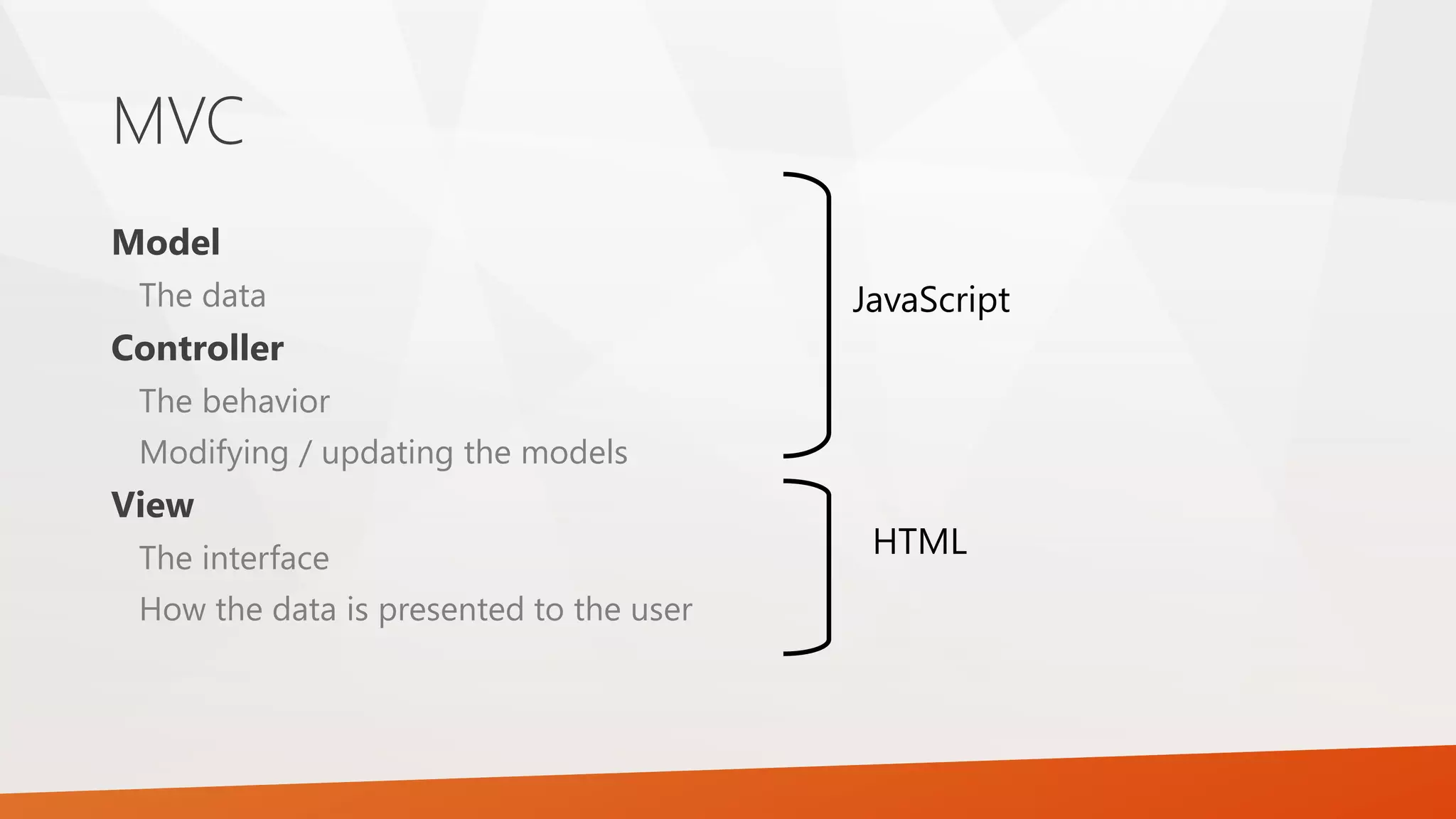
This document provides an overview of AngularJS, including what it is, why it is useful, basic concepts, and how to get started. AngularJS is an open-source JavaScript framework for building single-page applications. It uses HTML as the template language and allows binding data to HTML elements. Some key benefits are less boilerplate code, improved maintainability through separation of concerns using an MVC pattern, and efficient development through features like data binding. The document outlines how to include AngularJS scripts, core concepts like directives, controllers and models, and recommends resources for learning more.



















![Controller Typically also contains module loading angular.module(<name>, [<dependencies>]); Creates a module with the given name This module can then be configured Ex. • var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp’, []); myApp.controller(‘MyCtrl’, function($scope) { … }); myApp.controller(‘OtherCtrl’, [‘$scope’, ‘$http’, function($scope, $http) { … }]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-150324115453-conversion-gate01/75/Valentine-with-Angular-js-Introduction-21-2048.jpg)

![Modules var myControllers = angular.module(‘myControllers’, []); // Add controllers to the module myControllers.controller(…); var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp’, [‘myControllers’]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-150324115453-conversion-gate01/75/Valentine-with-Angular-js-Introduction-23-2048.jpg)

