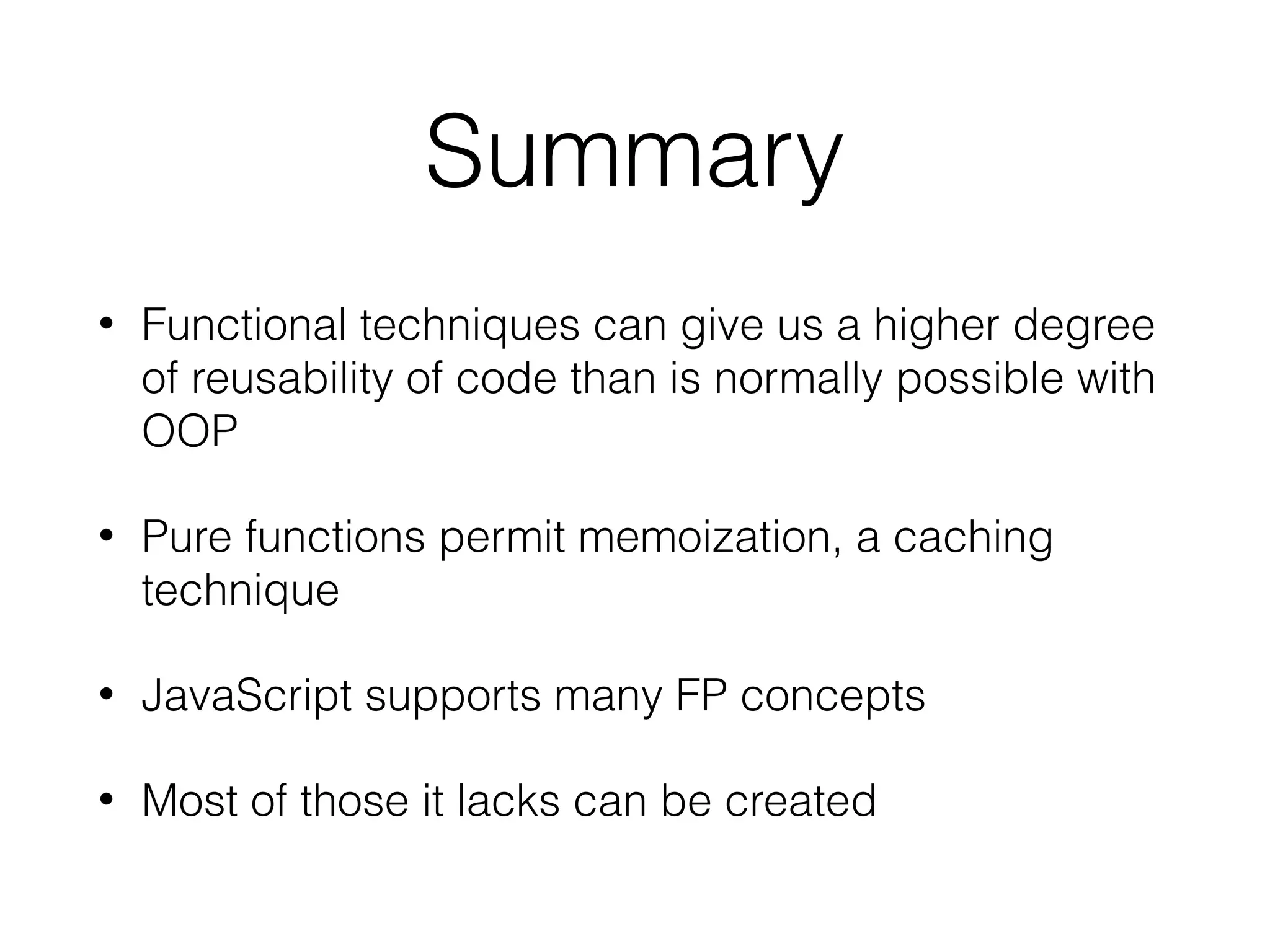
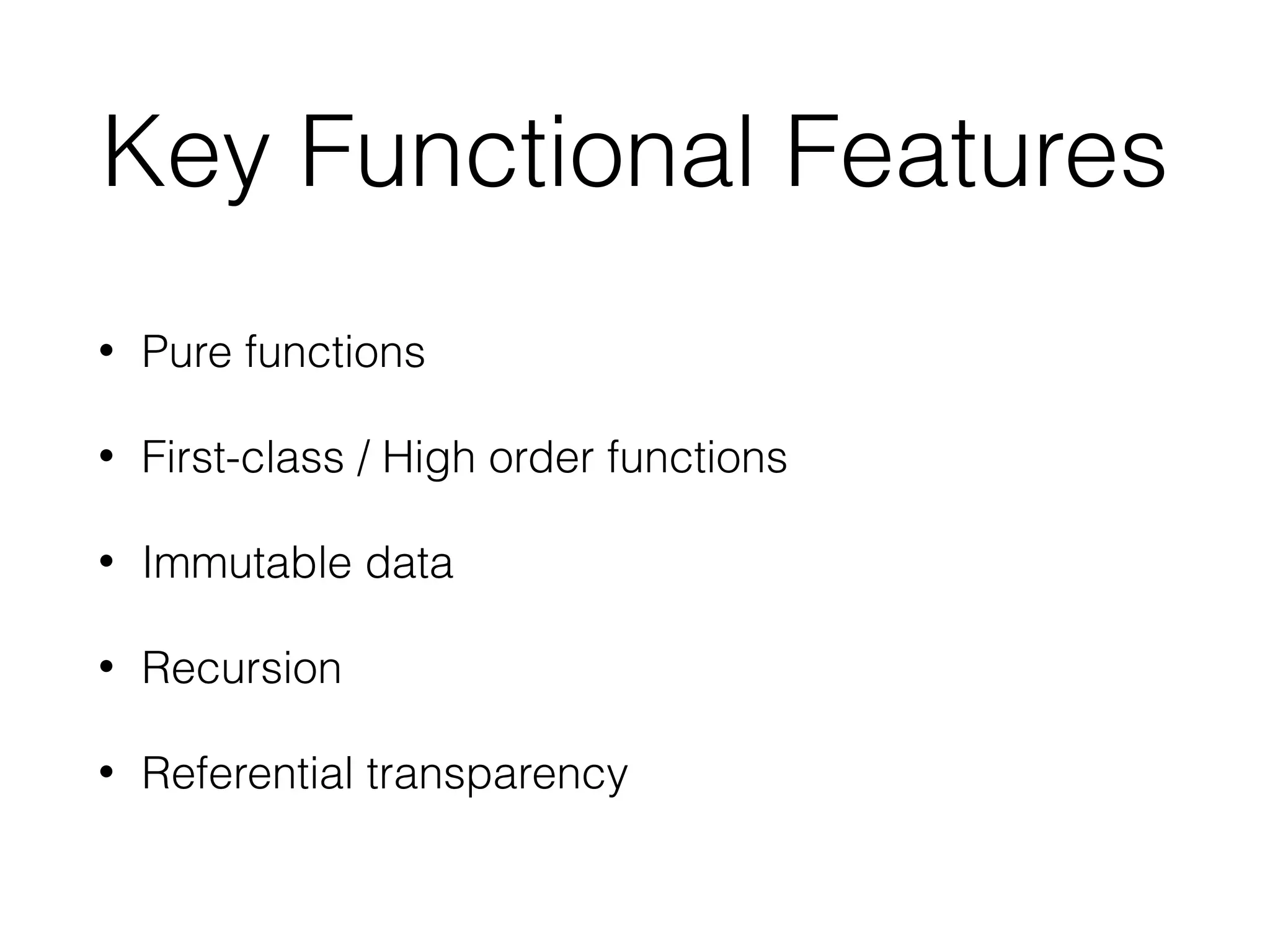
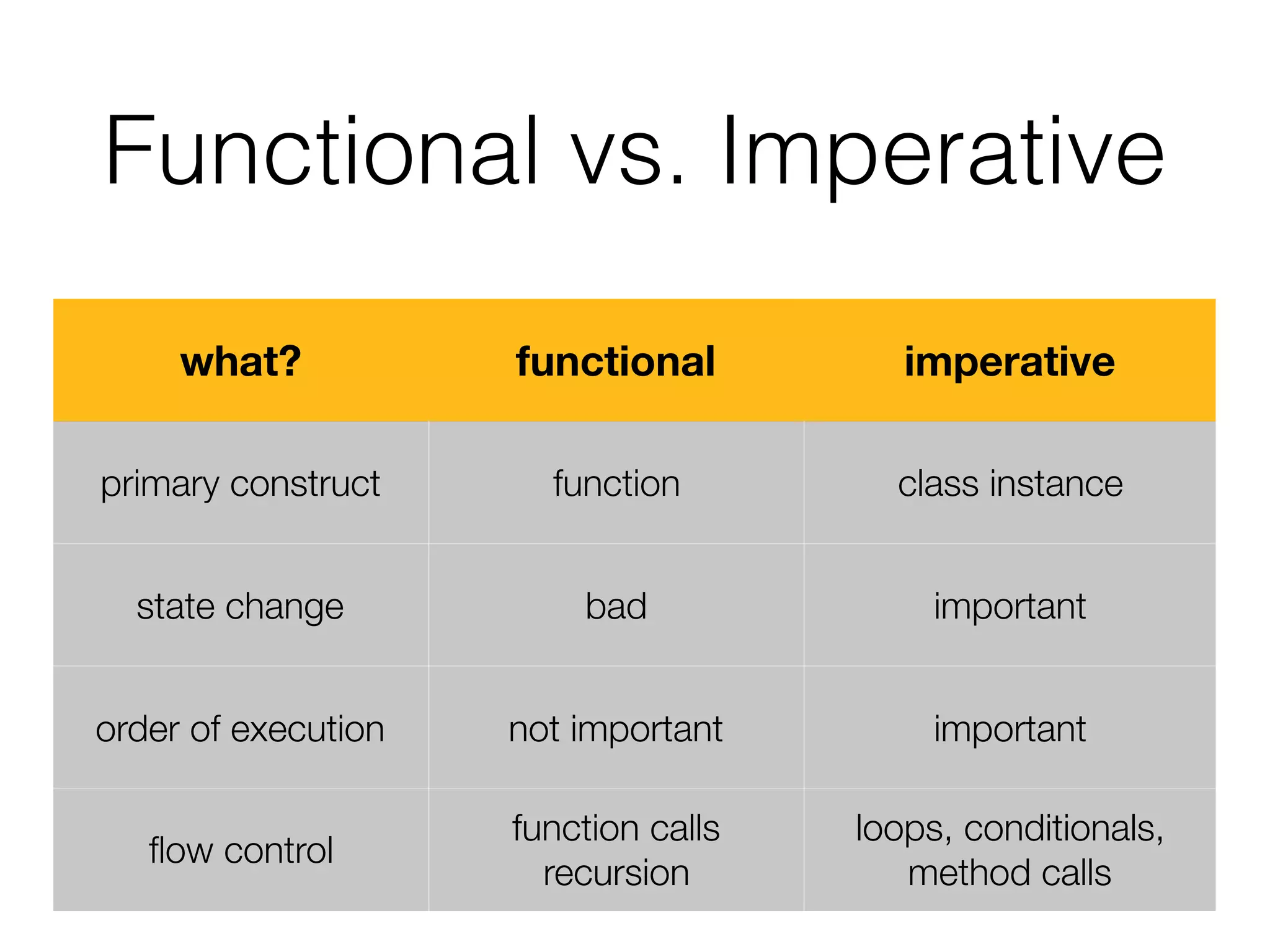
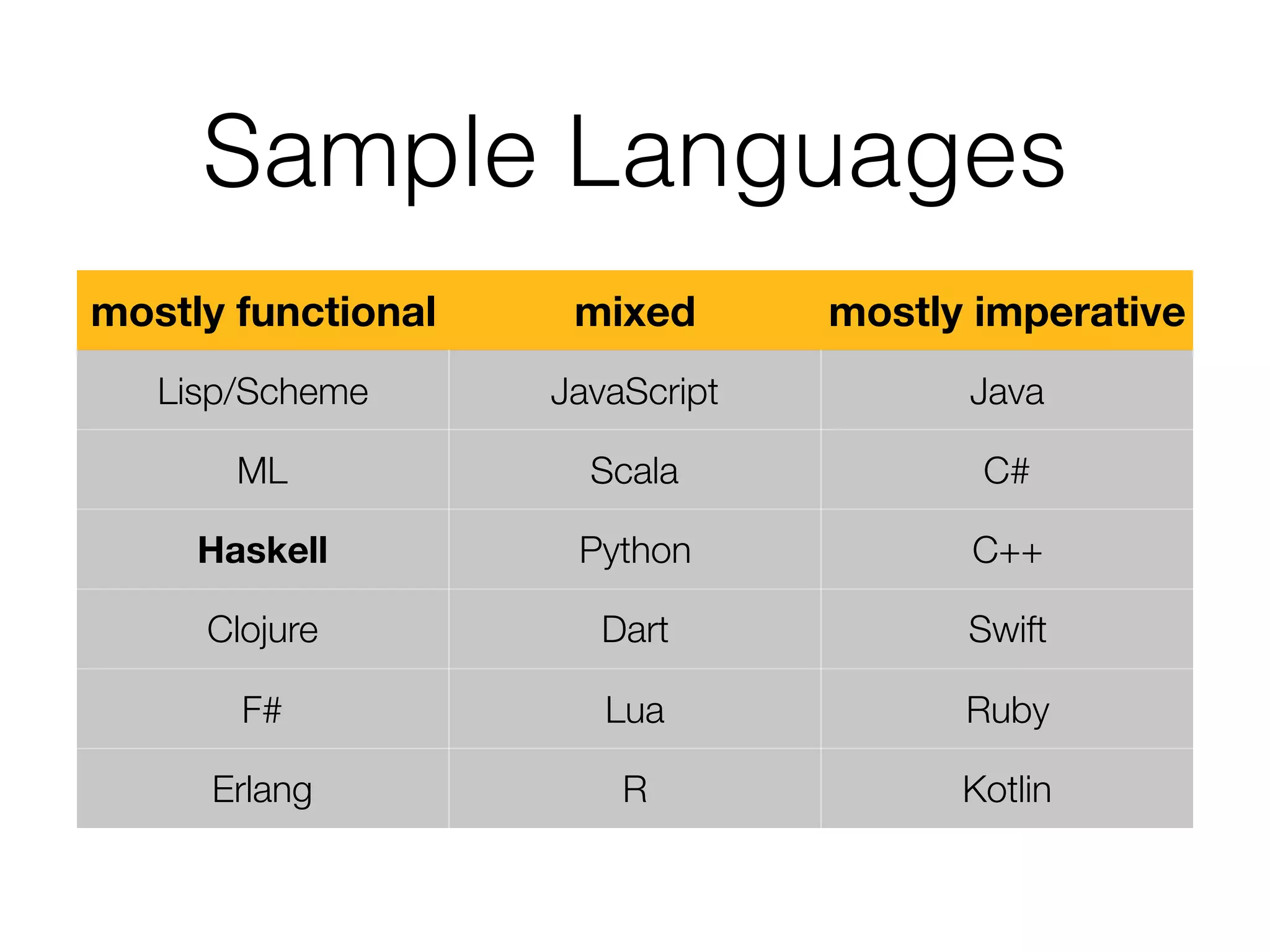
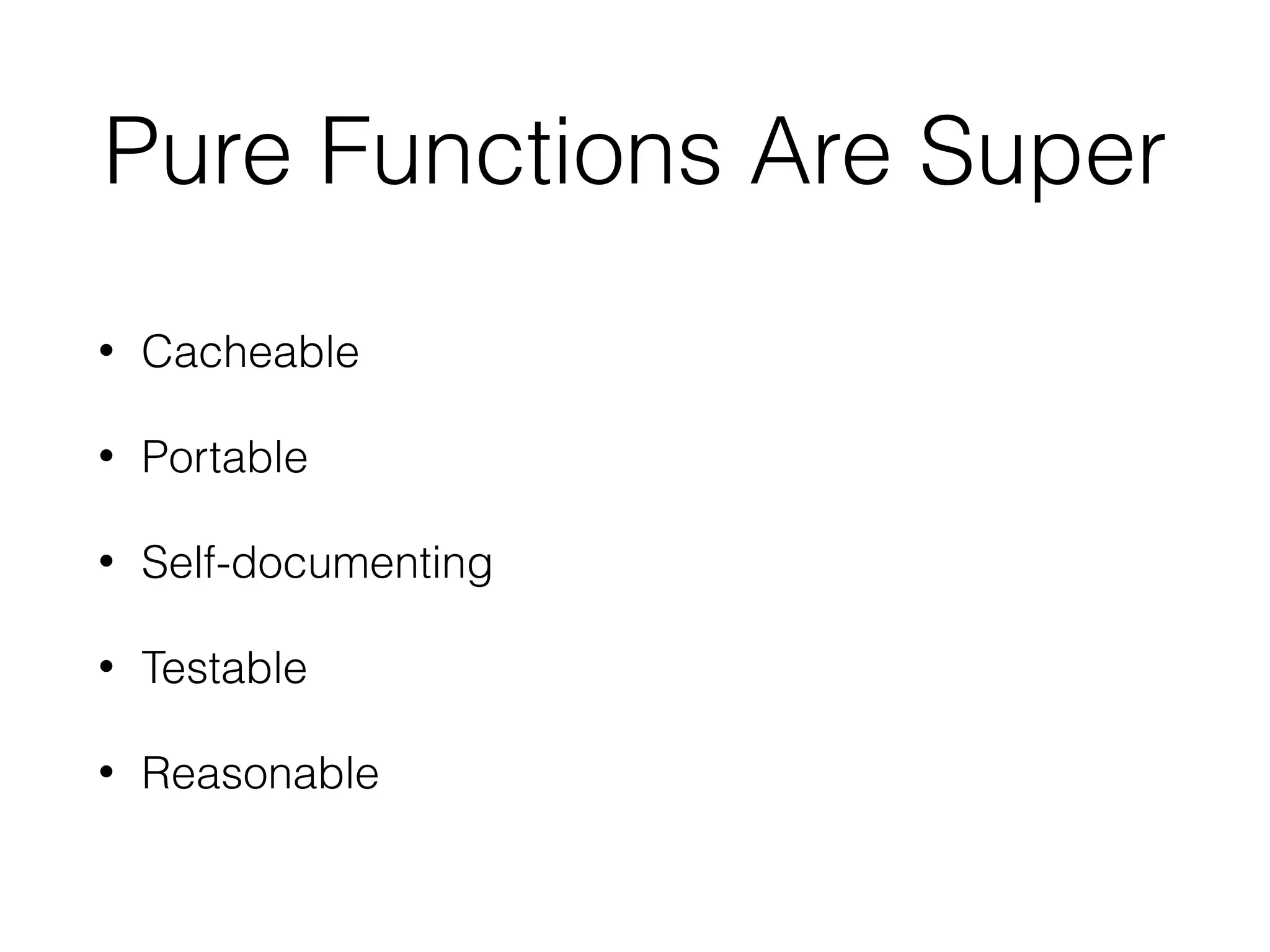
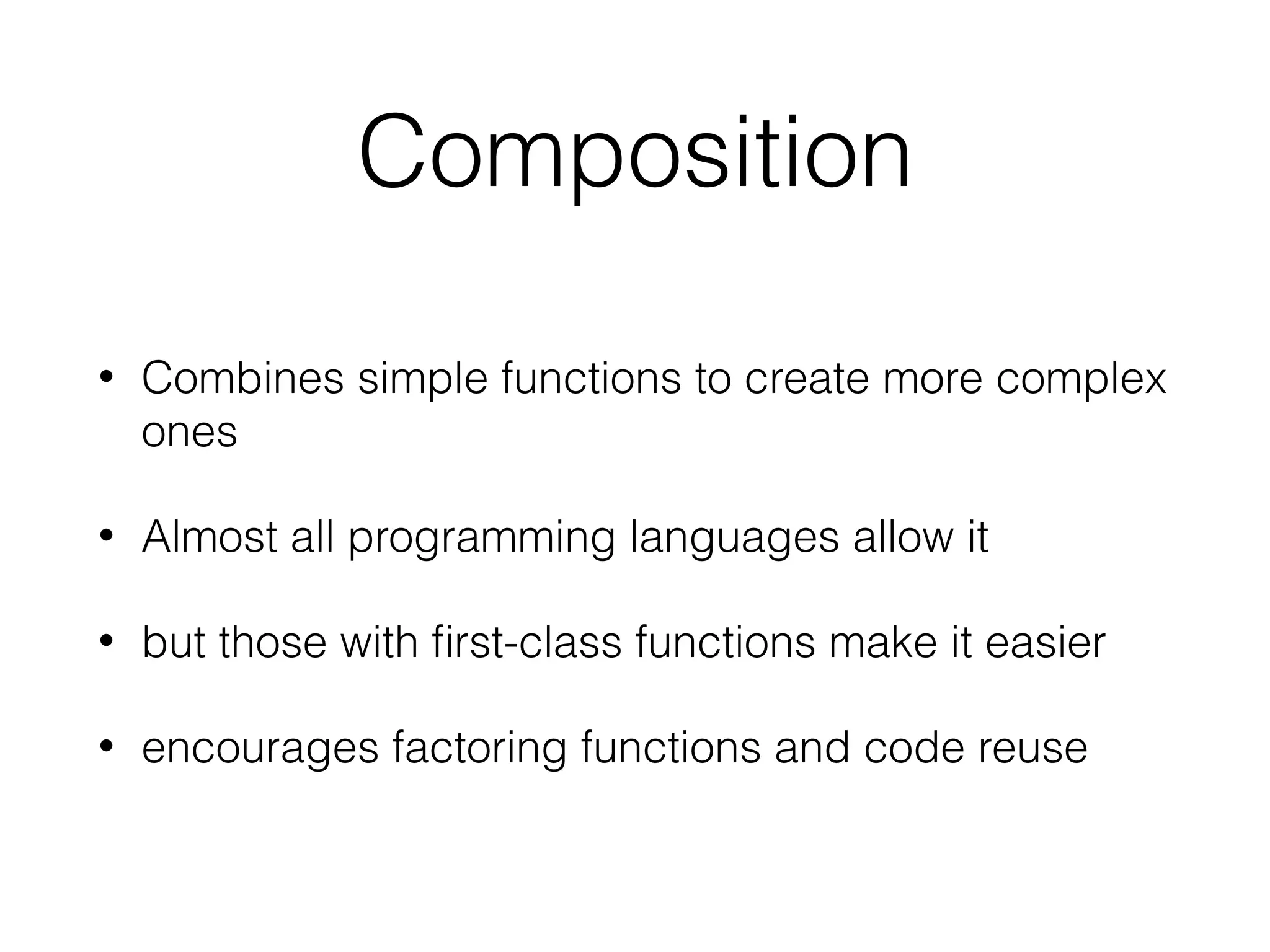
The document is a presentation on functional programming in JavaScript by Troy Miles, aimed at addressing the limitations of object-oriented programming in JavaScript. It covers fundamental concepts of functional programming, such as pure functions, first-class functions, and recursion, while providing practical examples and code samples. Additionally, it discusses the significance of functional techniques for enhancing code reusability and includes resources for further learning.






























![map let junk = [1, 2, 3, 4, 'Alpha', 5, {name: 'Jason'}];
let letters = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K'];
let nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20];
console.info(nums);
// map iterates over all of the elements and // returns a new array with the same number of elements
let nums2 = nums.map((elem) => elem * 2); console.info(nums2);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinjs-light-161114001644/75/Functional-Programming-in-JavaScript-36-2048.jpg)
![filter let junk = [1, 2, 3, 4, 'Alpha', 5, {name: 'Jason'}];
let letters = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K'];
let nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20];
console.info(nums);
// filter iterates over the array and returns a new array with only the elements // that pass the test
let nums3 = nums.filter((elem) => !!(elem % 2));
console.info(nums3);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinjs-light-161114001644/75/Functional-Programming-in-JavaScript-37-2048.jpg)
![reduce let junk = [1, 2, 3, 4, 'Alpha', 5, {name: 'Jason'}];
let letters = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K'];
let nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20];
console.info(nums);
// reduce iterates over the array passing the previous value and the current
// element it is up to you what the reduction does, let's concatenate the strings
let letters2 = letters.reduce((previous, current) => previous + current);
console.info(letters2);
// reduceRight does the same but goes from right to left
let letters3 = letters.reduceRight((previous, current) => previous + current);
console.info(letters3);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinjs-light-161114001644/75/Functional-Programming-in-JavaScript-38-2048.jpg)
![every let junk = [1, 2, 3, 4, 'Alpha', 5, {name: 'Jason'}];
let letters = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K'];
let nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20];
console.info(nums);
// every makes sure that all the elements match the expression
let isEveryNumbers = junk.every((elem) => typeof elem === 'number');
console.info('Are all members of junk numbers: ' + isEveryNumbers);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinjs-light-161114001644/75/Functional-Programming-in-JavaScript-39-2048.jpg)
![forEach let junk = [1, 2, 3, 4, 'Alpha', 5, {name: 'Jason'}];
let letters = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K'];
let nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20];
console.info(nums);
// forEach iterates over the array, once for each element, // but there is no way to break out of the loop (break doesn't work)
nums.forEach(function (elem, index, arr) {
console.info(index + ': ' + elem);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinjs-light-161114001644/75/Functional-Programming-in-JavaScript-40-2048.jpg)