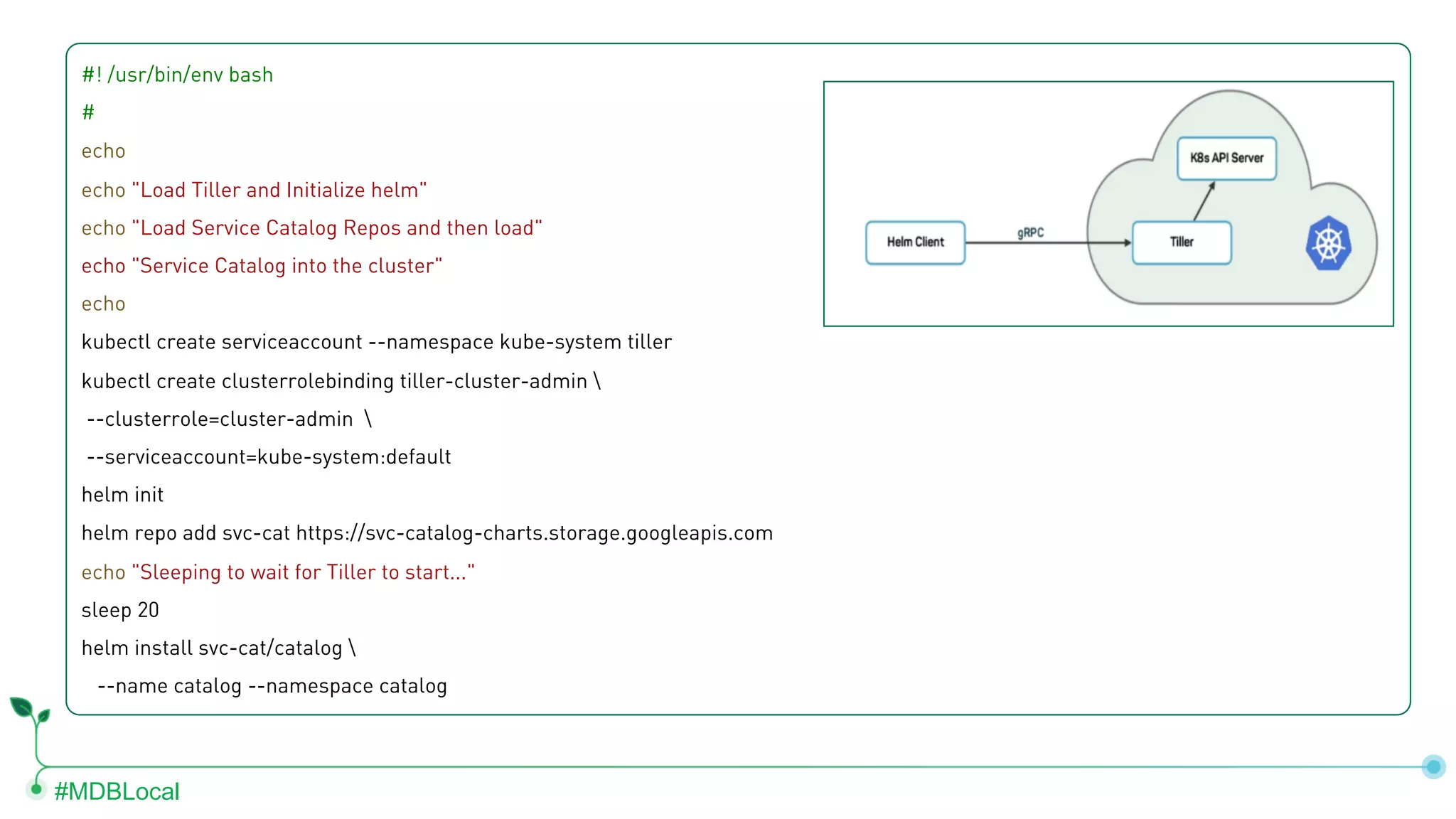
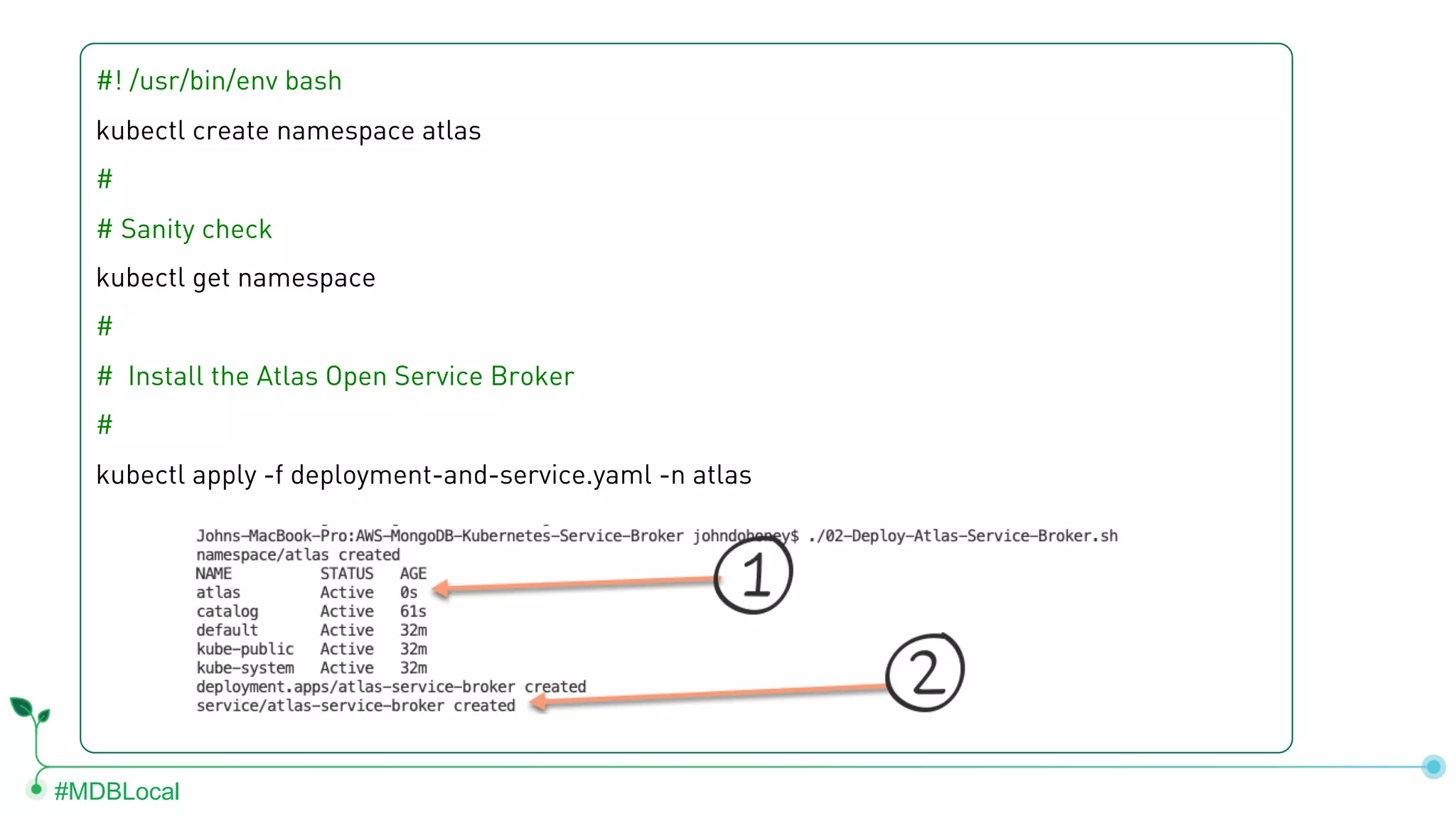
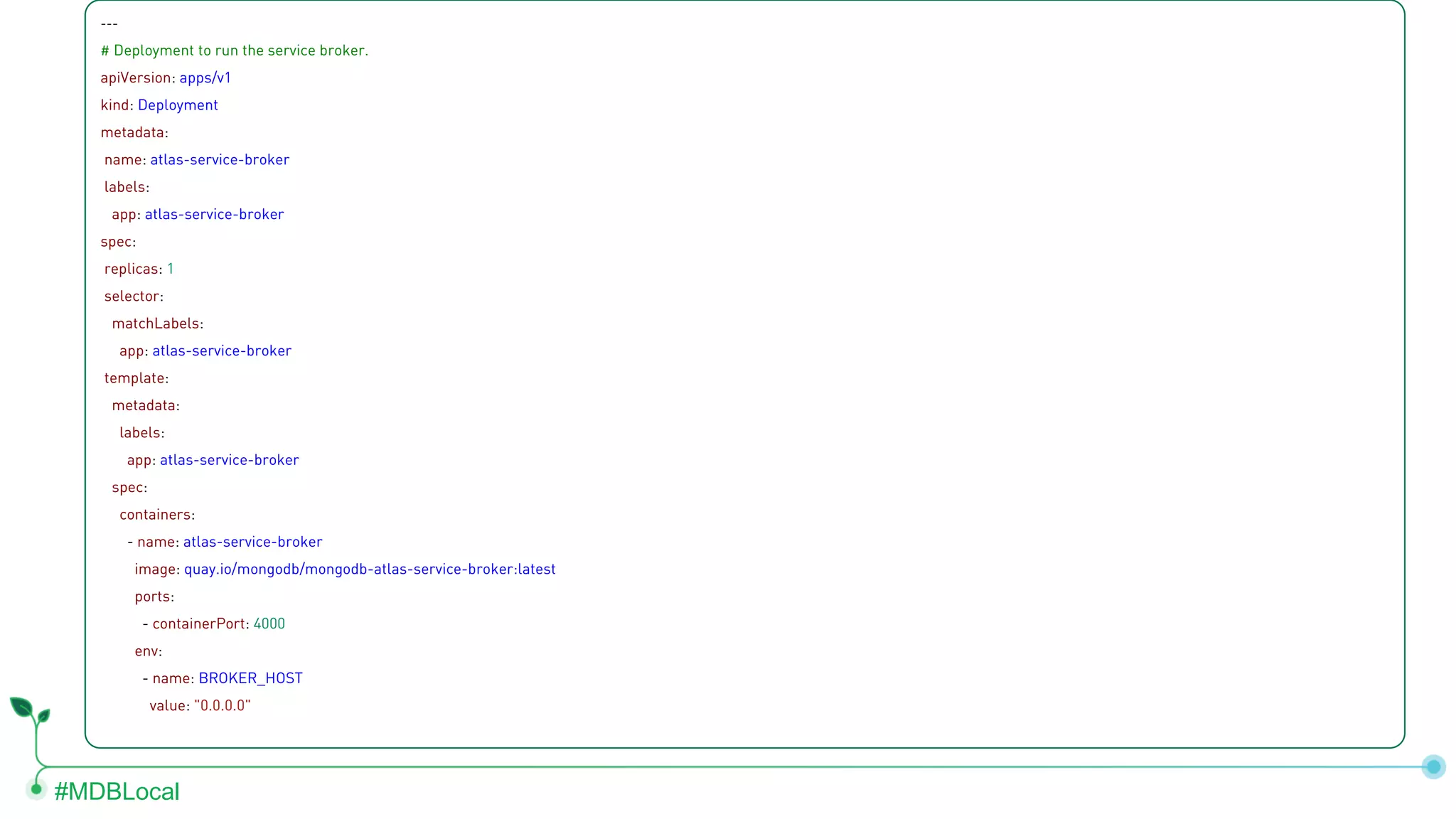
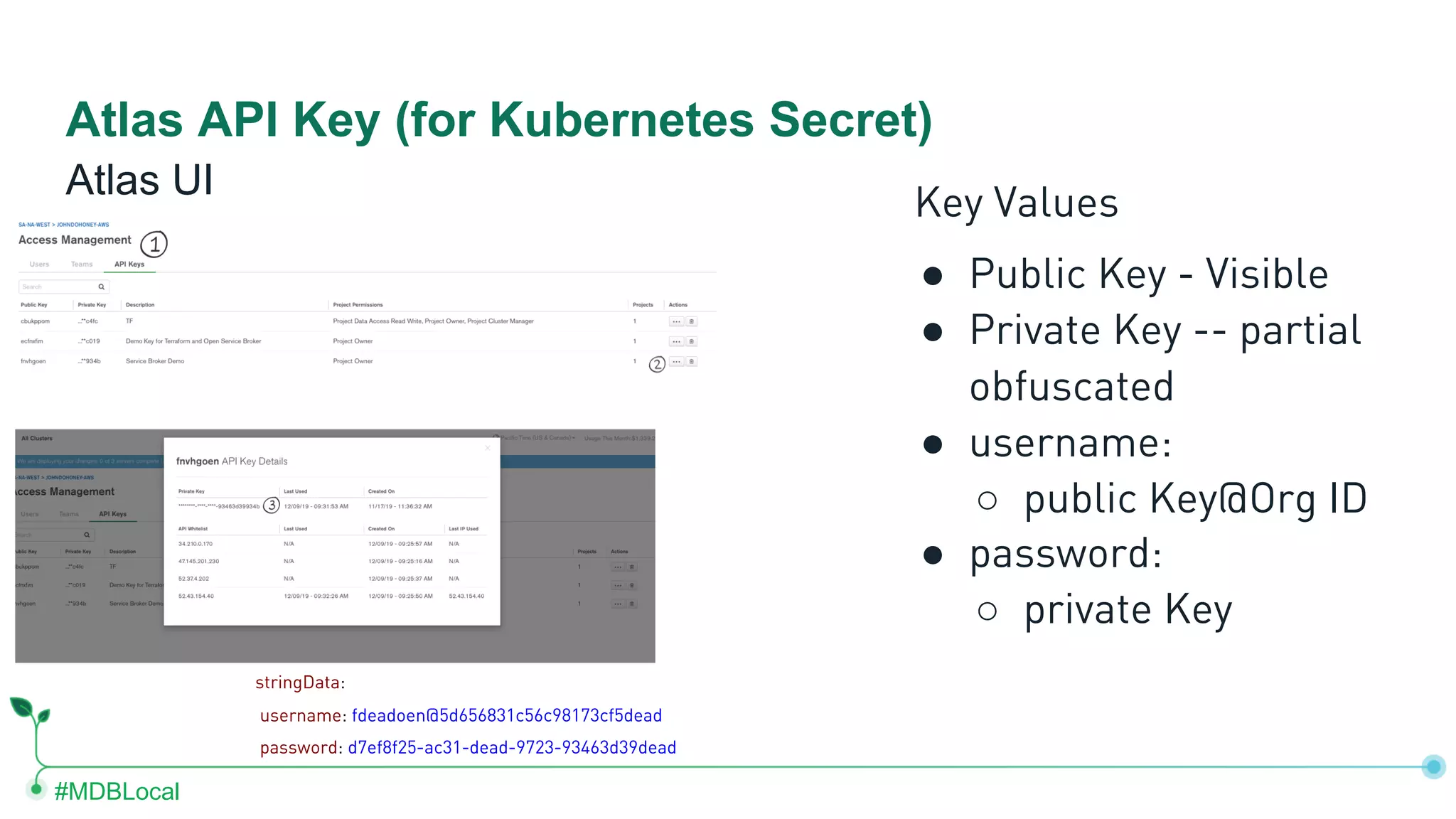
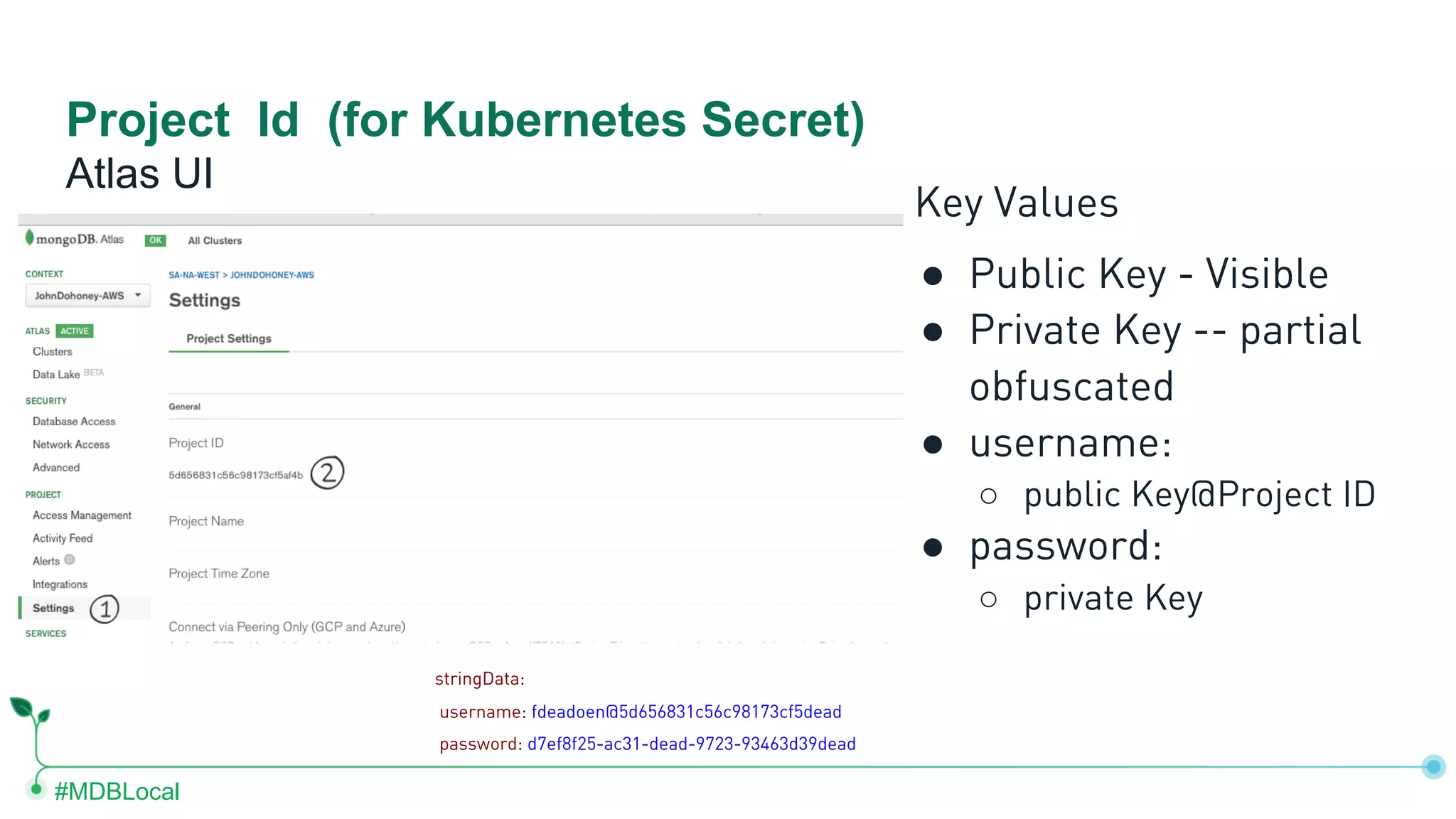
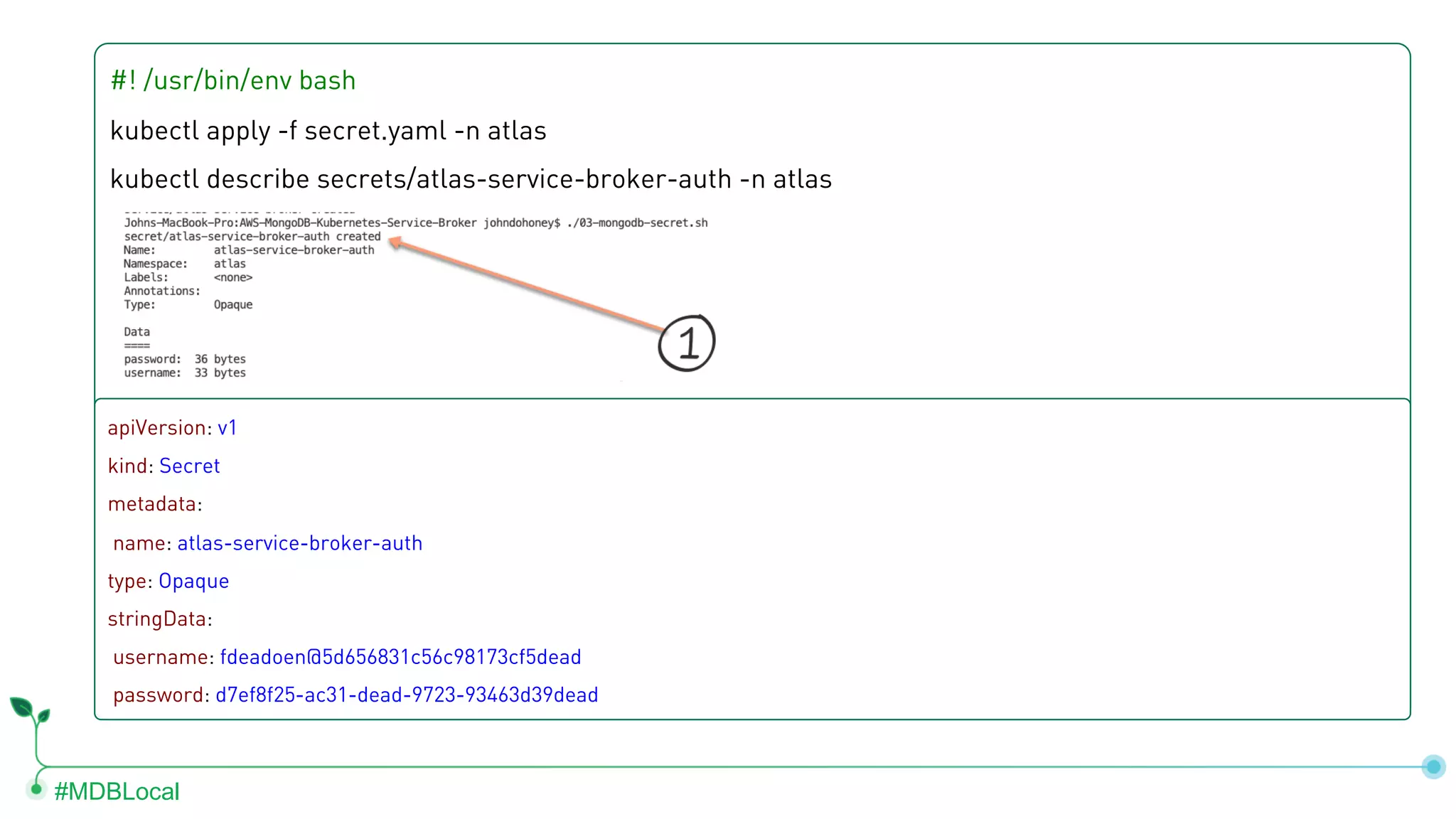
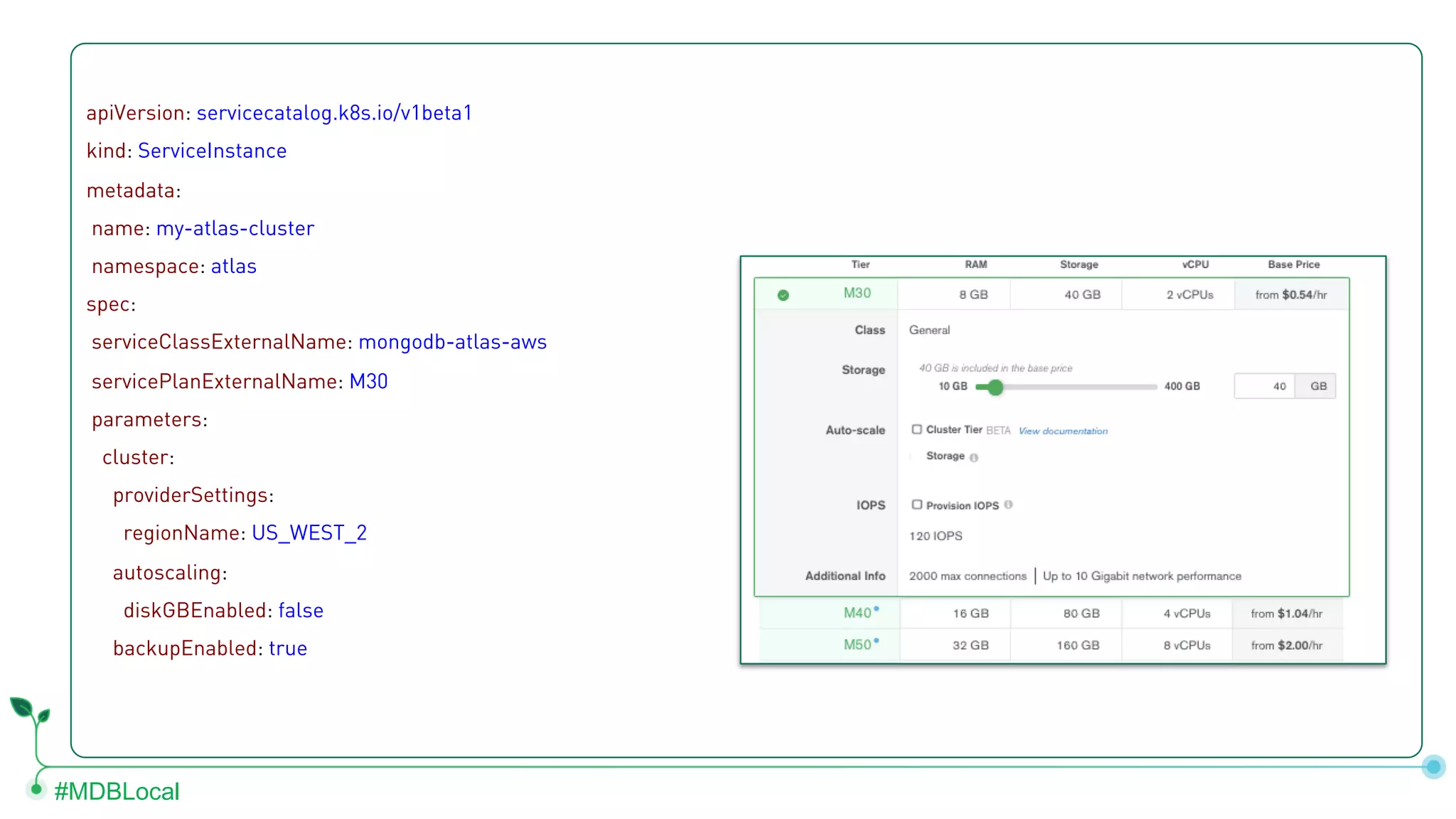
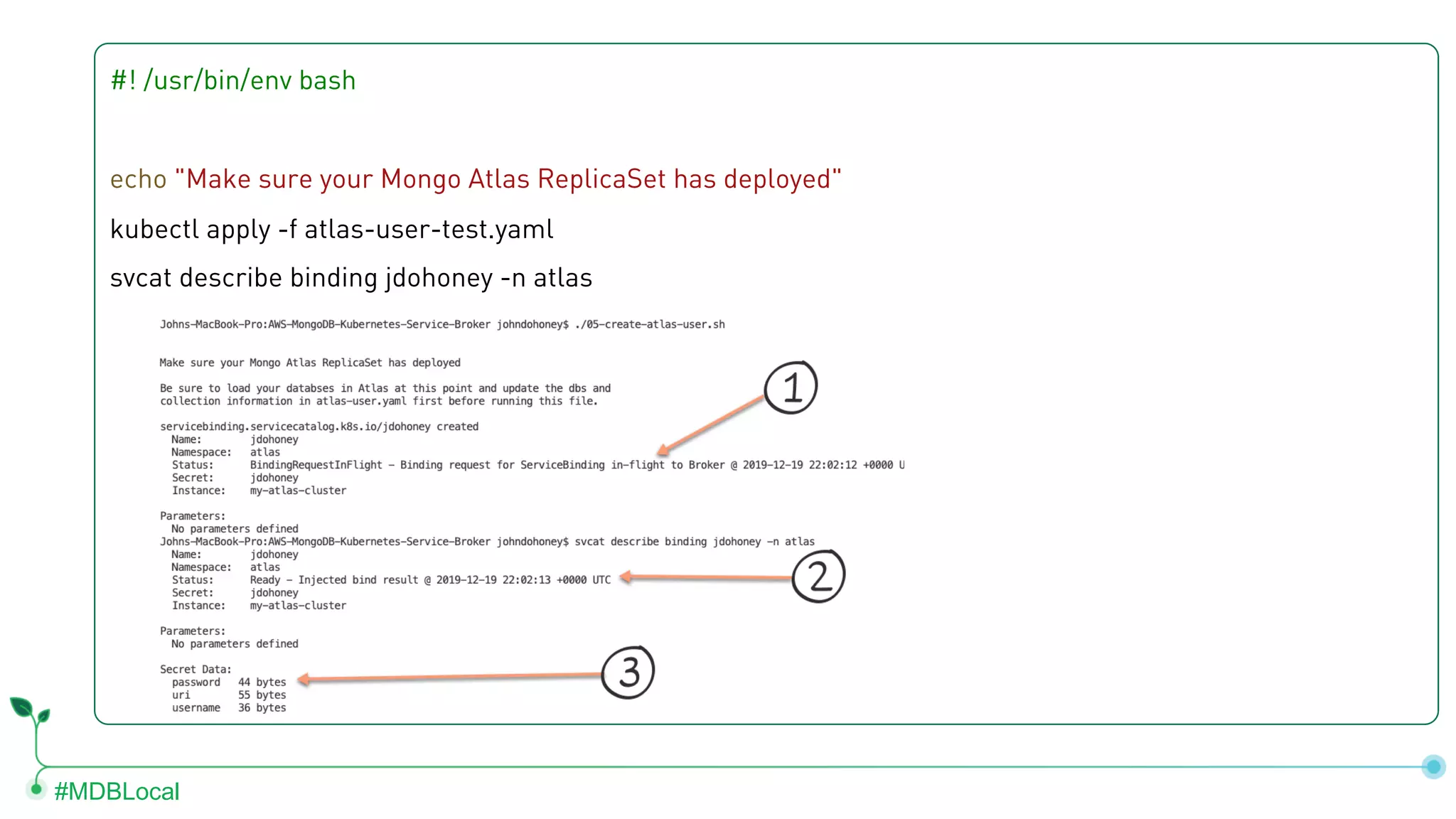
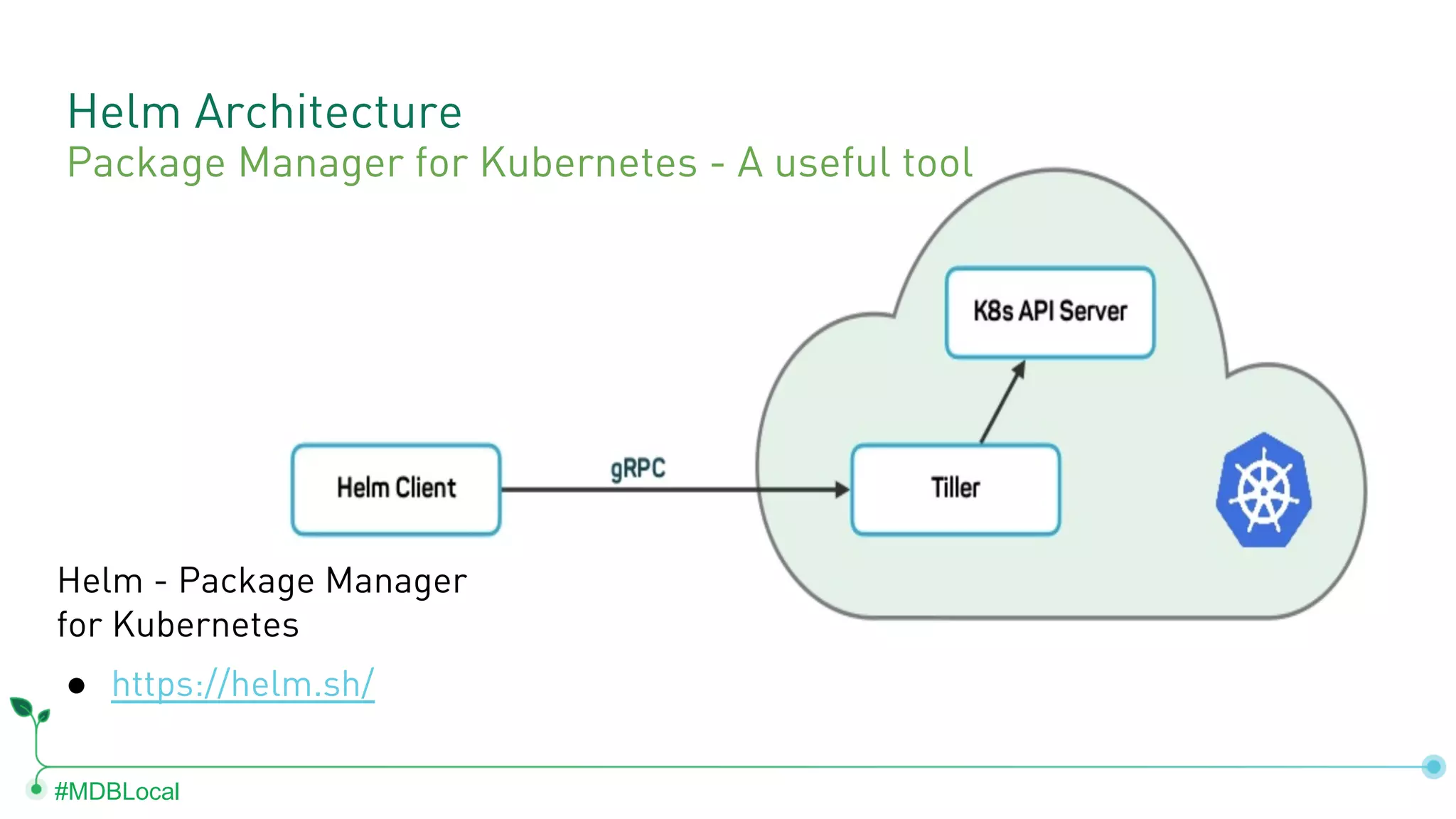
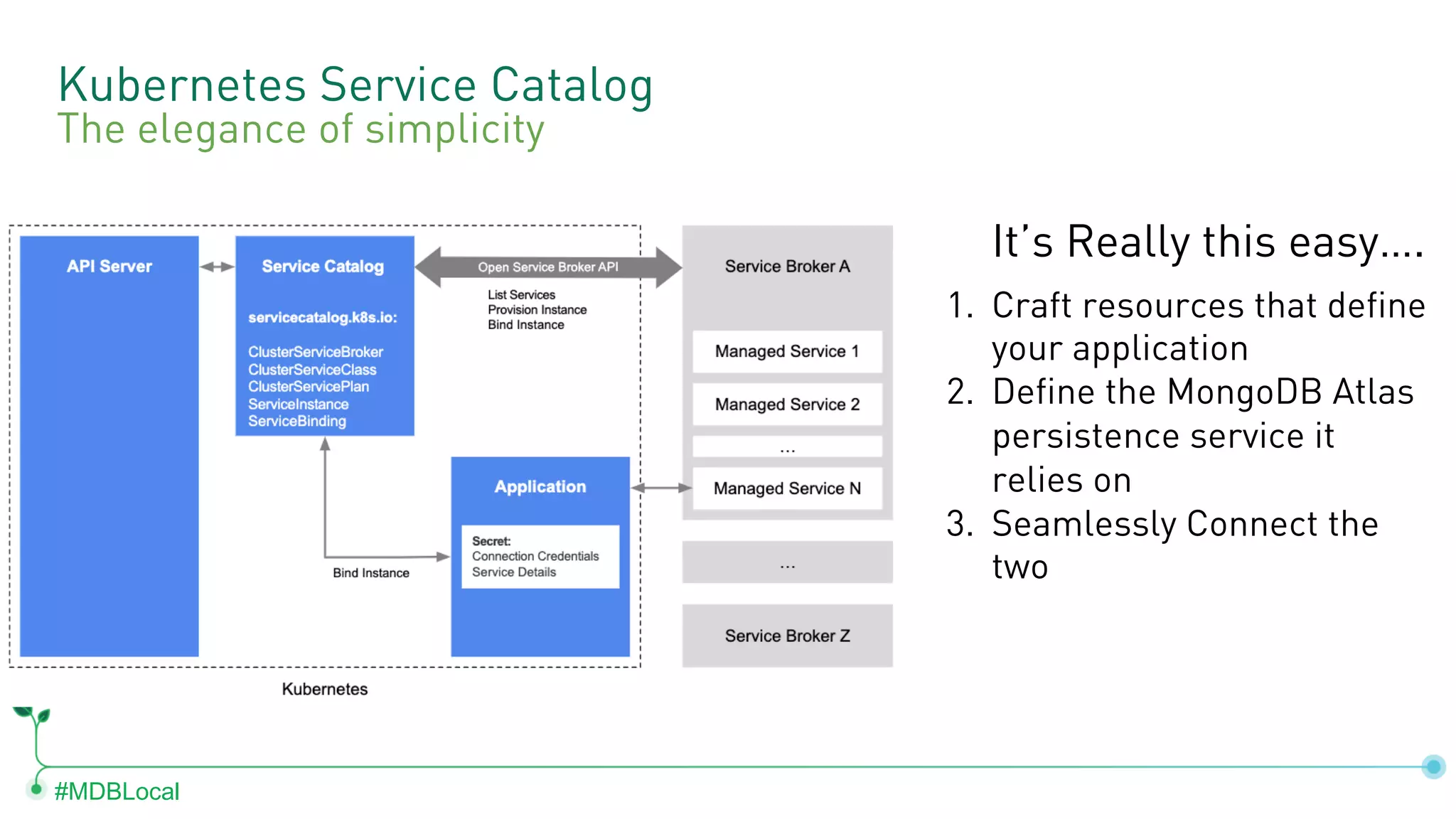
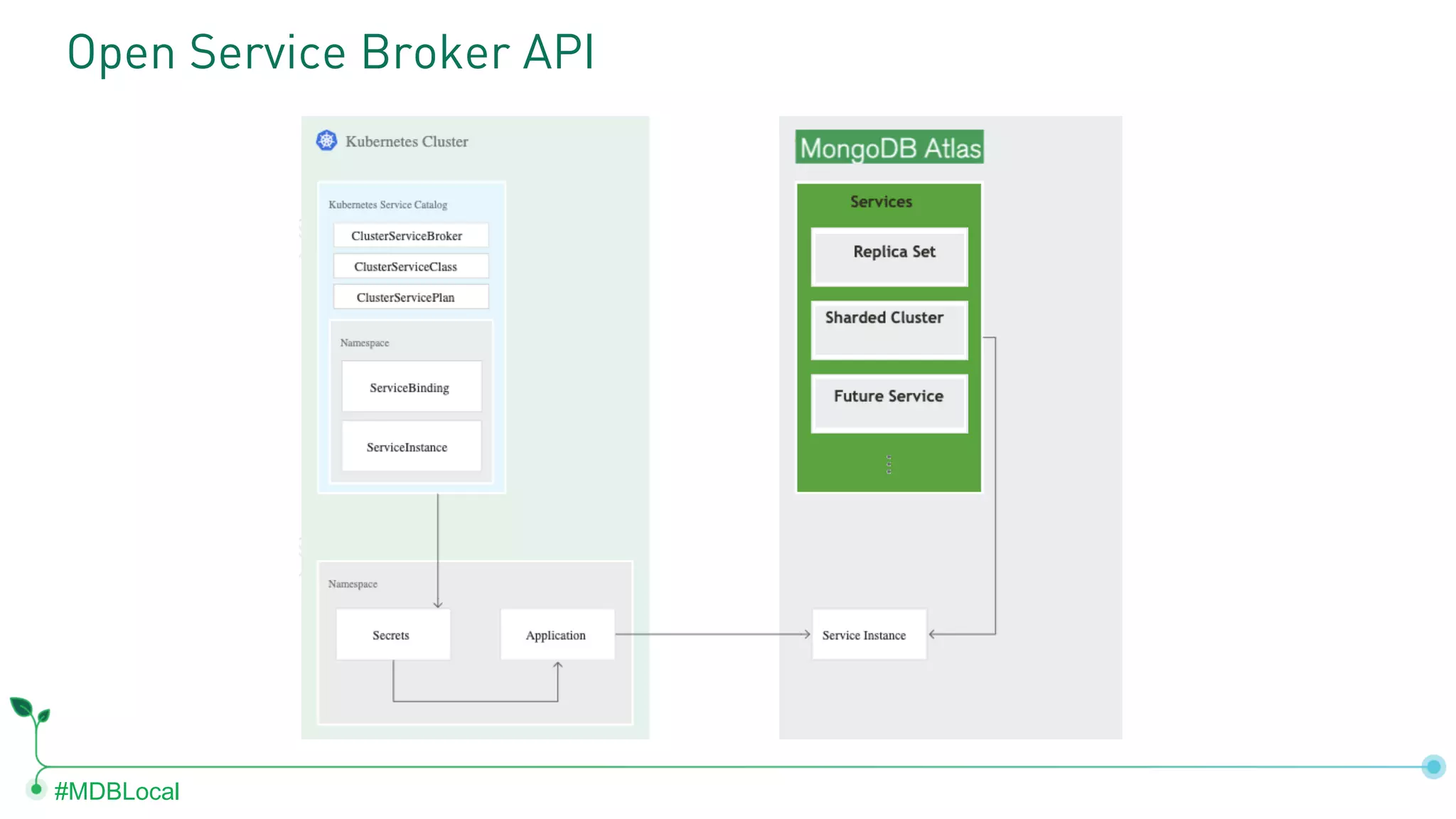
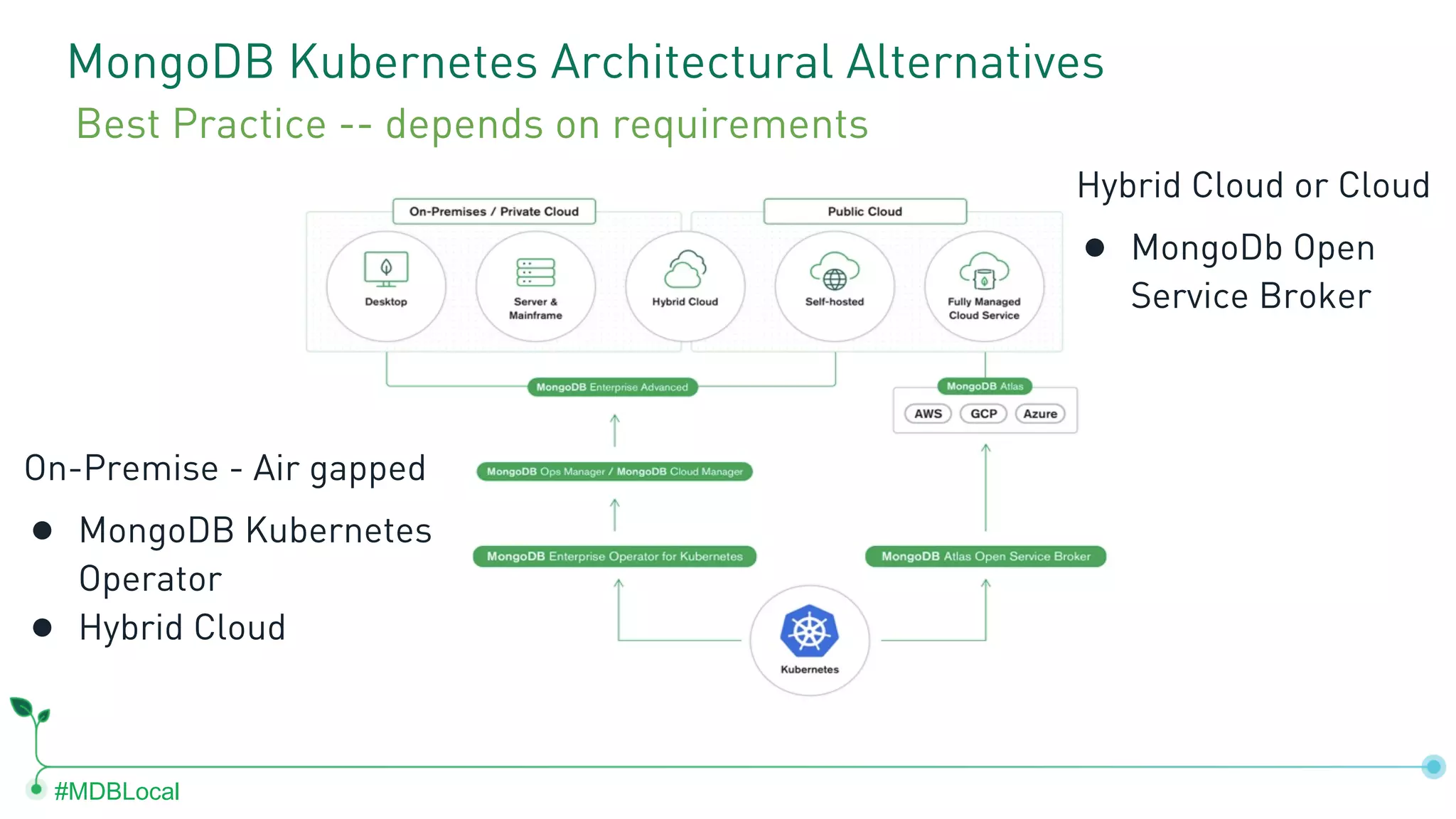
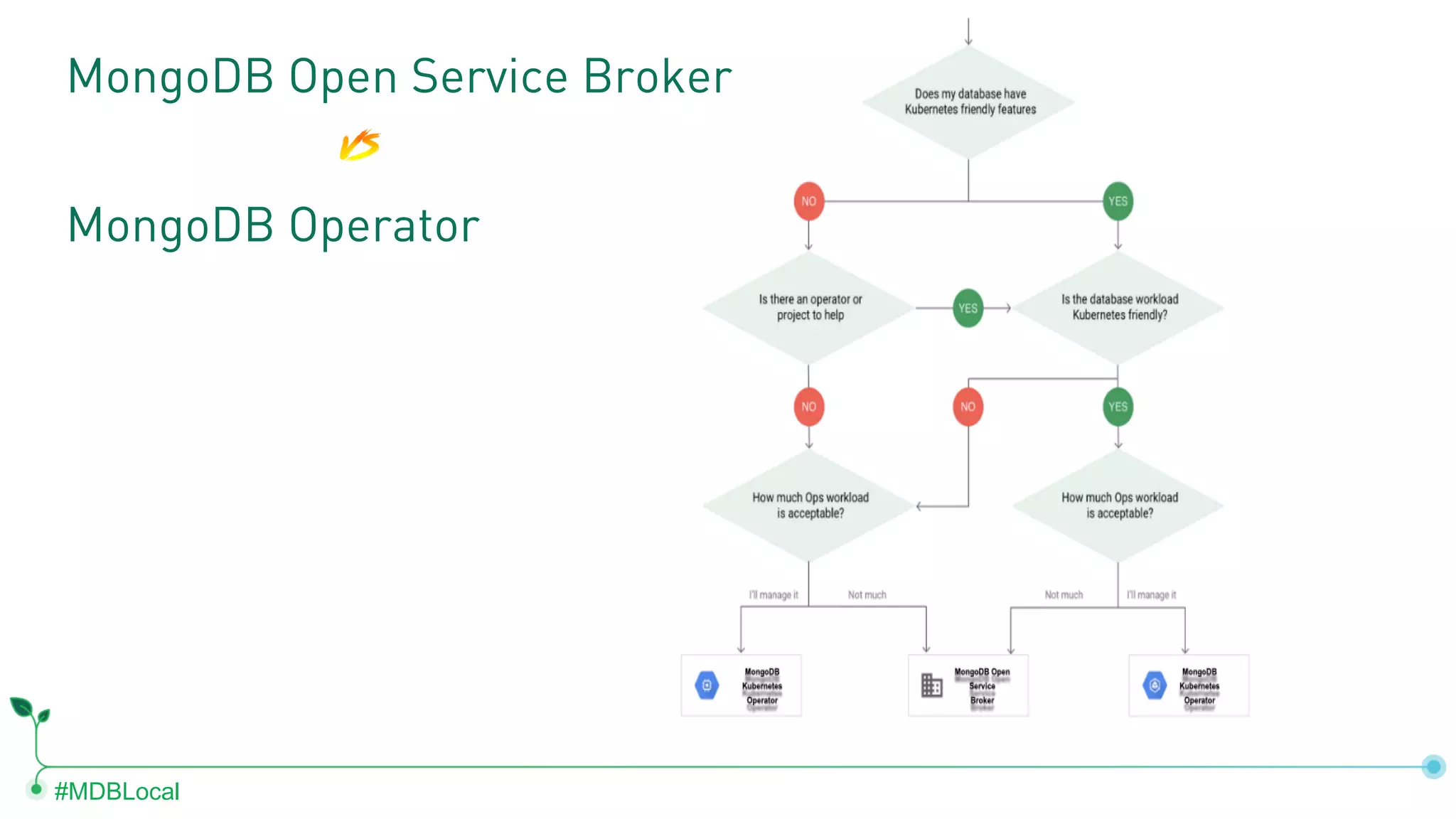
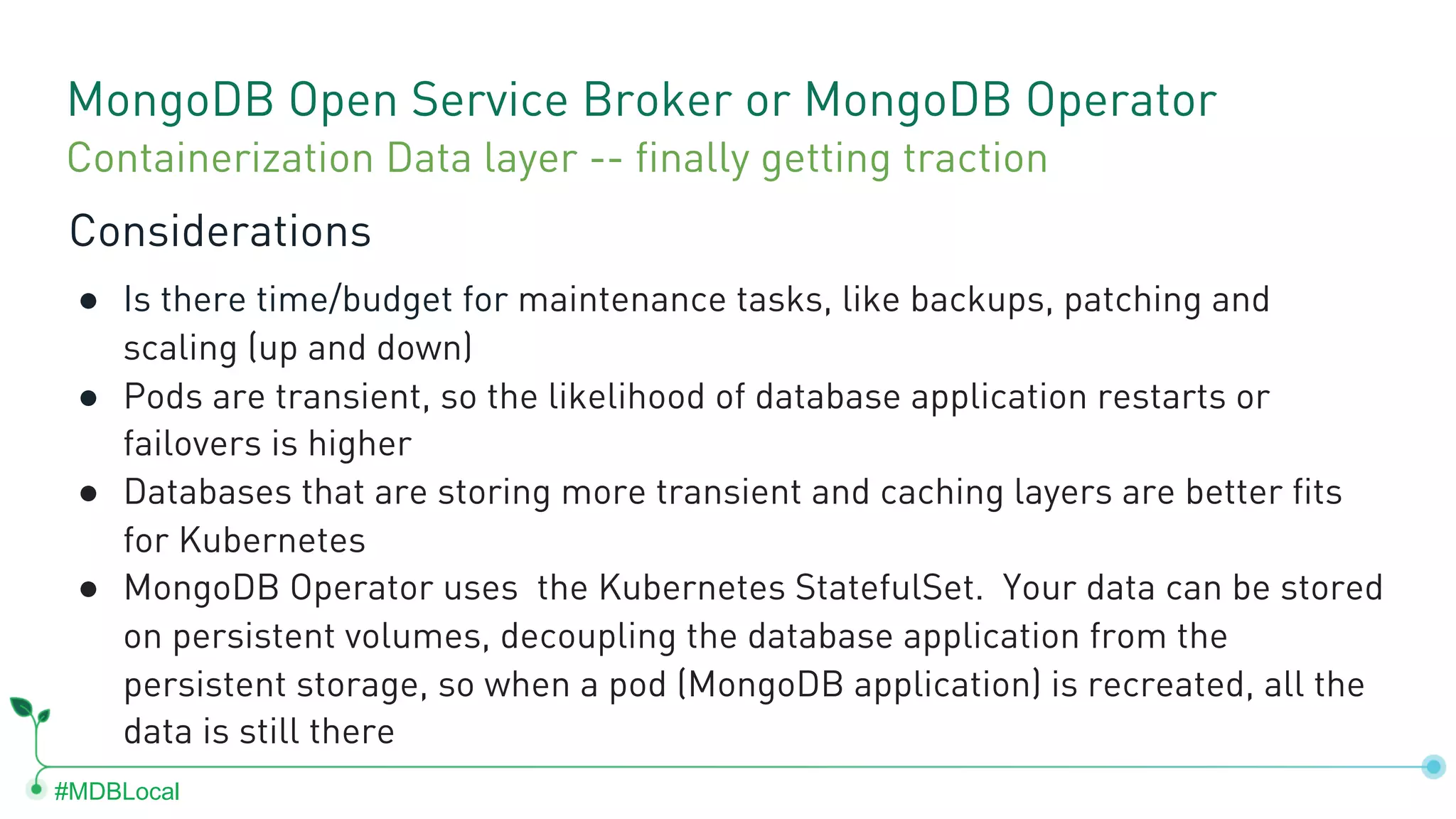
The document outlines the setup and use of MongoDB with Kubernetes through the MongoDB Operator and Open Service Broker, highlighting the necessary configurations and resources for deployment. It includes commands for cluster creation, service configuration, and secret management, emphasizing the ease of connecting MongoDB with Kubernetes services. Additionally, considerations for maintenance and architectural options are discussed to aid in decision-making for deployment strategies.


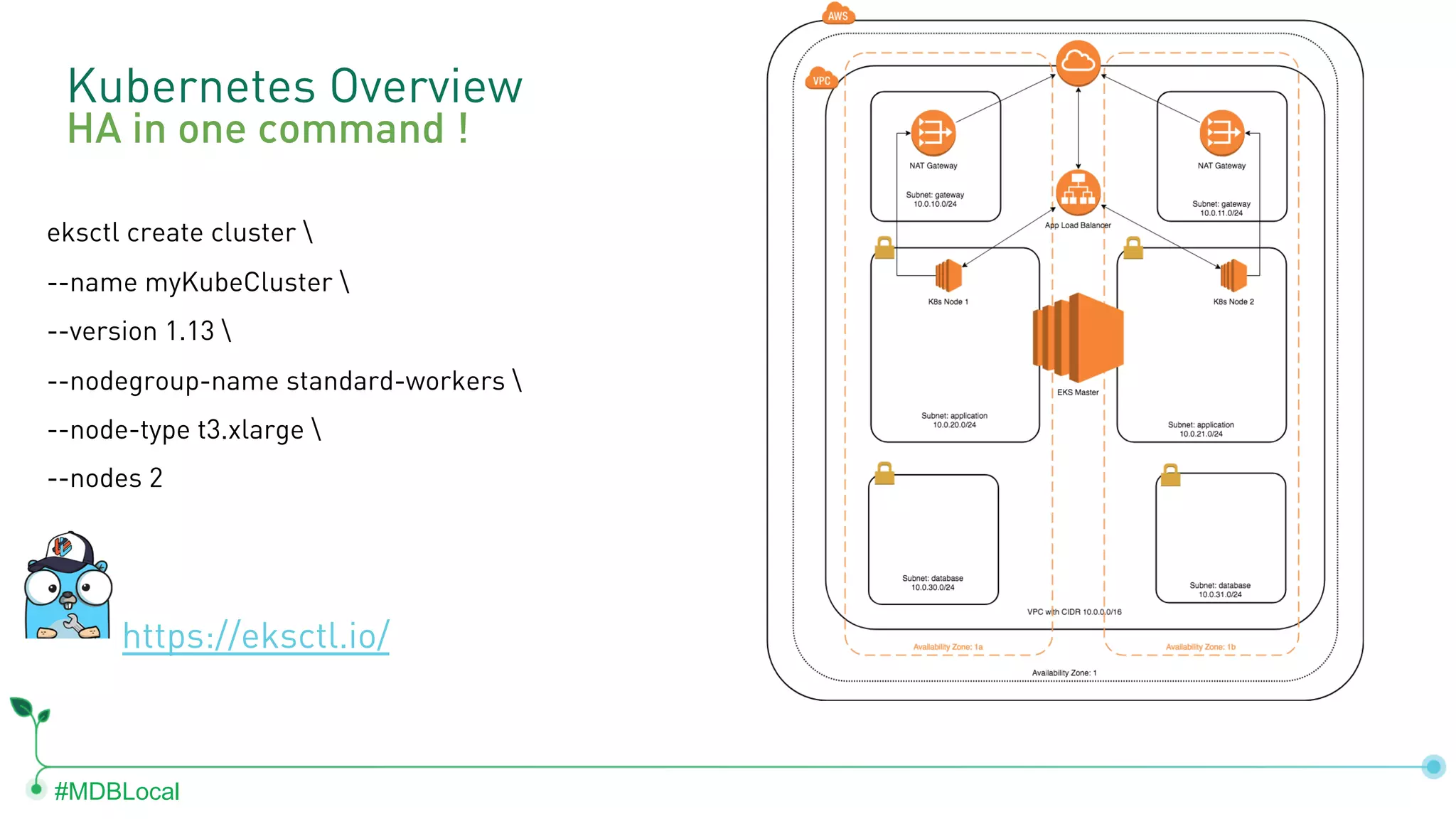



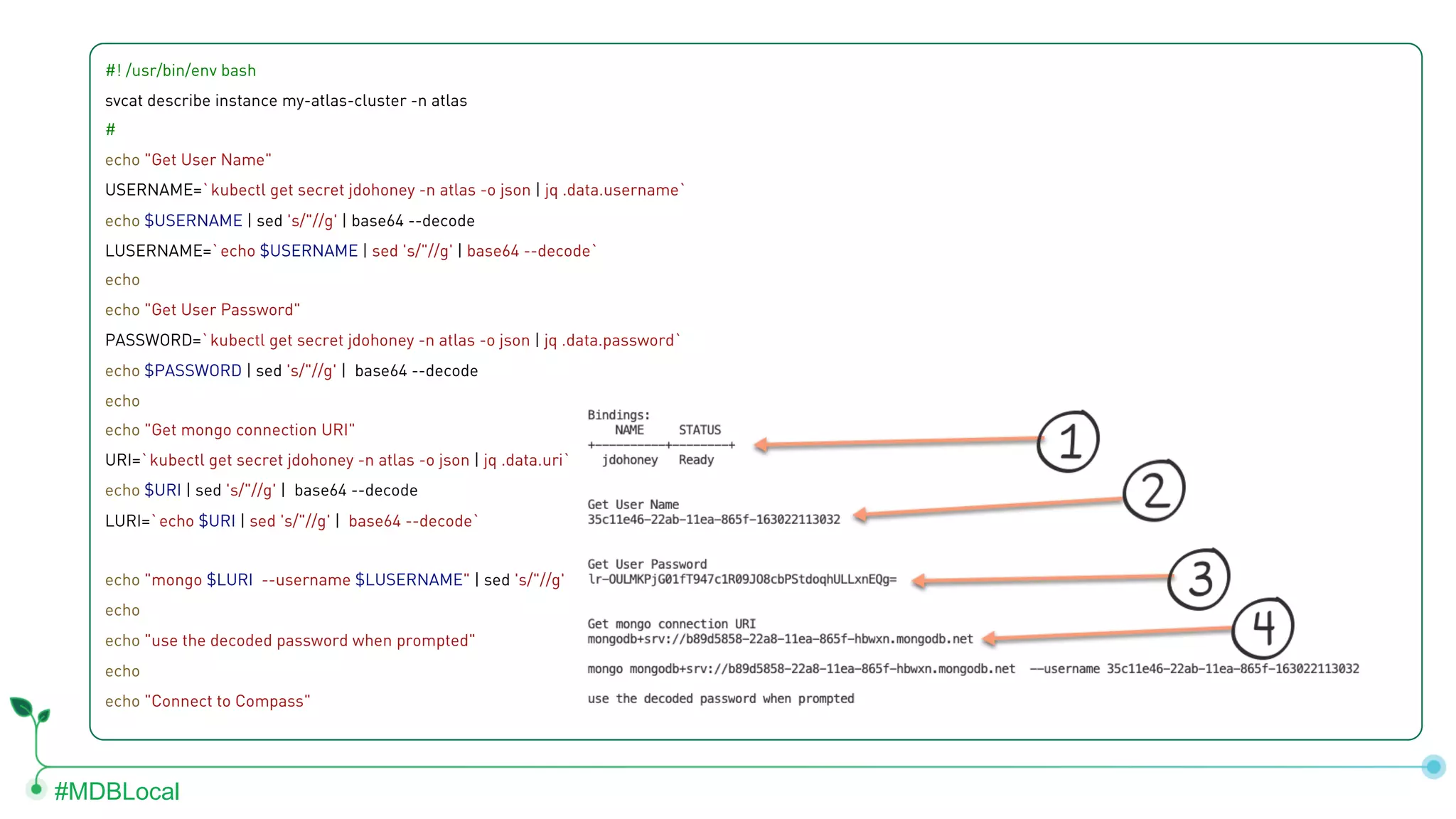
![#MDBLocal #! /usr/bin/env bash eksctl create cluster --name atlas-service-catalog --version 1.13 --nodegroup-name standard-workers --node-type t3.xlarge --nodes 3 # Get External IP kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{$.items[*].status.addresses[?(@.type=="ExternalIP")].address }' echo echo "Be sure to add external IPs to API Whitelist..."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-kubernetesoptions-paloalto-202001022020-200117190405/75/MongoDB-local-San-Francisco-2020-Using-MongoDB-Services-in-Kubernetes-any-platform-15-2048.jpg)