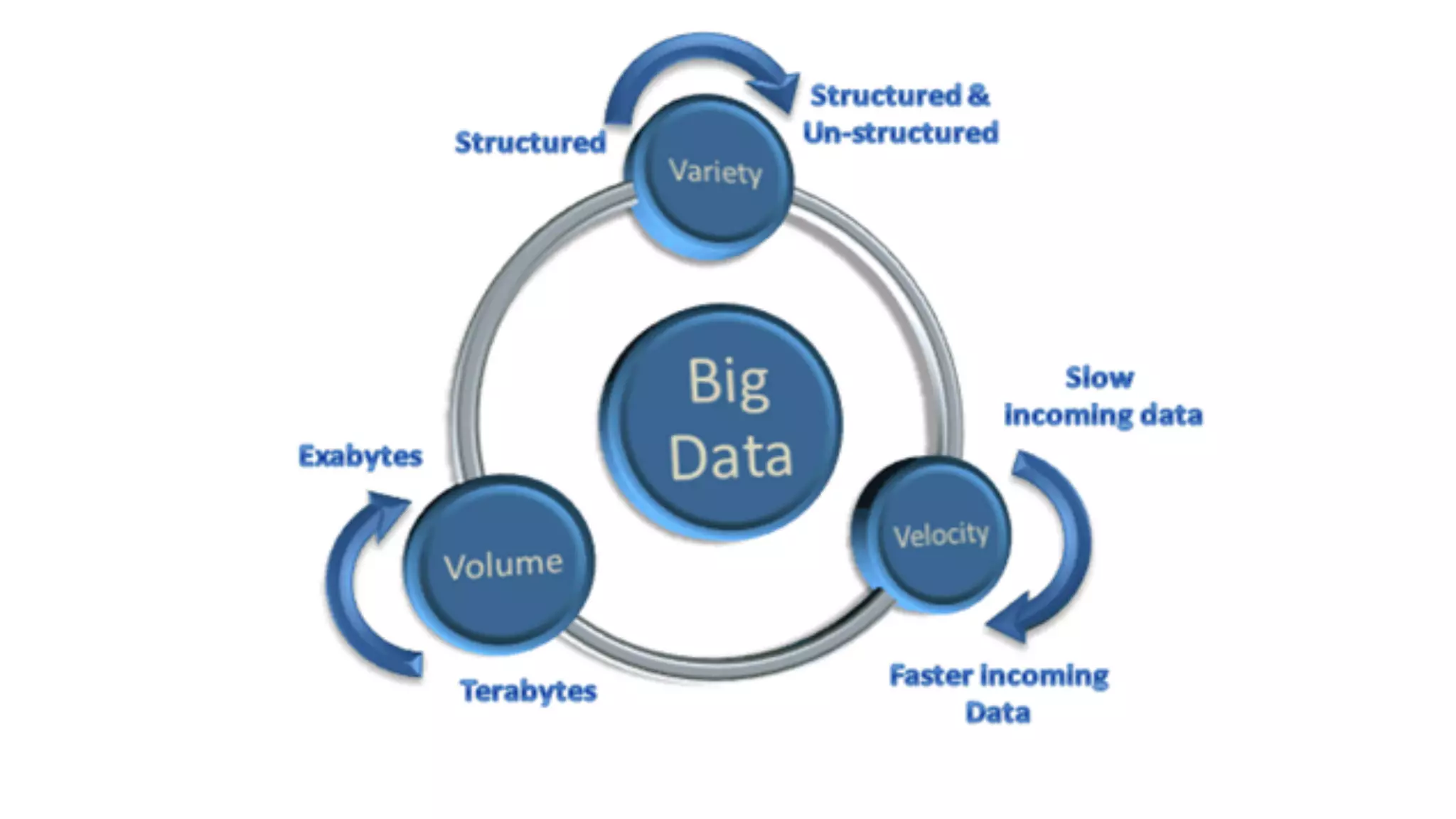
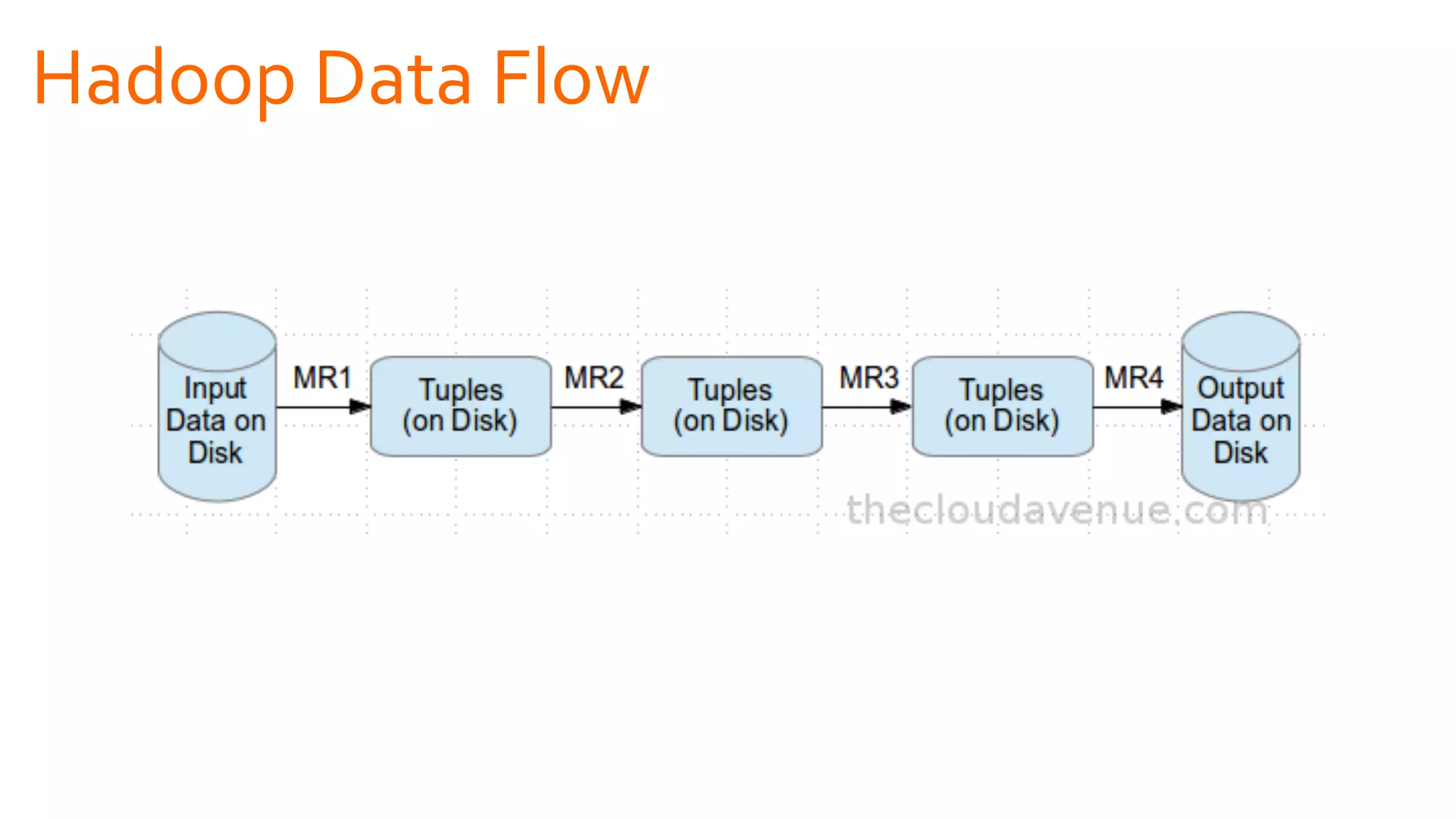
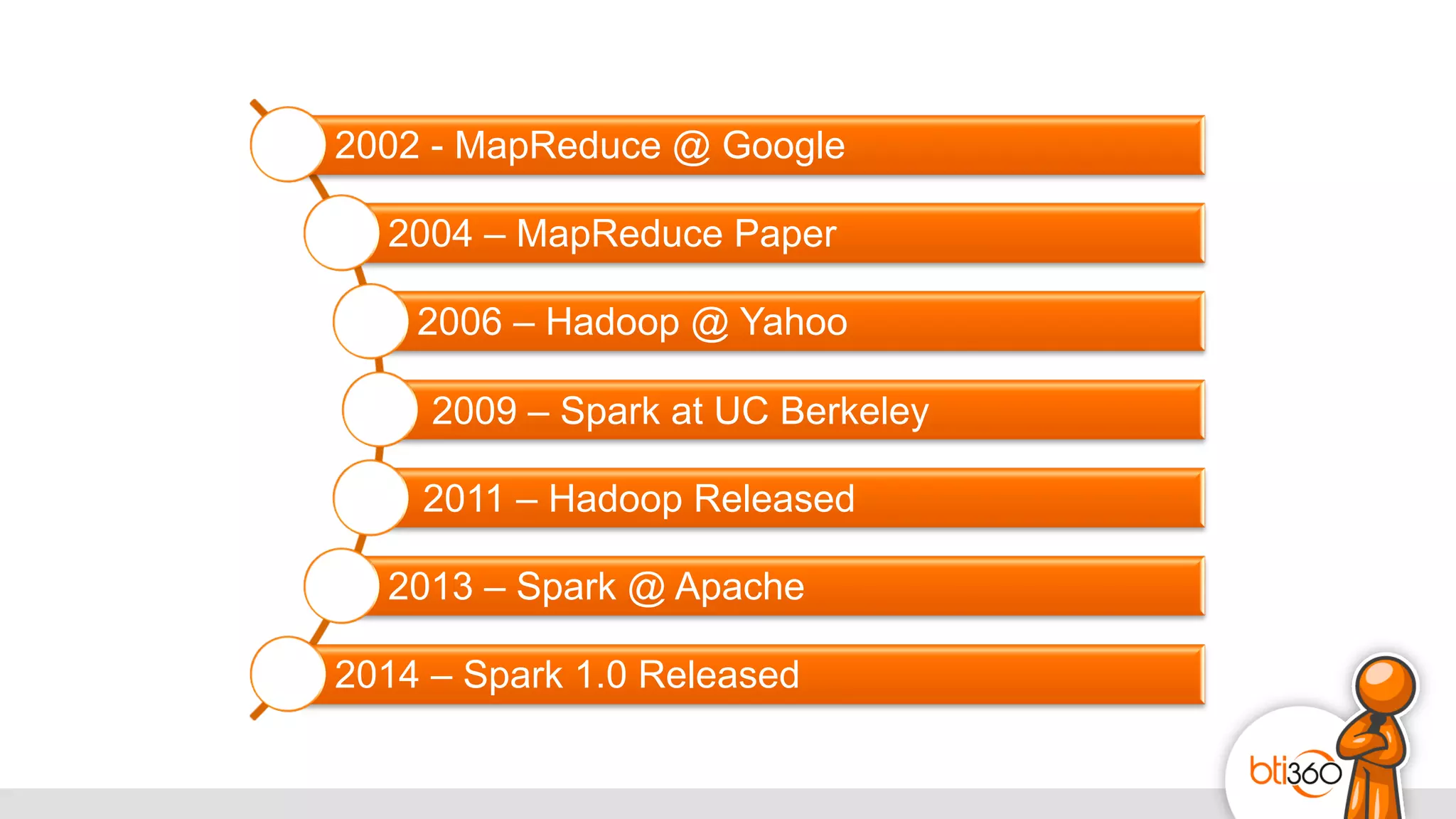
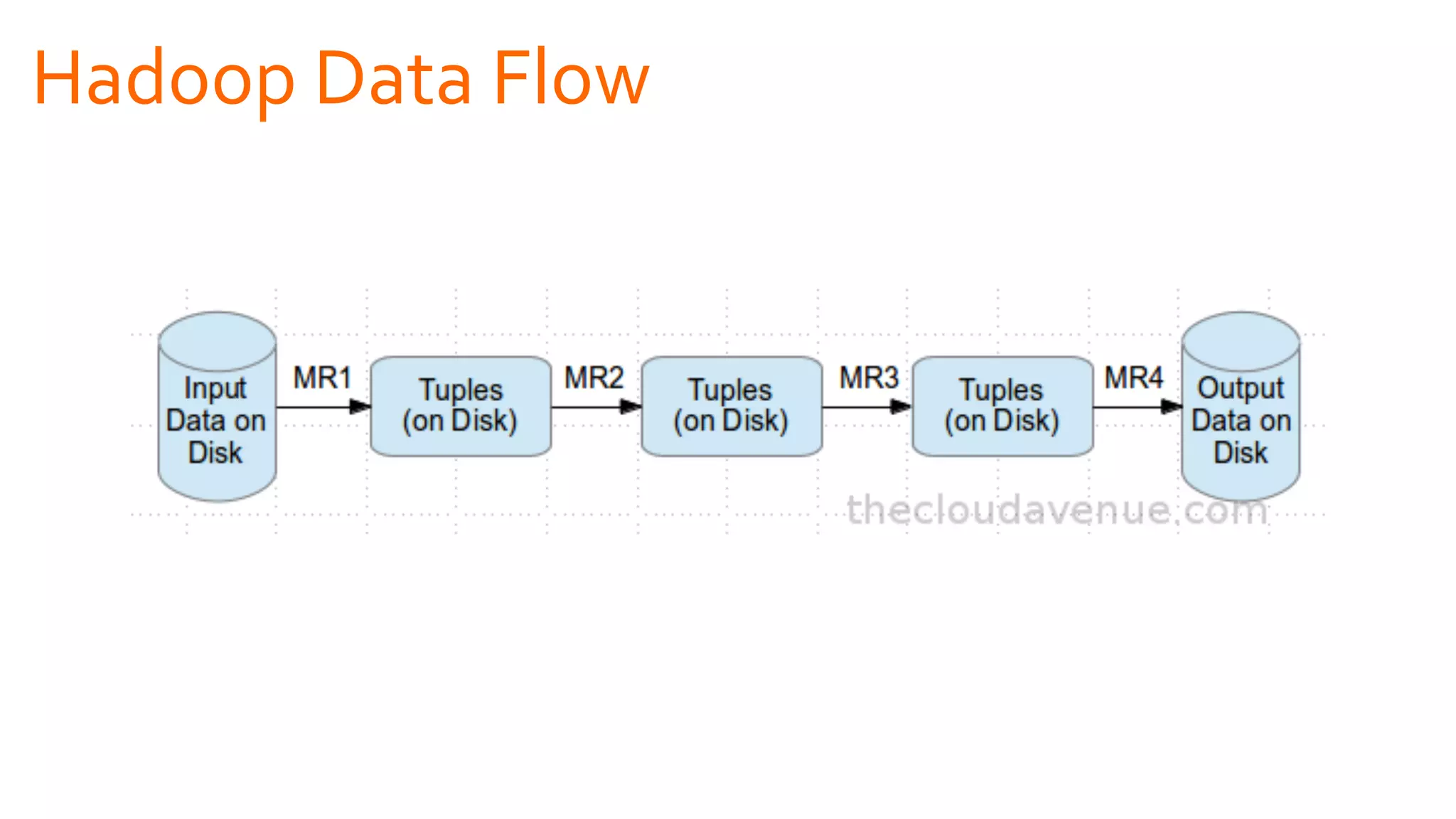
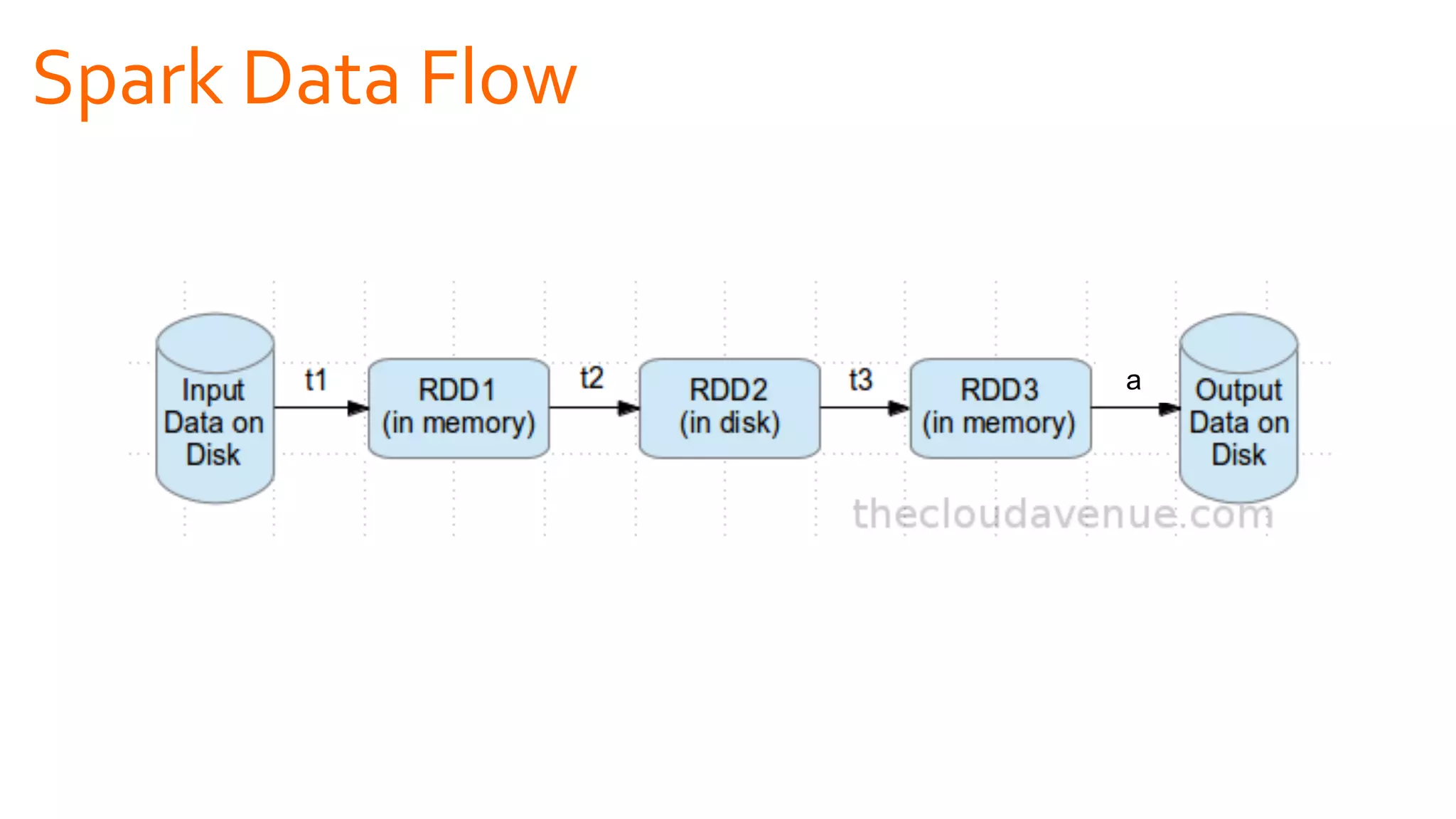
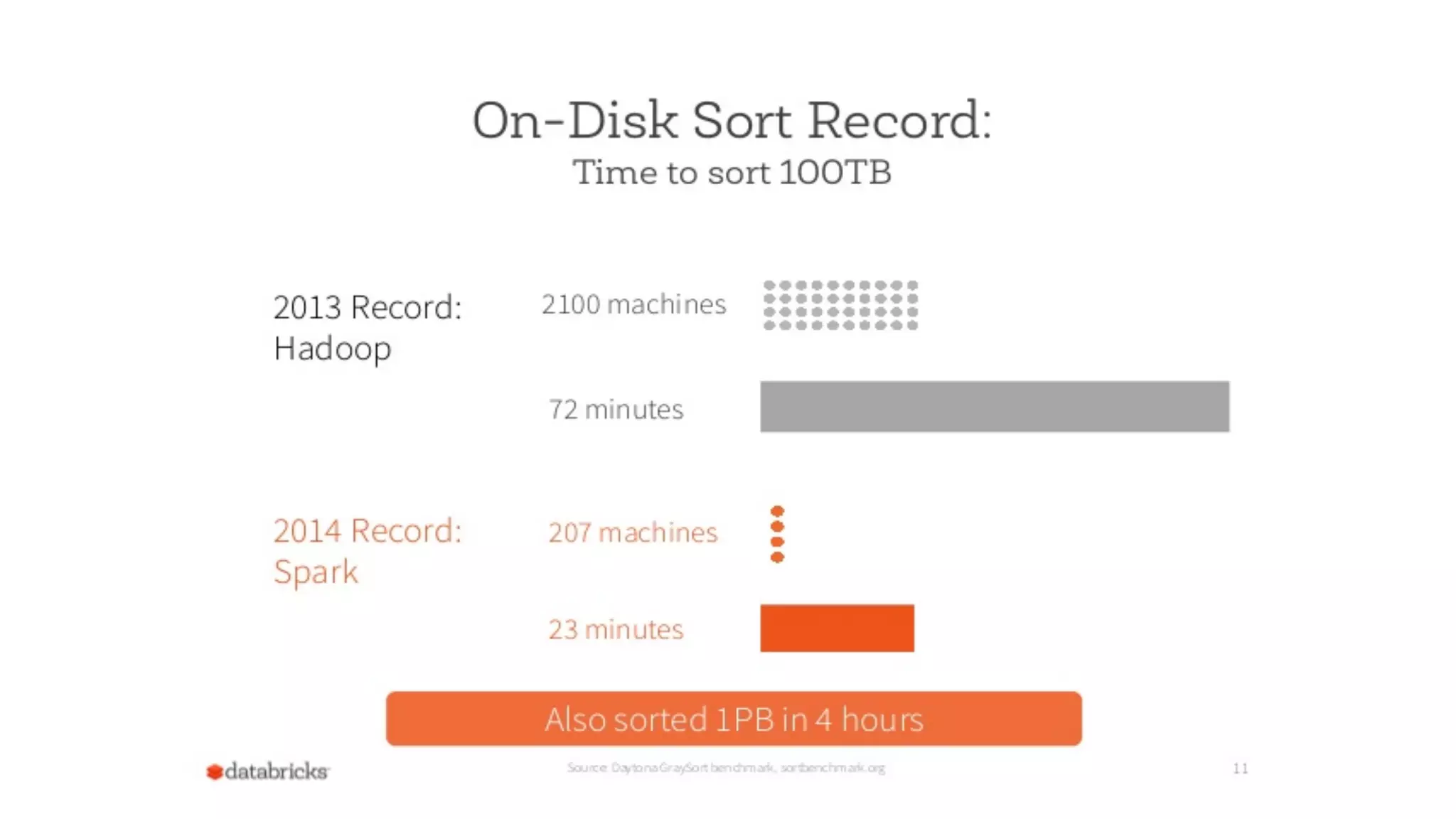
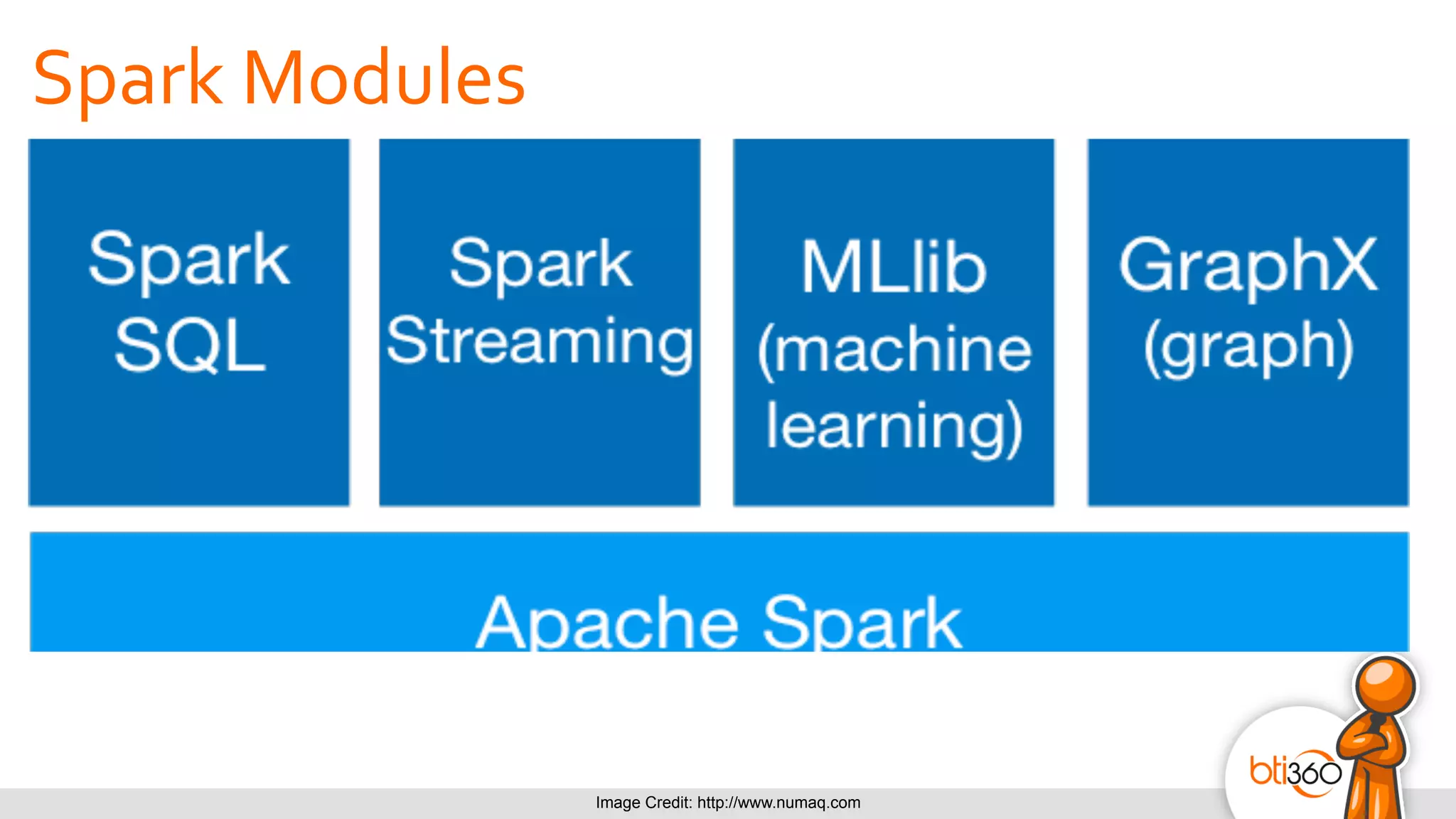
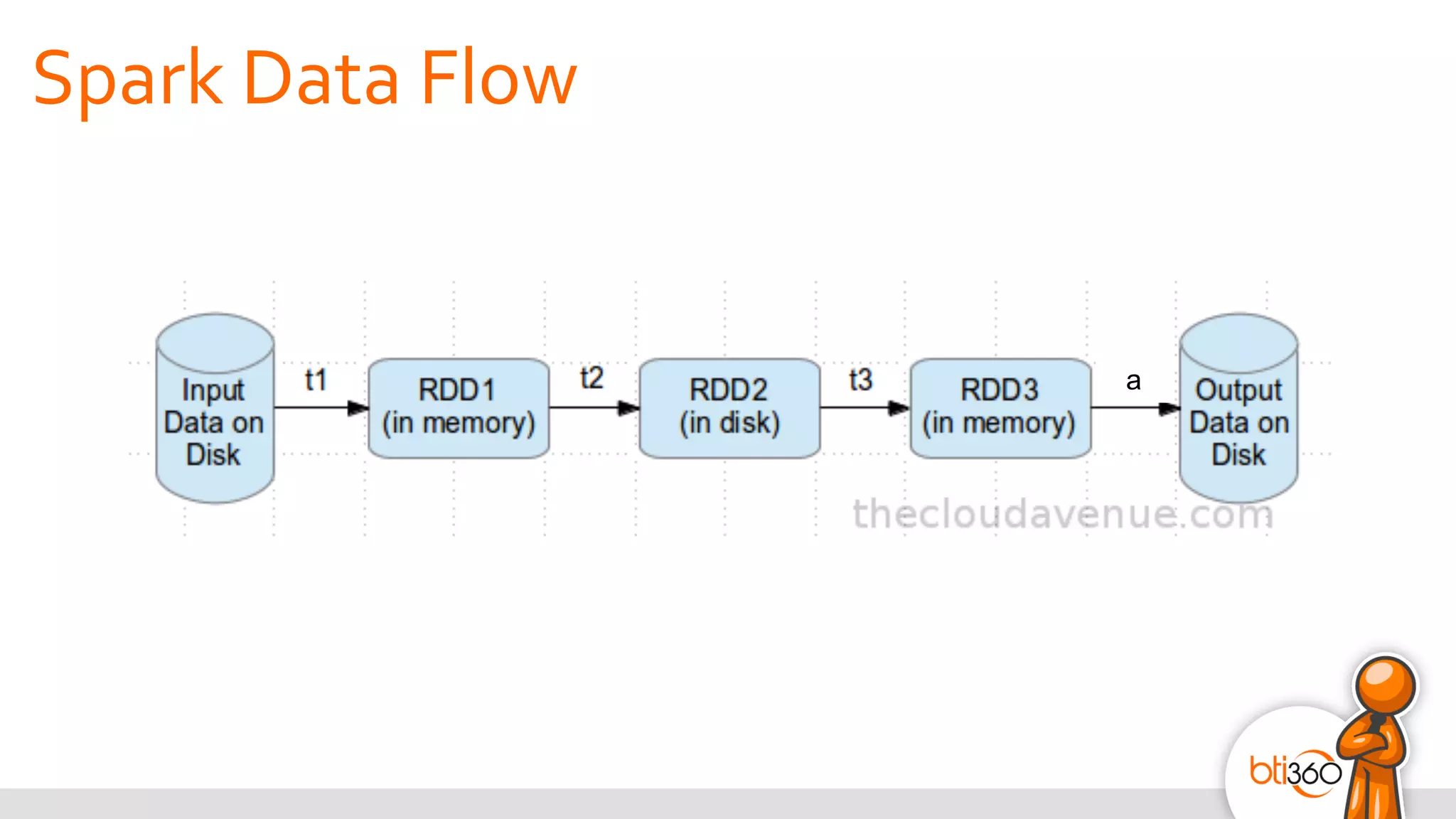
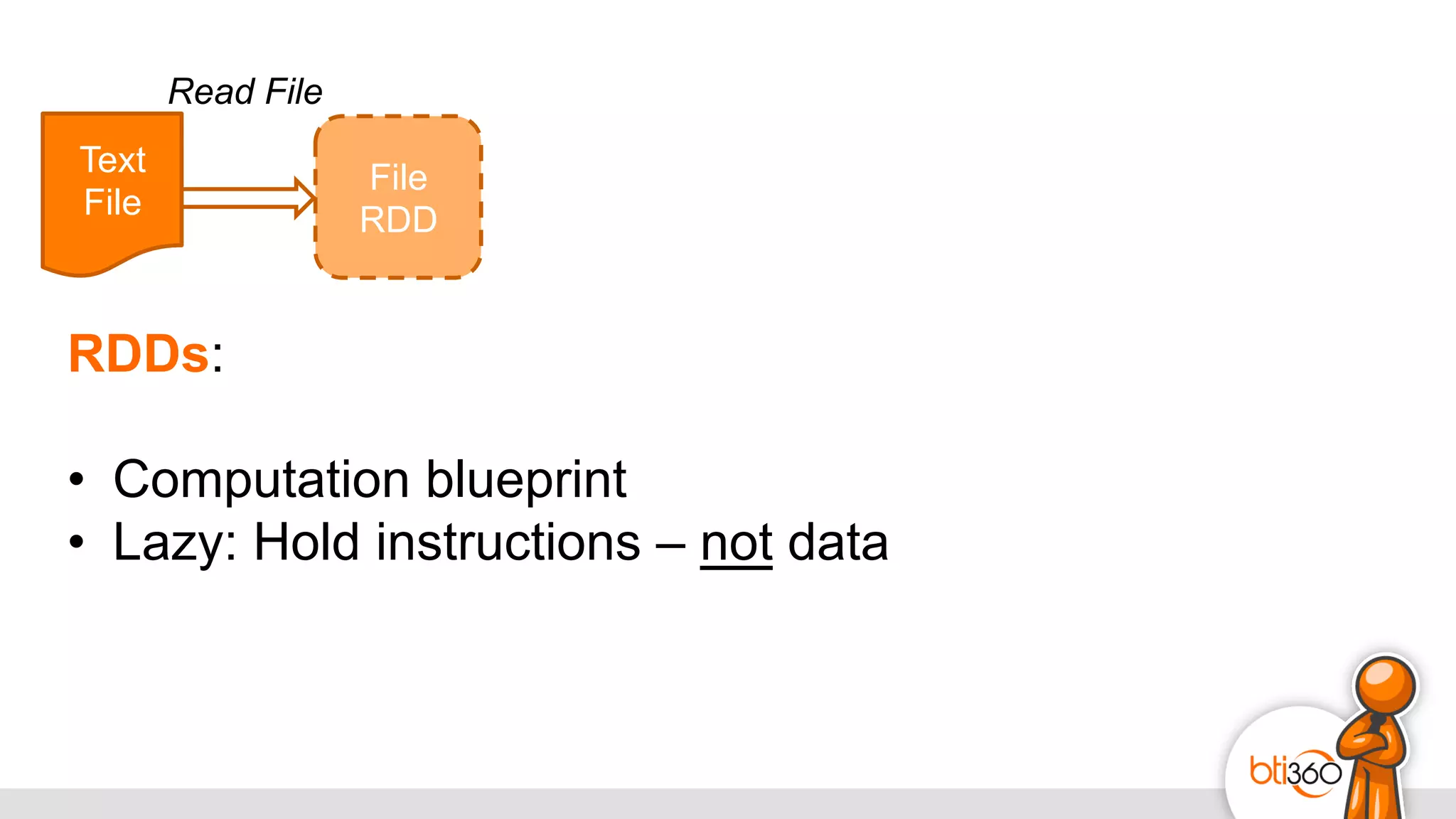
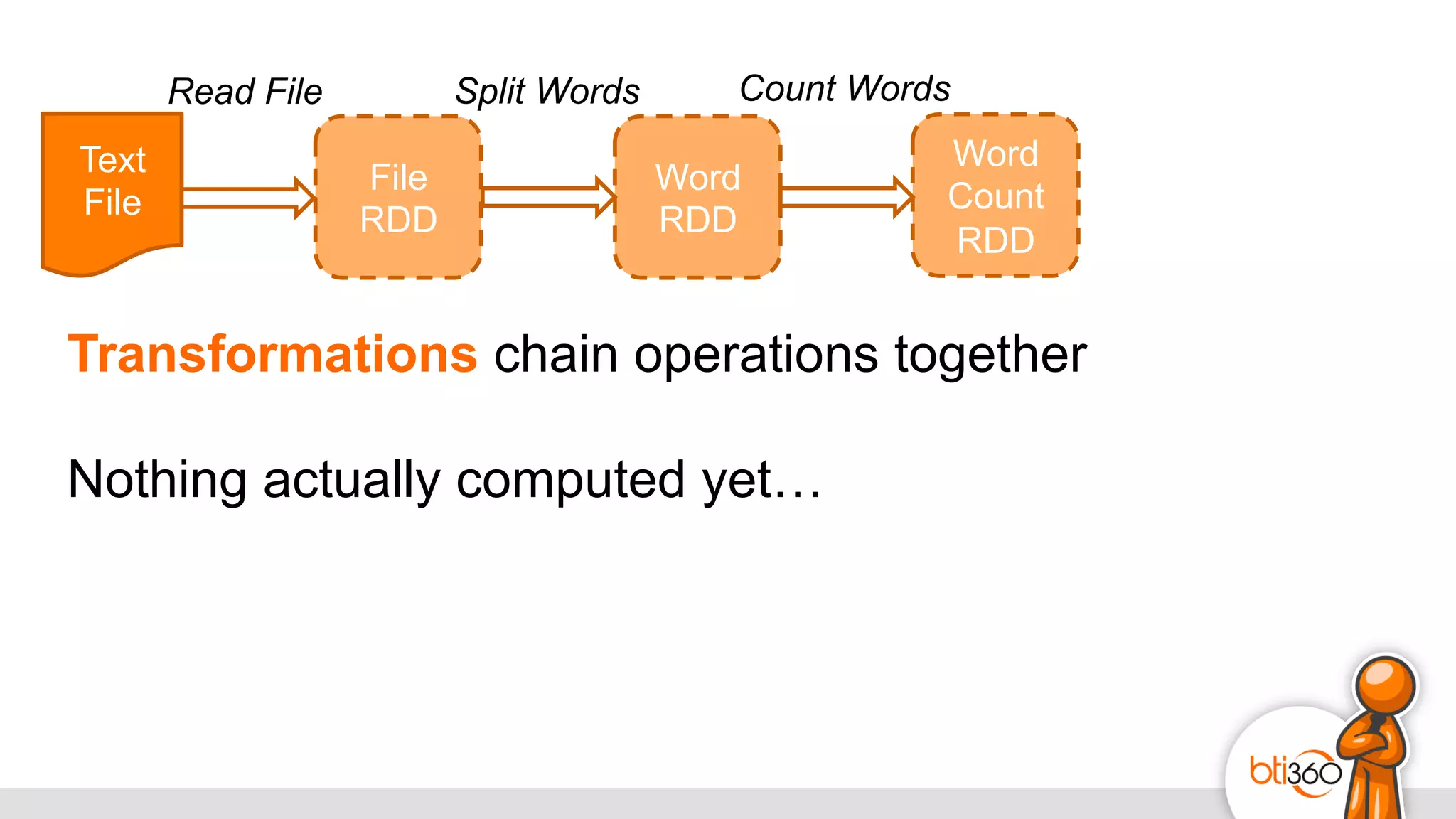
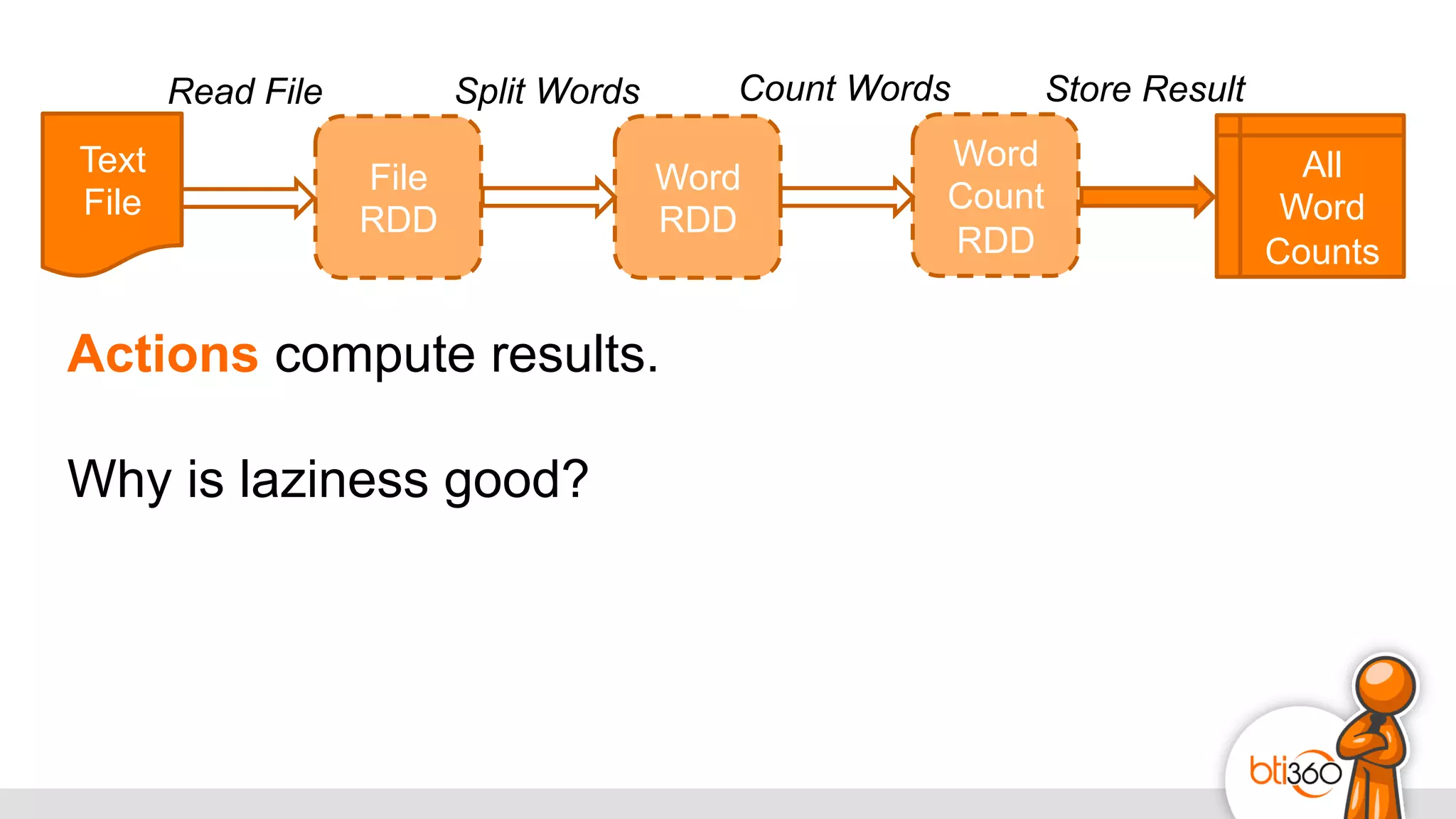
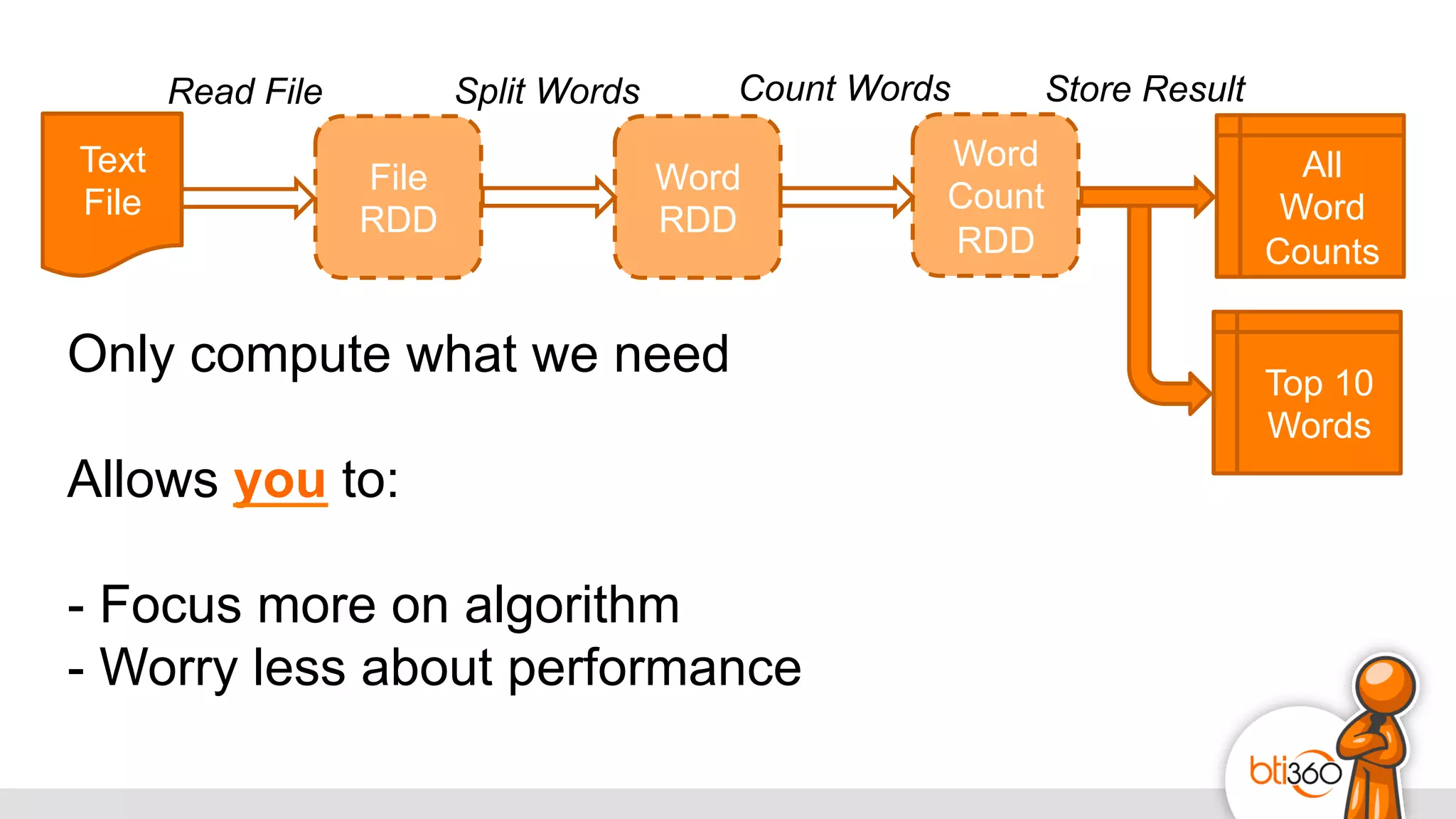
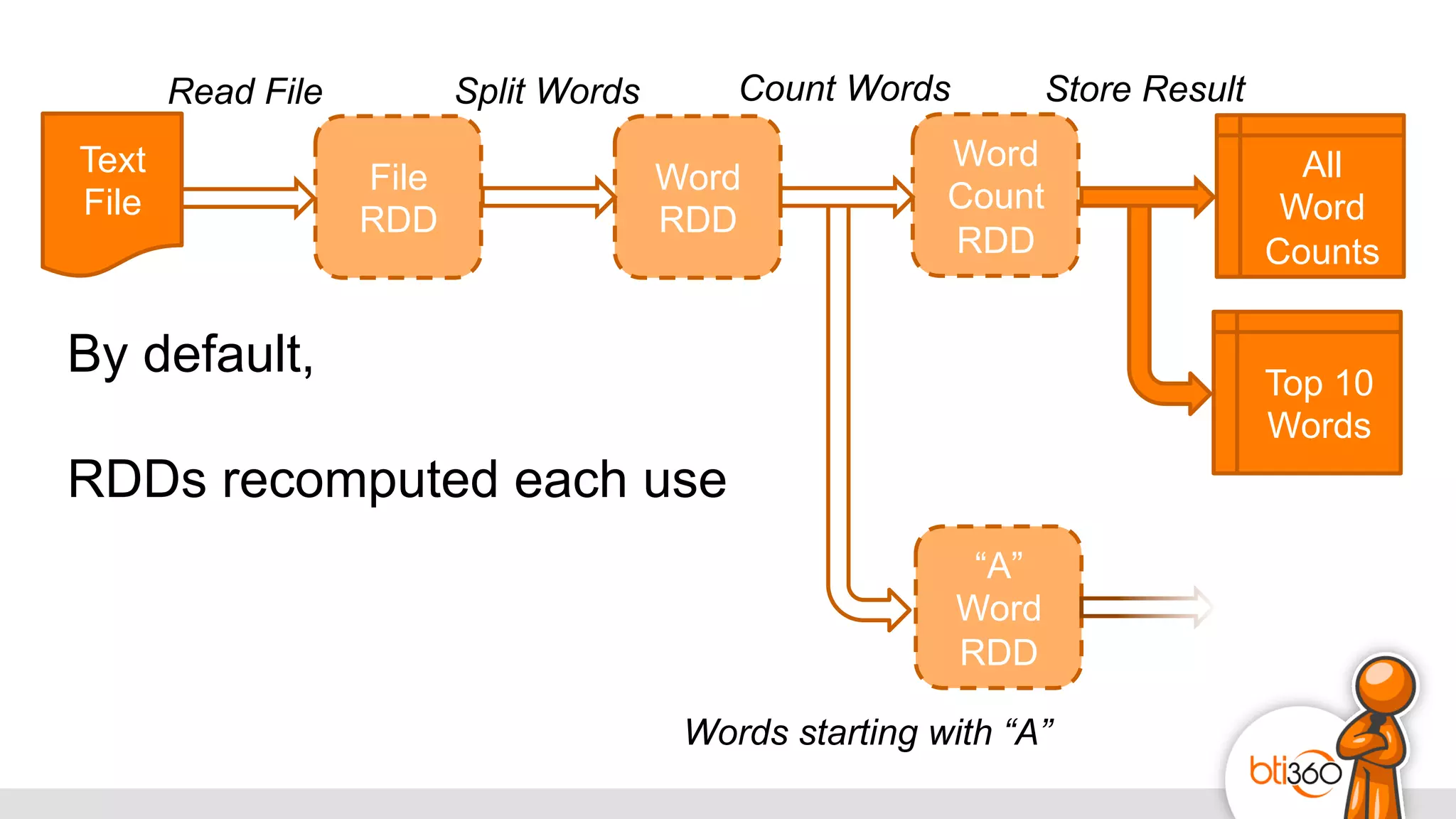
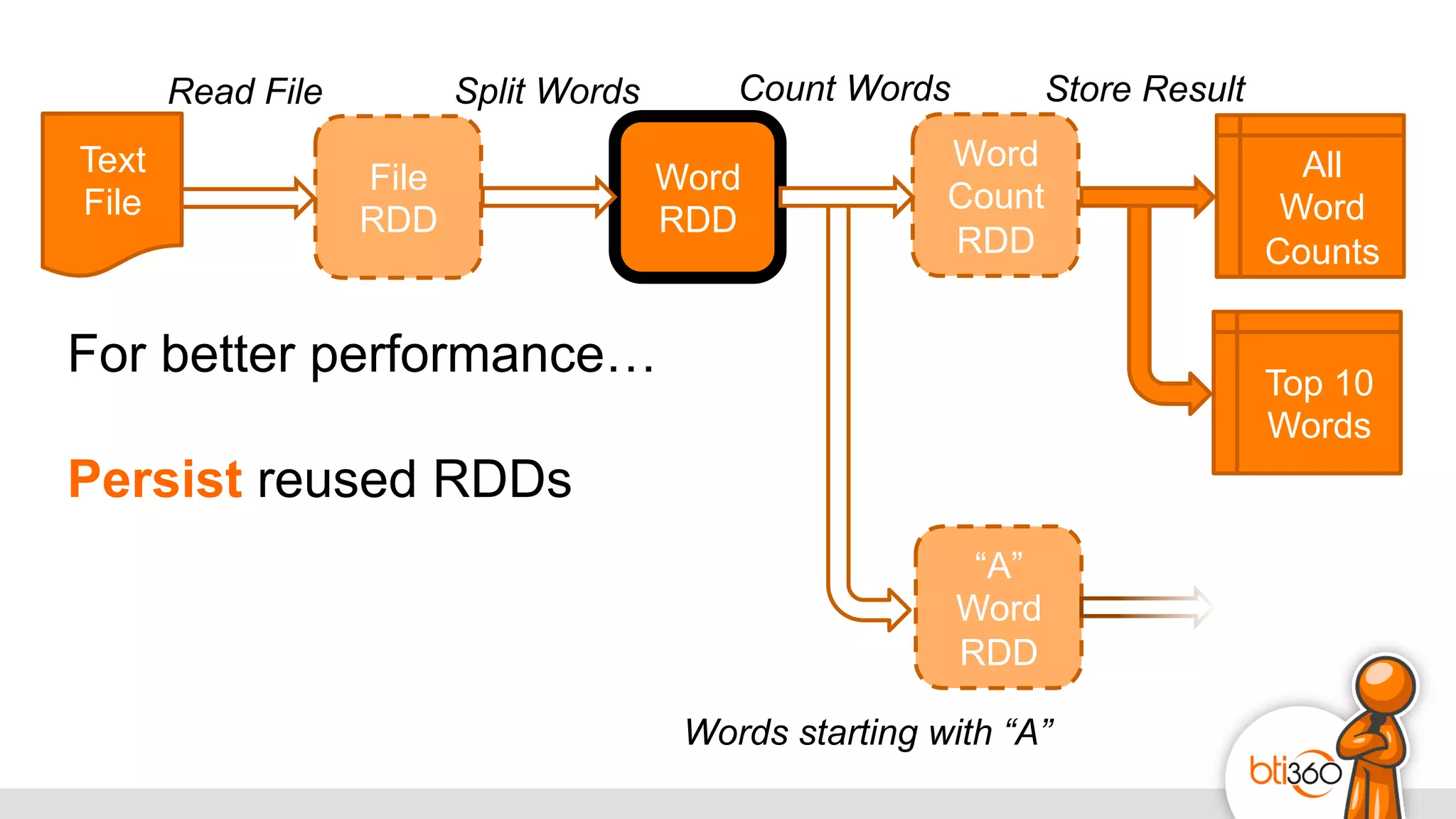
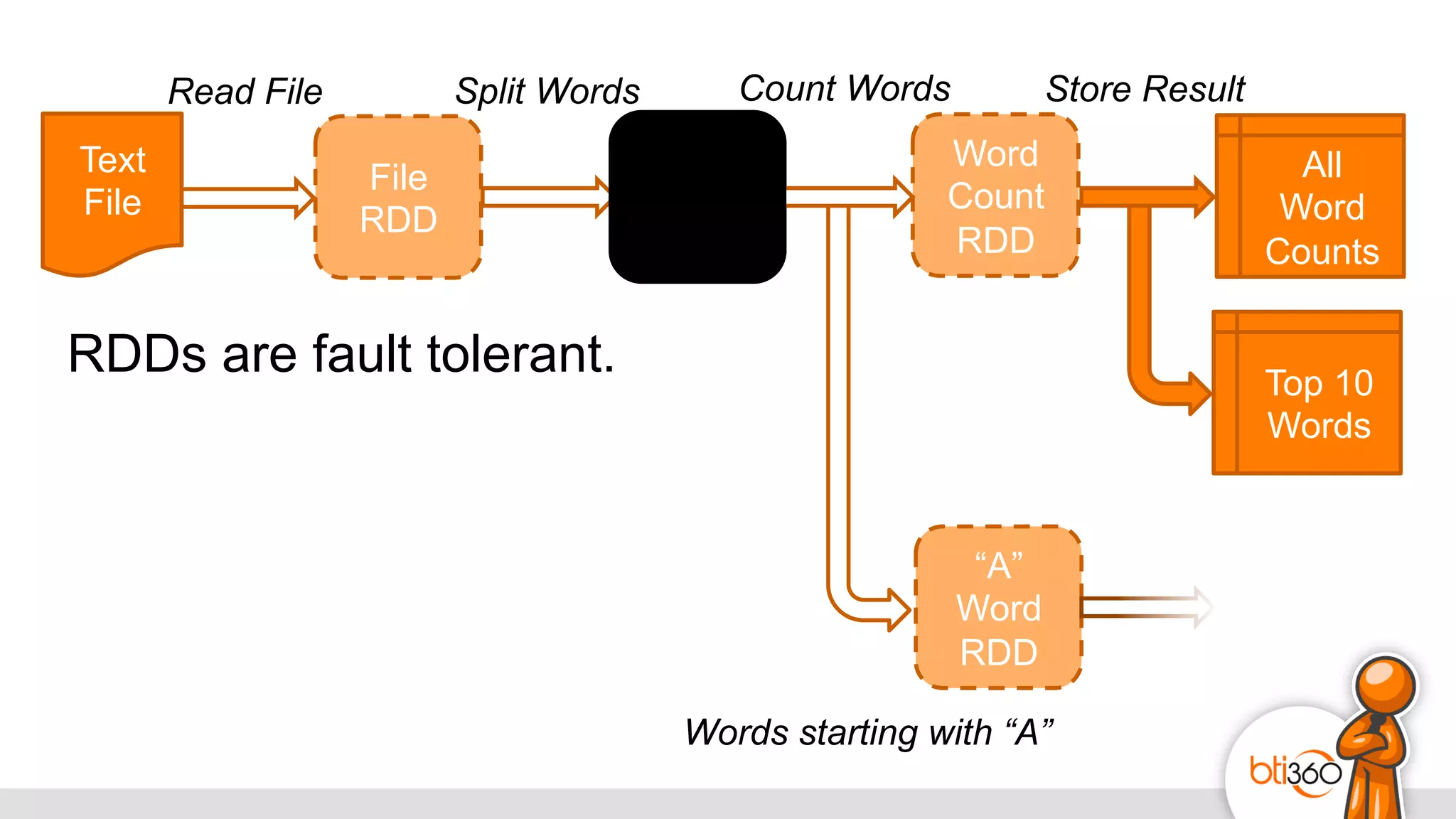
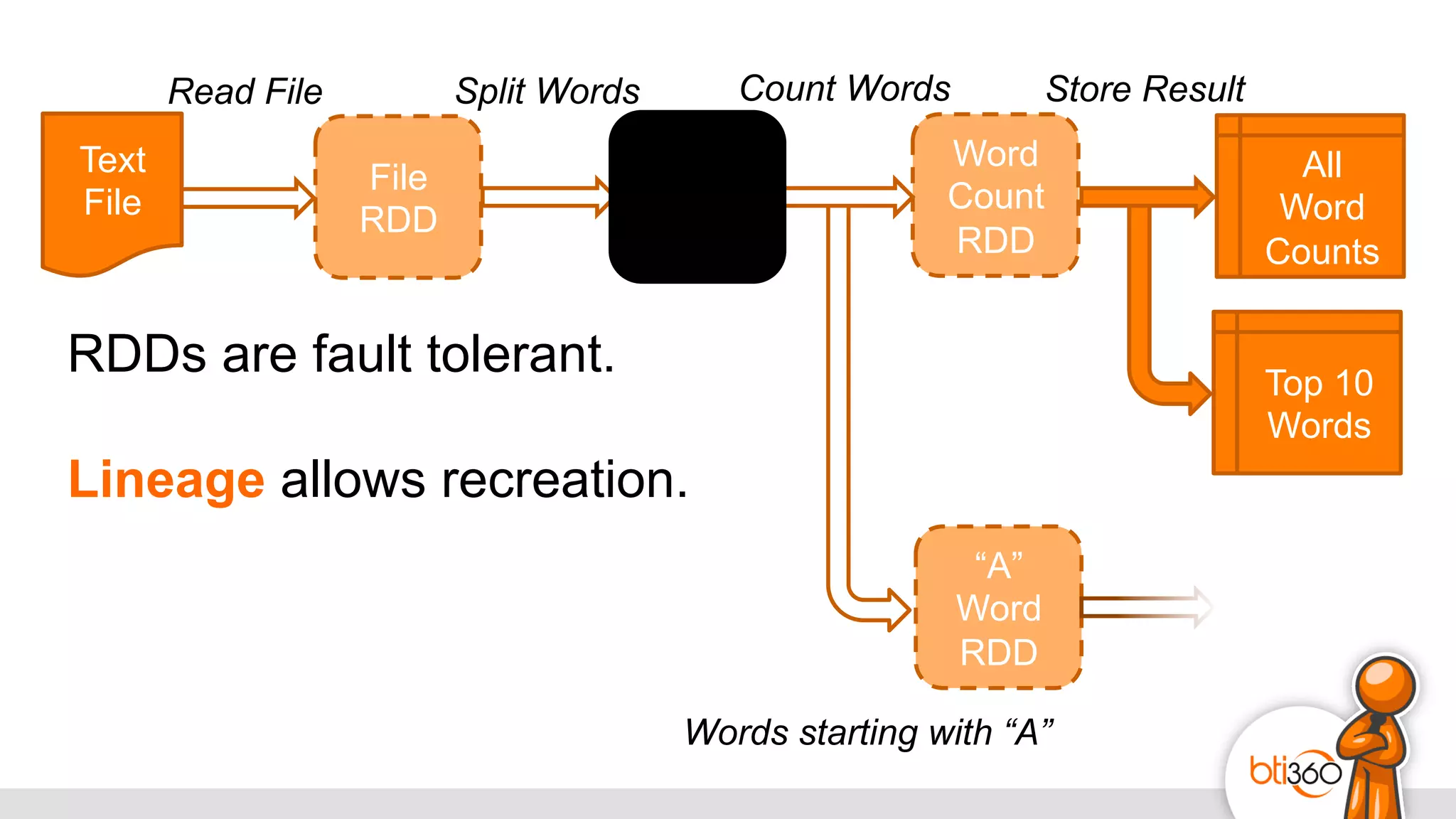
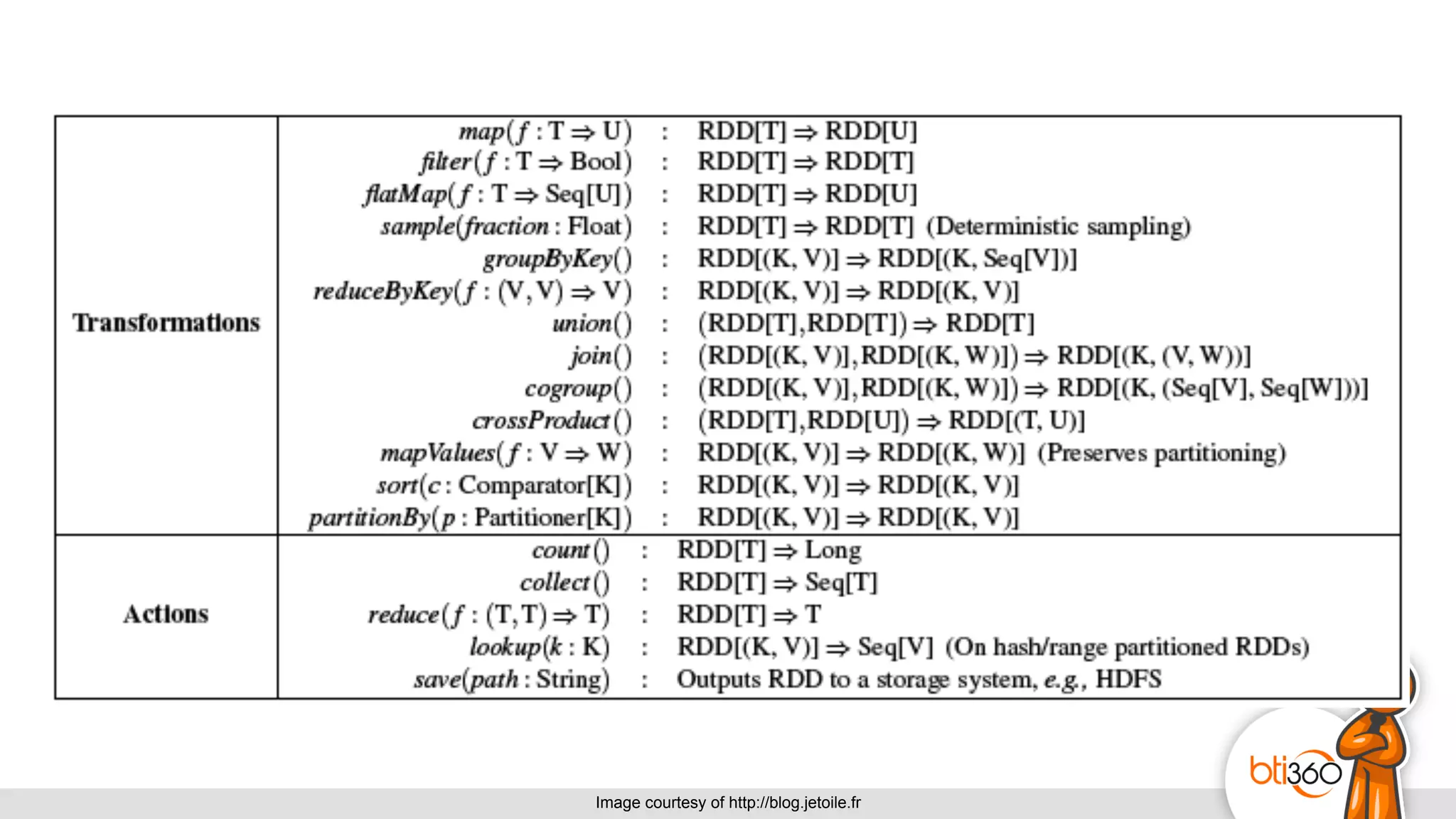
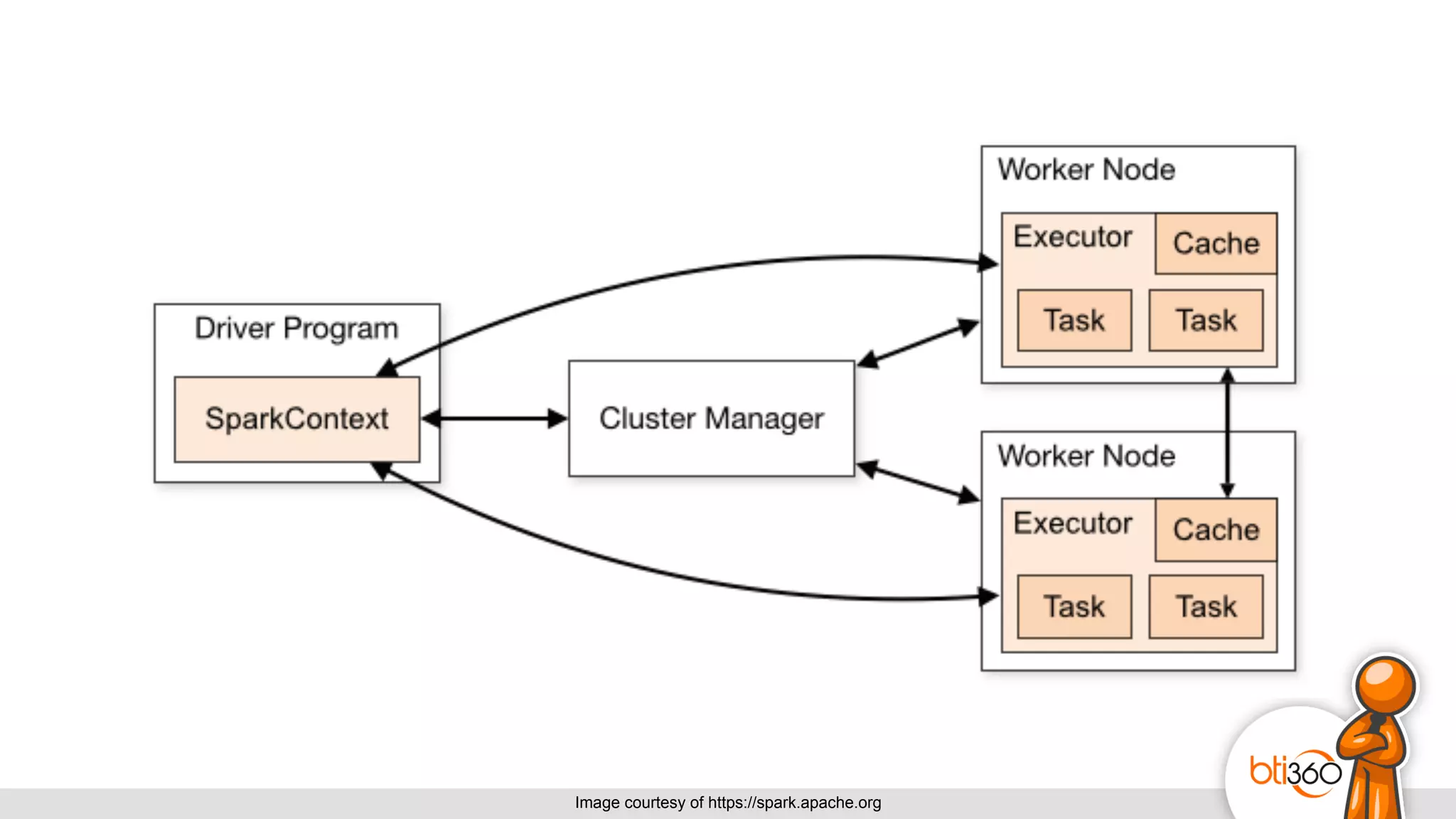
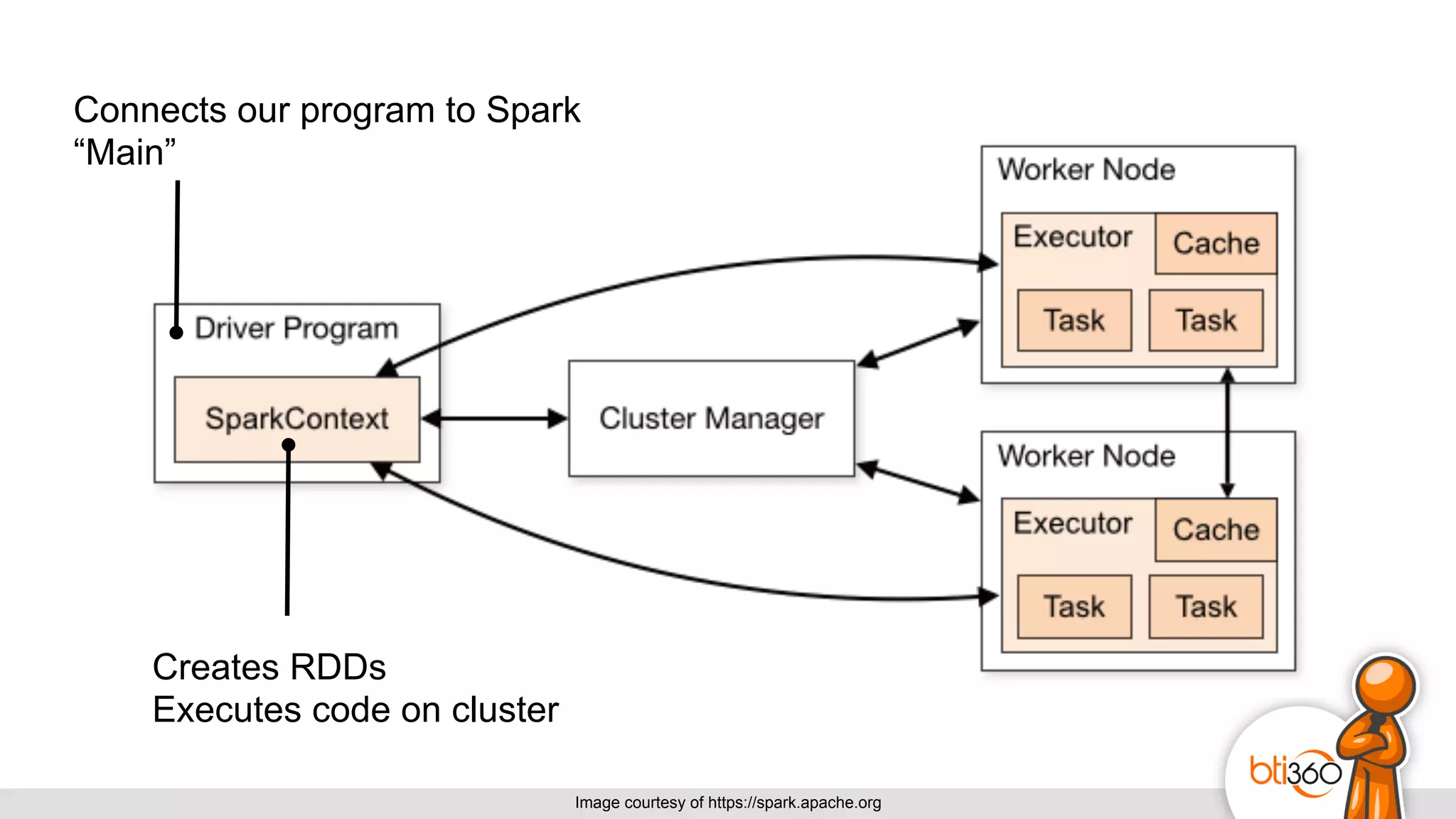
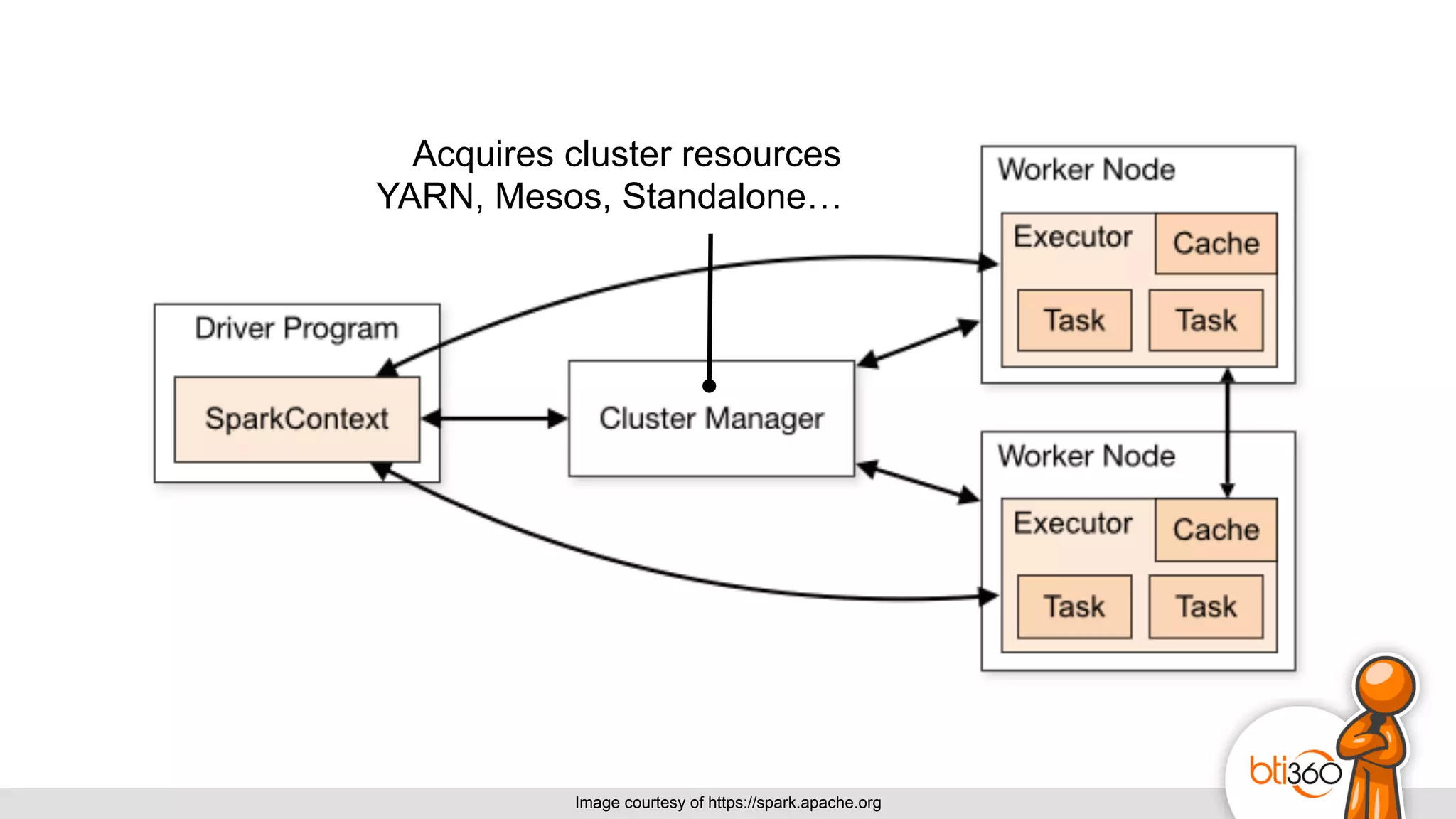
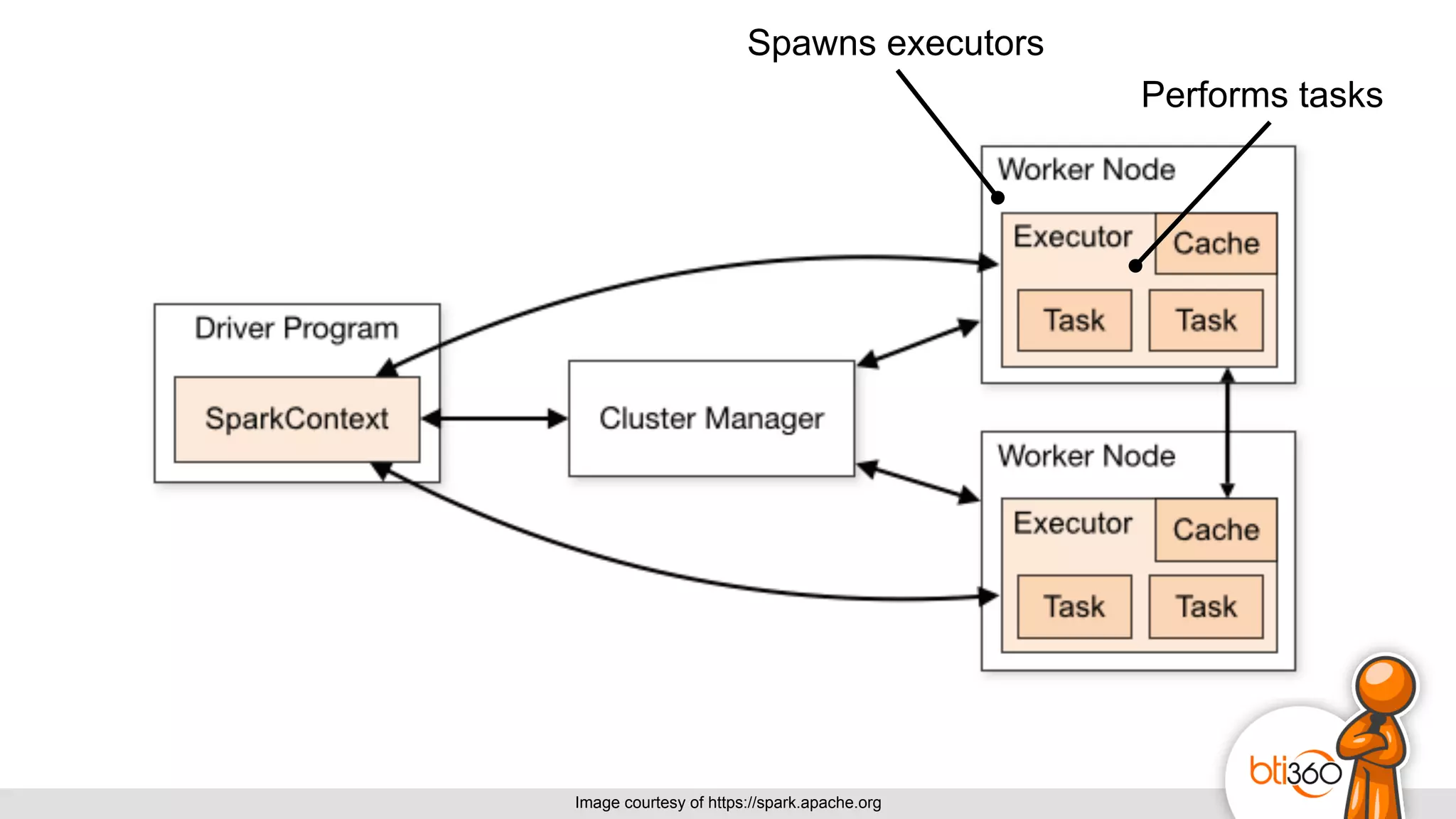
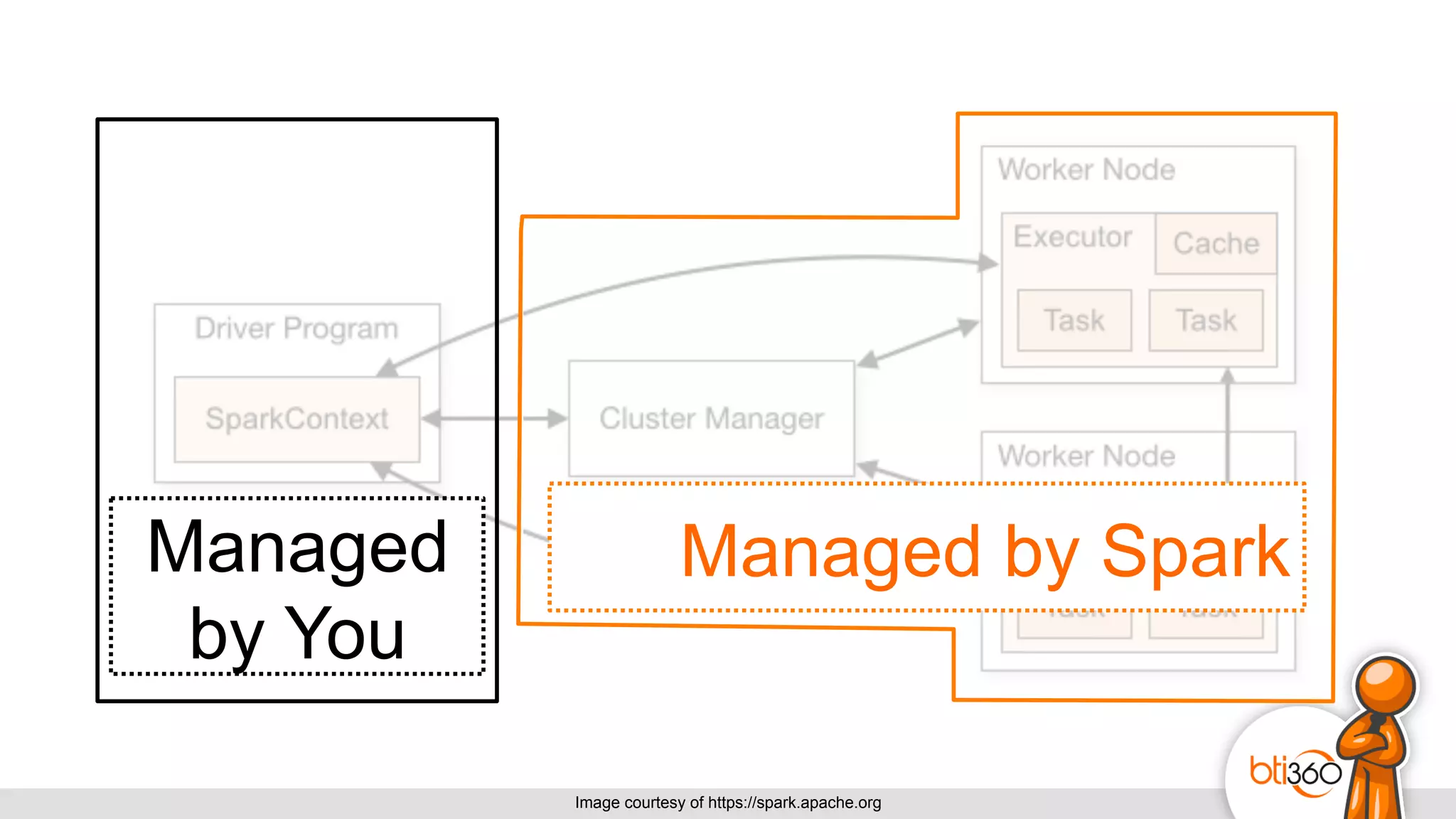
The document introduces Apache Spark as a powerful solution for handling big data, highlighting its key features such as resilient distributed datasets that enable fault-tolerant operations on large clusters. It contrasts Spark with earlier technologies like MapReduce and Hadoop, emphasizing Spark's advantages in speed and ease of use for various applications, including ETL, machine learning, and analytics. The document also outlines the creation and management of RDDs (Resilient Distributed Datasets) and shared variables in Spark.