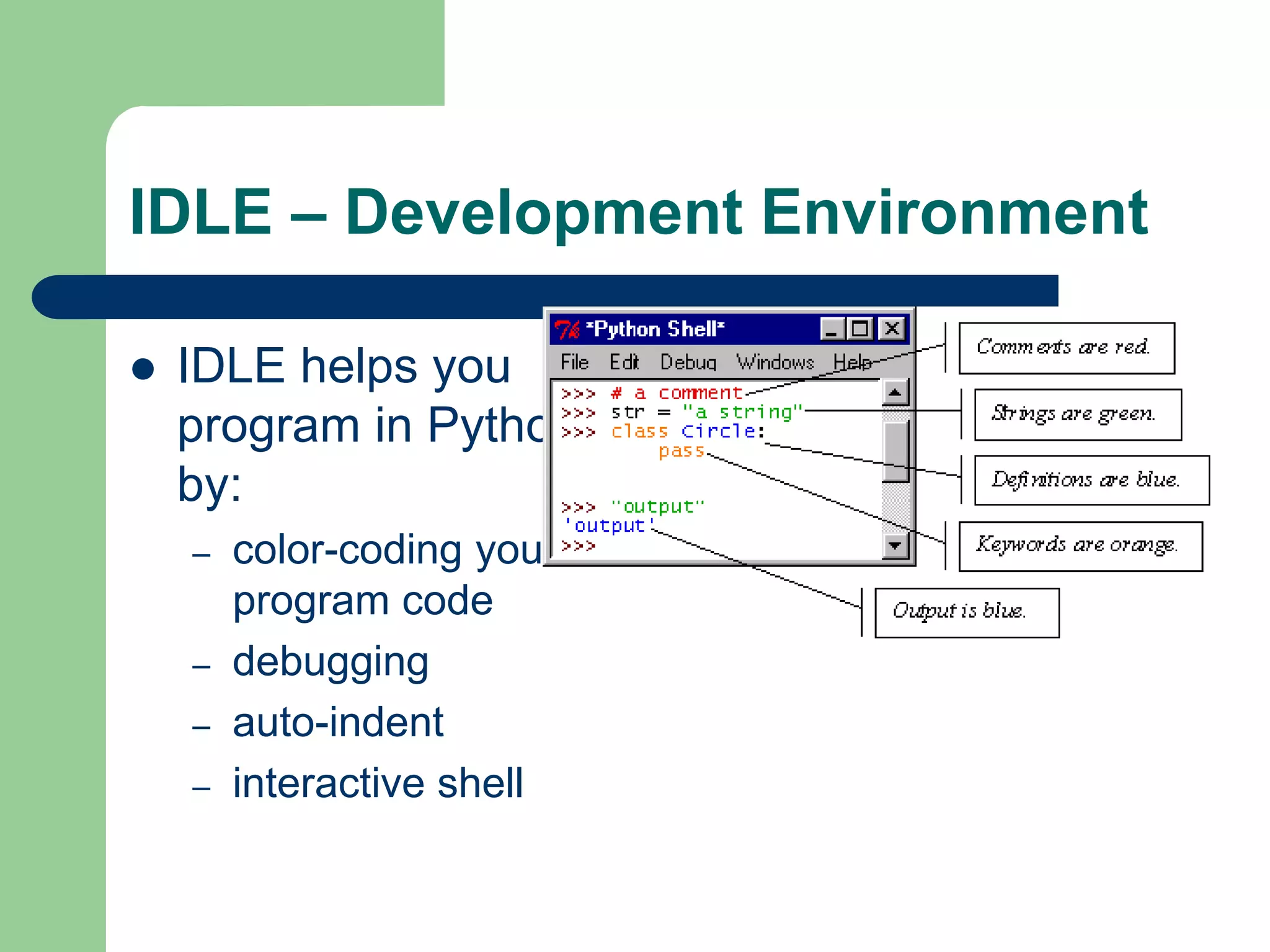
This document provides an introduction to Python programming for geospatial applications. It discusses why Python is useful, how it can interface with GIS tools, and recommends Python as an alternative to Visual Basic for writing scripts. The document also demonstrates how to get started with Python development using the IDLE integrated development environment, and provides some additional learning resources.