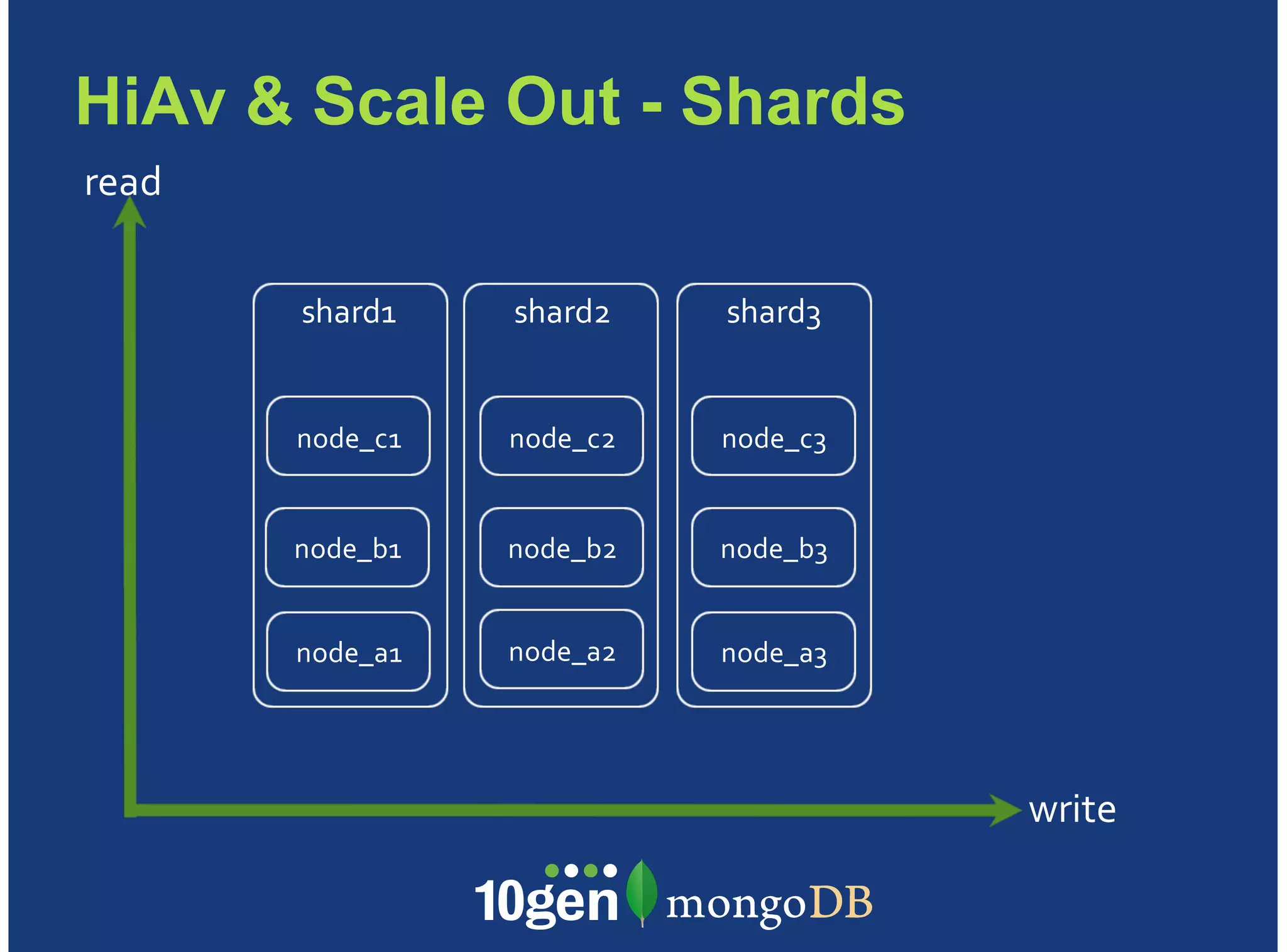
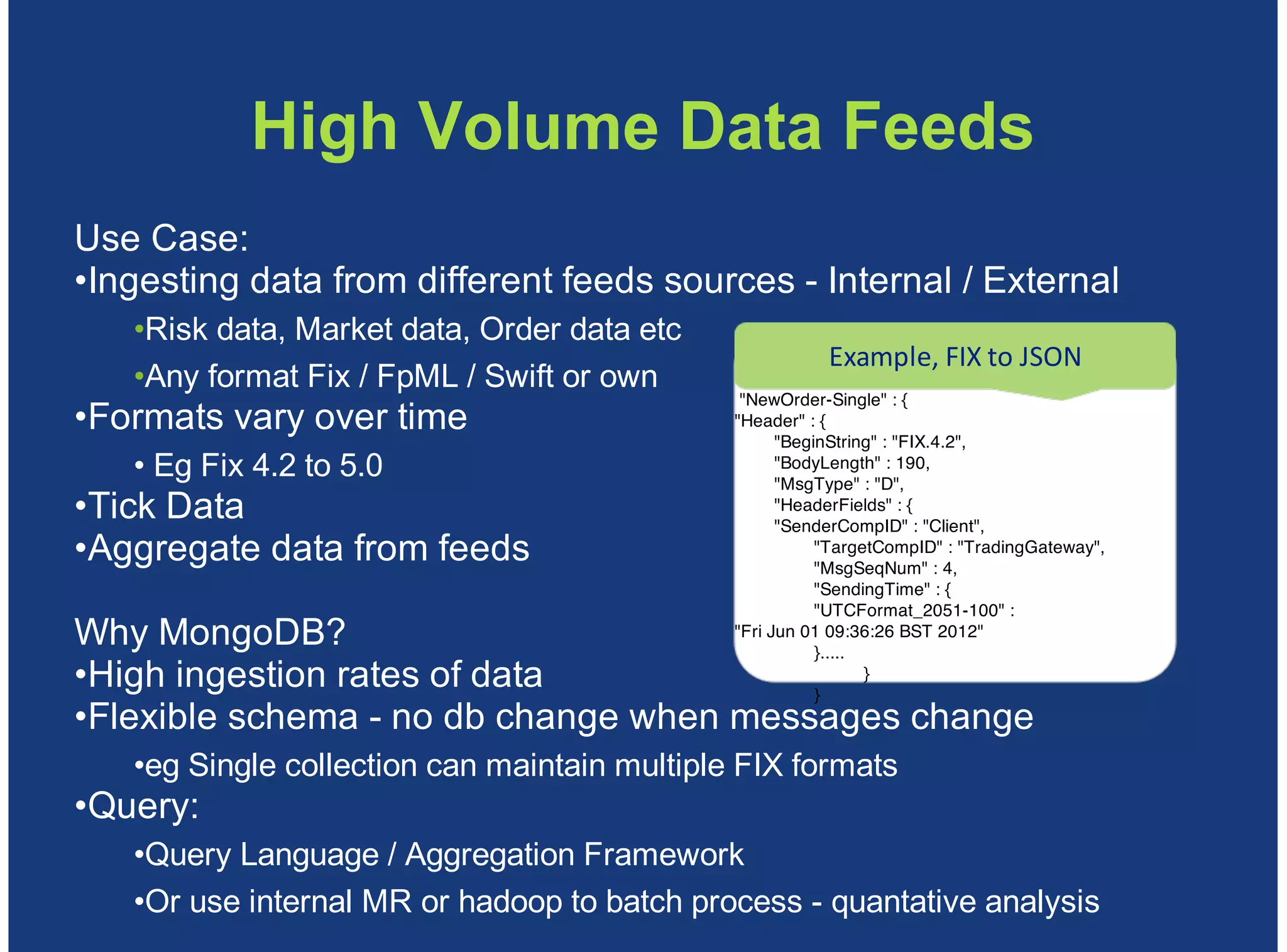
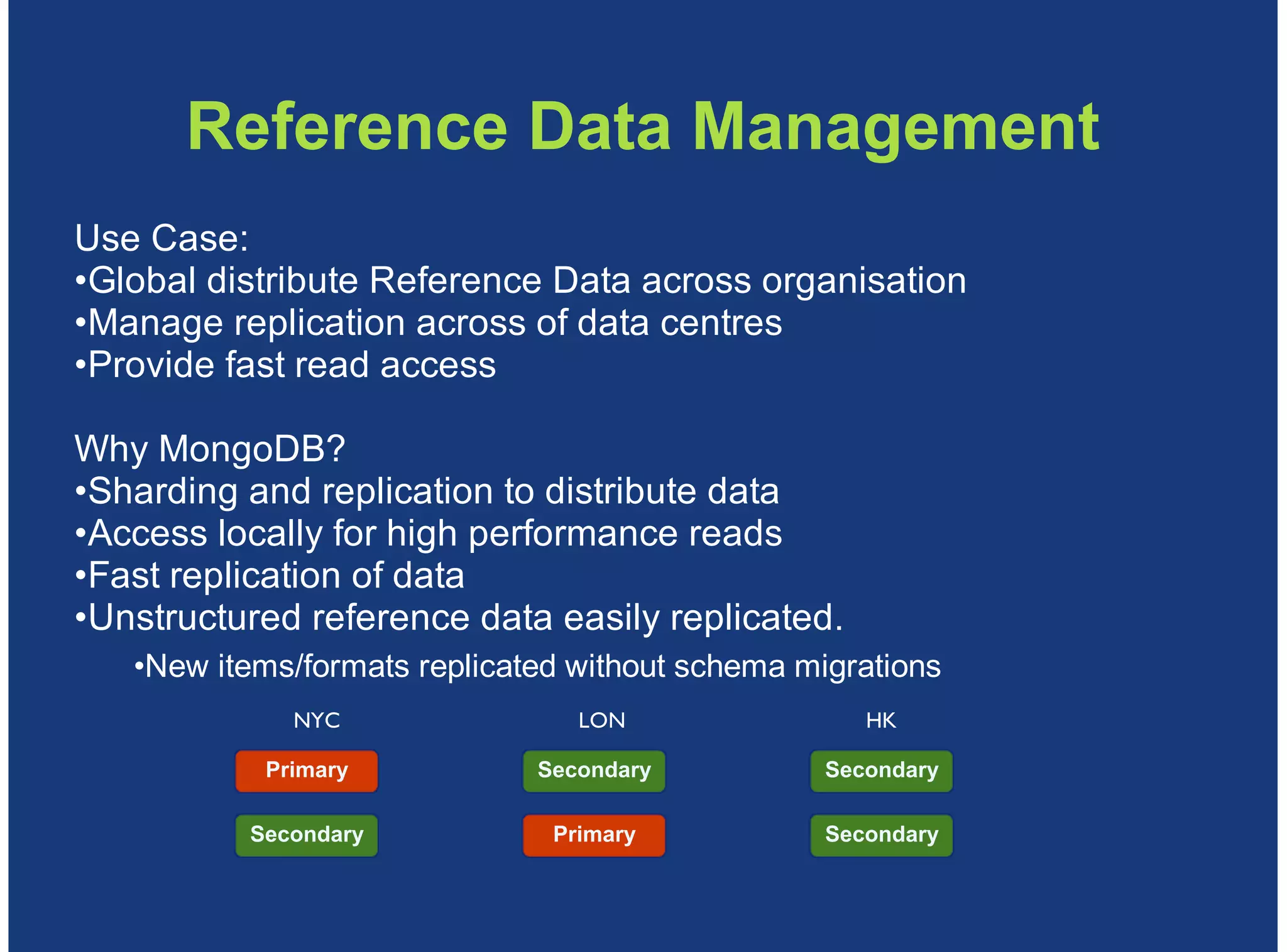
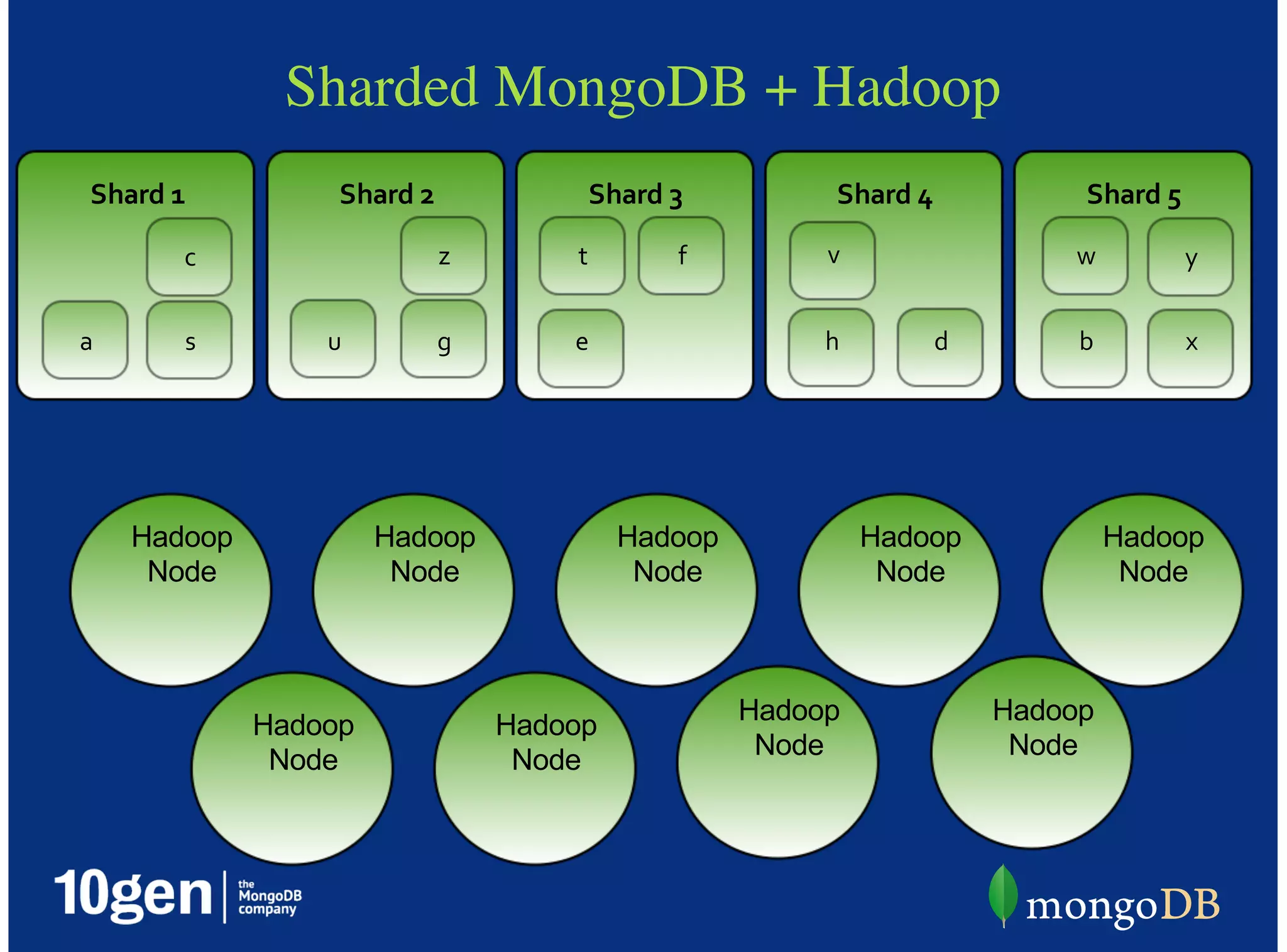
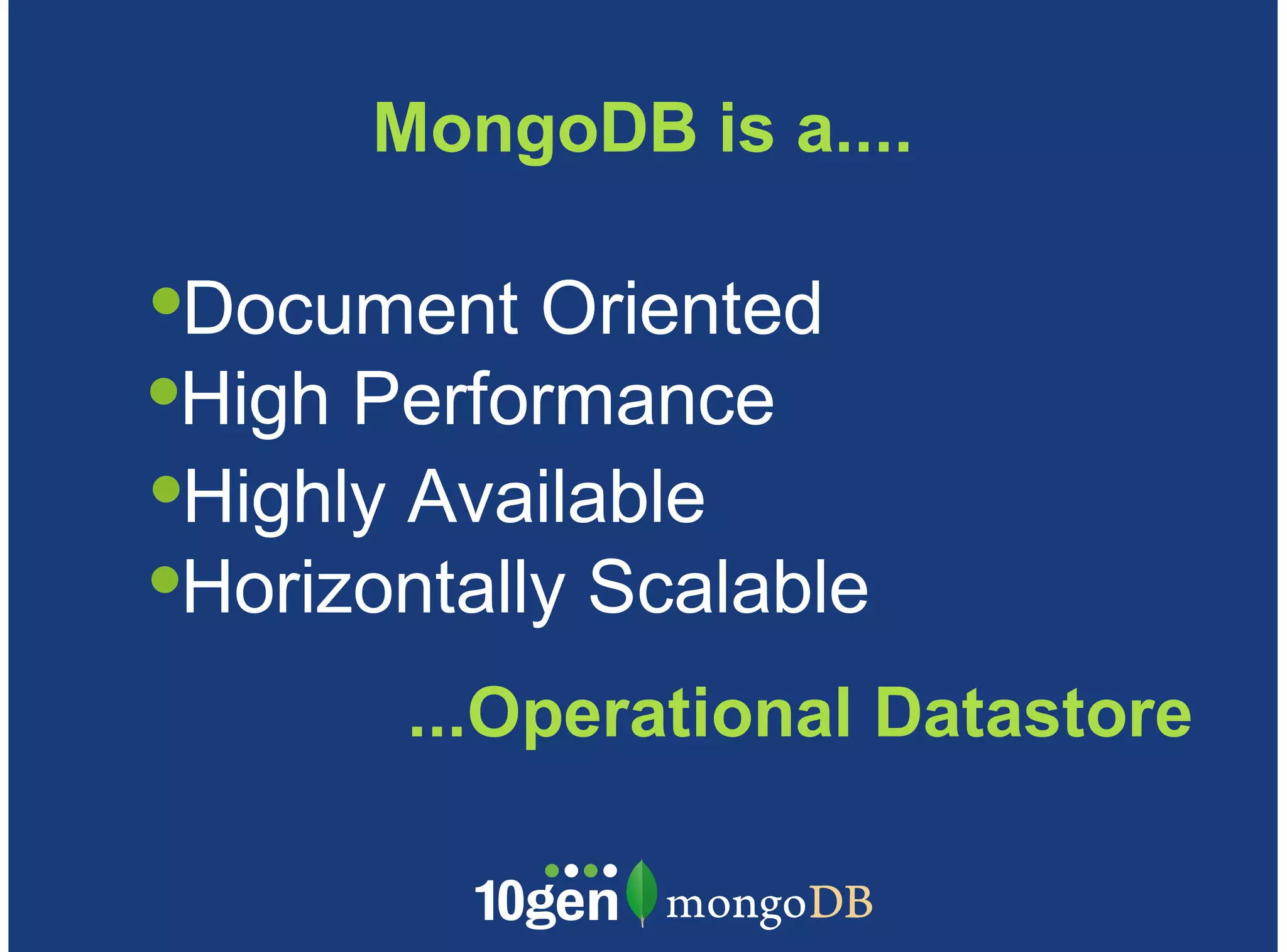
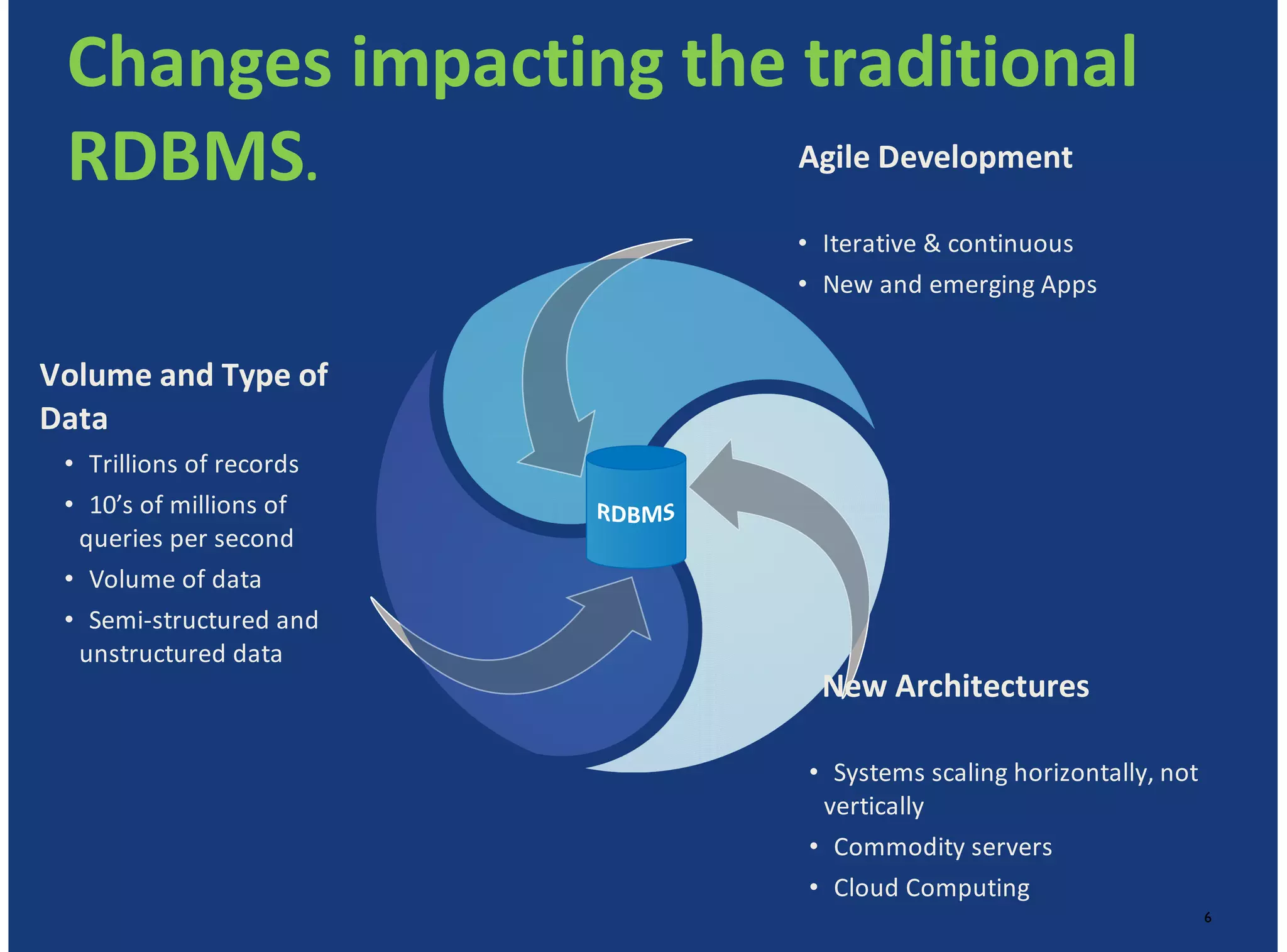
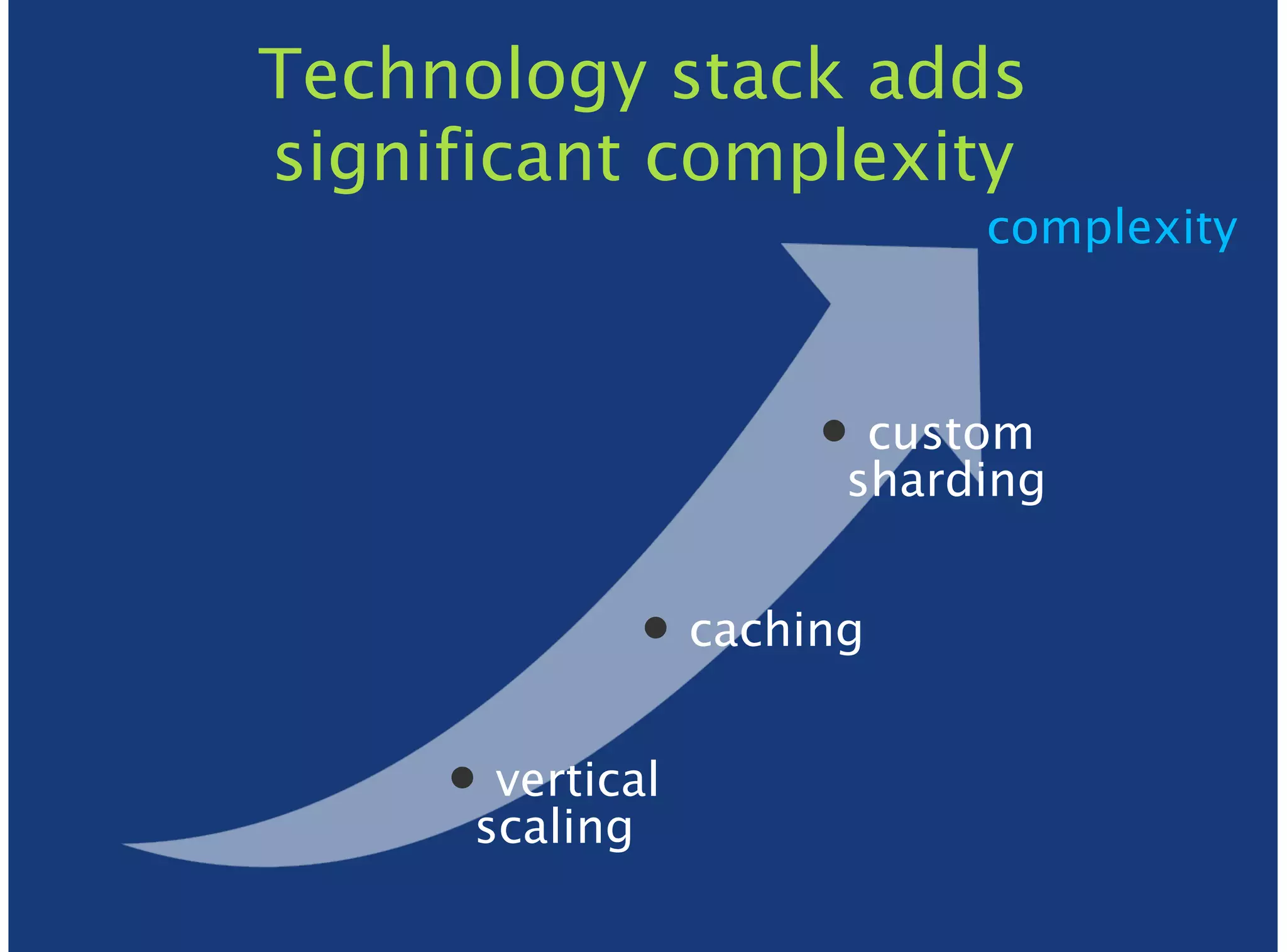
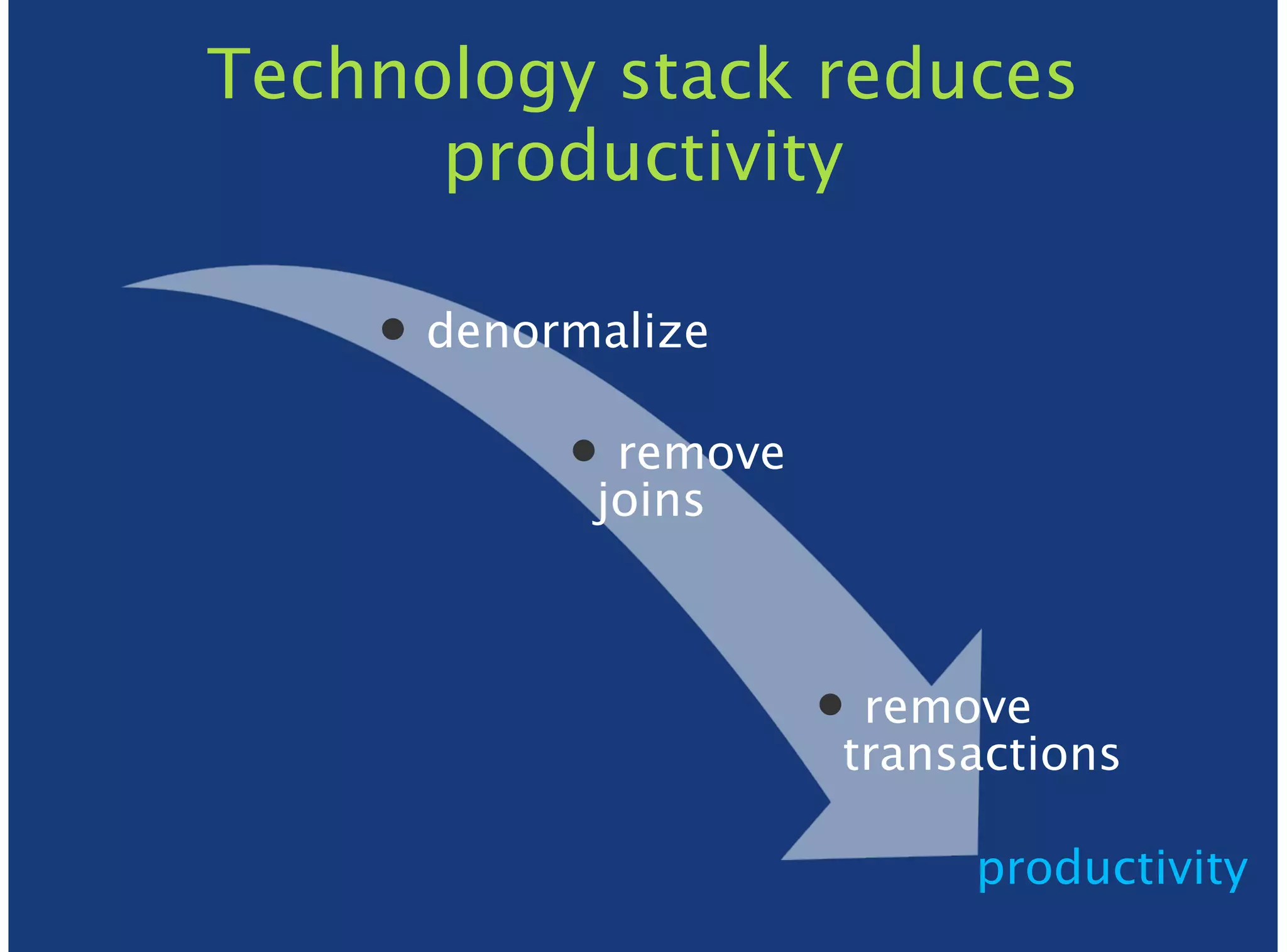
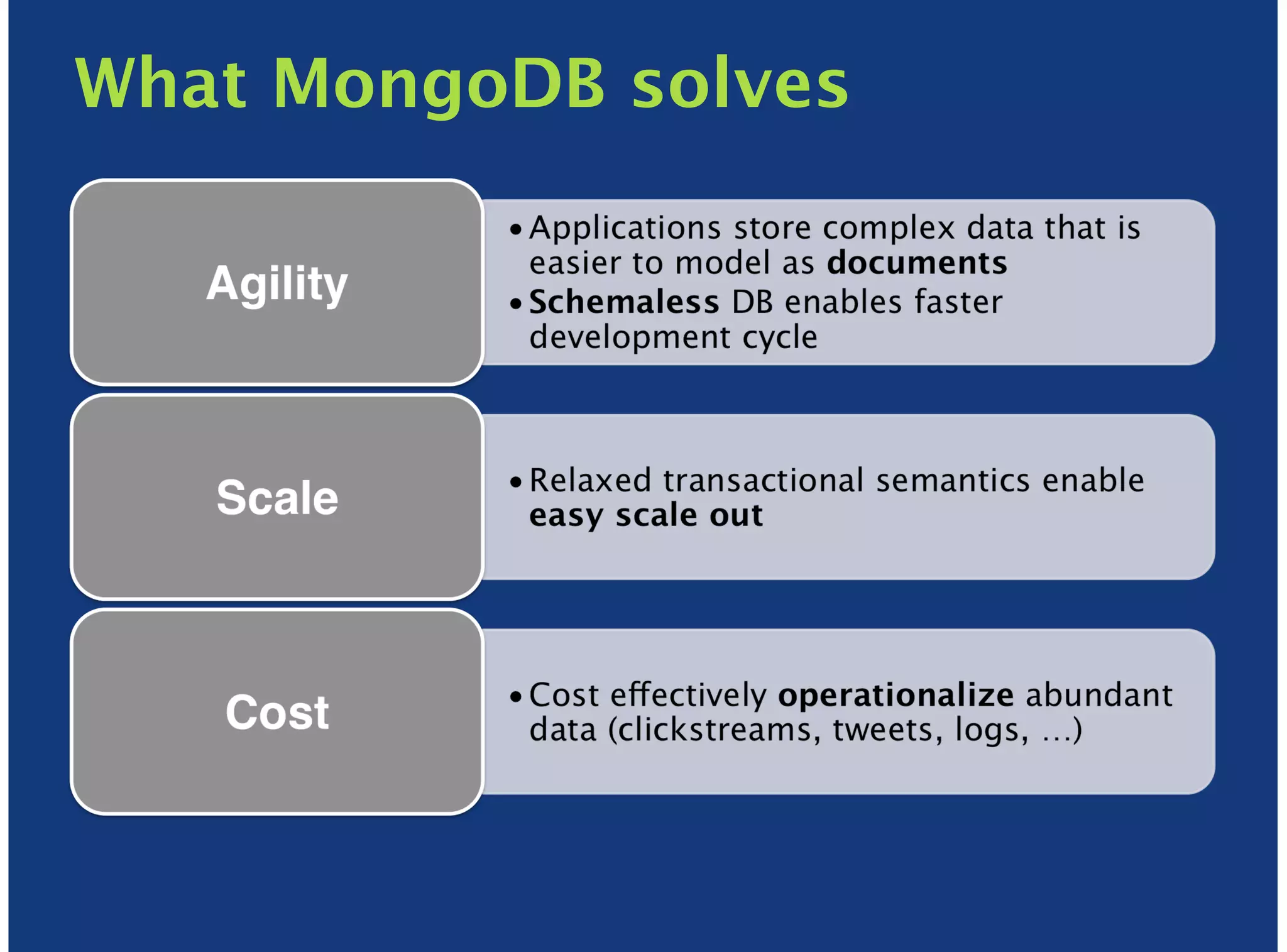
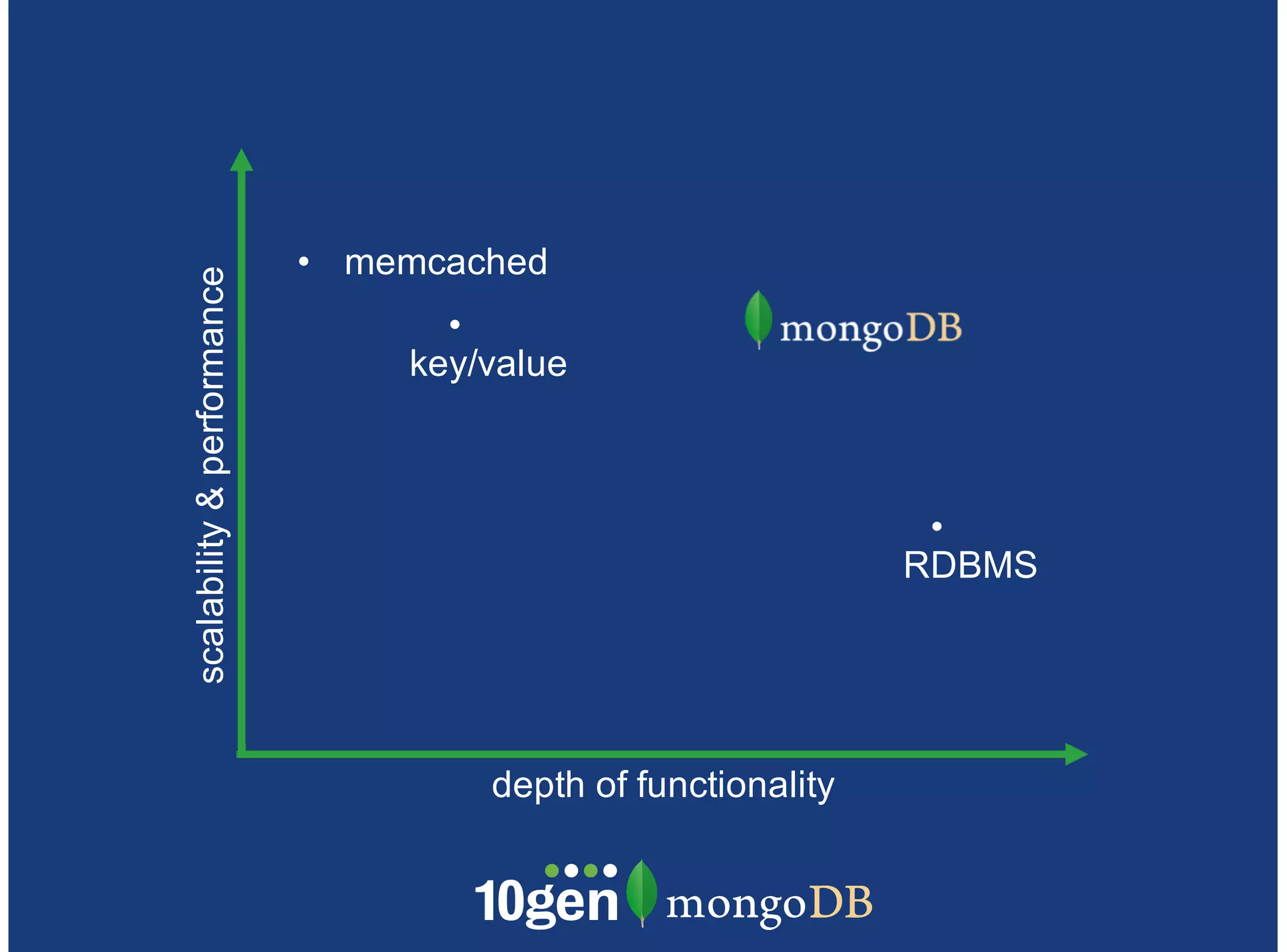
MongoDB is a document-oriented, high performance, highly available, and horizontally scalable operational database. It addresses challenges with traditional RDBMS like handling high volumes of data, semi-structured and unstructured data types, and the need for agile development. MongoDB can be used for financial services use cases like high volume data feeds, risk analytics, product catalogs, trade capture, reporting, reference data management, portfolio management, quantitative analysis, and automated trading. It provides features like flexible schemas, indexing, aggregation, scaling out through sharding, and integration with Hadoop.



![Complex Tables to Documents { title: ‘MongoDB’, contributors: [ { name: ‘Eliot Horowitz’, email: ‘eliot@10gen.com’ }, { name: ‘Dwight Merriman’, email: ‘dwight@10gen.com’ } ], model: { relational: false, awesome: true } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbinfsslides-121024122313-phpapp02/75/MongoDB-in-FS-10-2048.jpg)