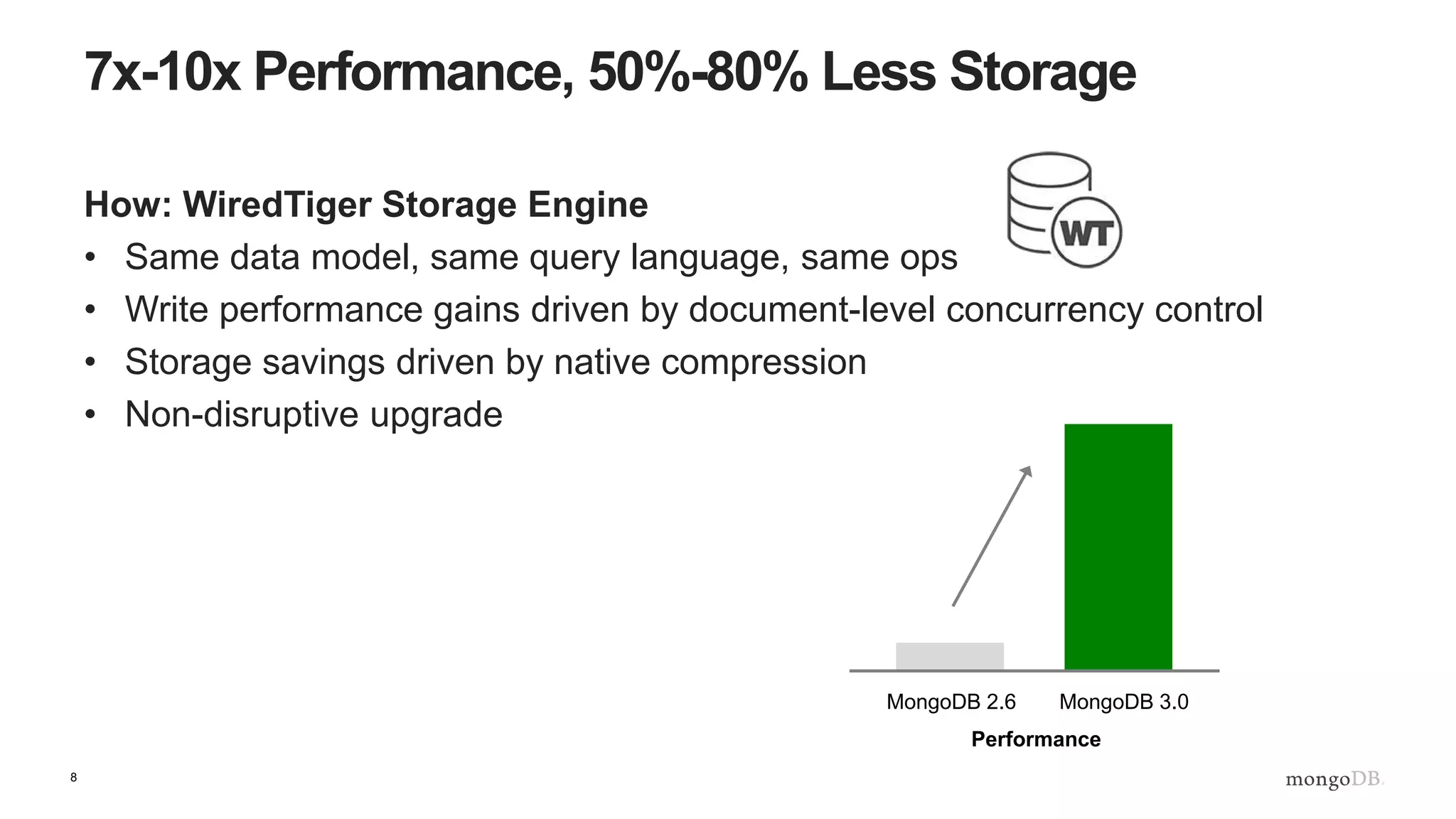
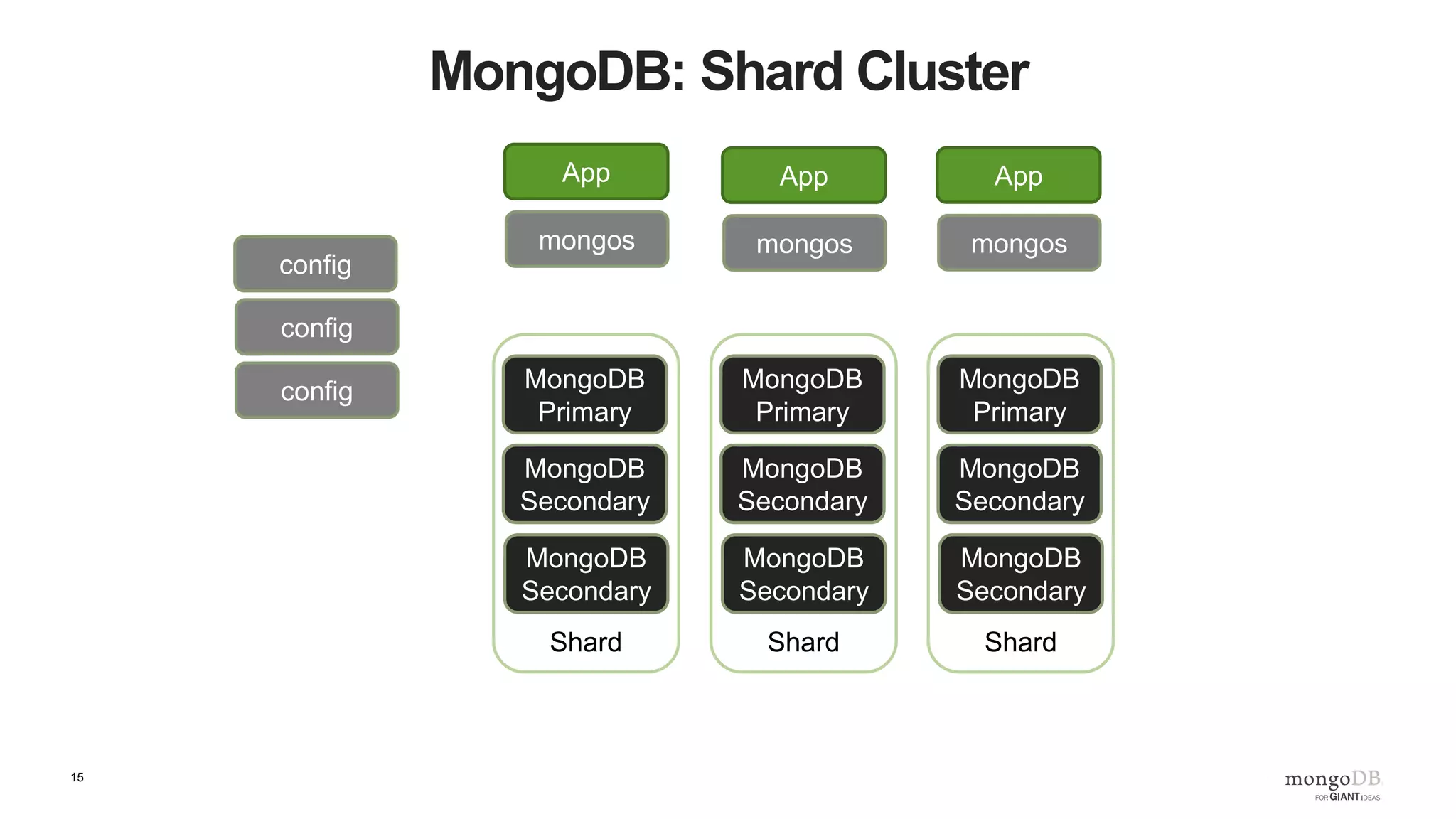
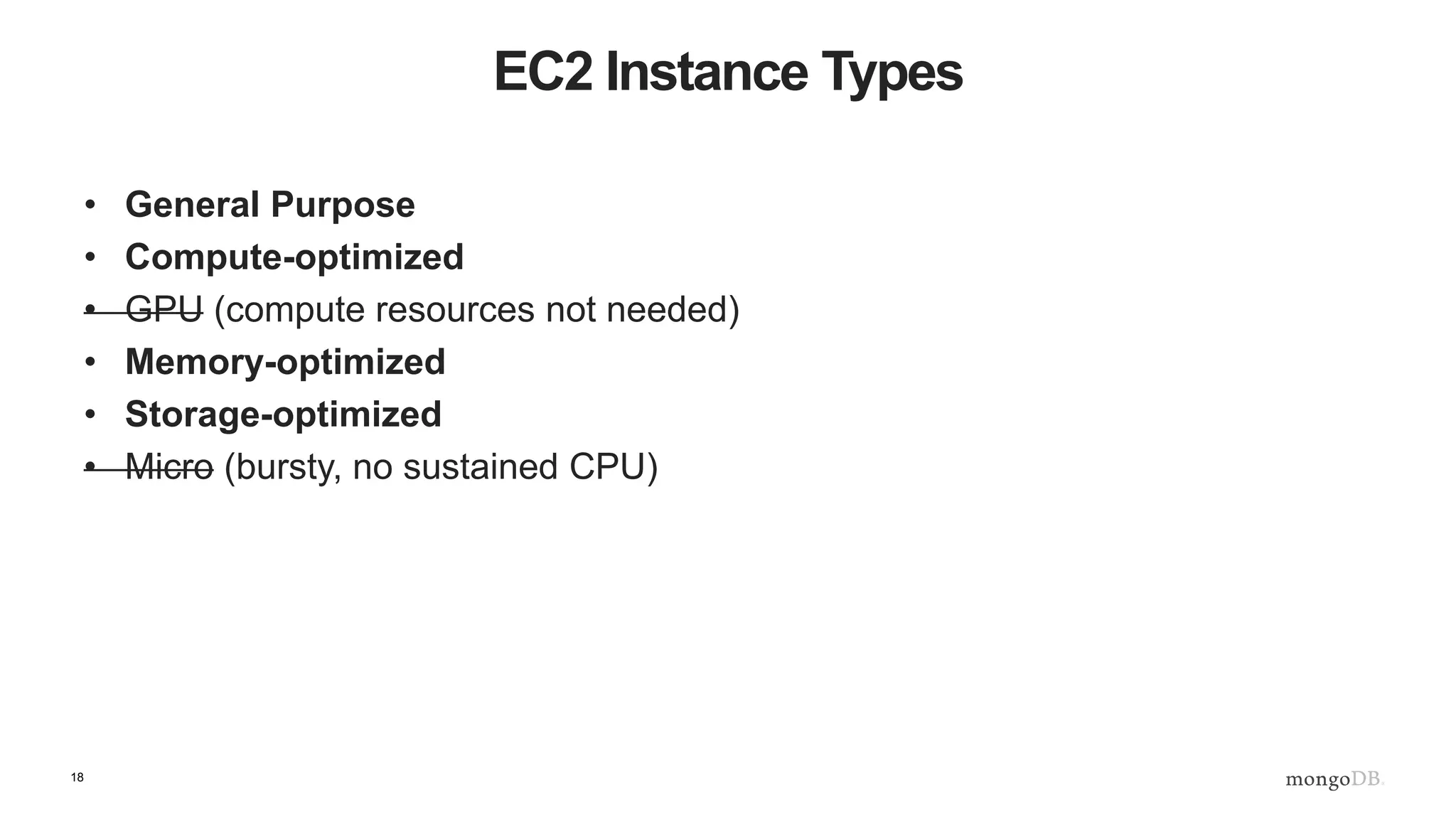
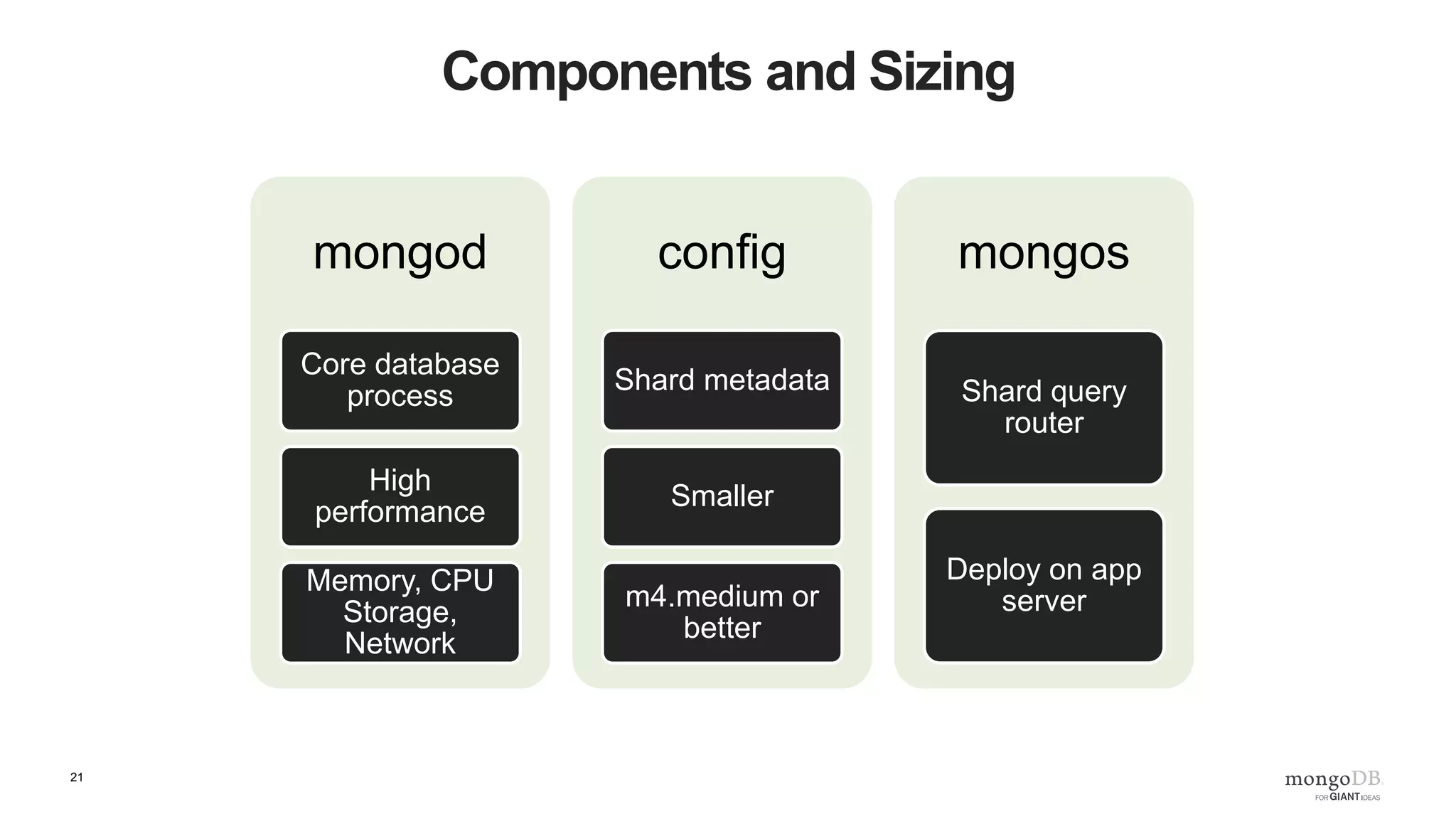
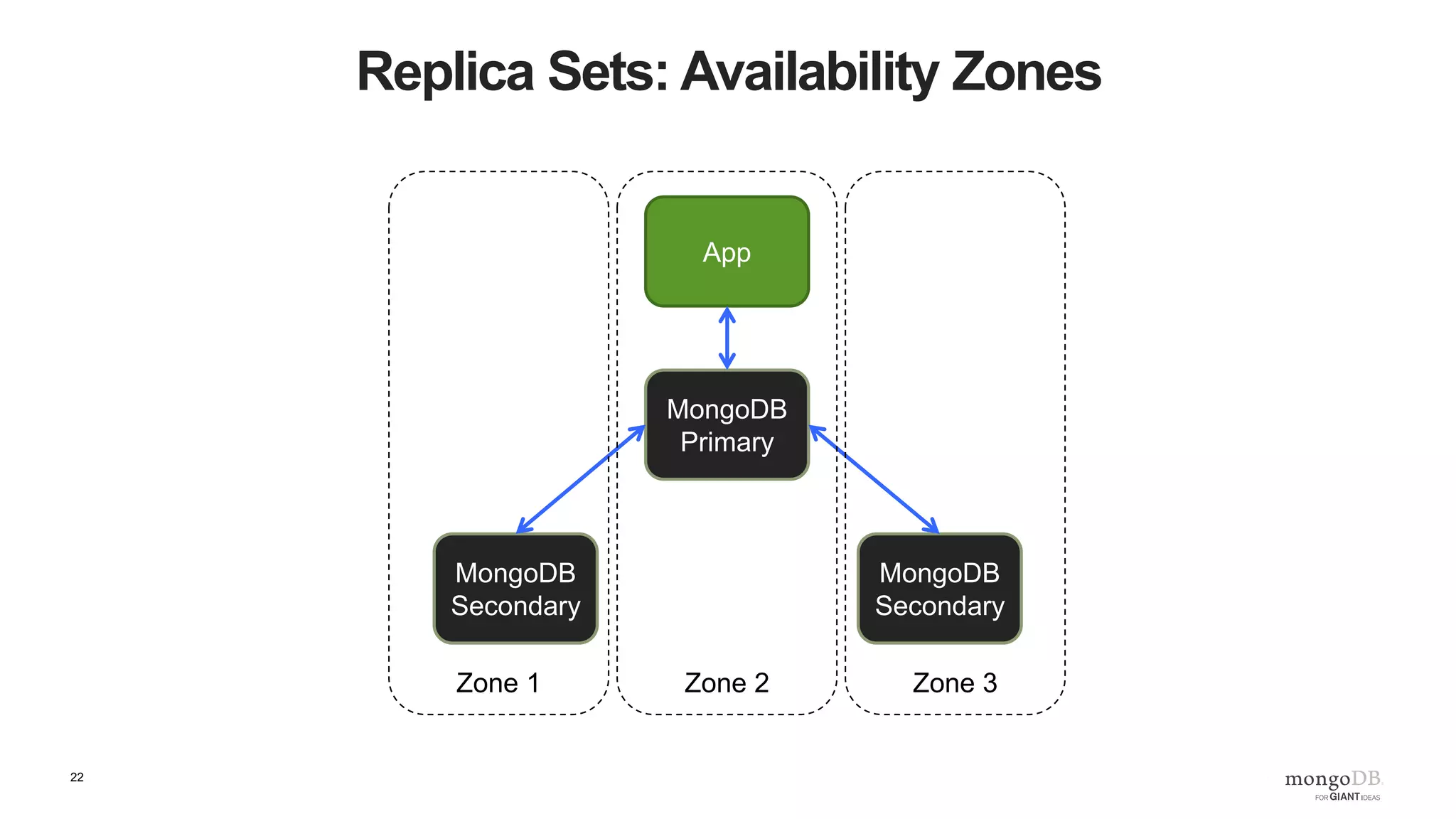
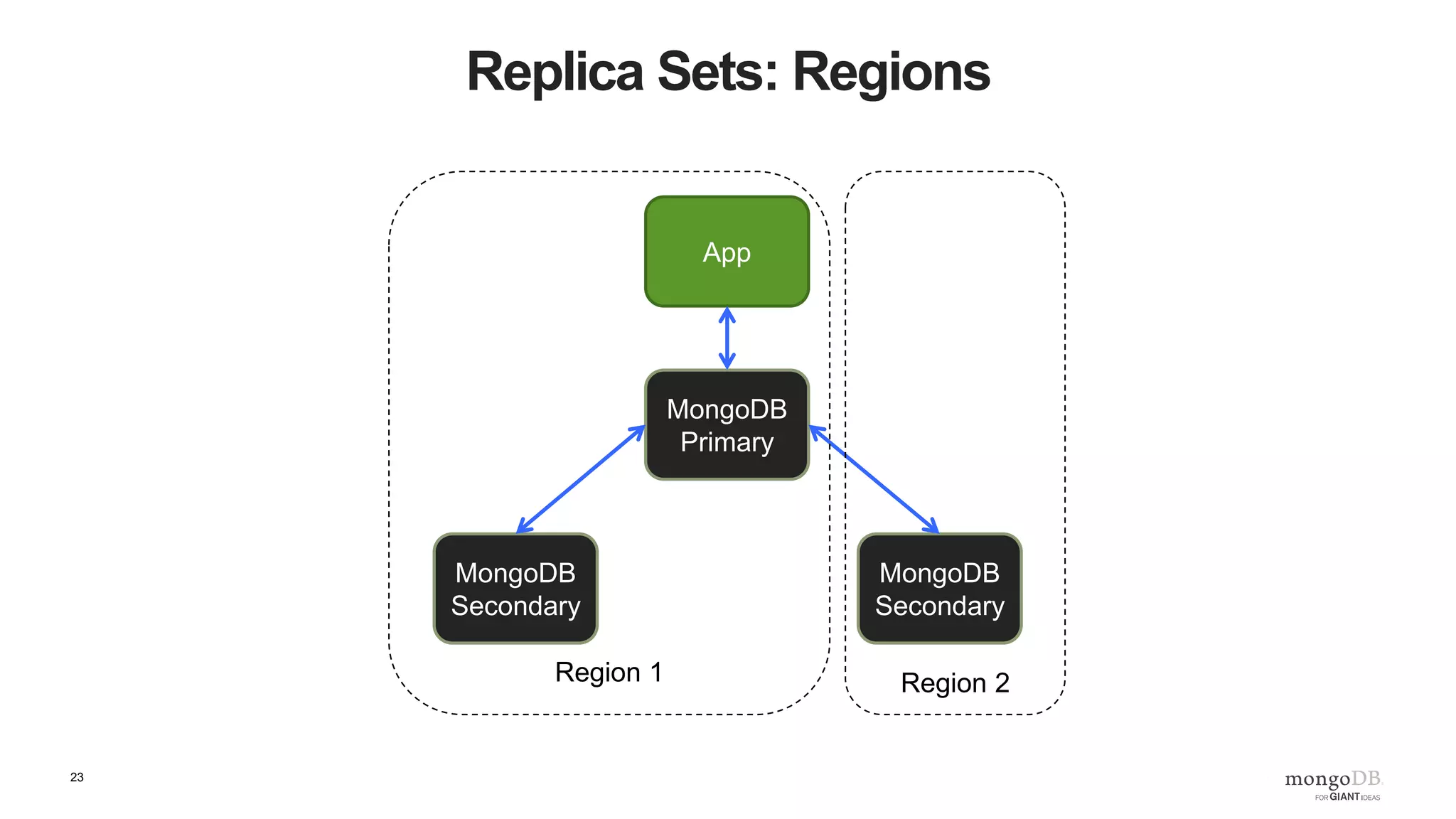
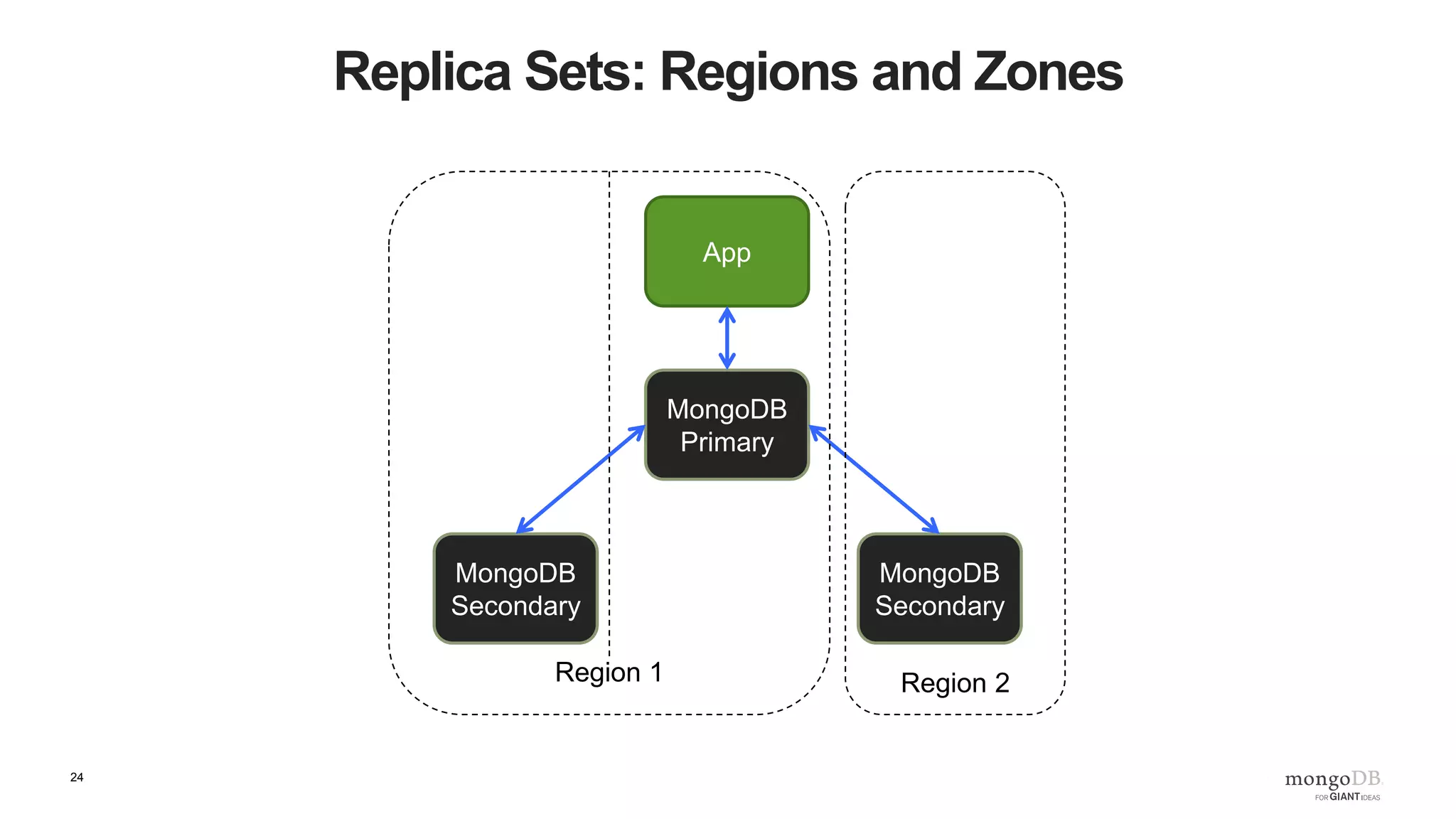
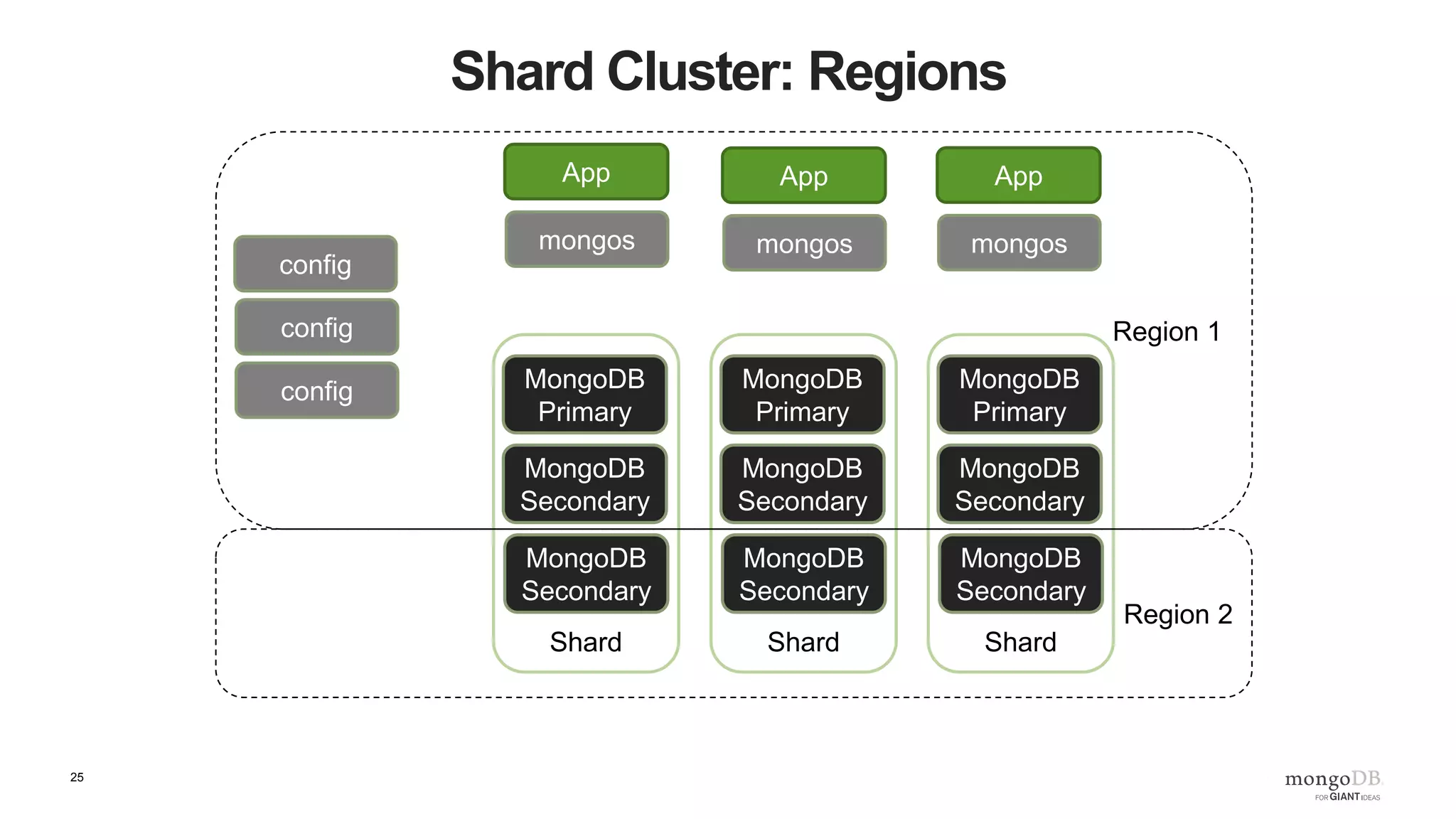
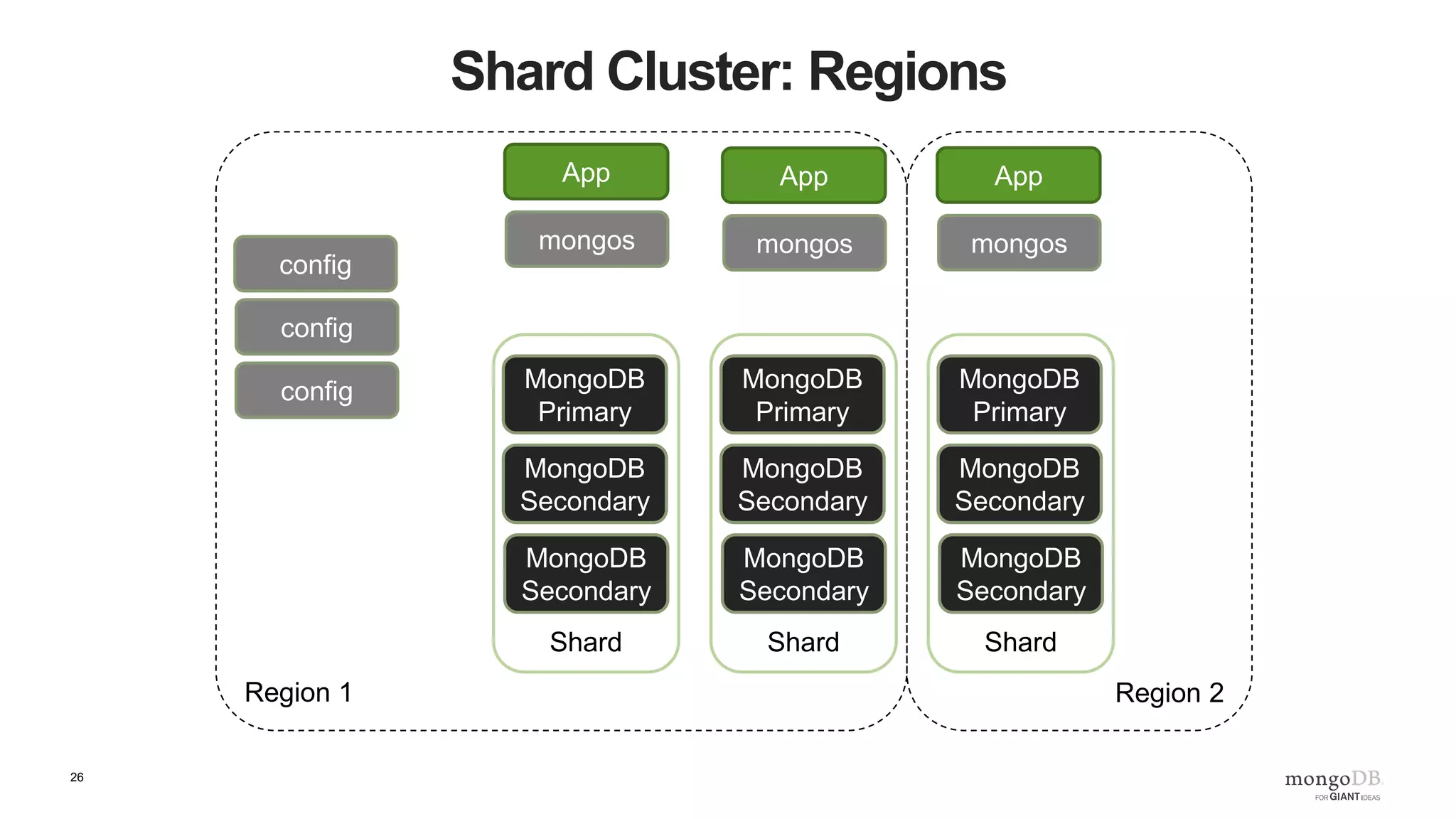
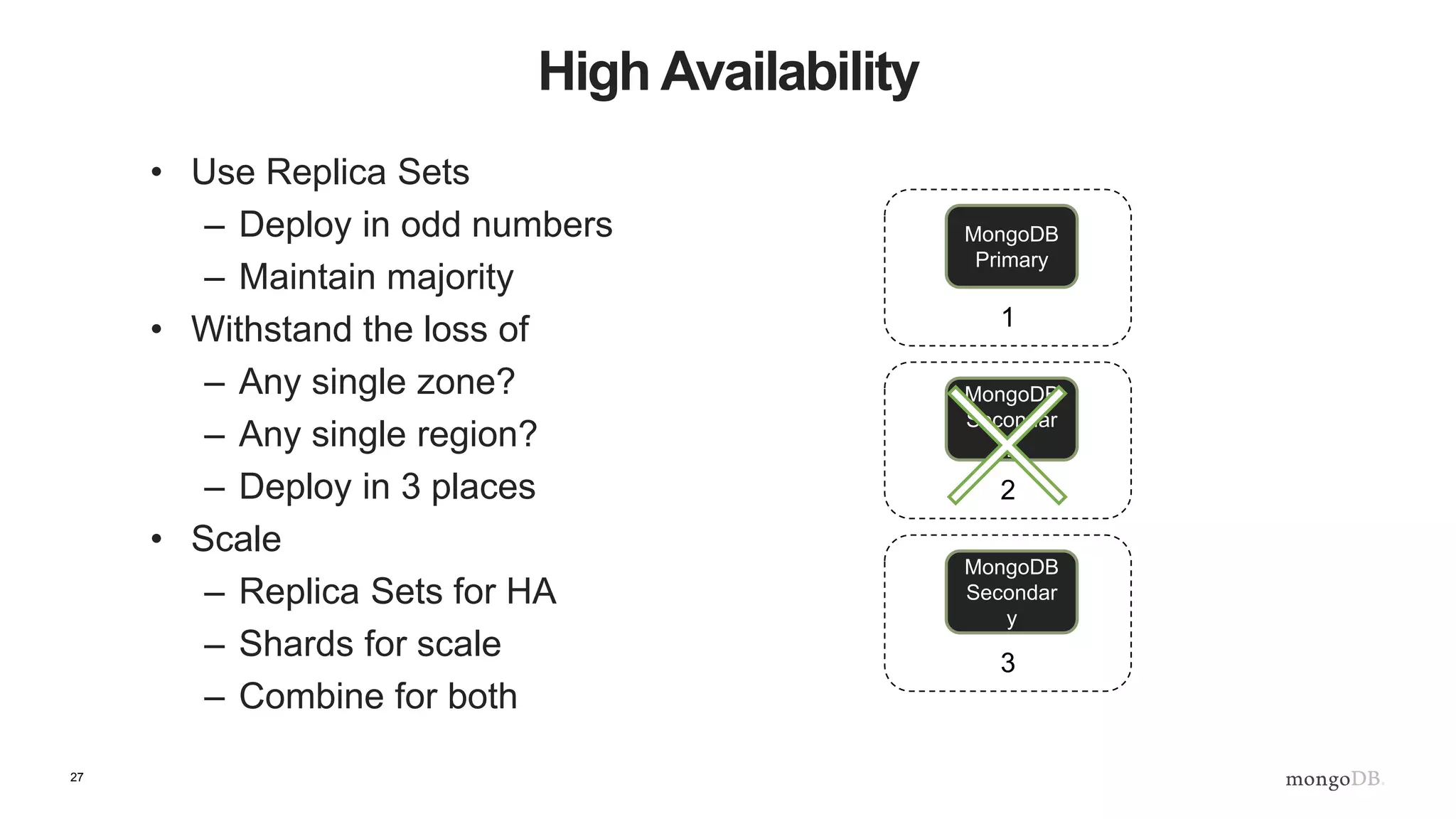
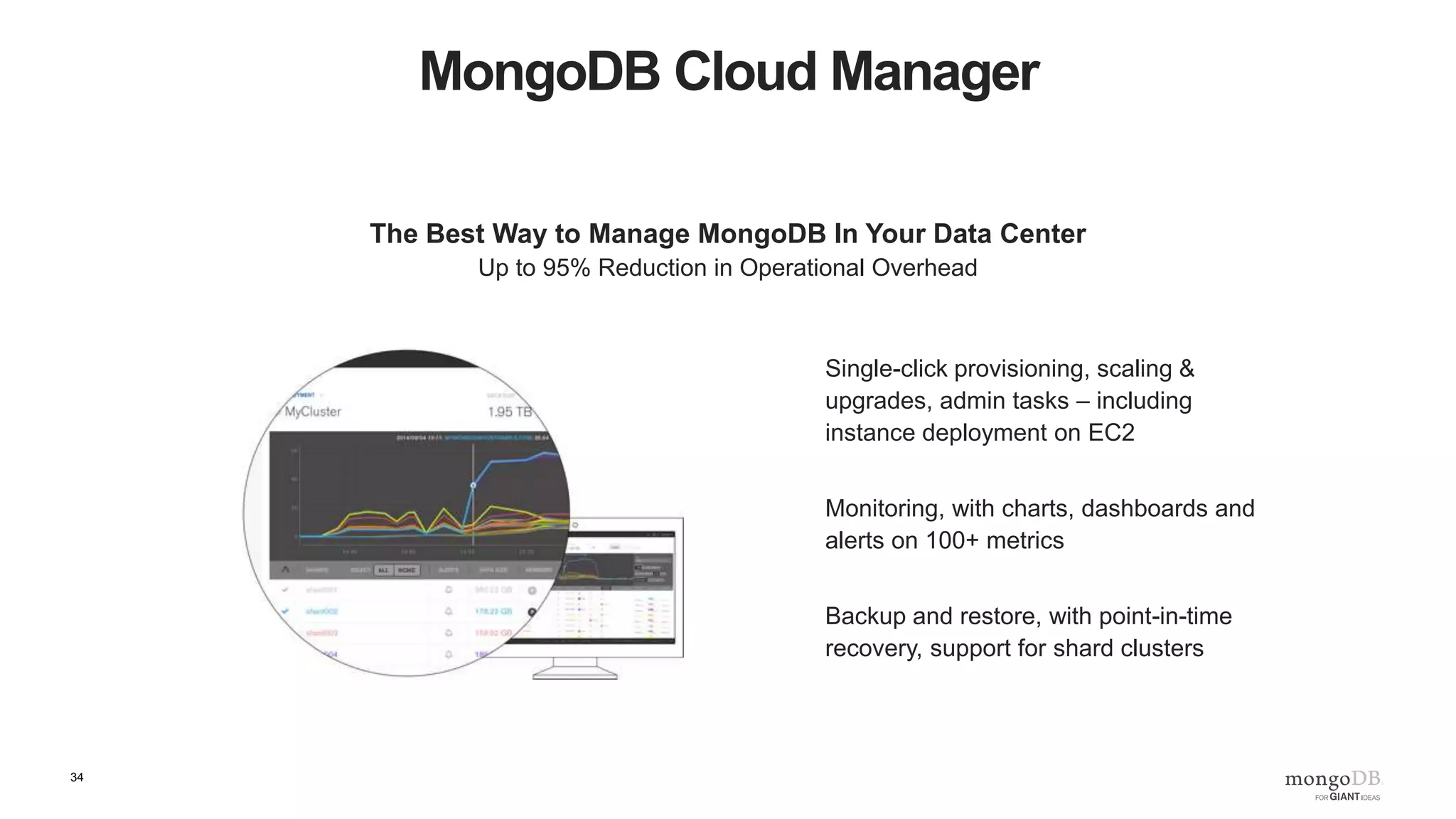
The document provides an overview of running MongoDB on AWS, detailing its features, deployment configurations, and best practices for performance and data safety. It discusses various EC2 instance types, considering factors like memory optimization and high availability through replica sets and sharded clusters. Additionally, it highlights the importance of proper backup plans and using MongoDB Cloud Manager for managing instances and operational tasks.