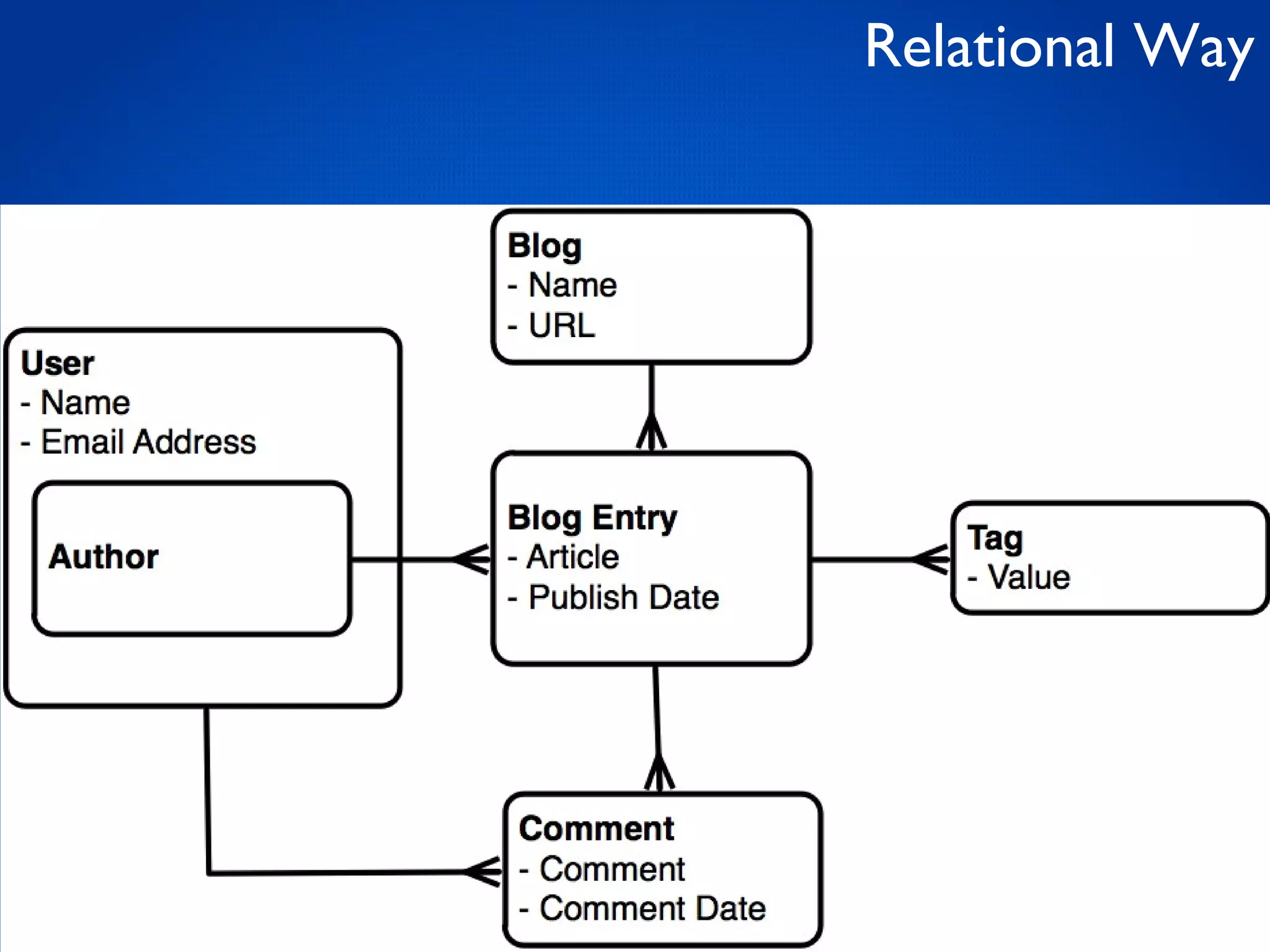
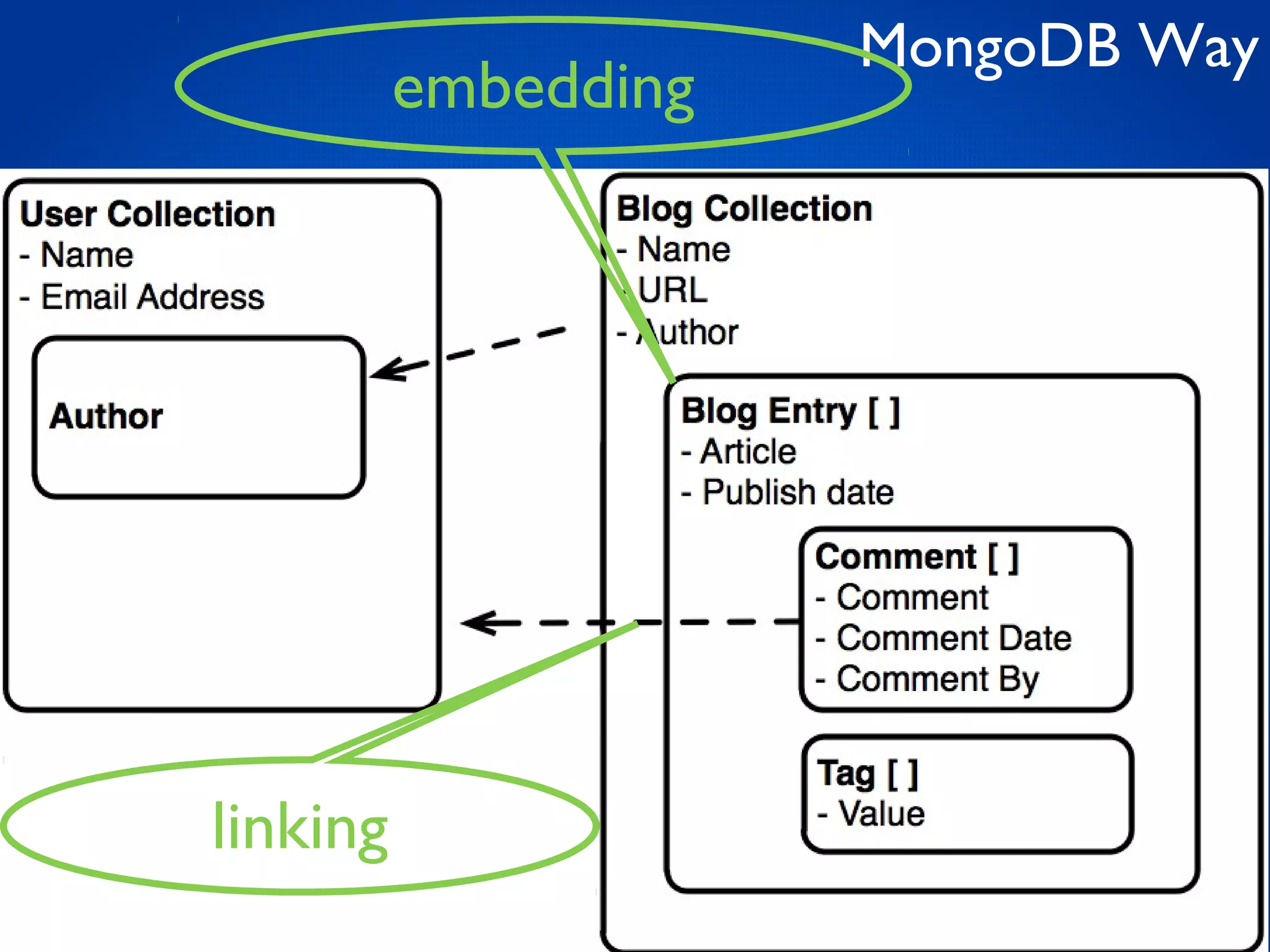
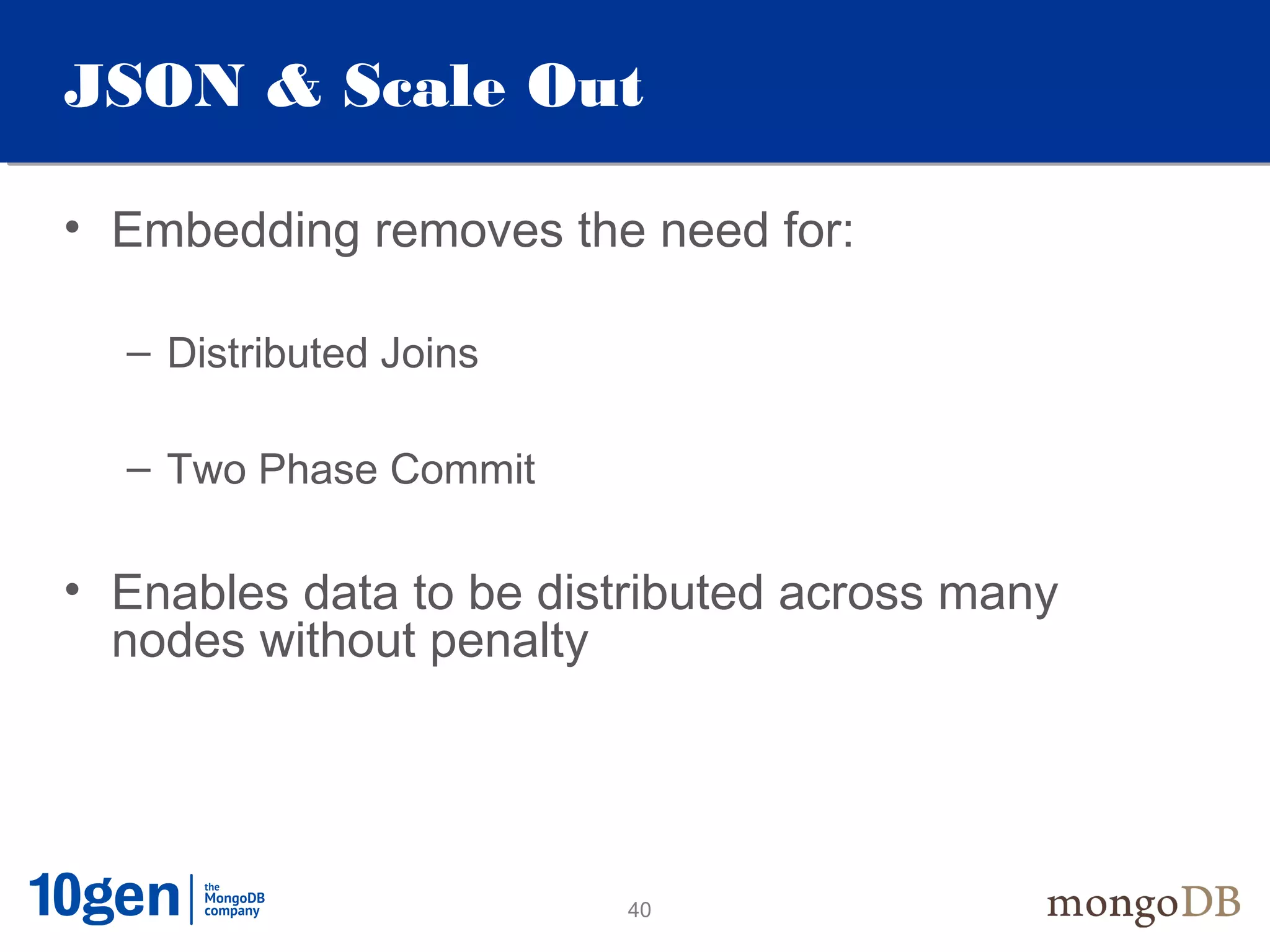
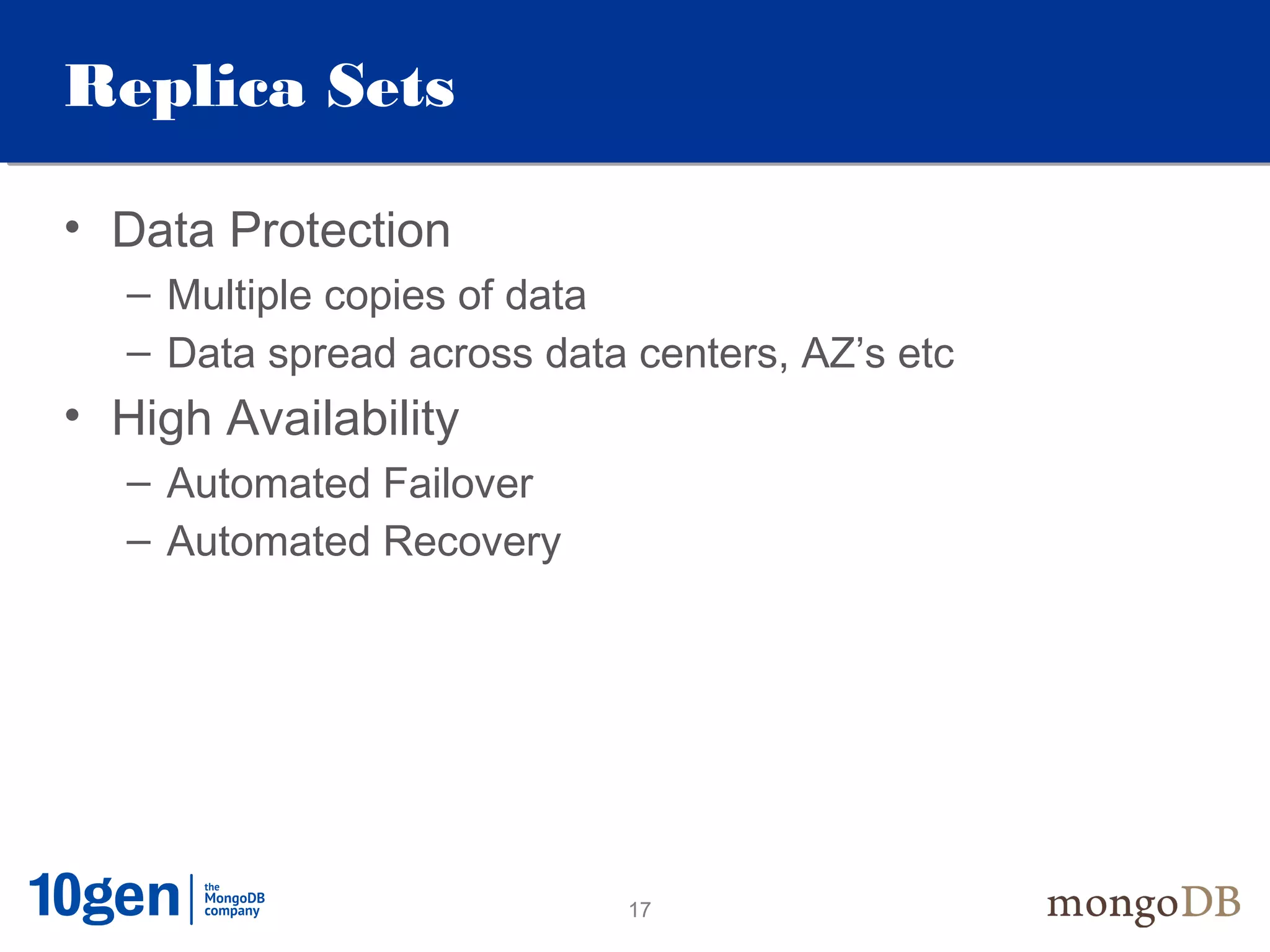
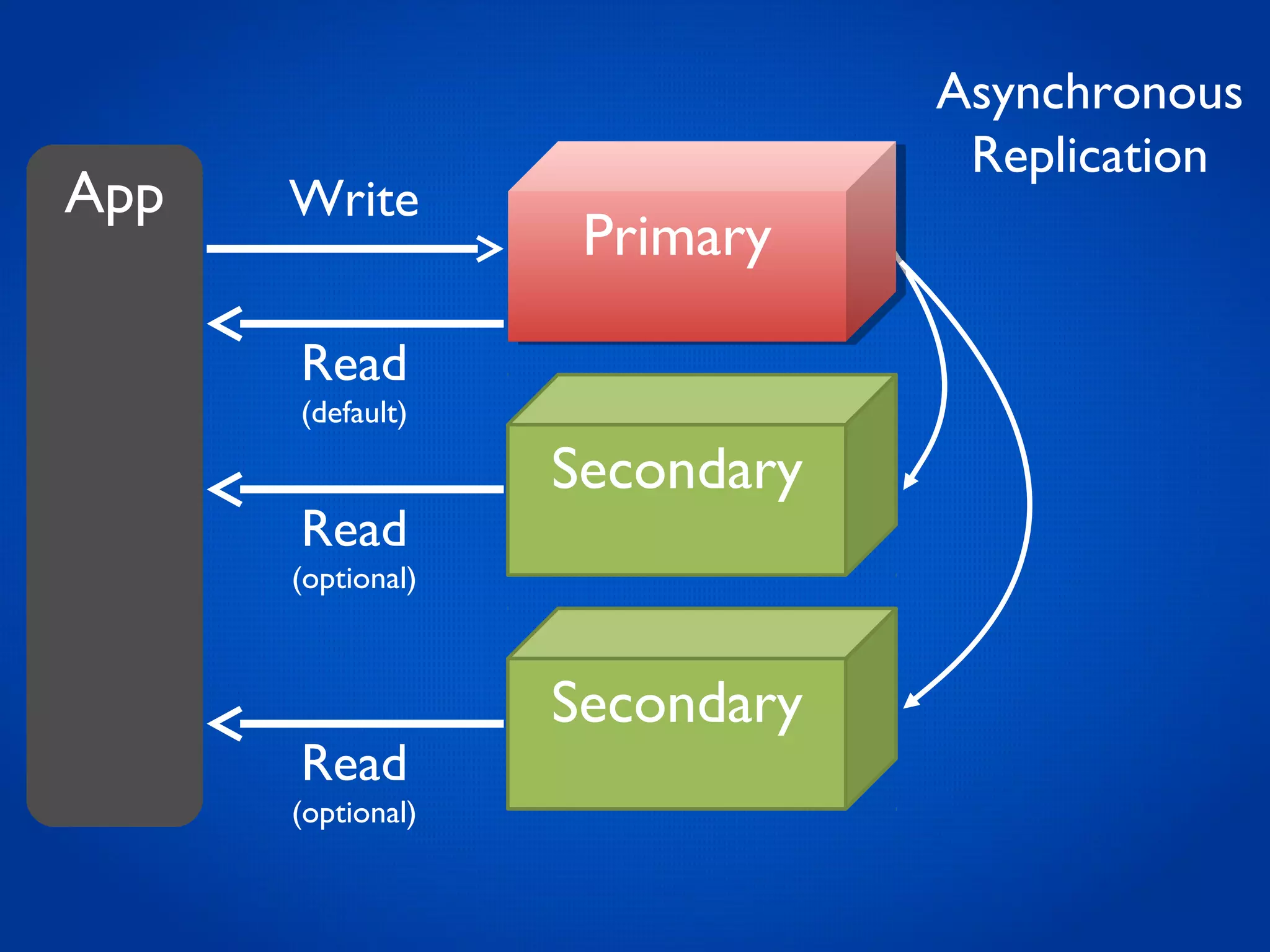
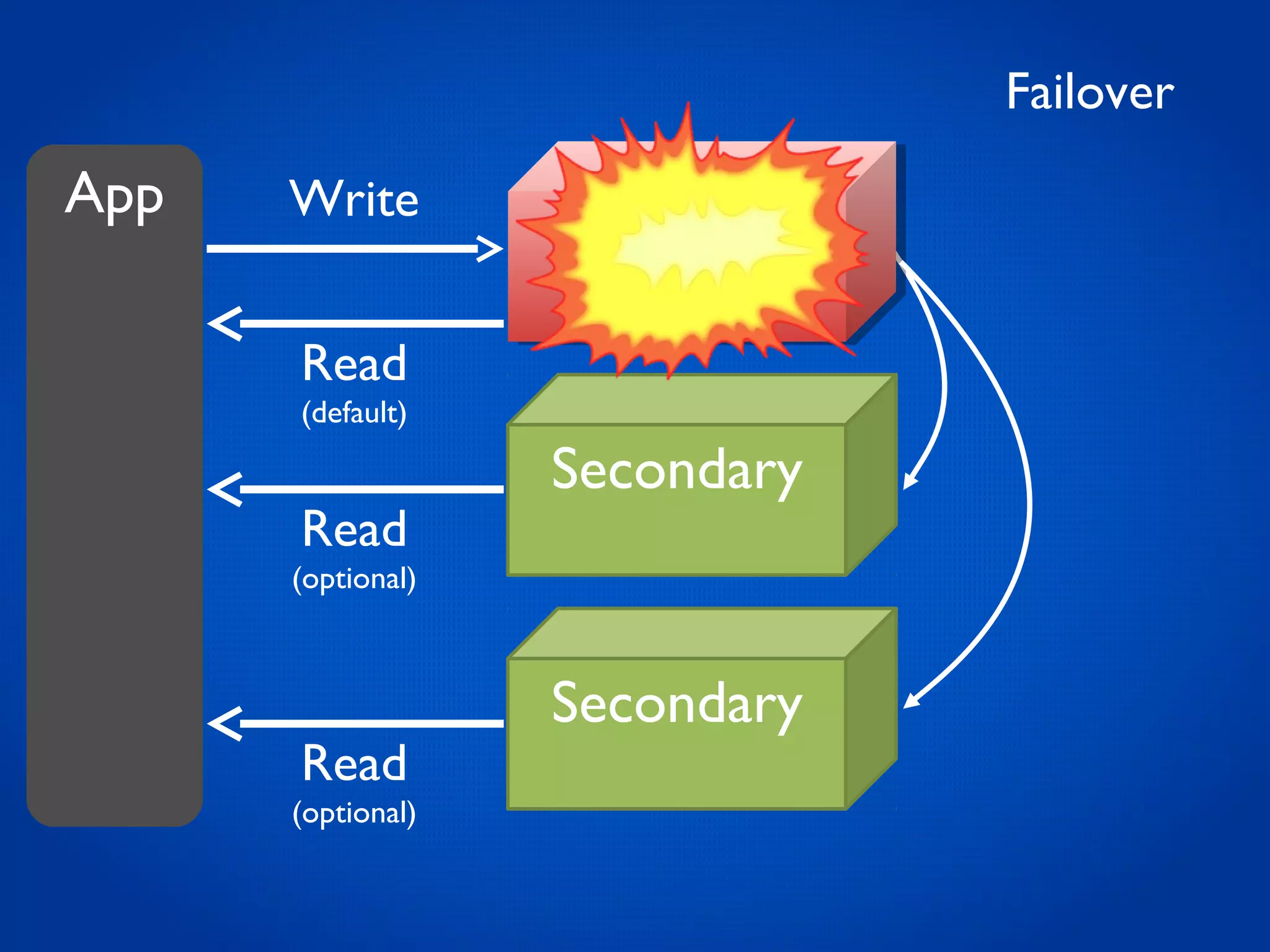
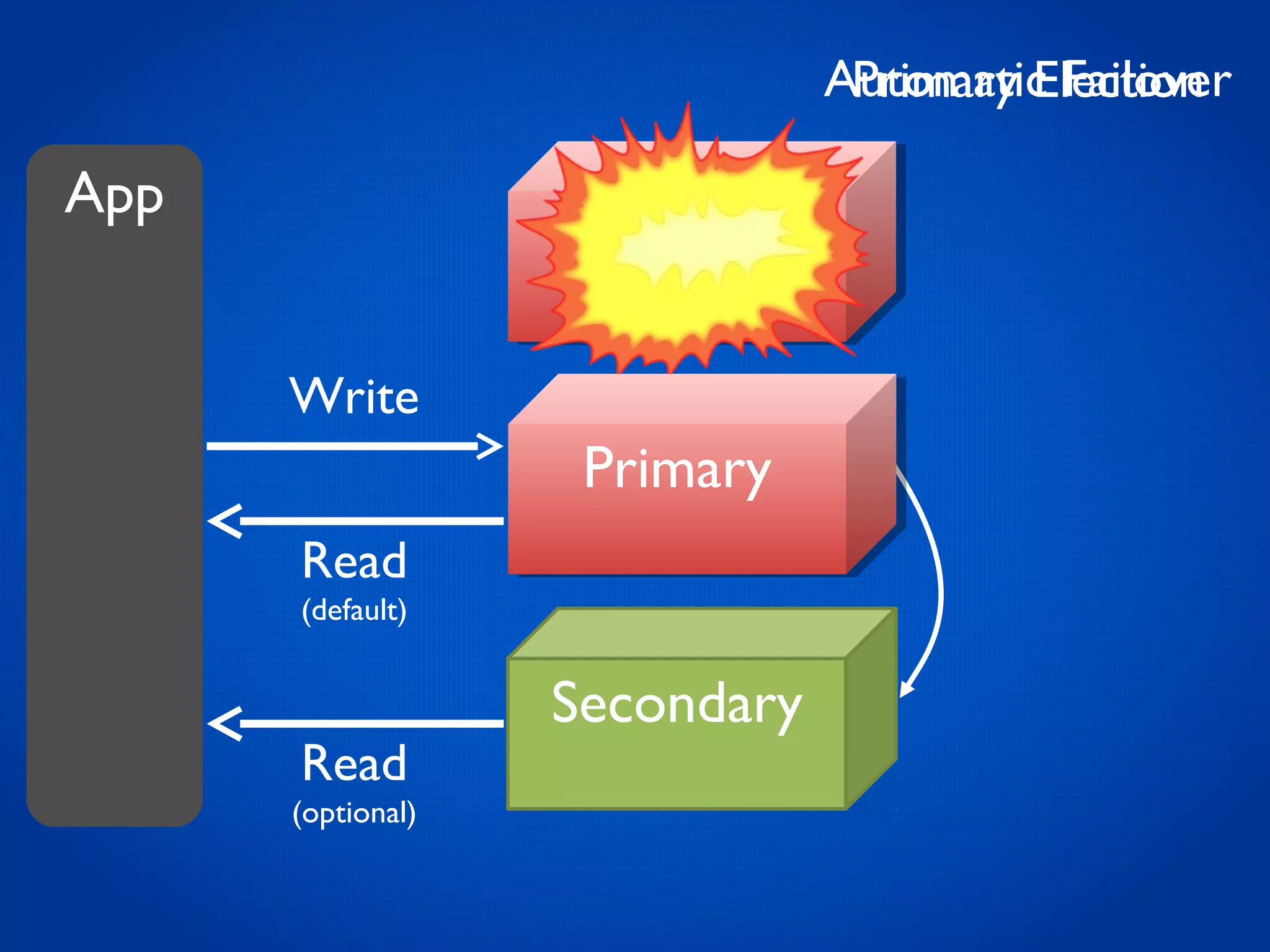
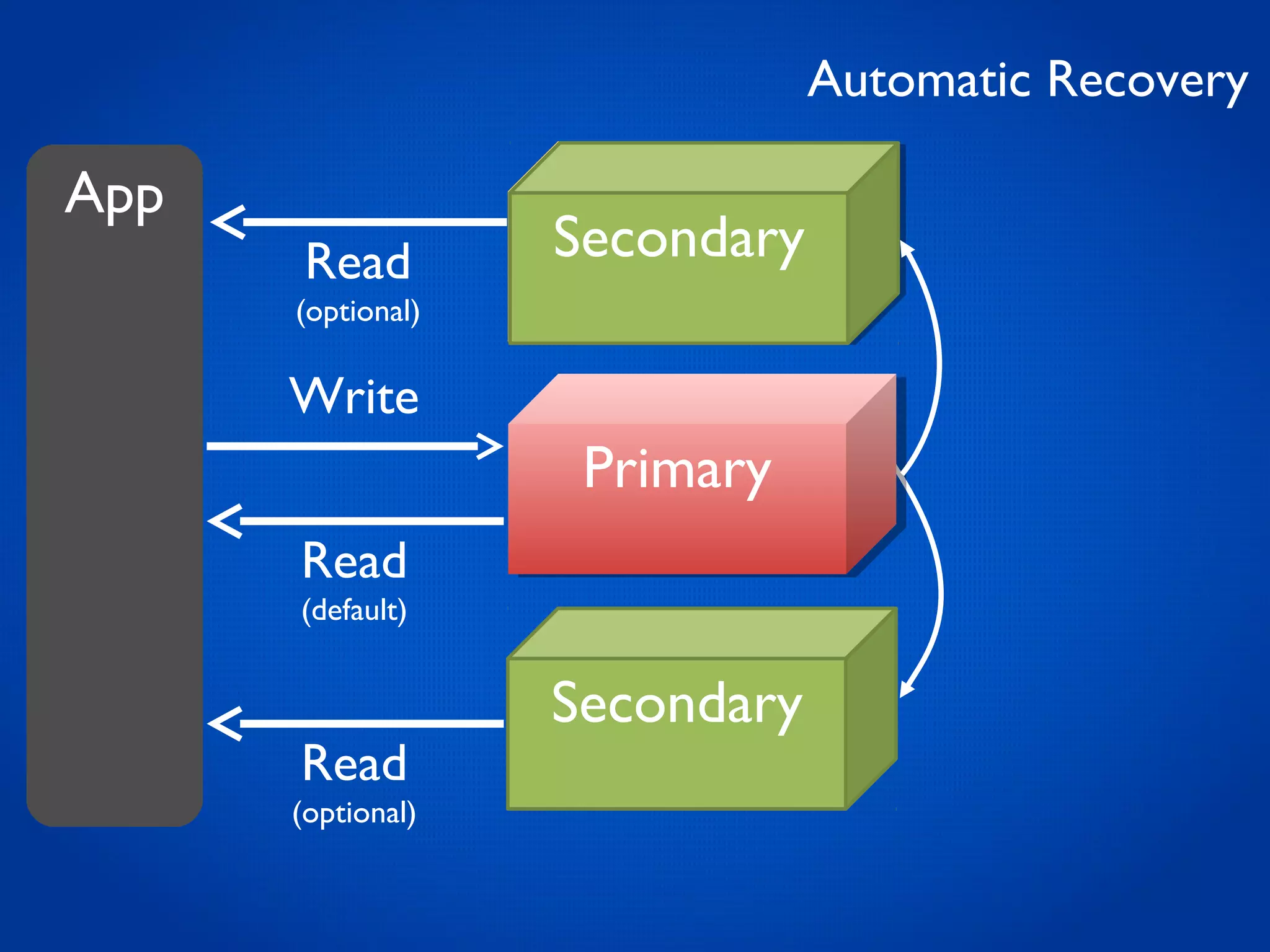
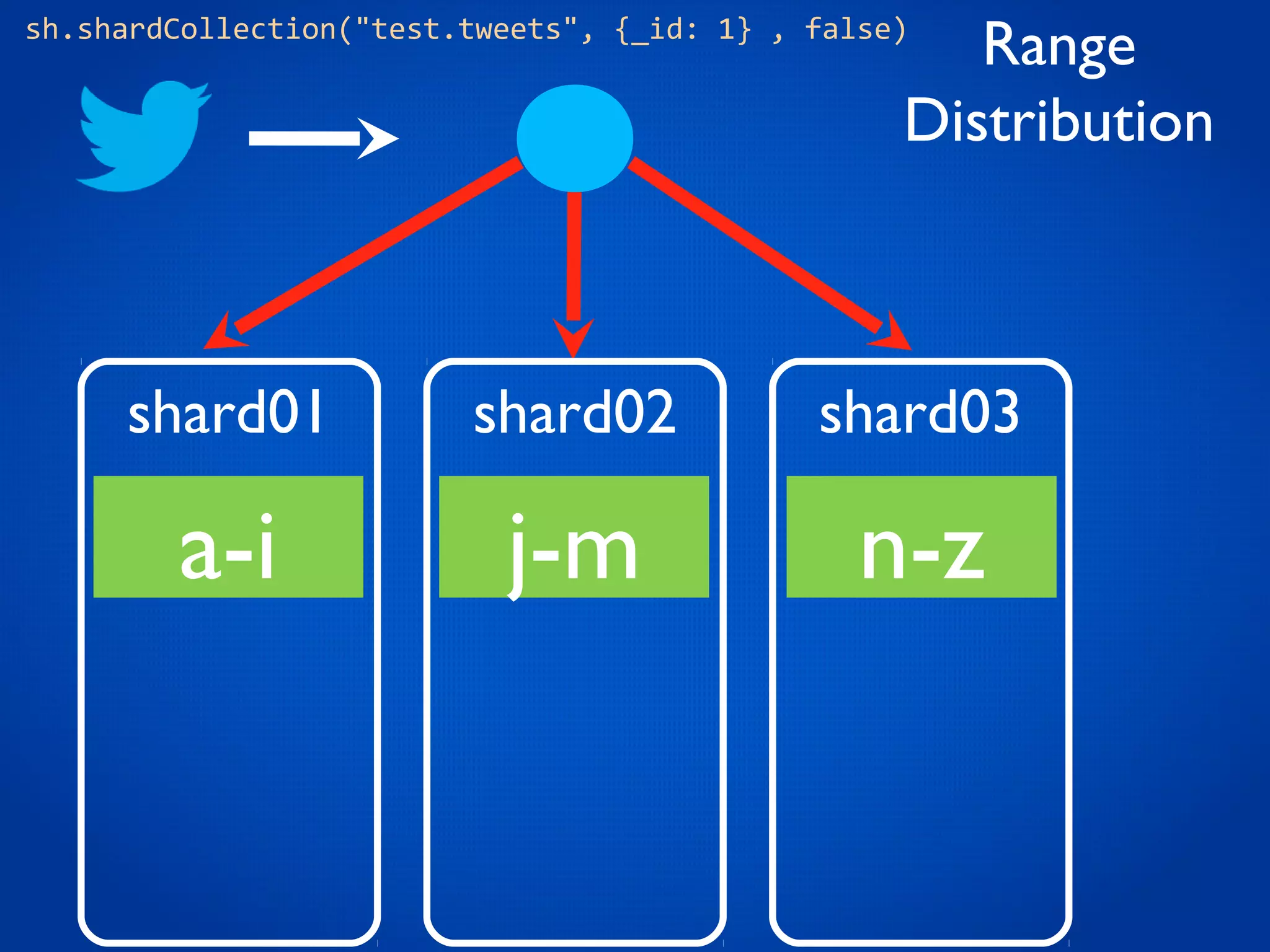
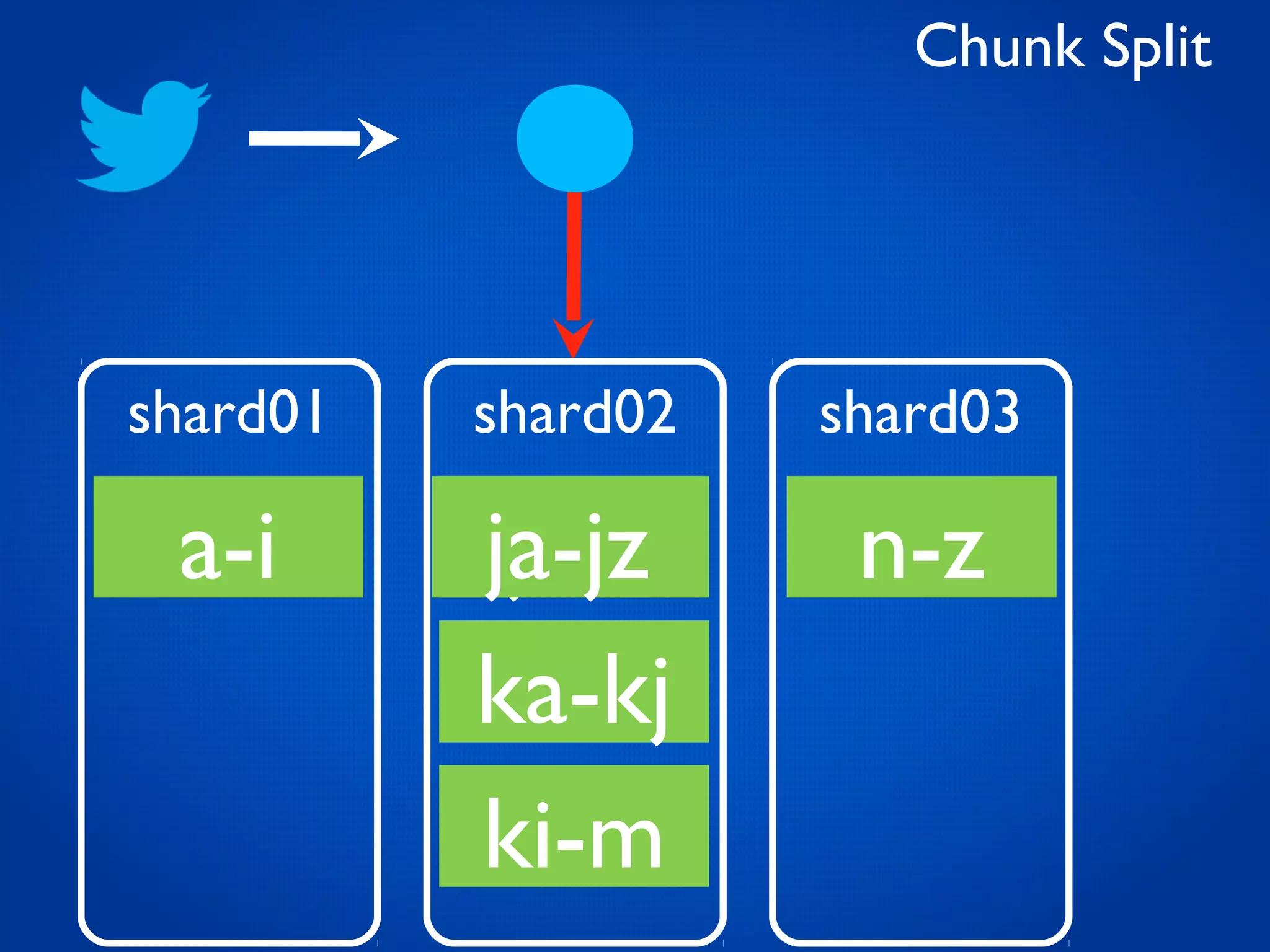
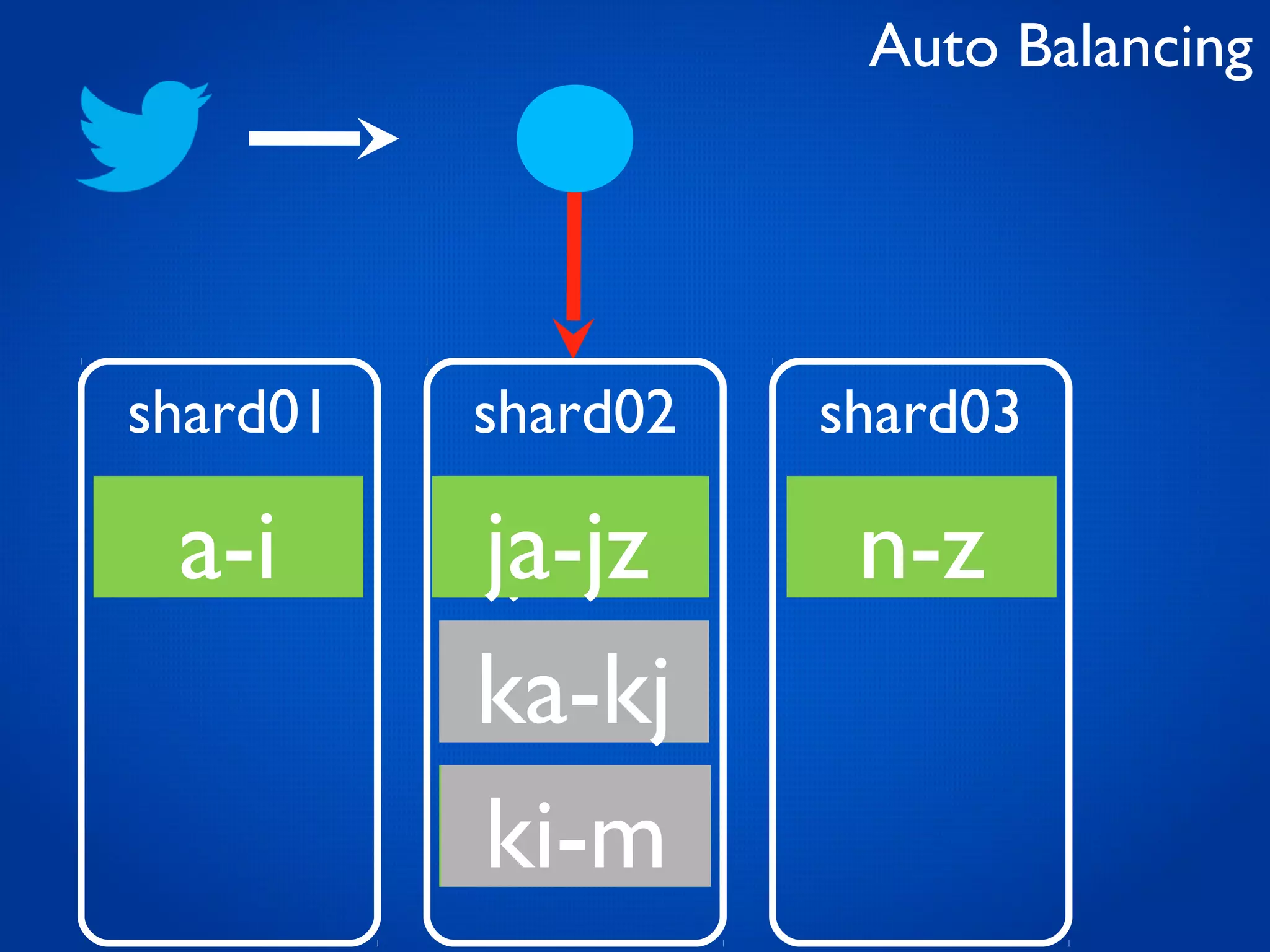
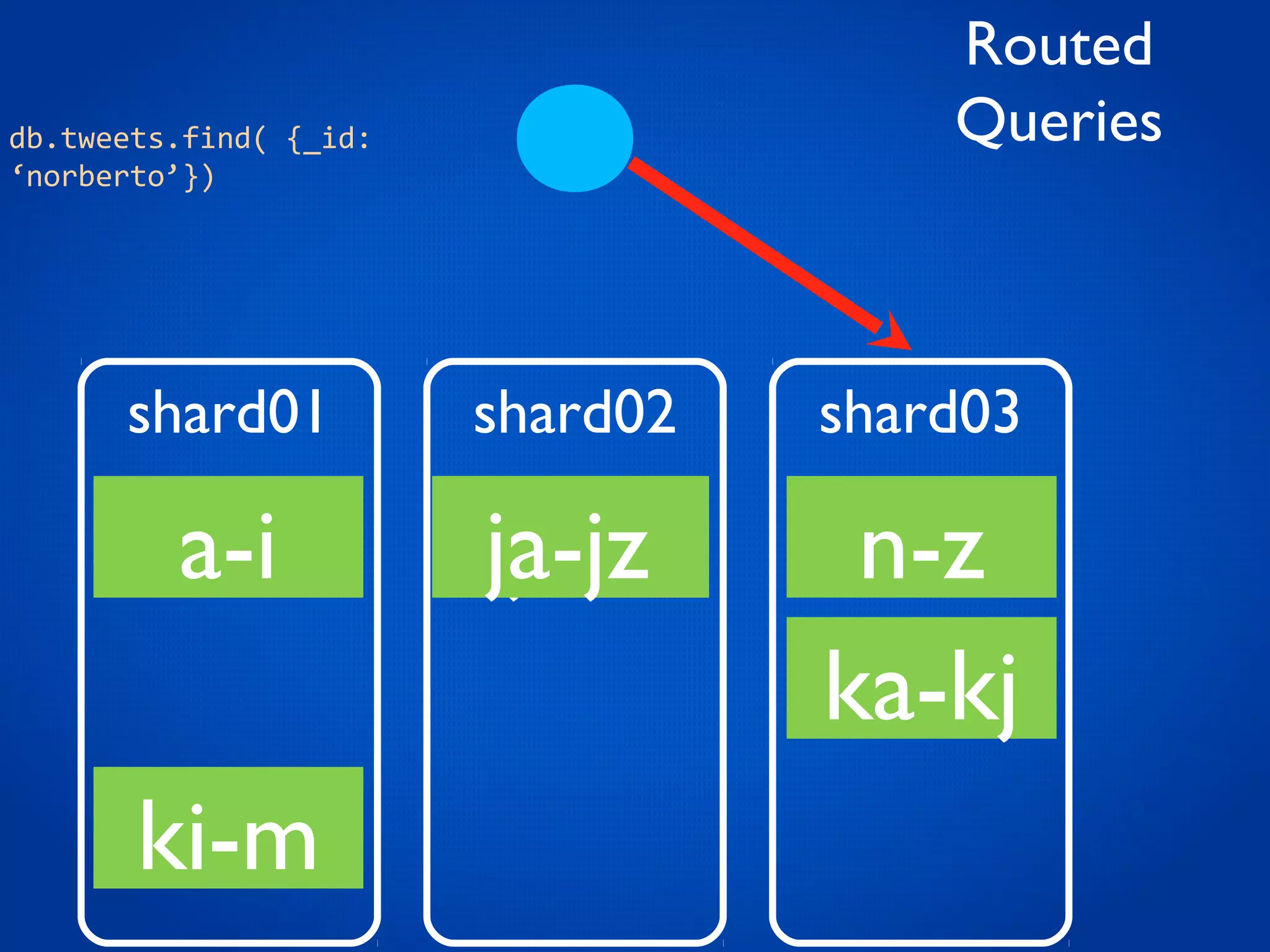
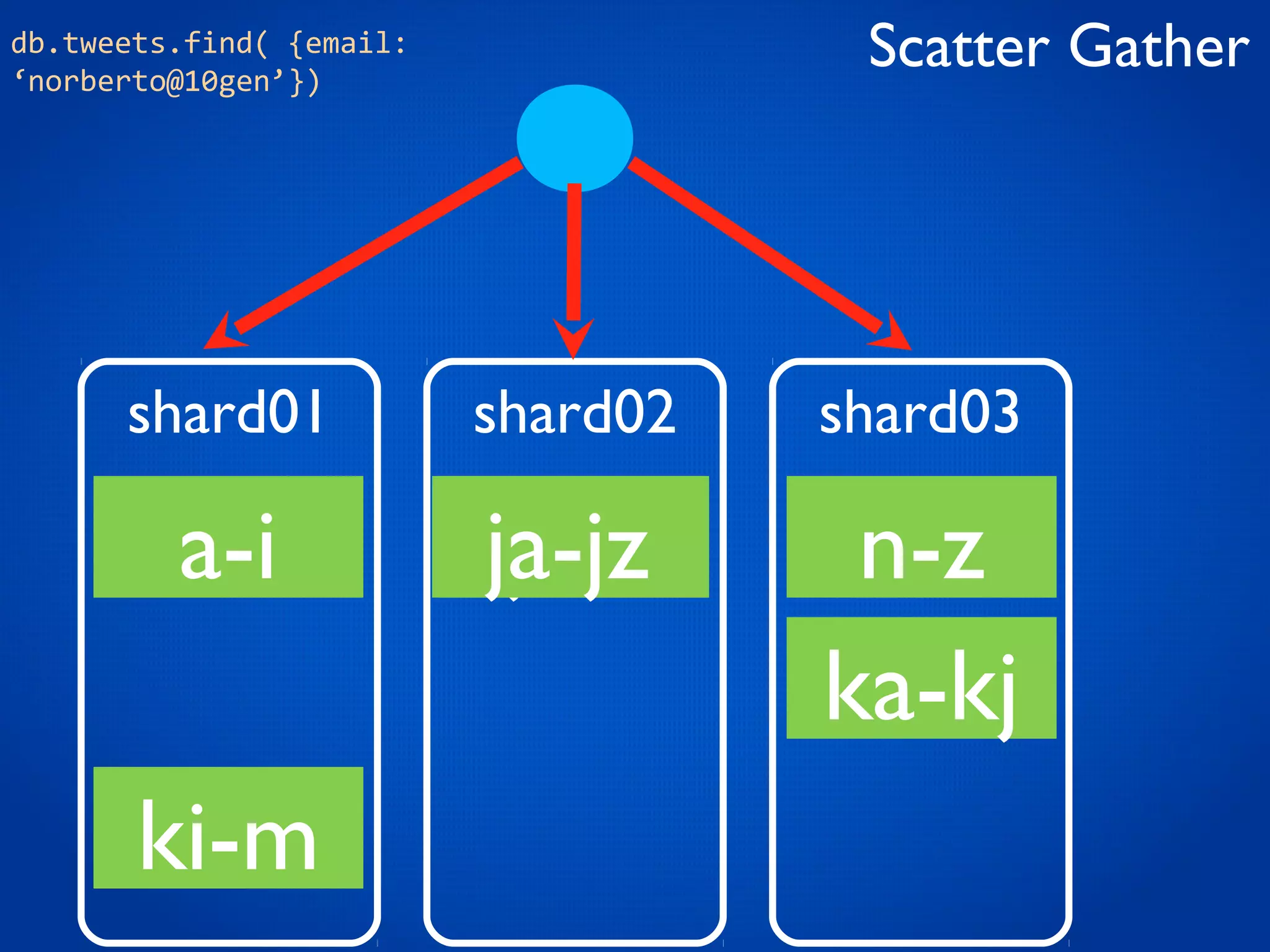
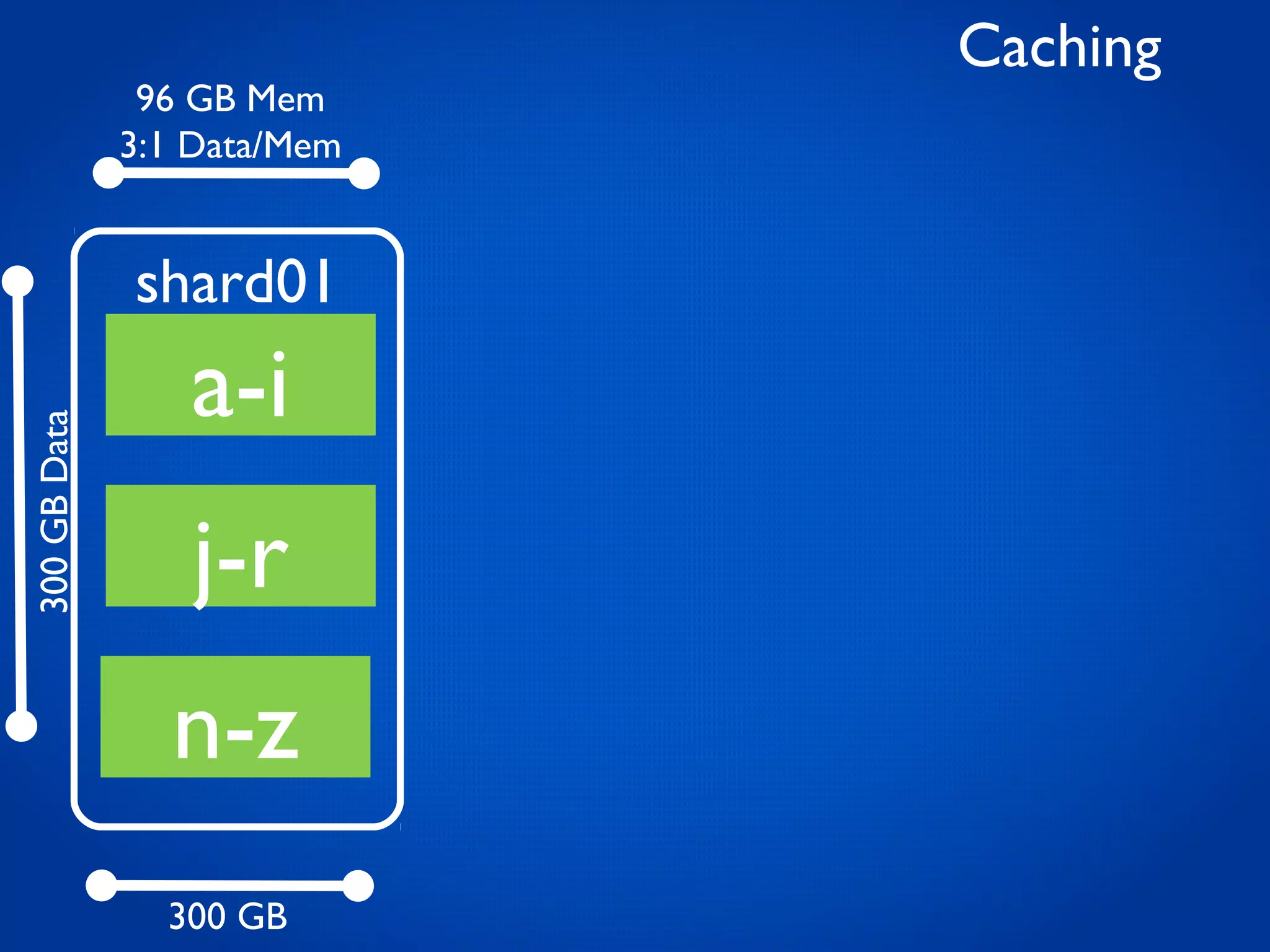
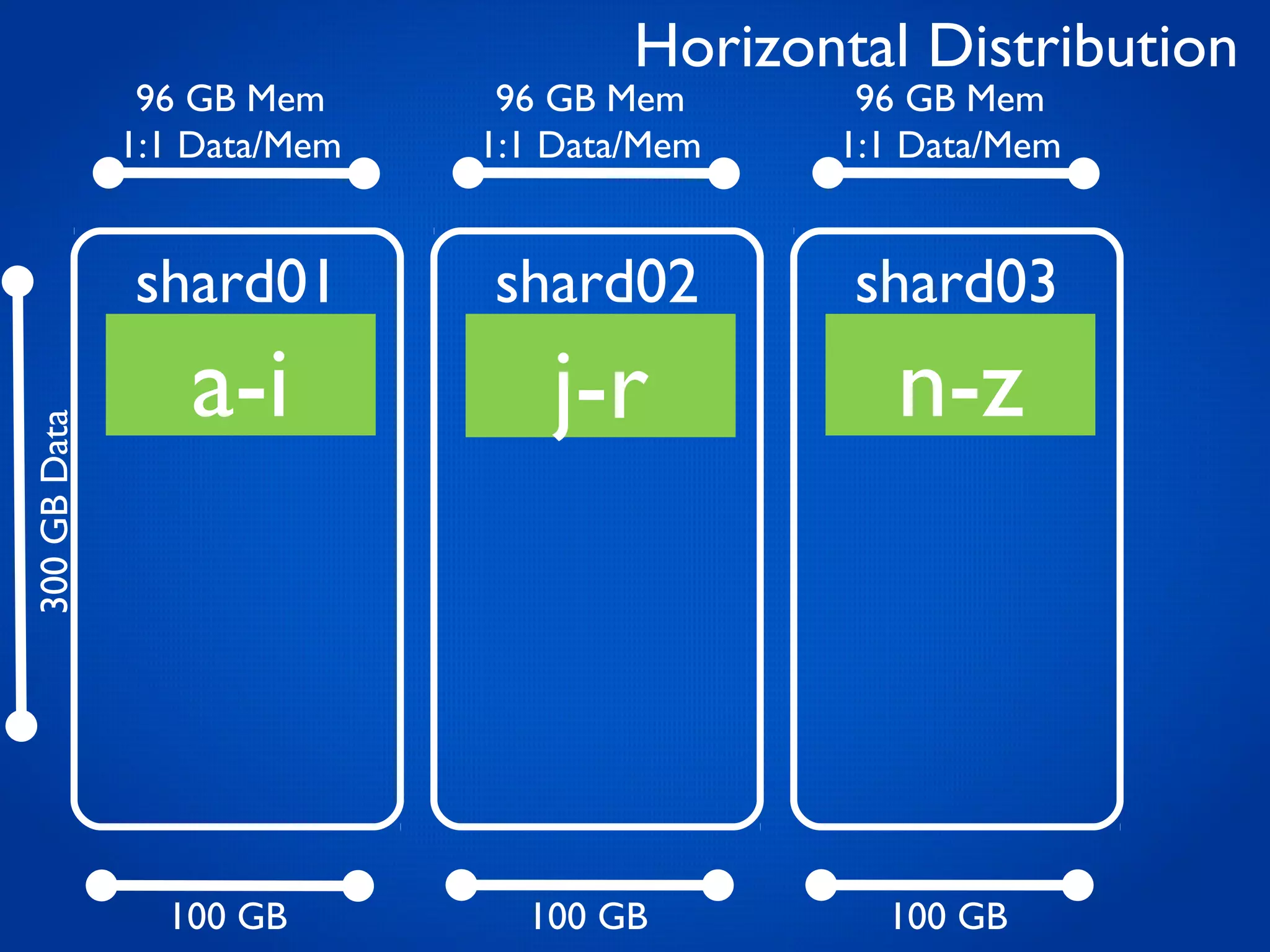
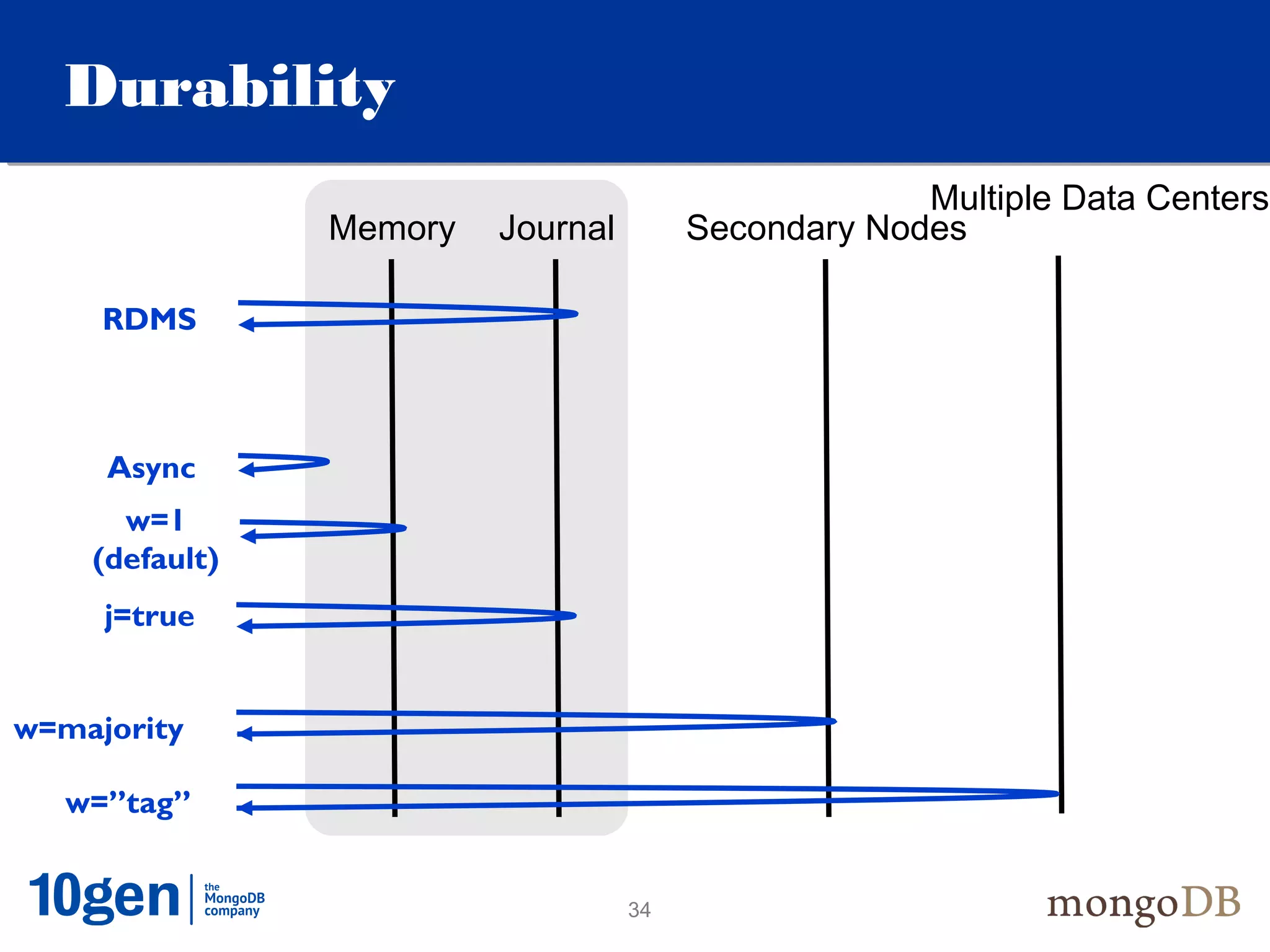
This document provides an overview and introduction to key MongoDB concepts including: - Replication which allows for failover, backups, and high availability through asynchronous replication across replica sets. - Sharding which provides horizontal scalability by automatically distributing and balancing data across multiple shards in a cluster. - Consistency and durability models including eventual consistency and different write acknowledgement options for ensuring data is safely written. - Flexibility in data modeling through embedding and linking of related data as well as the use of JSON which maps easily to objects.












![Fundamentals Document Application High Oriented { Performance name: ‘Norberto Leite’, position: ‘SA’, nick: ‘WingMan’, based: [‘Barcelona’, ‘London’] } mongoDB mongoDB mongoDB mongoDB Fully Consistent Horizontal Scalability 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbasicconcepts-121217130740-phpapp01/75/MongoDB-Basic-Concepts-13-2048.jpg)







![JSON place1 = { : "578 Broadway 7th Floor", name : "10gen HQ", address city : "New York", zip "business", "tech" ]} : "10011", tags : [ }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbasicconcepts-121217130740-phpapp01/75/MongoDB-Basic-Concepts-37-2048.jpg)