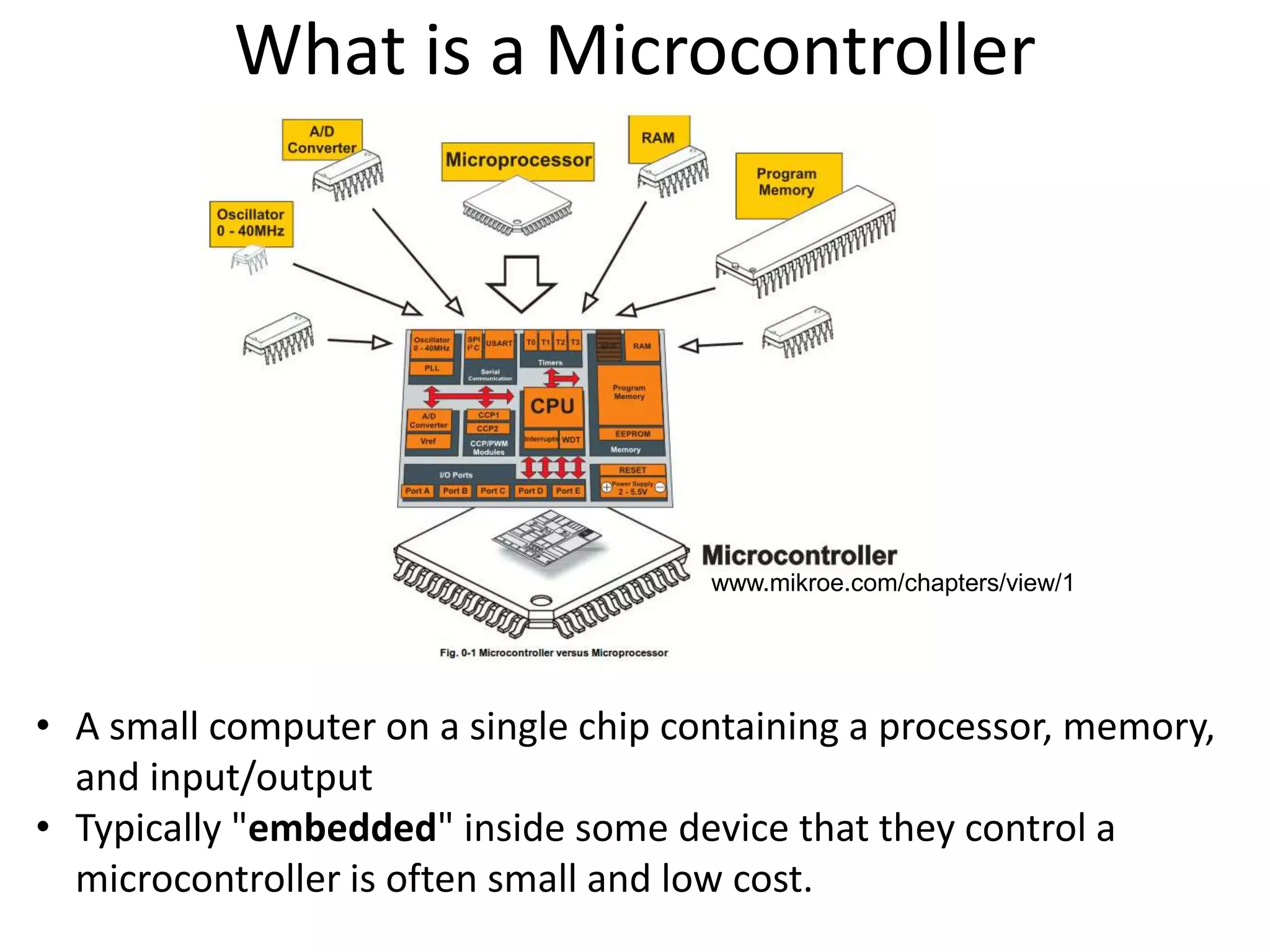
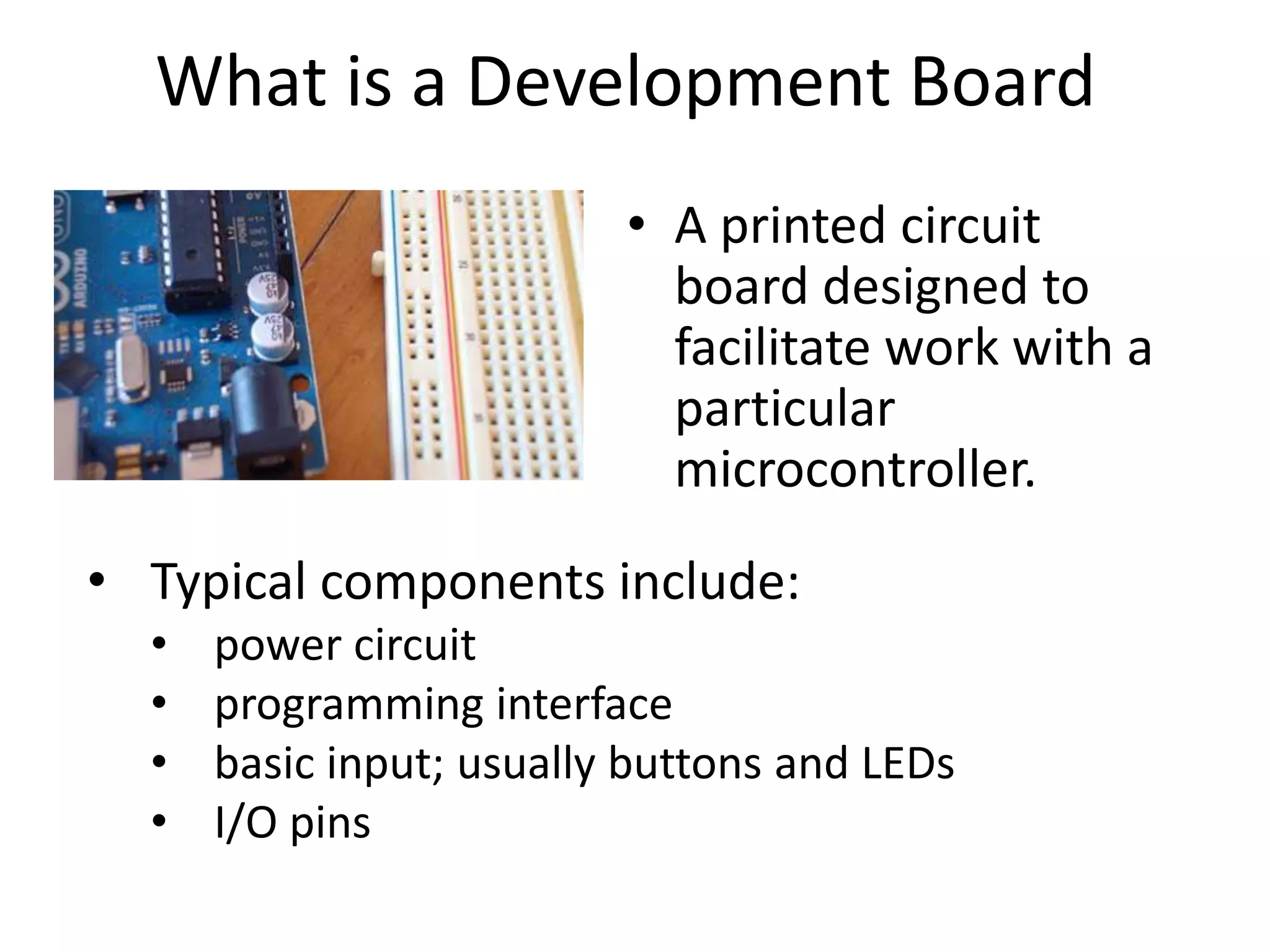
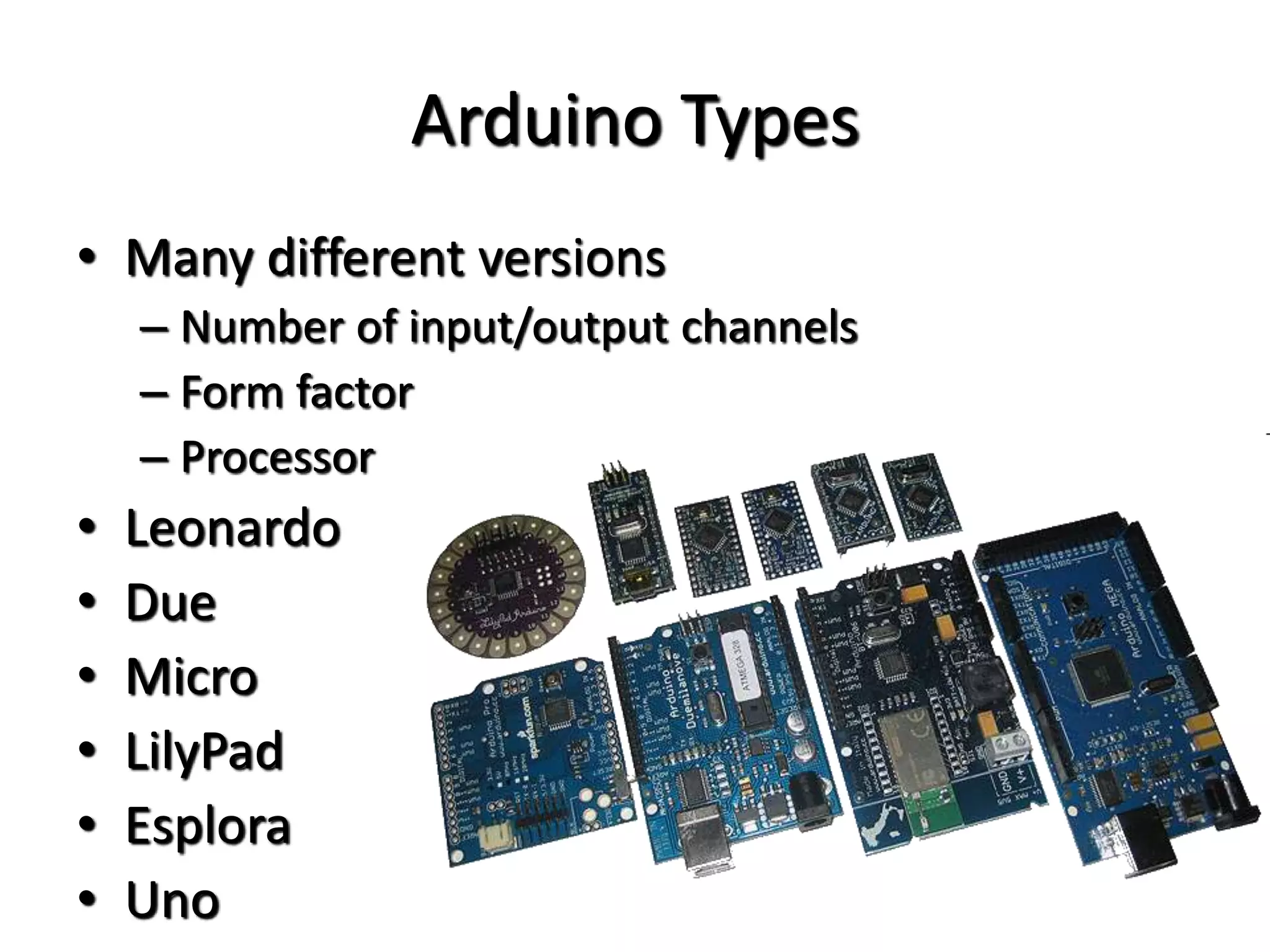
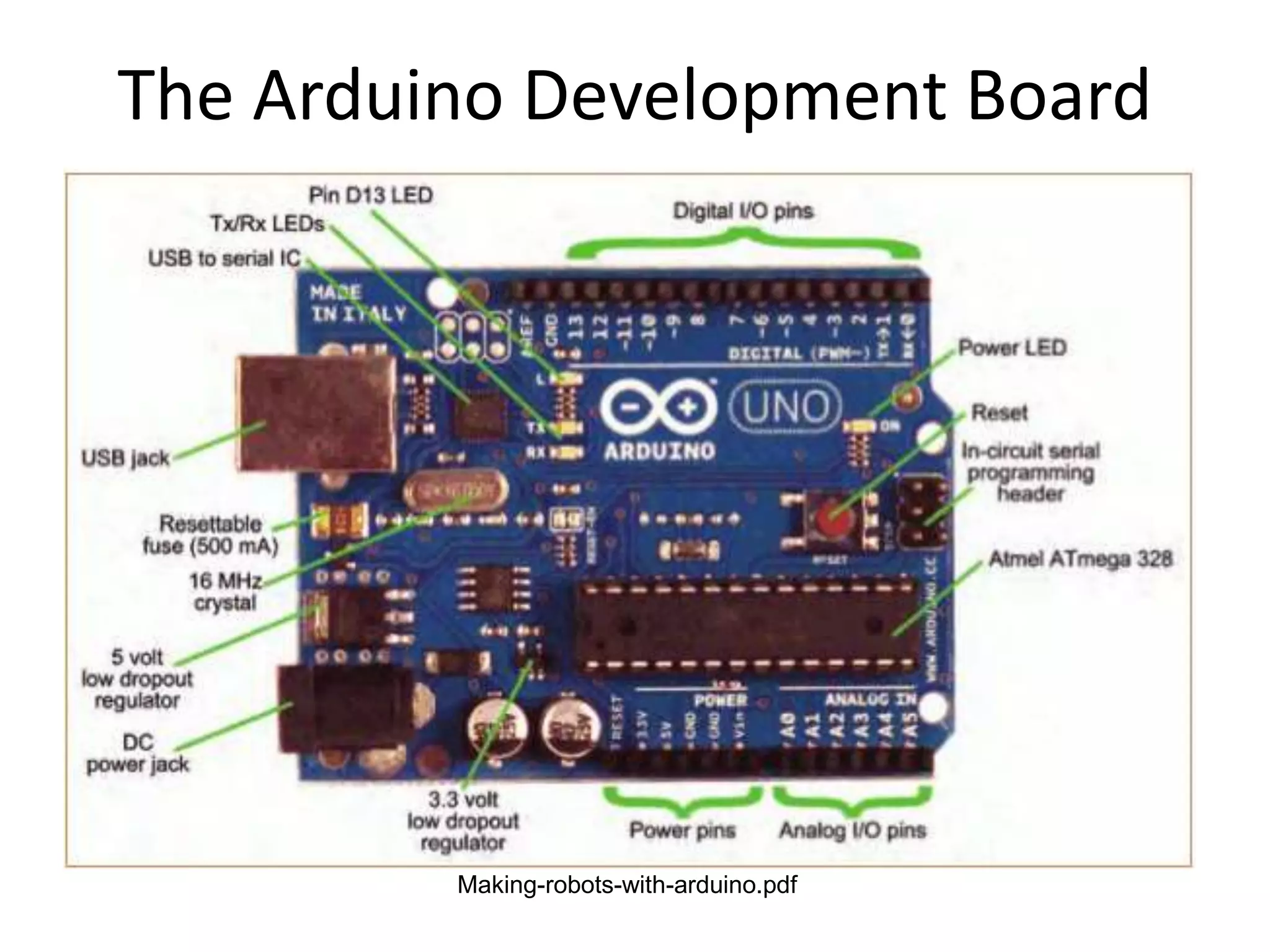
This document provides an overview of Arduino microcontrollers and the Arduino Uno development board. It discusses what a microcontroller and development board are, different Arduino board types, an overview of the Arduino Uno specifications including pins, memory, and processor. It also covers Arduino programming basics like digital input/output, analog to digital conversion, timing functions, and the Arduino IDE.