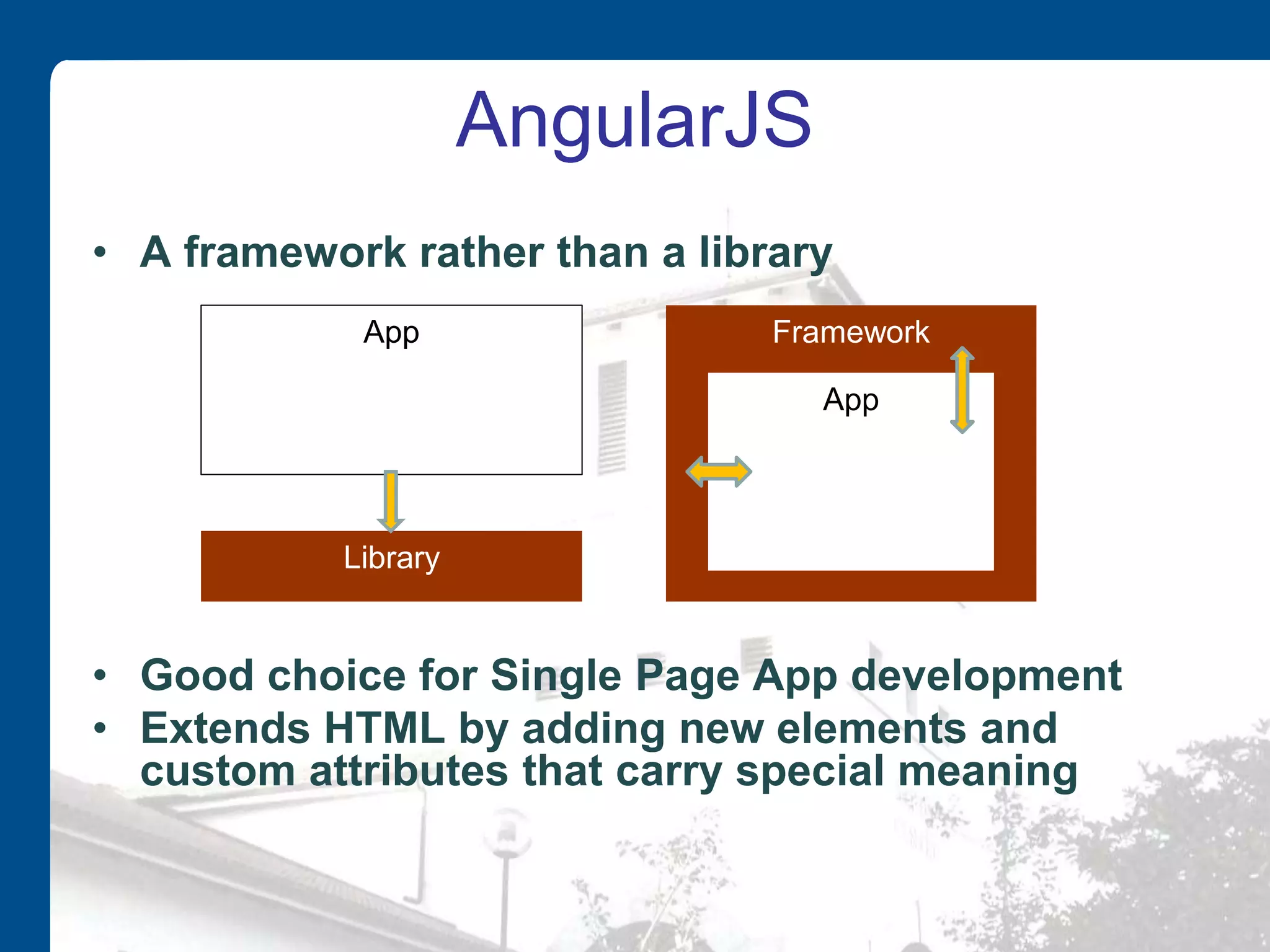
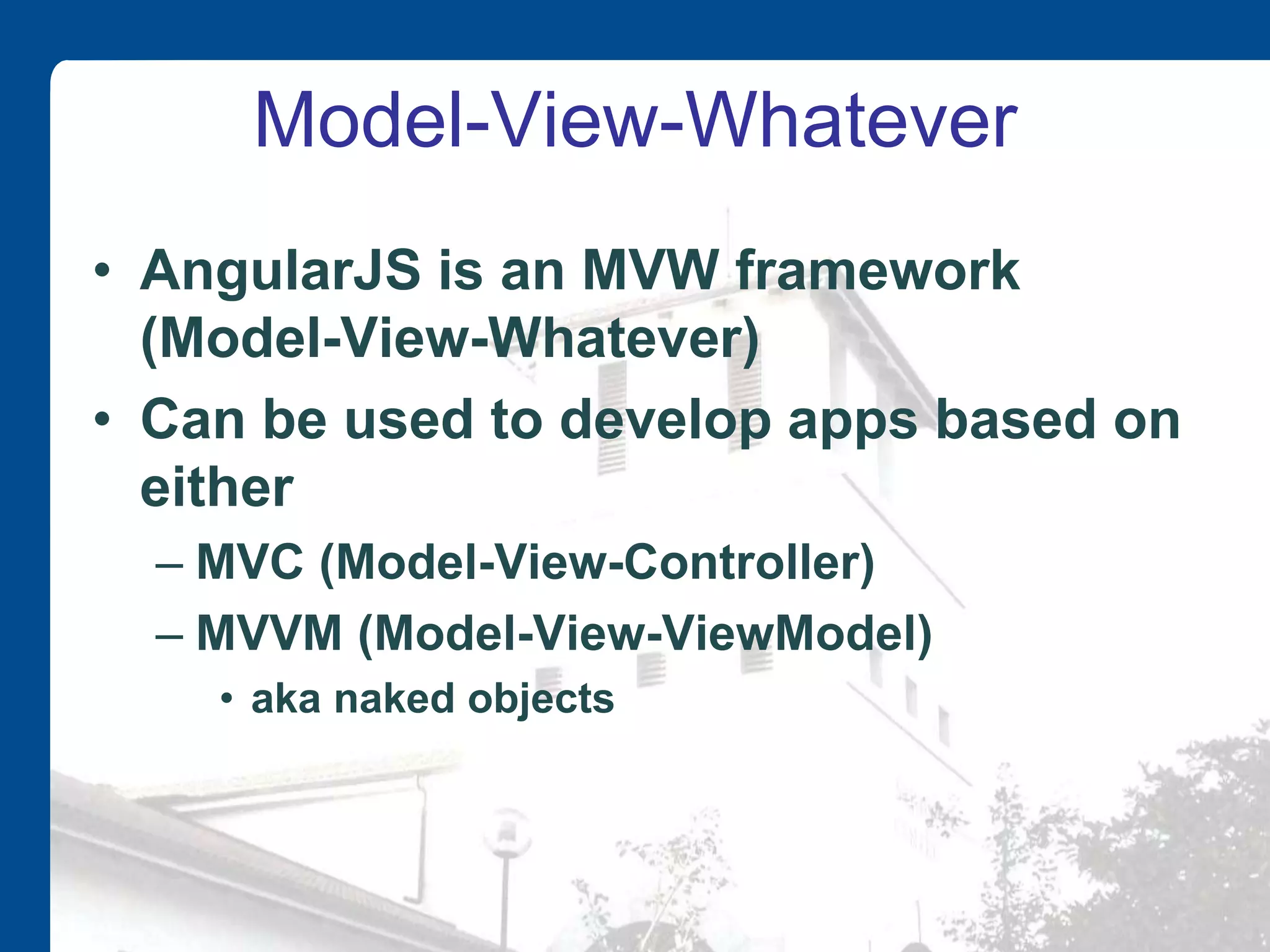
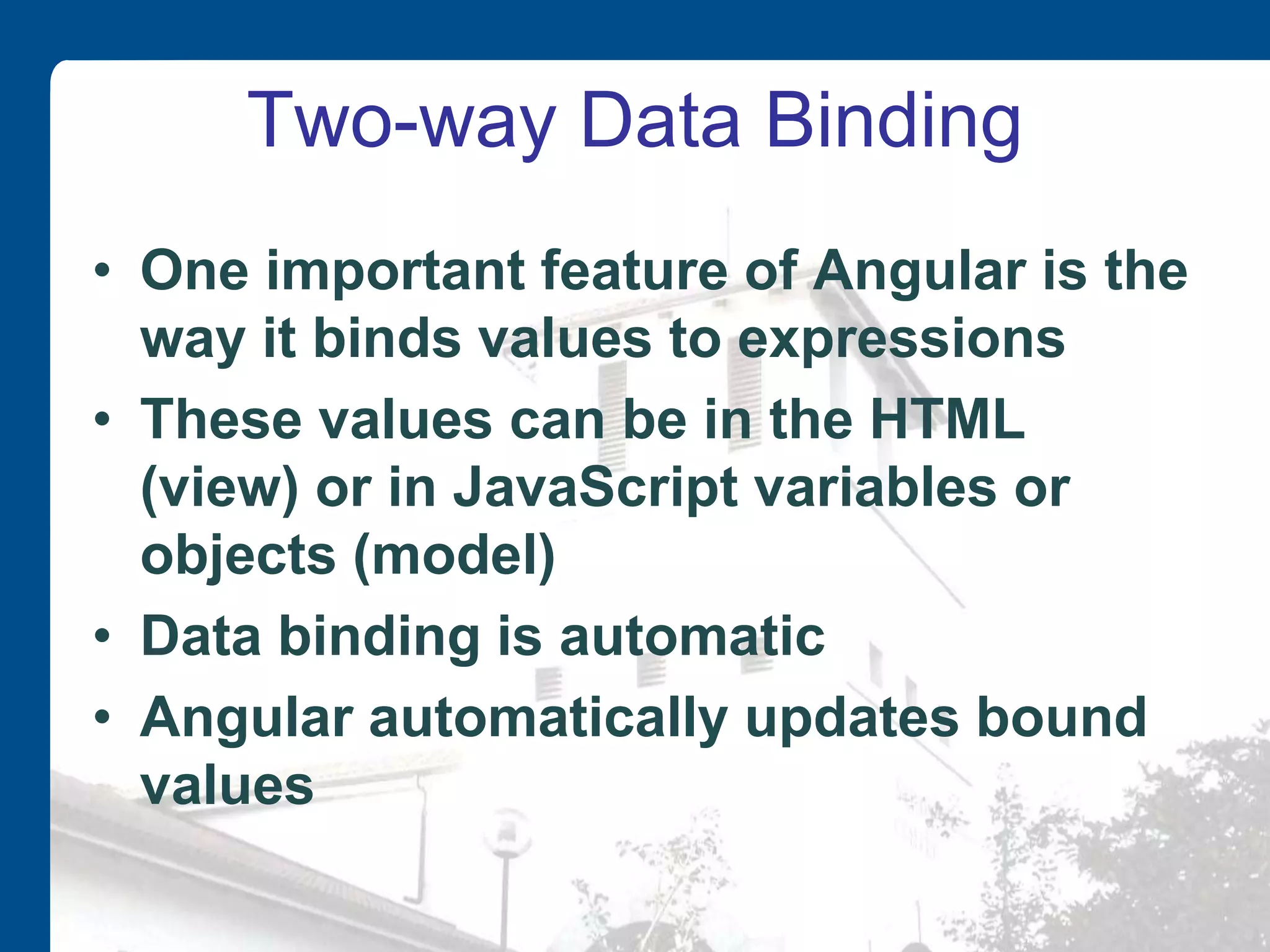
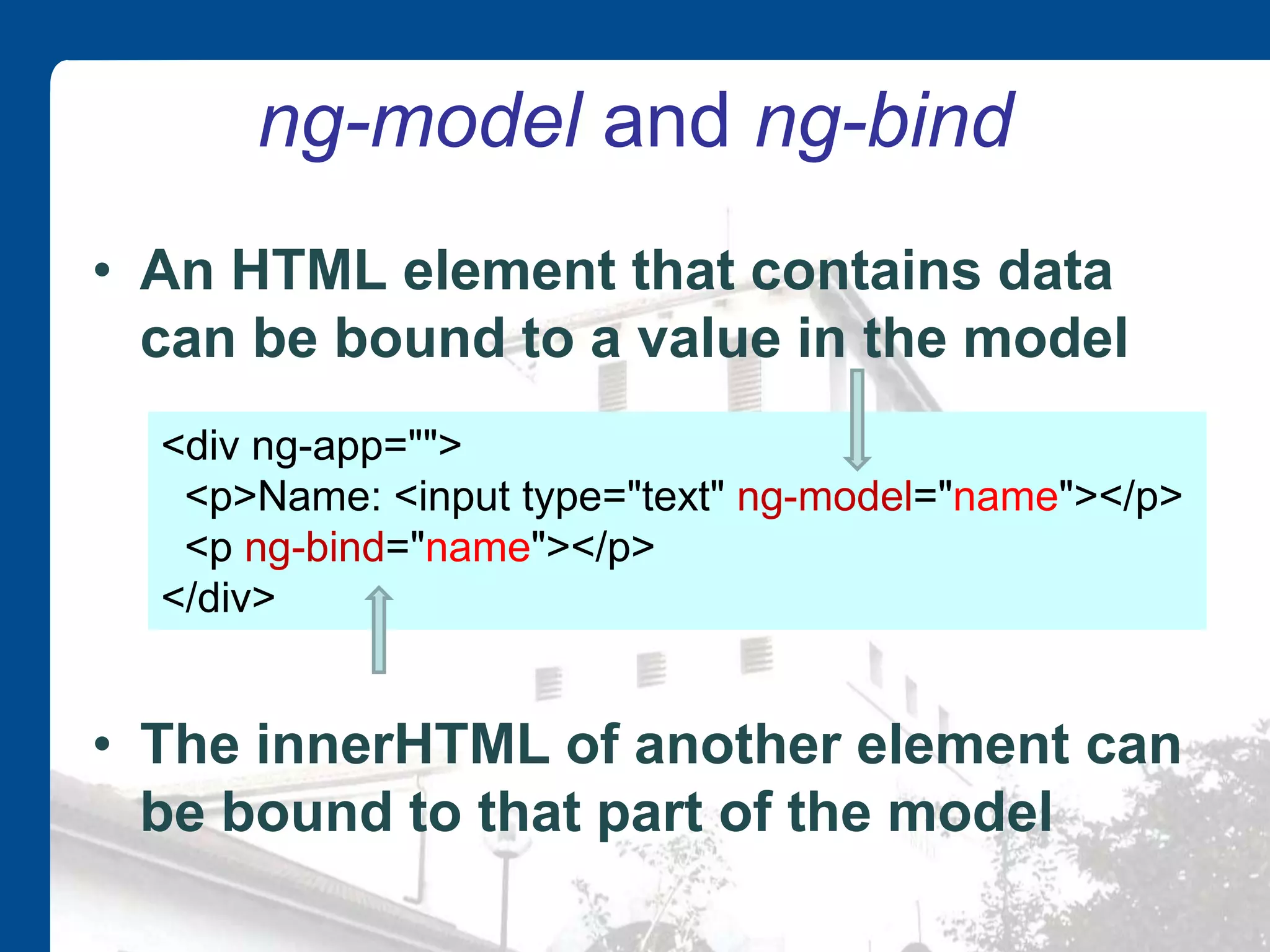
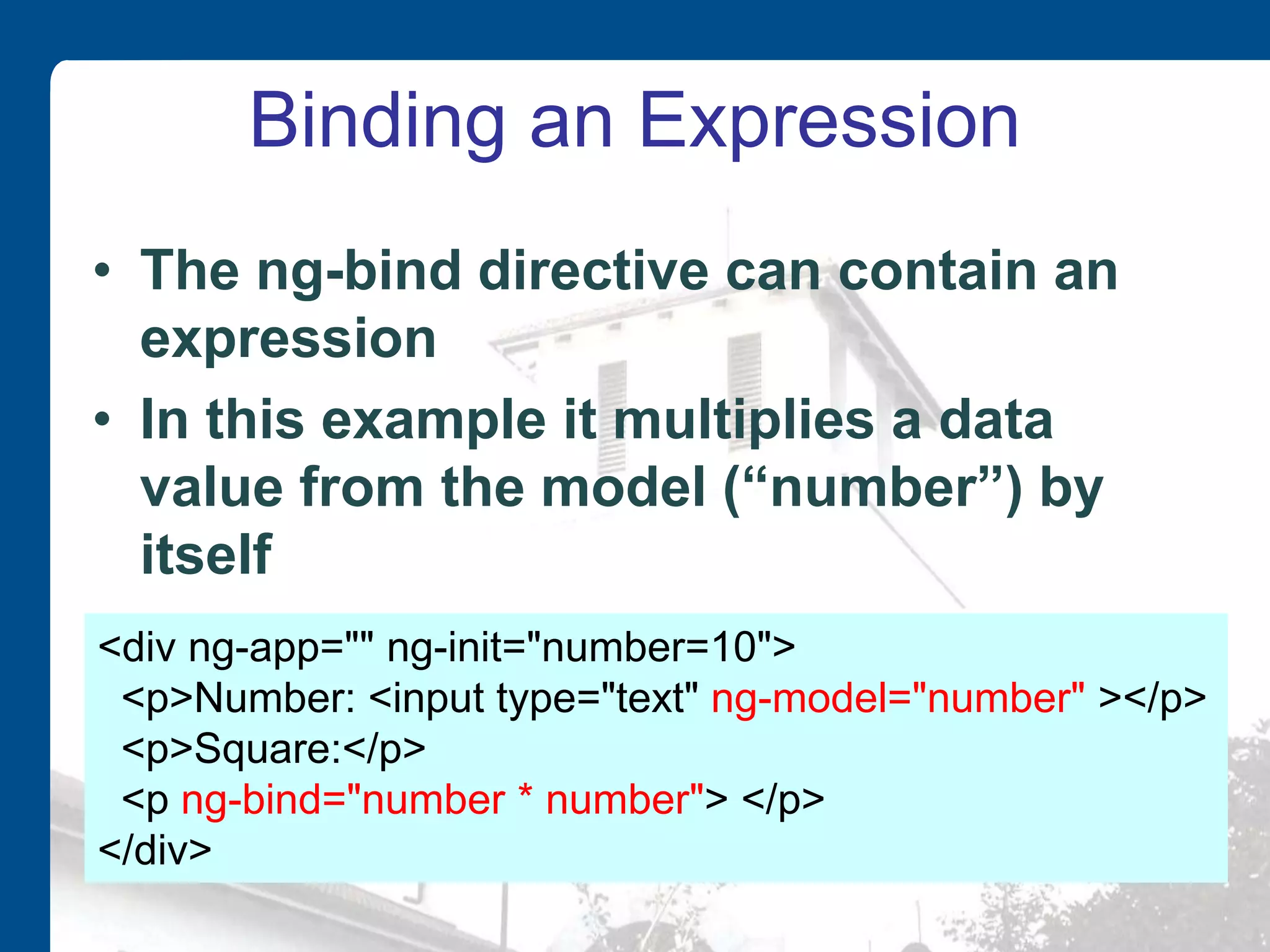
AngularJS is an open source JavaScript framework maintained by Google that extends HTML with new elements and attributes. It uses a Model-View-Whatever architecture to develop single-page applications. Key AngularJS components include directives, expressions, and controllers that allow two-way data binding between models and views.








![Modules • Angular code in external files is defined in modules • The first parameter is the name of the app module that can be referenced from an ng-app directive – The array is for any dependencies we may have on other modules (can be empty) var app = angular.module("ticketoffice", [ ]); <div ng-app="ticketoffice">](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoangularjs-150304192326-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-AngularJS-16-2048.jpg)
![Controllers • Apps have controllers • These are JavaScript functions • Given a name when added to an app as a controller • Name your controllers using Pascal Case – Controllers are really constructor functions – These are usually named in JavaScript using Pascal case var app=angular.module("ticketoffice", []); app.controller("TicketController", function() { // body of function });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoangularjs-150304192326-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-AngularJS-17-2048.jpg)

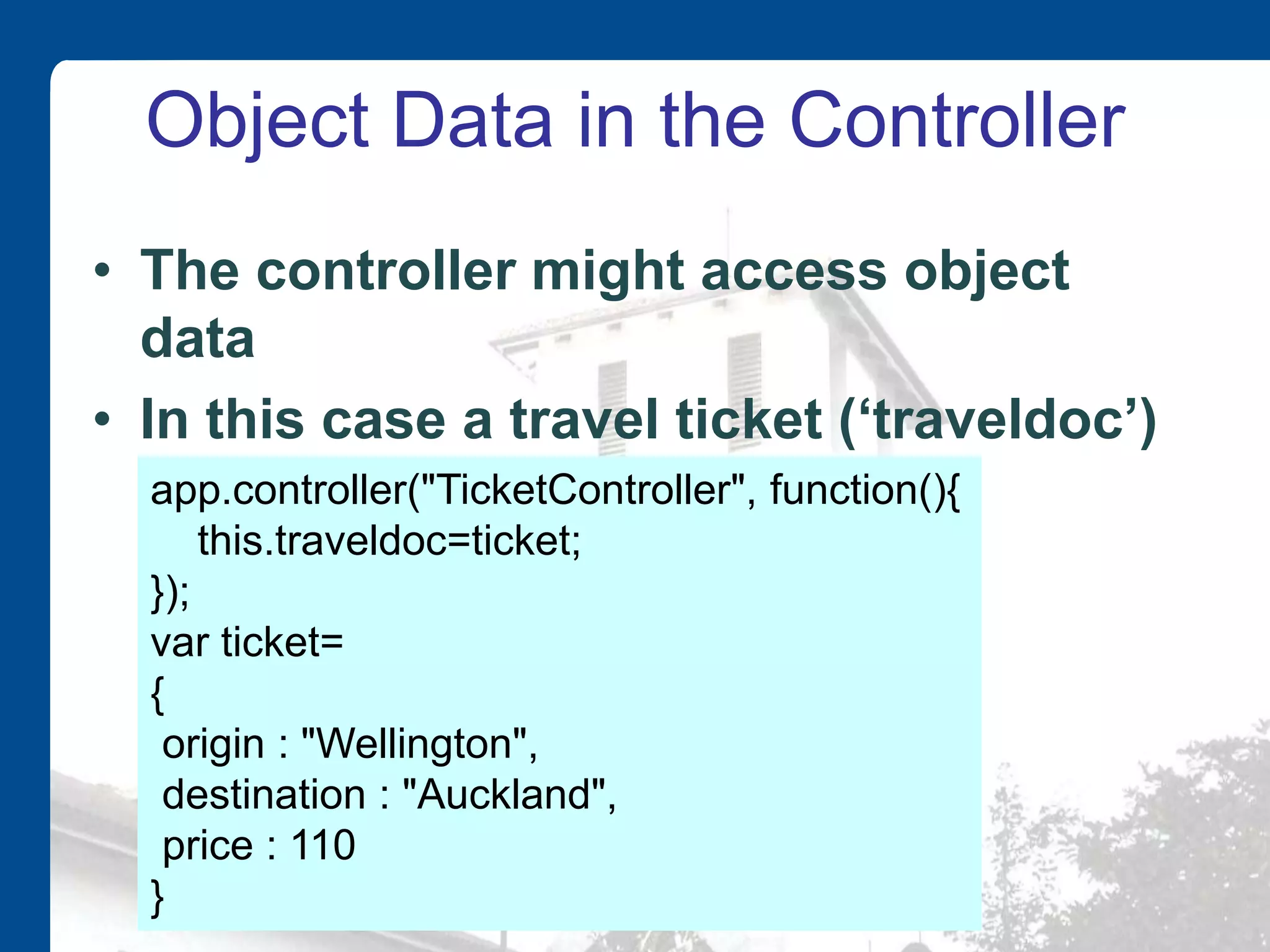
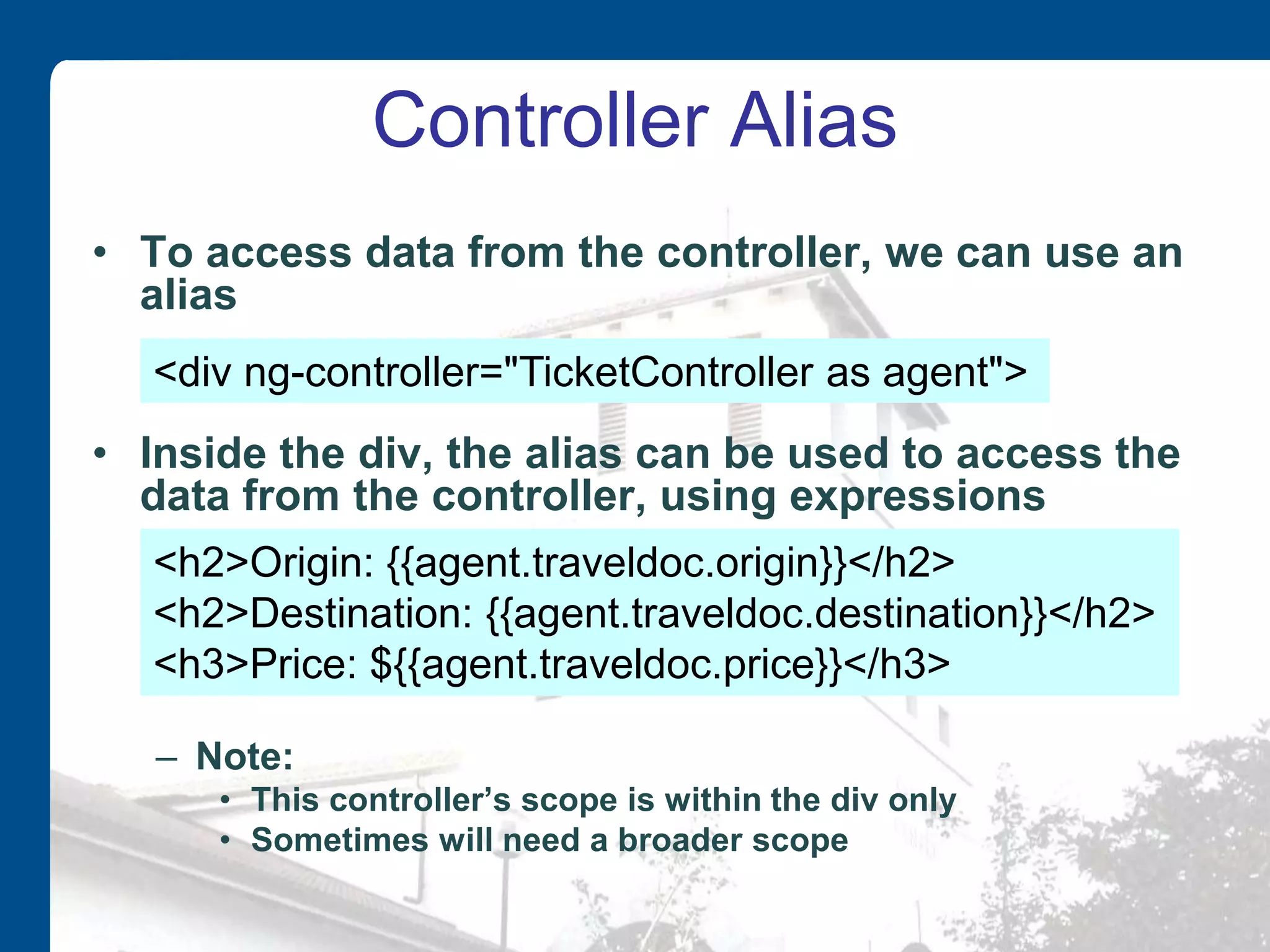
![Multiple Objects • We might have an array of objects • We also need to change the controller, since the name has changed, for readability (from ‘ticket’ to ‘tickets’) var tickets = [ { origin : "Wellington", destination : "Auckland", price : 110}, { origin : "Christchurch", destination : "Dundedin", price : 120}, … ]; this.traveldocs=tickets;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoangularjs-150304192326-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-AngularJS-21-2048.jpg)
![Array Access by Index • Access by index is now possible, e.g. • However, not good for displaying multiple objects on the same page <h2>{{agent.traveldocs[0].origin}}</h2> <h2>{{agent.traveldocs[0].destination}}</h2> <h3>${{agent.traveldocs[0].price}}</h3>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoangularjs-150304192326-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-AngularJS-22-2048.jpg)


![Using ng-src • In the HTML img tag, replace ‘src’ with ‘ng-src’, along with an Angular expression to locate the image. <img ng-src="{{traveldoc.images[0].full}}" />](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoangularjs-150304192326-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-AngularJS-25-2048.jpg)
