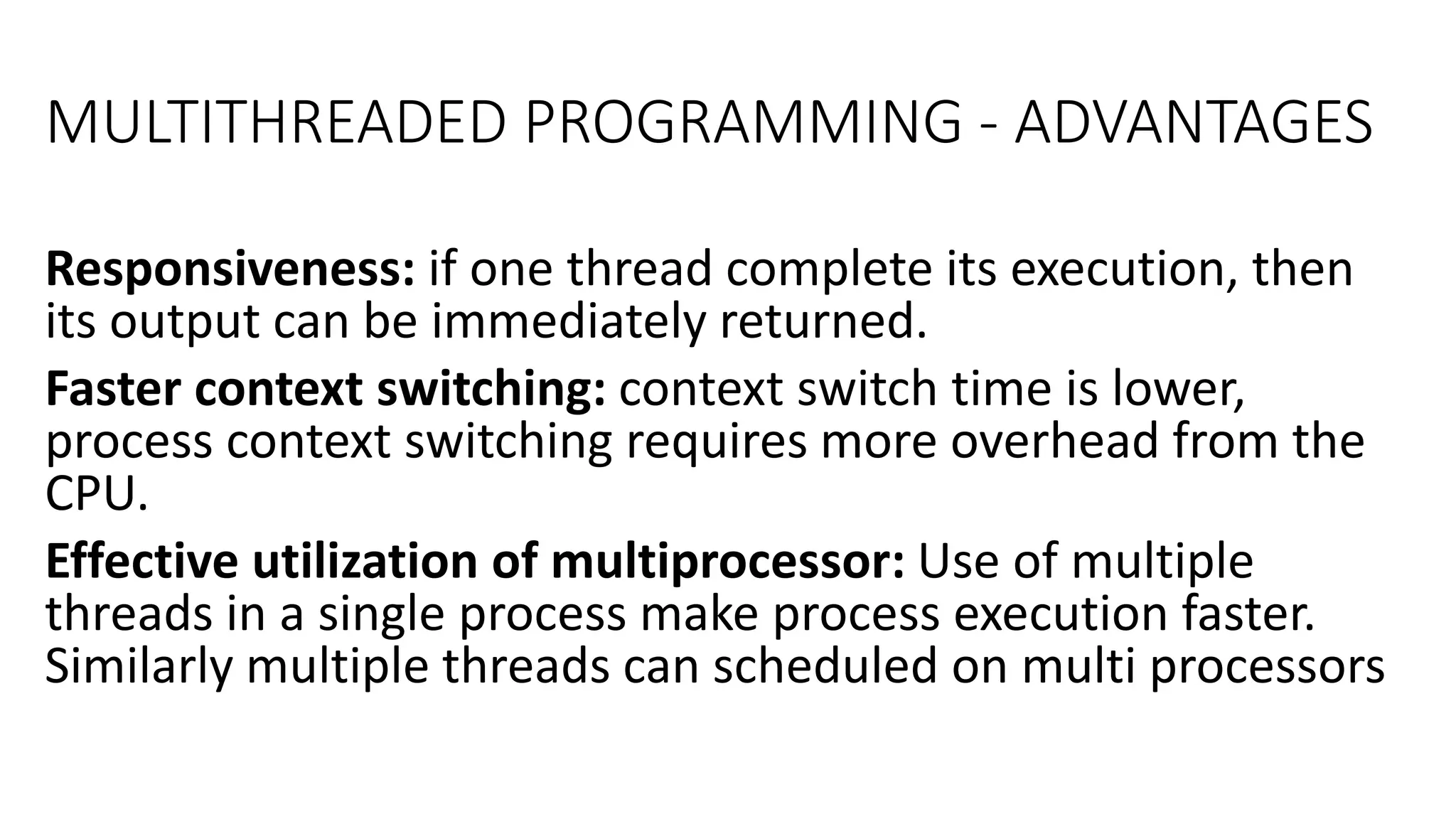
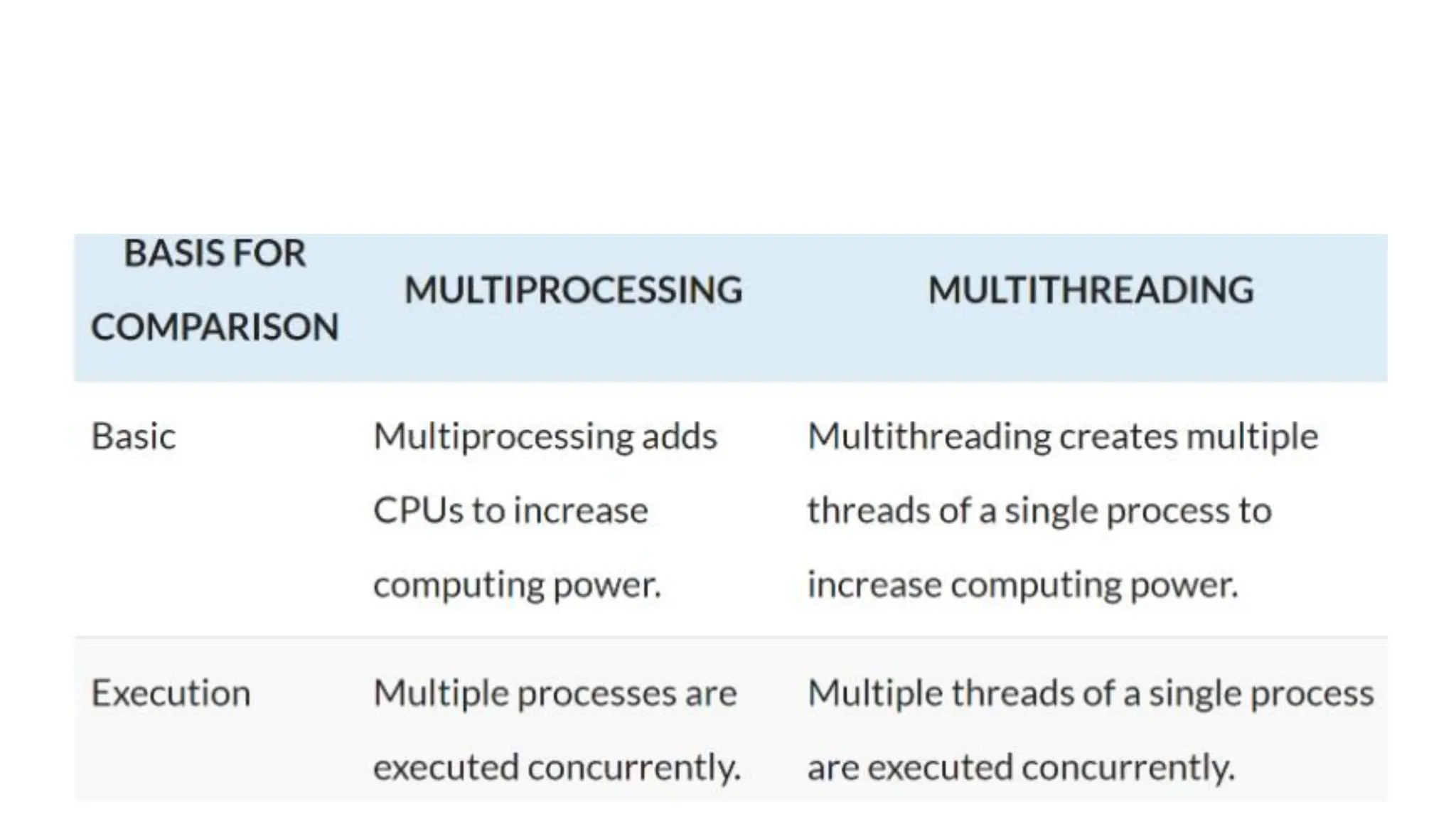
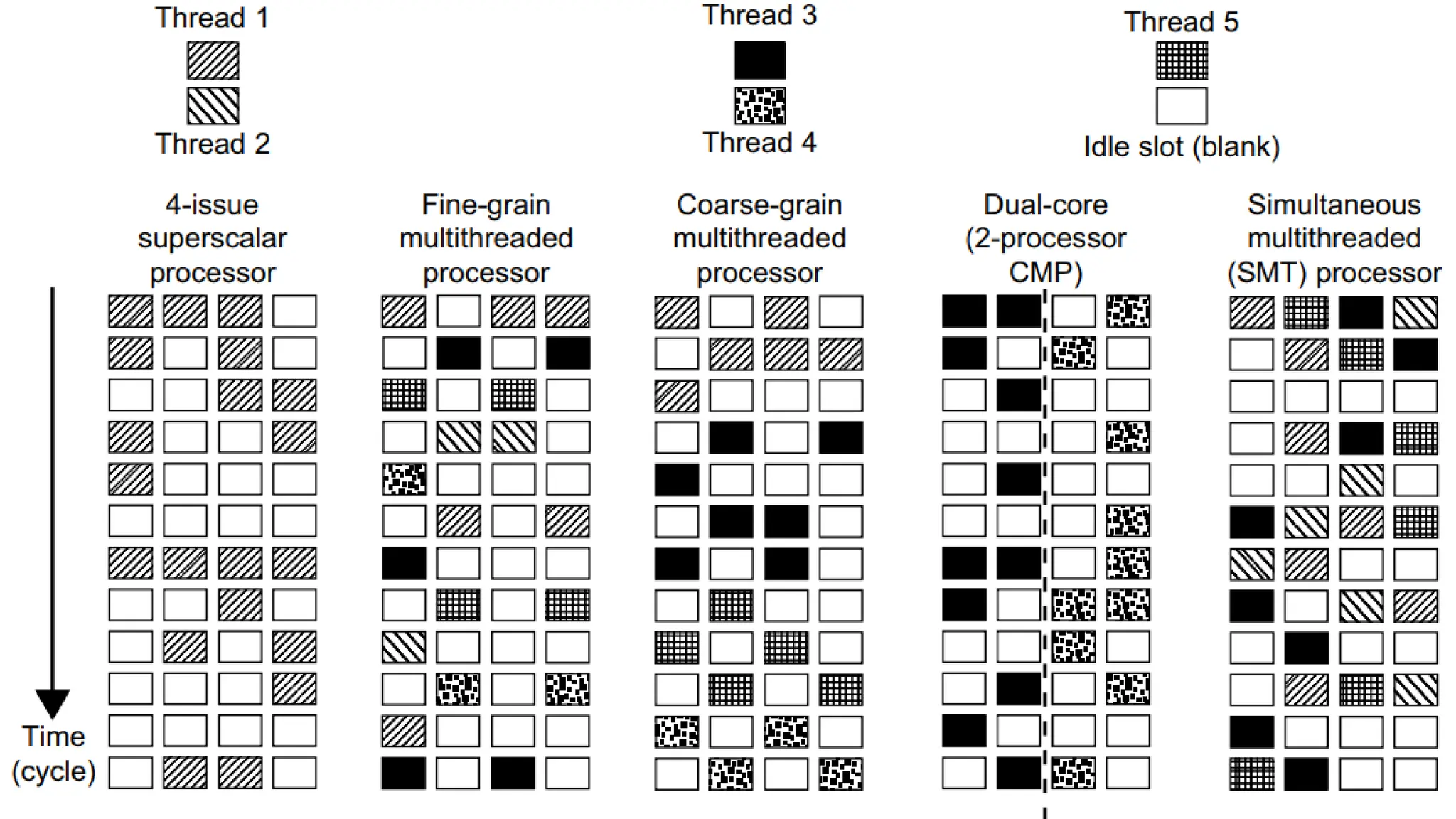
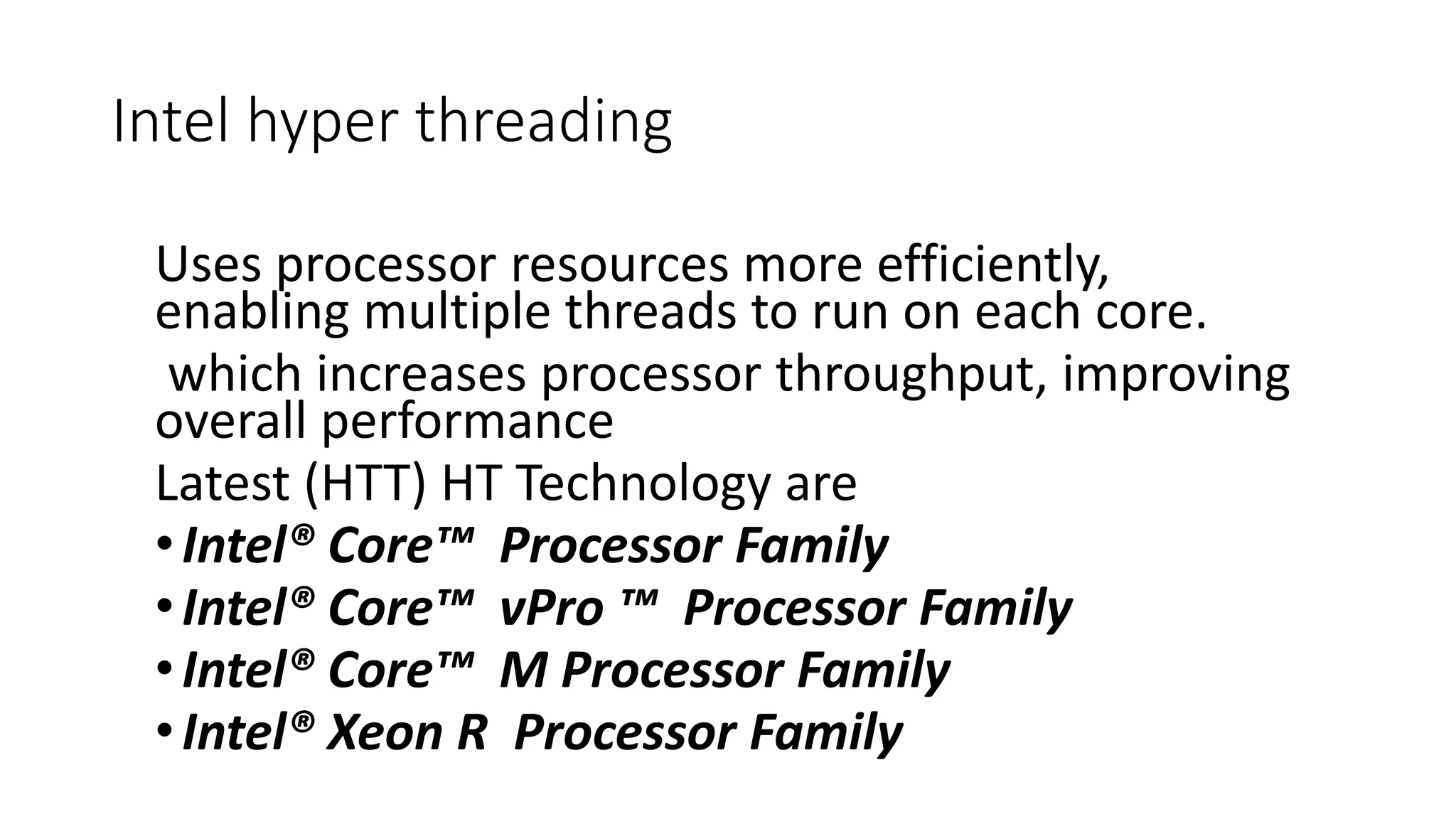
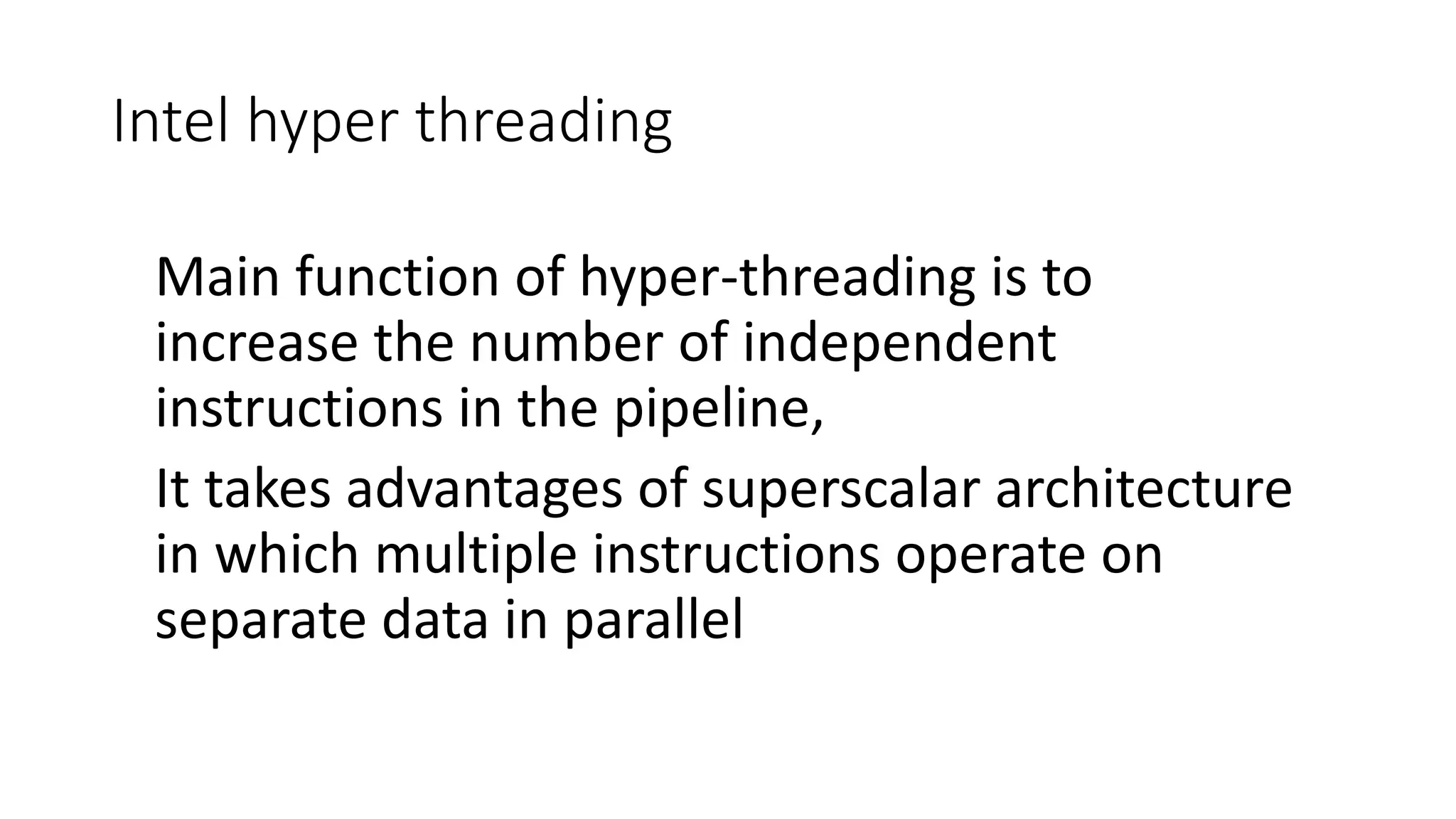
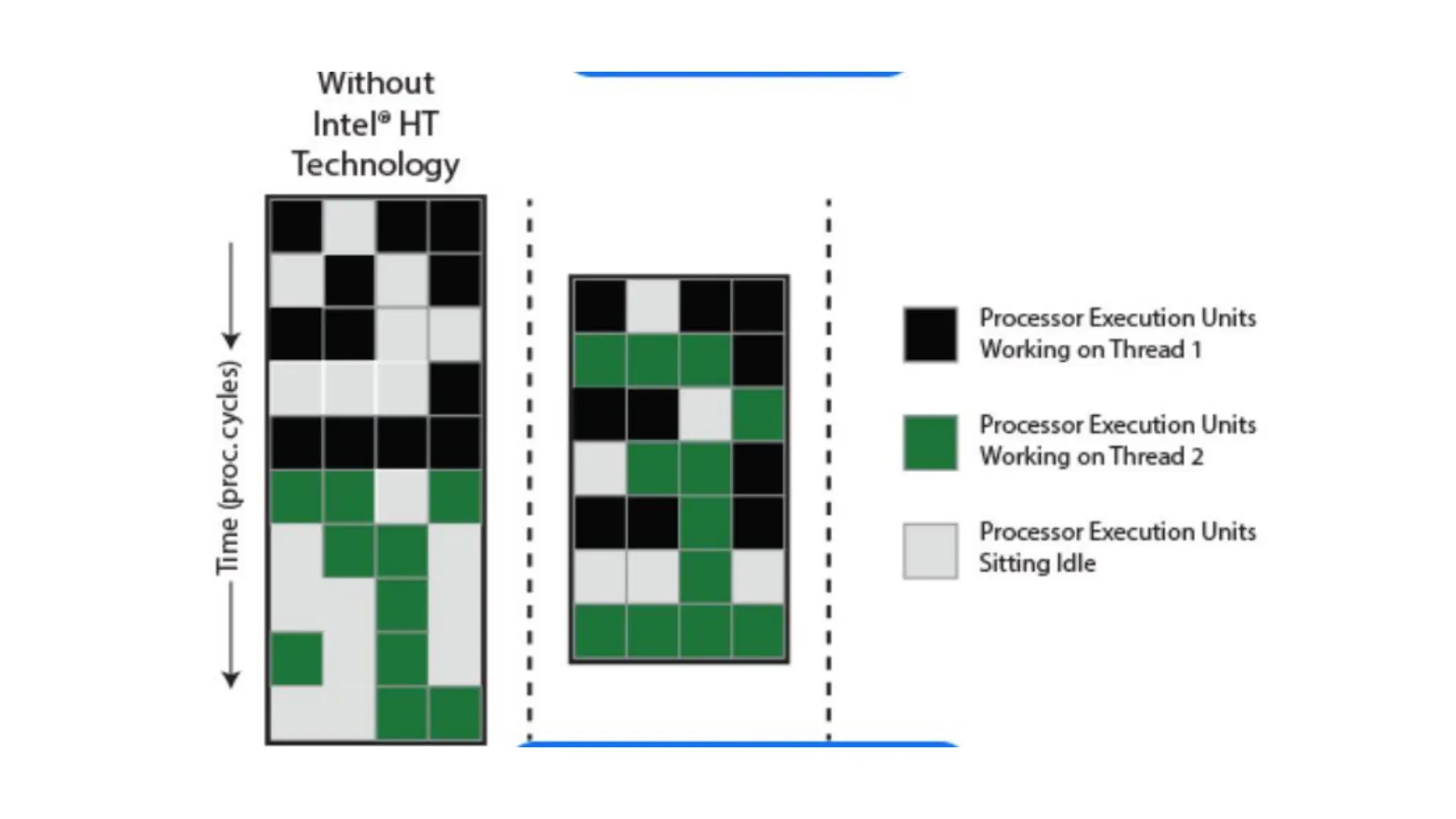
This document discusses parallel and distributed computing concepts like multithreading, multitasking, and multiprocessing. It defines processes and threads, with processes being heavier weight and using more resources than threads. While processes are isolated and don't share data, threads within the same process can share data and resources. Multitasking allows running multiple processes concurrently, while multithreading allows a single process to perform multiple tasks simultaneously. The benefits of multithreading include improved responsiveness, faster context switching, and better utilization of multiprocessor systems.