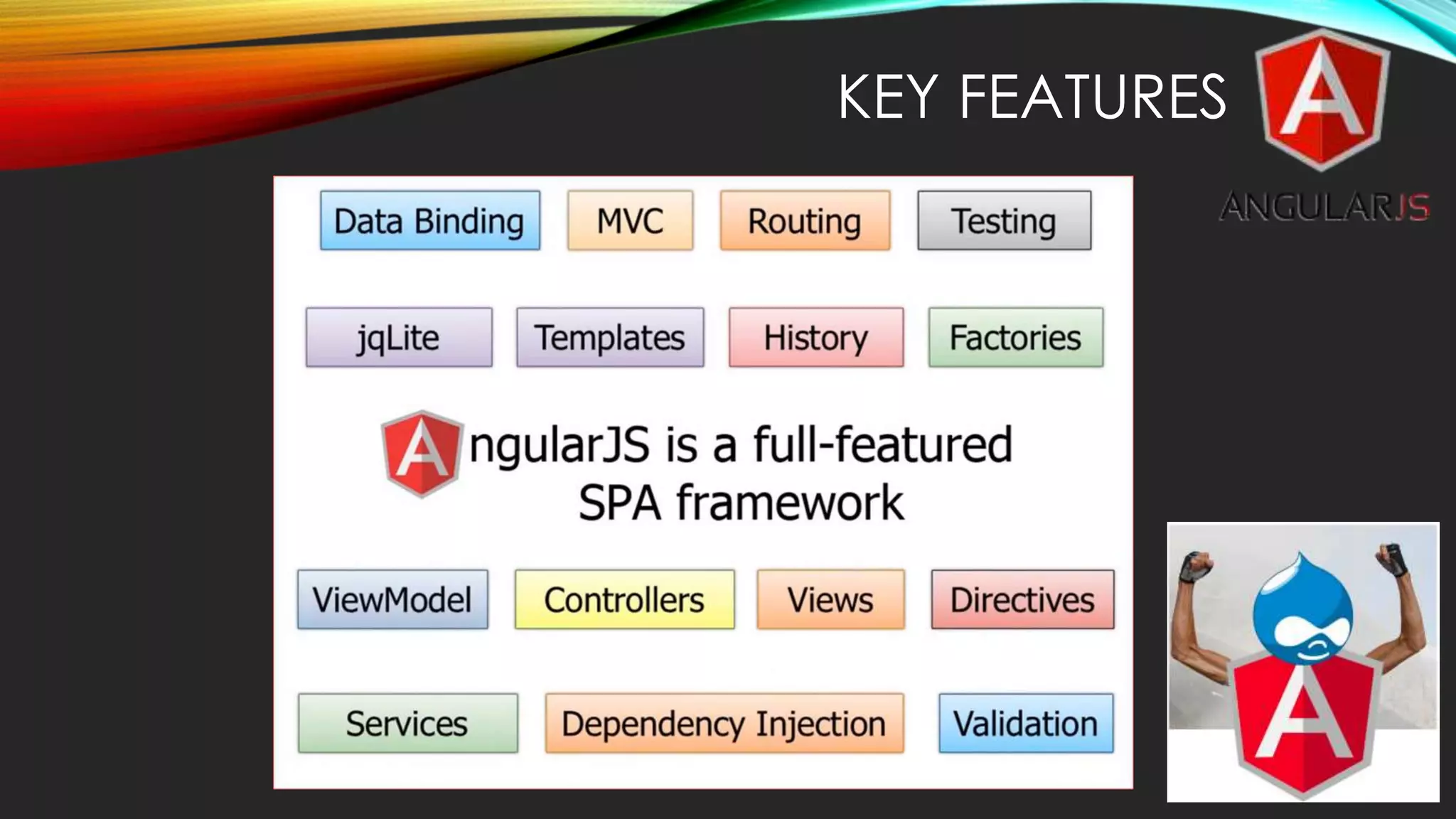
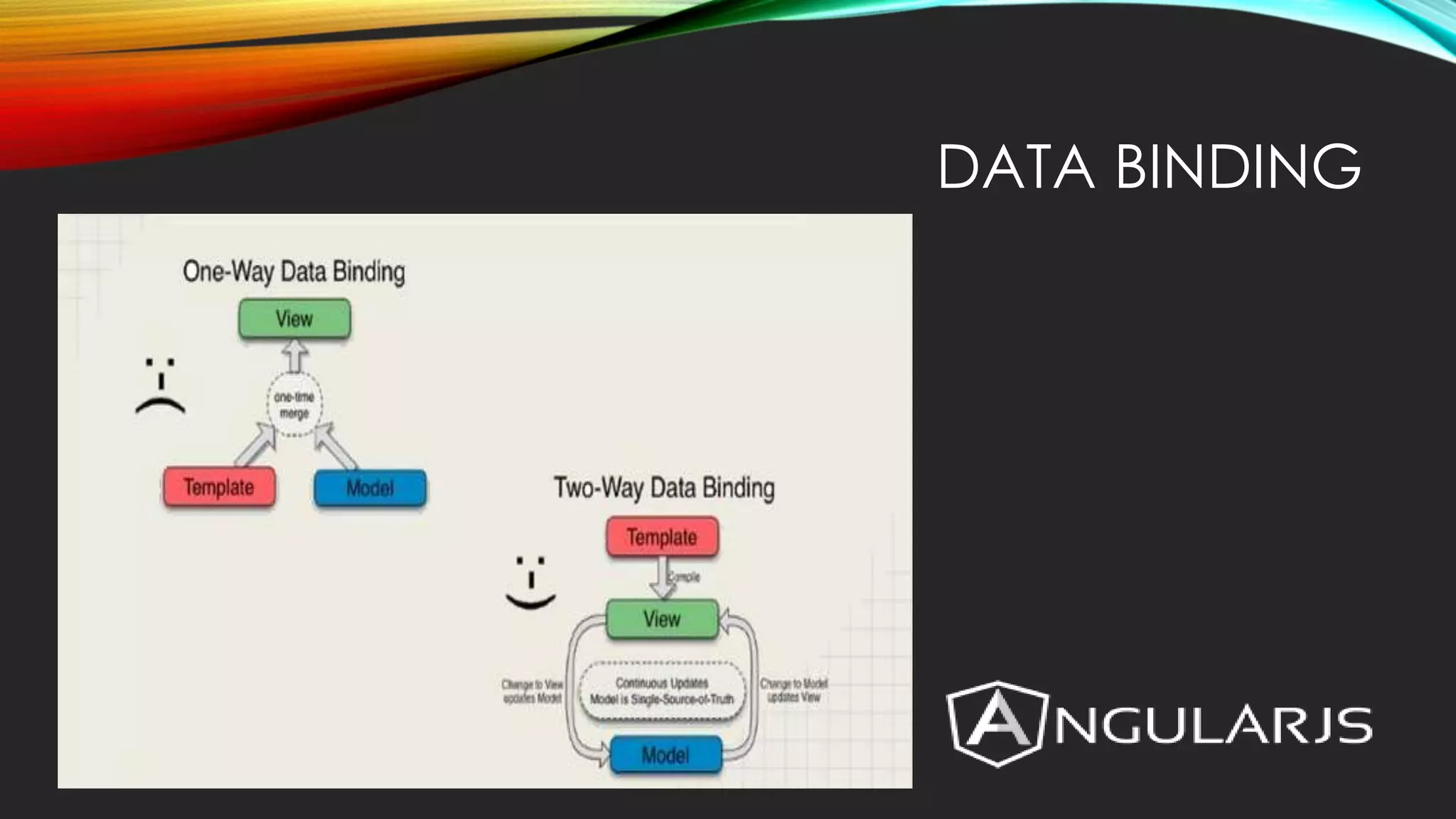
AngularJS is a JavaScript MVC framework created by Google to build maintainable web applications. It was released in 2012 and focuses on HTML and MVC/MVVM design patterns. Key features include data binding, controllers, directives, expressions, forms, modules, scopes, dependency injection, filters and services.





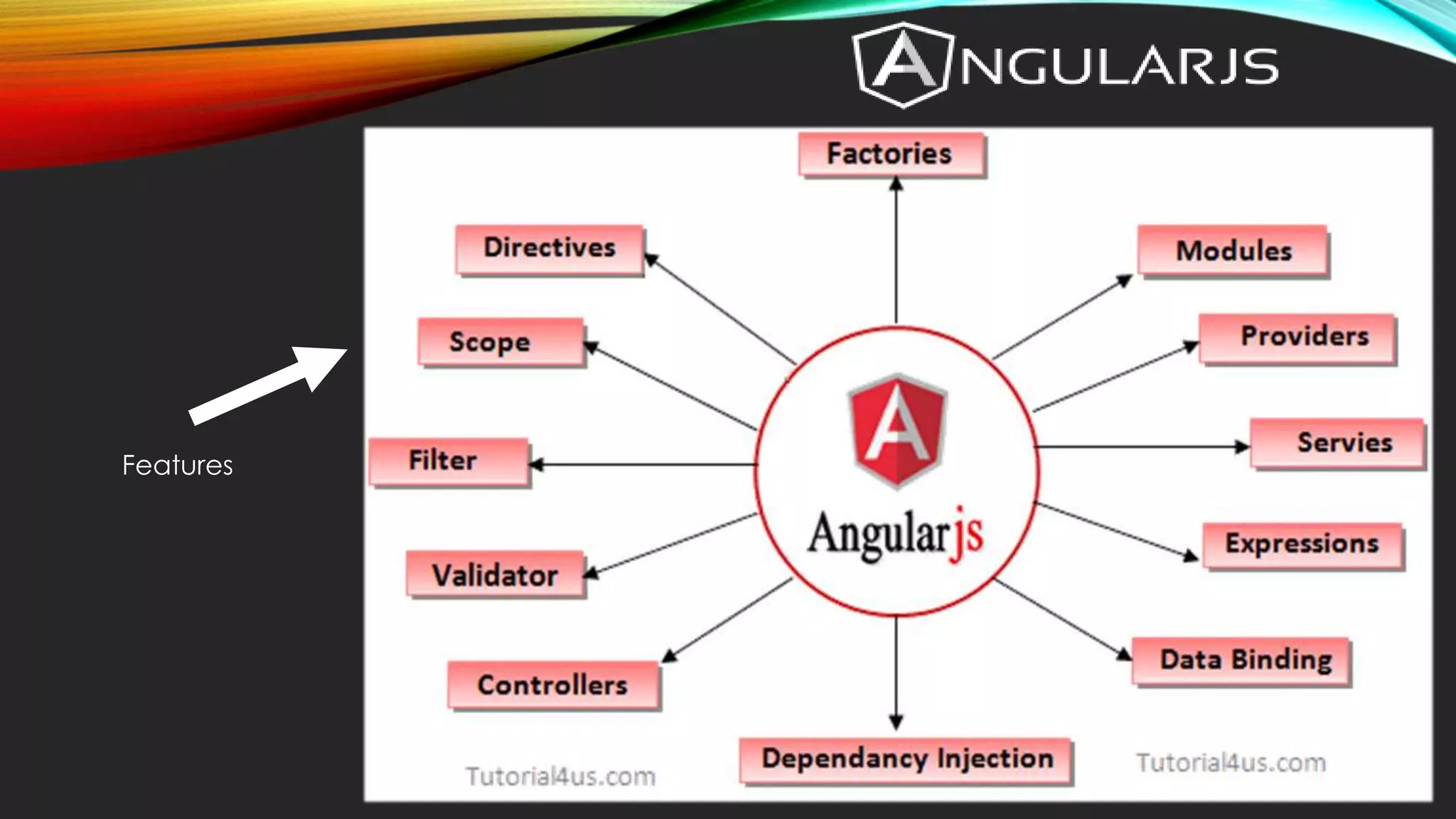







![MODULE • An AngularJS module defines an application. • A module is a container for the different parts of an application. • All application controllers should belong to a module. • There can be multiple module. //declare module: var myAppModule=angular.module(‘myApp’,[--here goes dependent modules--]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-150718191458-lva1-app6892/75/Angularjs-16-2048.jpg)

![FILTERS • AngularJS filters format data for display for the users. • Can create custom filters. //Declare Filters: {{expression [|filter_name[:parameter_value]..]}} {{uppercase_expression | uppercase}} {{expression |filter1|filter2}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-150718191458-lva1-app6892/75/Angularjs-19-2048.jpg)

