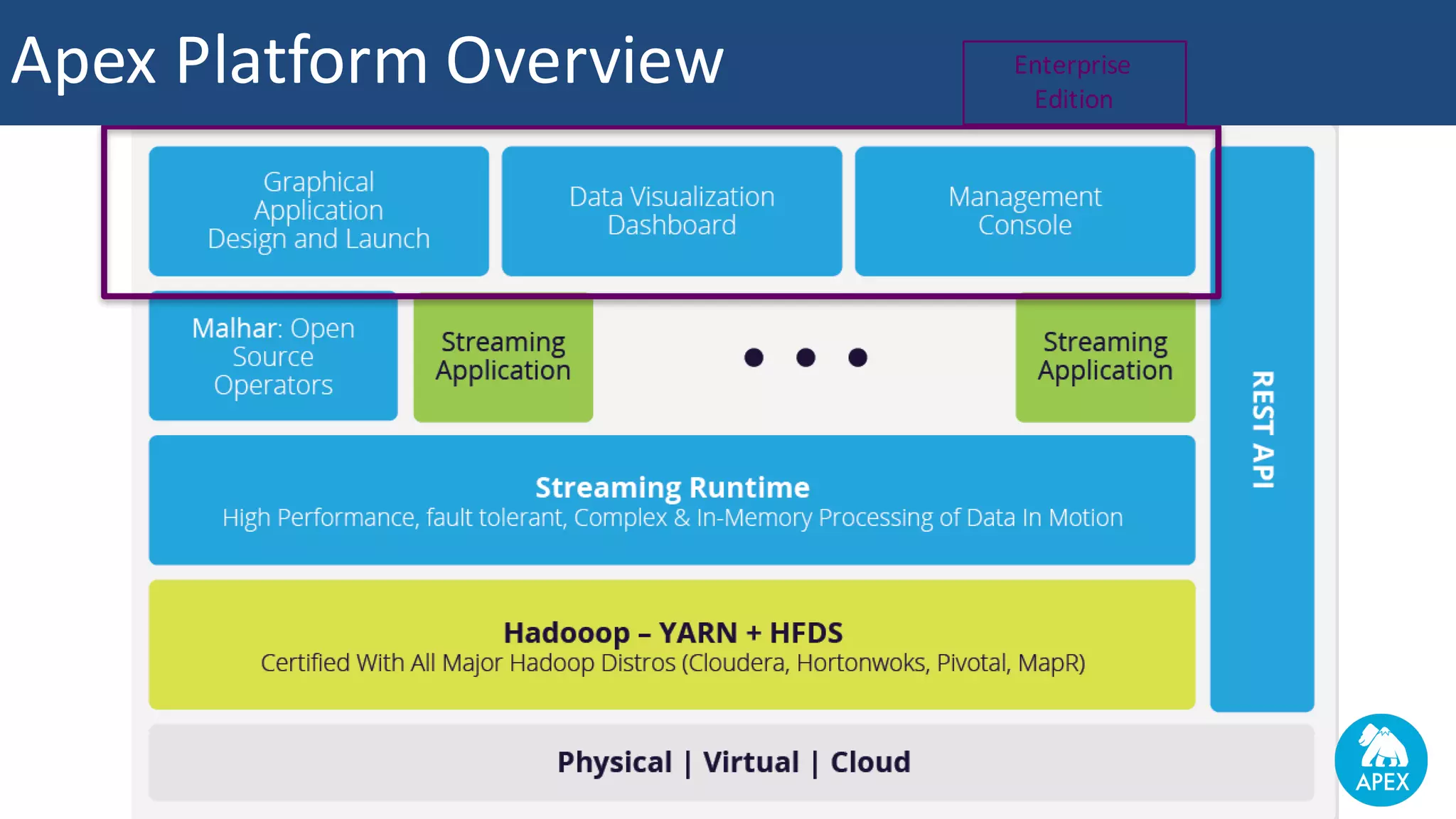
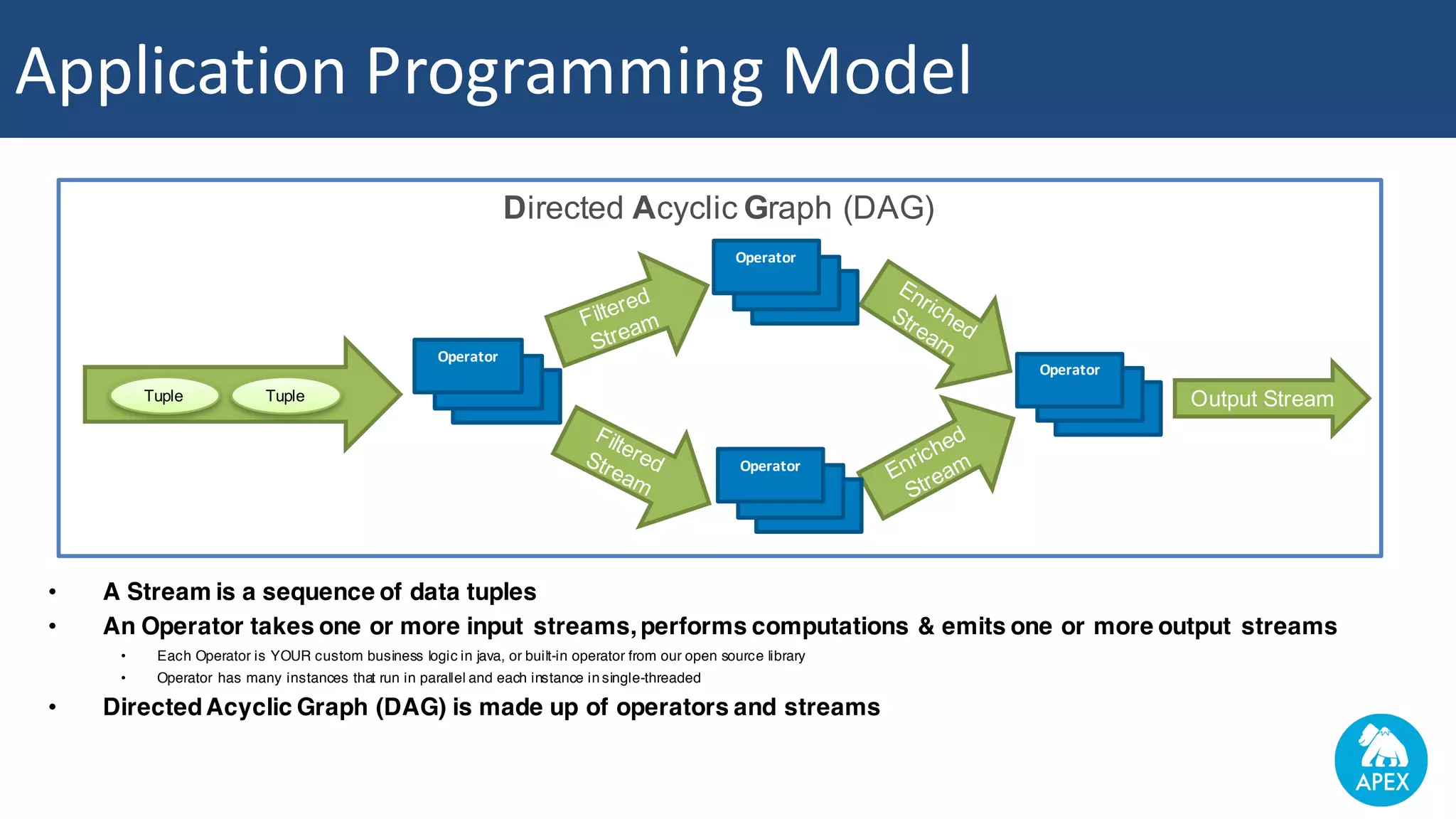
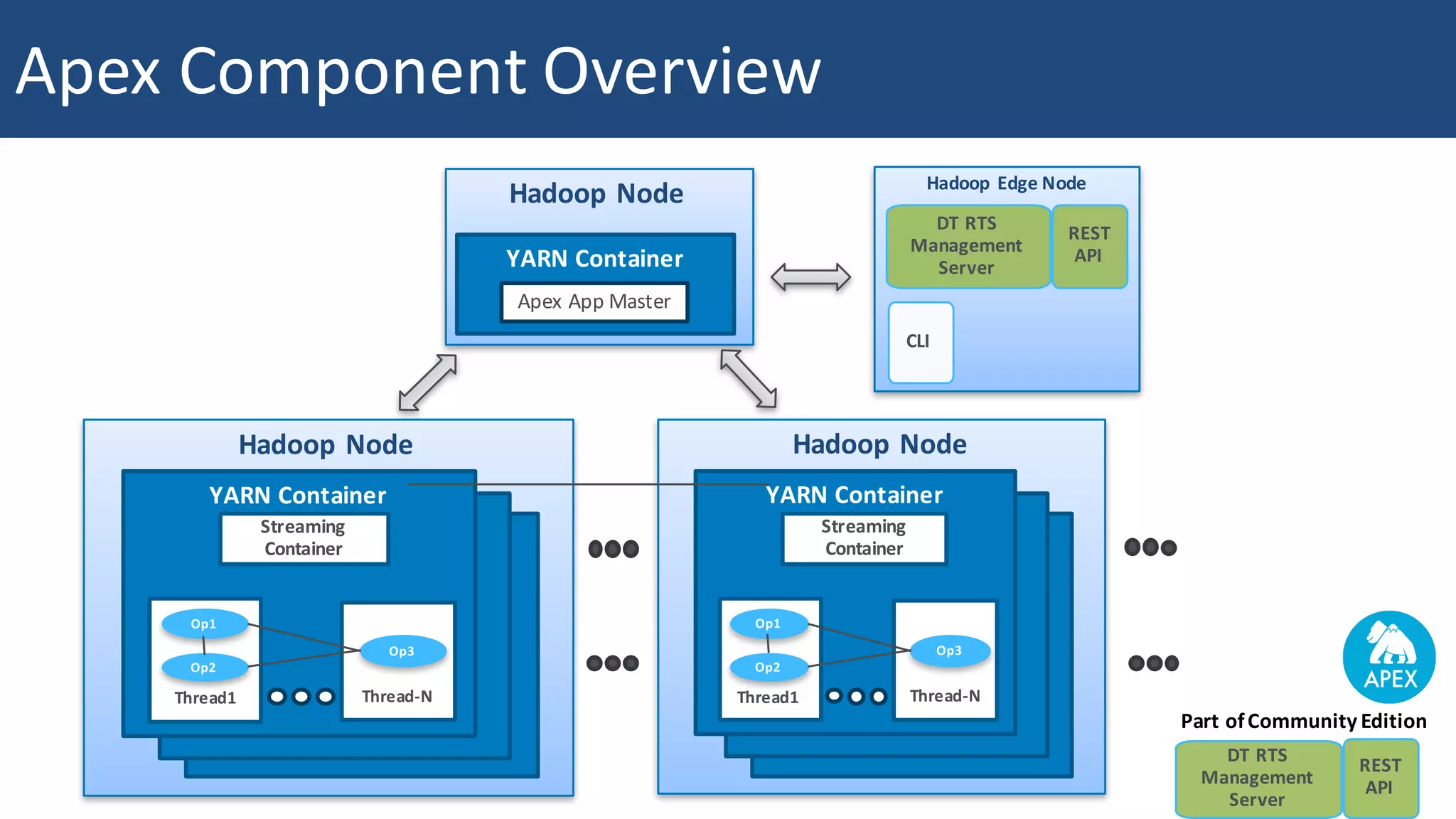
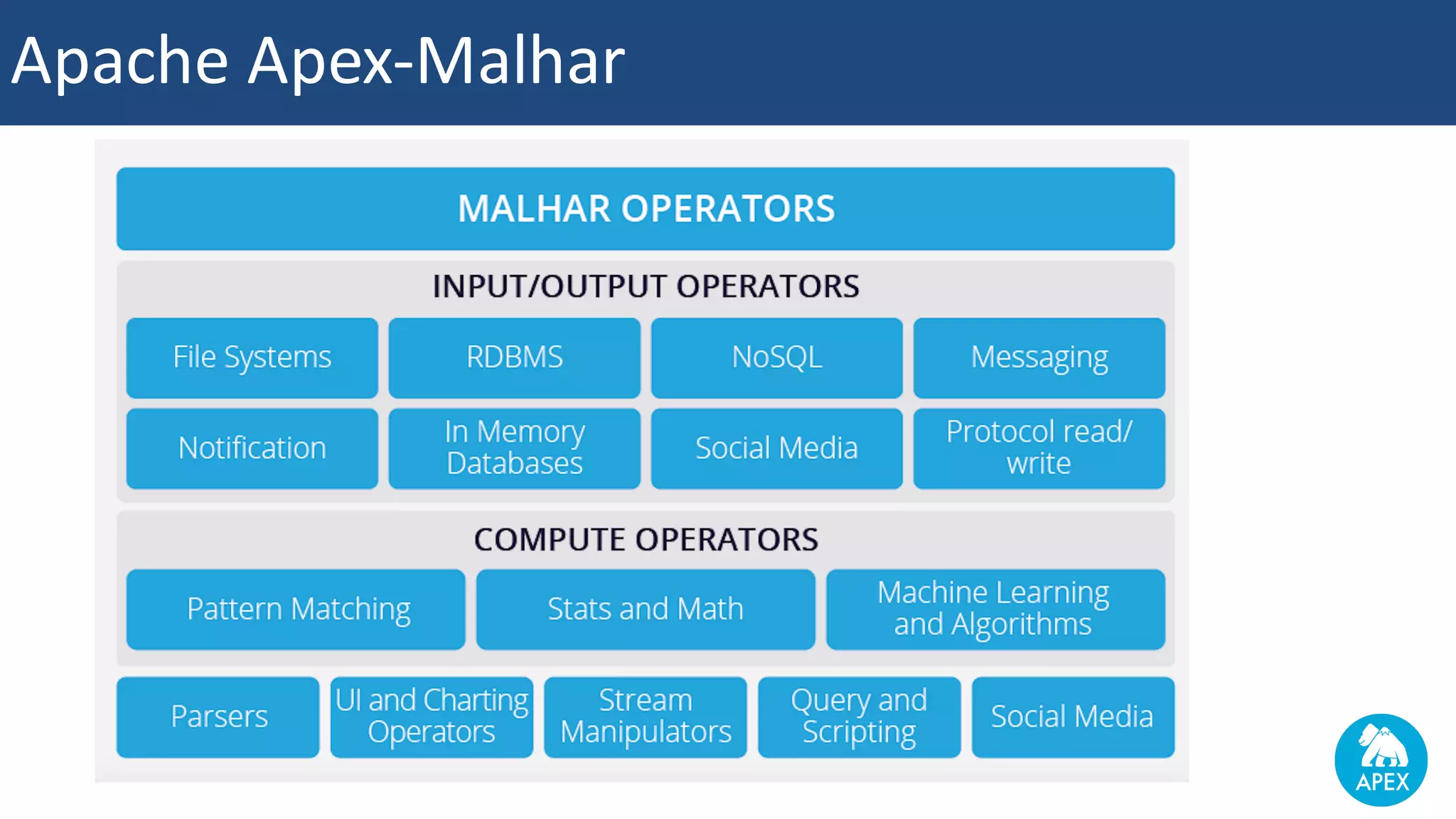
The document discusses Apache Apex and Apache Geode, highlighting their integration for in-memory computing, data storage, and analysis. It outlines the features and architecture of both platforms, including the benefits of in-memory data grids (IMDGs) such as performance improvements and high availability. Additionally, it presents a roadmap for future developments, emphasizing the potential of in-memory computing to disrupt traditional application design and enhance operational efficiencies.